|
|

Product Numbers: PA-100VG and PA-100VG=
This configuration note describes the installation and configuration of the 100VG 100-mega-bit-per-second (Mbps) AnyLAN port adapter. The 100VG port adapter (PA-100VG) can be used in the Cisco 7200 series routers, and on the second-generation Versatile Interface Processor (VIP2) in the Cisco 7500 series and Cisco 7000 series routers.
This configuration note is organized into the following three parts:
2. The following section includes information specific to the 100VG port adapters:
3. The following sections include information specific to the 100VG port adapter's use with the VIP2 in Cisco 7000 series and Cisco 7500 series routers, and its use in the Cisco 7200 series routers:
The Cisco IOS software running your router contains extensive features and functionality. For information on Cisco IOS software and for general installation and maintenance information for your router, use the following resources:
The following sections discuss general information and information about port adapter installation requirements:
The 100VG port adapter requires that the host Cisco 7000 series, Cisco 7200 series, or Cisco 7500 series routers are running Cisco IOS Release 11.1(10)CA or later. The 100VG port adapter is also supported in Cisco IOS Release 11.2(7)P or later, for the Cisco router series listed.
(Also refer to the Cisco IOS software release notes for the Cisco IOS software version you are running.)
In the Cisco 7000 series or Cisco 7500 series routers, the 100VG port adapter requires the following VIP2 models:
 | Caution To prevent system problems, the VIP2 requires that the Cisco 7000 series router has the 7000 Series Route Switch Processor (RSP7000) and the 7000 Series Chassis Interface (RSP7000CI) installed. The VIP2 will not operate properly with the Route Processor (RP), Switch Processor (SP), or Silicon Switch Processor (SSP) installed in the Cisco 7000 series router. |
Following are safety guidelines that you should follow when working with any equipment that connects to electrical power or telephone wiring.
Safety warnings appear throughout this publication in procedures that, if performed incorrectly, might harm you. A warning symbol precedes each warning statement.
Warning 
Means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury. Before you work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar with standard practices for preventing accidents. To see translations of the warnings that appear in this publication, refer to the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information document that accompanied this device.
Waarschuwing Dit waarschuwingssymbool betekent gevaar. U verkeert in een situatie die lichamelijk letsel kan veroorzaken. Voordat u aan enige apparatuur gaat werken, dient u zich bewust te zijn van de bij elektrische schakelingen betrokken risico's en dient u op de hoogte te zijn van standaard maatregelen om ongelukken te voorkomen. Voor vertalingen van de waarschuwingen die in deze publicatie verschijnen, kunt u het document Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (Informatie over naleving van veiligheids- en andere voorschriften) raadplegen dat bij dit toestel is ingesloten.
Varoitus Tämä varoitusmerkki merkitsee vaaraa. Olet tilanteessa, joka voi johtaa ruumiinvammaan. Ennen kuin työskentelet minkään laitteiston parissa, ota selvää sähkökytkentöihin liittyvistä vaaroista ja tavanomaisista onnettomuuksien ehkäisykeinoista. Tässä julkaisussa esiintyvien varoitusten käännökset löydät laitteen mukana olevasta Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information -kirjasesta (määräysten noudattaminen ja tietoa turvallisuudesta).
Attention Ce symbole d'avertissement indique un danger. Vous vous trouvez dans une situation pouvant causer des blessures ou des dommages corporels. Avant de travailler sur un équipement, soyez conscient des dangers posés par les circuits électriques et familiarisez-vous avec les procédures couramment utilisées pour éviter les accidents. Pour prendre connaissance des traductions d'avertissements figurant dans cette publication, consultez le document Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (Conformité aux règlements et consignes de sécurité) qui accompagne cet appareil.
Warnung Dieses Warnsymbol bedeutet Gefahr. Sie befinden sich in einer Situation, die zu einer Körperverletzung führen könnte. Bevor Sie mit der Arbeit an irgendeinem Gerät beginnen, seien Sie sich der mit elektrischen Stromkreisen verbundenen Gefahren und der Standardpraktiken zur Vermeidung von Unfällen bewußt. Übersetzungen der in dieser Veröffentlichung enthaltenen Warnhinweise finden Sie im Dokument Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (Informationen zu behördlichen Vorschriften und Sicherheit), das zusammen mit diesem Gerät geliefert wurde.
Avvertenza Questo simbolo di avvertenza indica un pericolo. La situazione potrebbe causare infortuni alle persone. Prima di lavorare su qualsiasi apparecchiatura, occorre conoscere i pericoli relativi ai circuiti elettrici ed essere al corrente delle pratiche standard per la prevenzione di incidenti. La traduzione delle avvertenze riportate in questa pubblicazione si trova nel documento Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (Conformità alle norme e informazioni sulla sicurezza) che accompagna questo dispositivo.
Advarsel Dette varselsymbolet betyr fare. Du befinner deg i en situasjon som kan føre til personskade. Før du utfører arbeid på utstyr, må du vare oppmerksom på de faremomentene som elektriske kretser innebærer, samt gjøre deg kjent med vanlig praksis når det gjelder å unngå ulykker. Hvis du vil se oversettelser av de advarslene som finnes i denne publikasjonen, kan du se i dokumentet Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (Overholdelse av forskrifter og sikkerhetsinformasjon) som ble levert med denne enheten.
Aviso Este símbolo de aviso indica perigo. Encontra-se numa situação que lhe poderá causar danos físicos. Antes de começar a trabalhar com qualquer equipamento, familiarize-se com os perigos relacionados com circuitos eléctricos, e com quaisquer práticas comuns que possam prevenir possíveis acidentes. Para ver as traduções dos avisos que constam desta publicação, consulte o documento Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (Informação de Segurança e Disposições Reguladoras) que acompanha este dispositivo.
¡Advertencia! Este símbolo de aviso significa peligro. Existe riesgo para su integridad física. Antes de manipular cualquier equipo, considerar los riesgos que entraña la corriente eléctrica y familiarizarse con los procedimientos estándar de prevención de accidentes. Para ver una traducción de las advertencias que aparecen en esta publicación, consultar el documento titulado Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (Información sobre seguridad y conformidad con las disposiciones reglamentarias) que se acompaña con este dispositivo.
Varning! Denna varningssymbol signalerar fara. Du befinner dig i en situation som kan leda till personskada. Innan du utför arbete på någon utrustning måste du vara medveten om farorna med elkretsar och känna till vanligt förfarande för att förebygga skador. Se förklaringar av de varningar som förkommer i denna publikation i dokumentet Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (Efterrättelse av föreskrifter och säkerhetsinformation), vilket medföljer denna anordning.
Follow these basic guidelines when working with any electrical equipment:
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage, which can occur when electronic cards or components are improperly handled, results in complete or intermittent failures. Port adapters and processor modules consist of printed circuit boards that are fixed in metal carriers. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding and connectors are integral components of the carrier. Although the metal carrier helps to protect the board from ESD, use a preventive antistatic strap during handling.
Following are guidelines for preventing ESD damage:
 | Caution For safety, periodically check the resistance value of the antistatic strap. The measurement should be between 1 and 10 megohms. |
This section contains information specific to the 100VG port adapter and its use with Cisco 7000 series, Cisco 7200 series, and Cisco 7500 series routers.
The following sections discuss information specific to the 100VG port adapter:
Each 100VG port adapter provides a single interface ports, which is compatible with and specified by IEEE 802.12, to provide 100-Mbps interface over Category 5, unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cable (with RJ-45 connectors), supporting 802.3 Ethernet packets. The 100VG port adapter operates at 120 Mbps with a 5B/6B coding scheme, which provides a data rate of 100 Mbps.
The 100VG port adapter is designed to conform to the following emissions standards: FCC Part 15 Class A, Cispr22 Class A, EN 55022 Class A, and VCCI Class 1.
The PA-100VG port adapter can be monitored with the IEEE 802.12 Interface MIB (DOT12-IF-MIB.my). (For information on accessing Cisco MIB files, refer to the Cisco MIB User Quick Reference.)
PA-100VG (see Figure 1) is used on the second-generation Versatile Interface Processors (VIP2s) for use with the Cisco 7500 series routers, and with Cisco 7000 series routers using the RSP7000. The 100VG port adapter can also be used in Cisco 7200 series routers. There are no chassis or port adapter slot restrictions for the 100VG port adapter. 100VG port adapters are available as spare parts (as PA-100VG=).

After system initialization, the enabled LED goes on to indicate that the 100VG port adapter has been enabled for operation. When a port is operational and ready, its link OK LED goes on and remains on. When a port is active, its activity LED is on when a port on the 100VG port adapter is receiving a carrier signal from the network and normally off. (The LEDs are shown in Figure 2.)

The following conditions must be met before the enabled LED goes on:
The single interface receptacle on the 100VG port adapter is an RJ-45. Each connection supports IEEE 802.12 interfaces. The RJ-45 connection does not require an external transceiver and can use Category 3 and Category 5 unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cable with RJ-45 terminations. (Cisco Systems does not supply Category 3 and Category 5, UTP RJ-45 cables; these cables are available from commercial cable vendors.)
Figure 3 shows the RJ-45 cable connectors. Table 1 lists the pinout and signal descriptions for the RJ-45 connector.

 | Warning The ports labeled "Ethernet," "10BaseT," "Token Ring," "Console," and "AUX" are safety extra-low voltage (SELV) circuits. SELV circuits should only be connected to other SELV circuits. Because the BRI circuits are treated like telephone-network voltage, avoid connecting the SELV circuit to the telephone network voltage (TNV) circuits. |
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Out1+ |
2 | Out1- |
3 | Out2+ |
4 | Out3+ |
5 | Out3- |
6 | Out2- |
7 | Out4+ |
8 | Out4- |
This section provides information about where you can install the 100VG port adapter on the VIP2 and in the Cisco 7200 series routers.
Figure 4 shows a VIP2-15 or VIP2-40 with two installed port adapters. With the VIP2 oriented as shown, the left port adapter is in port adapter slot 0, and the right port adapter is in port adapter slot 1.

Figure 5 shows a Cisco 7206 with port adapters installed. In the Cisco 7206, port adapter slot 1 is in the lower left position, and port adapter slot 6 is in the upper right position. (The Cisco 7204 is not shown, but has four port adapter slots; PA-100VG can be installed in any of these four slots.)

This section describes the 100VG port adapter and its use with the VIP2 and provides the following additional information that is specific to the 100VG port adapter and its use on the VIP2 in Cisco 7000 series and Cisco 7500 series routers:
The 100VG port adapter used on the VIP2 can be installed in either port adapter slot 0 or port adapter slot 1. Figure 6 shows two 100VG port adapters installed on a VIP2-15 or VIP2-40.

 | Caution Port adapters have a handle attached, but this handle is not shown to allow a full view of detail on each port adapter's faceplate. |
This section provides the standard procedures for installing or replacing a port adapter on the VIP2.
Depending on the circumstances, you might need to install a new port adapter on a VIP2 motherboard or replace a failed port adapter in the field. In either case, you need a number 1 Phillips screwdriver, an antistatic mat onto which you can place the removed interface processor, and an antistatic container into which you can place a failed port adapter for shipment back to the factory.
 | Caution To prevent system problems, do not remove port adapters from the VIP2 motherboard, or attempt to install other port adapters on the VIP2 motherboard while the system is operating. To install or replace port adapters, first remove the VIP2 from its interface processor slot. |
 | Caution To prevent interface reconfiguration requirements, you should replace a port adapter with the same type of port adapter you removed, but this is not a requirement. |
When only one port adapter is installed on a VIP2, a blank port adapter must fill the empty slot to allow the VIP2 and router chassis to conform to electromagnetic interference (EMI) emissions requirements, and so that air flows through the chassis properly. If you plan to install a new port adapter, you must first remove the blank port adapter.
Use the following standard procedure to remove and replace any type of port adapter on a VIP2:
Step 1 Attach an ESD-preventive wrist strap between you and an unfinished chassis surface.
Step 2 For a new port adapter installation or a port adapter replacement, disconnect any interface cables from the ports on the front of the port adapter, although, this is not required. You can remove VIP2s with cables attached; however, we do not recommend it.
Step 3 Remove the VIP2 from the system. (Follow the steps in the section "Removing a VIP2" in the configuration note Second-Generation Versatile Interface Processor (VIP2) Installation and Configuration [Document Number 78-2658-xx], which shipped with your VIP2.)
Step 4 Place the removed VIP2 on an antistatic mat.
Step 5 Locate the screw at the rear of the port adapter (or blank port adapter) to be replaced. (See Figure 7.) This screw secures the port adapter (or blank port adapter) to its slot.

Step 6 Remove the screw that secures the port adapter (or blank port adapter).
Step 7 With the screw removed, grasp the handle on the front of the port adapter (or blank port adapter) and carefully pull it out of its slot, away from the edge connector at the rear of the slot. (See Figure 8.)

Step 8 If you removed a port adapter, place it in an antistatic container for safe storage or shipment back to the factory. If you removed a blank port adapter, no special handling is required; however, store the blank port adapter for potential future use.
Step 9 Remove the new port adapter from its antistatic container and position it at the opening of the slot. (See Figure 9.)
Step 10 Carefully align the port adapter carrier between the upper and lower edges of the port adapter slot, as shown in Figure 9.
 | Caution To prevent jamming the carrier between the upper and lower edges of the port adapter slot, and to assure that the edge connector at the rear of the port adapter mates with the connector at the rear of the port adapter slot, make certain that the leading edges of the carrier are between the upper and lower slot edges, as shown in the cutaway in Figure 9. |

Step 11 Carefully slide the new port adapter into the port adapter slot (see Figure 10) until the connector on the port adapter is completely mated with the connector at the rear of the port adapter slot.

Step 12 Replace the screw in the rear of the port adapter slot. (See Figure 7 for its location.) Do not overtighten this screw.
Step 13 Reinstall the VIP2 in the system. (Follow the steps in the section "Installing a VIP2" in the configuration note Second-Generation Versatile Interface Processor (VIP2) Installation and Configuration [Document Number 78-2658-xx], which shipped with your VIP2.)
Step 14 If disconnected, reconnect the interface cables to the port adapters.
This completes the procedure for installing a new port adapter or replacing a port adapter on a VIP2.
RJ-45 cables are not available from Cisco Systems; they are available from outside commercial cable vendors.
Use the following procedure to connect RJ-45 cables to the 100VG port adapter:
Step 1 Attach the Category 5 UTP cable directly to the RJ-45 port on the 100VG port adapter. (See Figure 11.)
 | Warning The ports labeled "Ethernet," "10BASE-T," "Token Ring," "Console," and "AUX" are safety extra-low voltage (SELV) circuits. SELV circuits should only be connected to other SELV circuits. Because the BRI circuits are treated like telephone-network voltage, avoid connecting the SELV circuit to the telephone network voltage (TNV) circuits. |

Step 2 Attach the network end of your RJ-45 cable to your 100VG hub or repeater or other external 100VG equipment.
Step 3 Repeat Steps 1 and 2 for each additional 100VG interface.
This completes the 100VG port adapter installation.
After you verify that the new 100VG port adapter is installed correctly (the enabled LED goes on), use the privileged-level configure command to configure the new interfaces. Be prepared with the information you will need, such as the following:
For a summary of the configuration options available and instructions for configuring the 100VG AnyLAN interfaces on the 100VG port adapter, refer to the appropriate configuration publications listed in the section "If You Need More Information" on page 2.
The configure command requires privileged-level access to the EXEC command interpreter, which usually requires a password. Contact your system administrator if necessary to obtain EXEC-level access.
The following section describes how to identify chassis slot, port adapter, and interface port numbers.
In the router, physical port addresses specify the actual physical location of each interface port on the router interface processor end. (See Figure 12.) This address is composed of a three-part number in the format chassis slot number/port adapter number/interface port number, as follows:
Interface ports on the 100VG-equipped VIP2 maintain the same addresses regardless of whether other interface processors are installed or removed. However, when you move a VIP2 to a different slot, the first number in the address changes to reflect the new chassis slot number.
Figure 12 shows the port adapter slots and interface ports of a sample Cisco 7505 system. On a 100VG port adapter interface port numbers are always 0. For example, the 100VG AnyLAN interface port on a 100VG port adapter in the first port adapter slot in chassis slot 3, would be 3/0/0. (See Figure 12.) The 100VG port adapter in port adapter slot 1 would be numbered 3/1/0.

You can identify interface ports by physically checking the slot/port-adapter/interface port location on the back of the router or by using show commands to display information about a specific interface or all interfaces in the router.
The following steps describe a basic configuration. Press the Return key after each step unless otherwise noted. At any time you can exit the privileged level and return to the user level by entering disable at the prompt as follows:
Router# disable
Router>
Use the following procedure to perform a basic configuration:
Step 1 At the privileged-level prompt, enter configuration mode and specify that the console terminal will be the source of the configuration subcommands as follows:
Router# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#
Step 2 At the prompt, specify the first interface to configure by entering the subcommand interface, followed by the type (vg) and slot/port adapter/interface (interface processor slot number/port adapter slot number/interface number).
The example that follows is for the interface on the first port adapter on a 100VG port adapter in interface processor slot 1:
Router(config)# interface vg 1/0/0
Step 3 If IP routing is enabled on the system, you can assign an IP address and subnet mask to the interface with the ip address configuration subcommand, as in the following example:
Router(config-if)# ip address 1.1.1.10 255.255.255.0
Step 4 Add any additional configuration subcommands required to enable routing protocols and set the interface characteristics.
Step 5 Change the shutdown state to up and enable the interface as follows:
Router(config-if)# no shutdown
Step 6 Configure additional interfaces as required.
Step 7 When you have included all of the configuration subcommands to complete the configuration, press Ctrl-Z to exit configuration mode.
Step 8 Write the new configuration to nonvolatile memory as follows:
Router# copy running-config startup-config
[OK]
Router#
To check the interface configuration using show commands, proceed to the section "Checking the Configuration."
This section provides information for checking your configuration. After configuring the new interface, use the show commands to display the status of the new interface or all interfaces, and use the ping command to check connectivity.
The following steps use show commands to verify that the new interfaces are configured and operating correctly.
Step 1 Display the system hardware configuration with the show version command to ensure that the list includes the new interfaces.
Step 2 Display all the current interface processors and their interfaces with the show controllers cbus command. Verify that the new 100VG port adapter appears in the correct slot.
Step 3 Specify one of the new interfaces with the show interfaces type slot/port adapter/interface command and verify that the first line of the display specifies the interface with the correct slot number. Also verify that the interface and line protocol are in the correct state: up or down.
Step 4 Display the protocols configured for the entire system and specific interfaces with the show protocols command. If necessary, return to configuration mode to add or remove protocol routing on the system or specific interfaces.
Step 5 Display the running configuration file with the show running-config command. Display the configuration stored in NVRAM using the show startup-config command. Verify that the configuration is accurate for the system and each interface.
If the interface is down and you configured it as up, or if the displays indicate that the hardware is not functioning properly, ensure that the network interface is properly connected and terminated. If you still have problems bringing the interface up, contact a service representative for assistance.
To display information about a specific interface, use the show interfaces command with the interface type and port address in the format show interfaces type [slot/port adapter/interface].
Router# sh int vg 3/1/0
VG-AnyLAN3/1/0 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is cyBus VG-AnyLAN Interface, address is 0060.3e64.2468 (bia 0060.3e64.2468)
Internet address is 1.1.1.17/8
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set, keepalive set (10 sec)
(additional display text omitted)
The following example of the show interfaces vg slot/port adapter/interface command shows all of the information specific to the first 100VG AnyLAN interface port (interface port 0) in chassis slot 3, port adapter slot 1:
Router# sh int vg 3/1/0
VG-AnyLAN3/1/0 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is cyBus VG-AnyLAN Interface, address is 0060.3e64.2468 (bia 0060.3e64.2468)
Internet address is 10.1.1.17/8
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set, keepalive set (10 sec)
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input never, output 00:00:00, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters never
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
0 packets input, 0 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
0 input packets with dribble condition detected
35 packets output, 3655 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
0 vg alignment error, 0 vg balance error
0 vg invalid ipm error, 0 vg symbol error
0 vg skew error, 0 vg frame delimit error
0 vg high priority packets, 0 vg high priority octects
Explanations of the 100VG-specific portions of the show interfaces display follow:
For complete command descriptions and examples, refer to the publications listed in the section "If You Need More Information" on page 2.
Following is an example of the show version command:
Router> show version
Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software
IOS (tm) GS Software (RSP-JV-MZ), Version 11.1(9)CA1 [biff 240]
Synced to mainline version: 11.1(5.1)
Copyright (c) 1986-1996 by cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Wed 02-Oct-96 09:20 by biff
Image text-base: 0x600108A0, data-base: 0x60962000
ROM: System Bootstrap, Version 5.3.2(3.2) [biff 3.2], MAINTENANCE INTERIM SOFTWARE
ROM: GS Bootstrap Software (RSP-BOOT-M), Version 10.3(12), RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1)
Router uptime is 4 minutes
System restarted by reload
System image file is "biff/rsp-jv-mz.111", booted via tftp from 1.1.0.1
cisco RSP1 (R4600) processor with 16384K bytes of memory.
R4600 processor, Implementation 32, Revision 2.0
Last reset from power-on
G.703/E1 software, Version 1.0.
SuperLAT software copyright 1990 by Meridian Technology Corp).
Bridging software.
X.25 software, Version 2.0, NET2, BFE and GOSIP compliant.
TN3270 Emulation software (copyright 1994 by TGV Inc).
Chassis Interface.
1 100VG AnyLAN Ethernet 802.12 interface.
125K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory.
8192K bytes of Flash PCMCIA card at slot 0 (Sector size 128K).
8192K bytes of Flash internal SIMM (Sector size 256K).
Configuration register is 0x2
The show controllers cbus command shows assorted information about the interfaces installed in the router. Following is an example of partial output from the show controllers cbus command, showing a 100VG-equipped VIP2:
Router# sh cont cbus
(additional display text omitted)
slot3: VIP2, hw 2.3, sw 21.40, ccb 5800FF50, cmdq 48000098, vps 8192
software loaded from system
IOS (tm) VIP Software (SVIP-DW-M), Version 11.1(9)CA1 [biff 243]
ROM Monitor version 17.0
VG-AnyLAN3/1/0, addr 0060.3e64.2468 (bia 0060.3e64.2468)
gfreeq 48000138, lfreeq 480001B8 (1536 bytes), throttled 0
rxlo 4, rxhi 507, rxcurr 0, maxrxcurr 0
txq 48001A00, txacc 48001A02 (value 297), txlimit 297
To determine which type of port adapter is installed on a VIP2 in your system, use the show diag slot command. Specific port adapter information is displayed, as shown in the following example of an 100VG port adapter in a VIP2 in chassis slot 11:
Router# show diag 11
Slot 11:
Physical slot 11, ~physical slot 0x4, logical slot 11, CBus 0
Microcode Status 0xC
Master Enable, LED, WCS Loaded
Board is analyzed
Pending I/O Status: Console I/O
EEPROM format version 1
VIP2 controller, HW rev 2.2, board revision UNKNOWN
Serial number: 03507967 Part number: 73-1684-02
Test history: 0x00 RMA number: 00-00-00
Flags: cisco 7000 board; 7500 compatible
EEPROM contents (hex):
0x20: 01 15 02 02 00 35 86 FF 49 06 94 02 00 00 00 00
0x30: 12 2B 00 2A 1A 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Slot database information:
Flags: 0x4 Insertion time: 0x3E50 (6d14h ago)
Controller Memory Size: 16 MBytes DRAM, 1024 KBytes SRAM
PA Bay 1 Information:
VG-AnyLAN PA, 1 ports
EEPROM format version 1
HW rev FF.FF, Board revision 160
Serial number: 02023164 Part number: 73-1556-03
The show startup-config command displays the information from the configuration file used at system startup. Following is an example of partial output from the show startup-config command from a system with a 100VG port adapter installed and configured:
Router# sh startup-conf
(additional display text omitted)
hostname Router
!
boot system biff/rsp-jv-mz.111 8
!
interface VG-AnyLAN3/1/0
ip address 1.1.1.17 255.0.0.0
no mop enabled
no mop sysid
(additional display text omitted)
The packet internet groper (ping) command allows you to verify that an interface port is functioning properly and to check the path between a specific port and connected devices at various locations on the network. This section provides brief descriptions of the ping command. After you verify that the system and 100VG-equipped VIP2 have booted successfully and are operational, you can use this command to verify the status of interface ports. Refer to the publications listed in the section "If You Need More Information" on page 2, for detailed command descriptions and examples.
The ping command sends an echo request out to a remote device at an IP address that you specify. After sending a series of signals, the command waits a specified time for the remote device to echo the signals. Each returned signal is displayed as an exclamation point (!) on the console terminal; each signal that is not returned before the specified time-out is displayed as a period (.). A series of exclamation points (!!!!!) indicates a good connection; a series of periods (.....) or the messages [timed out] or [failed] indicate that the connection failed.
Following is an example of a successful ping command to a remote server with the address 1.1.1.10:
Router# ping 1.1.1.10 <Return>
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echoes to 1.1.1.10, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/15/64 ms
Router#
If the connection fails, verify that you have the correct IP address for the server and that the server is active (powered on); then repeat the ping command. For complete descriptions of interface subcommands and the configuration options available for 100VG-related interfaces, and which support 100VG functionality, refer to the publications listed in the section "If You Need More Information" on page 2.
The 100VG port adapters are used in the Cisco 7200 series routers and can be installed in any of the available port adapter slots. Figure 13 shows a 100VG port adapter installed in port adapter slot 3 of a Cisco 7206.

The following sections include information that is specific to the 100VG port adapters and their use in the Cisco 7200 series routers:
This section provides the standard procedures for installing or replacing port adapters in a Cisco 7200 series router.
Depending on your circumstances, you might need to install a new port adapter in a Cisco 7200 series router or replace a failed port adapter in the field. In either case no tools are necessary; all port adapters available for the Cisco 7200 series connect directly to the router midplane and are locked into position by a port adapter lever. When removing and replacing a port adapter, you will need an antistatic mat onto which you can place a removed port adapter and an antistatic container into which you can place a failed port adapter for shipment back to the factory.
When a port adapter slot is not in use, a blank port adapter must fill the empty slot to allow the router to conform to EMI emissions requirements and to allow proper air flow across the port adapters. If you plan to install a new port adapter in a slot that is not in use, you must first remove a blank port adapter.
Use the following standard procedure to remove a port adapter from a Cisco 7200 series router:
Step 1 Attach an ESD-preventative wrist strap between you and an unfinished chassis surface.
Step 2 Place the port adapter lever for the desired port adapter slot in the unlocked position. The port adapter lever remains in the unlocked position. (Refer to Figure 14.)

Step 3 Grasp the handle on the port adapter and pull the port adapter from the midplane, about halfway out of its slot. If you are removing a blank port adapter, pull the blank port adapter from the port adapter slot.
Step 4 With the port adapter halfway out of the slot, disconnect all cables from the port adapter.
Step 5 After disconnecting the cables, pull the port adapter from its port adapter slot.
 | Caution Always handle the port adapter by the carrier edges and handle; never touch the port adapter's components or connector pins. (Refer to Figure 15.) |

Step 6 Place the port adapter on an antistatic surface with its components facing upward, or in a static shielding bag. If the port adapter will be returned to the factory, immediately place it in a static shielding bag.
This completes the procedure for removing a port adapter from a Cisco 7200 series router.
Use the following standard procedure to install a new port adapter in a Cisco 7200 series router:
Step 1 Attach an ESD-preventative wrist strap between you and an unfinished chassis surface.
Step 2 Use both hands to grasp the port adapter by its metal carrier edges and position the port adapter so that its components are downward. (Refer to Figure 15).
Step 3 Align the left and right edge of the port adapter metal carrier between the guides in the port adapter slot. (Refer to Figure 16.)

Step 4 With the metal carrier aligned in the slot guides, gently slide the port adapter halfway into the slot.
 | Caution Do not slide the port adapter all the way into the slot until you have connected all required cables. Trying to do so will disrupt normal operation of the router. |
Step 5 With the port adapter halfway in the slot, connect all required cables to the port adapter.
Step 6 After connecting all required port adapter cables, carefully slide the port adapter all the way into the slot until you feel the port adapter's connectors mate with the midplane.
Step 7 Move the port adapter lever to the locked position. Figure 17 shows the port adapter lever in the locked position.
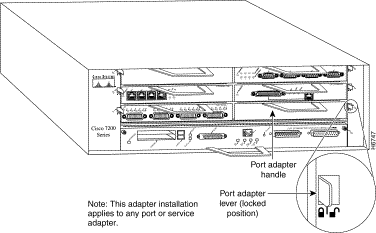
This completes the procedure for installing a new port adapter in a Cisco 7200 series router.
100VG RJ-45 cables are not available from Cisco Systems; they are available from outside commercial cable vendors.
Use the following procedure to connect 100VG cables to a 100VG port adapter:
Step 1 Attach the 100VG RJ-45 cable directly to the 100VG port on the 100VG port adapter. (See Figure 18.)

Step 2 Attach the network end of your 100VG cable to your external 100VG equipment.
Step 3 Repeat Steps 1 and 2 for each additional 100VG interface.
This completes the procedure for attaching 100VG port adapter cables.
If you installed a new 100VG port adapter or if you want to change the configuration of an existing interface, you must enter configuration mode using the configure command. If you replaced a 100VG port adapter that was previously configured, the system will recognize each new 100VG and bring it up in its existing configuration.
After you verify that the new 100VG port adapter is installed correctly (the enabled LED goes on), use the privileged-level configure command to configure the new interfaces. Be prepared with the information you will need, such as the following:
For a summary of the configuration options available and instructions for configuring the 100VG interfaces on a Cisco 7200 series router, refer to the appropriate configuration publications listed in the section "If You Need More Information" on page 2.
The configure command requires privileged-level access to the EXEC command interpreter, which usually requires a password. Contact your system administrator if necessary to obtain EXEC-level access.
The following section describes how to identify port adapter slot and 100VG port numbers.
Physical port addresses specify the actual physical location of each interface port on the router. (See Figure 19.) This address is composed of a two-part number in the format port adapter slot number/interface port number, as follows:
Interface ports maintain the same address regardless of whether other port adapters are installed or removed from the slot. However, when you move a port adapter to a different slot, the first number in the address changes to reflect the new chassis slot number.
Figure 19 shows the port adapter slots and interface ports of a Cisco 7206. The port adapter slot numbers start with 1 and continue through 6 (slot 0 is always reserved for the Fast Ethernet port on the I/O controller---if present). The individual interface port numbers always begin with 0. The number of additional ports depends on the number of ports on a port adapter.
For example, the 100VG port on a 100VG port adapter in port adapter slot 3 would have the address 3/0. (See Figure 19.) If the 100VG port adapter was in port adapter slot 1, this same interface port would be numbered 1/0.

You can identify interface ports by physically checking the slot/interface port location on the front of the router or by using show commands to display information about a specific interface or all interfaces in the router.
The following steps describe a basic interface configuration. Press the Return key after each step unless otherwise noted. At any time you can exit the privileged level and return to the user level by entering disable at the prompt as follows:
Router# disable
Router>
Following is an example of a basic configuration procedure:
Step 1 At the privileged-level prompt, enter configuration mode and specify that the console terminal will be the source of the configuration subcommands as follows:
Router# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#
Step 2 At the prompt, specify the first interface to configure by entering the subcommand interface, followed by the type (100vg) and slot/port (port adapter slot number and interface port number). The example that follows is for the first interface of the port adapter in slot 2:
Router(config)# interface 100vg 2/0
Step 3 If IP routing is enabled on the system, you can assign an IP address and subnet mask to the interface with the ip address configuration subcommand, as in the following example:
Router(config-if)# ip address 1.1.1.10 255.255.255.0
Step 4 Add any additional configuration subcommands required to enable routing protocols and set the interface characteristics.
Step 5 Change the shutdown state to up and enable the interface as follows:
Router(config-if)# no shutdown
Step 6 Configure additional interfaces as required.
Step 7 When you have included all of the configuration subcommands to complete the configuration, press Ctrl-Z to exit configuration mode.
Step 8 Write the new configuration to nonvolatile memory as follows:
Router# copy running-config startup-config
[OK]
Router#
To check the interface configuration using show commands, proceed to the section "Checking the Configuration."
After configuring the new interface, use the show commands to display the status of the new interface or all interfaces, and use the ping command to check connectivity.
The following steps use show commands to verify that the new interfaces are configured and operating correctly:
Step 1 Display the system hardware configuration with the show version command to ensure that the list includes the new interfaces.
Step 2 Display all the current port adapters and their interfaces with the show controllers command. Verify that the new 100VG port adapter appears in the correct slot.
Step 3 Specify one of the new interfaces with the show interfaces type [slot/interface] command and verify that the first line of the display specifies the interface with the correct slot number. Also verify that the interface and line protocol are in the correct state: up or down.
Step 4 Display the protocols configured for the entire system and specific interfaces with the show protocols command. If necessary, return to configuration mode to add or remove protocol routing on the system or specific interfaces.
Step 5 Display the running configuration file with the show running-config command. Display the configuration stored in NVRAM using the show startup-config command. Verify that the configuration is accurate for the system and each interface.
If the interface is down and you configured it as up, or if the displays indicate that the hardware is not functioning properly, ensure that the network interface is properly connected and terminated. If you still have problems bringing the interface up, contact a service representative for assistance.
To display information about a specific interface, use the show interfaces command with the interface type and port address in the format show interfaces type [slot/interface]. The following example of the show interfaces type [slot/interface] command shows all of the information specific to the first 100VG port (interface port 0) in port adapter slot 5:
Router# show int vg 5/0
VG-AnyLAN5/0 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is MC68852
Frame type is 802.3, address is 0060.09b9.9b28 (bia 0060.09b9.9b28)
Internet address is 10.1.1.6/16
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set, keepalive set (10 sec)
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input 00:00:00, output 00:00:01, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters never
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
687 packets input, 48114 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 69 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
0 input packets with dribble condition detected
855 packets output, 59743 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 3 interface resets
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
0 vg alignment error, 0 vg balance error
0 vg invalid ipm error, 0 vg symbol error
0 vg skew error, 0 vg frame delimit error
Display all the current interface processors and their interfaces with the show controllers command. Following is an example of the show controllers type [slot/interface] command that shows 100VG interface port 0 on a 100VG port adapter installed in chassis slot 5:
Router# show controllers vg 5/0
Interface VG-AnyLAN5/0
Hardware is MC68852
mc68852_ds=0x60975F48, registers=0x3C500000, ib=0x4B08EAA0
rx ring entries=31, tx ring entries=31
rxring=0x4B08EBA0, rxr shadow=0x60976460, rx_head=27, rx_tail=0
txring=0x4B08F9E0, txr shadow=0x60976AD4, tx_head=11, tx_tail=11, tx_count=0,
Actel Hardware CAM Register:
CAM DEVICE BASE: 0x3C500800 Register Address: 0x3C500C00
CSR: 0x81000000 CAMCR: 0x0
USAR: 0x60000000 MSAR: 0x643E0000 LSAR: 0x60240000
FIFOCR: 0x80000000 WRMASK: 0x80
COMPARAND REG: 0x0 0x6000 0x643E 0x6024
PERSISTENT SOURCE: 0x0 PERSISTENT DEST: 0x10000
MC68852 Registers:
hw_id: 5048, hw_id & page: 7053, opr1=0x26, opr2=0x2C, opr3=0x00
Page 0 - Performance:
isr=0x1000, imr=0x0E0A, flreg=0x0000
xfrct=0x800080, rxcnt=0, txcnt=1F
Page 1 - MAC Address/Hash Table:
addrlow= 6009B9, addrhigh=9B2809B9,hash bytes=FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF
Page 2 - Hardware Mapping:
mmmsw=0x0000, mmlsw=0x0000, bmreg =0x04
Page 4 - LAN Configuration:
tccnf1=0x00, tccnf2=0x01
vccnf=0xFF, vtrrg=0x0420, valow1=0x0000, valow2=0x0000
maccr1=0xFF, maccr2=0x00, maccr3=0x04, maccr4=0x01
Page 5 - MMU Registers:
rx mem stop addr=0xFF03, tx mem stop addr=0xFF07
MC68852 PCI registers:
bus_no=7, device_no=0
CFID=0x0005101A, CFCS=0x02800005, CFRV=0x02000000, CFLT=0x0000F800
CBIO=0x00008001, CBMA=0x00000000, CFIT=0x20080100, CFDA=0x00000008
The show version (or show hardware) command displays the configuration of the system hardware (the number of each port adapter type installed), the software version, the names and sources of configuration files, and the boot images. Following is an example of the output from the show version command:
Router# show version
Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software
IOS (tm) 7200 Software (C7200-J-M), Released Version 11.1(9)CA1 [biff 199]
Synced to mainline version: 11.1(8)
Copyright (c) 1986-1996 by cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Wed 18-Dec-96 18:27 by biff
Image text-base: 0x60008890, data-base: 0x60634000
ROM: System Bootstrap, Version 11.1(11855) [beta 2], INTERIM SOFTWARE
ROM: 7200 Software (C7200-BOOT-M), Version 11.1(9)CA1, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1)
Router uptime is 22 minutes
System restarted by reload
System image file is "biff/c7200-j-mz.111", booted via tftp from 1.1.0.1
cisco 7206 (NPE150) processor with 12288K/4096K bytes of memory.
R4700 processor, Implementation 33, Revision 1.0 (Level 2 Cache)
Last reset from power-on
Bridging software.
SuperLAT software copyright 1990 by Meridian Technology Corp).
X.25 software, Version 2.0, NET2, BFE and GOSIP compliant.
TN3270 Emulation software (copyright 1994 by TGV Inc).
(additional display text omitted)
1 100VG AnyLAN Ethernet 802.12 interface.
(additional display text omitted)
125K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory.
1024K bytes of packet SRAM memory.
8192K bytes of Flash PCMCIA card at slot 0 (Sector size 128K).
4096K bytes of Flash internal SIMM (Sector size 256K).
Configuration register is 0x2
To determine which type of port adapter is installed in your system, use the show diag slot command. Specific port adapter information is displayed, as shown in the following example of a 100VG port adapter in chassis slot 5:
Router# show diag 5
Slot 5:
100VG port adapter, 1 port
Port adapter is analyzed
Port adapter insertion time 15:50:11 ago
Hardware revision 255.255 Board revision UNKNOWN
Serial number 4294967295 Part number 255-65535-255
Test history 0xFF RMA number 255-255-255
EEPROM format version 1
EEPROM contents (hex):
0x20: 01 1B FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF
0x30: FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF
The packet internet groper (ping) command allows you to verify that an interface port is functioning properly and to check the path between a specific port and connected devices at various locations on the network. This section provides a brief description of the ping command. After you verify that the system has booted successfully and is operational, you can use this command to verify the status of interface ports. Refer to the publications listed in the section "If You Need More Information" on page 2, for detailed command descriptions and examples.
The ping command sends an echo request out to a remote device at an IP address that you specify. After sending a series of signals, the command waits a specified time for the remote device to echo the signals. Each returned signal is displayed as an exclamation point (!) on the console terminal; each signal that is not returned before the specified timeout is displayed as a period (.). A series of exclamation points (!!!!!) indicates a good connection; a series of periods (.....) or the messages [timed out] or [failed] indicate that the connection failed.
Following is an example of a successful ping command to a remote server with the address 1.1.1.10:
Router# ping 1.1.1.10 <Return>
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echoes to 1.1.1.10, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/15/64 ms
Router#
If the connection fails, verify that you have the correct IP address for the server and that the server is active (powered on); then repeat the ping command.
For complete descriptions of interface subcommands and the configuration options available for Cisco 7200 series-related interfaces and functionality, refer to the publications listed in the section "If You Need More Information" on page 2.
Cisco Connection Online (CCO) is Cisco Systems' primary, real-time support channel. Maintenance customers and partners can self-register on CCO to obtain additional information and services.
Available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, CCO provides a wealth of standard and value-added services to Cisco's customers and business partners. CCO services include product information, product documentation, software updates, release notes, technical tips, the Bug Navigator, configuration notes, brochures, descriptions of service offerings, and download access to public and authorized files.
CCO serves a wide variety of users through two interfaces that are updated and enhanced simultaneously: a character-based version and a multimedia version that resides on the World Wide Web (WWW). The character-based CCO supports Zmodem, Kermit, Xmodem, FTP, and Internet e-mail, and it is excellent for quick access to information over lower bandwidths. The WWW version of CCO provides richly formatted documents with photographs, figures, graphics, and video, as well as hyperlinks to related information.
You can access CCO in the following ways:
For a copy of CCO's Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ), contact cco-help@cisco.com. For additional information, contact cco-team@cisco.com.

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Tue Jul 20 08:42:48 PDT 1999
Copyright 1989-1999©Cisco Systems Inc.