|
|

RDP receives RADIUS protocol messages on one listener. The listener is configured in the RDP MBean.
RDP processes the messages using multiple handlers. Each handler performs some processing and calls the next handler. The chain of handlers that processes a message is configured in the RDP MBean and is determined by:
The RDP application is easily extensible because the chain of handlers is configurable in the MBeans. New handlers can be plugged in to handle new or customized configuration requirements.
 |
Note To maintain the correct processing sequence for the installed RDP application, do not change the name and nexthandler attributes in the RDP MBeans. |
See the "Summary of RDP Protocol Handlers" section for a summary of the chain of RDP handlers that processes RADUIS protocol messages in the installed RDP application.
RDP configuration options are chosen and configured during RDP installation. This section describes how to change those configuration options. The topics are:
The RDP can run in the following modes:
To change the RDP mode, we recommend that you reinstall the RDP component.
 |
Note The alternative is to manually edit the configuration files, commenting out the inappropriate handlers, removing the comments surrounding other handlers, and configuring those handlers. |
To change this option, we recommend that you reinstall the RDP component.
 |
Note The alternative is to manually edit the configuration files, commenting out the inappropriate handlers, removing the comments surrounding other handlers, and configuring those handlers. |
Choose this option if you want the SSG to perform automatic connections to services when a subscriber's profile includes the autoconnect attribute. When you choose this option, RDP includes the subscriber's service list and related information in replies to SSG. The service information consumes memory on the SSG device.
Do not choose this option if memory is a consideration on the SSG device. Instead, you can configure the SESM application to initiate automatic connections with the autoConnect attribute in the SESM MBean. See the "SESM MBean" section for more information.
This option is easily changed after installation. For instructions, see the addClientList attribute in the "RDP MBean" section.
In Proxy mode, the RDP forwards authentication requests to a configured RADIUS server. The basic meaning of authentication is validating the user. However, the RDP authentication handler also adds attributes from the subscriber profile to the access-accept message, as described in the "Summary of RDP Protocol Handlers" section.
In the case of Proxy mode, if you want to add additional authentication attributes for a subscriber, you must add them in the profiles used by the proxied RADIUS server. If you add the attributes to the profiles on the LDAP directory, they are ignored.
 |
Note In releases earlier than SESM Release 3.1(5), these additional authentication attributes are processed from the profiles on the LDAP directory. |
RDP uses the following MBeans:
To change attributes in these MBeans, you can either:
rdp
config
rdp.xml
tools
config
erp.xml
Default port numbers used by the installation process are:
The Logger MBean configures both logging and debugging tools. The logging tool logs RDP application activity. The debugging mechanism produces messages useful for debugging. This is the same logging and debugging mechanism used by the SESM portal applications. See the "Logger MBean" section, for more information.
The ManagementConsole MBean configures the RDP management console port, including valid user names and passwords for accessing the console. See the "Configuring the ManagementConsole MBean" section for more information.
For a list of the standard RADIUS attributes that are predefined in SESM, see Table C-2. For a list of the Cisco SSG VSAs that are predefined in SESM, see Table C-3.
Table 7-1 describes the attributes in the RADIUSDictionary MBean.
| Attribute Name | Explanation |
|---|---|
|
name(radiusAttributeId, vendorId, vendorSubattribute, datatype) Where:
An example follows:
Other valid syntax formats are represented below: name([[type=]26],[vendorId=]vendorId,[vendorType=]vendorType,[dataType=]dataType) For example:
|
The RDP MBean configures the RDP listener, including its thread pool and sockets (ports), and all of the handlers. Table 7-2 describes the configurable attributes in the RDP MBean.
 |
Note Unless you are customizing the RDP application, the attributes in Table 7-2 are the only ones you should change. All other attributes affect the processing sequence of the RDP protocol handler. See the "Changing Installed Configuration Options" section for more information. |
| Attribute Name | Explanation |
|---|---|
handler | Defines the type of listener being configured. The value must be RDP to configure an RDP protocol handler. |
dump |
Default: true |
RDP requires passwords to obtain service, group, and next hop profiles. The SSG sets the password in the request. Therefore, the values you configure here must match the values configured on the SSG, or, in the case of the groupPassword, in SESM configuration. If the configured password does not match the password in a profile, RDP returns an access-reject message.
ssg service-password servicePassword
ssg next-hop download nextHopTableName password
| |
Note The following attributes are in RDP MBean, RADIUSListener=RDP,component=Threadpool | |
Sets the minimum number of threads that this listener maintains during periods of low load. This listener always has system resources allocated for this number of threads. Default: 5 | |
Sets the maximum number of threads that this listener can allocate resources for, even during peak loads. This listener can have up to this number of threads. Default: 255 | |
Note The following attributes are in RDP MBean, RADIUSListener=RDP,component=RADIUSServerSocket | |
The shared secret that must be used in RADIUS protocol messages sent to the bundled SESM RADIUS server. This attribute sets a global shared secret for all clients. To specify different shared secrets for each client, use the allowedClients attribute. | |
The port the RADIUS server listens on. It uses the same port for RADIUS Accounting-Requests and Access-Requests. The installed configuration file defines this attribute as a Java system property, which is assigned a value at run time: application.portno | |
Note If you do not see the allowedClients attribute in the Agent View, check the configuration file (the XML file). The allowedClients attribute might be commented out. If so, remove the comment characters, save the XML file, and then restart the RDP. RDP clients are SSGs. You can add more clients by adding more elements to the allowedClients attribute. An element in allowedClients attribute has the following format:
Where: hostName or IPAddress identify a client (an SSG, for example) that has access to the RDP. localSecret identifies the secret that this client uses for RADIUS communication If the client is an SSG, this value must match the shared secret configured on the SSG device: radius-server key SharedSecret
| |
Note The following attributes are in RDP MBean, PROXY=ProxyHandler,component=RADIUSClientSocket. This component is used only when RDP is configured in Proxy mode. | |
The maximum number of simultaneous requests that RDP can send to a RADIUS server. This is a RADIUS protocol attribute. The RADIUS protocol queues additional requests and issues them as the server returns responses or timeout messages for previous requests. Default: 256 | |
The number of seconds that RDP waits before timing out RADIUS packets that it sends to the AAA server. Default: 4000 | |
The number of times RDP resends packets to the AAA server if no response is received. Default: 3 | |
The IP address or the host name of the primary AAA server. | |
The port number that the primary RADIUS server listens on. Default: 1812 | |
The shared secret used between the RADIUS server and RDP. The shared secret must be the same for the primary and secondary servers. It must match the secret specified when you configured RDP as a NAS client on the RADIUS server. Default: | |
The IP address or host name of the secondary AAA server. If you are not using a secondary RADIUS server, reenter the primary server. | |
The port number that the secondary RADIUS server listens on. If you are not using a secondary server, reenter the primary server. Default: 1812 | |
Figure 7-1 shows the processing sequence that RDP uses for handling packets.
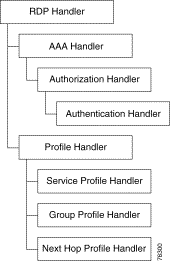
Each protocol handler has a special purpose:
 |
Note When RDP is running in Proxy mode, RDP performs all of the above authentication work using information in the profile obtained from a RADIUS server. If you are using Proxy mode, be sure to add these attributes to the subscriber profiles on the RADIUS server, as opposed to the ones on the LDAP server. |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Mon Aug 26 08:37:02 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.