|
|

This chapter describes the Cisco SESM captive portal solution and how to configure it. The chapter contains the following topics:
All of the above mentioned uses of captive portal are demonstrated in the sample captive portal solution that comes with the SESM package. With some customized programming and development, the following additional types of activities could be achieved using the SESM captive portal solution:
Figure 4-1 illustrates how the components in the SESM captive portal solution work together to provide appropriate content to the subscriber.
 |
Note Figure 4-1 shows the sample solution as it would be configured using all of the default values provided by the SESM installation program. There are many possible variations to this default deployment. |
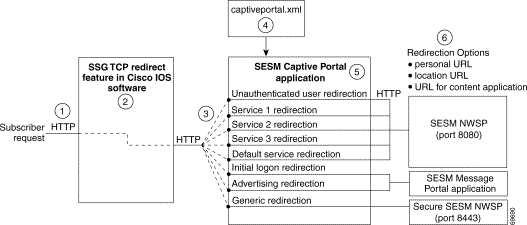
| 1 | Incoming HTTP requests from subscribers pass through the SSG. |
| 2 | When a packet qualifies for redirection, the SSG changes the destination IP address and port in the TCP packet. Cisco IOS configuration commands issued on the SSG host device define which packets qualify for redirection and the redirected destinations. |
| 3 | The sample SESM captive portal solution requires the following configurations for the TCP redirected destinations:
|
| 4 | The captiveportal.xml file associates an incoming port number to a content application URL. The SESM Captive Portal application uses the services of a JMX server to obtain the attribute values from the XML file. |
| 5 | The SESM Captive Portal application acts as a gateway to the content applications. It issues an HTTP redirect that redirects the subscriber's browser to an appropriate content application. The redirect request can include information from the original HTTP request, in the form of query parameters appended to the HTTP redirect URL. |
| 6 | The NWSP portal is the content application that services unauthenticated user redirection and service redirections. |
| 7 | The Message Portal is the content application that services initial logon and advertising redirections. |
This section describes the components of the sample captive portal solution installed with SESM:
Table 4-1 describes the SSG TCP redirection types and how the SESM captive portal solution supports those redirection types.
| Redirect Type | Role of SSG TCP Redirect Feature | Role of SESM Captive Portal Solution |
|---|---|---|
|
| Without TCP redirection, the SSG discards packets from unauthenticated users. That is, the subscriber needs to know the URL of a logon page, such as the SESM logon page, to authenticate with the SSG before accessing any services. With TCP redirection, these packets are allowed some controlled access to particular services within the SSG, such as access to a captive portal application. | Provides a logon page so the subscriber can authenticate. In a Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) client with single sign-on enabled, performs authentication transparently to the subscriber. After authentication, redirects the browser again to the subscriber's original request. |
Unconnected service redirection—Handles unauthorized attempts to access a service. | Without TCP redirection, the SSG discards packets directed at services for which the subscriber is not authorized. With TCP redirections, these packets are allowed controlled access to particular services within the SSG, such as the SESM captive portal solution. There are two types of service redirection:
| For specific service redirections, presents a logon page specific to the service being requested. For default service redirections, displays a default service selection page. In an LDAP deployment, displays a self-subscription page if the subscriber is not already subscribed to the service. |
Redirects all TCP packets destined to a configured list of ports when the host object is first created. Activates a timing mechanism for a specified duration, during which the subscriber is truly captivated and cannot redirect the browser. The configured Captive Portal application (as opposed to SSG) controls what occurs after the duration time elapses. | Provides the message content. After the message duration time elapses, optionally redirects the browser to the original request with no further action required from the subscriber. | |
Redirects all TCP packets destined to a configured list of ports at specified intervals. Activates a session timing mechanism to keep track of the time since the last advertisement. When the configured interval elapses, SSG performs an advertising redirection the next time the subscriber initiates a TCP packet. Activates a message duration timing mechanism as described above for the initial logon redirection. | Provides the advertising content. After the advertising duration time elapses, optionally redirects the browser to the previous URL with no further action required from the subscriber. | |
Handles all aspects of Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) redirection. | This type of redirection does not require a captive portal application. |
The SESM Captive Portal application performs the following functions:
This application also provides a timing mechanism to control the duration of the displays. Timing starts when the page is displayed and ends when the duration time elapses. When the duration time elapses, the message portal application can optionally redirect to the URL in the subscriber's original HTTP request. Otherwise, the message remains displayed until the subscriber enters another URL.
Table 4-2 summarizes the steps required to deploy the sample captive portal solution.
| Deployment Step | References |
|---|---|
| Cisco Subscriber Edge Services Manager Installation and Configuration Guide, Chapter 11, "Deploying a Captive Portal Solution" The online link is: http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/solution/ |
2. Use the ssgconfig.txt file to configure the SSG TCP redirect features.
| |
The following procedure assumes that you have a fully configured SESM deployment in RADIUS or LDAP mode. To demonstrate captive portal features:
Step 1 Start all of the applications in the captive portal solution by executing their startup scripts.
jetty
bin
startNWSP
startCAPTIVEPORTAL
startMESSAGEPORTAL
Step 2 Open a web browser from a network configured as an incoming network on the SSG. Enter a URL, such as www.yahoo.com, or allow the browser to attempt to display a home page setting.
Unauthenticated user redirection causes the NWSP logon page to appear.
Step 3 Sign on using a user ID and password from the subscriber profiles you created specifically for this demonstration. After successful authentication, the following occurs:
1. The NWSP home page appears in the main window.
2. A pop-up window appears, intended for the www.yahoo.com URL.
4. After the length of time specified by the duration parameter, the next action depends on how the redirectOn configuration parameter for Message Portal is set:
5. In response to a service redirection, NWSP displays one of the following in the main window:
Step 4 If the service redirection did not work, check the following configurations. To demonstrate service redirection for a service named yahoo, all of the following configurations must be set:
Step 5 To demonstrate a default service redirection, from the NWSP service selection list, select a service with an IP address outside the destination networks of all the specific service redirections. It does not matter if the subscriber is subscribed to the service or not.
Default service redirection is usually configured so that a service name is not passed to NWSP, which causes NWSP to display the page specified in the serviceNotGivenURI attribute in nwsp.xml. In the default configuration suggested during installation, the serviceNotGivenURI attribute points to the NWSP session status page. You could change this value to point to a different pages, such as the NWSP subscription page or home page.
Step 6 To demonstrate an advertising redirection:
1. Wait until the configured TCP advertising interval time has elapsed. (The default time interval used during installation is 60 seconds.)
2. Perform some action on the SESM web page, such as selecting another service or requesting the status page. The SSG intercepts the request with an advertising redirection. An advertisement page from the Message Portal application appears.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Mon Oct 28 07:51:24 PST 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.