|
|

July 31, 2001
These release notes support Cisco Enterprise Content Distribution Network (CDN) Software Version 3.0.2. This release does not ship with a user guide or configuration guide. Please refer to the Version 3.0 User Guide and Configuration Guide, which you can find at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/webscale/content/cdnent/ecdn30/index.htm.
These release notes describe the following topics:
Cisco Enterprise CDN Software Version 3.0.2 adds important new features to the product. Among the software enhancements in Version 3.0.2 are:
Users and CDN administrators interact with the product using a web-based graphical user interface to the CDM that provides easy access to most CDN functions. The following minimum hardware and software requirements apply to each machine that will be used as a workstation to access the CDM.
For more information on configuring your CDN devices, refer to the Cisco Enterprise CDN Software Configuration Guide.
The following sections are intended to help you upgrade from an earlier version of the CDN software to Version 3.0. If you are setting up the CDN for the first time, refer to Chapter 2, "Configuring and Activating Enterprise Content Delivery Network Devices," in the Cisco Enterprise CDN Software Configuration Guide.
To determine which version of the CDN software your devices are running, use the System feature of the CDM as follows:
http:// 172.16.0.1/start.html
Step 2 When prompted, log in to the CDM using an administrative username and password.
Step 3 From the Devices menu, choose System.
The System dialog box appears, displaying information on the selected device.
Step 4 Choose the name of the device you are inquiring about from the Device Selector list.
Information on the selected device appears in the System dialog box.
Step 5 Refer to the row labeled Software Version for information on what version of the CDN software the selected device is using, for example:
V1-7-rc6
You can upgrade your CDN software using the two upgrade CDs that accompany the product, or by downloading upgrade files from Cisco.com. Use the following procedure or refer to Chapter 4, "Maintaining the System Software," in the Cisco Enterprise CDN Software User Guide for instructions on downloading upgraded software from Cisco.com, and then performing a manual upgrade to install the downloaded software. Cisco supports the following upgrade sequences:
2.0 —> 2.1x —> 3.x
2.1x —> 3.x
2.9 —> 3.x
Two upgrade CDs ship with the product. The CDs contain the all the files necessary to upgrade CDN software without Windows Media Technology (WMT). Use the manual upgrade procedure described in the "Performing a Manual CDN Software Upgrade" section to distribute the upgrade files to all your CDN devices.
Upgrades of the CDN software are available from Cisco.com, the Cisco customer support portal. Once you have downloaded the appropriate software from Cisco.com, use the manual upgrade procedure described in the "Performing a Manual CDN Software Upgrade" section to distribute the upgrade files to all your CDN devices.
 |
Note In order to access Cisco.com and download your CDN software upgrade, you need a registered username and password for the site. If you are a Cisco customer and service contract owner, a Cisco reseller, Premier Certified Partner, the customer of a Cisco certified Partner Initiated Customer Access (PICA) partner, or a Cisco consultant, you can acquire a login from the Cisco website. |
CDN software can be downloaded from Cisco.com using either a browser pointed to Cisco.com, or an FTP application connected to the Cisco FTP site. Use the appropriate directions that follow to connect to Cisco.com.
To connect to Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/cdn-ent
Step 2 You are prompted to log on. Enter your Cisco.com username and password.
 |
Note You need to have a Cisco.com username and password before attempting to download a software upgrade from Cisco.com. In order to acquire a Cisco.com login, you need a service contract number, Cisco.com registration number and verification key, PICA registration number and verification key, or packaged service registration number. |
Step 3 In the download area, locate the upgrade file or files for the version of the CDN software that you need. Version numbers are listed in the column labeled Release.
Step 4 For each upgrade file you need to download, click the filename to initiate the download.
Step 5 If you are prompted to open the file or save it to a disk, choose Save to save the file to a disk. Locate a directory on your hard drive or LAN to temporarily hold the upgrade file and click OK.
 |
Note You will later import upgrade files to the CDN, so be sure to place the files in a location that is easy to remember and which you will be able to access later. |
Step 6 Proceed to the "Performing a Manual CDN Software Upgrade" section for instructions on using the upgrade file to upgrade the software on your CDN devices.
In addition to downloading software upgrades for the CDN product from Cisco.com, you can also use your web browser to download CDN software from Cisco's designated FTP site: ftp://ftp.cisco.com.
Step 2 Log on to the Cisco FTP server as a registered user or as a guest.
ftp://userid:password@ftp.cisco.com
ftp://ftp.cisco.com
ftp://access_code:userid@host.domain/coded
Step 3 Navigate to the following download directory:
cisco/content-delivery/cdn/enterprise/
 |
Note Guest users are only able to see images that are located under the /pub directory. |
Step 4 Click the filename for each upgrade file to download the file to your local machine, or right-click the filename and choose the Save Link As or Save Target As options to save the target file to your local machine.
If you are prompted to open the file or save it to a disk, choose to save the file to a disk. Locate a directory on your hard drive or LAN to temporarily hold the upgrade file and click OK.
 |
Note You will later import these files to the CDN, so be sure to place them in a location from which they are easy to retrieve for import later. |
Step 5 Proceed to the "Performing a Manual CDN Software Upgrade" section for instructions on using the upgrade file to upgrade the software on your CDN devices.
In order to upgrade your CDN software manually, you must:
1. Create a manual upgrade channel that will distribute the updated license.
2. Subscribe any CDN devices requiring a software upgrade to the manual upgrade channel.
3. Import software upgrade files to the manual upgrade channel.
4. Distribute software upgrade files to all devices marked for upgrade.
Once these steps are complete, you can use the Software Update feature to install the software upgrade files to subscribed devices. See the following sections for more details on completing each step.
 |
Note It is imperative that you upgrade the software on your Content Engines (CEs) before upgrading the software on your CDM. Once your CDM software has been upgraded, any remaining CEs that have not also been upgraded will be unable to communicate with the CDM. Contact Cisco Technical Support if you have any questions regarding the proper procedure for upgrading your CDN devices. |
To create a manual upgrade channel:
Step 2 Log on using your administrator logon.
Step 3 From the Channels menu, choose Channel Console.
Step 4 Click Add Channel.
Step 5 Check the check box next to the channel name Channel # and click Edit.
 |
Note "Channel #" is the default channel name. If you have added other channels and have not renamed them, the channel that you added will be named "Channel #" (# being the next incremental number). |
Step 6 In the Name field, change the name of the channel to MANUAL_UPGRADE.
The channel must use this name (and letter case, as well) in order for it to function as an upgrade channel.
Step 7 In the Size Limit field, enter a value that accommodates your upgrade files.
For example, entering 1000 in the field provided and then clicking the MB button sets the size limit of the MANUAL_UPGRADE channel to 1000 MB.
Step 8 Check both the Auto Subscribe and Auto Replicate check boxes.
Step 9 Click Save Changes.
Once you have created your upgrade channel, subscribe all the devices requiring a software upgrade to that channel.
Step 2 From the Channel Selector, choose the MANUAL_UPGRADE channel.
Step 3 In the Unsubscribed CEs column, click the unsubscribed devices that you would like subscribe to the upgrade channel. If you want to select all the devices in the list, you can click All instead of clicking them individually.
Step 4 Click Subscribe.
The selected CEs are subscribed to the MANUAL_UPGRADE channel and receive upgrade files once they are imported to the channel.
To unsubscribe CEs from the MANUAL_UPGRADE channel, refer to Chapter 3, "Working with the Content Delivery Network," in the Cisco Enterprise CDN Software User Guide Version 3.0 for instructions on unsubscribing devices from a channel.
To import the software upgrade files to the manual upgrade channel:
You will need to import the following files from the CDs (the order in which you do this is not important):
Step 2 From the Channels menu, choose Media Importer and follow the directions for importing the files you have on your CD or the files that you downloaded from Cisco.com using the web server, PC folders option, or FTP option.
Step 3 From the Channels menu, choose Import Progress to monitor the progress of your import.
When the import is finished, the import status is "complete." Wait 20 minutes before proceeding with the next step.
Step 4 Once you have imported your software upgrade to the manual upgrade channel, refer to the information on updating your CDN software to complete the upgrade process in Chapter 4, "Maintaining the System Software," of the Cisco Enterprise CDN Software User Guide Version 3.0.
The Cisco CDN Installation Wizard for the Cisco Enterprise CDN Software Version 3.0 has changed since the previous version. You can now also configure Content Routers (CRs) using the Installation Wizard.
Refer to the Cisco Enterprise CDN Software Configuration Guide Version 3.0 for information on using the updated Installation Wizard to activate your CDN devices.
The following section contains important notes about the Cisco Enterprise CDN Software Version 3.0.2 that are not covered in the standard product documentation.
 |
Note The multicast server referred to in the Cisco Enterprise CDN documentation is the Digital Fountain Server. Refer to the Digital Fountain documentation for procedures pertaining to the multicast server that cannot be performed through the CDM user interface. |
A lag occurs between the multicast server stopping the serving of a file and the user interface updating the channel replication status to reflect this. To avoid overloading the server by importing new content while the server is still serving files, you need to (1) check the status on the channel console, and (2) check whether the multicast server is serving files. Refer to the documentation accompanying your multicast server (Digital Fountain documentation) for the latter procedure.
The multicast server has a bandwidth limitation. The maximum transmission rate that it can handle is determined by what the bandwidth limitation of the multicast server you acquire is. If you try to replicate a large number of files through multicast, then the multicast server may serve only a few of these if the total transmission rate of the files (which you set on the Channel Settings page) exceeds the maximum bandwidth setting on the multicast server.
When setting up and configuring your CDN, remember that if the multicast Time to Live (TTL) for the Multicast Server is configured to be too low (through the multicast editor), then the multicast may be dropped by some of the L3 hops after the TTL count is reached. All CEs that lie more than the TTL number of hops away will not receive this file through multicast.
The maximum file size that the multicast server can replicate is 2 GB.
There is a limitation on the number of files that the multicast server can serve at one time. To determine the maximum number of files it can serve, do the following calculation.
 |
Note The total number of files in your multicast channels should not exceed 140. |
If average_file_size is less than 128 MB, then the maximum number of files that can be served is 140.
If average_file_size is greater than 128 MB, proceed to Step 2.
 |
Note average_file_size value must be in megabytes (MB). |
Step 2 Divide average_file_size by 128.
Step 3 Divide 140 by the value_you_arrived_at_in_Step_2.
The value you arrive at in Step 3 is the maximum number of files that can be served.
For more information on file size and file number limitations, refer to Digital Fountain documentation.
If you try to have the multicast server serve more files than its configured bandwidth allows, then it does not serve the files that cause it to exceed its bandwidth limitation. Once the multicast server is in this state, removing all the uploads from it does not help it recover; you need to reboot the server.
If you overload the multicast server by pushing more uploads than the server can handle, it will not start the uploads that exceed its capacity. To prevent this, do not set the multicast timeout (on the Multicast Editor page) to anything over 100,000 minutes.
If you want to manually start or stop the multicast server, then you need to allow the CDM enough time to recognize that the multicast server has gone offline or come online. After issuing the server stop shell command (refer to Digital Fountain documentation for this procedure), you need to wait 15 minutes before issuing the server start shell command. You can check the Multicast Console page to see whether or not the CDM has detected the change in device status.
When you set a new multicast timeout value, only files imported after the change use this value; files that were imported before the change continue to use the old timeout value. To force the old files to use the new value, you need to create a new channel with the new timeout and move the files to this channel.
When CDN devices connect to routers or switches that have not been configured to automatically negotiate data transfer modes but have been configured to force the use of one data transfer mode (usually 100 Mbps full duplex), some customers have experienced slow performance and "choppy" playback of media from their CEs.
Decreased playback performance results because the CDN device Ethernet card switches from 100 Mbps full-duplex mode to 100 Mbps half-duplex mode, in which data transmission and reception cannot take place simultaneously.
Most Ethernet cards that negotiate duplex settings and port speeds are programmed to avoid conflicts when transmitting data by switching to half-duplex mode automatically when they detect that they are connected to a device (for example, a hub) that does not negotiate duplex mode and port speed. Ports that are configured to force the use of one duplex setting and port speed prompt this response.
We recommend making one of the two following changes to alleviate the problem of choppy media playback and slow performance resulting from this conflict:
The decision about which device to reconfigure should be made in consultation with your network administrators and in keeping with your own corporate Information Technology (IT) policies and procedures.
To change the configuration of the router or switch that your CDN devices connect to so that it negotiates duplex settings and speeds, refer to the installation or configuration documentation that came with the hardware.
If you are unsure of the correct procedure for reconfiguring your hardware, contact the manufacturer's technical support center before proceeding. For questions regarding your CDN software or Cisco hardware, contact Cisco's Technical Assistance Center (TAC). See the "Obtaining Technical Assistance" section for more information on contacting the TAC.
To change the configuration of the CDN device Ethernet card so that it uses full-duplex mode as a default instead of half-duplex mode when autonegotiation fails, use the administrative Set Ethernet Fallback feature. This feature forces your CDM or CE Ethernet card to use full-duplex mode by default, as opposed to half-duplex mode.
To change the Ethernet card to full-duplex mode:
Step 2 In the field provided for the web page URL, enter the following information, substituting the IP address of the CDM or CE where appropriate:
http://< CDN_DEVICE_IP_ADDRESS>/cgi-bin/restricted/set-mii-fd
You are prompted to log on to the device.
Step 3 Enter the administrative username and password and click OK. For example:
User Name: admin
Password: default
The Set Ethernet Fallback dialog box appears.
Step 4 Click the drop-down list and choose Full Duplex from the list.
Step 5 Click Submit Change.
A message appears, confirming the default mode that will be used by the Ethernet card when autonegotiation fails.
Step 6 Reboot the device. Refer to Chapter 4, "Maintaining the System Software," in the Cisco Enterprise CDN Software User Guide Version 3.0 for instructions on rebooting CDN devices.
If autonegotiation with the router fails, the device will use the duplex mode you specified.
For questions regarding your CDN software or Cisco hardware, contact the TAC. See the "Obtaining Technical Assistance" section for more information on contacting the TAC.
The following sections list resolved and open caveats for Cisco Enterprise CDN Software
Version 3.0.2.
The following caveats are open (unresolved) at the time of shipment.
The following caveats have been resolved for the Version 3.0.2 release.
The following section details omissions to the published Enterprise CDN Software Version 3.0documents.
The Cisco Enterprise CDN includes support for LAN-based back-channel multicasting of media as part of its support for RealNetworks' RealServer Version 7. This feature, which is built into the RealServer Version 7 release, enables CDN installations to conserve network bandwidth by sending a single media stream to multiple clients on a LAN, rather than streaming media to each requesting client individually.
Back-channel multicasting streams content between the RealServer and clients while maintaining a simultaneous accounting control channel between each client and the RealServer. This extra control channel is used to transmit authentication information as well as client commands like "start" and "stop." Back-channel multicasting enables the RealServer to track client behavior and display statistics during viewing, including real-time data on the number of clients receiving a presentation. Data collected can be reviewed and analyzed using the Java Monitor or RealSystem Administrator.
Once enabled, back-channel multicasting is applied to all streams broadcast from your RealServer. Clients that have been preconfigured to use multicasting will do so, maximizing the bandwidth available to multicasting and unicasting clients alike.
Although you typically use the built-in administrative features of RealServer to configure multicasting, it is possible to enable multicasting remotely from your CDM interface.
To use the CDM to enable multicasting:
http:// your_Content_Distribution_Manager_ip_address/cgi-bin/mc
where your_Content_Distribution_Manager_ip_address represents the IP address or DNS domain name of your Content Distribution Manager.
Step 2 With the Enable Multicast options displayed in your browser window, click the Enable Multicast drop-down list and choose Yes.
This enables the multicasting feature on the RealServer used by your CDM.
Step 3 Enter the range of addresses to which you will be sending multicast streams in the IP Address Range fields.
Remember that broadcasts of video content require two addresses—one for video content and
one for audio content. Refer to "Calculating Addresses for Back-Channel Multicasts" in the RealServer Version 7 Administration Guide for more information. The RealServer uses the first available address in the range you specify.
Step 4 Set the maximum distance that streamed packets can travel over a network, as measured in hops from one multicast-enabled router to another, by entering a Time To Live value in the Time to Live field provided.
Each time a multicast data packet passes through a multicast-enabled router, its Time To Live value is decreased by 1. Once the value reaches 0, the RealServer discards the packet.
 |
Note For typical networks, a Time To Live value of 16 is adequate to keep packets within the network. |
Step 5 Click Set when you are finished.
The multicast settings are saved back to the RealServer used by your CDM.
To add a list of media files from a channel to the play list, send the following URL command:
http://< CE IP>/cgi/videocontrol?OP=PLAYLIST&CMD=ADD-BY-NAME&CHANNEL-NAME=<channel
name>&FILENAME=<file1,file2,...>
where:
CE IP is the IP address of the CE.
channel name is the name of the channel from which media files are to be added to the playlist.
file1,file2 is the list of media files to be added to the playlist. Filenames should be separated by commas.
To delete the list of media files belonging to the playlist, send the following URL command:
http://< CE IP>/cgi/videocontrol?OP=PLAYLIST&CMD=REMOVE-BY-NAME&CHANNEL-NAME=<channel
name>&FILENAME=<file1,file2,...>
where:
CE IP is the IP address of the CE.
channel name is the name of the channel to which the media files belong.
file1,file2 is the list of media files to be removed from the playlist. Filenames should be separated by commas.
To clear the playlist, send the following URL command:
http://< CE IP>/cgi/videocontrol?OP=PLAYLIST&CMD=CLEAR
where:
CE IP is the IP address of the CE.
To define start and stop times for playing the playlist, send the following URL command:
http://< CE IP>/cgi/videocontrol?OP=PLAYTIMES&CMD=ADD&EVENT=<start time>,<stop time>>
where:
CE IP is the IP address of the CE.
start time is the start time in seconds since 1970.
stop time is the stop time in seconds since 1970.
 |
Note The start or stop time (in seconds from epoch) must be based on accurate GMT/UTC time; this is then translated into the local time of the TV Out device. |
To remove the defined schedules from the playlist, send the following URL command:
http://< CE IP>/cgi/videocontrol?OP=PLAYTIMES&CMD=REMOVE&EVENT=<start time>,<stop time>
where:
CE IP is the IP address of the CE.
start time is the start time in seconds since 1970.
stop time is the stop time in seconds since 1970.
 |
Note The start/stop time (in seconds from epoch) must be based on accurate GMT/UTC time; this is then translated into the local time of the TV Out device. |
To clear all schedules defined for the playlist, send the following URL command:
http://< CE IP>/cgi/videocontrol?OP=PLAYTIMES&CMD=CLEAR
where:
CE IP is the IP address of the CE.
To play the programs from the playlist, send the following URL command:
http://< CE IP>/cgi/videocontrol?OP=CONTROL&CMD=PLAY
where:
CE IP is the IP address of the CE.
To stop playback, send the following URL command:
http://< CE IP>/cgi/videocontrol?OP=CONTROL&CMD=STOP
where:
CE IP is the IP address of the CE.
To pause playback, send the following URL command:
http://< CE IP>/cgi/videocontrol?OP=CONTROL&CMD=PAUSE
where:
CE IP is the IP address of the CE.
To play the next program, while the playlist is playing, send the following URL command:
http://< CE IP>/cgi/videocontrol?OP=CONTROL&CMD=NEXT
where:
CE IP is the IP address of the CE.
To play the previous program, while the playlist is playing, send the following URL command:
http://< CE IP>/cgi/videocontrol?OP=CONTROL&CMD=BACK
where:
CE IP is the IP address of the CE.
To restart playback, send the following URL command:
http://< CE IP>/cgi/videocontrol?OP=CONTROL&CMD=RESTART
where:
CE IP is the IP address of the CE.
To set the playlist to loop to the beginning of the playlist when it reaches the end, send the following URL command:
http://< CE IP>/cgi/videocontrol?OP=FEATURE&CMD=LOOP&VALUE=<flag>
where:
CE IP is the IP address of the CE.
flag is set to 1 or 0, to enable or disable the loop setting respectively.
To set the playlist to play programs in random order, send the following URL command:
http://< CE IP>/cgi/videocontrol?OP=FEATURE&CMD=RANDOM&VALUE=<flag>
where:
CE IP is the IP address of the CE.
flag is set to 1 or 0, to enable or disable the random order setting respectively.
By default, Soft Stop is not enabled and a Stop command causes the currently playing video to abort before the playlist has been stopped. If you enable Soft Stop, a Stop command will stop the playlist only after the currently playing video has ended. To enable Soft Stop, send the following URL command:
http://< CE IP>/cgi/videocontrol?OP=FEATURE&CMD=SOFTSTOP&VALUE=<flag>
where:
CE IP is the IP address of the CE.
flag is set to 1 or 0, to enable or disable the Soft Stop setting respectively.
You must first create a playlist to be able to associate an overlay image with it. For instructions on how to create a playlist using the TV Controls API, refer to the "Adding Programs to the Playlist" section. For instructions on how to create a playlist using the CDM, refer to the Cisco Enterprise CDN Software User Guide.
To add an overlay image to a playlist and set its properties, send the following URL command:
http://< CE IP>/cgi/videocontrol?OP=PLAYLIST&CMD=ADD-OVERLAY&OVL-IMAGE-CHN=<channel name> &OVL-IMAGE=<file
name>&OVL-PLACEMENT=<placement>&OVL-IMAGE-HEIGHT=-<height offset>&OVL-IMAGE-WIDTH=<width
offset>&OVL-OPACITY=<opacity>&OVL-TRANSCOLOR=<transparent color flag>
where:
CE IP is the IP address of the CE.
channel name is the name of the channel from which the overlay image file is to be added to the playlist.
file name is the name of the overlay image file.
placement is the region of the display where the overlay image should appear. Your options are:
height offset adjusts placement along the vertical axis. The valid range is from -40 to 40 pixels.
-40 = moves the image to the lowest possible position on the display
40 = moves the image to the uppermost position on the display
width offset adjusts placement along the horizontal axis. The valid range is from -60 to 60 pixels.
-60 = moves the image to the left most possible position on the display
60 = moves the image to the right most possible position on the display
opacity adjusts the opacity of the overlay image. The valid range is from 0 to 15.
0 = renders the image completely opaque
15 = renders the image nearly transparent
transparent color flag is set to 1 or 0 to enable or disable the use of transparency, respectively. When enabled, the color of the pixel in the lower left corner of the image is transparent over the entire image. When a transparency-enabled image is placed over a video, the background color of the overlay image is not visible against the video playing behind it. This is useful if you want to use a non-rectangular image as your overlay.
To remove an overlay image file from a playlist, send the following URL command:
http://< CE IP>/cgi/videocontrol?OP=PLAYLIST&CMD=REMOVE-OVERLAY&OVL-IMAGE-CHN=<channel
name> &OVL-IMAGE=<file name>
where:
CE IP is the IP address of the CE.
channel name is the name of the channel from which the overlay image file is to be added to the playlist.
file name is the name of the overlay image file to be removed from the playlist.
You can modify the properties of an overlay image while the playlist is playing, but the modified settings do not take effect until the next video in the playlist starts playing. To modify the properties of an overlay image, send the following URL command:
http://< CE IP>/cgi/videocontrol?OP=PLAYLIST&CMD=ADD-OVERLAY&OVL-IMAGE-CHN=<channel name> &OVL-IMAGE=<file
name>&OVL-PLACEMENT=<placement>&OVL-IMAGE-HEIGHT=-<height offset>&OVL-IMAGE-WIDTH=<width
offset>&OVL-OPACITY=<opacity>&OVL-TRANSCOLOR=<transparent color flag>
where:
CE IP is the IP address of the CE.
channel name is the name of the channel from which the overlay image file was added to the playlist.
file name is the name of the overlay image file.
placement is region of the display where the overlay image should appear. Your options are:
height offset adjusts placement along the vertical axis. The valid range is from -40 to 40 pixels.
-40 = moves the image to the lowest possible position on the display
40 = moves the image to the uppermost position on the display
width offset adjusts placement along the horizontal axis. The valid range is from -60 to 60 pixels.
-60 = moves the image to the left-most possible position on the display
60 = moves the image to the right-most possible position on the display
opacity adjusts the opacity of the overlay image. The valid range is from 0 to 15.
0 = renders the image completely opaque
15 = renders the image least opaque or nearly transparent
transparent color flag is set to 1 or 0 to enable or disable the use of transparency, respectively. When enabled, the color of the pixel in the lower left corner is transparent over the entire image.
You can associate one overlay image with each playlist. The enduser sees this image displayed in a determinable screen location when the playlist it is associated with is playing. This feature is useful for displaying logos.
 |
Note Overlay images can only be Windows BMP files with 16 colors. They must have 4 bits per pixel, must be less than 64 KB in size, and the width of the image (in pixels) must be divisible by 8. Before associating an overlay image with a playlist, open the image file in an image editor and view its properties to make sure that it meets the above requirements. |
You must first create a playlist to be able to associate an overlay image with it. For instructions on how to create a playlist using the TV Controls API, refer to the "Adding Programs to the Playlist" section. For instructions on how to create a playlist using the CDM, refer to the Cisco Enterprise CDN Software User Guide.
To add an overlay image from the CDM:
Step 2 Click on the TV-out enabled device that has the playlist to which you want to add an overlay image.
Step 3 If prompted, enter a username and password and click OK.
Step 4 From the Channel Selector drop-down list, select the channel which contains the image file you wish to use as an overlay image. A list of available media appears on the left.
Step 5 Click the check box next to the image file that you want to use as an overlay image.
Step 6 Click the Add Overlay button. The names of the image file and the channel it is obtained from appear under the heading Overlay Image, which appears under the list of files with the heading Playlist.
You can now edit the parameters of the overlay image by specifying and adjusting where on the TV Monitor it should display, specifying the overall opacity of the image, and choosing whether or not you want to set one color to be transparent. For information on how to change the parameters, refer to the "Removing an Overlay Image from a Playlist Using the TV Controller" section or the "Changing the Parameters of a Playlist's Overlay Image Using the TV Controller" section.
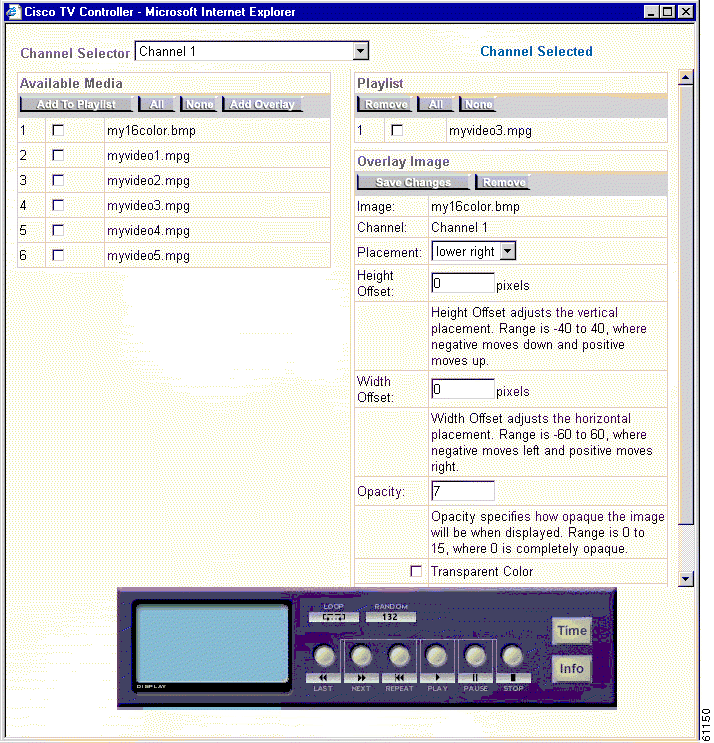
Step 2 Click on the TV-out enabled device that has the playlist to which you want to add an overlay image.
Step 3 If prompted, enter a username and password and click OK.
Step 4 From the Channel Selector drop-down list, select the channel that has the playlist whose overlay image you wish to remove.
Step 5 Under the heading Overlay Image, click the Remove button.

Step 2 Click the TV-out enabled device that has the playlist whose overlay image you want to modify.
Step 3 If prompted, enter a username and password.
Step 4 Under the Overlay Image heading, modify the parameters described in the table below.
| Image Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Placement | Specify where the overlay image should appear on the TV Out Monitor. Your options are upper left, upper right, lower left, lower right, and center. |
Height offset | Adjust placement along the vertical axis. The valid range is from -40 to 40 pixels. -40 = moves the image to the lowest possible position on the display 40 = moves the image to the uppermost position on the display |
Width offset | Adjust placement along the horizontal axis. The valid range is from -60 to 60 pixels. -60 = moves the image to the left most possible position on the display 60 = moves the image to the right most possible position on the display |
Opacity | Adjust the opacity of the overlay image. The valid range is from 0 to 15. 0 = renders the image completely opaque 15 = renders the image nearly transparent |
Transparency | Set this to 1 or 0 to enable or disable the use of transparency respectively. When enabled, the color of the pixel in the lower left hand corner of the image is transparent over the entire image. When a transparency-enabled image is placed over a video, the background color of the overlay image is not visible against the video playing behind it. This is useful if you want to use a non-rectangular image as your overlay. |
If your storage requirements have changed or if want to replace nonsystem drives on your CDN, you can put additional Cisco storage disks on your Content Engines and Content Distribution Manager. Additional storage disks only serve the purpose of adding storage capacity. If you are using a CDM-4650, you can add storage disks that also support hot-swap and redundancy functionality. Refer to the documentation that came with your CDM-4650 for information on how to configure such storage disks with your CDM. You can also delete existing nonsystem disks.
 |
Warning If you delete storage disks from the CDM, you could lose some of the original content stored on your CDM. You would then have to re-import it. |
Before you add a storage disk to a CE or CDM, consult Table 2 to determine whether or not your device will support the Storage Array you have chosen.
CE 507 None CE-560 Storage Array 6 CDM-4630 Storage Array 6 CDM-4650 Storage Array 6 with RAID 5 Storage Array 12 with RAID 5 See the section "Configuring Additional Storage Disks on a CDM-4650 as RAID-5" for instructions on how to configure storage arrays as RAID-5 on a CDM-4650.
Table 2: Storage Array Support for CDN Devices
This CDN device...
Is compatible with this Storage Array...
On a CDM-4650, the eight internal disk-drives come pre-configured as a RAID-5 storage array. Any additional disks that are attached externally must be configured as a RAID-5 array; otherwise, they will not be recognized by Cisco Enterprise CDN Software. There are two steps involved in configuring additional disks as a RAID-5 array:
1. Identifying extra disks as part of an external Storage Array 6 or Storage Array 12
2. Striping the disks to form a RAID-5 array
There is no command-line utility or user interface to automate this process; you must enter a SCSI-BIOS configuration utility during device power-up and manually configure the SCSI-BIOS settings to do the above.
To configure external disks as RAID-5 arrays:
Step 2 Attach the external disk drive while the CDM-4650 is powered off.
Step 3 Power up the CDM-4650. You see boot-time messages appear on the screen.
Step 4 When you see the following message during bootup, press <Ctrl> <M>.
PowerEdge Expandable RAID Controller
Copyright (c) AMERICAN MEGATRENDS INC.
Press <Ctrl> <M> to run Configuration Utility
You see the following setup screen, indicating that you have entered the configuration utility:
PERC BIOS Configuration Utility Ver. 2.50
Management Menu
Configure
Step 5 Use the up or down arrow keys on your keyboard to move the cursor to the Configure menu. Press Enter.
Step 6 Go to the View/Add Configuration sub-menu and press Enter. The Array Selection Menu appears.
 |
Note You need to know the following keyboard shortcuts for the subsequent steps, in
which you will create additional logical hardware drives for the attached external
disk-drives: - Space bar—Select - Enter—End Array - F10—Configure array These shortcuts are also described at the bottom of your screen. |
Step 7 There are two channels listed in the View/Add Configuration - Array Selection Menu—Channel-0 and Channel-1. All the internal hard-disks are already configured as Array "A0" in Channel-0. In Channel-1, you see a list of individual disks of the external drives (Storage Array-6 or Storage Array-12), with a label READY, which indicates that those disks are still not part of a RAID-5 array. For the Storage Array of type RAID-5 (default), you can choose a maximum of eight disks for each RAID-5 Storage Array.
 |
Warning DO NOT change any configurations in Channel-0. The logical hardware drive mapped to Channel-0 contains Cisco Enterprise CDN Software. Any changes made to Channel-0 will lead to loss of the CDN software, and will render the system useless. |
Select the first eight disks (press the space bar to select them). You see labels A1-0, A1-1, and so on being created as you keep selecting additional disks. Once you select up to eight disks (or all the disks if there are less than eight), you can complete the array by pressing Enter. The labels A1-0, A1-1, ........, A1-7 stop blinking after you have pressed Enter to end the new array.
Step 8 To configure the newly added array, press Enter again or Press F10. This leads you to a screen that shows existing logical drives, and also presents a sub-menu for the logical drive or array you just created.
Step 9 In the logical drive menu, make sure that the type is RAID-5, and then press Enter on the Accept sub-menu.
Step 10 Press Enter on Accept once more to go back to the "View/Add Configuration - Array Selection Menu" screen.
 |
Note Logical Drive-0 corresponds to the factory-configured drive that corresponds to the internal hard-disks. You should not make any modifications to this logical drive. |
Step 11 If there are additional disks which are still not labelled with an array name (or are still marked as READY), repeat the steps from Step 7 onwards.
Step 12 After you have configured all the disks as new logical drives, save the configuration when prompted and press Escape to come out of the Configure menu.
Step 13 Press Enter on the Initialize sub-menu which is present on the initial screen. Select the logical drives that were added just now (press the space bar to select them) and then press F10 to initialize the drives.
 |
Note Logical-drive-0 is the factory-configured drive which has internal harddisks and should NOT be changed. |
Step 14 Press Escape and click Yes, when prompted to exit from the configuration utility. You are asked to reboot the box once you exit from the Configuration Utility.
Step 15 After the CDM-4650 boots up, it has additional hardware logical drives that are ready for installation through the CDM user interface.
For information on how to install or uninstall storage disks, refer to the Cisco Storage Array 6 Installation and Configuration Guide or the Cisco Storage Array 12 Installation and Configuration Guide. After you have changed the storage capacity of a CE or CDM by adding or deleting storage disks from your hardware, do the following:
Step 2 To update the system to recognize the new storage capacity, from the Devices menu, choose System.
The System dialog box appears (see Figure 3).
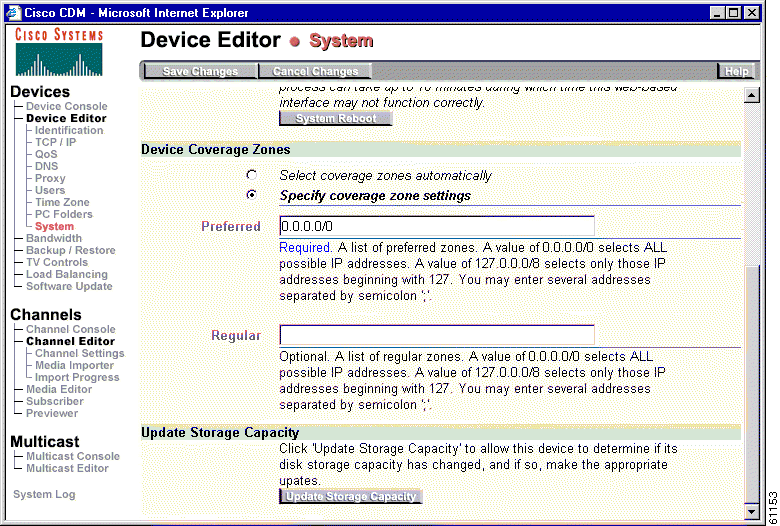
Step 3 Click the Update Storage Capacity button. The amount of Available Storage displays.
Step 4 Calculate the storage you had available before you added or deleted a storage disk. You can calculate this using the following equation:
<prior_available_storage> = <total_storage_capacity_of_device_before_addition/deletion> - <total_storage_reserved_for_channels>
 |
Note The documentation that came with your CDM or CE should tell you how much storage capacity the device has the time of manufacture. This should give you the value for <total_storage_capacity_of_device_before_addition/deletion>. The <total_storage_reserved_for_channels> can be determined by adding the Capacity value for all the channels the device is subscribed to. The capacity for all the channels is listed on the Channel Console page. |
Step 5 Compare this amount to the amount of storage you had before adding or deleting a disk to verify whether or not the new Storage Capacity is recognized.
Step 6 If the new Available Storage does not reflect the addition or deletion of a storage disk, use the following command-line commands to reinitiate the update and then go to Step 2:
a. stop
b. check-disk --force --format
c. reboot
A CE cannot have a storage capacity that is less than the sum of the space required by all the channels subscribed to it. If, as a result of deleting a disk, the storage capacity of the CEs falls below the required size, the system prompts you to unsubscribe the CE for some of the channels. For information on how to unsubscribe your CE, refer to the section "Removing a Content Engine from a Subscribed Devices List" in Chapter 3 of the Cisco Enterprise CDN Software User Guide.
To replace the content that was lost when you deleted a storage disk, the CE automatically initiates content replication from its parent CE or CDM. It replicates only that content which was lost.
If you remove a storage disk that was on the CDM before you imported content, you risk losing some of the media content on your CDM. This can cause performance degradation in the CDM routing and replication processes and can also affect the performance of CEs that were subscribed to the deleted content. To avoid this, you can either:
To delete missing content from the CDM user interface:
The System dialog box appears (see Figure 4).

Step 2 Click the Identify Lost Content button. A new page appears, with a table listing lost media files and the channels with which those files were associated. Make a note of the lost media files.
Step 3 From the Channels menu, choose Media Editor.
The Media Editor dialog box appears (see Figure 5).
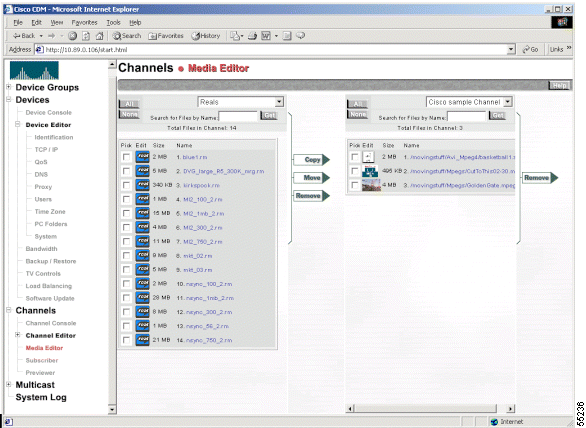
Step 4 Make sure that the correct channel is displayed in the appropriate drop-down list box. If it is not, choose the correct channel from the list.
Step 5 Check the Pick check box next to each file that you want to remove.
Step 6 Click Remove. You are prompted to confirm that you want to remove the selected media.
When the CDM replicates files to the CEs, filesnames that contain special characters may be altered. Some special characters are removed from the filename; others are replaced with different characters. Table 3 summarizes how special characters in filenames are handled during replication.
If a filename does not contain an extension and all the characters in the filename are removed, the file is renamed "content." For example, a file named & would be renamed content, but a file named &.txt
would be renamed .txt.
| This special character | Is removed | Is replaced with | Is unchanged |
|---|---|---|---|
ampersand [ & ] | · |
|
|
asterisk [ * ] | · |
|
|
at sign [ @ ] | · |
|
|
backquote [ \Q ] | · |
|
|
backslash [ \ ] | · |
|
|
caret [ ^ ] | · |
|
|
closing brace [ } ] | · |
|
|
closing bracket [ ] ] | · |
|
|
closing parenthesis [ ) ] | · |
|
|
colon [ : ] | · |
|
|
comma [ , ] | · |
|
|
dash [ - ] |
|
| · |
dollar sign [ $ ] | · |
|
|
double-quote [ " ] | · |
|
|
equals sign [ = ] | · |
|
|
exclamation point [ ! ] | · |
|
|
forward slash [ / ] | · |
|
|
greater than [ > ] | · |
|
|
less than [ < ] | · |
|
|
opening brace [ { ] | · |
|
|
opening bracket [ [ ] | · |
|
|
opening parenthesis [ ( ] | · |
|
|
percent sign [ % ] | · |
|
|
period [ . ] |
|
| · |
plus sign [ + ] | · |
|
|
pound sign [ # ] | · |
|
|
question mark [ ? ] | · |
|
|
semicolon [ ; ] | · |
|
|
single-quote [ ' ] | · |
|
|
space [ ] |
| underscore [ _ ] |
|
tilde [ ~ ] | · |
|
|
underscore [ _ ] |
|
| · |
vertical-bar [ | ] | · |
|
|
The Cisco Enterprise CDN software comes with both printed documentation and online help to assist you in learning to use the features of the CDN. Refer to the following documents when you have questions regarding the CDN software.
In addition, you can find information related to the installation, configuration, and maintenance of your CDN hardware in the following Cisco Systems documents:
The following sections provide sources for obtaining documentation from Cisco Systems.
You can access the most current Cisco documentation on the World Wide Web at the following sites:
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available in a CD-ROM package, which ships with your product. The Documentation CD-ROM is updated monthly and may be more current than printed documentation. The CD-ROM package is available as a single unit or as an annual subscription.
Cisco documentation is available in the following ways:
If you are reading Cisco product documentation on the World Wide Web, you can submit technical comments electronically. Click Feedback in the toolbar and select Documentation. After you complete the form, click Submit to send it to Cisco.
You can e-mail your comments to bug-doc@cisco.com.
To submit your comments by mail, use the response card behind the front cover of your document, or write to the following address:
Attn Document Resource Connection
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-9883
We appreciate your comments.
Cisco provides Cisco.com as a starting point for all technical assistance. Customers and partners can obtain documentation, troubleshooting tips, and sample configurations from online tools. For Cisco.com registered users, additional troubleshooting tools are available from the TAC website.
Cisco.com is the foundation of a suite of interactive, networked services that provides immediate, open access to Cisco information and resources at anytime, from anywhere in the world. This highly integrated Internet application is a powerful, easy-to-use tool for doing business with Cisco.
Cisco.com provides a broad range of features and services to help customers and partners streamline business processes and improve productivity. Through Cisco.com, you can find information about Cisco and our networking solutions, services, and programs. In addition, you can resolve technical issues with online technical support, download and test software packages, and order Cisco learning materials and merchandise. Valuable online skill assessment, training, and certification programs are also available.
Customers and partners can self-register on Cisco.com to obtain additional personalized information and services. Registered users can order products, check on the status of an order, access technical support, and view benefits specific to their relationships with Cisco.
To access Cisco.com, go to the following website:
The Cisco TAC website is available to all customers who need technical assistance with a Cisco product or technology that is under warranty or covered by a maintenance contract.
If you have a priority level 3 (P3) or priority level 4 (P4) problem, contact TAC by going to the TAC website:
P3 and P4 level problems are defined as follows:
In each of the above cases, use the Cisco TAC website to quickly find answers to your questions.
To register for Cisco.com, go to the following website:
http://www.cisco.com/register/
If you cannot resolve your technical issue by using the TAC online resources, Cisco.com registered users can open a case online by using the TAC Case Open tool at the following website:
http://www.cisco.com/tac/caseopen
If you have a priority level 1(P1) or priority level 2 (P2) problem, contact TAC by telephone and immediately open a case. To obtain a directory of toll-free numbers for your country, go to the following website:
http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/687/Directory/DirTAC.shtml
P1 and P2 level problems are defined as follows:
This document is to be used in conjunction with the documents listed in the "Related Documentation" section.
The RealServer(TM) is included under license from RealNetworks, Inc. Copyright 1995-2000, RealNetworks, Inc. All rights reserved.
AccessPath, AtmDirector, Browse with Me, CCDA, CCDE, CCDP, CCIE, CCNA, CCNP, CCSI, CD-PAC, CiscoLink, the Cisco NetWorks logo, the Cisco Powered Network logo, Cisco Systems Networking Academy, the Cisco Systems Networking Academy logo, Fast Step, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, FrameShare, GigaStack, IGX, Internet Quotient, IP/VC, iQ Breakthrough, iQ Expertise, iQ FastTrack, the iQ Logo, iQ Net Readiness Scorecard, MGX, the Networkers logo, Packet, PIX, RateMUX, ScriptBuilder, ScriptShare, SlideCast, SMARTnet, TransPath, Unity, Voice LAN, Wavelength Router, and WebViewer are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn, Discover All That's Possible, and Empowering the Internet Generation, are service marks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; and Aironet, ASIST, BPX, Catalyst, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, the Cisco IOS logo, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Enterprise/Solver, EtherChannel, EtherSwitch, FastHub, FastSwitch, IOS, IP/TV, LightStream, MICA, Network Registrar, Post-Routing, Pre-Routing, Registrar, StrataView Plus, Stratm, SwitchProbe, TeleRouter, and VCO are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and certain other countries.
All other brands, names, or trademarks mentioned in this document or Web site are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (0104R)
Copyright © 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc.
All rights reserved.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Tue Jul 31 10:48:58 PDT 2001
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2001 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.