|
|

A circuit line is the physical line that carries data, voice, Frame Relay, or ATM traffic between a BPX node (or IGX node) and customer premises equipment. Each piece of customer premises equipment is attached to a node through a circuit line.
You must first establish or "up" a card by using the upcd command, before you can "up" and configure a circuit line on that card.
This chapter:
Use the cnfln to configure commands (the cnfcln command is obsolete). The switch software prompts for the parameters appropriate for the card type it detects. For details on each circuit line command, see the Cisco WAN Switching Command Reference. Note: Line commands are the same as "circuit line" commands.
Table 19-1 shows the permissible card combinations for CPE-to-IGX lines.
| Type | Country | Electrical Signal Format | Ones Density Enforcement | Multiplexing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
J1 | Japan | Coded Mark Inversion (CMI) |
| 31 channels @ 64kbps each |
E1 | Others | Alternate Mark Inversion (AMI) | High density bipolar 3 (HDB3) | 31 channels @ 64kbps each 1 E1 line on CDP/CVM, 8 E1 lines on UFM |
T1 | USA ASIA | Alternate Mark Inversion (AMI) | Bipolar Zero Substitution (B8ZS) | 24 channels @ 64kbps each 1 T1 line on CDP/CVM, 8 T1 lines on UFM |
E3 | Europe | Physical Layer Convergence Protocol per AT&T publication; ITU I-361 with HEC for E3 | HDB3 | ITU-T G.804, G.832 |
T3 | USA | Physical Layer Convergence Protocol per AT&T publication TA-TSY-00772 and 000773 for T3 | B3ZS+ | M13 mode |
| Service | Node Type | Front Card | Back Card |
|---|---|---|---|
ATM | IGX | UXM | BC-UAI BC-UAI-1T1 BC-UAI-1OC3 |
ATM | IGX | ALM/A | BC-UAI-1T3 |
Frame Relay | IGX | UFM-4C, UFM-8C | UFI-8T1-DB15, UFI-8E1-DB15, UFI-8E1-BNC |
Frame Relay | IGX | FRP-6, FRP-31/FRM-6, | FRI-T1, FRI-E1 |
Frame Relay | IGX | UFM-C | UFI-8T1-DB15 |
High Speed Data | IGX | SDP/HDM | SDI/RS-232 |
High Speed Data | IGX | SDP/HDM | SDI/RS-232 |
Voice | IGX | UVM | BC-UVI-2T1EC |
Voice | IGX | CDP/CVM | BC-T1 |
Frame relay, data, and voice connections require an active line. Before you can execute this procedure, you must first up the card by using upcd.
To establish (or "up") an active line:
Step 2 Use upln to activate a circuit line in a slot that contains the appropriate circuit line card set.
Step 3 Use cnfln to configure the circuit line.
The upln and cnfln commands establish the general parameters for the line but do not establish specific Frame Relay, data, or voice parameters. Refer to applicable chapters for details on a particular service.
To down a line:
Step 2 Use dnln to down the line. A downed line is inactive, so no signals or statistics are generated.
The command sequences for setting up lines for:
A yes/no decision branch for "Other Side?" and the vt command in the sequence indicates command sequences on local and far nodes.
"Multiplex" refers to channelized streams.
s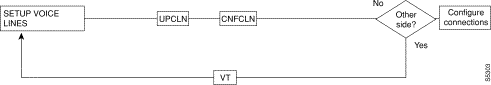
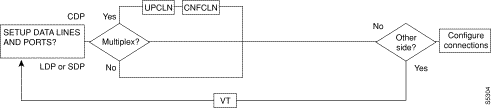
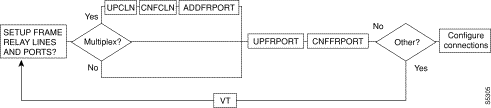
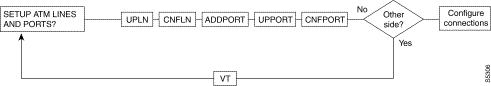
Table 19-3 Here are the names and descriptions for each line command:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
cnfcassw | Configure CAS switching |
cnfln | Configure line (same as cnfcln) |
cnfrsrc | Configure resources |
dnln | Down line (same as dncln). A downed line is inactive, so no signals or statistics are generated. You must remove all connections on a line (delcon or delcongrp) before you down the line by uising dnln. |
dsplncnf | Display line configuration (same as dspclncnf). Displays the configuration of a specified circuit line. |
dsplns | Displays the circuit line configuration and alarm status for the node (same as dspclns) |
dsptsmap | Display time slot map |
prtlns | Prints the circuit line configuration and circuit line alarm status for the node (same as prtclns) |
upln | Up line (same as upcln) |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Fri Jul 27 16:13:07 PDT 2001
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2001 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.