Chapter 19. The java.security.cert Package
The java.security.cert package contains classes for working with identity certificates and certificate revocation lists (CRLs). It defines generic Certificate and CRL classes and X509Certificate and X509CRL classes that provide full support for standard X.509 certificates and CRLs. The CertificateFactory class serves as a certificate parser, providing the ability to convert a stream of bytes into a Certificate or CRL object. This package replaces the deprecated java.security.Certificate interface. Figure 19-1 shows the class hierarchy of this package.
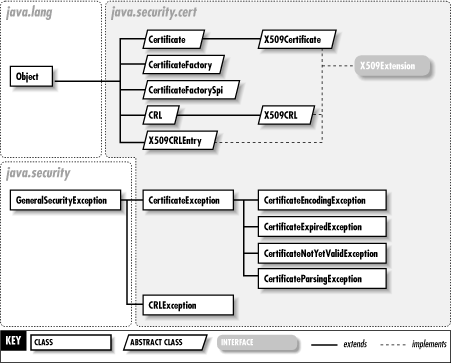
Figure 19-1. The java.security.cert package
| Certificate | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.security.cert | serializable | |
This abstract class represents an identity certificate. A certificate is an object that contains the name of an entity and a public key for that entity. Certificates are issued by, and bear the digital signature of,x a (presumably trusted) third party, typically a certificate authority (CA). By issuing and signing the certificate, the CA is certifying that, based on their research, the entity named on the certificate really is who they say they are and that the public key in the certificate really does belong to that entity.
Use a CertificateFactory to parse a stream of bytes into a Certificate object; getEncoded() reverses this process. Use verify() to verify the digital signature of the entity that issued the certificate. If the signature cannot be verified, the certificate should not be trusted. Call getPublicKey() to obtain the java.security.PublicKey of the subject of the certificate. Note that this class does not define a method for obtaining the Principal that is associated with the PublicKey. That functionality is dependent on the type of the certificate. See X509Certificate.getSubjectDN(), for example.
Do not confuse this class with the java.security.Certificate interface that was defined in Java 1.1 and has been deprecated in Java 1.2.
| public abstract class Certificate implements Serializable { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected Certificate (String type); | ||
| // | Inner Classes | |
| 1.3 | ; | |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract byte[ ] getEncoded () throws CertificateEncodingException; | ||
| public abstract java.security.PublicKey getPublicKey (); | ||
| public final String getType (); | ||
| public abstract void verify (java.security.PublicKey key) throws CertificateExceptionjava.security.NoSuchAlgorithmExceptionjava.security.InvalidKeyExceptionjava.security.NoSuchProviderExceptionjava.security.SignatureException; | ||
| public abstract void verify (java.security.PublicKey key, String sigProvider) throws CertificateExceptionjava.security.NoSuchAlgorithmExceptionjava.security.InvalidKeyExceptionjava.security.NoSuchProviderExceptionjava.security.SignatureException; | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public boolean equals (Object other); | ||
| public int hashCode (); | ||
| public abstract String toString (); | ||
| // | Protected Instance Methods | |
| 1.3 | protected Object writeReplace () throws java.io.ObjectStreamException; | |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->java.security.cert.Certificate(Serializable)
Subclasses: X509Certificate
Passed To: java.security.CodeSource.CodeSource(), java.security.KeyStore.{getCertificateAlias(), setCertificateEntry(), setKeyEntry()}, java.security.KeyStoreSpi.{engineGetCertificateAlias(), engineSetCertificateEntry(), engineSetKeyEntry()}, java.security.Signature.initVerify(), java.security.UnresolvedPermission.UnresolvedPermission(), CRL.isRevoked()
Returned By: java.net.JarURLConnection.getCertificates(), java.security.CodeSource.getCertificates(), java.security.KeyStore.{getCertificate(), getCertificateChain()}, java.security.KeyStoreSpi.{engineGetCertificate(), engineGetCertificateChain()}, CertificateFactory.generateCertificate(), CertificateFactorySpi.engineGenerateCertificate(), java.util.jar.JarEntry.getCertificates()
| Certificate.CertificateRep | Java 1.3 Beta | |
|
|
||
| java.security.cert | serializable | |
This protected inner class provides an alternate representation of a certificate that can be used for serialization purposes by the writeReplace() method of some Certificate implementations. Applications do not typically need this class.
| protected static class Certificate.CertificateRep implements Serializable { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected CertificateRep (String type, byte[ ] data); | ||
| // | Protected Instance Methods | |
| protected Object readResolve () throws java.io.ObjectStreamException; | ||
| } | ||
| CertificateEncodingException | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.security.cert | serializable checked | |
Signals an error while attempting to encode a certificate.
| public class CertificateEncodingException extends CertificateException { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public CertificateEncodingException (); | ||
| public CertificateEncodingException (String message); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Throwable(Serializable)-->Exception-->java.security.GeneralSecurityException-->CertificateException-->CertificateEncodingException
Thrown By: java.security.cert.Certificate.getEncoded(), X509Certificate.getTBSCertificate()
| CertificateException | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.security.cert | serializable checked | |
This class is the superclass of several more specific exception types that may be thrown when working with certificates.
| public class CertificateException extends java.security.GeneralSecurityException { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public CertificateException (); | ||
| public CertificateException (String msg); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Throwable(Serializable)-->Exception-->java.security.GeneralSecurityException-->CertificateException
Subclasses: CertificateEncodingException, CertificateExpiredException, CertificateNotYetValidException, CertificateParsingException
Thrown By: java.security.KeyStore.{load(), store()}, java.security.KeyStoreSpi.{engineLoad(), engineStore()}, java.security.cert.Certificate.verify(), CertificateFactory.{generateCertificate(), generateCertificates(), getInstance()}, CertificateFactorySpi.{engineGenerateCertificate(), engineGenerateCertificates()}
| CertificateExpiredException | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.security.cert | serializable checked | |
Signals that a certificate has expired or will have expired by a specified date.
| public class CertificateExpiredException extends CertificateException { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public CertificateExpiredException (); | ||
| public CertificateExpiredException (String message); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Throwable(Serializable)-->Exception-->java.security.GeneralSecurityException-->CertificateException-->CertificateExpiredException
Thrown By: X509Certificate.checkValidity()
| CertificateFactory | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.security.cert | ||
This class defines methods for parsing CRLs from byte streams. Obtain a CertificateFactory by calling one of the static getInstance() factory methods and specifying the type of certificate or CRL to be parsed, and, optionally, the desired service provider to perform the parsing. The default "SUN" provider defines only a single "X.509" certificate type. Once you have obtained a CertificateFactory for the desired type of certificate, call generateCertificate() or generateCRL() to parse a single certificate or CRL from a stream. Or call generateCertificates() or generateCRLs() to parse a Collection of certificates or CRLs from the stream. These CertificateFactory methods read to the end of the specified stream. If the stream supports mark() and reset(), however, the CertificateFactory resets the stream to the position after the end of the last certificate or CRL read.
If you specified a certificate type of "X.509", the Certificate and CRL objects returned by a CertificateFactory can be cast safely to X509Certificate and X509CRL. The X.509 certificate factory can parse certificates encoded in binary or printable hexadecimal form. If the certificate is in hexadecimal form, it must begin with the string "-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----" and end with the string "-----END CERTIFICATE-----".
| public class CertificateFactory { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected CertificateFactory (CertificateFactorySpi certFacSpi, java.security.Provider provider, String type); | ||
| // | Public Class Methods | |
| public static final CertificateFactory getInstance (String type) throws CertificateException; | ||
| public static final CertificateFactory getInstance (String type, String provider) throws CertificateExceptionjava.security.NoSuchProviderException; | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public final java.security.cert.Certificate generateCertificate (java.io.InputStream inStream) throws CertificateException; | ||
| public final java.util.Collection generateCertificates (java.io.InputStream inStream) throws CertificateException; | ||
| public final CRL generateCRL (java.io.InputStream inStream) throws CRLException; | ||
| public final java.util.Collection generateCRLs (java.io.InputStream inStream) throws CRLException; | ||
| public final java.security.Provider getProvider (); | ||
| public final String getType (); | ||
| } | ||
Returned By: CertificateFactory.getInstance()
| CertificateFactorySpi | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.security.cert | ||
This abstract class defines the service provider interface, or SPI, for the CertificateFactory class. A security provider must implement this class for each type of certificate it wishes to support. Applications never need to use or subclass this class.
| public abstract class CertificateFactorySpi { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public CertificateFactorySpi (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract java.security.cert.Certificate engineGenerateCertificate (java.io.InputStream inStream) throws CertificateException; | ||
| public abstract java.util.Collection engineGenerateCertificates (java.io.InputStream inStream) throws CertificateException; | ||
| public abstract CRL engineGenerateCRL (java.io.InputStream inStream) throws CRLException; | ||
| public abstract java.util.Collection engineGenerateCRLs (java.io.InputStream inStream) throws CRLException; | ||
| } | ||
Passed To: CertificateFactory.CertificateFactory()
| CertificateNotYetValidException | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.security.cert | serializable checked | |
Signals that a certificate is not yet valid or will not yet be valid on a specified date.
| public class CertificateNotYetValidException extends CertificateException { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public CertificateNotYetValidException (); | ||
| public CertificateNotYetValidException (String message); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Throwable(Serializable)-->Exception-->java.security.GeneralSecurityException-->CertificateException-->CertificateNotYetValidException
Thrown By: X509Certificate.checkValidity()
| CertificateParsingException | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.security.cert | serializable checked | |
Signals an error or other problem while parsing a certificate.
| public class CertificateParsingException extends CertificateException { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public CertificateParsingException (); | ||
| public CertificateParsingException (String message); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Throwable(Serializable)-->Exception-->java.security.GeneralSecurityException-->CertificateException-->CertificateParsingException
| CRL | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.security.cert | ||
This abstract class represents a certificaterevocation list (CRL). A CRL is an object issued by a certificate authority (or other certificate signer) that lists certificates that have been revoked, meaning that they are now invalid and should be rejected. Use a CertificateFactory to parse a CRL from a byte stream. Use the isRevoked() method to test whether a specified Certificate is listed on the CRL. Note that type-specific CRL subclasses, such as X509CRL, may provide access to substantially more information about the revocation list.
| public abstract class CRL { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected CRL (String type); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public final String getType (); | ||
| public abstract boolean isRevoked (java.security.cert.Certificate cert); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public abstract String toString (); | ||
| } | ||
Subclasses: X509CRL
Returned By: CertificateFactory.generateCRL(), CertificateFactorySpi.engineGenerateCRL()
| CRLException | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.security.cert | serializable checked | |
Signals an error or other problem while working with a CRL.
| public class CRLException extends java.security.GeneralSecurityException { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public CRLException (); | ||
| public CRLException (String message); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Throwable(Serializable)-->Exception-->java.security.GeneralSecurityException-->CRLException
Thrown By: CertificateFactory.{generateCRL(), generateCRLs()}, CertificateFactorySpi.{engineGenerateCRL(), engineGenerateCRLs()}, X509CRL.{getEncoded(), getTBSCertList(), verify()}, X509CRLEntry.getEncoded()
| X509Certificate | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.security.cert | serializable | |
This class represents an X.509 certificate. Its various methods provide complete access to the contents of the certificate. For example, verify() checks the digital signature of the certificate to verify that it is not a forged certificate, while checkValidity() checks whether the certificate has expired or has not yet gone into effect. getSubjectDN() returns the Principal to whom this certificate applies, and getPublicKey() returns the PublicKey for that Principal. Note that verify() and getPublicKey() are inherited from Certificate.
Obtain an X509Certificate object by creating a CertificateFactory for certificate type "X.509" and then using generateCertificate() to parse an X.509 certificate from a stream of bytes. Finally, cast the Certificate returned by this method to an X509Certificate.
| public abstract class X509Certificate extends java.security.cert.Certificate implements X509Extension { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected X509Certificate (); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public abstract int getBasicConstraints (); | ||
| public abstract java.util.Set getCriticalExtensionOIDs (); | Implements:X509Extension | |
| public abstract java.security.Principal getIssuerDN (); | ||
| public abstract boolean[ ] getIssuerUniqueID (); | ||
| public abstract boolean[ ] getKeyUsage (); | ||
| public abstract java.util.Set getNonCriticalExtensionOIDs (); | Implements:X509Extension | |
| public abstract java.util.Date getNotAfter (); | ||
| public abstract java.util.Date getNotBefore (); | ||
| public abstract java.math.BigInteger getSerialNumber (); | ||
| public abstract String getSigAlgName (); | ||
| public abstract String getSigAlgOID (); | ||
| public abstract byte[ ] getSigAlgParams (); | ||
| public abstract byte[ ] getSignature (); | ||
| public abstract java.security.Principal getSubjectDN (); | ||
| public abstract boolean[ ] getSubjectUniqueID (); | ||
| public abstract byte[ ] getTBSCertificate () throws CertificateEncodingException; | ||
| public abstract int getVersion (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract void checkValidity () throws CertificateExpiredExceptionCertificateNotYetValidException; | ||
| public abstract void checkValidity (java.util.Date date) throws CertificateExpiredExceptionCertificateNotYetValidException; | ||
| // | Methods Implementing X509Extension | |
| public abstract java.util.Set getCriticalExtensionOIDs (); | ||
| public abstract byte[ ] getExtensionValue (String oid); | ||
| public abstract java.util.Set getNonCriticalExtensionOIDs (); | ||
| public abstract boolean hasUnsupportedCriticalExtension (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->java.security.cert.Certificate(Serializable)-->X509Certificate(X509Extension)
| X509CRL | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.security.cert | ||
This class represents an X.509 CRL, which consists primarily of a set of X509CRLEntry objects. The various methods of this class provide access to all the details of the CRL. Use verify() to check the digital signature of the CRL to ensure that it does indeed originate from the the source it specifies. Use the inherited isRevoked() method to determine whether a given certificate has been revoked. If you are curious about the revocation date for a revoked certificate, obtain the X509CRLEntry for that certificate by calling getRevokedCertificate(). Call getThisUpdate() to obtain the date this CRL was issued. Use getNextUpdate() to find if the CRL has been superseded by a newer version.
Obtain an X509CRL object by creating a CertificateFactory for certificate type "X.509" and then using the generateCRL() to parse an X.509 CRL from a stream of bytes. Finally, cast the CRL returned by this method to an X509CRL.
| public abstract class X509CRL extends CRL implements X509Extension { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected X509CRL (); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public abstract java.util.Set getCriticalExtensionOIDs (); | Implements:X509Extension | |
| public abstract byte[ ] getEncoded () throws CRLException; | ||
| public abstract java.security.Principal getIssuerDN (); | ||
| public abstract java.util.Date getNextUpdate (); | ||
| public abstract java.util.Set getNonCriticalExtensionOIDs (); | Implements:X509Extension | |
| public abstract java.util.Set getRevokedCertificates (); | ||
| public abstract String getSigAlgName (); | ||
| public abstract String getSigAlgOID (); | ||
| public abstract byte[ ] getSigAlgParams (); | ||
| public abstract byte[ ] getSignature (); | ||
| public abstract byte[ ] getTBSCertList () throws CRLException; | ||
| public abstract java.util.Date getThisUpdate (); | ||
| public abstract int getVersion (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract X509CRLEntry getRevokedCertificate (java.math.BigInteger serialNumber); | ||
| public abstract void verify (java.security.PublicKey key) throws CRLExceptionjava.security.NoSuchAlgorithmExceptionjava.security.InvalidKeyExceptionjava.security.NoSuchProviderExceptionjava.security.SignatureException; | ||
| public abstract void verify (java.security.PublicKey key, String sigProvider) throws CRLExceptionjava.security.NoSuchAlgorithmExceptionjava.security.InvalidKeyExceptionjava.security.NoSuchProviderExceptionjava.security.SignatureException; | ||
| // | Methods Implementing X509Extension | |
| public abstract java.util.Set getCriticalExtensionOIDs (); | ||
| public abstract byte[ ] getExtensionValue (String oid); | ||
| public abstract java.util.Set getNonCriticalExtensionOIDs (); | ||
| public abstract boolean hasUnsupportedCriticalExtension (); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public boolean equals (Object other); | ||
| public int hashCode (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->CRL-->X509CRL(X509Extension)
| X509CRLEntry | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.security.cert | ||
This class represents a single entry in an X509CRL. It contains the serial number and revocation date for a revoked certificate.
| public abstract class X509CRLEntry implements X509Extension { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public X509CRLEntry (); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public abstract java.util.Set getCriticalExtensionOIDs (); | Implements:X509Extension | |
| public abstract byte[ ] getEncoded () throws CRLException; | ||
| public abstract java.util.Set getNonCriticalExtensionOIDs (); | Implements:X509Extension | |
| public abstract java.util.Date getRevocationDate (); | ||
| public abstract java.math.BigInteger getSerialNumber (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract boolean hasExtensions (); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing X509Extension | |
| public abstract java.util.Set getCriticalExtensionOIDs (); | ||
| public abstract byte[ ] getExtensionValue (String oid); | ||
| public abstract java.util.Set getNonCriticalExtensionOIDs (); | ||
| public abstract boolean hasUnsupportedCriticalExtension (); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public boolean equals (Object other); | ||
| public int hashCode (); | ||
| public abstract String toString (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->X509CRLEntry(X509Extension)
Returned By: X509CRL.getRevokedCertificate()
| X509Extension | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.security.cert | ||
This interface defines methods for handling a set of extensions to X.509 certificates and CRLs. Each extension has a name, or OID (object identifier), that identifies the type of the extension. An extension may be marked critical or noncritical. Noncritical extensions whose OIDs are not recognized can safely be ignored. However, if a critical exception is not recognized, the Certificate or CRL should be rejected. Each extension in the set has a byte array of data as its value. The interpretation of these bytes depends on the OID of the extension, of course.
| public interface X509Extension { | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract java.util.Set getCriticalExtensionOIDs (); | ||
| public abstract byte[ ] getExtensionValue (String oid); | ||
| public abstract java.util.Set getNonCriticalExtensionOIDs (); | ||
| public abstract boolean hasUnsupportedCriticalExtension (); | ||
| } | ||
Implementations: X509Certificate, X509CRL, X509CRLEntry

Copyright © 2001 O'Reilly & Associates. All rights reserved.