|
|

Cisco documentation and additional literature are available in a CD-ROM package, which ships with your product. The Documentation CD-ROM, a member of the Cisco Connection Family, is updated monthly. Therefore, it might be more current than printed documentation. To order additional copies of the Documentation CD-ROM, contact your local sales representative or call customer service. The CD-ROM package is available as a single package or as an annual subscription. You can also access Cisco documentation on the World Wide Web at http://www.cisco.com, http://www-china.cisco.com, or http://www-europe.cisco.com.
If you are reading Cisco product documentation on the World Wide Web, you can submit comments electronically. Click Feedback in the toolbar, select Documentation, and click Enter the feedback form. After you complete the form, click Submit to send it to Cisco. We appreciate your comments.
The 9.2 software release supports the Cisco WAN switching products, BPX 8600 series and IGX 8400 series. This release does not support IPX switch.
The MSSBU rollout plans for the 9.2 release is based upon a series of incremental feature releases. This
phased feature release strategy is designed to allow the earliest customer availability of key new features, consistent with maintaining high product quality. For the latest status of each 9.2 feature please see below.
The minimum release version noted in the table below represents the minimum switch software version required for each feature. As usual, it is recommended that the most current maintenance releases be used by customers.
Generally Available (GA) - Feature is ready for wide deployment with no restrictions. Customers deploying GA features are supported by the Technical Assistance Center (TAC).
First Customer Ship (FCS) - Feature is available for controlled introduction by selected customers. To trial an FCS feature, please contact your account representative.
Customers selected for controlled introduction will receive assistance with test plan review and special support from the New Product Team (NPT) in addition to the normal Technical Assistance Center (TAC) support.
Pre-First Customer Ship (Pre-FCS) - Feature is not yet available in the Switch Software baseline.
Target Date - This is the date for feature delivery that is supported by current Engineering and Marketing plans. This date is subject to change.
This is a maintenance release including all features supported up to release 9.2.30. The following files will be extracted from a TAR file upon upgrading to software release 9.2.33.
This is a maintenance release including all features supported up to release 9.2.30.
Including all features supported up to release 9.2.20 and introducing the following additional features:
Including all features supported up to release 9.2.20
Including all features supported up to release 9.2.10 and introducing the following additional features:
Including all features supported up to release 9.2.01 and introducing the following additional features:
Including all features supported in release 9.2.00 and introducing the following additional features:
Introducing the following features:
1. Release 9.2.31 introduces a new command - cnffdrlmiparms which makes the feeder LMI timers and counters configurable. This command is currently supported on BPX only and can not be added in the Job mode.
Usage: cnffdrlmiparms slot.port T393 T394 T396 N394 N395
Where slot.port specifies the feeder trunk to configure. The details of the other parameters is as follow:
|
2. In release 9.2.31 the system parameter 2 (cnfsysparm 2) is changed from "Fail Connections On Communication Break" to "Allow CPU Starvation of Fail Handler".
The old parameter has been removed as it violated the principle of separating control and data plane. The new parameter allows a new feature to be turned off that gives CPU to the Fail Handler at the expense of the Transaction Handler in case the Fail Handler does not get scheduled for a long time.
3. Do not mix MEE and MEF (or higher) in yred pair for BXM 2 port group enhanced cards (OC3 or OC12 port). Addyred will fail if both are in standby mode, or the primary card has been activated with MEF (or higher) and the secondary card has MEE.
4. For BXM 2 port group, enhanced cards activated with MEF or higher, downrev to MEE will bring the cards into MISMATCH mode. This applies to both single cards and yred pairs.
5. Release 9.2.30 introduces four new commands in BPX:
6. There are changes in the following command starting from release 9.2.30:
7. The multiple partitions introduces 2 VSI partitions on trunk and port interfaces on the BXM card. So, one partition can be used for MPLS, one can be used for PNNI. Virtual Trunk can have only one VSI partition or can be used for Autoroute, but cannot be used for both VSI and Autoroute simultaneously. This project introduces 6 service class templates in addition to the 3 existing templates.
Even though tag ABR is supported in Service Class Template (SCT), the MPLS controller and the BXM firmware currently do not support this.
The configurable VPI/VCI introduces 2 new parameters in addctrlr and addshelf commands, through which the user can specify the VPI and VCI of the master-slave control channels.
8. There is a change in reporting of port group number in this release 9.2.32. Previous image (MEC) of BXM used to report 1 port group for the 2 port group cards at the channel stats level 2 and 3. This made the port belonging to 2nd port group unusable.
Upgrading to 9.2.30 software first and then burning BXM card with the MED firmware, BXM will report 2 port groups for 2 port cards all the time. The smooth transition between the earlier 1port group and the newly reported 2 port groups also displays message in dspcd "Inconsistency with logical PG #" (port group number). All earlier software will mismatch the card.
If the BXM card is programmed with MEC or earlier firmware revision and the Channel Stats level 2 or 3 will report 1 port group. Burning a MED image will result in 2 port groups but for backward compatibility the software will not do the re-computation of LCNs based on the new port groups. In its logical database this will not impact the Auto Route connections.
For VSI controller the reported value will be higher than the actual available LCNs. That means a VSI controller may not be able to add connection even though the available connections are non zero. If the user wishes to remove the above discrepancy, he has to bring the card to the standby mode.
Note that the newly configured card or the card in standby mode programmed with MED image brought to the active state will not have above discrepancy.
9. In BPX nodes that use processor cards with 32Meg of RAM, it is possible to run out of memory in the Hitless Region. This can happen if the node is too heavily configured with cards and connections. The recommendation below should prevent memory aborts.
In nodes that have processor cards with 64Meg of RAM, there should be no Hitless Region memory problem. This is because 64Meg processors contain a second Hitless Region, which is larger than the first.
The following calculation will help prevent memory aborts on BPX processors with 32Meg. For simplicity, the numbers are approximate. It is necessary to add up the number of cards in the node, as well as the number of connections, and make sure that the total does not exceed the recommendation.
During system initialization, roughly 17,100 blocks of the available 40,000 are used for the card database.
In addition, assume that 1500 blocks will be needed for each BXM card that can support 16K conns, which is the more common configuration. Some BXM cards can support 32K conns, and these will need 3000 blocks of the Hitless Region. This chunk of memory is allocated at the insertion of the BXM card and will not be released until a card of different card type is inserted.
Also, 300 blocks will be needed for each 1000 via connections on the node. This can be viewed with the user command dspload.
10. The minimum software required to run MPLS are:
The BPX with external 7x00 label switch controller (router) with Switch Software Release 9.2.10 and IOS release 12.0(5)T can function as an ATM-LSR. The enhancements to dynamic label switching that was supported in Release 9.1 include support for MPLS Class of Service. The BPX as an ATM-LSR supports the "Multi-Label VC" model to support MPLS Class of Service. 5 Qbins (Qbin 10-14)are reserved for MPLS Class of Service. Class based WFQ is supported on these IP queues.
The BPX can also function as a "P" ATM-LSR in the MPLS-VPN architecture.
Hot Redundancy of MPLS connections on the BPX is supported by BXM hot card redundancy. Continuous message forwarding, and keep-alive between the BXM redundant pair ensures the connection continuity on BXM switchover. On Failure of a BXM card, the standby card becomes active with the label-vc's. Re-synchronization between the MPLS Label Switch controller and the BPX ensures that their databases are in sync.
11. The 16K connections feature increases the number of connections terminating on the BPX switch to 16,000. The count includes connections terminating on BXM or ASI endpoints on cards within the node as well as connections terminating on service modules in the feeder shelves connected to the BPX switch. For example, a Frame Relay connection that originates on a FRSM in an MGX 8220 connected to a BPX counts as one of the 16,000 terminated connections on that BPX.
This feature requires a BCC-3-64 or BCC-4 controller in the BPX as well as switch software 9.2.10 or higher.
12. Version 2.2 of the VSI (Virtual Switch Interface) provides the BPX switch with the ability to support multiple network protocols and multiple controllers per switch (e.g., MPLS, PNNI, etc.). Switch resources can be dedicated to a specific controller or shared by multiple controllers.
This feature is supported on BXM ports, trunks, and virtual trunks and requires a BCC-3-64 or BCC-4 controller in the BPX as well as switch software 9.2.10 or higher and firmware MEA or higher.
Following are the VSI features:
13. The combinations of system limits such as the number of trunks, lines, ports, and connections as well as enabled TFTP interval statistics should be provisioned so that the node has at least 50% idle time usage. Use the command dspprfhist to verify.
14. When cost based routing is used, increasing the cost of a trunk will result in deleting the preferred path on connections in the database if the sum of the preferred path cost exceeds the connection of configured cost. The connections will remain routed on its current path.
15. On the BXM and UXM, for the OC-3 MultiMode Fiber backcards, Y-Redundancy/hot standby is not supported due to hardware restriction.
16. The trunk reconfiguration feature does not support IMA trunk.
17. HDM to UVM interworking for Nx64K connections is not supported in this release.
Please consult your Support Representative before performing any software upgrade
1. The earliest release supported for graceful upgrade is 9.1.03.
2. 9.2 switch software requires MEX or MFA BXM firmware.
3. Before upgrading to this release when UXM cards are to be used, certain legacy card firmware must be upgraded. See the compatibility matrix for cards affected and the exact versions to be used.
 |
Note Standards compliant IMA is not compatible with the proprietary IMA protocol used in revision A firmware. Both ends of an IMA trunk must have the same protocol. |
 |
Caution : Failure to follow this procedure may result in the card not operating. The card should be returned to Cisco if this occurs: |
In order to run Model B firmware on an UXM, the card needs to be running boot code revision 6 or greater. To determine the boot code running on the card, issue the following command from CLI (user must be logged in as Service level or greater to use this command):
Step 2 Upgrade UXM's boot code if necessary
The process for loading boot code is exactly the same process you would use to load firmware. The only part which changes is the name of the file.
 |
Note Burning the boot code will cause the card to reset. |
Step 3 Upgrade UXM's firmware
Step 4 When Y-redundant trunks are used, the red alarm in/out values must be configured to 1.25/1.5 seconds or greater, or else INVMUX failures will occur and trunk failures will be observed during a Y-redundancy switchover. Use the following command:
This is due to the IMA protocol and may cause re-route of connections.
Step 5 Upgrade NPM software to 9.2
4. Procedure for Upgrading UXM-to-IMATM Trunks from Proprietary IMA Protocol to ATM Forum Compliant IMA Protocol.
Step 2 On IGX to have firmware upgrade, issue command cnffunc 15 d to disable the UXM from resetting automatically after the firmware is burned in.
Step 3 On each MGX-8220 equipped with IMATM-B, upgrade the ASC to 5.0.10.
Step 4 Download the Forum Compliant-Firmware version imatm_5.0.10.fw but do NOT reset IMATM-B card.
Step 5 On each IGX-UXM with IMA to be upgrade, burn firmware A.B.E or later to each UXM with IMA trunks.
Step 6 Simultaneously reset the card at each end of each IMA trunk to minimize trunk outage.
Step 7 Upgrade 9.1 nodes to 9.2 via loadrev and runrev.
Step 8 Issue the command cnffunc 15 e after each IGX is upgraded to 9.2.20 or later.
 |
Note The above procedure also applies to the UXME. |
5. .Procedure for Upgrading UXM-to-UXM Trunks From Proprietary IMA Protocol to ATM Forum Compliant IMA Protocol
 |
Note For Y-redundant UXMs, issue the command cnftrkparm 18 100000 100000 prior to this procedure and return to default values after this procedure |
Step 2 On IGX to have firmware upgraded, issue command cnffunc 15 d to disable the UXM from resetting automatically after the firmware is burned in.
Step 3 On each IGX-UXM with IMA to be upgraded, burn firmware A.B.E or later to each UXM with IMA trunks.
Step 4 Simultaneously reset the card at each end of each IMA trunk to minimize trunk outage.
Step 5 Upgrade 9.1 nodes to 9.2 via loadrev and runrev.
Step 6 Issue the command cnffunc 15 e after each IGX is upgraded to 9.2.20 or later.
 |
Note The above procedure also applies to the UXME. |
6. Procedure for Upgrading BXM cards to the 9.2 Firmware Release
To enable BXM cards to utilize 9.2 features, all BXM cards must be upgraded to the 9.2 firmware release. The following steps should be taken to avoid card mismatch:
Perform the following steps to avoid card mismatch:
Step 2 Upgrade BCC software to 9.2.30 or higher.
Step 3 Upgrade BXM firmware to MEF.
For all other cases, do the following steps:
Step 2 Upgrade BCC software to 9.2.30 or higher.
 |
Note See the Compatibility Matrix for the exact versions to be used |
7. Procedure for Adding New BCC cards as a Part of Upgrading to the 9.2 Release
 |
Note See the Compatibility Matrix for the tested/supported versions of other firmware and software that work with this release. |
8. Upgrading VSI 1.1 in release 9.1 to VSI 2.2 in release 9.2
The TSC is upgraded to CoS VSI Version capable release (IOS 12.XX). This image is VSI bilingual, meaning it understands both VSI Version 1 and Version 2.
Step 2 Upgrade the BXMs
All the BXM cards in the node are upgraded to Revision E, which is VSI Version 2 and CoS capable. After each BXM card is downloaded with the Revision E image, it temporarily experiences VSI outage until the BCC software is upgraded to the 9.2.33 image. The VSI outage during the upgrade is caused by the Revision E firmware not being backward compatible with VSI Version 1 features.
Note that from the TSC perspective, after a BXM is upgraded to Revision E image the interfaces that used to be on the card will "disappear." The TDP sessions that were on the interfaces will be lost. When all the BXMs are upgraded to the Revision E while still running Release 9.1 software on the BCC, the node will experience a complete outage of MPLS traffic. Autoroute will have a hitless upgrade.
Step 3 Upgrade the BCC
As the BCC is upgraded from software Release 9.1 to Release 9.2.33, the BCC recognizes the Revision E BXMs and downloads the VSI partition configuration. This causes the BXMs to issue ifc cfg traps to the TSC, allowing the TSC to rediscover all the MPLS interfaces on the BPX. The TDP sessions are reestablished and MPLS traffic starts flowing again through the BPX.
 |
Note The VSI 1.1 and VSI 2.2 are not interoperable. |
Revision Interoperating upgrades are supported, from the 9.1 to 9.2 releases of switch software, with Secondary Revision Incorporation for Network Lowest Revision. This will lessen the risk of new features being enabled in a mixed network after the downgrade.
"Secondary Revision" field in the node is used for the determination of the network lowest revision. Previous to this change, software uses only the nodes primary revision. The interoperability functionality uses network lowest revision for:
For a complete list of firmware revisions supported, see the Compatibility Matrix document, which is included in this release package.
All processor cards must be configured with a minimum of 32 MB of RAM. This includes BCC's and NPMs. NPMs require at least 1 MB of BRAM. To verify the BRAM size on IGX 8400 nodes, use the dspcd command.
 |
Note If any control cards contain less than 32 MB of DRAM (these would be NPMs) then they must be replaced with cards containing at least 32MB of DRAM prior to upgrading to Release 9.2. The physical upgrade of the nodes with these control cards must be done according to the upgrade procedure defined below. |
As specified below, the correct version of CC boot firmware must be installed on the cards prior to a software upgrade to Release 9.2.
With the new version of NPM boot code (RXS), the boot code upgrading does not require physical card resetting with the following steps:
Step 2 Execute the switchcc command and wait until the NPM(1) becomes standby. NPM(2) is now active.
Step 3 Execute the resetcd command to reset the standby (resetcd 1 h). Wait until the reset card NPM(1) becomes standby.
Step 4 Burn the boot code on the active NPM(2).
Step 5 Execute the switchcc command and wait until the NPM(2) becomes standby. NPM(1) is now active.
Step 6 Execute the resetcd command to reset the standby (resetcd 2 h). Wait until the reset card NPM(2) become standby
Each redundant pair of BCC cards in a given BPX 8600 node must be of the identical type and memory configuration. That is, for example, if the active card is a BCC-3-32, then so must be the standby. BCC-3 cards with 32MB of RAM can not be mixed with BCC-3 cards with 64MB of RAM.
Each redundant pair of NPM cards in a given IGX 8400 node must be of the identical type and memory configuration. That is, for example, if the active card is an NPM-32, then so must be the standby. NPM cards with 32MB of RAM cannot be mixed with NPM cards with 64MB of RAM. Also, NPM-64 cards cannot be mixed with NPM-64B cards.
This is a requirement for all software upgrade and downgrade procedures. It does not apply to the physical card upgrade procedure, as described below.
When performing a Control Card (CC) upgrade, the following procedure must be used. This applies to all processors: BCCs, and/or NPMs.
Step 2 Replace with new CC front and back cards. (Replace back card only apply to BCC)
Step 3 Wait for the standby updates on the newly installed standby CC to complete.
Step 4 Issue a switchcc command to utilize the newly installed CC.
Step 5 Verify that the network is stable.
Step 6 Remove the current standby CC front and back card. (Remove back card only apply to BCC)
Step 7 Replace with new CC front and back cards that are identical to the current active CC. (Replace back card only apply to BCC)
Step 8 Wait for the standby updates on the newly installed standby CC to complete.
Step 9 The CC physical upgrade is now complete.
Step 10 With the secondary card in the standby state, cause a switchover using the switchcc command. This will test that the hardware is working correctly.
 |
Note After Step 2, the node will contain a mix of an old type CC and the new type CC. This condition is only permitted while the standby updates to the new CC are in progress, which will take less than one hour. The time during which this mixture of CC types exists must be kept to a minimum, by immediately replacing the second old type CC with the matching one of the new type. |
1. Switch Software Release 9.2 is not compatible with UXM Firmware Model A.
2. If attempting to burn UXM firmware Model B into an UXM firmware Model A with 9.2 software, the firmware Model B will not be burned into the UXM card due to the incompatibility of software 9.2 and UXM Firmware Model A. The UXM has to be returned to Cisco for service.
3. If using M.E.A/M.E.B/M.E.C BXM firmware and upgrading to M.E.D or later, the 9.2.30 or later software has to be upgraded first so that the BXM will report 2 port groups for 2 port cards all the time. The smooth transition between the earlier 1 port group and the newly reported 2 port groups also displays message in dspcd "Inconsistency with logical PG #" (port group number). All earlier software will mismatch the card. This applied to BXM-OC3 or BXM-OC12 and configure to channel stat level 2 or higher.
4. Firmware MED and earlier supports APS Redundancy on Legacy BXM only.
5. Because of the hardware limitation, BXM hardware is not able to recognize all user programmed cell transmission rates. Rather only discrete transmission rates can be used instead.
The equation below shows what the BXM hardware actually transmits given a user configured cell rate. The transmitted cell rate is always less than or equal to the configured cell rate. To prevent any cell loss, the transmitted cell rate must be equal to the configured rate. To do so, a cell rate must be chosen from the table below.
The rate table below lists the highest 200 cell rates supported be BXM such that if used, will result in no cell loss (given cell traffic is less than configured cell rate). Additional rates can be calculated using 1470588/[n + (1/256)], where n is an integer.
The logic to calculate the actual cell transmission rate in a BXM card is as followed:
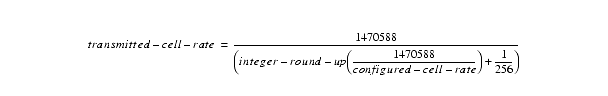
If a trunk is configured at 100,000 cps, the actual transmitted cell rate is then 98,013 cps, any traffic sent over 98,013 cps would be discarded.
If a trunk is configured at 98,013 cps, then the actual transmitted cell rate is 98,013 cps with no cell loss.
Therefore, only rates in the table should be used. Otherwise, cell loss may be experienced. The table will not be exhausted at the end but still go on with the computing from the above equation.
|
|
6. On the BPX with MGX 8220 feeder(s), regardless of the setting of the Node Parameter "42 Enable Feeder Alert", a feeder alert message will be sent to all MGX 8220 feeders immediately before a hitless rebuild takes place. The feeder alert message will temporarily disable the LMI polling from the MGX 8220 feeders. The MGX 8220 polling will resume as soon as the BPX is ready to exchange LMI messages.
7. The amount of traffic allowed on a VP Tunneling connection is 2/3 bandwidth of that connection. The minimum bandwidth must be 100 cells per second. For example, CBR connection with peak cell rate 1500 cps then can pass traffic up to 1000 cps.
8. For IMA trunk, the configuration is blocked if the converted cps (cells per second) of the number of links to be decremented is MORE than the transmit rate. (CSCdm71616)
1. For Switch Software 9.2, MPLS and PNNI controllers cannot coexist.
2. In release 9.2.30 and later, we have seen nodes declare communication break when using the BXM virtual trunking feature. The problem has been observed under the following conditions:
node_A ------ vtrk ----- node_B -----vtrk -----node_C
On the above diagram, node_B is a virtual trunk share a common port
With this topology, "node_A" sees "node_C" as unreachable and vice-versa; however, "node_A" communicates to "node_B", and "node_B" communicates to "node_C".
3. When cnfrsrc command is used to delete VSI partitions on an interface, software does not check if any Soft Permanent Virtual Circuit (SPVC) connections exists on that partition. Even if there are SPVC connections on a partition, the partition can be deleted using the cnfrsrc command. The only protection is that the user is provided with a warning when he tries to delete the partition.
If there are SPVC connections on a partition and if the partition is deleted, the SPVC connections will be left in a undefined and un-recoverable state. Hence, before deleting a VSI partition, ensure that all the SPVC connections are deleted on that partition.
4. Switch software 9.2.30 or later and BXM firmware MFC and later support the attachment of multiple MPLS controllers.
Switch software 9.2.30 or later and BXM firmware MFB and later support the attachment of a PNNI controller.
5. For UVM cards, there will be no new revisions of Model-A firmware. When attempting to download Model-A firmware to a UVM, software will give the user an error message indicating that the firmware does not match the card type. Note that there is no problem with continuing to use existing UVM cards running the old firmware. (CSCdp08741)
6. For a virtual trunk on a BXM/UXM, the Transmit Trunk Rate (the transmit rate of the virtual trunk) is configurable to match the PCR value of the subscribed public VPC service. In this release, the actual shaping rate for a virtual trunk is higher than the configured Transmit Trunk Rate (CSCdm80482). The actual virtual trunk shaping rates are 1/(n x 680 x 10-9) cells per second, where n is an integer from 1 to 29,411. In this release, the user configured Transmit Trunk Rate is rounded to the next higher (as opposed to lower) actual shaping rate for shaping.
To configure a virtual trunk so that the actual shaping rate is no greater than the PCR value of the subscribed public VPC service, the following steps can be taken:
Step 2 Configure the Transmit Trunk Rate for the virtual trunk to be less than 1/(n x 680 x 10-9) cps but greater than 1/((n+1) x 680 x 10-9) cps. For example, if the PCR value of the subscribed public VPC service is 10 Mbps or 23,585 cps, configure the Transmit Trunk Rate for the virtual trunk to be less than 1/(63 x 680 x 10-9)=23,342.67 cps but greater than 1/(64 x 680 x 10-9)=22,977.94 cps.
7. There is a new traffic class added in release 9.2.20 that causes a trunk parameter conflict with pre-9.2.20 node. The conflict fails adding trunk between 9.2.20 BTM/ATM and pre- 9.2.20 BTM/ATM.
All ATM traffic classes are set for BTM/ALM trunks and is hidden to user. Introducing of rt-VBR traffic class in 9.2.20 makes it different from pre-9.2.20 BTM/ALM trunk traffic class. The user can not change ATM traffic class for BTM/ALM trunk.
This problem exists with a new BTM/ALM trunk on an upgraded 9.2.20 node and does not exist with an upgraded BTM/ALM trunk since the rt-VBR traffic class is not set while upgrading. (CSCdm64345)
8. The cloud port to which a virtual trunk is connected should have ILMI polling disabled. Otherwise, it could lead to a virtual trunk being clear on one end and declaring Virtual Trunk Path Failure at the other end. (CSCdm52909)
9. In a BPX that contains BCC cards with 64MB, there is no limitation. All 12 available slots can contain BXM or Enhanced-BXM cards.
In a BPX that contains BCC cards with 32MB, a maximum of 10 legacy BXM cards are allowed. If some Enhanced-BXM cards are used in place of BXM, then each Enhanced-BXM will count as two BXM cards.
10. Due to performance reasons, AIS status of connections is not sent to the standby BCC. After switchcc, it may take few minutes to update the AIS status of connections. If dspcon does not show the proper status of AIS or dspalms screen shows incorrect number of AIS, (after switchcc) wait for few minutes so that the status gets updated. (dspalms and dspcon commands show the status of AIS).
11. Hitless Rebuild has similar limitations to that of a "switchcc" and full rebuild:
Some will be re-enabled automatically. These include:
All other stats have to be re-enabled for collection after a hitless rebuild takes place. These mainly include the user stats.
12. UVM cards in y-redundancy will mismatch if one is burned with Idle Code Suppression Firmware and the other is not.
When installing / burning Idle Code Suppression Firmware on UVM pairs, the y-redundancy must be removed, firmware in both UVM cards burned, and then the y-redundancy can be restored.
13. Mismatch is reported when replacing a BXM card with another BXM card that has different Port Group, even though both BXM cards have identical channel number.
14. When upgrading from release 9.1 to 9.2, the 9.1 statistics on BXM/UXM cards are supported to maintain compatibility. However, once a user configures a statistics level in 9.2, he can not configure back to 9.1 stats.
There is no 9.1 stats support for BXM/UXM cards that were shipped with 9.2 firmware since the BXM/UXM card has the default level 1 stats.
Therefore, when using an UXM with 9.2, a user must either:
15. The BXM and UXM channel stat level feature gives these cards the capability of collecting more than 4 statistics per connection. However it is the controller card's limitations, available memory and performance, that indicates how many statistics can actually be collected from the cards and then reported to the Cisco Wan Manager (CWM).
The BCC-3-64 can collect at most 3 interval statistics per connection when there are 16,000 AutoRoute (AR) connections configured on the node. (Interval statistics are those statistics that are reported to the CWM. They are often referred to as TFTP statistics).
You can collect approximately 48,000 statistics (3 x 16,000) on the BCC-3-64. This is approximate because there are many variables that will affect this value such as: are peaks enabled, how many buckets are collected, are all connection of the same type, are trunk, line or port stats enabled, etc.
With this approximation of 48,000 statistics on the BCC-3-64, this then means that as a rough estimate you could enable 32 stats on 1,500 connections, 48 stats on 1,000 connections or 9 stats on 5,000 connections, etc. The approximation formula being:
max_stats_per_connection = 48,000 / number_of_connections
16. In release 9.1, the UXM card ran a proprietary IMA communication protocol. This protocol matched that used on the MGX 8220 4 IMATM-B cards and hence could be connected together to form a trunk. In release 9.2, we now support standards compliant IMA on the UXM card and the standards compliant IMATM-B on MGX 8220 5.0 is not yet released. Hence, when the network is upgraded to 9.2.00, the UXM will be running compliant IMA protocol and the IMATM-B will still be running the proprietary IMA communication protocol. They will no longer communicate and the trunk will fail. This will be fixed in the MGX 8220 5.0 release containing IMATM-B. However, it should be noted that an upgrade at that time will also incur some amount of downtime as there will be a difference in timing between the MGX 8220 upgrade and the switch software upgrade. There should be no effect to UXM-IMA trunks connected to other UXM-IMA trunks in 9.1 to 9.2 interoperability mode.
17. We allow the transmit rate on an IGX IMA trunk to be altered at the local node with any trunk outage. It is possible that the transmit rates are different at the two ends of an IMA trunk. After this trunk is deleted, we cannot add it back unless the transmit rates are the same.
18. When doing a grouped upgrade from release 9.1 to 9.2, the software error 1427 may be logged on the BPX/IGX node during non-graceful upgrade. This error can be ignored since it is harmless to the network.(CSCdm14613)
19. Reconfiguring trunk parameter may cause connection to be rerouted if the changed bandwidth load is smaller than what was used by the connections that use the trunk.
20. If LMI/ILMI is provided by the BCC:
The maximum possible number of ports on the BPX 8600 that can be configured with LMI/ILMI enabled is 52. However, each BPX will support up to a total of 16 feeder trunks and each feeder trunk will have LMI enabled. That is, if a BPX 8600 is configured with only 2 feeder trunks, then only (52 - 2) = 50 ports can have LMI/ILMI enabled.
If LMI/ILMI is provided by the BXM firmware:
21. Virtual Path Connections with cells whose VCI values are above 4095 will be transmitted correctly if and only if the path is exclusively through BXM trunks and terminate at BXM ports.
22. The feature of CIR=0 for Frame Relay connections is not supported for connections terminating between FRM cards in IGX nodes and FRSM cards in an MGX 8220 shelf.
23. SVC Connections are derouted after decreasing the allocated bandwidth (increasing Stat Reserve). It is the design intent that increasing the statistical reserve will cause SVC conns to derouted and not be rerouted.(See bug CSCst92308).
24. For the loadrev operation, it is important that the Cisco Wan Manager/TFTP buffers are maintained at their default size.
25. Due to a hardware limitation, the BNI trunk will send 13 -15% more traffic than what it is configured for when the trunk is configured for less speed (cps) than the maximum port speed. This is especially important when the BNI trunk is connected to IMATM pairs, which carry less than T3 bandwidth.
26. When using the shift/no-shift feature on a BPX 8600 node's port card, controlled via the cnfport command, the other end of the connection must have the same setting. Otherwise, there will be a loss of continuity.
27. When deleting trunks, there is a known limitation with the switch software. The deltrk command should always be executed on the node which remains as part of the network, rather than from the node which ends up being removed from the network. This is to ensure that all the necessary updates are sent to the rest of the network. (CSCdi85134). Also, If the command is not used as recommended here, a software error 419 could occur (CSCdi91285).
28. Due to Trunk Based Loading, any commands having to do with trunk loading and the load model (dspload chklm dsplm, etc.) need to be done only after waiting a certain period of time. This time is directly a function of the trunk load update interval time (as configurable) plus the conditional update latency time.
29. The external ABR segment control loop on ForeSight (ABRFST) is an option at the User Interface. It is supported by UXM-E/BXM-E but is not supported by UXM/BXM hardware. The user should not enable this option on ForeSight connections (CSCdi92451). In any case, there is no coupling between the loops.
30. On a heavily loaded BPX 8600 node, during connection re-routing, the status of a particular connection is indicated as OK even though the line status of the other end of the connection is listed as failed. The connection is in fact OK, because the conditioning of the connection (to update the status for both ends) is done by a low-priority process so that the re-routing of the connections can be given high priority. The status will be eventually updated. (CSCdj10762)
31. A node whose number is greater than 63 cannot have a clrcnf operation performed on it. This is as designed. A clrallcnf can be done, or the node must be renumbered to less than 63 before running clrcnf. (CSCdj14920)
32. The interface between a BXM feeder trunk and an MGX 8220 feeder is always considered to be an NNI interface. (CSCdj16808)
33. When adding more than 4000 connections on a BPX node, the VC polling rate must be changed to a higher interval, to accommodate the additional time needed to poll for the statistics for each VC. The cnfsysparm command, parameter 24 must be changed according to the following:
|
|
|||||||||
34. Given a connection that terminates on an IGX 8400 FRM at one end and an ASI on the other end, tstdelay initiated at the FRM end may not work if the ASI firmware is below the appropriate revision and does not support OAM cells as opposed to supervisory cells. This is because the updated BTM on the IGX will always generate OAM cells. Please check the Compatibility Matrix.
35. Because the detailed card error event log is not retained within BRAM, this information will be lost should a processor rebuild occur. Therefore, when issuing a dspcderrs command on a particular slot, the display will not show the detailed card error information should rebuild event occur. This functionality has not been modified from previous releases.
36. When a physical-layer failure (e.g., LOS) is detected on the BXM, a Major Alarm is generated, and any connection routed over that port is downed (Fail state). The software sends a command to the remote end of the connection to generate AIS in the egress direction. (CSCdj30543).
Since the connection is in a failed state, AIS is generated in the upstream direction (in addition to the downstream direction). Although this does conform to the letter of the I.610 standard, this is not necessarily what a user would expect to see, because it interferes with the RDI response from the end-to-end connection termination point. (A fault in the downstream direction causes a fault in the upstream direction.)
Reason for the current implementation:
The BNI can not generate AIS. If there is a fault at a BNI trunk, the current mechanism is to cause AIS to be generated by the BXM port by downing the connection. Since the BXM can only generate OAM cells from the RCMP, and the RCMP is in the ingress path, the cells must be backward routed to the egress (egress QE). Also, since end-to-end OAM cells are required, the ingress QE must be configured to drop ALL cells in the ingress path. This creates a break in continuity in the opposite direction, and AIS cells must also be generated at the other end of the same connection, in the upstream direction of the original fault.
37. There are problems in the downgrade mechanism which can cause database corruption. If downgrade is performed immediately after upgrading, the Stby_Info revision fields are not yet filled in on the new active CC. They don't get filled in until the upcard response from the new locked CC. This causes restart instead of a switchcc. If the locked CC is reset, then downgrade immediately, a restart will occur instead of a switchcc. (CSCdj30811).
38. In order to test/simulate the Y-redundant switchover of ASI T3 or E3 pairs the resetcd command must be used, or by pulling out the active card. It will not be correctly simulated by doing a dncd (down card) on the active card. Using dncd will cause cell discards. (CSCdj08923).
39. UBR traffic gains an advantage over ABR traffic when UBR and ABR PVC's are combined on the same network. This is because UBR and ABR PVC's share the same QBIN (Class of Service Queue) on the BXM card. ABR PVC's use a flow control mechanism, VSVD, which ensures that traffic sources slow down when the QBIN usage exceeds the EFCI threshold. However, UBR PVC's do not have this throttling mechanism. Therefore, ABR will throttle back whereas UBR will not. This unfair advantage is not considered a problem, since the decision to share a QBIN for ABR and UBR traffic was intentional. Any best-effort service that one would route over UBR can be routed over ABR(VSVD), with the additional benefit of protecting resources in the network. If UBR and ABR PVC's are required then:
Option 1 - Consider adding all best-effort PVC's as UBR, or
Option 2 - Isolate the ABR and UBR paths by using cnfpref command to ensure that ABR and UBR PVC's do not share the same queues.
Option 3 - To provide UBR service on a connection, rather than setting up a UBR connection, do the following:
Step 2 Enable VSVD
Step 3 Disable FCES (Flow Control External Segment)
Step 4 Disable DEFAULT EXTENDED PARAMETERS
Step 5 Choose policing option "4" to allow access as UBR.1 (PCR policing only). This connection has ABR VSVD in the network and allows UBR.1 access. The MCR for such ABRSTD connection may be set at the minimum acceptable value of 6 cell per second (explained later why doing so).
To provide ABR service on a connection, set up an ABRSTD connection, enable VSVD and enable FCES to allow RM cells to be passed to and from customer equipment. The MCR for such ABRSTD connection can be set at any user desired value.
When the network is experiencing congestion, all the affected ABRSTD connections, regardless of the services (ABR or UBR) they are carrying, will all be throttled back at the VSVD points at the network edge. During network congestion, connections carrying UBR services are virtually stopped (to a through put of mere 6 cps) while connections carrying ABR services can send at a much higher, user desired MCR. This option would avoid that UBR service gains an unfair advantage over ABR service while sharing the same CoS queue.
40. Combining Frame Base Traffic Control (FBTC) and non-FBTC connections within a Class of Service can cause FBTC connections to not receive a fair share of bandwidth. For example, if VBR connections are added at a terminating port, and some of these VBR connections have FBTC enabled while other VBR connections have FBTC disabled, the VBR connections with FBTC disabled may obtain all of the excess bandwidth before the connections with FBTC enabled receive any of the excess bandwidth. The same holds true for ABR or UBR connections. This only is relevant where FBTC and non-FBTC connections share a QBIN, either at a port or at a trunk.
41. The maximum number of VC PARMs supported: 749 for BCC-32 MB, 2,999 for BCC-64 MB. (CSCdj48589).
VC PARMs are Virtual Circuit Parameters combinations/sets. One set of VC Parameter is used for each unique Virtual Circuit that has been provisioned. Identically provisioned VC's (exclusive of endpoints) use the same set of parameters. Thus, on a 32MB BCC, a total of 749 uniquely configured Virtual Circuits can be provisioned.
42. Care must be taken when changing the Deroute Delay parameter, which is controlled by the cnftrk command. This defaults to zero, but if set to anything but zero, connection re-routing, due to a trunk failure, will be delayed as provided by the parameter.
1. When adding a node into an existing network, ensure that its node number is unique prior to a actually adding it into the network. Use the rnmnd command, and renumber the individual node while it is still stand-alone. This will make the joining of this node much simpler, and will avoid the problem of node renumbering an active network, as described below.
2. There is a problem with node renumbering. Node renumbering (the rnmnd command) should be executed only during a stable network environment and only if absolutely necessary. A stable network environment would be, for example, one in which no connection was added for the past 30 minutes and no topology change was made in the last hour and there are no alarms or node unreachabilities. Node renumbering must only be done when the network is stable to reduce the possibility of certain temporarily blocked messages during the node renumbering process being delivered to the wrong nodes. This would occur after the completion of the node renumbering process.It is recommended that a node be renumbered prior to being added to the network.
3. The settling time for network wide updates can take a long time in certain situations. Specifically, the settling time for updates due to network wide topology changes and connections in a large network when a processor switchover occurs can take a long time. The time is proportional to the number of nodes as well as the number of connections. A general estimate would be 30 seconds per node. During the period of transitions (when the updates are occurring) some network operations such as adding connections might in some cases take somewhat longer to complete.
4. When using Cisco Wan Manager, there could be a problem with communicating with a node that just had a processor switchover. The problem is within the SPARCstation itself and its caching of EtherNet addresses. It can be solved by execution the following command on the workstation as the superuser: # arp -d <node_name>
5. Users may not use the command addcon slot.1-24 v to add 24 voice connections to a CVM/UVM at once. Instead, they must separate this activity into two or more commands, so that no more than 16 connections are added at once. This is only an issue for voice connections. Data connections can be added using the "1-24" syntax. This also applies when the CVM/UVM circuit line is an E1, in which case "1-32" would apply. (CSCdj14319)
6. Statistics must be disabled prior to the start of an upgrade, prior to the issuing of the first loadrev command. Stats should be disabled from Cisco Wan Manager which is Stats collection manager.
7. Statistics sampling must be disabled prior to the start of an upgrade (using off1/off2), prior to the issuing of the first loadrev command. Stats sampling state machine should be disabled from Command Line Interface.
8. When a switchcc is executed on a BPX 8600 configured with two BCC-4 cards and contains a BXM-622 trunk card, there may be a bad clock path problem reported. It is indicated as a Minor Alarm - bad clock path. This is a transitory problem, although the alarm indication persists. To clear this, execute the clrclkalm command.
9. Currently, T3-3 and T3-2 backcards are not interchangeable between ASI and BNI front cards, as this has been the case since the introduction of these cards. The back cards must be configured using cnfbkcd (with setnovram) so as to avoid backcard mismatch. (CSCdj41999)
The command dspbpnv can be issued to verify if the node had the new back plane or the old back plane. The following table details the bit fields for the BCC Backplane NOVRAM format, the display of word 2 describes the back plane type
The command cnfbpnv can be used to configure the backplane, if backplane is so enabled.
On the node on which it is executed, creates a loop back within the port such that the cells do not leave the card.
On the node on which it is executed, creates a loop such that incoming cells are looped back to the other end.
Removes the loopback added by either of the above two commands.
This will enable the card synchronization feature.
This will disable the card synchronization feature.
In order for the feature to work, the line statistics sampling should always be enabled (via on2 1 command) and the front card installed must support the card synchronization feature. The dspcd command provides any easy way to determine whether the front card supports this new feature. If the front card supports the feature, the following message is shown on the dspcd screen:
Front card supports card synchronization
Additional debug commands are added to allow synchronization between the interface card and the CC database:
<slot_number> for a particular slot that supports the card synchronization feature; * for all cards that support the card synchronization feature.
This command displays the number of connections reconciled during the synchronization process after a switchcc for different slots.
* for all slots supporting this feature.
For a complete list of firmware revisions supported, see the Compatibility Matrix document, which is included in this release package.
This release will run with Release 4.0.0x, 4.1.0x, or 5.0.0x of the MGX 8220.
 |
Note IGX-UVM model E is a superset of models A, B, C firmware. A, B, and C are obsoleted and should not be used. |
The following is the list of known anomalies in this Switch Software delivery. Included with each is a brief discussion of the problem. A more in depth discussion is available in the release note enclosure of the problem record in Bug Navigator
| Bug ID | Description |
|---|---|
|
The specifications require that when we have more than 10 consecutive SESs, then we should enter UAS. This feature is not implemented; therefore, no UAS alarm is generated. In order for this feature to be implemented, a combination of fixes on firmware and switch software must be completed; namely: CSCdk48827—Firmware bug to fix the thresholds for SES to start kicking in. This is fixed in firmware image BXMMCB or later images. CSCdk48816—The software portion of this problem to alarm based on UAS. Without the software fix to this bug, customers cannot upgrade firmware beyond MBY. This situation is caused by the following: When the switch enters UAS, per specification, it stops counting Bip8 ES and SES. Therefore, there is no alarming on the ES SES. MBY provides a temporary fix to keep the ES alarming on by raising this threshold. Continue to use MBY firmware, thus preventing SES alarming to kick in. The side effect is that this will prevent the customer from using the features introduced in the MC firmware. |
|
|
The command dspport is not available to level 6 user IDs. This symptom is visible after an upgrade from 7.x software to 8.1+ software. The privileged level of the dspport command was changed in release 8.1 to level 2 from level 6. This difference was first noticed by an offsite user after upgrade from 7.4 to 8.5.05. Users running 8.x.x software hasven't noticed this difference until the current time. |
|
|
The NPM 2 restarts due to a Watchdog Timeout. Occurs after running the resetsys command to reset all the cards (except the active NPM card) on an IGX node with a lot of active connections. When the standby NPM comes up, the event log mentions that: "NPM 2 Restarted due to a Watchdog Timeout" where 2 refers to the slot number of the standby NPM card. This does not affect any functionality except for the information added to the event log. Instead of running the resetsys command, individually reset the cards using the resetcd command. |
|
|
The switch software system idle time is below 30% when more than 10 UVMs are activated Switch software polls each activated UVM for modem status every 1 second for each port. Switch software also spends time in processing the responses of the modem polling. When many UVMs are activated, the modem polling handling consumes a lot of system time and resources (buffer queue) which affect system performance. UVM firmware has supported asynchonous event to report modem event. Switch software needs to stop polling modem status if the firmware in UVM supports the async event. Use the cnfnodeparm 46 command to increase the polling timer to improve system performance. |
|
|
Using the command dspchstats on a BXM does not display all channel statistic values. During 9.1.08 system software testing, lab personnel discovered that the BXM statistics usually recorded in an enhancement in switch software 8.4.09 had been removed. |
|
|
When a bus error occurs on a node, and a rebuild results, other nodes in the network will see the rebuilding node in the degraded state. This shows up as "UNDeg" in the dspnds screen. A log message will also appear on these other nodes indicating that the rebuilding node went unreachable due to degradation. The unreachability will recover automatically. Only occurs if a node rebuilds due to a bus error, and degraded mode is enabled in cnfnodeparm. Will not occur if a node switches processors due to a bus error. |
|
|
It takes longer than expected to clear unreachability with a node that has rebuilt due to a bus error. Other nodes in the network will declare the node unreachable due to degradation ("UNDeg"). The unreachability will eventually clear automatically. Only occurs if a node rebuilds due to a bus error, and if degraded mode is enabled in cnfnodeparm on that node. |
|
|
The BXM-T3 line is configured to be in the Direct-mapping (HEC) mode and the CAC override is Disable at the port. When attempting to add a single connection to a BXM-T3 line with a PCR=104268cps, the system rejects and return an error "CAC override disabled on port". This indicates that the request will over subscribe on the line but in fact it is NOT CAC override is Disabled. BXM-T3 line is set for Direct-mapping (HEC). Attempt to add connection with PCR=104268. |
|
|
IGX node stopped responding to console and lan port. Node logged Abort 3000000, software error 504 and multiple software error 52's. Node had to be powered off and on to clear problem. This problem occurred immediately after configuring a UXM. This appears to be CBUS flooding issue. Instead of powering down the node immediately, pull out the cards in the node one by one in order to reset a card that is possibly flooding the processor. |
|
|
Upping a line via on ALM-A cards fails when using SNMP. SNMP set was given for an ALM-A card as follows: switchIfAdmStatus Up(1) switchIfService atmAccessPort (3) Use the command upln from the CLI in order to up a line on an ALM-A card. |
|
|
ILMI manager works only on one sub-interface. On a Cisco 7500 switch, if multiple subinterfaces are configured on an ATM interface connected to a BPX switch, each of the subinterfaces with 1 PVC and BPX is configured to send ILMI traps. When the PVC's state is changed on a BPX, the BPX will send out traps for all the PVCs; however, the Cisco 7500 switch only brings down one subinterface (one PVC). |
|
|
Inverse Mux Failure appears after upping an IMA line or trunk and does not clear. Occurs when upping an IMA line or trunk. This problem is observed only on T1 lines, and only when a combination of commands are used to bring up and configure the remaining IMA group members on the primary line: Up the line or trunk quickly on both ends using the upln or uptrk command to include all the physical lines of the IMA group. That is, do not use upln and uptrk to establish the line or turnk, then use cnfln and cnftrk to add the group members. |
|
|
Switch software error 532 is logged while doing snmpwalk or snmp MIB browsing. BXM feeder trunk with YRED pair and secondary card is active. |
|
|
Equipment MGR can't tell the difference between a BXM legacy card or a BXM-E (enhanced) card. Log into the BPX node and issue the command dspcd <node> to view the number of channels supported. The BXM legacy card supports less than 61K channels, and the BXM-E card supports 61K channels. |
|
|
The command cnftrkparm does not alter non ts transmit queue size correctly. NTM subrate trunk (with number of DS0 <= 8) and cnftrkparm is issued to increase NTS Q depth to either 84 or 85 (maximum) for an added trunk. |
|
|
The ASI Qbin configuration is lost when Y-Red switches over to secondary card. This problem can occur when the ASI Y-Red - Secondary Card is active |
|
|
The BPX is not sending APS robust alarm messages to CWMs for multiple APS events. APS events are being lost. The BPX only sends APS robust alarm messages to one CWM. The problem of the BPX not sending all events happens when multiple events happen in a short span of time. The problem with only sending the APS robust alarm message to one CWM will always happen. The robust alarm mechanism currently used needs to be enhanced for APS robust alarm messages in order to handle mutliple APS events occuring in a short period of time. Also a fix needs to be made to allow a BPX switch to send APS robust messages to all attached CWMs. |
|
|
Switch software error 136 is logged This problem occurs during an upgrade from 9.1/9.2/9.3 to 9.1/9.2/9.3. During upgrade, the error message sw136 fills the software log.(swlog). This is due to conv_parm which is called with 0. |
|
|
No redundancy after certain events occur. 1. A frame relay connection from UFMU card in same chassis working well over UXM to UXM Yred trunk. 2. Yred Trunk fails and moves to standby, connection still working normally 3. Trunk forced back to Primary in Yred pair using the commands dncd or No errors logged in node logs. dsplog, cderr, swlog. dsptrkstats show OAM and BDataB traffic stopped only. Hi pri cells still traverse trunk. |
|
|
The ILMI protocol keeps running on the BXM card even after it is disabled using the cnfport command. The problem occurs only when all of the below conditions are true: 1. The ILMI protocol should have been running on the BXM card for the port. 2. Disable ILMI protocol on the port. 3. Say NO for Protocol by the card. Disable the ILMI protocol on the port. Let the protocol run by the card to be set to YES. as before. |
|
|
BPX returns an error indicating there are no channels available for networking when attempting to create a trunk or line. A precondition is that all channels on this card are currently being used by existing trunks or lines. When a trunk or line is deleted (then theoretically freeing up channels for another trunk/line), and a user attempts to subsequently recreate this trunk or another trunk (intending to usethe very channels that were just freed by the removal of the previously mentioned trunk/line), the user finds that no channels are available to create a new trunk. Perform a hardware reset on the involved BXM card, and then the channels will be available that are no longer in use by the deleted trunk/line. |
|
|
For an ATM port. When addjob is used to configure existing the ATM port as a Frame Relay port and all the parameters are not given in the same line.
Node aborts when you try to add a job to configure EXISTING ATM port to Frame Relay port. This does not affect any other commands like configure port Do not use the command addjob to configure existing ATM port to Frame Relay port. |
|
|
While the UFMU port is up, removing the back card results in the port status still showing active—it should be FAIL. In all previous switch software supporting the UFMU card, this problem exists. Install the UFMU card with any type of back card, run upport, remove the back card, and check the port status. It is still ACTIVE. Further problem: The port status is sent to CWM by robust message, for old SWSW without the fixin, this could cause a problem within CWM if CWM is only checking the port status without checking the back card missing alarm (to do some other configuration, such as addcon, addtrk. In the old switch software, the card missing is checked before addcon. |
|
|
BXM cards go to Active-F state. |
|
No release note information is currently available on this item. |
|
|
Connections get rerouted when the active line of an APS goes in yellow alarm. Active line is in Yellow alarm and Standby line is OK. This behaviour occurs on a regular trunk. On APS, even if the active line is in alarm there can exist a path to transmit and receive the data. For example, if the Active line is in Yellow and the Standby line is in LOS, then using Rx of active it can receive the data and using Tx of standby it can send the data. |
|
|
Value of the reroute timer displayed in cnfcmparm after the commands clrallcnf or clrcnf are executed is 0 seconds instead of 3 seconds (default). This problem is created by clearing the configuration with clrallcnf<cncmdBold> or clrcnf. Use cnfcmparm 9 to set the reroute timer value. Problem is due to using different units for the reroute timer value during initialization and modification. After running clrallcnf or clrcnf, the reroute timer is initialized to 3 seconds (default). Whereas, cnfcmparm treats the value as the number of ticks. Therefore, for a default value of less than number of ticks per sec (100 ticks/sec), cnfcmparm displays a reroute timer value of zero. When the reroute timer value is set using cnfcmparm, conversion to the number of ticks before updating the reroute timer solves the problem. |
|
|
The trunk utilization display appears inaccurate for a BXM-OC3 trunk. A BXM-OC3 trunk always shows 1% utilization when transferring data over the OC3 trunk from 0% to 10% to 50% to 100% of OC3 rate. |
|
No release note information is currently available on this item. |
|
No release note information is currently available on this item. |
|
|
IGX switch software won't update the trunk and gateway channels of a trunk if that trunk doesn't belong (connected) to this node. This problem can occur only when channel reconfiguration is attempted using the commands cnrsrc or cnftrk. |
|
No release note information is currently available on this item. |
|
No release note information is currently available on this item. |
|
|
The average cell per second (CPS) values displayed when the dspchstats command is issued do not always reflect the correct transmit rate. It ramps up to the transmit rate, sometimes very slowly, some times more quickly. This problem occur whenever the dspchstats command is issued. For the dspchstats screen the only values that are incorrect are theCollection Time and Rate (cps) field values. We can extrapolate this information from the TFTP or USER interval statistics, which has a minimum granularity of 5, 10 or 15 minutes based upon the number of connections they have in the network. If we divide the Port Cells Received on Channel statistic by the interval (5, 10 or 15 minutes), the result is the approximate average CPS. The root cause was that a timer's initialization was removed by a different defect fix. The result or removing this initialization is that vcs_cur_ticks timer does not get reset so it contains the last time that the previous response was received rather than when this response was received, so the time value is too large. Then when we calculate the average CPS, since the time value is too large the average is way to small. It will eventually (over an extremly long period of time) approach the correct value, asymptotically. t = A Normal statistics polling response is received from the card, vcs_cur_ticks is set to now (A). t = B The command clrchstats is issued, which sets flags to drop the next sample (for summary statistics) and to reinitialize the vcs_cur_ticks field. t = C The command dspchstats is issued, which causes a statistics poll to be sent to the card and a response to be sent back nearly instantaneously. When the response is received we see that the summary statistics filter flag is set, so we drop the first response (and we should set the vcs_cur_ticks field at this point but we don't). t = D The command dspchstats sends its second poll request, and we get back the response. We update the data for cells RX/TX, etc. We calculate the amount of time this data is for by subtracting the vcs_cur_ticks count (A) from the current time(D) so the time delta is (D - A). The problem is, the time value should be (D - C) but because the intialization code was removed it is (D - A), too big. The connection polling rate can be configured to 5, 10 or 15 minutes, therefore the amount of time that this can be off by is 4'59", 9'59" or 14'59". It can also coincidentally be correct if t=A and t=C are very close to each other. |
|
|
Gateway LCNs count may exceed trunk channel count if the cfrsrc command is executed at the BXM and trunk channel is reduced and falls below the gateway LCNs. Occurs only in the above scenario. Configure the trk channels and gw lcns at the UXM end (using cnftrk). |
|
|
UXM mismatch occurs following a card rebuild. 1. Reset the controller card with a standby UXM in the node. 2. Activate the UXM which has the number of channels smaller than 8000. 3. Remove and reinsert the UXM card (or reset UXM card). Deactivating the card, then reactivating the card, clears the problem. |
|
|
The trunk temporarily failed after switchapsln due to the Yellow alarm When an active APS line is in Yellow alarm, doing a switchapsln on the APS line fails the trunk for 30-40 seconds. |
|
|
Neither the dsplog (displays no record) nor CWM (receives no trap) when an APS active line goes into Yellow alarm. An APS line in yellow is expected to be shown under dsplog as well as having a trap sent to CWM. This bug is introduced because of 9.2.32 fix MR 000253 (CSCdr26613). Said fix set the trunk status to clear if the active line is Yellow and the standby line is OK. We will remain dsptrks command to show the active line status and trigger trap, unless we can find a clean and easy path to send trap without setting the trunk to the Yellow alarm status. The user can run the dspapsln command to monitor the APS line status. |
|
|
Can't stop switchcc command—switchcc continues executing evenif user says "n" when asked to "Continue?" Issue switchcc on a BPX node, and if standby updates are pending, if the user replies "n" to not continue the switchcc, switchcc still continues. Do switchcc only after updates are over. Use dspcds and dspqs to verify that the standby card is in "Standby" state and that no updates are pending. |
|
|
In 9.2.3z, the APS dsptrks command can show a communication failure when it has LOS. When an active APS line is in LOS, the following can occur: Doing a switchapsln with option 4 to switch from a protection line to a working line can cause the trunk to fail. |
|
|
Control VC establishment failure in ports. Condition: Total sum of VSI Bandwidth(BW) on all interfaces on the card exceeds the OC12 BW range of 1412830. Reconfigure the VSI BW on the various interfaces on the card, so that total VSI BW does not exceed OC12 BW. |
Following is the list of fixed problems in the 9.2.33 Switch Software release. Included with each is a brief discussion of the problem.
| Bug ID | Description |
|---|---|
|
A node whose number is greater than 63 cannot have a clrcnf operation performed on it. Workaround: Use the command clrallcnf on such a node; otherwise, the node must be renumbered before running the command clrcnf. |
|
|
Switch software error 921 is flooding to the software log. Occurs after a switch software upgrde from 8.1.73, 8.4.21 and then 9.1.04. This problem also has been experienced after upgrades from 8.2.59 to 9.1.04, and from 9.1.10 to 9.1.19. Workaround only to be performed by qualified personnel. Please contact Cisco TAC. |
|
|
Customer cannot free up any VCPARMS from the VCPARMS table (limit of 255 has been reached). Despite reconfiguring connections to make them join an existing VCPARMS index, the parameters cannot be successfully matched. Only Frame Relay connections are affected. Connections on UFM Model A have variable configurations for VCq and ECN threshold. This causes use of different VCPARMS entries. 1. Use the command cnfcon from both ends of connection, cnfcon * ... from both ends. 2. Delete and readd the connection. 9.1.06 has two defects CSCdk83358 fixed in 9.1.07 and CSCdk63187 fixed in 9.1.10, both dealing with the modification of VC queues. As a result, the VCPARMs indices are not reused. Furthermore, UFM model A has altered VCq and ECN thresholds creating new profiles. UFM model B firmware will allow reconfiguring the queues to FRM values. |
|
|
A trunk configured for VSI only is then reconfigured for VSI + Auto Route. After the configuration change, the command addtrk was issued, and failed. This is most likely caused due to VSI database inconsistancies during switchyred. This problem occurs only if VSI is configured on the trunk. Delete and add the partitions on both the trunks. After this, the addtrk command will work successfully. |
|
|
After performing a software upgrade on a node, the node rebuilds after the loadrev of the new release is executed. After the rebuild, the card that was active is failed. The detailed card display shows the failure reason as "Flash EEPROM Program Failure." The rebuild may also be observed if the active CC fails while the standby CC is in the Upgraded state, or if a standby CC is inserted while an active CC is failed. Card failure on active CC when the standby CC is in the Upgraded or Downloaded state. One example is a flash EEPROM failure after using loadrev to program the upgraded version of software in flash memory. Another example is inserting a standby CC while the active CC has an EEPROM or SAR failure. 1. Use the standby control card unlocking procedure that specifies a dummy revision name for the first loadrev. The unlocking procedure is to accomodate flash failures during the unlocking process. This procedure is part of most upgrade procedures, but if ommitted during the upgrade, can result in the problem described above. 2. Do not reseat the standby CC while there is a card failure on the active CC. Allow the standby CC to become standby, or clear the failure on the active CC prior to inserting the standby CC. |
|
|
Characters are not echoed to the user as they are entered during a telnet session to the switch. Occurs during Telnet sessions initiated from a host running AIX. Explicitly set the mode of the telnet session to character at a time mode. Enter mode char from the telnet command line prior to logging into the switch. |
|
|
1. The command dspsloterrs shows "SIU Phase Errs" for one or more slots with BXM cards. 2. A cbus trace on the 0x50 function code message sent to BXMs shows the 19.2 G backplane configuration object (0C 01 01). A BPX switch with a BCC-4 active processor, one or more BXMs, and a 9.6 G (old type) back plane. This probable is most to occur after a non-graceful upgrade. 1. Switchcc on a node with a standby BCC, or reset the active BCC on a node without a standby BCC. |
|
|
1. Different values for the statistical reserve are displayed when the commands dsptrkcnf and dspload commands are issued. 2. Value of statistical reserve gets truncated to less than 65535 if trunks are deleted and readded. Value of statistical reserve is configured greater than 65535. Problem (1) has been fixed by CSCdk89096. Problem (2) has been fixed in this case. Both were caused due to a "round-off" problem (32 bit to 16 bit casting). |
|
|
Run job having subsequent addcons and delcons on the same connection experiences failures. Job scripts can be rewritten such that: 1. Commands to the connections alternate between different connections instead of having addcons and delcons on the same connection. 2. Increase the number of rc/ra counts in the jobs. Jobs doing an addcon on a connection immediately after a delcon on the same connection has failures. This is because the software gives control back to the CLI during a delcon before releasing all the connection resources. The resources are released after a timer expires, which can be maximum of 2 seconds. Addcon on the same connection before the timeout would fail. |
|
|
1. UXM physical line alarms are not sent to the SV+ maintenance log, but are instead logged in the node's local event log. 2. If the node terminating an IMA trunk is a SV+ gateway node, the alarm is logged in the SV+ maintenance log for the gateway node only. Problem occurs when an IGX node using UXM IMA T1/E1 trunks experience a physical line failure. |
|
|
Using the upln command on ALM-A cards fails when tried via SNMP. |
|
|
An SNMP get or walk on the atmTrunkStatsTable for virtual trunks returns only 5 of the 11 valid statistics values. The following conditions are needed for this problem to occur. 1. A UXM card with virtual trunks up. 2. Traffic is passing through the trunk. An SNMP get for a virtual trunk returns valid data only for the following mib objects: atmTrkStatsTotalCellsRxFromPorts There is no distinction between virtual and physical trunks with respect to the ATM trunk counter statistics collected by the switch. Hence, the following mib objects, currently return a (0), should also be valid for virtual trunks: atmTrkStatsTxBdataBCellDrps Customer Impact: No workaround. This has been fixed. The main cause for this problem is explained below: The get function for the atmTrunkStatsTable differentiates between virtual and physical atm trunks and defines only a subset of the offsets of physical trunks to be valid for virtual trunks. This is probably a sideeffect of the attempt to add virtual trunking function to BTM trunks. There is no difference in the statistics supported for virtual or physical trunks and this code has been cleaned up. |
|
|
The software logs 961 while downing the last trunk or last line on a BXM card. This problem occurs only under the following conditions: 1. Have connections routed over any BXM trk. 3. Issue a deltrk command. Make sure that this is the last trk on the slot. |
|
|
Switch software error 129 is seen on a node. There can be a number of different reasons why this error is seen. This fix is simply trying to reduce the possibility of multiple tasks trying to access the same software error buffer simultaneously (i.e. a race condition). If one task is already accessing the buffer, the other task which tries to generate another software error is prohibited from doing so. |
|
|
Background test errors are seen on cards with ports with VSI partition configured. The VSI partition is assigned VPI=0, and data is sent on the port that uses VPI=0. |
|
|
When the line is downed, the LED remains on The line is downed by using dnln command, but the LED does not reflect the DOWN condition. Instead, it remains in the UP condition, and stays green. The LED sould be in RED when the line is downed or inactive. It should be in green when it is active and up. |
|
|
The value of the "conids used" and the "vpc conids" used is wrong in the DNIB display/dspload information for a trunk at the remote nodes. The value of the conids used is displayed as the actual value of the vpc conids used and the value of the vpc conids used is displayed as zero. Problem can occur when some connections are added or deleted such that the total load (as well as the total load of each type) on the trunk remained the same, but the number of conids used changed. This condition should change automatically as soon as there is a change in the load on that trunk. |
|
|
Switch software errors 614 or 612 or 325 are displayed after a fall back to software release 9.2 or 9.3. 'dlcon 11049' in 9.2.30+ shows lcon index as 0. |
|
|
The second physical line on an UVM cannot send an alarm to the attaching CPE. This can cause one of the following symptoms: 1. T1 CCS line conditioning (cnflnsigparm command, option 12) does not work on the second physical line on any UVM 2. 2. The second physical line on a UVM will not function as the secondary line in a line passthrough configuration 1. T1 CCS line conditioning is enabled (cnflnsigparm, option 12), and at least one of the channel connections on UVM second physical line fails. 2. Using the second physical line on an UVM in a line passthru configuration (cnflnpass) The IGX does not send an alarm to the CPE which attachs to the second line on a UVM card. If T1 CCS line conditioning is enabled, IGX sends the yellow-alarm to the CPE (PBX) whenever one of the channel connections on the T1 line fails, or when the remote CPE (PBX) sends a yellow-alarm to the IGX network. This defect prevents the IGX from sending the alarm to the CPE which attachs to the second line of a UVM card. |
|
|
Several 618 switch software errors are logged, followed by a group of 429 switch software errors. Subsequently, it is possible that a third group of 2085 switch software errors are logged. The situation happens under the following conditions: 1. The node is configured with the maximum allowable number of virtual trunks on a physical port; for example, 32 virtual trunks on a BNI-T3 port. 2. A local rebuild is performed on the node. If it is imperative to retain the maximum number of virtual trunks on a port for the node, make sure that local rebuild is not triggered on the node. A better alternative is to refrain from configuring to the maximum number of virtual trunks. For instance, 31 virtual trunks on a BNI-T3 is okay. Once the problem occurs, the trunk database has been corrupted. In many test instances, bringing the trunk down (dntrk command) followed by rebuild or switchcc did not cure the corrupted database. The only foolproof way to restore the node is to clear the configuration (clrallcnf command). |
|
|
Bringing a UXM line up causes the user command line interface to be sluggish or unresponsive for a short time. On UXM cards, upping a line with the upln command causes CPU usage to increase greatly if there are a great many connections on other ports on that UXM card. This problem is due to connection conditioning. |
|
|
When a port or VI summary statistic (displayed through the dspportstats command) overflows, only that statistic is cleared. The other statistics are not cleared. The following conditions are needed for this problem to occur. 1. A BXM/ASI card with ports up. 2. Traffic is passing through the port. After some time, one of the statistics overflows. The summary statistics collected for the port/VI are inaccurate as they are collected over different time intervals. The inaccuracy results from the fact that if one statistic overflows and wraps around, it would contain information for a shorter time periodwhile other statistics would contain information for a much longer time. None. This problem has been fixed. The main cause for this problem is explained below: Every <polling interval>, summary statistic databases (of size ULONG) are updated with the statistics obtained from the firmware. Before updating a summary statistic counter, a check to verify if adding the new data would cause an overflow should be performed, in which case the entire summary statistic database should be cleared. This is to ensure that all the summary statistics are collected over the same period of time. There was a bug found in the code, wherein, we add the new data to the counter and then check to see if an overflow occured. Since adding the data first would already have caused the overflow and wraparound, the ensuing check will not be able to detect it and hence, the entire database is not cleared. |
|
|
Switch software error 2000 is logged when snmpwalk is done or snmpget is done for switchIfCtrlVPI and switchIfCtrlVCIStart mib variables on an IGX. |
|
|
Cross point test from a BXM card to ASI card fails The port on the BXM card is configured as NO SHIFT. 1. Change it to SHIFT or have a lower number port on the same card with SHIFT. 2. Add a connection that ends on the "SHIFT" BXM port using VPI/VCI 1/257. |
|
|
The Channel count reported to Cisco Wan Manager in the SVR_TRUNK_OBJect for virtual trunks is the sum of all the virtual trunk channels. |
|
|
Over allocation of bandwidth on qbin 2, used for HP traffic (CC traffic). This problem is seen when switch software 9.2.3x,which doesn't contain this fix but recognizes the object 0x0C/0x53 message, and going to switch software 9.3.0. This problem occurs only for the above scenario. Normally, while going from 9.2.3x software (which doesn't contain this fix) to 9.3.00 software, the firmware will be burnt first as part of the process. In this scenario, it may result in the condition as said above. |
|
|
The VT session is broken by a timeout when running the command dsprts . BPX is running switch software release 9.2.30, and the BXM is BXM-155 FFA SM-8 BB and in Active mode. USe the dsprts command when logged in through telnet or through the Control Port rather than logged in through VT. |
|
|
Burning firmware on a stand alone card generates an error. |
|
|
Not all IMA line/trunk group members are being tested for alarms when running line loop diagnostics. This problem occurs for IMA lines and trunks with more than one link. |
|
|
Cannot run the command tstdelay while the card is being initialized. BXM in line configuration with y-red and the redundancy is currently active. |
|
|
Doing addshelf and VSI partition using the same VPI can cause a communications break. When addshelf (i, a, or x) is done using the command cnfrsrc to configure VSI range to cover VPI = 1 and/or 3. |
|
|
After a FAIL return of the cnfpwd command, echo is not turned on. The failure has to be "Communication Error, try again later." Log out and log back in again. Echo is turned on after the password is entered again. |
|
|
The LMI channel on a feeder trunk is not deleted after the delshelf command is issued. |
|
|
The error message "Card does not support High Priority traffic" is overwritten by another error message "Invalid Bandwidth Parameter." |
|
|
Trunk failed if a mapping device is used in middle of the trunk and the ds0 mappings on both ends are different. The problem occurs when a trunk is added—the mapping device used in middle of the trunk and the ds0 mappings on both ends are different. None. For a trunk having a mapping device, it is not supported in the software to change the line DS-0 map after the trunk is added. |
|
|
After a Y-red switchover, all connections failed. This problem occurs only when the standby card is in self-test when addyred is executed. Do not execute addyred while the standby card is in self-test. If Y-red has been added while the standby card is in self-test, then reset the standby card to force the configuration to be sent to the card. |
|
|
The summary trunk Qbin statistics displayed via the dspqbinstats command on the BPX switch cannot be cleared by any of the existing clrear statistics commands; for example, clrtrkstats for trunk Qbin statistics. The symptom is seen under the following conditions: 1. Line statistic sampling is ON (on2 1). 2. The switch collects non-zero summary Qbin statistics for trunks which are displayed by the dspqbinstats command. 3. Issue a clrtrkstats command to clear all summary trunk statistics collected for one or more trunks. 4. Issuing the dspqbinstats command on the cleared trunks indicates that the summary Qbin statistics for the trunk have not been cleared. The trunk Qbin summary statistics cannot be cleared unless the trunk is brought down and then brough back up again. None. This problem has been fixed, and issuing the command clrtrkstats <trunk> clears the QBin trunk statistcis, too. In switch software release 9.2 (when the dspqbinstats command was added on the BPX), the code for clearing the Qbin statistics was not added to the clrtrkstats command. This problem has been fixed. |
|
|
Node aborts when the command addloclp is issued on a DAX connection terminating on a BNI feeder. The following conditions must be true for this to happen: 1. A BNI feeder is added using SNMP 2. The BNI feeder was the last line/trunk added to the node. 3. The node has not been rebuilt since adding the BNI feeder. If the node has already aborted, the problem will not happen again, unless the above conditions are re-established. If the node has not yet aborted, the problem can be avoided by upping any line or trunk on the node using the CLI. |
|
|
Switch software error 1012 is logged when the total connection channels on a UXM card exceeds the available LCNs on that card. The events hitless rebuild, switchcc, node rebuild, and reset card triggers the recalculation of LCNs configured on ports and trunks activated on the card and during this process, if software finds the total configured channels exceeds the available LCNs, then it logs software error 1012. As soon as software error 1012 is triggered, the software resets the the total used card LCNs to the endpoints on that card. For example, if there are 1000 connections originating or terminating on this card, the "total number of LCNs used" field points to only 1000, though this card has trunks activated if any which is not accounted. It is strongly recommended to execute the workaround enclosed here before doing any connection provisioning (addition, rerouting ) on this card. The symptom may occur when "connection channels" configured per UXM trunk become corrupted during the collision of "connection channel" reconfiguration at the same time on one side of the trunk. For example, reconfiguring the connection channels on any one trunk (UXM_1) and any one trunk (UXM_2) at the same time may lead to the corruption of the "connection channels" field. This is a very rare condition. 1. Loop through all the trunks activated and check for the number of channels configured per trunk. 2. Add (270 times the number of trunks upped) to the above (270 is for networking traffic) if it a legacy UXM card. If it is UXM-E, just add 270 to the above irrespective of the number of trunks activated. 3. Add "total # endpoints originating or terminating on this card" count to the above. 4. Make sure the total of all the above does not exceed the "total LCNs" supported. If it does exceed the total, reconfigure in such a way to meet the above condition. |
|
|
Switch software error message 987 is logged. This symptom occurs when Configure a port to run LMI or ILMI |
|
|
Potential problems in connections setup using VSI controller (either PNNI controller or an MPLS controller) if the connection uses VPI=1, VCI=257. Condition: A VSI based connection uses VPI=1, VCI=257 and BCC selftest is enabled using the cnftstparm command. |
|
|
When the dspchoid command is issued, the IP relay channels are not displayed. For example: should display information on channel 8009, but it displays the following error instead: "Channel # 8009, greater than 8006, out of range" This symptom occurs when (8000 + (2 * max_port)) is not within 8009-8016 |
|
|
An snmpset request is rejected when the value for atmPortQueueDepth is set higher than 11000. This symptom occurs due to a limitation of the interface. Through SNMP, the maximum value for atmPortQueueDepth is 11000. However, the comand line interface permits a maximum value higher than 11000. Use the CLI command cnfporq for configuring an atmPortQueueDepth value larger than 11000. |
|
|
Traffic is dropped on the vpi.vci 0.18. A path connection was added on the port using the vpi zero. ILMI protocol was enabled on the port and was using 0.16 as the vpi.vci. Configure the ILMI/LMI protocol to use a different VPI, or do not add a path connection on the VPI 0. Basically do not have the path connection and the ILMI/LMI protocol use the same VPI on the same port. |
|
|
For Y-red UFMs, and if the active card is secondary. Under such conditions, when switch software receives an 0xB5 message, the feeder port database updating for the standby NPM and feeder port robust message is wrong. This symptom occurs when the active card is secondary for Y-red, and the standby NPM gets incorrect database updating. |
|
|
Adding a connection (addcon command) between the UFM and UXM fails from the UFM end. This symptom occurs due to uninitialized cd_type; therefore, failing of addcon may be random. |
|
|
NMS does not move connections to the standby node when the card in the primary node is removed and the standby node/port lifts the lead state. NMS cannot detect hardware failure or a missing card in the switch. When the card is removed, the connection needs to be moved to standby node by operation. |
|
|
NTS connections get bit errors when FrameRelay bursts fill up the trunk capacity. The symptom occurrs when Voice, FAX and NTS data are competing for bandwidth usage with Frame relay data(burst). This symptom is likely seen when there are a lot of FAX connections with modem upgrades. |
|
|
While deleting a trunk, the user gets the prompt "Delete this line (y/n)?". Symptom always occurs while deleting a trunk. None. This problem is now fixed. While deleting a trunk, the user now gets a prompt "Delete this trunk (y/n)?". |
|
|
The Trns Handler uses up most of the resources on the CPU; many connections fail to route, but the Trns Handler continues trying. This symptom occurs under trunk failures that reduce available bandwidth. |
|
|
A card on a BXM to which an SES-PNNI controller is attached errors. This symptom occurs when the VSI capability of an SES-PNNI contoller is removed using delctrlr command, then readded using the addctrlr command. Before issuing the addctrlr command, delete the AAL5 shelf and readd it using the delshelf and addshelf commands. |
|
|
The IGX switch softwarewon't update the trunk and gateway channels of a trunk if that trunk doesn't belong (is connected to) this node. This symptom occurs only when channel reconfiguration is attempted using the commands cnrsrc and cnftrk. |
|
|
If the commands cnftrk or cnfrsrc are used on a trunk to decrease the number of connection channels to less than the number of connections routed on the trunk, then the via connections or slave connections on that trunk will not get rerouted. This symptom occurs under the following conditions: 1. If four or more nodes are connected in the following manner: A—B—C—D 2. If cnftrk or cnfrsrc commands are issued for trunk B—C from either node B or node C, such that the connection channels are less than the number of connections routed over that trunk. 3. If some connections are mastered at either node A or node D. It is these connections that may not get rerouted. Do not use the commands cnftrk/cnfrsrc on a trunk carrying via connections/slave connections. |
|
|
The average cell per second (CPS) values displayed when the command dspchstat is issued does not always reflect the correct transmit rate. Instead, the true CPS values take some time to be accurately displayed. This symptom occurs whenever the dspchstats command is issued for software images after 9.2.30. When the dspchstats command is issued, the only values displayed that are incorrect are the fields: Collection Tim, Avg CPS, %util. This information can be extrapolated from the TFTP or USER interval statisticss which have a minimum granularity of 5, 10 or 15 minutes based upon the number of connections they have in the network. If we divide the "Port Cells Received on Channel" statistic by the interval (5, 10 or 15 minutes) they will get the approximate average CPS. Therefore: <Port Cells Received on Channel> / <interval> = avg. CPS The root cause of this problems was that a timer's initialization was removed by a different defect fix. The result of this removal is that vcs_cur_ticks timer does not get reset. Therefore, it contains the last time that the previous response was received rather than when the current response was received, making the time value is too large. Since the time value is too large, this in turn, when plugged into the formula shown above, calculates a very small and incorrect CPS average. It will eventually (over an extremely long period of time) approach the correct value, asymptotically. t = A Normal statistics polling response is received from the card, vcs_cur_ticks is set to now (A). t = B Command clrchstats is issued, which sets flags to drop the next sample (for summary statisticss) and to reinitialize the vcs_cur_ticks field. t = C Command dspchstats is issued, which causes a statistics poll to be sent to the card and a response to be sent back nearly instantaneously. When the response is received, the summary statistic filter flag is set so we drop the first response (and we should set the vcs_cur_ticks field at this point but we don't). t = D Command dspchstats sends its second poll request, and we get back the response. We update the data for cells RX/TX, etc. We calculate the amount of time this data is for by subtracting the vcs_cur_ticks count (A) from the current time(D) so the time delta is (D - A). Here is the problem. This time value should be (D - C) but because the intialization code was removed it is (D - A), too big. The connection polling rate can be configured to 5, 10 or 15 minutes, therefore the amount of time that this can be off by is 4'59", 9'59" or 14'59". It also can coincidentally be correct if t=A and t=C are very close to each other. |
Following is the list of fixed problems in the 9.2.32 Switch Software release. Included with each is a brief discussion of the problem.
| Bug ID | Description |
|---|---|
|
Trunk information is inconsistent. dsptrks reports trunk as Clear-OK dsptrkmcons reports trunk is in alarm dsptrkutil will report terminating and via connections (if connections exist) on the trunk chkconids reports trunk conids as 0 (when conids are used on the trunk) Connections will not be routed on this trunk since the routing component of switch software believes the trunk to be failed. All versions of switch software that support trunk deroute delay feature. Only seen when deroute delay is enabled and non zero on a trunk. |
|
|
Connections get rerouted when active line of APS goes in yellow alarm Active line is in Yellow alarm and Standby line is OK This behaves on regular trunk. On APS even if active line is in alarm there can exist a path to transmit and receive the data. For example: Active line in Yellow and Standby in LOS then using Rx of active it can receive the data and using Tx of standby it can send the data. |
|
|
Can not stop switchcc command. i.e. switchcc continues executing evenif user says "n" when asked to "Continue?". Issue switchcc on bpx node, and if standby updates are pending, if the user reply "n" to not to continue the switchcc, it still does the switchcc. Do switchcc only after updates are over. Use dspcds and dspqs to verify that standby card is in "Standby" state and no updates are pending. |
The SNMP IGX/BPX switch SNMP MIB is being provided with the delivery of Release 9.2.33 Switch Software. The MIB is in standard ASN.1 format and is located in the ASCII text files agent.m, ilmi.m, ilmi_ctl.m, ilmiaddr.m, switch.m, swtraps.m, and errors.m which are included in the same directory as the Switch Software images. These files may be compiled with most standards-based MIB compilers.
The following Switch MIB changes were introduced since Release 9.2.00. The changes include Obsolete objects, Modified objects, and New objects:
The following objects are associated with the switchShelf configuration branch.
The default values for BXM and Enhanced-BXM cards are the same.
For service and support for a product purchased from a reseller, contact the reseller. Resellers offer a wide variety of Cisco service and support programs, which are described in the section "Service and Support" in the information packet that shipped with your chassis.
 |
Note If you purchased your product from a reseller, you can access Cisco Connection On-line (CCO) as a guest. CCO is Cisco Systems' primary, real-time support channel. Your reseller offers programs that include direct access to CCO's services. |
For service and support for a product purchased directly from Cisco, use CCO.
Cisco Connection On-line (CCO) is Cisco Systems' primary, real-time support channel. Maintenance customers and partners can self-register on CCO to obtain additional information and services.
Available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, CCO provides a wealth of standard and value-added services to Cisco's customers and business partners. CCO services include product information, product documentation, software updates, release notes, technical tips, the Bug Navigator, configuration notes, brochures, descriptions of service offerings, and download access to public and authorized files.
CCO serves a wide variety of users through two interfaces that are updated and enhanced simultaneously: a character-based version and a multimedia version that resides on the World Wide Web (WWW). The character-based CCO supports Zmodem, Kermit, Xmodem, FTP, and Internet e-mail, and it is excellent for quick access to information over lower bandwidths. The WWW version of CCO provides richly formatted documents with photographs, figures, graphics, and video, as well as hyperlinks to related information.
You can access CCO in the following ways:
For a copy of CCO's Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ), contact cco-help@cisco.com. For additional information, contact cco-team@cisco.com.
Note If you are a network administrator and need personal technical assistance with a Cisco product that is under warranty or covered by a maintenance contract, contact Cisco's Technical Assistance Center (TAC) at 800 553-2447, 408 526-7209, or tac@cisco.com. To obtain general information about Cisco Systems, Cisco products, or upgrades, contact 800 553-6387, 408 526-7208, or cs-rep@cisco.com.

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Tue Jul 15 03:40:46 PDT 2003
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.