Chapter 15. The java.awt.font Package
The java.awt.font package contains classes and interfaces related to fonts; it is new in Java 1.2. Note, however, that the Font class itself is part of the java.awt package. This package contains low-level classes for obtaining information about the measurements of font glyphs and lines of text. It also contains classes for the low-level layout of text. LineMetrics and TextLayout are the two most important classes in this package. Figure 15-1 shows the class hierarchy of this package.
Most programs can rely on the higher-level text display features of java.awt and javax.swing and do not have to use this package.
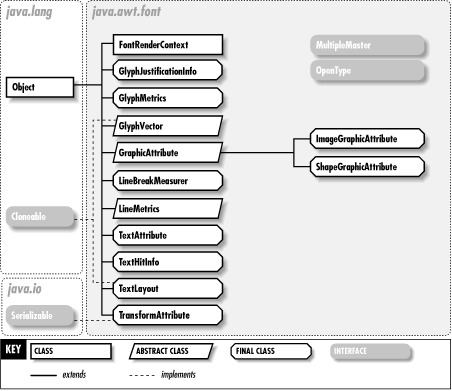
Figure 15-1. The java.awt.font package
| FontRenderContext | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.font | ||
This class stores the information necessary to precisely measure the size of text. It is used by a number of Font methods and also by TextLayout and LineBreakMeasurer. Although FontRenderContext has a public constructor, it is more common to obtain a FontRenderContext by calling the getFontRenderContext() method of a Graphics2D object.
| public class FontRenderContext { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public FontRenderContext (java.awt.geom.AffineTransform tx, boolean isAntiAliased, boolean usesFractionalMetrics); | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected FontRenderContext (); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public boolean isAntiAliased (); | ||
| public java.awt.geom.AffineTransform getTransform (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public boolean usesFractionalMetrics (); | ||
| } | ||
Passed To: Too many methods to list.
Returned By: Graphics2D.getFontRenderContext(), GlyphVector.getFontRenderContext()
| GlyphJustificationInfo | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.font | ||
This class contains information about how much whitespace may be added to or removed from the left and right sides of a glyph without unduly compromising the appearance of the text output. This information is used by algorithms that perform fill justification to force a line of text to an exact size. Only applications that perform high-end typography need to use this class.
| public final class GlyphJustificationInfo { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public GlyphJustificationInfo (float weight, boolean growAbsorb, int growPriority, float growLeftLimit, float growRightLimit, boolean shrinkAbsorb, int shrinkPriority, float shrinkLeftLimit, float shrinkRightLimit); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final int PRIORITY_INTERCHAR ; | =2 | |
| public static final int PRIORITY_KASHIDA ; | =0 | |
| public static final int PRIORITY_NONE ; | =3 | |
| public static final int PRIORITY_WHITESPACE ; | =1 | |
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public final boolean growAbsorb ; | ||
| public final float growLeftLimit ; | ||
| public final int growPriority ; | ||
| public final float growRightLimit ; | ||
| public final boolean shrinkAbsorb ; | ||
| public final float shrinkLeftLimit ; | ||
| public final int shrinkPriority ; | ||
| public final float shrinkRightLimit ; | ||
| public final float weight ; | ||
| } | ||
Returned By: GlyphVector.getGlyphJustificationInfo(), GraphicAttribute.getJustificationInfo()
| GlyphMetrics | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.font | ||
This class contains measurements for a single glyph of a font. Although GlyphMetrics has a public constructor, the only way to obtain actual metrics for a glyph is by calling the getGlyphMetrics() method of a GlyphVector.
Each glyph has an origin. The getAdvance() method returns the standard distance between the origin of this glyph and the origin of the next glyph in the GlyphVector from which the GlyphMetrics was obtained. getBounds2D() returns the bounding box of the glyph. This rectangle is positioned relative to the origin of the glyph. getLSB() returns the left-side bearing of the glyph: the distance between the origin and the left side of the bounding box. getRSB() returns the right-side bearing: the distance between the right side of the bounding box and the start of the next glyph. For some glyphs, these bearing values may be negative.
getType() returns the type of the glyph; the return value is one of the constants defined by the class. Most glyphs are of STANDARD type. Glyphs with no visible representation are of type WHITESPACE. Glyphs that represent more than one character have type LIGATURE. Accents and other diacritical marks that modify other glyphs have type COMBINING. Finally, when one character is represented by two or more glyphs, the extra glyph or glyphs have the type COMPONENT.
| public final class GlyphMetrics { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public GlyphMetrics (float advance, java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D bounds, byte glyphType); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final byte COMBINING ; | =2 | |
| public static final byte COMPONENT ; | =3 | |
| public static final byte LIGATURE ; | =1 | |
| public static final byte STANDARD ; | =0 | |
| public static final byte WHITESPACE ; | =4 | |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public float getAdvance (); | ||
| public java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | ||
| public boolean isCombining (); | ||
| public boolean isComponent (); | ||
| public boolean isLigature (); | ||
| public float getLSB (); | ||
| public float getRSB (); | ||
| public boolean isStandard (); | ||
| public int getType (); | ||
| public boolean isWhitespace (); | ||
| } | ||
Returned By: GlyphVector.getGlyphMetrics()
| GlyphVector | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.font | cloneable | |
This class represents an array of glyphs taken from a single font that are to be drawn on a single line. You obtain a GlyphVector by calling the createGlyphVector() method of a Font object, and you draw a GlyphVector with the drawGlyphVector() method of a Graphics2D object.
When a string is drawn using the drawString() method of Graphics or Graphics2D, the characters of the string first must be converted to font glyphs, and then those glyphs must be drawn. Thus, if a string is to be drawn repeatedly, it can be more efficient to separate these two steps, converting the string to a GlyphVector once and then drawing that GlyphVector multiple times.
| public abstract class GlyphVector implements Cloneable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public GlyphVector (); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public abstract Font getFont (); | ||
| public abstract FontRenderContext getFontRenderContext (); | ||
| public abstract java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D getLogicalBounds (); | ||
| public abstract int getNumGlyphs (); | ||
| public abstract Shape getOutline (); | ||
| public abstract Shape getOutline (float x, float y); | ||
| public abstract java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D getVisualBounds (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract boolean equals (GlyphVector set); | ||
| public abstract int getGlyphCode (int glyphIndex); | ||
| public abstract int[ ] getGlyphCodes (int beginGlyphIndex, int numEntries, int[ ] codeReturn); | ||
| public abstract GlyphJustificationInfo getGlyphJustificationInfo (int glyphIndex); | ||
| public abstract Shape getGlyphLogicalBounds (int glyphIndex); | ||
| public abstract GlyphMetrics getGlyphMetrics (int glyphIndex); | ||
| public abstract Shape getGlyphOutline (int glyphIndex); | ||
| public abstract java.awt.geom.Point2D getGlyphPosition (int glyphIndex); | ||
| public abstract float[ ] getGlyphPositions (int beginGlyphIndex, int numEntries, float[ ] positionReturn); | ||
| public abstract java.awt.geom.AffineTransform getGlyphTransform (int glyphIndex); | ||
| public abstract Shape getGlyphVisualBounds (int glyphIndex); | ||
| public abstract void performDefaultLayout (); | ||
| public abstract void setGlyphPosition (int glyphIndex, java.awt.geom.Point2D newPos); | ||
| public abstract void setGlyphTransform (int glyphIndex, java.awt.geom.AffineTransform newTX); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->GlyphVector(Cloneable)
Passed To: Graphics2D.drawGlyphVector(), GlyphVector.equals()
Returned By: Font.createGlyphVector()
| GraphicAttribute | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.font | ||
This abstract class represents a graphic to be embedded in a line of text in lieu of a regular font glyph. A GraphicAttribute is used as the value of an TextAttribute.CHAR_REPLACEMENT attribute in a java.text.AttributedString or java.text.AttributedCharacterIterator. Most applications use one of the two subclasses ImageGraphicAttribute and ShapeGraphicAttribute. Few applications need to create custom subclasses of their own.
The draw() method is responsible for actually drawing the desired graphic. The other methods return various measurements for the graphic. The constants are possible alignment values returned by getAligment().
| public abstract class GraphicAttribute { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected GraphicAttribute (int alignment); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final int BOTTOM_ALIGNMENT ; | =-2 | |
| public static final int CENTER_BASELINE ; | =1 | |
| public static final int HANGING_BASELINE ; | =2 | |
| public static final int ROMAN_BASELINE ; | =0 | |
| public static final int TOP_ALIGNMENT ; | =-1 | |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public abstract float getAdvance (); | ||
| public final int getAlignment (); | ||
| public abstract float getAscent (); | ||
| public java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D getBounds (); | ||
| public abstract float getDescent (); | ||
| public GlyphJustificationInfo getJustificationInfo (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract void draw (Graphics2D graphics, float x, float y); | ||
| } | ||
Subclasses: ImageGraphicAttribute, ShapeGraphicAttribute
| ImageGraphicAttribute | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.font | ||
This concrete subclass of GraphicAttribute allows an image to be drawn within a string of text. Create an ImageGraphicAttribute by specifying an image to draw, an alignment (one of the constants defined by GraphicAttribute), and, optionally, an origin for the image. The origin coordinates are relative to the image itself. Use the ImageGraphicAttribute by specifying it as the value of a TextAttribute.CHAR_REPLACEMENT attribute in a java.text.AttributedString or java.text.AttributedCharacterIterator.
See also ShapeGraphicAttribute.
| public final class ImageGraphicAttribute extends GraphicAttribute { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public ImageGraphicAttribute (Image image, int alignment); | ||
| public ImageGraphicAttribute (Image image, int alignment, float originX, float originY); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public boolean equals (ImageGraphicAttribute rhs); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding GraphicAttribute | |
| public void draw (Graphics2D graphics, float x, float y); | ||
| public float getAdvance (); | ||
| public float getAscent (); | ||
| public java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D getBounds (); | ||
| public float getDescent (); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public boolean equals (Object rhs); | ||
| public int hashCode (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->GraphicAttribute-->ImageGraphicAttribute
Passed To: ImageGraphicAttribute.equals()
| LineBreakMeasurer | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.font | ||
This class breaks a paragraph of text into individual lines of a specified width, where each line is represented by a TextLayout object. When you create a LineBreakMeasurer, you must specify the paragraph to be broken with a java.text.AttributedCharacterIterator, which is usually is obtained from a java.text.AttributedString. You may optionally specify a java.text.BreakIterator to indicate where line breaks are allowed. The default is to use the line breaking rules of the current locale. You must also pass a FontRenderContext to the LineBreakMeasurer() constructor. The FontRenderContext is usually obtained with the getFontRenderContext() method of Graphics2D.
Once you have created a LineBreakMeasurer for your paragraph, you use it by repeatedly calling nextLayout() to create TextLayout objects that represent lines. nextLayout() returns null when it reaches the end of the paragraph. The desired width of each line is passed as an argument to nextLayout(). This allows the first line of a paragraph to be made shorter than the following lines, for example.
| public final class LineBreakMeasurer { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public LineBreakMeasurer (java.text.AttributedCharacterIterator text, FontRenderContext frc); | ||
| public LineBreakMeasurer (java.text.AttributedCharacterIterator text, java.text.BreakIterator breakIter, FontRenderContext frc); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void deleteChar (java.text.AttributedCharacterIterator newParagraph, int deletePos); | ||
| public int getPosition (); | ||
| public void insertChar (java.text.AttributedCharacterIterator newParagraph, int insertPos); | ||
| public TextLayout nextLayout (float maxAdvance); | ||
| public TextLayout nextLayout (float wrappingWidth, int offsetLimit, boolean requireNextWord); | ||
| public int nextOffset (float maxAdvance); | ||
| public int nextOffset (float wrappingWidth, int offsetLimit, boolean requireNextWord); | ||
| public void setPosition (int newPosition); | ||
| } | ||
| LineMetrics | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.font | ||
This class provides access to various measurements for the characters in a font. The name LineMetrics is somewhat confusing; it refers to the general line metrics of a font, not the metrics of some particular line of text rendered with the font. LineMetrics provides more accurate metrics than java.awt.FontMetrics and also includes some metrics that are simply not available through that class.
Obtain a LineMetrics object by calling one of the getLineMetrics() methods of Font or FontMetrics. These methods require that you supply some form of text to measure. The returned LineMetrics object does not contain the width of that text, but the font measurements it does return may depend on the content of the text. For example, the metrics for English text may differ from metrics for Japanese text. (Note, however, that the initial implementation from Sun simply ignores the text you specify.) If the supplied text contains characters from more than one language, the returned metrics may apply only to a prefix of the text. The getNumChars() method returns the length of this prefix.
Once you have obtained a LineMetrics object, you can call its various accessor methods to obtain information about the font. getAscent() returns the distance between the baseline and the top of the tallest character. getDescent() returns the distance between the baseline and the bottom of the lowest descender. getLeading() returns the recommended interline spacing for the font (so named for the strips of lead that used to be placed between rows of movable type). getHeight() returns the distance between the baseline of one line and the baseline of the next. It is equal to the sum of the ascent, descent, and leading. getUnderlineOffset() returns the recommended position of an underline, relative to the baseline for the font, and getUnderlineThickness() returns the recommended thickness of an underline. Two similar methods return the position and thickness of lines used to strike through characters in the font.
| public abstract class LineMetrics { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public LineMetrics (); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public abstract float getAscent (); | ||
| public abstract int getBaselineIndex (); | ||
| public abstract float[ ] getBaselineOffsets (); | ||
| public abstract float getDescent (); | ||
| public abstract float getHeight (); | ||
| public abstract float getLeading (); | ||
| public abstract int getNumChars (); | ||
| public abstract float getStrikethroughOffset (); | ||
| public abstract float getStrikethroughThickness (); | ||
| public abstract float getUnderlineOffset (); | ||
| public abstract float getUnderlineThickness (); | ||
| } | ||
Returned By: Font.getLineMetrics(), FontMetrics.getLineMetrics()
| MultipleMaster | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.font | ||
This interface describes capabilities of Type 1 Multiple Master fonts. If a Font object represents a Multiple Master font, it implements the MultipleMaster interface. Most fonts have only one parameter that you can vary: the point size. A Multiple Master font is a generalization that allows you to vary any number of design axes of the font. These design axes may be things such as font weight, average glyph width, italic angle, and so forth. The methods of the MultipleMaster interface allow you to query the names, defaults, and valid ranges of these design axes and derive new versions of the font by specifying values for each axis.
| public abstract interface MultipleMaster { | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public abstract float[ ] getDesignAxisDefaults (); | ||
| public abstract String[ ] getDesignAxisNames (); | ||
| public abstract float[ ] getDesignAxisRanges (); | ||
| public abstract int getNumDesignAxes (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract Font deriveMMFont (float[ ] axes); | ||
| public abstract Font deriveMMFont (float[ ] glyphWidths, float avgStemWidth, float typicalCapHeight, float typicalXHeight, float italicAngle); | ||
| } | ||
| OpenType | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.font | ||
This interface is implemented by Font objects that represent OpenType and TrueType fonts. It allows access to tables of raw font data. You should use this interface only if you are intimately familiar with the font data format for OpenType and TrueType fonts.
| public abstract interface OpenType { | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final int TAG_ACNT ; | =1633906292 | |
| public static final int TAG_AVAR ; | =1635148146 | |
| public static final int TAG_BASE ; | =1111577413 | |
| public static final int TAG_BDAT ; | =1650745716 | |
| public static final int TAG_BLOC ; | =1651273571 | |
| public static final int TAG_BSLN ; | =1651731566 | |
| public static final int TAG_CFF ; | =1128678944 | |
| public static final int TAG_CMAP ; | =1668112752 | |
| public static final int TAG_CVAR ; | =1668702578 | |
| public static final int TAG_CVT ; | =1668707360 | |
| public static final int TAG_DSIG ; | =1146308935 | |
| public static final int TAG_EBDT ; | =1161970772 | |
| public static final int TAG_EBLC ; | =1161972803 | |
| public static final int TAG_EBSC ; | =1161974595 | |
| public static final int TAG_FDSC ; | =1717859171 | |
| public static final int TAG_FEAT ; | =1717920116 | |
| public static final int TAG_FMTX ; | =1718449272 | |
| public static final int TAG_FPGM ; | =1718642541 | |
| public static final int TAG_FVAR ; | =1719034226 | |
| public static final int TAG_GASP ; | =1734439792 | |
| public static final int TAG_GDEF ; | =1195656518 | |
| public static final int TAG_GLYF ; | =1735162214 | |
| public static final int TAG_GPOS ; | =1196445523 | |
| public static final int TAG_GSUB ; | =1196643650 | |
| public static final int TAG_GVAR ; | =1735811442 | |
| public static final int TAG_HDMX ; | =1751412088 | |
| public static final int TAG_HEAD ; | =1751474532 | |
| public static final int TAG_HHEA ; | =1751672161 | |
| public static final int TAG_HMTX ; | =1752003704 | |
| public static final int TAG_JSTF ; | =1246975046 | |
| public static final int TAG_JUST ; | =1786082164 | |
| public static final int TAG_KERN ; | =1801810542 | |
| public static final int TAG_LCAR ; | =1818452338 | |
| public static final int TAG_LOCA ; | =1819239265 | |
| public static final int TAG_LTSH ; | =1280594760 | |
| public static final int TAG_MAXP ; | =1835104368 | |
| public static final int TAG_MMFX ; | =1296909912 | |
| public static final int TAG_MMSD ; | =1296913220 | |
| public static final int TAG_MORT ; | =1836020340 | |
| public static final int TAG_NAME ; | =1851878757 | |
| public static final int TAG_OPBD ; | =1836020340 | |
| public static final int TAG_OS2 ; | =1330851634 | |
| public static final int TAG_PCLT ; | =1346587732 | |
| public static final int TAG_POST ; | =1886352244 | |
| public static final int TAG_PREP ; | =1886545264 | |
| public static final int TAG_PROP ; | =1886547824 | |
| public static final int TAG_TRAK ; | =1953653099 | |
| public static final int TAG_TYP1 ; | =1954115633 | |
| public static final int TAG_VDMX ; | =1447316824 | |
| public static final int TAG_VHEA ; | =1986553185 | |
| public static final int TAG_VMTX ; | =1986884728 | |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract byte[ ] getFontTable (String strSfntTag); | ||
| public abstract byte[ ] getFontTable (int sfntTag); | ||
| public abstract byte[ ] getFontTable (String strSfntTag, int offset, int count); | ||
| public abstract byte[ ] getFontTable (int sfntTag, int offset, int count); | ||
| public abstract int getFontTableSize (String strSfntTag); | ||
| public abstract int getFontTableSize (int sfntTag); | ||
| public abstract int getVersion (); | ||
| } | ||
| ShapeGraphicAttribute | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.font | ||
This concrete subclass of GraphicAttribute allows an arbitrary shape to be drawn within a string of text. Create a ShapeGraphicAttribute by specifying a shape to draw and an alignment (one of the constants defined by GraphicAttribute) that specifies how the shape is aligned with the rest of the text. Pass true for the third argument, stroke, if the shape should simply be drawn, or pass false if the shape should be filled. Use the ShapeGraphicAttribute by specifying it as the value of a TextAttribute.CHAR_REPLACEMENT attribute in a java.text.AttributedString or java.text.AttributedCharacterIterator
See also ImageGraphicAttribute.
| public final class ShapeGraphicAttribute extends GraphicAttribute { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public ShapeGraphicAttribute (Shape shape, int alignment, boolean stroke); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final boolean FILL ; | =false | |
| public static final boolean STROKE ; | =true | |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public boolean equals (ShapeGraphicAttribute rhs); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding GraphicAttribute | |
| public void draw (Graphics2D graphics, float x, float y); | ||
| public float getAdvance (); | ||
| public float getAscent (); | ||
| public java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D getBounds (); | ||
| public float getDescent (); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public boolean equals (Object rhs); | ||
| public int hashCode (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->GraphicAttribute-->ShapeGraphicAttribute
Passed To: ShapeGraphicAttribute.equals()
| TextAttribute | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.font | serializable | |
This class defines constants that serve as attribute names and attribute values for use with java.text.AttributedString and java.text.AttributedCharacterIterator objects. The constants of type TextAttribute serve as attribute names. The other constants define commonly used values for those attributes. Note that the value of the CHAR_REPLACEMENT attribute should be a GraphicAttribute object, and the value of the TRANSFORM attribute should be a TransformAttribute object.
| public final class TextAttribute extends java.text.AttributedCharacterIterator.Attribute { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected TextAttribute (String name); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final TextAttribute BACKGROUND ; | ||
| public static final TextAttribute BIDI_EMBEDDING ; | ||
| public static final TextAttribute CHAR_REPLACEMENT ; | ||
| public static final TextAttribute FAMILY ; | ||
| public static final TextAttribute FONT ; | ||
| public static final TextAttribute FOREGROUND ; | ||
| public static final TextAttribute INPUT_METHOD_HIGHLIGHT ; | ||
| public static final TextAttribute JUSTIFICATION ; | ||
| public static final Float JUSTIFICATION_FULL ; | ||
| public static final Float JUSTIFICATION_NONE ; | ||
| public static final TextAttribute POSTURE ; | ||
| public static final Float POSTURE_OBLIQUE ; | ||
| public static final Float POSTURE_REGULAR ; | ||
| public static final TextAttribute RUN_DIRECTION ; | ||
| public static final Boolean RUN_DIRECTION_LTR ; | ||
| public static final Boolean RUN_DIRECTION_RTL ; | ||
| public static final TextAttribute SIZE ; | ||
| public static final TextAttribute STRIKETHROUGH ; | ||
| public static final Boolean STRIKETHROUGH_ON ; | ||
| public static final TextAttribute SUPERSCRIPT ; | ||
| public static final Integer SUPERSCRIPT_SUB ; | ||
| public static final Integer SUPERSCRIPT_SUPER ; | ||
| public static final TextAttribute SWAP_COLORS ; | ||
| public static final Boolean SWAP_COLORS_ON ; | ||
| public static final TextAttribute TRANSFORM ; | ||
| public static final TextAttribute UNDERLINE ; | ||
| public static final Integer UNDERLINE_ON ; | ||
| public static final TextAttribute WEIGHT ; | ||
| public static final Float WEIGHT_BOLD ; | ||
| public static final Float WEIGHT_DEMIBOLD ; | ||
| public static final Float WEIGHT_DEMILIGHT ; | ||
| public static final Float WEIGHT_EXTRA_LIGHT ; | ||
| public static final Float WEIGHT_EXTRABOLD ; | ||
| public static final Float WEIGHT_HEAVY ; | ||
| public static final Float WEIGHT_LIGHT ; | ||
| public static final Float WEIGHT_MEDIUM ; | ||
| public static final Float WEIGHT_REGULAR ; | ||
| public static final Float WEIGHT_SEMIBOLD ; | ||
| public static final Float WEIGHT_ULTRABOLD ; | ||
| public static final TextAttribute WIDTH ; | ||
| public static final Float WIDTH_CONDENSED ; | ||
| public static final Float WIDTH_EXTENDED ; | ||
| public static final Float WIDTH_REGULAR ; | ||
| public static final Float WIDTH_SEMI_CONDENSED ; | ||
| public static final Float WIDTH_SEMI_EXTENDED ; | ||
| // | Protected Methods Overriding AttributedCharacterIterator.Attribute | |
| protected Object readResolve () throws java.io.InvalidObjectException; | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->java.text.AttributedCharacterIterator.Attribute(Serializable)-->TextAttribute
Type Of: Too many fields to list.
| TextHitInfo | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.font | ||
This class encapsulates the position of a character within a string of text and the bias, or side, of the character. The hitTestChar() method of TextLayout takes the position of a mouse click and returns a TextHitInfo that specifies where the click occurred.
getCharIndex() returns the position of the character that was hit. getInsertionIndex() returns the position at which characters should be inserted or deleted. This may or may not be the same as the value returned by getCharIndex(). isLeadingEdge() specifies whether the hit was on the leading edge of the character.
If you want to place the insertion cursor at the position of the mouse click, it is not sufficient to know which character was clicked on; you must also know whether the leading edge or the trailing edge of the character was clicked on. This is particularly important when working with bidirectional text, such as Arabic or Hebrew. If the TextHitInfo specifies that the trailing edge was selected, the insertion cursor should be placed before the character. Otherwise, it should be placed after the character.
In bidirectional text, positioning the cursor correctly in response to user requests to move it left or right can be quite tricky. TextHitInfo is also returned by the getNextLeftHit() and getNextRightHit() methods of TextLayout, to help solve this problem.
| public final class TextHitInfo { | ||
| // | No Constructor | |
| // | Public Class Methods | |
| public static TextHitInfo afterOffset (int offset); | ||
| public static TextHitInfo beforeOffset (int offset); | ||
| public static TextHitInfo leading (int charIndex); | ||
| public static TextHitInfo trailing (int charIndex); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public int getCharIndex (); | ||
| public int getInsertionIndex (); | ||
| public boolean isLeadingEdge (); | ||
| public TextHitInfo getOtherHit (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public boolean equals (TextHitInfo hitInfo); | ||
| public TextHitInfo getOffsetHit (int delta); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public boolean equals (Object obj); | ||
| public int hashCode (); | ||
| public String toString (); | ||
| } | ||
Passed To: Too many methods to list.
Returned By: Too many methods to list.
| TextLayout | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.font | cloneable | |
This class represents and displays a line of styled, possibly bidirectional, text and provides algorithms for the visual manipulation of that text. This is a powerful and complex class. Many applications prefer to use high-level Swing components, such as JTextField and JTextPane, to handle text display and editing. Some applications may want to use the lower-level GlyphVector class for maximum text drawing speed.
Using the TextLayout() constructor, you can create a TextLayout from a java.text.AttributedCharacterIterator, from a string and a font, or from a string and a java.util.Map of attributes. All versions of the constructor also require a FontRenderContext, obtained with the getFontRenderContext() method of Graphics2D.
Once you have created a TextLayout, you can draw it by calling its draw() method. TextLayout also provides various other methods to support applications that allow the user to edit the text. If the user clicks on the text, you can determine what character was clicked on with hitTestChar(), which returns a TextHitInfo. Once you have an insertion position specified with a TextHitInfo, you can obtain a Shape appropriate for use as an insertion cursor by calling getCaretShape(). The returned shape is relative to the origin of the TextLayout, and it takes into account whether the text is italic. getCaretShapes() is passed a character index within the TextLayout; it returns an array of one or two Shape objects that represent insertion cursors for that character position. Usually this array contains only one cursor, but in bidirectional text, it may contain both a primary insertion cursor and a secondary insertion cursor.
If the user selects text by clicking and dragging with the mouse, you can call getVisualHighlightShape() to determine how to highlight the selected text. This method returns a Shape object suitable for drawing the highlighted regions. Alternatively, you can use getLogicalHightlightShape() to highlight a specified contiguous group of characters in the TextLayout. Note, however, that in bidirectional text, this logical highlight might map to two visually disjoint regions.
| public final class TextLayout implements Cloneable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public TextLayout (java.text.AttributedCharacterIterator text, FontRenderContext frc); | ||
| public TextLayout (String string, Font font, FontRenderContext frc); | ||
| public TextLayout (String string, java.util.Map attributes, FontRenderContext frc); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final TextLayout.CaretPolicy DEFAULT_CARET_POLICY ; | ||
| // | Inner Classes | |
| ; | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public float getAdvance (); | ||
| public float getAscent (); | ||
| public byte getBaseline (); | ||
| public float[ ] getBaselineOffsets (); | ||
| public java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D getBounds (); | ||
| public int getCharacterCount (); | ||
| public float getDescent (); | ||
| public float getLeading (); | ||
| public boolean isLeftToRight (); | ||
| public boolean isVertical (); | ||
| public float getVisibleAdvance (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void draw (Graphics2D g2, float x, float y); | ||
| public boolean equals (TextLayout rhs); | ||
| public Shape getBlackBoxBounds (int firstEndpoint, int secondEndpoint); | ||
| public float[ ] getCaretInfo (TextHitInfo hit); | ||
| public float[ ] getCaretInfo (TextHitInfo hit, java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D bounds); | ||
| public Shape getCaretShape (TextHitInfo hit); | ||
| public Shape getCaretShape (TextHitInfo hit, java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D bounds); | ||
| public Shape[ ] getCaretShapes (int offset); | ||
| public Shape[ ] getCaretShapes (int offset, java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D bounds); | ||
| public Shape[ ] getCaretShapes (int offset, java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D bounds, TextLayout.CaretPolicy policy); | ||
| public byte getCharacterLevel (int index); | ||
| public TextLayout getJustifiedLayout (float justificationWidth); | ||
| public Shape getLogicalHighlightShape (int firstEndpoint, int secondEndpoint); | ||
| public Shape getLogicalHighlightShape (int firstEndpoint, int secondEndpoint, java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D bounds); | ||
| public int[ ] getLogicalRangesForVisualSelection (TextHitInfo firstEndpoint, TextHitInfo secondEndpoint); | ||
| public TextHitInfo getNextLeftHit (int offset); | ||
| public TextHitInfo getNextLeftHit (TextHitInfo hit); | ||
| public TextHitInfo getNextLeftHit (int offset, TextLayout.CaretPolicy policy); | ||
| public TextHitInfo getNextRightHit (int offset); | ||
| public TextHitInfo getNextRightHit (TextHitInfo hit); | ||
| public TextHitInfo getNextRightHit (int offset, TextLayout.CaretPolicy policy); | ||
| public Shape getOutline (java.awt.geom.AffineTransform tx); | ||
| public Shape getVisualHighlightShape (TextHitInfo firstEndpoint, TextHitInfo secondEndpoint); | ||
| public Shape getVisualHighlightShape (TextHitInfo firstEndpoint, TextHitInfo secondEndpoint, java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D bounds); | ||
| public TextHitInfo getVisualOtherHit (TextHitInfo hit); | ||
| public TextHitInfo hitTestChar (float x, float y); | ||
| public TextHitInfo hitTestChar (float x, float y, java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D bounds); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public boolean equals (Object obj); | ||
| public int hashCode (); | ||
| public String toString (); | ||
| // | Protected Methods Overriding Object | |
| protected Object clone (); | ||
| // | Protected Instance Methods | |
| protected void handleJustify (float justificationWidth); | empty | |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->TextLayout(Cloneable)
Passed To: TextLayout.equals(), TextLayout.CaretPolicy.getStrongCaret()
Returned By: LineBreakMeasurer.nextLayout(), TextLayout.getJustifiedLayout()
| TextLayout.CaretPolicy | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.font | ||
This class defines a policy for deciding which insertion position is the dominant one in bidirectional text. Most applications never need to use this class.
If you want to specify a policy other than the default, you should subclass this class and override getStrongCaret() to choose between two TextHitInfo objects, returning the one that represents the dominant insertion position. Then pass an instance of your subclass to the getCaretShapes(), getNextLeftHit(), and getNextRightHit() methods of TextLayout.
| public static class TextLayout.CaretPolicy { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public CaretPolicy (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public TextHitInfo getStrongCaret (TextHitInfo hit1, TextHitInfo hit2, TextLayout layout); | ||
| } | ||
Passed To: TextLayout.{getCaretShapes(), getNextLeftHit(), getNextRightHit()}
Type Of: TextLayout.DEFAULT_CARET_POLICY
| TextLine.TextLineMetrics | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.font | ||
This public inner class is defined within a private class. It was inadvertently included in the public API of java.awt.font but should be considered private.
| public static final class TextLine.TextLineMetrics { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public TextLineMetrics (float ascent, float descent, float leading, float advance); | ||
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public final float advance ; | ||
| public final float ascent ; | ||
| public final float descent ; | ||
| public final float leading ; | ||
| } | ||
| TransformAttribute | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt.font | serializable | |
This class is a simple immutable wrapper around a java.awt.geom.AffineTransform. This wrapper makes it safe to use a transform as the value of a TextAttribute.TRANSFORM attribute.
| public final class TransformAttribute implements Serializable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public TransformAttribute (java.awt.geom.AffineTransform transform); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public java.awt.geom.AffineTransform getTransform (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->TransformAttribute(Serializable)

Copyright © 2001 O'Reilly & Associates. All rights reserved.