|
|

This chapter describes the basic steps for configuring the Cisco DVB CAR100:
The Cisco DVB CAR100 is configured using an SNMP agent and the Cisco Cable DVB/DAVIC Management Program. The SNMP agent included with the Cisco DVB CAR100 has also been verified with the following MIB browsers:
Using these tools, you can view and change settings for each Cisco DVB CAR100 and monitor the data traffic and user profiles.
 |
Tips Configuration can either be done remotely via the HFC network or you can connect a management PC directly to the Cisco DVB CAR100 using a standard Ethernet cable. This allows the cable modems to be preconfigured prior to installation. |
The Cisco DVB CAR100 is configured using the Cisco Cable DVB/DAVIC Management Program installed on your management PC, or another MIB browser.
 |
Note If you want to take advantage of the time and date MIBs, you will need to connect the Cisco DVB CAR100 by either providing the IP address to an SNTP server, via a BootP server, or by entering an IP address in the Cisco Cable DVB/DAVIC Management Program using the rcm SNTPServer MIB. This is an option and not a pre-requisite for using the Cisco DVB CAR100. |
To start configuring the Cisco DVB CAR100:
 |
Note You can also connect a management PC directly to the Cisco DVB CAR100 via the Ethernet interface, without it being connected to the HFC cable network. Remember that the default Ethernet IP address is 192.168.128.2 and that you must be on the same subnet (255.255.255.0) as the cable modem, for example 192.168.128.10 |
Step 2 Ensure you have the IP addresses of the cable modems you want to configure.
These are supplied by your BOOTP or DHCP server.
Step 3 Open the Cisco Cable DVB/DAVIC Management Program, click New in the Network Devices menu and enter the Name (optional), IP address, and Community of the cable modem to which you want to connect. Click OK. The details you have just entered will now appear in the top frame of the browser window.
 |
Note In the Options menu, you can select whether to view the MIB labels as they are defined in the MIB or have them converted to text. This manual uses the text format. |
Step 4 Now select the cable modem you have just entered and click Get All (F5) from the Value menu.
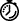 |
TimeSaver Use SNMP scripting if you want to address a group of cable modems at one time. This cannot be done using the Cisco Cable DVB/DAVIC Management Program. |
 |
Tips Double-clicking on a variable in the description column will open a dialog box where new values can be entered, including a description of that parameter. Alternatively, you can highlight a parameter and select Show Properties from the Value menu. |
The Cisco DVB CAR100 can be configured for one client PC only or for multiple client PCs (LAN).
The Cisco DVB CAR100 can be configured to operate as either an IP router or as an Ethernet bridge. In the bridge mode, the Cisco DVB CAR1000 operates as an Ethernet MAC bridge between the cable network and the local Ethernet. All routing related features are disabled in this mode.
To view or change the routing/bridging mode for a Cisco DVB CAR100:
Step 2 Open Object>System>rcm Operation Mode.
Step 3 Choose router (default) or bridge.
Step 4 Open Object>System>Settings.
Step 5 Choose saveSettings.
Step 6 Press Set.
 |
Note For bridging to work, the Cisco DVB cable system must employ DVB LLC/SNAP encapsulated Ethernet frames on the HFC cable network. |
When working as a router, the Cisco DVB CAR100 supports one of three DHCP service operating modes:
DHCP Server
The default configuration for the Cisco DVB CAR100 is as a router with the built-in Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server and Network Address Port Translation (NAPT) enabled. This configuration allows for automatic configuration of host interfaces on its Ethernet side LAN. Interfaces are configured from the pool of addresses implicitly defined by the DVB CAR100 Ethernet side IP configuration (IP address and IP sub net mask). Furthermore a DNS server name for the DHCP host configurations may be supplied through the BOOTP configuration of the Cisco DVB CAR100 cable side interface itself.
DHCP Relay
When the Cisco DVB CAR100 is configured to operate as a DHCP relay agent, the Ethernet hosts are centrally configured by a DHCP server on the cable side backbone.
No DHCP Services
In this mode the Cisco DVB CAR100 supplies no DHCP services to hosts (PCs) on its Ethernet side LAN. Either the hosts must be manually IP configured or configured by a local DHCP server.
To view or change the DHCP service operation mode for a Cisco DVB CAR100:
Step 2 Open Object>System>rcm DHCPMode.
Step 3 Choose between dhcp-server (default), dhcp-relay or static-configuration.
Step 4 Open Object>System>Settings.
Step 5 Choose saveSettings.
Step 6 Press Set.
An overview of the different router/bridging options and their implications is provided below.
| Mode | DVB MAC Level Encapsulation | IP Configuration of Cisco DVB CAR100 | Cisco DVB CAR100 Traffic Management |
|---|---|---|---|
Router | Direct IP | The Cisco DVB CAR100 has two IP interfaces. Each may be statically or dynamically BOOTP configured. | Traffic is IP-routed between the cable and Ethernet interfaces. On the Ethernet side, MAC encapsulation is discarded. |
Router | LLC/SNAP | The Cisco DVB CAR100 has two IP interfaces. Each may be statically or dynamically BOOTP configured. | The cable side network is ARP'ed for IP to MAC address mapping. |
Bridge | Direct IP | Only one interface is applied (for Cisco DVB CAR100 configuration). The interface MAC address is the cable side Cisco DVB CAR100 factory MAC address. | When configured like this, the Cisco DVB CAR100 responds by automatically reconfiguring itself for router mode and rebooting. |
Bridge | Direct IP | Only one interface is applied (for Cisco DVB CAR100 configuration). The interface MAC address is the cable side Cisco DVB CAR100 factory MAC address. | Traffic is passed at the Ethernet MAC level between interfaces, while traffic addressed to the MAC address of the |
Three security levels for community strings are available:
| Community Type | Location | Function | Default Setting |
Read community | rcm System | Used to read the current cable modem settings | public |
Write community | rcm System | Used to read and change the current cable modem settings | private |
Software upgrade community | rcm System | Used to perform a software upgrade to the cable modem | default |
 |
Note It is important to synchronize the passwords in the MIB browser with those in the MIB file of the Cisco DVB CAR100. Note that community strings (passwords) are case sensitive. |
 |
Caution If you change the software upgrade password from the factory default (that is, default) and then lose or forget the new password, there is no backdoor solution. You will have effectively rendered the Cisco DVB CAR100 unconfigurable. |
The Cisco DVB CAR100 can be configured to support a single PC (called the Cisco DVB CAR100-PC) or multiple PCs (called the Cisco DVB CAR100-LAN). The default setting is the single PC version. To change this setting to the LAN version:
Step 2 Open the Software group of MIBs
Step 3 Double-click rcmSwType.
Step 4 In the Properties window, select the LAN value.
Step 5 Click Set.
The change will first become active after performing a saveSettings. For instructions on how to do this, see the section "System" in "Management Information Base"
Figure 4-1 gives an overview of the different communication parameters (IP addresses, subnet mask, and gateway) for the Cisco DVB CAR100 and the subscriber's computer.

Cisco DVB CAR100 HFC Interface
Each Cisco DVB CAR100 includes a DHCP server, a DHCP relay agent and a BOOTP client, and arrives preconfigured with a unique Ethernet MAC address. This address is also printed on a sticker affixed to the bottom of each cable modem, and is included with the documentation accompanying the Cisco DVB CAR100. During the sign-on process, the BOOTP client automatically sends a request to the service provider's BOOTP or DHCP server, quoting the cable modem's Ethernet MAC address. In return, it is assigned a unique IP address, a subnet mask, and a default gateway. These communication parameters are subsequently used for all data traffic to and from the HFC network.
Cisco DVB CAR100 Ethernet Interface
To enable the Cisco DVB CAR100-PC to communicate with the subscriber's PCs or, in the instance of the Cisco DVB CAR100-LAN, the LAN, it uses a default, factory-installed Ethernet IP address (192.168.128.2) and subnet mask (255.255.255.0).
You can also change the default private IP address and subnet mask for all data traffic to PCs connected to the Ethernet. For more information, see the section "Changing Cisco DVB CAR100 Settings" in "Cisco Cable DVB/DAVIC Management Program".
PC Ethernet Interface
The subscriber's PC must be configured with an IP address (that lies in the cable modem's Ethernet subnet), a subnet mask, a default gateway (the Cisco DVB CAR100) and the address of a DNS server defined by the service provider. If the Cisco DVB CAR100 is configured to run in its default operating mode (i.e. with the built-in DHCP server enabled), this is done automatically. Subscribers cannot change the default Ethernet interface IP address and subnet mask—this can only be done by the service provider.
 |
Note If you want to use the Cisco DVB CAR100's built-in DHCP server, the DNS server address must be configured manually. |
By default, the Cisco DVB CAR100 supports Network Address Translation (NAPT) at port level. This means all IP addresses on the connected PCs are private and cannot be reached by the outside world. However, NAPT is disabled if the Cisco DVB CAR100 is configured to use the DHCP relay agent. NAT can also be switched off manually using SNMP (see the section "Switching NAPT On and Off" section).
 |
Note It is the responsibility of the service provider to ensure that globally available IP addresses are assigned correctly. |
 |
Note With NAPT switched on, the Cisco DVB CAR100-LAN supports up to eight public IP addresses that are not subject to translation on the subscriber's LAN. These are set up by the service provider at the subscriber's request. |
 |
Note The Cisco DVB CAR100-LAN only supports one subnet. Using the routing tables you can address multiple subnets via an external router. The default value for the subnet can be changed by the service provider. |
With NAPT switched on (default), you can configure up to 8 public IP addresses on the subscriber's PC that are not subject to NAPT. These public IP addresses will be visible on and behind the HFC network and might, for example, be used as a web server on one of the subscriber's PCs.
To set a public IP address:
Step 2 In the section IP, click NAPT and then double-click one of the eight IP addresses. Enter the global IP address and click Set.
Step 3 To activate the changes you have made, click rcm System and then double-click the variable Settings. In the dialog box that appears, select saveSettings from the pull-down menu and click Set. This will write the new settings to Cisco DVB CAR100's Flash memory.
 |
Note The public IP address must be on the same subnet as all other IP addresses on the Ethernet side of the cable modem. Only one subnet is supported, unless you choose to go via a router, in which case you can address multiple subnets using the Cisco DVB CAR100's routing tables. |
The Cisco DVB CAR100 supports downstream and upstream IP multicasts. These settings are configured in the Interfaces MIB group in the Downstream and Upstream subgroups, respectively.
Downstream IP multicast is enabled by default, while upstream IP multicast is disabled by default.
To change these settings:
Step 2 Double-click the Multicast MIB.
Step 3 Select a new value in the Properties window.
Step 4 Click Set.
Changes take effect immediately.
The Cisco DVB CAR100 supports NAPT (Network Address Translation at port level) and the factory default setting is On. To switch NAPT off:
Step 2 In the IP section, click NAPT and double-click Status.
Step 3 Set to off (1).
Step 4 Save settings to activate the change.
 |
Caution Switching off NAPT will make all the private IP addresses of the PCs connected to the Cisco DVB CAR100 publicly available on the HFC network interface side of the cable modem. |
 |
Note If NAPT is disabled, you must not use the same subnet on the Ethernet side for two or more cable modems. You should make an entry in the routing tables on the headend and backbone router regarding the addresses for which NAPT has been disabled. |
General
The first time a Cisco DVB CAR100 signs on, it will search for a valid downstream frequency (this can take up to 20 minutes). When it finds a valid downstream frequency, it is written into the cable modem's Flash memory.
 |
Note The first time the Cisco DVB CAR100 is installed, the sign-on can take up to 20 minutes. In extreme circumstances, this period can be even longer—as much as an hour. This does not necessarily indicate a problem with the cable modem, but Cisco does advise that subscribers contact their cable service provider for assistance. |
 |
Tips To view these values for the pre programmed frequencies using the Cisco Cable DVB/DAVIC Management Program, see Interfaces>DVB>Downstream>Programmed Freq and Default Fre 1 .. 4. |
The Cisco DVB CAR100 uses an editable "hit list" of five frequencies that it has connected to in the past. These five programmable frequencies are checked first each time the cable modem starts up. If the Cisco DVB CAR100 does not find a valid INA, the Cisco DVB CAR100 begins checking the ordinary downstream frequencies, while at factory-determined interleaved intervals checking the "hit list" again.
Table 4-2 shows the order and series of frequencies checked by the Cisco DVB CAR100 during sign-on.
| Step | Downstream Frequencies checked |
1 | Programmed Freq (DvbDsDefaultFreqP)
|
2 .. 5 | Default Freq 1 .. 4 (DvbDsDefaultFreq1..4)
|
6 | Scans 306 MHz to 862 MHz in step sizes of 8 MHz |
7 | Scans a number of VHF channels from 171 MHz to 227 MHz in step sizes of 1 MHz, specifically: 171, 178 to 179, 179.75, 186 to 187, 187.75, 194 to 195, 195.75, 202 to 203, 203.75, 210 to 211, 211.75, 218 to 219, 219.75, 226 to 227 |
8 | Scans 234 MHz to 250 MHz in a step of 16 MHz |
9 | Scans 118 MHz to 300 MHz in step sizes of 1 MHz |
9 | Scans 301 MHz to 862 MHz in step sizes of 1 MHz |
10 | Scans 301.25 MHz to 862 MHz in step sizes of 1 MHz |
11 | Scans 301.5 MHz to 862 MHz in step sizes of 1 MHz |
12 | Scans 301.75 MHz to 862 MHz in step sizes of 1 MHz |
To change the default values for the five "hit list" frequencies:
Step 2 Address the desired Cisco DVB CAR100 using its IP address.
Step 3 Find the Downstream group of MIBs in Interfaces>DVB and click either: Programmed Freq (rcmDvbDsDefaultFreqP) or Default Freq 1 .. 4 (rcmDvbDsDefaultFreq1..4).
Step 4 Enter the new value (in Hertz) and confirm your selection by clicking Set.
The new settings will become operational after a SaveSettings is done.
The software for the Cisco DVB CAR100 is stored in two Flash memories. The first contains the original factory-installed software, while the second can be updated with new software. If a problem occurs during an update, the Cisco DVB CAR100 typically reverts to the factory-installed software until a new version is downloaded successfully.
 |
Note Cisco offers a free software application for monitoring and managing modem pool upgrades. The application can be found on www.cisco.com by following this path. A CCO log-in is required. |
The software of the Cisco DVB CAR100 is downloaded using the Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) and activated via SNMP using your MIB browser.
To perform a software upgrade:
The management PC must be connected to the backbone of your HFC network where the units to be upgraded are installed.
Step 2 Copy the new software file to the root directory or a subfolder of the TFTP server program.
Step 3 Start the Cisco Cable DVB/DAVIC Management Program or MIB browser.
Step 4 Double-click on the Cisco DVB CAR100 you want to upgrade (or use the Edit command in the Network Devices menu and enter the relevant device's IP address). Check that the Community password matches the password defined for the Software Upgrade Community (rcmSwUpgradeCommunity) password in the System (rcmSoftware) section of your MIB browser. The factory default is default.
 |
Caution If you change the software upgrade password from the factory default (that is, default) and then lose or forget the new password, there is no backdoor solution. You will have effectively rendered the Cisco DVB CAR100 unconfigurable. |
Step 5 Enter the Software section (rcmSoftware).
Step 6 Click Server (rcmSwServer).
Step 7 Enter the IP address of the TFTP server to be used for the upgrade and click Set.
Step 8 Click Filename (rcmSwFilename).
Step 9 Enter the TFTP filename (*.bin), and if necessary a path, and click Set.
Step 10 Set Admin status (rcmSwAdminStatus) to upgradeNow and click Set.
This causes the Cisco DVB CAR100 to load the new software file—the status line of the TFTP servers will show a confirmation message.
 |
Tips To verify if the software upgrade has been successful, check that the value for Upgrade version (rcmSwUpgradeVer) in rcm Software matches the version you have just uploaded. |
Step 11 Reset the Community password back to the current read or write community password for the unit.
Step 12 Now reset the cable modem by opening the section rcm System and clicking Reset now. In the Properties box that appears, select reset (2) from the pull-down menu and click Set.
The Cisco DVB CAR100 is manufactured with two identical software images: Image 1 and Image 2. Image 1 is the fallback image. Image 2 is the primary image selected for execution by the Cisco DVB CAR100, and is directly upgradable from a TFTP server. If Image 2 becomes corrupted, Image 1 is selected for execution at the next reboot by the Cisco DVB CAR100.
If Image 2 has been successfully upgraded more than once, Image 1 will be out of date, and it is therefore recommended that this image also be upgraded regularly. Upgrading the Image 1 can only be performed from a successfully running Image 2. This is done by copying Image 2 over the Image 1. If the operation fails for some reason, the operation is retried at the next reboot until successful. This should ensure that there is always at least one valid image available for the
Cisco DVB CAR100 to reboot from successfully.
To upgrade the fallback image:
Step 2 Choose copyUpgradeToFallBack (instead of upgradeNow) and click Set.
Step 3 Then complete the process by performing Steps 11and 12.
SNMP traps are unsolicited events sent by the Cisco DVB CAR100 to the cable operator and are used for network management and troubleshooting purposes. To enable this functionality:
Step 2 Enter a valid IP address and press Set.
Step 3 Open Object>IP>Traps and, if desired, redefine the variables listed there. The default settings allow a maximum of 60 traps to be sent each hour, and has the authentication failure trap enabled.
 |
Tips An easy way to verify if the SNMP traps feature is correctly enabled, is to try to perform an action that is guaranteed to fail, and then to check if a new table has been created under Object>Event. For example, double-click on a specific cable modem to call up the Edit Network Device panel, enter an invalid community name and click OK. Then select for example one of the DVB objects and press F4 to get the values. |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Fri Feb 16 06:35:36 PST 2001
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2001 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.