Chapter 16. The java.awt.geom Package
The java.awt.geom package contains Java 2D classes and interfaces related to shapes and geometry; the package is new in Java 1.2. Most of the classes in this package are java.awt.Shape implementations that can be drawn and filled by a java.awt.Graphics2D object. Note that some implementations store data using single-precision floating-point coordinates, while others use double-precision coordinates. Other important classes include AffineTransform, Area, GeneralPath, and PathIterator. Figure 16-1 shows the class hierarchy of this package.
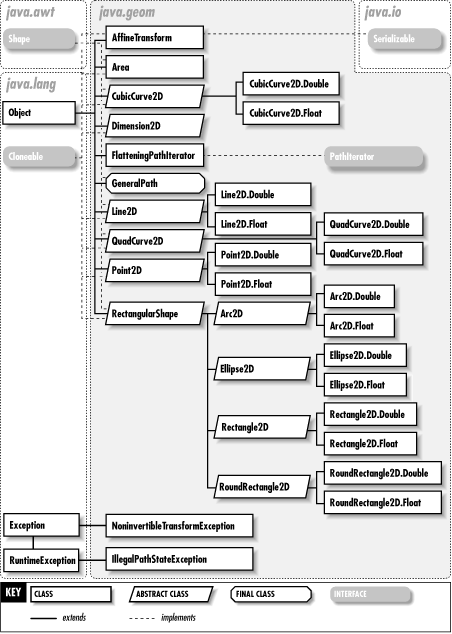
Figure 16-1. The java.awt.geom package
| AffineTransform | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable serializable | |
An AffineTransform represents an arbitrary linear transformation of a point, vector, shape, or coordinate system by any combination of translation, rotation, scaling, flipping, and skewing. This is one of the most fundamental classes in Java 2D: the Java 2D rendering process uses an AffineTransform to convert from user coordinate space to the coordinate space of the physical device. In addition to this implicit use of AffineTransform, the class is often used explicitly in Java 2D programming.
The transformations specified by AffineTransform objects are quite general. But they are all linear: straight lines remain straight, and parallel lines remain parallel under any AffineTransform. Although it is possible to imagine more general, nonlinear, transformations, Java 2D works only with affine transformations. AffineTransform is not an implementation of some more general Transform interface.
Mathematically, an affine transformation is represented by a 2-by-3 matrix of six numbers. The AffineTransform class has constructors and methods that allow you to work with this matrix directly, but unless you remember your linear algebra, you typically use the higher-level methods of this class.
You can use a constructor to create an AffineTransform, but it is usually easier to use one of the static methods to create an AffineTransform suitable for rotation about the origin, rotation about an arbitrary point, scaling, shearing, or translation. Or, if you have an existing AffineTransform object that you want to reuse, you can use one of the setTo() methods to specify a rotation, scale, shear, or translation to replace the existing transform. Note that a flip transform is simply scaling by -1.0 in the X or Y dimension.
Often, however, you have an AffineTransform that you want to transform further. The rotate(), scale(), shear(), and translate() methods do this. Or, more generally, you can use concatenate() or preConcatenate() to transform one AffineTransform by another.
Once an AffineTransform object is set to the desired transformation, the transform() method can be used to transform points, or arrays of points, in the desired way. deltaTransform() transforms a point or array of points, leaving out any translation component of the transform. This is useful for transforming dimensions and position-independent vectors, rather than transforming absolute coordinates. inverseTransform() performs the inverse of the transformation specified by an AffineTransform. Finally, createTransformedShape() returns a java.awt.Shape that represents a transformed version of the specified Shape.
isIdentity() returns true if an AffineTransform is an identity transform--that is, if it performs no transform at all. getType() returns a value that provides basic information about the transform. The value returned is TYPE_IDENTITY, TYPE_GENERAL_TRANSFORM, or a bitmask of the remaining type constants.
| public class AffineTransform implements Cloneable, Serializable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public AffineTransform (); | ||
| public AffineTransform (double[ ] flatmatrix); | ||
| public AffineTransform (float[ ] flatmatrix); | ||
| public AffineTransform (AffineTransform Tx); | ||
| public AffineTransform (double m00, double m10, double m01, double m11, double m02, double m12); | ||
| public AffineTransform (float m00, float m10, float m01, float m11, float m02, float m12); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final int TYPE_FLIP ; | =64 | |
| public static final int TYPE_GENERAL_ROTATION ; | =16 | |
| public static final int TYPE_GENERAL_SCALE ; | =4 | |
| public static final int TYPE_GENERAL_TRANSFORM ; | =32 | |
| public static final int TYPE_IDENTITY ; | =0 | |
| public static final int TYPE_MASK_ROTATION ; | =24 | |
| public static final int TYPE_MASK_SCALE ; | =6 | |
| public static final int TYPE_QUADRANT_ROTATION ; | =8 | |
| public static final int TYPE_TRANSLATION ; | =1 | |
| public static final int TYPE_UNIFORM_SCALE ; | =2 | |
| // | Public Class Methods | |
| public static AffineTransform getRotateInstance (double theta); | ||
| public static AffineTransform getRotateInstance (double theta, double x, double y); | ||
| public static AffineTransform getScaleInstance (double sx, double sy); | ||
| public static AffineTransform getShearInstance (double shx, double shy); | ||
| public static AffineTransform getTranslateInstance (double tx, double ty); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public double getDeterminant (); | default:1.0 | |
| public boolean isIdentity (); | default:true | |
| public double getScaleX (); | default:1.0 | |
| public double getScaleY (); | default:1.0 | |
| public double getShearX (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getShearY (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getTranslateX (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getTranslateY (); | default:0.0 | |
| public int getType (); | default:0 | |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void concatenate (AffineTransform Tx); | ||
| public AffineTransform createInverse () throws NoninvertibleTransformException; | ||
| public Shape createTransformedShape (Shape pSrc); | ||
| public Point2D deltaTransform (Point2D ptSrc, Point2D ptDst); | ||
| public void deltaTransform (double[ ] srcPts, int srcOff, double[ ] dstPts, int dstOff, int numPts); | ||
| public void getMatrix (double[ ] flatmatrix); | ||
| public Point2D inverseTransform (Point2D ptSrc, Point2D ptDst) throws NoninvertibleTransformException; | ||
| public void inverseTransform (double[ ] srcPts, int srcOff, double[ ] dstPts, int dstOff, int numPts) throws NoninvertibleTransformException; | ||
| public void preConcatenate (AffineTransform Tx); | ||
| public void rotate (double theta); | ||
| public void rotate (double theta, double x, double y); | ||
| public void scale (double sx, double sy); | ||
| public void setToIdentity (); | ||
| public void setToRotation (double theta); | ||
| public void setToRotation (double theta, double x, double y); | ||
| public void setToScale (double sx, double sy); | ||
| public void setToShear (double shx, double shy); | ||
| public void setToTranslation (double tx, double ty); | ||
| public void setTransform (AffineTransform Tx); | ||
| public void setTransform (double m00, double m10, double m01, double m11, double m02, double m12); | ||
| public void shear (double shx, double shy); | ||
| public Point2D transform (Point2D ptSrc, Point2D ptDst); | ||
| public void transform (float[ ] srcPts, int srcOff, float[ ] dstPts, int dstOff, int numPts); | ||
| public void transform (Point2D[ ] ptSrc, int srcOff, Point2D[ ] ptDst, int dstOff, int numPts); | ||
| public void transform (float[ ] srcPts, int srcOff, double[ ] dstPts, int dstOff, int numPts); | ||
| public void transform (double[ ] srcPts, int srcOff, double[ ] dstPts, int dstOff, int numPts); | ||
| public void transform (double[ ] srcPts, int srcOff, float[ ] dstPts, int dstOff, int numPts); | ||
| public void translate (double tx, double ty); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public Object clone (); | ||
| public boolean equals (Object obj); | ||
| public int hashCode (); | ||
| public String toString (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->AffineTransform(Cloneable,Serializable)
Passed To: Too many methods to list.
Returned By: Font.getTransform(), Graphics2D.getTransform(), GraphicsConfiguration.{getDefaultTransform(), getNormalizingTransform()}, java.awt.font.FontRenderContext.getTransform(), java.awt.font.GlyphVector.getGlyphTransform(), java.awt.font.TransformAttribute.getTransform(), AffineTransform.{createInverse(), getRotateInstance(), getScaleInstance(), getShearInstance(), getTranslateInstance()}, java.awt.image.AffineTransformOp.getTransform(), java.awt.image.renderable.RenderContext.getTransform()
| Arc2D | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable shape | |
This abstract class is a java.awt.Shape that represents an arc. The arc is defined as a portion of an ellipse, where the ellipse is defined by a rectangle. The start and end points of the arc on that ellipse are defined by a start angle and an extent angle, measured in degrees counterclockwise from the positive X axis. Unless the ellipse is actually a perfect circle, the specified angles are not true angles: a line drawn from the center of the ellipse to the upper-right corner of the bounding rectangle is always considered to form a 45-degree angle with the X axis, regardless of the true angle it forms.
In addition to the coordinates of the rectangle and the angles that specify the start and end points of the arc, the shape of an Arc2D is also specified by its arcType property. If the type of the arc is specified as CHORD, the two end points are joined by a straight line. If the type is specified as PIE, each of the two end points is joined to the center of the ellipse, forming a wedge, or slice of pie. If the type is specified as OPEN, the end points are not joined and the resulting shape is an open curve that does not enclose a region.
Arc2D is an abstract class and cannot be instantiated. Arc2D.Float and Arc2D.Double are concrete subclasses that use float and double fields to store arc coordinates and angles.
| public abstract class Arc2D extends RectangularShape { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected Arc2D (int type); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final int CHORD ; | =1 | |
| public static final int OPEN ; | =0 | |
| public static final int PIE ; | =2 | |
| // | Inner Classes | |
| ; | ||
| ; | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public abstract double getAngleExtent (); | ||
| public abstract void setAngleExtent (double angExt); | ||
| public abstract double getAngleStart (); | ||
| public void setAngleStart (Point2D p); | ||
| public abstract void setAngleStart (double angSt); | ||
| public int getArcType (); | ||
| public void setArcType (int type); | ||
| public Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | Overrides:RectangularShape | |
| public Point2D getEndPoint (); | ||
| public Point2D getStartPoint (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public boolean containsAngle (double angle); | ||
| public void setAngles (Point2D p1, Point2D p2); | ||
| public void setAngles (double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2); | ||
| public void setArc (Arc2D a); | ||
| public void setArc (Rectangle2D rect, double angSt, double angExt, int closure); | ||
| public void setArc (Point2D loc, Dimension2D size, double angSt, double angExt, int closure); | ||
| public abstract void setArc (double x, double y, double w, double h, double angSt, double angExt, int closure); | ||
| public void setArcByCenter (double x, double y, double radius, double angSt, double angExt, int closure); | ||
| public void setArcByTangent (Point2D p1, Point2D p2, Point2D p3, double radius); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding RectangularShape | |
| public boolean contains (Rectangle2D r); | ||
| public boolean contains (double x, double y); | ||
| public boolean contains (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| public PathIterator getPathIterator (AffineTransform at); | ||
| public boolean intersects (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| public void setFrame (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| // | Protected Instance Methods | |
| protected abstract Rectangle2D makeBounds (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->RectangularShape(Cloneable,Shape)-->Arc2D
Subclasses: Arc2D.Double, Arc2D.Float
Passed To: Arc2D.setArc()
| Arc2D.Double | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable shape | |
This class is a concrete implementation of Arc2D that uses double fields to store the coordinates and angles of the arc. For efficiency, these x, y, width, height, start, and extent fields are declared public and may be used directly by Java programs. See Arc2D for more information.
| public static class Arc2D.Double extends Arc2D { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Double (); | ||
| public Double (int type); | ||
| public Double (Rectangle2D ellipseBounds, double start, double extent, int type); | ||
| public Double (double x, double y, double w, double h, double start, double extent, int type); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Arc2D | |
| public double getAngleExtent (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getAngleStart (); | default:0.0 | |
| public void setAngleExtent (double angExt); | ||
| public void setAngleStart (double angSt); | ||
| public void setArc (double x, double y, double w, double h, double angSt, double angExt, int closure); | ||
| // | Protected Methods Overriding Arc2D | |
| protected Rectangle2D makeBounds (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding RectangularShape | |
| public double getHeight (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getWidth (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getX (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getY (); | default:0.0 | |
| public boolean isEmpty (); | default:true | |
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public double extent ; | ||
| public double height ; | ||
| public double start ; | ||
| public double width ; | ||
| public double x ; | ||
| public double y ; | ||
| } | ||
| Arc2D.Float | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable shape | |
This class is a concrete implementation of Arc2D that uses float fields to store the coordinates and angles of the arc. For efficiency, these x, y, width, height, start, and extent fields are declared public and may be used directly by Java programs. See Arc2D for more information.
| public static class Arc2D.Float extends Arc2D { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Float (); | ||
| public Float (int type); | ||
| public Float (Rectangle2D ellipseBounds, float start, float extent, int type); | ||
| public Float (float x, float y, float w, float h, float start, float extent, int type); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Arc2D | |
| public double getAngleExtent (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getAngleStart (); | default:0.0 | |
| public void setAngleExtent (double angExt); | ||
| public void setAngleStart (double angSt); | ||
| public void setArc (double x, double y, double w, double h, double angSt, double angExt, int closure); | ||
| // | Protected Methods Overriding Arc2D | |
| protected Rectangle2D makeBounds (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding RectangularShape | |
| public double getHeight (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getWidth (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getX (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getY (); | default:0.0 | |
| public boolean isEmpty (); | default:true | |
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public float extent ; | ||
| public float height ; | ||
| public float start ; | ||
| public float width ; | ||
| public float x ; | ||
| public float y ; | ||
| } | ||
| Area | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable shape | |
Area is an implementation of java.awt.Shape that represents an arbitrary enclosed area. The Area() constructor is passed an arbitrary Shape that defines the initial area. If this Shape object represents an open curve that does not enclose an area, the curve is automatically closed with a straight line between the end points. Once an Area object has been created, it can be combined with another Area object with the add(), subtract(), intersect(), and exclusiveOr() methods. For example, you can construct an Area object that represents a hexagon minus the intersection of two circles.
| public class Area implements Cloneable, Shape { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Area (); | ||
| public Area (Shape s); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public Rectangle getBounds (); | Implements:Shape | |
| public Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | Implements:Shape default:Rectangle2D.Double | |
| public boolean isEmpty (); | default:true | |
| public boolean isPolygonal (); | default:true | |
| public boolean isRectangular (); | default:true | |
| public boolean isSingular (); | default:true | |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void add (Area rhs); | ||
| public Area createTransformedArea (AffineTransform t); | ||
| public boolean equals (Area other); | ||
| public void exclusiveOr (Area rhs); | ||
| public void intersect (Area rhs); | ||
| public void reset (); | ||
| public void subtract (Area rhs); | ||
| public void transform (AffineTransform t); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing Shape | |
| public boolean contains (Point2D p); | ||
| public boolean contains (Rectangle2D p); | ||
| public boolean contains (double x, double y); | ||
| public boolean contains (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| public Rectangle getBounds (); | ||
| public Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | default:Rectangle2D.Double | |
| public PathIterator getPathIterator (AffineTransform at); | ||
| public PathIterator getPathIterator (AffineTransform at, double flatness); | ||
| public boolean intersects (Rectangle2D p); | ||
| public boolean intersects (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public Object clone (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Area(Cloneable,Shape)
Passed To: Area.{add(), equals(), exclusiveOr(), intersect(), subtract()}
Returned By: Area.createTransformedArea()
| CubicCurve2D | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable shape | |
This abstract class is a java.awt.Shape that represents a smooth cubic Bezier curve (or spline) between end points p1 (x1, y1) and p2 (x2, y2). The precise shape of the curve is defined by two control points, cp1 (ctrlx1, ctrly1) and cp2 (ctrlx2, ctrly2). Note that the curve does not pass through cp1 and cp2 but that it does remain inside the quadrilateral defined by p1, cp1, cp2, and p2.
CubicCurve2D does not itself enclose an area, so the contains() methods test whether a point or rectangle is within the area defined by the curve and the straight line between its end points.
CubicCurve2D is an abstract class and cannot be instantiated. CubicCurve2D.Float and CubicCurve2D.Double are concrete subclasses that use float and double fields to store the end points and control points. See also QuadCurve2D, which is a quadratic Bezier curve that uses only a single control point.
| public abstract class CubicCurve2D implements Cloneable, Shape { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected CubicCurve2D (); | ||
| // | Inner Classes | |
| ; | ||
| ; | ||
| // | Public Class Methods | |
| public static double getFlatness (double[ ] coords, int offset); | ||
| public static double getFlatness (double x1, double y1, double ctrlx1, double ctrly1, double ctrlx2, double ctrly2, double x2, double y2); | ||
| public static double getFlatnessSq (double[ ] coords, int offset); | ||
| public static double getFlatnessSq (double x1, double y1, double ctrlx1, double ctrly1, double ctrlx2, double ctrly2, double x2, double y2); | ||
| public static int solveCubic (double[ ] eqn); | ||
| public static void subdivide (CubicCurve2D src, CubicCurve2D left, CubicCurve2D right); | ||
| public static void subdivide (double[ ] src, int srcoff, double[ ] left, int leftoff, double[ ] right, int rightoff); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public Rectangle getBounds (); | Implements:Shape | |
| public abstract Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | Implements:Shape | |
| public abstract Point2D getCtrlP1 (); | ||
| public abstract Point2D getCtrlP2 (); | ||
| public abstract double getCtrlX1 (); | ||
| public abstract double getCtrlX2 (); | ||
| public abstract double getCtrlY1 (); | ||
| public abstract double getCtrlY2 (); | ||
| public double getFlatness (); | ||
| public double getFlatnessSq (); | ||
| public abstract Point2D getP1 (); | ||
| public abstract Point2D getP2 (); | ||
| public abstract double getX1 (); | ||
| public abstract double getX2 (); | ||
| public abstract double getY1 (); | ||
| public abstract double getY2 (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void setCurve (CubicCurve2D c); | ||
| public void setCurve (double[ ] coords, int offset); | ||
| public void setCurve (Point2D[ ] pts, int offset); | ||
| public void setCurve (Point2D p1, Point2D cp1, Point2D cp2, Point2D p2); | ||
| public abstract void setCurve (double x1, double y1, double ctrlx1, double ctrly1, double ctrlx2, double ctrly2, double x2, double y2); | ||
| public void subdivide (CubicCurve2D left, CubicCurve2D right); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing Shape | |
| public boolean contains (Point2D p); | ||
| public boolean contains (Rectangle2D r); | ||
| public boolean contains (double x, double y); | ||
| public boolean contains (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| public Rectangle getBounds (); | ||
| public abstract Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | ||
| public PathIterator getPathIterator (AffineTransform at); | ||
| public PathIterator getPathIterator (AffineTransform at, double flatness); | ||
| public boolean intersects (Rectangle2D r); | ||
| public boolean intersects (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public Object clone (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->CubicCurve2D(Cloneable,Shape)
Subclasses: CubicCurve2D.Double, CubicCurve2D.Float
Passed To: CubicCurve2D.{setCurve(), subdivide()}
| CubicCurve2D.Double | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable shape | |
This class is a concrete implementation of CubicCurve2D that uses double fields to store the end points and control points of the curve. The X and Y coordinates of these four points are stored in public fields and may be used directly by Java programs. See CubicCurve2D for more information.
| public static class CubicCurve2D.Double extends CubicCurve2D { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Double (); | ||
| public Double (double x1, double y1, double ctrlx1, double ctrly1, double ctrlx2, double ctrly2, double x2, double y2); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding CubicCurve2D | |
| public Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | default:Rectangle2D.Double | |
| public Point2D getCtrlP1 (); | default:Point2D.Double | |
| public Point2D getCtrlP2 (); | default:Point2D.Double | |
| public double getCtrlX1 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getCtrlX2 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getCtrlY1 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getCtrlY2 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public Point2D getP1 (); | default:Point2D.Double | |
| public Point2D getP2 (); | default:Point2D.Double | |
| public double getX1 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getX2 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getY1 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getY2 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public void setCurve (double x1, double y1, double ctrlx1, double ctrly1, double ctrlx2, double ctrly2, double x2, double y2); | ||
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public double ctrlx1 ; | ||
| public double ctrlx2 ; | ||
| public double ctrly1 ; | ||
| public double ctrly2 ; | ||
| public double x1 ; | ||
| public double x2 ; | ||
| public double y1 ; | ||
| public double y2 ; | ||
| } | ||
| CubicCurve2D.Float | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable shape | |
This class is a concrete implementation of CubicCurve2D that uses float fields to store the end points and control points of the curve. The X and Y coordinates of these four points are stored in public fields and may be used directly by Java programs. See CubicCurve2D for more information.
| public static class CubicCurve2D.Float extends CubicCurve2D { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Float (); | ||
| public Float (float x1, float y1, float ctrlx1, float ctrly1, float ctrlx2, float ctrly2, float x2, float y2); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void setCurve (float x1, float y1, float ctrlx1, float ctrly1, float ctrlx2, float ctrly2, float x2, float y2); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding CubicCurve2D | |
| public Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | default:Rectangle2D.Float | |
| public Point2D getCtrlP1 (); | default:Point2D.Float | |
| public Point2D getCtrlP2 (); | default:Point2D.Float | |
| public double getCtrlX1 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getCtrlX2 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getCtrlY1 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getCtrlY2 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public Point2D getP1 (); | default:Point2D.Float | |
| public Point2D getP2 (); | default:Point2D.Float | |
| public double getX1 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getX2 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getY1 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getY2 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public void setCurve (double x1, double y1, double ctrlx1, double ctrly1, double ctrlx2, double ctrly2, double x2, double y2); | ||
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public float ctrlx1 ; | ||
| public float ctrlx2 ; | ||
| public float ctrly1 ; | ||
| public float ctrly2 ; | ||
| public float x1 ; | ||
| public float x2 ; | ||
| public float y1 ; | ||
| public float y2 ; | ||
| } | ||
| Dimension2D | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable | |
This class represents a two-dimensional size in terms of its width and height. The accessor methods defined by this class query and set the width and height using values of type double. Note, however, that this class is abstract and does not actually store a size itself. java.awt.Dimension is a concrete subclass that stores a width and height as integers.
| public abstract class Dimension2D implements Cloneable { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected Dimension2D (); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public abstract double getHeight (); | ||
| public abstract double getWidth (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void setSize (Dimension2D d); | ||
| public abstract void setSize (double width, double height); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public Object clone (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Dimension2D(Cloneable)
Subclasses: Dimension
Passed To: Arc2D.setArc(), Dimension2D.setSize(), RectangularShape.setFrame()
| Ellipse2D | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable shape | |
This abstract class is a java.awt.Shape that represents an ellipse (or a circle). Ellipse2D is a subclass of RectangularShape, and for this reason, the ellipse is defined by its bounding rectangle. The width and height of the bounding rectangle specify the length of the two axes of the ellipse. (If the width and height are equal, the ellipse is a circle.) The X and Y coordinates of the ellipse specify the upper-left corner of the bounding rectangle; note that this point actually falls outside of the ellipse. The setFrameFromCenter() method, inherited from RectangularShape, allows you to define the ellipse by specifying the center and one corner. Note that Ellipse2D can only represent ellipses whose axes are parallel to the X and Y axes of the coordinate system. In order to work with rotated ellipses, use the createTransformedShape() method of AffineTransform or some other transformation method.
Ellipse2D is an abstract class and cannot be instantiated. The concrete subclasses Ellipse2D.Double and Ellipse2D.Float represent ellipses using double and float fields to contain the rectangular coordinates.
| public abstract class Ellipse2D extends RectangularShape { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected Ellipse2D (); | ||
| // | Inner Classes | |
| ; | ||
| ; | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding RectangularShape | |
| public boolean contains (double x, double y); | ||
| public boolean contains (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| public PathIterator getPathIterator (AffineTransform at); | ||
| public boolean intersects (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->RectangularShape(Cloneable,Shape)-->Ellipse2D
Subclasses: Ellipse2D.Double, Ellipse2D.Float
| Ellipse2D.Double | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable shape | |
This class is a concrete implementation of Ellipse2D that uses double fields to store the coordinates of the bounding rectangle of the ellipse. These x, y, width, height fields are declared public and may be used directly by Java programs. See Ellipse2D for more information.
| public static class Ellipse2D.Double extends Ellipse2D { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Double (); | ||
| public Double (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding RectangularShape | |
| public Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | default:Rectangle2D.Double | |
| public double getHeight (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getWidth (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getX (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getY (); | default:0.0 | |
| public boolean isEmpty (); | default:true | |
| public void setFrame (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public double height ; | ||
| public double width ; | ||
| public double x ; | ||
| public double y ; | ||
| } | ||
| Ellipse2D.Float | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable shape | |
This class is a concrete implementation of Ellipse2D that uses float fields to store the coordinates of the bounding rectangle of the ellipse. Note that these x, y, width, height fields are declared public and may be used directly by Java programs. See Ellipse2D for more information.
| public static class Ellipse2D.Float extends Ellipse2D { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Float (); | ||
| public Float (float x, float y, float w, float h); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void setFrame (float x, float y, float w, float h); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding RectangularShape | |
| public Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | default:Rectangle2D.Float | |
| public double getHeight (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getWidth (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getX (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getY (); | default:0.0 | |
| public boolean isEmpty (); | default:true | |
| public void setFrame (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public float height ; | ||
| public float width ; | ||
| public float x ; | ||
| public float y ; | ||
| } | ||
| FlatteningPathIterator | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | ||
This class is a PathIterator that flattens the curves returned by another PathIterator, approximating them with straight-line segments that are easier to work with. The currentSegment() methods of FlatteningPathIterator are guaranteed never to return SEG_QUADTO or SEG_CUBICTO curve segments.
The flatness of a cubic or quadratic curve is the distance from the curve to its control points. Smaller distances imply flatter curves (i.e., curves that are closer to a straight line). The flatness argument to the FlatteningPathIterator() constructor specifies how flat a curve must be before it is approximated with a flat line. Smaller values of flatness result in increasingly accurate approximations of the curves.
When a FlatteningPathIterator encounters a curve that is not flat enough to approximate with a straight line, it subdivides the curve into two curves, each of which is flatter than the original curve. This process of subdivision continues recursively until the subdivided curves are flat enough to be approximated with line segments, up to the num ber of times specified by the limit argument. If limit is not specified, a default of 10 is used, which means that no curve is broken down into more than 1,024 separate line segments.
You should rarely need to use a FlatteningPathIterator explicitly in Java 2D programming. The two-argument version of the getPathIterator() method of Shape takes a flatness argument and returns a flattened path that does not contain any curves. Implementations of this method typically use FlatteningPathIterator internally.
| public class FlatteningPathIterator implements PathIterator { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public FlatteningPathIterator (PathIterator src, double flatness); | ||
| public FlatteningPathIterator (PathIterator src, double flatness, int limit); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public double getFlatness (); | ||
| public int getRecursionLimit (); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing PathIterator | |
| public int currentSegment (double[ ] coords); | ||
| public int currentSegment (float[ ] coords); | ||
| public int getWindingRule (); | ||
| public boolean isDone (); | ||
| public void next (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->FlatteningPathIterator(PathIterator)
| GeneralPath | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable shape | |
This class represents an arbitrary path or shape that consists of any number of line segments and quadratic and cubic Bezier curves. After creating a GeneralPath object, you must define a current point by calling moveTo(). Once an initial current point is established, you can create the path by calling lineTo(), quadTo(), and curveTo(). These methods draw line segments, quadratic curves, and cubic curves from the current point to a new point (which becomes the new current point).
The shape defined by a GeneralPath need not be closed, although you may close it by calling the closePath() method, which appends a line segment between the current point and the initial point. Similarly, the path need not be continuous: you can call moveTo() at any time to change the current point without adding a connecting line or curve to the path. The append() method allows you to add a Shape or PathIterator to a GeneralPath, optionally connecting it to the current point with a straight line.
The GeneralPath() constructor allows you to specify an estimate of the number of path segments that will be added. Specifying an accurate estimate can increase efficiency. It also allows you to specify the winding rule to use for the path. A winding rule is used to determine what points are contained within a GeneralPath. The choice of winding rules matters only for those paths that intersect themselves. The two choices are WIND_EVEN_ODD and WIND_NON_ZERO.
Note the close correspondence between the path elements (lines, quadratic curves, and cubic curves) that may be appended to a GeneralPath and those that are enumerated by a PathIterator object.
| public final class GeneralPath implements Cloneable, Shape { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public GeneralPath (); | ||
| public GeneralPath (int rule); | ||
| public GeneralPath (Shape s); | ||
| public GeneralPath (int rule, int initialCapacity); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final int WIND_EVEN_ODD ; | =0 | |
| public static final int WIND_NON_ZERO ; | =1 | |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public Rectangle getBounds (); | Implements:Shape | |
| public Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | Implements:Shape synchronized default:Rectangle2D.Float | |
| public Point2D getCurrentPoint (); | synchronized default:null | |
| public int getWindingRule (); | synchronized default:1 | |
| public void setWindingRule (int rule); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void append (Shape s, boolean connect); | ||
| public void append (PathIterator pi, boolean connect); | ||
| public void closePath (); | synchronized | |
| public Shape createTransformedShape (AffineTransform at); | synchronized | |
| public void curveTo (float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2, float x3, float y3); | synchronized | |
| public void lineTo (float x, float y); | synchronized | |
| public void moveTo (float x, float y); | synchronized | |
| public void quadTo (float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2); | synchronized | |
| public void reset (); | synchronized | |
| public void transform (AffineTransform at); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing Shape | |
| public boolean contains (Rectangle2D r); | ||
| public boolean contains (Point2D p); | ||
| public boolean contains (double x, double y); | ||
| public boolean contains (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| public Rectangle getBounds (); | ||
| public Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | synchronized default:Rectangle2D.Float | |
| public PathIterator getPathIterator (AffineTransform at); | ||
| public PathIterator getPathIterator (AffineTransform at, double flatness); | ||
| public boolean intersects (Rectangle2D r); | ||
| public boolean intersects (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public Object clone (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->GeneralPath(Cloneable,Shape)
| IllegalPathStateException | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | serializable unchecked | |
Signals that a path is not in an appropriate state for some requested operation. This exception is thrown if you attempt to append a path segment to a GeneralPath before performing an initial moveTo().
| public class IllegalPathStateException extends RuntimeException { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public IllegalPathStateException (); | ||
| public IllegalPathStateException (String s); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Throwable(Serializable)-->Exception-->RuntimeException-->IllegalPathStateException
| Line2D | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable shape | |
This abstract class is a java.awt.Shape that represents a line segment between two end points. Line2D defines various methods for computing the distance between a point and a line or line segment and for computing the position of a point relative to a line. Note, however, that the setLine() method for specifying the end points of the line segment is abstract. The concrete subclasses Line2D.Double and Line2D.Float use double and float fields to store the coordinates of the end points. They define the setLine() method and constructors that accept the line segment end points as arguments. Since a line does not contain an area, the contains() methods of Line2D and of its subclasses always return false.
| public abstract class Line2D implements Cloneable, Shape { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected Line2D (); | ||
| // | Inner Classes | |
| ; | ||
| ; | ||
| // | Public Class Methods | |
| public static boolean linesIntersect (double X1, double Y1, double X2, double Y2, double X3, double Y3, double X4, double Y4); | ||
| public static double ptLineDist (double X1, double Y1, double X2, double Y2, double PX, double PY); | ||
| public static double ptLineDistSq (double X1, double Y1, double X2, double Y2, double PX, double PY); | ||
| public static double ptSegDist (double X1, double Y1, double X2, double Y2, double PX, double PY); | ||
| public static double ptSegDistSq (double X1, double Y1, double X2, double Y2, double PX, double PY); | ||
| public static int relativeCCW (double X1, double Y1, double X2, double Y2, double PX, double PY); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public Rectangle getBounds (); | Implements:Shape | |
| public abstract Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | Implements:Shape | |
| public abstract Point2D getP1 (); | ||
| public abstract Point2D getP2 (); | ||
| public abstract double getX1 (); | ||
| public abstract double getX2 (); | ||
| public abstract double getY1 (); | ||
| public abstract double getY2 (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public boolean intersectsLine (Line2D l); | ||
| public boolean intersectsLine (double X1, double Y1, double X2, double Y2); | ||
| public double ptLineDist (Point2D pt); | ||
| public double ptLineDist (double PX, double PY); | ||
| public double ptLineDistSq (Point2D pt); | ||
| public double ptLineDistSq (double PX, double PY); | ||
| public double ptSegDist (Point2D pt); | ||
| public double ptSegDist (double PX, double PY); | ||
| public double ptSegDistSq (Point2D pt); | ||
| public double ptSegDistSq (double PX, double PY); | ||
| public int relativeCCW (Point2D p); | ||
| public int relativeCCW (double PX, double PY); | ||
| public void setLine (Line2D l); | ||
| public void setLine (Point2D p1, Point2D p2); | ||
| public abstract void setLine (double X1, double Y1, double X2, double Y2); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing Shape | |
| public boolean contains (Point2D p); | constant | |
| public boolean contains (Rectangle2D r); | constant | |
| public boolean contains (double x, double y); | constant | |
| public boolean contains (double x, double y, double w, double h); | constant | |
| public Rectangle getBounds (); | ||
| public abstract Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | ||
| public PathIterator getPathIterator (AffineTransform at); | ||
| public PathIterator getPathIterator (AffineTransform at, double flatness); | ||
| public boolean intersects (Rectangle2D r); | ||
| public boolean intersects (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public Object clone (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Line2D(Cloneable,Shape)
Subclasses: Line2D.Double, Line2D.Float
Passed To: Line2D.{intersectsLine(), setLine()}, Rectangle2D.intersectsLine()
| Line2D.Double | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable shape | |
This class is a concrete implementation of Line2D that uses double fields to store the end points of the line segment. These end points are stored in public fields and may be directly set and queried by programs. See Line2D for more information.
| public static class Line2D.Double extends Line2D { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Double (); | ||
| public Double (Point2D p1, Point2D p2); | ||
| public Double (double X1, double Y1, double X2, double Y2); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Line2D | |
| public Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | default:Rectangle2D.Double | |
| public Point2D getP1 (); | default:Point2D.Double | |
| public Point2D getP2 (); | default:Point2D.Double | |
| public double getX1 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getX2 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getY1 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getY2 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public void setLine (double X1, double Y1, double X2, double Y2); | ||
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public double x1 ; | ||
| public double x2 ; | ||
| public double y1 ; | ||
| public double y2 ; | ||
| } | ||
| Line2D.Float | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable shape | |
This class is a concrete implementation of Line2D that uses float fields to store the end points of the line segment. These end points are stored in public fields and may be directly set and queried by programs. See Line2D for more information.
| public static class Line2D.Float extends Line2D { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Float (); | ||
| public Float (Point2D p1, Point2D p2); | ||
| public Float (float X1, float Y1, float X2, float Y2); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void setLine (float X1, float Y1, float X2, float Y2); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Line2D | |
| public Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | default:Rectangle2D.Float | |
| public Point2D getP1 (); | default:Point2D.Float | |
| public Point2D getP2 (); | default:Point2D.Float | |
| public double getX1 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getX2 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getY1 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getY2 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public void setLine (double X1, double Y1, double X2, double Y2); | ||
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public float x1 ; | ||
| public float x2 ; | ||
| public float y1 ; | ||
| public float y2 ; | ||
| } | ||
| NoninvertibleTransformException | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | serializable checked | |
Thrown when the inverse of a noninvertible AffineTransform is required. An example of a noninvertible transformation is scaling the X dimension by a factor of 0. This maps all points onto a vertical line, leaving no information about transforming those points back to their original locations. This transform is noninvertible because division by zero is not possible.
| public class NoninvertibleTransformException extends Exception { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public NoninvertibleTransformException (String s); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Throwable(Serializable)-->Exception-->NoninvertibleTransformException
Thrown By: AffineTransform.{createInverse(), inverseTransform()}
| PathIterator | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | ||
This interface is the basic Java 2D mechanism for defining arbitrary shapes. The most important requirement of the java.awt.Shape interface is that every shape be able to return a PathIterator that traverses the outline of the shape. The information returned by a PathIterator is sufficient to allow the Java 2D rendering engine to stroke (draw) or fill arbitrarily complex shapes.
A PathIterator breaks a shape or path down into individual path segments. The currentSegment() method returns the current segment. The next() method moves the iterator on to the next segment, and isDone() returns true if there are no more segments left to iterate. getWindingRule() returns the winding rule for the shape--this value is used to determine which points are inside complex self-intersecting shapes. The two possible values are WIND_EVEN_ODD and WIND_NON_ZERO.
currentSegment() is the most important method of PathIterator. Its return value, one of the five integer constants whose names begin with SEG, specifies the type of the current segment. currentSegment() returns the coordinates of the current segment in the float or double array passed as an argument. This array must have at least six elements. The segment types and their meanings are as follows:
- SEG_MOVETO
-
Defines a path starting point rather than an actual segment. The current point of the path is set to the X,Y point specified in the first two elements of the array. This is the first segment type of all paths. Paths may be disjoint, and may have more than one SEG_MOVETO segment.
- SEG_LINETO
-
Defines a line between the current point and the X,Y end point stored in the first two elements of the array. The end point of the line segment becomes the new current point.
- SEG_QUADTO
-
Defines a quadratic Bezier curve between the current point and an end point stored in the third and fourth elements of the array, using a control point stored in the first and second elements of the array. The end point of the curve becomes the current point.
- SEG_CUBICTO
-
Defines a cubic Bezier curve between the current point and an end point stored in the fifth and sixth elements of the array, using two control points stored in the first through fourth elements of the array. The end point of the curve becomes the current point.
- SEG_CLOSE
-
Specifies that the path should be closed by drawing a straight line from the current point back to the point specified by the most recent SEG_MOVETO segment. No values are stored in the array for this segment type.
| public abstract interface PathIterator { | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final int SEG_CLOSE ; | =4 | |
| public static final int SEG_CUBICTO ; | =3 | |
| public static final int SEG_LINETO ; | =1 | |
| public static final int SEG_MOVETO ; | =0 | |
| public static final int SEG_QUADTO ; | =2 | |
| public static final int WIND_EVEN_ODD ; | =0 | |
| public static final int WIND_NON_ZERO ; | =1 | |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract int currentSegment (float[ ] coords); | ||
| public abstract int currentSegment (double[ ] coords); | ||
| public abstract int getWindingRule (); | ||
| public abstract boolean isDone (); | ||
| public abstract void next (); | ||
| } | ||
Implementations: FlatteningPathIterator
Passed To: FlatteningPathIterator.FlatteningPathIterator(), GeneralPath.append()
Returned By: Too many methods to list.
| Point2D | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable | |
This abstract class represents a point in two-dimensional space. It has methods for getting and setting the X and Y coordinates of the point as double values and for computing the distance between points.
Point2D is abstract; it does not store actual coordinates and cannot be instantiated. You must use one of its concrete subclasses instead. Point2D.Double stores the coordinates of a point using double fields, while Point2D.Float stores the coordinates using float fields. Finally, java.awt.Point stores the coordinates using int fields.
| public abstract class Point2D implements Cloneable { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected Point2D (); | ||
| // | Inner Classes | |
| ; | ||
| ; | ||
| // | Public Class Methods | |
| public static double distance (double X1, double Y1, double X2, double Y2); | ||
| public static double distanceSq (double X1, double Y1, double X2, double Y2); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public abstract double getX (); | ||
| public abstract double getY (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public double distance (Point2D pt); | ||
| public double distance (double PX, double PY); | ||
| public double distanceSq (Point2D pt); | ||
| public double distanceSq (double PX, double PY); | ||
| public void setLocation (Point2D p); | ||
| public abstract void setLocation (double x, double y); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public Object clone (); | ||
| public boolean equals (Object obj); | ||
| public int hashCode (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Point2D(Cloneable)
Subclasses: Point, Point2D.Double, Point2D.Float
Passed To: Too many methods to list.
Returned By: Too many methods to list.
| Point2D.Double | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable | |
This class is a concrete implementation of Point2D that stores the X and Y coordinates of a point using double fields. These fields are public and can be queried and set directly, without using accessor methods.
| public static class Point2D.Double extends Point2D { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Double (); | ||
| public Double (double x, double y); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Point2D | |
| public double getX (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getY (); | default:0.0 | |
| public void setLocation (double x, double y); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public String toString (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public double x ; | ||
| public double y ; | ||
| } | ||
| Point2D.Float | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable | |
This class is a concrete implementation of Point2D that stores the X and Y coordinates of a point using float fields. These fields are public and can be queried and set directly, without using accessor methods.
| public static class Point2D.Float extends Point2D { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Float (); | ||
| public Float (float x, float y); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void setLocation (float x, float y); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Point2D | |
| public double getX (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getY (); | default:0.0 | |
| public void setLocation (double x, double y); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public String toString (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public float x ; | ||
| public float y ; | ||
| } | ||
| QuadCurve2D | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable shape | |
This abstract class is a java.awt.Shape that represents a smooth quadratic Bezier curve (or spline) between end points p1 (x1, y1) and p2 (x2, y2). The precise shape of the curve is defined by a control point, cp (ctrlx, ctrly). Note that the curve does not pass through cp but that it does remain inside the triangle defined by p1, cp, and p2.
QuadCurve2D does not itself enclose an area, so the contains() methods test whether a point or rectangle is within the area defined by the curve and the straight line between its end points.
QuadCurve2D is an abstract class and cannot be instantiated. QuadCurve2D.Float and QuadCurve2D.Double are concrete subclasses that use float and double fields to store the end points and control point. See also CubicCurve2D, which is a cubic Bezier curve that uses two control points.
| public abstract class QuadCurve2D implements Cloneable, Shape { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected QuadCurve2D (); | ||
| // | Inner Classes | |
| ; | ||
| ; | ||
| // | Public Class Methods | |
| public static double getFlatness (double[ ] coords, int offset); | ||
| public static double getFlatness (double x1, double y1, double ctrlx, double ctrly, double x2, double y2); | ||
| public static double getFlatnessSq (double[ ] coords, int offset); | ||
| public static double getFlatnessSq (double x1, double y1, double ctrlx, double ctrly, double x2, double y2); | ||
| public static int solveQuadratic (double[ ] eqn); | ||
| public static void subdivide (QuadCurve2D src, QuadCurve2D left, QuadCurve2D right); | ||
| public static void subdivide (double[ ] src, int srcoff, double[ ] left, int leftoff, double[ ] right, int rightoff); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public Rectangle getBounds (); | Implements:Shape | |
| public abstract Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | Implements:Shape | |
| public abstract Point2D getCtrlPt (); | ||
| public abstract double getCtrlX (); | ||
| public abstract double getCtrlY (); | ||
| public double getFlatness (); | ||
| public double getFlatnessSq (); | ||
| public abstract Point2D getP1 (); | ||
| public abstract Point2D getP2 (); | ||
| public abstract double getX1 (); | ||
| public abstract double getX2 (); | ||
| public abstract double getY1 (); | ||
| public abstract double getY2 (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void setCurve (QuadCurve2D c); | ||
| public void setCurve (double[ ] coords, int offset); | ||
| public void setCurve (Point2D[ ] pts, int offset); | ||
| public void setCurve (Point2D p1, Point2D cp, Point2D p2); | ||
| public abstract void setCurve (double x1, double y1, double ctrlx, double ctrly, double x2, double y2); | ||
| public void subdivide (QuadCurve2D left, QuadCurve2D right); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing Shape | |
| public boolean contains (Point2D p); | ||
| public boolean contains (Rectangle2D r); | ||
| public boolean contains (double x, double y); | ||
| public boolean contains (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| public Rectangle getBounds (); | ||
| public abstract Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | ||
| public PathIterator getPathIterator (AffineTransform at); | ||
| public PathIterator getPathIterator (AffineTransform at, double flatness); | ||
| public boolean intersects (Rectangle2D r); | ||
| public boolean intersects (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public Object clone (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->QuadCurve2D(Cloneable,Shape)
Subclasses: QuadCurve2D.Double, QuadCurve2D.Float
Passed To: QuadCurve2D.{setCurve(), subdivide()}
| QuadCurve2D.Double | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable shape | |
This class is a concrete implementation of QuadCurve2D that uses double fields to store the end points and control point of the curve. The X and Y coordinates of these three points are stored in public fields and may be used directly by Java programs. See QuadCurve2D for more information.
| public static class QuadCurve2D.Double extends QuadCurve2D { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Double (); | ||
| public Double (double x1, double y1, double ctrlx, double ctrly, double x2, double y2); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding QuadCurve2D | |
| public Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | default:Rectangle2D.Double | |
| public Point2D getCtrlPt (); | default:Point2D.Double | |
| public double getCtrlX (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getCtrlY (); | default:0.0 | |
| public Point2D getP1 (); | default:Point2D.Double | |
| public Point2D getP2 (); | default:Point2D.Double | |
| public double getX1 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getX2 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getY1 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getY2 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public void setCurve (double x1, double y1, double ctrlx, double ctrly, double x2, double y2); | ||
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public double ctrlx ; | ||
| public double ctrly ; | ||
| public double x1 ; | ||
| public double x2 ; | ||
| public double y1 ; | ||
| public double y2 ; | ||
| } | ||
| QuadCurve2D.Float | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable shape | |
This class is a concrete implementation of QuadCurve2D that uses float fields to store the end points and control point of the curve. The X and Y coordinates of these three points are stored in public fields and may be used directly by Java programs. See QuadCurve2D for more information.
| public static class QuadCurve2D.Float extends QuadCurve2D { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Float (); | ||
| public Float (float x1, float y1, float ctrlx, float ctrly, float x2, float y2); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void setCurve (float x1, float y1, float ctrlx, float ctrly, float x2, float y2); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding QuadCurve2D | |
| public Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | default:Rectangle2D.Float | |
| public Point2D getCtrlPt (); | default:Point2D.Float | |
| public double getCtrlX (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getCtrlY (); | default:0.0 | |
| public Point2D getP1 (); | default:Point2D.Float | |
| public Point2D getP2 (); | default:Point2D.Float | |
| public double getX1 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getX2 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getY1 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getY2 (); | default:0.0 | |
| public void setCurve (double x1, double y1, double ctrlx, double ctrly, double x2, double y2); | ||
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public float ctrlx ; | ||
| public float ctrly ; | ||
| public float x1 ; | ||
| public float x2 ; | ||
| public float y1 ; | ||
| public float y2 ; | ||
| } | ||
| Rectangle2D | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable shape | |
This abstract java.awt.Shape represents a rectangle specified by the location of its upper-left corner, its width, and its height. Various methods compute intersections and unions of rectangles, test whether a rectangle contains a point or contains another rectangle, and test whether a rectangle intersects a line or another rectangle. The outcode() method determines the spatial relationship between a point and a rectangle. The return value is the sum of the OUT_ constants that specify which edges of the rectangle a point is outside of. A value of 0 means that the point is inside the rectangle, of course. Other interesting methods include setFrameFromDiagonal() and setFrameFromCenter(), inherited from RectangularShape.
Rectangle2D is an abstract class that does not define any fields to store the size and position of the rectangle and cannot be instantiated. Choose a concrete subclass based on the type of data fields you desire: Rectangle2D.Double uses double fields, Rectangle2D.Float uses float fields, and java.awt.Rectangle uses int fields.
| public abstract class Rectangle2D extends RectangularShape { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected Rectangle2D (); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final int OUT_BOTTOM ; | =8 | |
| public static final int OUT_LEFT ; | =1 | |
| public static final int OUT_RIGHT ; | =4 | |
| public static final int OUT_TOP ; | =2 | |
| // | Inner Classes | |
| ; | ||
| ; | ||
| // | Public Class Methods | |
| public static void intersect (Rectangle2D src1, Rectangle2D src2, Rectangle2D dest); | ||
| public static void union (Rectangle2D src1, Rectangle2D src2, Rectangle2D dest); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void add (Point2D pt); | ||
| public void add (Rectangle2D r); | ||
| public void add (double newx, double newy); | ||
| public abstract Rectangle2D createIntersection (Rectangle2D r); | ||
| public abstract Rectangle2D createUnion (Rectangle2D r); | ||
| public boolean intersectsLine (Line2D l); | ||
| public boolean intersectsLine (double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2); | ||
| public int outcode (Point2D p); | ||
| public abstract int outcode (double x, double y); | ||
| public void setRect (Rectangle2D r); | ||
| public abstract void setRect (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding RectangularShape | |
| public boolean contains (double x, double y); | ||
| public boolean contains (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| public Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | ||
| public PathIterator getPathIterator (AffineTransform at); | ||
| public PathIterator getPathIterator (AffineTransform at, double flatness); | ||
| public boolean intersects (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| public void setFrame (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public boolean equals (Object obj); | ||
| public int hashCode (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->RectangularShape(Cloneable,Shape)-->Rectangle2D
Subclasses: Rectangle, Rectangle2D.Double, Rectangle2D.Float
Passed To: Too many methods to list.
Returned By: Too many methods to list.
| Rectangle2D.Double | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable shape | |
This concrete subclass of Rectangle2D stores the position and size of the rectangle in fields of type double. These fields are declared public and can be set and queried directly without relying on accessor methods.
| public static class Rectangle2D.Double extends Rectangle2D { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Double (); | ||
| public Double (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Rectangle2D | |
| public Rectangle2D createIntersection (Rectangle2D r); | ||
| public Rectangle2D createUnion (Rectangle2D r); | ||
| public Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | default:Rectangle2D.Double | |
| public int outcode (double x, double y); | ||
| public void setRect (Rectangle2D r); | ||
| public void setRect (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding RectangularShape | |
| public double getHeight (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getWidth (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getX (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getY (); | default:0.0 | |
| public boolean isEmpty (); | default:true | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public String toString (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public double height ; | ||
| public double width ; | ||
| public double x ; | ||
| public double y ; | ||
| } | ||
| Rectangle2D.Float | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable shape | |
This concrete subclass of Rectangle2D stores the position and size of the rectangle in fields of type float. These fields are declared public and can be set and queried directly without relying on accessor methods.
| public static class Rectangle2D.Float extends Rectangle2D { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Float (); | ||
| public Float (float x, float y, float w, float h); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void setRect (float x, float y, float w, float h); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Rectangle2D | |
| public Rectangle2D createIntersection (Rectangle2D r); | ||
| public Rectangle2D createUnion (Rectangle2D r); | ||
| public Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | default:Rectangle2D.Float | |
| public int outcode (double x, double y); | ||
| public void setRect (Rectangle2D r); | ||
| public void setRect (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding RectangularShape | |
| public double getHeight (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getWidth (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getX (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getY (); | default:0.0 | |
| public boolean isEmpty (); | default:true | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public String toString (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public float height ; | ||
| public float width ; | ||
| public float x ; | ||
| public float y ; | ||
| } | ||
| RectangularShape | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable shape | |
This abstract class is the base class for several java.awt.Shape implementations that have a rectangular outline or bounding box. Its methods allow you to set and query the size and position of the bounding rectangle in several interesting ways.
| public abstract class RectangularShape implements Cloneable, Shape { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected RectangularShape (); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public Rectangle getBounds (); | Implements:Shape | |
| public abstract Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | Implements:Shape | |
| public double getCenterX (); | ||
| public double getCenterY (); | ||
| public abstract boolean isEmpty (); | ||
| public Rectangle2D getFrame (); | ||
| public void setFrame (Rectangle2D r); | ||
| public void setFrame (Point2D loc, Dimension2D size); | ||
| public abstract void setFrame (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| public abstract double getHeight (); | ||
| public double getMaxX (); | ||
| public double getMaxY (); | ||
| public double getMinX (); | ||
| public double getMinY (); | ||
| public abstract double getWidth (); | ||
| public abstract double getX (); | ||
| public abstract double getY (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void setFrameFromCenter (Point2D center, Point2D corner); | ||
| public void setFrameFromCenter (double centerX, double centerY, double cornerX, double cornerY); | ||
| public void setFrameFromDiagonal (Point2D p1, Point2D p2); | ||
| public void setFrameFromDiagonal (double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing Shape | |
| public boolean contains (Point2D p); | ||
| public boolean contains (Rectangle2D r); | ||
| public abstract boolean contains (double x, double y); | ||
| public abstract boolean contains (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| public Rectangle getBounds (); | ||
| public abstract Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | ||
| public abstract PathIterator getPathIterator (AffineTransform at); | ||
| public PathIterator getPathIterator (AffineTransform at, double flatness); | ||
| public boolean intersects (Rectangle2D r); | ||
| public abstract boolean intersects (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public Object clone (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->RectangularShape(Cloneable,Shape)
Subclasses: Arc2D, Ellipse2D, Rectangle2D, RoundRectangle2D
| RoundRectangle2D | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable shape | |
This abstract java.awt.Shape represents a rectangle with rounded corners, specified by the position of the upper-left corner (before rounding), the width and height of the rectangle, and the width and height of the arc used to round the corners. RoundRectangle2D is abstract and may not be instantiated. Use the concrete subclasses RoundRectangle2D.Double and RoundRectangle2D.Float, depending on the precision you desire for the rectangle coordinates and dimensions.
| public abstract class RoundRectangle2D extends RectangularShape { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected RoundRectangle2D (); | ||
| // | Inner Classes | |
| ; | ||
| ; | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public abstract double getArcHeight (); | ||
| public abstract double getArcWidth (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void setRoundRect (RoundRectangle2D rr); | ||
| public abstract void setRoundRect (double x, double y, double w, double h, double arcWidth, double arcHeight); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding RectangularShape | |
| public boolean contains (double x, double y); | ||
| public boolean contains (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| public PathIterator getPathIterator (AffineTransform at); | ||
| public boolean intersects (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| public void setFrame (double x, double y, double w, double h); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->RectangularShape(Cloneable,Shape)-->RoundRectangle2D
Subclasses: RoundRectangle2D.Double, RoundRectangle2D.Float
Passed To: RoundRectangle2D.setRoundRect(), RoundRectangle2D.Double.setRoundRect(), RoundRectangle2D.Float.setRoundRect()
| RoundRectangle2D.Double | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable shape | |
This concrete subclass of RoundRectangle2D stores the position and size of the rectangle and the size of the rounded corners in fields of type double. These fields are declared public and can be set and queried directly without relying on accessor methods.
| public static class RoundRectangle2D.Double extends RoundRectangle2D { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Double (); | ||
| public Double (double x, double y, double w, double h, double arcw, double arch); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding RoundRectangle2D | |
| public double getArcHeight (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getArcWidth (); | default:0.0 | |
| public void setRoundRect (RoundRectangle2D rr); | ||
| public void setRoundRect (double x, double y, double w, double h, double arcw, double arch); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding RectangularShape | |
| public Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | default:Rectangle2D.Double | |
| public double getHeight (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getWidth (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getX (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getY (); | default:0.0 | |
| public boolean isEmpty (); | default:true | |
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public double archeight ; | ||
| public double arcwidth ; | ||
| public double height ; | ||
| public double width ; | ||
| public double x ; | ||
| public double y ; | ||
| } | ||
| RoundRectangle2D.Float | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.geom | cloneable shape | |
This concrete subclass of RoundRectangle2D stores the position and size of the rectangle and the size of the rounded corners in fields of type float. These fields are declared public and can be set and queried directly without relying on accessor methods.
| public static class RoundRectangle2D.Float extends RoundRectangle2D { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Float (); | ||
| public Float (float x, float y, float w, float h, float arcw, float arch); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void setRoundRect (float x, float y, float w, float h, float arcw, float arch); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding RoundRectangle2D | |
| public double getArcHeight (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getArcWidth (); | default:0.0 | |
| public void setRoundRect (RoundRectangle2D rr); | ||
| public void setRoundRect (double x, double y, double w, double h, double arcw, double arch); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding RectangularShape | |
| public Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | default:Rectangle2D.Float | |
| public double getHeight (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getWidth (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getX (); | default:0.0 | |
| public double getY (); | default:0.0 | |
| public boolean isEmpty (); | default:true | |
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public float archeight ; | ||
| public float arcwidth ; | ||
| public float height ; | ||
| public float width ; | ||
| public float x ; | ||
| public float y ; | ||
| } | ||

Copyright © 2001 O'Reilly & Associates. All rights reserved.