|
|

The RealProxy software from RealNetworks, Inc., included as a software option to ACNS 4.1 software, supports both stream splitting (distributing live feeds) and streaming media caching (on-demand content) in the Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP)-based format.
When performing stream splitting, the RealProxy accepts a live stream from a RealServer and re-serves the stream to multiple requesting RealPlayer clients, thus eliminating multiple connections to the RealServer. The RealServer is preconfigured to act as a RealMedia transmitter and the RealProxy is preconfigured to act as a RealMedia receiver.
 |
Note The RealNetworks, Inc. RealProxy product is licensed software. To activate the RealProxy, you must have a license keyword, which is supplied on a certificate shipped with the Content Engine. If you are downloading the ACNS 4.1 software, you can purchase a RealProxy license though the Cisco.com website. |
Streaming media caching provides content on demand. If one user has viewed a cached streaming media file, it can be served to subsequent users without the requirement to connect with the origin server. Live broadcasts are not files and are not cached.
Table 14-1 lists the different types of streaming media protocols, control channels, the corresponding data format, and transport types supported by ACNS 4.1 software.
| Streaming Media Protocol | Control Channel | Data Format | Transport Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
Windows Media format | TCP | MMS1 | UDP2, TCP, HTTP, IP multicast |
RealNetworks media format | TCP | RTSP, PNA3 | UDP, TCP, HTTP, IP multicast |
| 1MMS = Microsoft Media Server. 2UDP = User Datagram Protocol. 3PNA = Progressive Networks Audio. |
Table 14-2 describes the features and benefits of RealProxy software.
| RealProxy Feature | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
Proxy for RealPlayer 8.01 | The RealProxy makes requests for content on behalf of client RealPlayer users. |
|
Splitting support for live broadcasts | The RealProxy "splits" a single inbound live broadcast feed to multiple client RealPlayers. See the "Live Splitting" section of the Configuring Windows Media Technologies 7.01 Streaming Media Caching chapter for more information on live-splitting. |
|
Caching of RealSystem G2 and PNA (progressive network Audio) content. | The RealProxy caches all proxied streaming media traffic from RealNetworks servers. RealProxy caches content locally after authentication with origin RealNetworks server. | Significantly reduces inbound bandwidth usage by eliminating redundant file transmissions across the network. |
Authentication/accounting | The RealProxy authenticates every content request with the origin RealNetworks server before delivering the cached content to the client. |
|
Aggregate bandwidth thresholds | Setting thresholds caps inbound and outbound bandwidth to the RealProxy. | Provides control over aggregate bandwidth usage within the network and prevents stress on mission-critical applications. |
Proxy routing | Ability to tier proxies and manage bandwidth at lower nodes in the network. "Parent" proxies can be chosen based on logical sets of rules on the downstream proxy. | Allows network administrators to proxy route requests, providing an additional level of control. |
 |
Note For an overview of streaming media technology, see the "Streaming Media Overview" section. For information on how to enable Windows Media Technologies (WMT) streaming on the Content Engine, see the "Configuring Microsoft Windows Media Player 7.01" section. |
The Content Engine can be configured to accept transparently redirected RTSP requests as well as traditional proxy-style RTSP requests from RealPlayer client software. The redirection of RTSP traffic to the Content Engine media cache is enabled with the Content Engine CLI. The RealProxy software is configured with the RealAdministrator GUI, accessed from the RealProxy page of the Content Engine management GUI.
Detailed configuration, statistics, and reporting of RealProxy status are obtained through the RealAdministrator GUI. Table 14-3 lists RealProxy-related CLI commands.
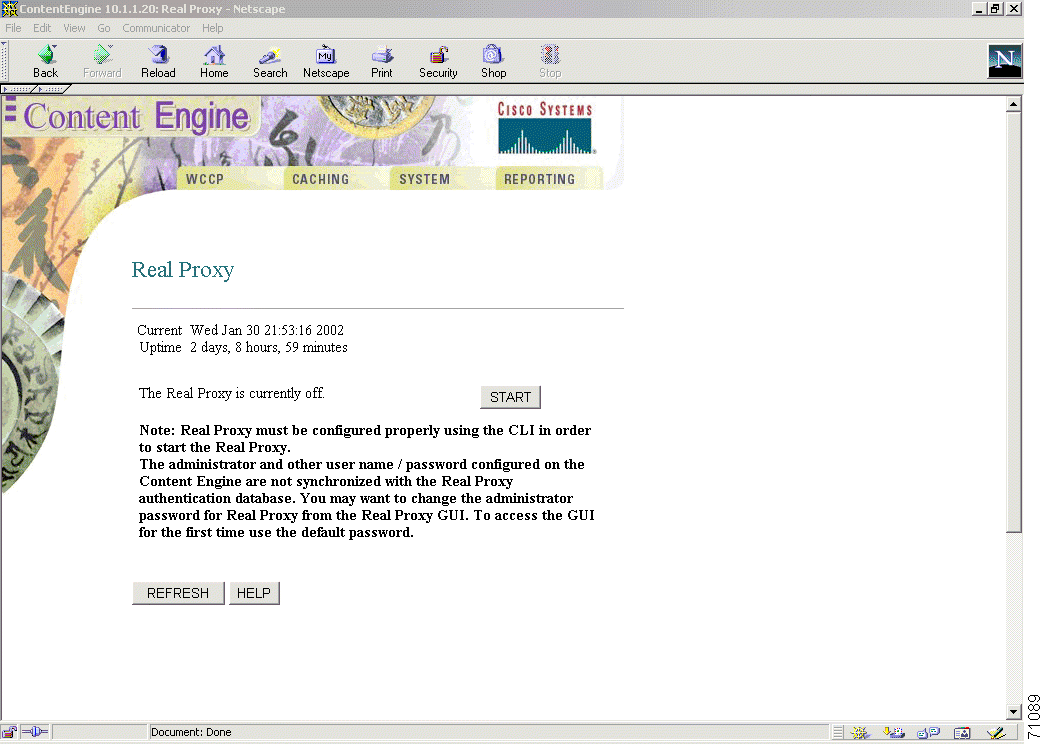
A RealProxy page has been added to the Content Engine management GUI. To access the RealSystem administrator, click the Admin button on the RealProxy page. (See Figure 14-2.) The Admin button is active when the RealProxy software is installed and enabled. You will be provided with a default user and password to access this administration page from the Content Engine GUI.
 |
Note You must configure disk space to include mediafs storage with the disk config command before you can run RTSP traffic through the Content Engine. |
Use the rtsp proxy global configuration command to configure the Content Engine to accept redirected RTSP traffic from either a Layer 4-enabled switch or a WCCP-enabled router, or to configure the Content Engine as a media proxy to receive RTSP proxy-style requests from RealPlayer clients. RTSP requests not from RealPlayer clients are directed to the specified origin server.
The wccp media-cache global configuration command registers the Content Engine with WCCP Version 2-enabled routers that can transparently redirect RTSP traffic to the Content Engine.
The rtsp proxy l4-switch global configuration command enables the configuration of Layer 4 switch interoperability for media caching using RTSP.
The RTSP proxy redirector listens to port 554 traffic or any other port configured to listen to this traffic, and if the player is a RealPlayer, it redirects the RTSP request to use the RealProxy for RealMedia traffic. Traffic that is not supported (for instance, QuickTime), is bypassed by the Content Engine.
Use the following CLI commands to display RealProxy statistics. In ACNS 4.1 software, only requests and savings statistics are supported. See the "RealProxy Examples" section for sample outputs of the show statistics command.
ContentEngine# show statistics mediacache real requests
ContentEngine# show statistics mediacache real savings
 |
Note The mediacache real statistics relate only to objects transported over RTSP that were requested by a RealPlayer client. Objects transported over HTTP are counted in the HTTP statistics. Streaming objects requested by other clients or transported over other protocols other than MMS bypass the Content Engine. |
During transparent caching, the user's network traffic flows through the WCCP-enable router rather than the Content Engine to access streaming media.
To enable transparent redirection of RTSP traffic to the RealProxy, follow these steps:
Step 1 On the routers running WCCP Version 2, turn the WCCP feature on for the specified service group used to redirect RTSP traffic to the Content Engine. For more information on router commands, see "Web Cache Communication Protocol Version 2."
router(config)# ip wccp 80
Step 2 Configure the outbound interfaces to the Internet and enter interface configuration mode. In the following example, the outbound interface is the Ethernet 0 device.
router(config)# interface Ethernet 0
Step 3 Enable WCCP redirection to service group 80 on the interface specified in Step 2.
router(interface)# ip wccp 80 redirect out
Step 4 Set the WCCP Version 2 parameters on the Content Engine.
In the following example, the WCCP Version 2-enabled routers have the IP addresses 172.16.25.25 and 172.16.24.24.
ContentEngine(config)# wccp version 2
ContentEngine(config)# wccp router-list 1 172.16.25.25 172.16.24.24
ContentEngine(config)# wccp media-cache router-list-num 1
Step 5 Set the IP address for the RealProxy. Make sure that the IP address of the RealProxy is visible to the RealPlayers that use it. This step is required before you can enable RealProxy media cache.
ContentEngine(config)# rtsp proxy media-real ip-address 172.16.16.16
 |
Note This IP address is the external address of the Content Engine in case the Content Engine and the RealPlayer requesting content are separated by a firewall. |
Step 6 Enter the RealProxy license number.
ContentEngine(config)# rtsp proxy media-real license-key mylicense
Step 7 Accept the license agreement.
ContentEngine(config)# rtsp proxy media-real accept-license-agreement
Step 8 Enable the RealProxy.
ContentEngine(config)# rtsp proxy media-real enable
Step 9 Save the new configuration.
ContentEngine# copy running-config startup-config
Step 10 Configure the RealProxy parameters as needed with the RealSystem administrator GUI, shown in Figure 14-3.
During conventional proxy caching, the user media player is pointed to the Content Engine rather than a WCCP-enabled router to access streaming media.
To configure the Content Engine to service RealPlayer clients with the RealProxy on the Content Engine, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Set the IP address for the RealProxy. Make sure that the IP address of the RealProxy is visible to the RealPlayers that use it.
ContentEngine(config)# rtsp proxy media-real ip-address 172.16.16.16
Step 2 Enter the RealProxy license number shipped with the Content Engine.
ContentEngine(config)# rtsp proxy media-real license-key mylicense
Step 3 Accept the license agreement.
ContentEngine(config)# rtsp proxy media-real accept-license-agreement
Step 4 Enable the RealProxy.
ContentEngine(config)# rtsp proxy media-real enable
Step 5 Configure the Content Engine to listen for RTSP traffic on a specified port. The standard RTSP port is 554.
ContentEngine# rtsp proxy incoming 554
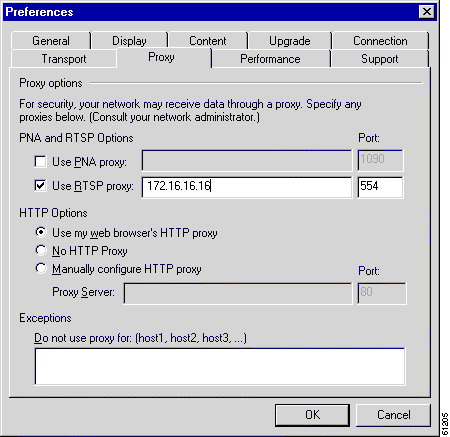
Step 6 Configure RealPlayer 8.01 clients to use the RealProxy on the Content Engine. (See Figure 14-1.)
a. Open RealPlayer.
b. Choose View > Preferences.
c. Click the Proxy tab.
d. Check the Use RTSP proxy check box.
e. Enter the IP address of the Content Engine in the Use RTSP proxy field.
f. In the port field, enter the port number that you entered in Step 5.
g. Click OK.
Step 7 Configure the RealProxy parameters as needed with the RealSystem administrator GUI.
To access the RealSystem administrator GUI, click the Admin button on the RealProxy page in the Content Engine Management GUI. (See Figure 14-2.) The Admin button is active when the RealProxy software is installed and enabled. Use admin as a default user and diamond as password to access this administration page from the Content Engine GUI.
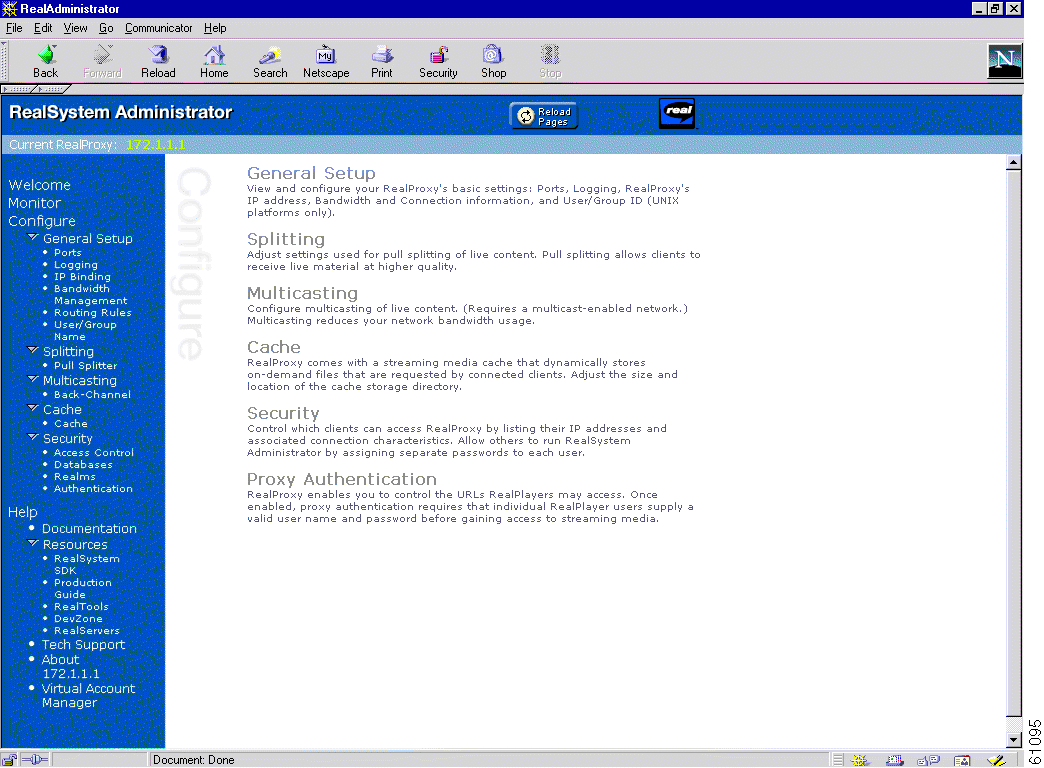
The RealSystem Administrator Configuration page is shown in Figure 14-3. For appropriate documentation regarding the RealSystem administrator GUI, click Documentation on this page.

RealPlayer is now able to use the Content Engine as a RealProxy to fetch streaming objects.
For more information on setting up the RealSystem components used with the RealProxy, refer to the readme "Setting Up RealSystem Server" and "Setting Up RealSystem Player" sections at the following URL:
http://service.real.com/help/library/guides/p roxy/readme.htm#5
Step 8 Save the Content Engine configuration to Flash memory.
ContentEngine# copy running-config startup-config
Use the following sections to help you configure additional features on the RealProxy.
The RealProxy player comes with a streaming media cache of its own for the replication of on-demand content. However an administrator may wish to disable caching due to a variety of reasons:
To prevent caching of all material from all servers and the RealProxy, complete the following procedure:
 |
Note The administrator, usernames, and all associated passwords configured on the Content Engine are not synchronized with the RealProxy authentication database. Use admin as a default user and diamond as password to access the RealSystem administration page from the Content Engine GUI. See Figure 14-2. Use this administrator authentication to configure other RealProxy users. |
Step 1 Access the RealSystem Administrator GUI page by clicking the Admin button on the RealProxy page of the Content Engine management GUI. (See Figure 14-2. You must enable the RealProxy before you can access the Admin button on this page.)
Step 2 Choose Configure > Cache.
Step 3 In the Enable Caching field, choose No.
Step 4 Click Apply.
Step 5 Restart the RealProxy by restarting the Content Engine GUI.
All on-demand clips are automatically available to the Content Engine. If there is content served by your RealServer that you do not want to be cached, see the "Disabling RealMedia Caching" section.
Live clips are not available to caching software; the RealProxy will still proxy the live broadcasts for clients. RealServer acts as a source for live splitting, and the RealProxy acts as a splitter.
If a client requests a cached stream, the RealProxy sends the request to the source RealServer for permission before allowing the client to play the stream. If RealServer denies the request, the RealProxy does not allow the client to receive the stream.
You can block a single RealProxy from caching the material served by your RealServer by creating an access control rule from the RealSystem Administrator GUI that prohibits the IP address of that RealProxy from connecting to your RealServer. You can also restrict access to content based on the number of players and bandwidth.
The RealProxy cannot cache live broadcasts, because no actual downloadable file is there to cache. However, the RealProxy includes an ability to "share" live streams among clients and thus reduce the bandwidth required from a transmitter. RealServer and the RealProxy communicate through live splitting; RealServer is preconfigured to act as a transmitter, and the RealProxy is automatically set up to act as a receiver.
A description of the Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) is available as IETF RFC 2326.
The following example displays request statistics. The statistics reported are the total number of requests served, the total number of cache hits and misses, the total demand pass-through, and the total number of live connections, either by splitting or by live pass-through.
ContentEngine# show statistics mediacache real requests
Media Cache Statistics - Requests
Total % of Requests
---------------------------------------------------
Total Received Requests: 17 -
Demand Cache Hit: 11 64.7
Demand Cache Miss: 6 35.3
Demand Pass-Through: 0 0.0
Live Split: 0 0.0
Live Pass-Through: 0 0.0
The following example displays savings statistics. In this example, the statistics reported are the total number of requests served, the total number of cache hits and misses, the bytes delivered, and the savings incurred by caching.
ContentEngine# show statistics mediacache real savings
Media Cache Statistics - Savings
Requests Bytes
-----------------------------------------------------------
Total: 17 16666028
Hits: 11 3656524
Miss: 6 13009504
Savings: 64.7 % 21.9 %
ContentEngine#
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Mon Nov 18 11:30:53 PST 2002
Copyright 1989-2000©Cisco Systems Inc.