|
|

After you determine where you want to put the Cache Engine, complete the following tasks to install the Cache Engine:
1. Collecting the Information Required for Configuration
2. Installing the Cache Engine
3. Initializing the Cache Engine Configuration
4. Enabling Cache Support on the Router
Read the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information document that came with the Cache Engine before you begin the installation.
This chapter also covers the following tasks:
 | Warning Read the installation instructions before you connect the system to its power source. |
Before you install the Cache Engine, collect the following information required for the basic configuration:
When you power up the Cache Engine for the first time, you will be prompted to provide the information listed above.
 | Warning
The device is designed to work with TN power systems. |
 | Warning The ports labeled "Ethernet 0" and "Ethernet 1" are safety extra-low voltage (SELV) circuits. SELV circuits should only be connected to other SELV circuits. Because the BRI circuits are treated like telephone-network voltage, avoid connecting the SELV circuit to the telephone network voltage (TNV) circuits. |
 | Warning This product relies on the building's installation for short-circuit (overcurrent) protection. Ensure that a fuse or circuit breaker no larger than 120 VAC, 15A U.S. (240 VAC, 10A international) is used on the phase conductors (all current-carrying conductors). |
 | Warning This equipment is intended to be grounded. Ensure that the host is connected to earth ground during normal use. |
 | Warning Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of lightning activity. |
 | Warning Before working on equipment that is connected to power lines, remove jewelry (including rings, necklaces, and watches). Metal objects will heat up when connected to power and ground and can cause serious burns or weld the metal object to the terminals. |
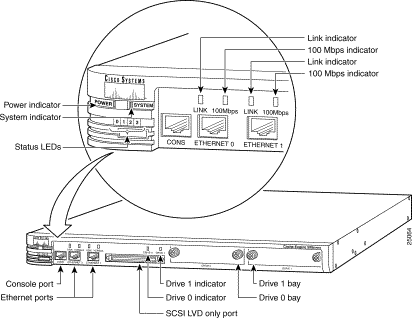
Refer to Figure 2-1 and Figure 2-2 when installing the Cache Engine, to help you identify the connectors on the front and rear of the Cache Engine.
* = led is on o = led is off - = rolling appearance
During boot:
| 0 1 2 3 | Appearance | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
* * * * | steady | Power on, first, and second level bootstrap |
* o o o | steady | Image loaded and running |
- - - - | rolling | Network hardware initialization |
o * o o | steady | Network hardware initialization complete |
- - - - | rolling | Disk hardware initialization |
* * o o | steady | Disk hardware initialization complete |
o o * o | steady | First IP packet received |
o o o o | steady | First HTTP cache request received |
Cache Engine is up and running:
| 0 1 2 3 | Appearance | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
o o o o | steady | Normal operation |
o * * * | steady | An exception has occurred (software or hardware failure) |
* * * * | steady | A panic has occurred (software failure) |
- - - - | rolling | Reboot has begun |
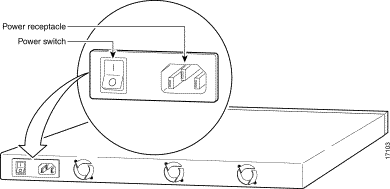
To install the Cache Engine, perform the following steps:
Step 2 Plug in the Cache Engine.
Step 3 Plug the network connection into the Ethernet port on the Cache Engine.
Step 4 Plug the console into the console port on the Cache Engine using the supplied serial cable. Open a window for the engine console using your terminal emulation program.
Step 5 Turn on the Cache Engine. The Cache Engine begins booting and sends messages to the console window. Once the operating system boots, you are ready to initialize the basic software configuration.
To initialize the Cache Engine's basic configuration once it has booted the operating system, perform the following steps:
---- System Configuration Dialog ----
You may use Ctrl-D to abort Configuration Dialog at any prompt.
Would you like to enter the initial configuration? [yes]: yes
host name: cache
domain name: cisco.com
admin password: test
cache IP address: 10.1.58.5
IP network mask: 255.255.255.0
gateway IP address: 10.1.58.1
DNS server: 171.69.2.132
Step 2 If the basic configuration is acceptable, enter yes. The Cache Engine indicates whether the configuration is accepted. At this point, the basic configuration is finished.
Use this configuration? [yes]: yes
>> Building configuration...
>> . . START - phase complete
Step 3 Once you have entered an acceptable basic configuration, the Cache Engine displays the URL that you would use to connect to it with a web browser. For example, http://10.1.1.1:8001. You must use the complete URL to connect to the Cache Engine and manage it.
The username is admin and the password is supplied by the user on the Login window.
Before the router can use the Cache Engine, it must know that the Cache Engine exists. This notification is done automatically by communications between the engine and the router. However, you must enable cache support in the router so that the router listens for the Cache Engine.
If you later want to disable caching temporarily, you can do so by disabling cache support in the router, rather than by turning off or otherwise disabling the individual Cache Engines. (Use the no ip wccp command on the router to disable caching.)
You must already know how to configure the router to make these configuration changes. If you do not know how to configure the router, consult the Cisco IOS documentation supplied with the router. Detailed information for the commands mentioned here is in the Cisco IOS documentation. See Appendix B, Web Cache Communication Protocol Version 1, and Appendix C, Web Cache Communication Protocol Version 2, for information on which IOS software supports which version of WCCP on which platform.
To enable cache support on the router for WCCP Version 1:
IOS versions before 12.0(3)T support only WCCP Version 1. IOS versions between 12.0(3)T and 12.0(5)T support only WCCP Version 2. IOS version 12.0(5)T or later support both WCCP Version 1 and Version 2. In IOS version 12.0(5)T or later, the default WCCP version is Version 2. You can override the WCCP default, by using the global configuration command ip wccp version 1.
If you have WCCP Version 1 configured and attempt to configure any WCCP Version 2 specific features, you will receive a configuration error.
ip wccp enable
For example, to enable redirection, enter:
ip web-cache redirect
You can confirm your settings using the following show commands on the router:
To enable cache support on the router for WCCP Version 2:
In global configuration mode, use the ip wccp command to enable cache support. For example, enter:
ip wccp {web-cache | services}
where serices is the number of predefined services (0 to 99)
For example, to enable redirection, enter:
ip wccp {web-cache | services} redirect out
where serices is the number of predefined services (0 to 99)
You can confirm your settings using the following show commands on the router:
Once you have installed and configured the Cache Engine and enabled caching on the router, check to ensure the Cache Engines working properly:
Step 2 From the command-line interface (CLI), enter the following to display the Cache Engine HTTP caching saving statistics:
show statistics http savings
Step 3 Open a window for the engine console using your terminal emulation program to connect to the home router or routers, and enter the show ip wccp web-cache command to display information about the Cache Engines. The entry for the Cache Engine should show a number greater than 0 for packets redirected. Also, check for hash assignments.
If the router shows that no packets are being redirected to the Cache Engine, you need to troubleshoot your setup.
You can manage the Cache Engine using the CLI or the Cache Engine management interface. To connect to the Cache Engine's management interface:
Step 2 Open the URL for the engine, using the URL given to you during basic configuration. For example, http://10.1.1.1:8001.
You must include the port number, such as 8001, in the URL.You are prompted for a username and password (see Figure 2-3).
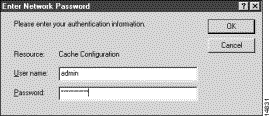
Step 3 Enter a correct username and password. The Cache Engine returns the initial management page, which contains links to other management pages.
If you forget your password, you must have another administrator reset your password.
 | Warning Before working on a system that has an On/Off switch, turn OFF the power and unplug the power cord. |
 | Warning Ultimate disposal of this product should be handled according to all national laws and regulations. |
To remove a Cache Engine from a system, turn off the engine's power and physically remove it from the network.
The router and the Cache Engine are in constant communication: thus, when the router notices that the engine is no longer responding to it, the router stops sending requests to the engine. This is transparent to your users.
If there are other Cache Engines attached to the router, the router continues sending requests to the other engines.
When you remove a Cache Engine, the pages that were cached on the engine are no longer available to the router or other caches. Thus, you might see an increase in outgoing web traffic that might have otherwise been fulfilled by the engine you are removing. However, after a time, the router and other Cache Engines will have redistributed the load of web traffic.
If you remove the last Cache Engine from a router, you can also disable cache support on the router. However, this is not necessary; having cache support enabled when there are no Cache Engines attached has no effect on the router's performance.
To replace a Cache Engine, remove the old engine from the network. Then, add the new engine and configure it using the same configuration parameters (IP address, and so forth) that you used for the removed engine.
The Cache Engine includes the following cables and adapters:
Use these cables to connect the Cache Engine console port to the COM port of a console or computer that is running a console program.
In addition to the console cable, you must supply your own standard Ethernet cable to connect the Cache Engine to your network.
This section details the pinout information for these cables, so that you can purchase the correct cable for your network connection, and replace the console cable and adapters, if that becomes necessary.
To connect the Cache Engine to your network, you must use one of the following cables:
Use a CAT 5 UTP cable at minimum to connect to a 100BaseT network. Use a CAT 3 UTP cable at minimum to connect to a 10BaseT network.
Table 2-1 shows the pinouts for a straight-through 100BaseT cable.
| RJ-45 Pin | Signal | Direction | RJ-45 Pin |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | TX+ | —> | 1 |
2 | TX- | —> | 2 |
3 | RX+ | <— | 3 |
4 | — | — | 4 |
5 | — | — | 5 |
6 | RX- | <— | 6 |
7 | — | — | 7 |
8 | — | — | 8 |
Table 2-2 shows the pinouts for a crossed-over 100BaseT cable.
| RJ-45 Pin | Signal | Direction | RJ-45 Pin |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | TX+ | —> | 3 |
2 | TX- | —> | 6 |
3 | RX+ | <— | 1 |
4 | — | — | 4 |
5 | — | — | 5 |
6 | RX- | <— | 2 |
7 | — | — | 7 |
8 | — | — | 8 |
The EIA/TIA-232 console port on the Cache Engine is configured as data terminal equipment (DTE) and uses a DB-9 connector. A console cable kit is provided with your Cache Engine to connect a console (an ASCII terminal or PC running terminal emulation software) to the console port. The console cable kit contains an RJ-45 to RJ-45 rollover cable and two RJ-45 to DB-9 female DTE adapters.
By attaching the two RJ-45 to DB-9 adapters to the RJ-45 to RJ-45 rollover cable, you create a DB-9 to DB-9 null modem cable. Table 2-3 shows the pinouts for this configuration.
| Cache Engine Console Port (DB9) | DB-9 | Signal |
|---|---|---|
1 | — | DTR |
2 | 3 | TD |
3 | 2 | RD |
4 | 6 | DCD |
5 | 5 | SG |
6 | 4 | DSR |
7 | 8 | CTS |
8 | 7 | RTS |
9 | — | — |
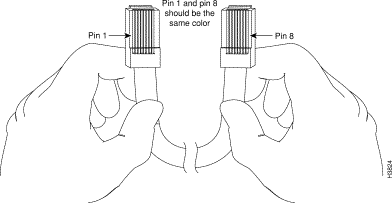
You can identify a rollover cable by comparing the two modular ends of the cable, as shown in Figure 2-4. Holding the cables in your hand, side-by-side, with the tab at the back, the wire connected to the pin on the outside of the left connector (pin 1) should be the same color as the pin on the outside of the right connector (pin 8).
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Tue Jun 5 11:51:17 PDT 2001
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2001 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.