|
|

This appendix provides you with information about version 1.0 of Cisco's Internetworking Operating System (IOS) Web Cache Control Protocol (WCCP) feature. For additional information about WCCP, see the section "What is the Web Cache Control Protocol?"
This appendix contains the following topics:
Web caches optimizes transmissions costs and the amount of time required to download web files. If a client requests a web page that is already cached, the request and data only have to travel between the Cache Engine and the client. Without a web cache, the request and reply must travel over the Internet or wide-area network. Cached pages can be loaded faster than non-cached pages and do not have to be transmitted from the Internet to your network.
In Cisco IOS Release 11.1(20)CA and Release 11.2(15)P, the following changes were made:
In IOS Release 11.1 CA,WCCP is supported on these platforms:
In IOS Release 11.2 P, WCCP is supported on these platforms:
To use WCCP, IP must be configured on the interface connected to the Internet and the interface connected to the Cache Engine. The interface connected to the Cache Engine must be an Ethernet or Fast Ethernet interface.
To configure WCCP on the router, you must perform the following tasks. The first task is required, while the second is optional.
To enable an interface to redirect web traffic to the Cache Engine using WCCP, perform the following tasks at the console beginning in global configuration mode:
Step 1 Enable the router to use WCCP.
ip wccp enable
Step 2 (Optional) Specify the redirect access list. Only packets that match this access list are redirected. If you do not configure this command, all web-based packets are redirected.
ip wccp redirect-list {number | name}
Step 3 Enter interface configuration mode.
interface interface
Step 4 Configure the interface connected to the Internet to redirect web traffic to the Cache Engine.
ip web-cache redirect
Step 5 (Optional) If the client or web server and a Cache Engine are located on the same network, configure the router to use the fast switching path on the interface.
ip route-cache same-interface
Step 6 Exit configuration mode.
end
Step 7 Save the configuration.
copy running-config startup-config
To monitor WCCP, perform any of the following tasks in EXEC mode:
Step 1 Display global WCCP statistics.
show ip wccp
Step 2 Display information about all known Cache Engines.
show ip wccp web-caches
Step 3 Show whether web cache redirecting is enabled on an interface.
show ip interface
The show ip wccp and show ip wccp web-caches commands display a count of the number of packets redirected. Use the clear ip wccp EXEC command to clear this counter.
The following example configures a router to support WCCP, and to redirect web-related packets from Ethernet interface 0 to the Cache Engine:
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# ip wccp enable
Router(config)# interface Ethernet 0
Router(config-if)# ip web-cache redirect
Router(config-if)# end
Router#
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console.
Router# copy running-config startup-config
After the router has been configured, use the show ip wccp web-cache command to verify that WCCP is enabled and aware of Cache Engines. In this example, the show ip wccp web-cache command is entered immediately after the router has been configured. After a few seconds, the cache engine becomes usable, as seen in the second output.
Router# show ip wccp web-cacheWCCP Web-Cache information:
IP Address: 10.1.1.1
Protocol Version: 1.0
State: NOT Usable
Initial Hash Info: FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
Assigned Hash Info: 000000000000000000000000000000000
000000000000000000000000000000000
Hash Allotment: 0 (0.00%)
Packets Redirected: 0
Connect Time: 00:00:06
WCCP Web-Cache information:
IP Address: 10.1.1.1
Protocol Version: 1.0
State: Usable
Initial Hash Info: FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
Assigned Hash Info: 000000000000000000000000000000000
000000000000000000000000000000000
Hash Allotment: 256 (100.00%)
Packets Redirected: 0
Connect Time: 0:00:31
This section documents the most common WCCP commands. Additional and related commands are documented in the Cisco IOS Release 11.1 or Release 11.2 command reference documentation.
To clear the counter for packets redirected by WCCP, use the clear ip wccp EXEC command.
clear ip wccpThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 P and Cisco IOS Release 11.1 CA.
The "Packets Redirected" count is displayed by the show ip wccp and show ip wccp web-caches commands.
The following example shows output from the show ip wccp web-caches command before and after the clear ip wccp command is used:
Router# show ip wccp web-caches
WCCP Web-Cache information:
IP Address: 10.1.1.1
Protocol Version: 1.0
State: Usable
Initial Hash Info: FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
Assigned Hash Info: 000000000000000000000000000000000
000000000000000000000000000000000
Hash Allotment: 256 (100.00%)
Packets Redirected: 21345
Connect Time: 00:13:46
Router# clear ip wccp
Router# show ip wccp web-caches
WCCP Web-Cache information:
IP Address: 10.1.1.1
Protocol Version: 1.0
State: Usable
Initial Hash Info: FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
Assigned Hash Info: 000000000000000000000000000000000
000000000000000000000000000000000
Hash Allotment: 256 (100.00%)
Packets Redirected: 0
Connect Time: 00:13:46
To enable the router to support WCCP group lists, use the ip wccp group-list global configuration command. The no form of this command disables support for group lists in WCCP.
access-list-number
The WCCP group lists are not enabled on the router.
Global configuration
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 11.2(15) P and Release 11.1(20) CA.
The ip wccp group-list command ensures that WCCP grants access per Cache Engine as a security measure.
Read the show ip wccp command's new status lines, group access-list and total packets denied to group, to see which access lists have been configured to secure the group of caches and how many WCCP packets were dropped because their source IP address was not in the group list.
Use the debug ip wccp events command to see the source IP address of packets that are dropped.
The following example configures a router to support WCCP group lists. A group list is a combination of cache engine IP addresses.
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# ip wccp group-list 1
Router(config)# ip wccp enable
Router(config)# interface Ethernet 0
Router(config-if)# ip web-cache redirect
Router(config)# end
Router#
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
To enable the router to support WCCP, use the ip wccp enable global configuration command. The no form of this command disables support for WCCP.
This command has no arguments or keywords.
The WCCP is disabled on the router.
Global configuration
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 P and Release 11.1 CA.
This command and the ip web-cache redirect interface command are the only commands required to start redirecting requests to the Cache Engine using WCCP. To see if WCCP is enabled on the router, use the show ip wccp command.
When this command is enabled but the ip web-cache redirect command is disabled, the router is aware of caches but does not use them.
Use the ip wccp redirect-list command to limit the redirection of packets to those matching an access list.
The following example configures a router to support WCCP and redirects web-related packets from Ethernet interface 0 to the Cache Engine:
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# ip wccp enable
Router(config)# interface Ethernet 0
Router(config-if)# ip web-cache redirect
Router(config-if)# end
Router#
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console.
number
Standard or extended IP access list number from 1 to 199.
name
Standard or extended IP access list name. This argument is only available in Release 11.2 P.
All HTTP packets are redirected to the Cache Engine.
Global configuration
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 P and Release 11.1 CA.
Use this command to specify which packets should be redirected to the Cache Engine. When WCCP is enabled but this command is not configured, all web-related packets are redirected to the Cache Engine. When you enter this command, only packets that match the access list are redirected.
Some Web sites use the source IP address of packets for authentication. The Cache Engine uses its own IP address when sending requests to Web sites. Thus, the requests from the Cache Engine may not be authenticated. Use this command to bypass the Cache Engine in these cases.
Use the ip wccp enable and ip web-cache redirect commands to configure WCCP.
The following example configures a router to redirect web-related packets without a destination of 10.1.1.1 to the Cache Engine:
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# access-list 100 deny ip any host 10.1.1.1
Router(config)# access-list 100 permit ip any any
Router(config)# ip wccp enable
Router(config)# ip wccp redirect-list 100
Router(config)# interface Ethernet 0
Router(config-if)# ip web-cache redirect
Router(config-if)# end
Router#
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console.
To instruct an interface to check for appropriate outgoing packets and redirect them to a Cache Engine, use the ip web-cache redirect interface configuration command. The no form of this command disables the redirection of messages to the Cache Engine.
ip web-cache redirectThis command has no arguments or keywords.
The interface does not redirect messages to the Cache Engine.
Interface configuration
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 P and Release 11.1 CA.
This command and the ip wccp enable command are the only commands required to start redirecting requests to the Cache Engine using WCCP.
The following example configures a router to support WCCP and redirects web-related packets from Ethernet interface 0 to the Cache Engine:
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# ip wccp enable
Router(config)# interface Ethernet 0
Router(config-if)# ip web-cache redirect
Router(config-if)# end
Router#
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console.
To display the usability status of interfaces configured for IP, use the show ip interface EXEC command.
show ip interface [type number]type
(Optional) Interface type.
number
(Optional) Interface number.
EXEC
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 10.0.
The Cisco IOS software automatically enters a directly connected route in the routing table if the interface is usable. A usable interface is one through which the software can send and receive packets. If the software determines that an interface is not usable, it removes the directly connected routing entry from the routing table. Removing the entry allows the software to use dynamic routing protocols to determine backup routes to the network (if any).
If the interface can provide two-way communication, the line protocol is marked "up." If the interface hardware is usable, the interface is marked "up."
If you specify an optional interface type, you will see only information on that specific interface.
If you specify no optional arguments, you will see information on all the interfaces.
When an asynchronous interface is encapsulated with PPP or SLIP, IP fast switching is enabled. A show ip interface command on an asynchronous interface encapsulated with PPP or SLIP displays a message indicating that IP fast switching is enabled.
The following is sample output from the show ip interface command:
Router# show ip interface
Ethernet0 is up, line protocol is up
Internet address is 10.1.1.1, subnet mask is 255.255.255.0
Broadcast address is 255.255.255.255
Address determined by non-volatile memory
MTU is 1500 bytes
Helper address is not set
Secondary address 10.1.1.2, subnet mask 255.255.255.0
Directed broadcast forwarding is enabled
Outgoing access list is not set
Inbound access list is not set
Proxy ARP is enabled
Security level is default
Split horizon is enabled
ICMP redirects are always sent
ICMP unreachables are always sent
ICMP mask replies are never sent
IP fast switching is enabled
IP fast switching on the same interface is disabled
IP SSE switching is disabled
Router Discovery is disabled
IP output packet accounting is disabled
IP access violation accounting is disabled
TCP/IP header compression is disabled
Probe proxy name replies are disabled
Web Cache Redirect is enabled
Table C-1 describes the fields shown in the display.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Ethernet0 is up | If the interface hardware is usable, the interface is marked "up." For an interface to be usable, both the interface hardware and line protocol must be up |
line protocol is up | If the interface can provide two-way communication, the line protocol is marked "up." For an interface to be usable, both the interface hardware and line protocol must be up. |
Broadcast address | Shows the broadcast address. |
Address determined by... | Indicates how the IP address of the interface was determined. |
MTU | Shows the MTU value set on the interface. |
Helper address | Shows a helper address, if one has been set. |
Secondary address | Shows a secondary address, if one has been set. |
Directed broadcast forwarding | Indicates whether directed broadcast forwarding is enabled. |
Multicast groups joined | Indicates the multicast groups this interface is a member of. |
Outgoing access list | Indicates whether the interface has an outgoing access list set. |
Inbound access list | Indicates whether the interface has an incoming access list set. |
Proxy ARP | Indicates whether Proxy ARP is enabled for the interface. |
Security level | Specifies the IPSO security level set for this interface. |
ICMP redirects | Specifies whether redirects will be sent on this interface. |
ICMP unreachables | Specifies whether unreachable messages will be sent on this interface. |
ICMP mask replies | Specifies whether mask replies will be sent on this interface. |
IP fast switching | Specifies whether fast switching has been enabled for this interface. It is generally enabled on serial interfaces, such as this one. |
IP SSE switching | Specifies whether IP SSE switching is enabled. |
Router Discovery | Specifies whether the discovery process has been enabled for this interface. It is generally disabled on serial interfaces. |
IP output packet accounting | Specifies whether IP accounting is enabled for this interface and what he threshold (maximum number of entries) is. |
TCP/IP header compression | Indicates whether compression is enabled or disabled. |
Probe proxy name | Indicates whether HP Probe proxy name replies are generated. |
Web Cache Redirect | Indicates whether HTTP packets are redirected to a Cache Engine. |
To display global statistics related to WCCP, use the show ip wccp EXEC command.
show ip wccpThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 P and Release 11.1 CA.
Use the clear ip wccp command to reset the counter for the "Packets Redirected" information.
The following example shows sample show ip wccp output:
Router# show ip wccp
Global WCCP information:
Number of web-caches: 2
Total Packets Redirected: 101
Redirect access-list: no_linux
Total Packets Denied Redirect: 88
Total Packets Unassigned: 6565
Group access-list: 1
Total Packets Denied to Group: 457
Table C-2 describes fields shown in this example.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Number of web-caches | Number of Cache Engines using the router as their home router. |
Total Packets Redirected | Total number of packets redirected by the router. |
Redirect access-list | Name or number of the redirect access list. Only packets matching the access list are redirected. |
Total Packets Denied Redirect | Number of packets that were not redirected because they did not match the access list. |
Total Packets Unassigned | Number of packets that were not redirected because they were not assigned to any web cache. Packets may not be assigned during initial discovery of cache engines or when a cache is dropped from a farm. |
Group access-list | Access list configured to secure the group of caches. |
Total Packets Denied to Group | Number of WCCP packets dropped because their source address was not in the group list. |
To display information about the router's known Cache Engines, use the show ip wccp web-caches EXEC command.
show ip wccp web-cachesThis command has no arguments or keywords.
EXEC
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 P and Release 11.1 CA.
Use the clear ip wccp command to reset the counter for the "Packets Redirected" information.
The following example shows sample show ip wccp web-caches output:
Router# show ip wccp web-caches
WCCP Web-Cache information:
IP Address: 10.1.1.1
Protocol Version: 1.0
State: Usable
Initial Hash Info: FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
Assigned Hash Info: 000000000000000000000000000000000
000000000000000000000000000000000
Hash Allotment: 256 (100.00%)
Packets Redirected: 21345
Connect Time: 00:13:46
Table C-3 explains the fields shown in this display.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
IP Address | IP address of the Cache Engine. |
Protocol Version | Version of WCCP the Cache Engine is running. |
State | State of the Cache Engine. Possible values are "Usable" and "NOT Usable." |
Initial contents of the hash field. The hash field contains information about how the router intends to use the Cache Engine. | |
Assigned Hash Info | Current hash information for the Cache Engine.The hash information field contains information about how the router intends to use the Cache Engine. |
Hash Allotment | Percentage of all possible web servers for which the router redirects HTTP requests to this web cache. In this example, there is only one cache engine, so all HTTP requests are redirected to it. |
Packets Redirected | Number of packets redirected to this Cache Engine. |
Connect Time | Indicates how long the Cache Engine has used this router as its home router. |
To use WCCP, the Cache Engine must be properly configured. Keep these important points in mind:
This section contains a few sample network configurations.
If your Cache Engine, client, and web servers are using separate WCCP router interfaces, only packets that would have travelled through the Ethernet 0 interface are redirected to the Cache Engine (see Figure C-3.) Mark an outbound interface using the ip web-cache redirect command toward the web servers from which you want to cache objects. Configure the router as follows:
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# ip wccp enable
Router(config)# interface Ethernet 1
Router(config-if)# ip web-cache redirect
Router(config)# end
Router#
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
Router(config)# copy running-config startup-config
After the router has been configured, use the show ip wccp web-cache command to verify that WCCP is enabled and aware of your Cache Engine.
Router# show ip wccp web-cache
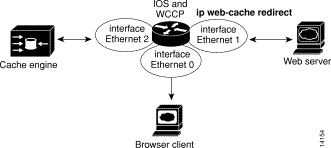
We do not recommend that you use the Cache Engine with the following network setup since performance will not be optimal. However, if your Cache Engine is using the same WCCP router interface as your client (see Figure C-2), configure the router as follows:
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# ip wccp enable
Router(config)# interface Ethernet 1
Router(config-if)# ip web-cache redirect
Router(config)# interface Ethernet 0
Router(config-if)# ip route-cache same-interface
Router(config)# end
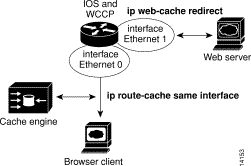
We do not recommend that you use the Cache Engine with the following network setup since performance will not be optimal.
The route cache tables in the router will not be populated unless the Cache Engine comes back to the same router to populate the cache. If your Cache Engine is using the same Ethernet interface on the WCCP router as the web servers being cached (see Figure C-1), configure the router interface as follows:
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# ip wccp enable
Router(config)# interface Ethernet 1
Router(config-if)# ip web-cache redirect
Router(config-if)# ip route-cache same-interface
Router(config-if)# no ip redirect
Router(config)# end
Router#
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console

We do not recommend that you use the Cache Engine with a network topologiy as follows:
This scenario (see Figure C-4) increases the traffic on the user-to-web server path, the ISP 1 backbone, because the packets must return through the Cache Engine on the ISP 1 backbone instead of using the ISP 2 backbone.

To specify which packets are redirected to a Cache Engine, use the ip wccp redirect-list command. Then use the ip web-cache redirect command to instruct an Ethernet interface to start redirecting packets to the Cache Engine.
In the following example, a router is configured to redirect web packets without a destination of 10.1.1.1 to the Cache Engine (see Figure C-5). Packets addressed to 10.1.1.1 will pass through the router without redirection by WCCP.
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# access-list 100 deny ip any host 10.1.1.1
Router(config)# access-list 100 permit ip any any
Router(config)# ip wccp enable
Router(config)# ip wccp redirect-list 100
Router(config)# interface Ethernet 0
Router(config-if)# ip web-cache redirect
Router(config)# end
Router#
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console

WCCP distributes web traffic according to the destination web server's IP address (see Figure C-6).
If you have set up a Cache Engine farm and most users access a few key web sites, it's possible that all data is cached on one (or more) Cache Engines, and the remaining Cache Engines are idle.

This section documents the following new debug commands:
Use the debug ip wccp events EXEC command to display information about significant WCCP events. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
[no] debug ip wccp eventsFigure C-7 shows sample debug ip wccp events output when a Cache Engine is added to the list of available Web caches.
Router# debug ip wccp events
WCCP-EVNT: Built I_See_You msg body w/1 usable web caches, change 0000000A
WCCP-EVNT: Web Cache 10.1.1.1 added
WCCP-EVNT: Built I_See_You msg body w/2 usable web caches, change 0000000B
WCCP-EVNT: Built I_See_You msg body w/2 usable web caches, change 0000000C
Use the debug ip wccp packets EXEC command to display information about every WCCP packet received or sent by the router. The no form of this command disables debugging output.
[no] debug ip wccp packetsFigure C-8 shows sample debug ip wccp packets output. The router is sending keepalive packets to the Cache Engines at 10.1.1.2 and 10.1.1.1. Each keepalive packet has an identification number associated with it. When the Cache Engine receives a keepalive packet from the router, it sends a reply with the identification number back to the router.
Router# debug ip wccp packets
WCCP-PKT: Received valid Here_I_Am packet from 10.1.1.2 w/rcvd_id 00003532
WCCP-PKT: Sending I_See_You packet to 10.1.1.2 w/ rcvd_id 00003534
WCCP-PKT: Received valid Here_I_Am packet from 10.1.1.1 w/rcvd_id 00003533
WCCP-PKT: Sending I_See_You packet to 10.1.1.1 w/ rcvd_id 00003535
WCCP-PKT: Received valid Here_I_Am packet from 10.1.1.2 w/rcvd_id 00003534
WCCP-PKT: Sending I_See_You packet to 10.1.1.2 w/ rcvd_id 00003536
WCCP-PKT: Received valid Here_I_Am packet from 10.1.1.1 w/rcvd_id 00003535
WCCP-PKT: Sending I_See_You packet to 10.1.1.1 w/ rcvd_id 00003537
WCCP-PKT: Received valid Here_I_Am packet from 10.1.1.2 w/rcvd_id 00003536
WCCP-PKT: Sending I_See_You packet to 10.1.1.2 w/ rcvd_id 00003538
WCCP-PKT: Received valid Here_I_Am packet from 10.1.1.1 w/rcvd_id 00003537
WCCP-PKT: Sending I_See_You packet to 10.1.1.1 w/ rcvd_id
00003539
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Sat Sep 28 02:31:17 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.