|
|

Cisco documentation and additional literature are available in a CD-ROM package, which ships with your product. The Documentation CD-ROM, a member of the Cisco Connection Family, is updated monthly. Therefore, it might be more current than printed documentation. To order additional copies of the Documentation CD-ROM, contact your local sales representative or call customer service. The CD-ROM package is available as a single package or as an annual subscription. You can also access Cisco documentation on the World Wide Web at http://www.cisco.com, http://www-china.cisco.com, or http://www-europe.cisco.com.
If you are reading Cisco product documentation on the World Wide Web, you can submit comments electronically. Click Feedback in the toolbar, select Documentation, and click Enter the feedback form. After you complete the form, click Submit to send it to Cisco. We appreciate your comments.
The 9.2 software release supports the Cisco WAN switching BPX 8600 series and IGX 8400 series switches. This release does not support the IPX switch.
The MSS BU rollout plans for the 9.2 release is based upon a series of incremental feature releases. This phased feature release strategy is designed to allow the earliest customer availability of key new features, consistent with maintaining high product quality. For the status of each 9.2 feature at the time these release notes were published, please see below. For the latest status of each 9.2 feature, please see your account representative.
Generally Available (GA) - Feature is ready for wide deployment with no restrictions. Customers deploying GA features are supported by the Technical Assistance Center (TAC).
First Customer Ship (FCS) - Feature is available for controlled introduction by selected customers. To trial an FCS feature, please contact your account representative.
Customers selected for controlled introduction will receive assistance with test plan review and special support from the New Product Team (NPT) in addition to the normal Technical Assistance Center (TAC) support.
Includes all features supported up to release 9.2.20
Includes all features supported up to release 9.2.20
Includes all features supported up to release 9.2.20
Includes all features supported in release 9.2.10, release 9.2.01 and release 9.2.00 and introduced the following additional features:
1. Support for Real Time VBR (rt-VBR)
2. Support for Early A-Bit Notification (This feature is an enhancement to the Early A-Bit Notification feature in release 9.1)
3. Support for the Service Extension Shelf (SES) Feeder to IGX
4. Software support for Enhanced BXM and UXM
5. Support for UXM-XLR back card
Includes all features supported in release 9.2.01 and release 9.2.00 and introduced the following additional features:
1. Support for Virtual Switch Interface (VSI) 2.2
2. Support for 16K connections
3. Support for UXM VP tunneling
5. Support for Multiple Protocol Label Switching (MPLS); MPLS-Virtual Private Network (VPN); and MPLS-Class Of Service (COS) - See the Clarifications section for more details
Includes all features supported in release 9.2.00 and introduced the following additional features:
1. Support for Virtual Trunking on the BXM card
2. SONET line protection: APS on BXM-OC3 and BXM-OC12 (1+1)
Software release 9.2.00 introduced the following features:
1. Support for Virtual Trunking on the UXM card
2. Support for both ports and trunks simultaneously on the same UXM and BXM cards
3. Support for Hitless Rebuild including Disable Auto Bus Diagnostics
4. Support for BXM and UXM Multi-Level Channel Statistics
5. Alarms for all service affecting events
6. Supports revision interoperability between 9.1 and 9.2
7. Supports for IGX and BPX trunk reconfiguration without outage
8. Supports ATM Forum Standard Compliant IMA with UXM (IGX 8400) Firmware Model B
9. Includes SONET line protection: APS on BXM-OC3 and BXM-OC12 (2 card, 1:1)
10. Support for LMI/ILMI on BXM card
11. Supports feature mismatch on BXM and UXM cards
12. Support for Idle code suppression for video on UVM and CVM cards
13. Supports VC traffic shaping on UXM ports
14. Support for UXM STM-1 Electrical back card
1. In BPX nodes that use processor cards with 32Meg of RAM, it is possible to run out of memory in the Hitless Region. This can happen if the node is too heavily configured with cards and connections. The recommendation below should prevent memory aborts.
In nodes that have processor cards with 64Meg of RAM, there should be no Hitless Region memory problem. This is because 64Meg processors contain a second Hitless Region, which is larger than the first.
The following calculation will help prevent memory aborts on BPX processors with 32Meg. For simplicity, the numbers are approximate. It is necessary to add up the number of cards in the node, as well as the number of connections, and make sure that the total does not exceed the recommendation.
During system initialization, roughly 17,100 blocks of the available 40,000 are used for the card database.
In addition, assume that 1500 blocks will be needed for each BXM card that can support 16K conns, which is the more common configuration. Some BXM cards can support 32K conns, and these will need 3000 blocks of the Hitless Region. This chunk of memory is allocated at the insertion of the BXM card and will not be released until a card of different card type is inserted.
Also, 300 blocks will be needed for each 1000 via connections on the node. This can be viewed with the user command dspload.
2. The minimum software and firmware versions required to run MPLS are:
The BPX with external 7x00 label switch controller (router) with Switch Software Release 9.2.10 and IOS release 12.0(5)T can function as an ATM-LSR. The enhancements to dynamic label switching that was supported in Release 9.1 included support for MPLS Class of Service. The BPX as an ATM-LSR supports the "Multi-Label VC" model to support MPLS Class of Service. Five Qbins (Qbin 10-14)are reserved for MPLS Class of Service. Class based WFQ is supported on these IP queues.
The BPX can also function as a "P" ATM-LSR in the MPLS-VPN architecture.
Hot Redundancy of MPLS connections on the BPX is supported by BXM hot card redundancy. Continuous message forwarding, and keep-alive between the BXM redundant pair ensures the connection continuity on BXM switchover. On failure of a BXM card, the standby card becomes active with the label-vcs. Re-synchronization between the MPLS Label Switch controller and the BPX ensures that their databases are in sync.
3. The 16K connections feature increases the number of connections terminating on the BPX switch to 16,000. The count includes connections terminating on BXM or ASI endpoints on cards within the node as well as connections terminating on service modules in the feeder shelves connected to the BPX switch. For example, a Frame Relay connection that originates on a FRSM in an MGX 8220 connected to a BPX counts as one of the 16,000 terminated connections on that BPX.
This feature requires a BCC-3-64 or BCC-4 controller in the BPX as well as switch software 9.2.10 or higher.
4. Version 2.2 of the VSI (Virtual Switch Interface) provides the BPX switch with the ability to support multiple network protocols and multiple controllers per switch (e.g., MPLS, PNNI, etc.). Switch resources can be dedicated to a specific controller or shared by multiple controllers.
This feature is supported on BXM ports, trunks, and virtual trunks and requires a BCC-3-64 or BCC-4 controller in the BPX as well as switch software 9.2.10 or higher and BXM firmware MEA or higher.
Following are the VSI features:
5. The combinations of system limits such as number of trunks, lines, ports, and connections as well as enabled TFTP interval statistics should be provisioned so that the node has at least 50% idle time usage. Use the command dspprfhist to verify.
6. When cost based routing is used, increasing the cost of a trunk will result in deleting the preferred path on connections in the database if the sum of the preferred path cost exceeds the actual sum of configured connection cost. The connections will remain routed on its current path.
7. On the BXM and UXM, for the OC-3 MultiMode Fiber backcards, Y-Redundancy/hot standby is not supported due to a hardware restriction.
8. In order to maintain the database consistency between switch software and the card, after the switchcc, rebuild, or Y-redundancy switchover, switch software will first disable and then re-enable the OAM loopback feature if the feature was enabled previously. After the OAM loopback is re-enabled, firmware will need to test the OAM loopback and report the status to switch software. This will cause a minimum 10 minute delay in displaying the OAM loopback status.
9. The trunk reconfiguration feature does not support IMA trunks.
10. HDM to UVM interworking for Nx64K connections is not supported in this release.
1. Release 9.2 supports graceful upgrades from 9.1.03 and later only.
2. When UXM cards are to be used, certain legacy card firmware must be upgraded before upgrading to this release. See the compatibility matrix for cards affected and the exact versions to be used.
Note Standards compliant IMA is not compatible with the proprietary IMA protocol used in revision A firmware. Both ends of an IMA trunk must have the same protocol.
Caution Failure to follow this procedure may result in the card not operating. The card should be returned to Cisco if this occurs. |
In order to run Model B firmware on an UXM, the card needs to be running boot code revision 6 or greater. To determine the boot code running on the card, issue the following command from the CLI (you must be logged in as Service level or greater to use this command):
Step 2 Upgrade the UXM's boot code if necessary.
The process for loading boot code is exactly the same process you would use to load firmware. The only part which changes is the name of the file.
Step 3 Upgrade the UXM's firmware.
Step 4 When Y-redundant trunks are used, the red alarm in/out values must be configured to 1.25/1.5 seconds or greater, or else INVMUX failures will occur and trunk failures will be observed during a Y-redundancy switchover. Use the following command:
This is due to the IMA protocol and may cause re-route of connections.
Step 5 Upgrade NPM software to 9.2.
Step 2 On IGX to have firmware upgrade, issue command cnffunc 15 d to disable the UXM from resetting automatically after the firmware is burned in.
Step 3 On each MGX-8220 equipped with IMATM-B, upgrade the ASC to 5.0.10
Step 4 Download the Forum Compliant-Firmware version imatm_5.0.10.fw but do NOT reset IMATM-B card
Step 5 On each IGX-UXM with IMA to be upgrade, burn firmware A.B.E or later to each UXM with IMA trunks.
Step 6 Simultaneously reset the card at each end of each IMA trunk to minimize trunk outage.
Step 7 Upgrade 9.1 nodes to 9.2 via loadrev and runrev
Step 8 Issue the command cnffunc 15 e after each IGX is upgraded to 9.2.20 or later
The above procedure also applies to the UXME.
Note For Y-redundant UXMs, issue the command cnftrkparm 18 100000 100000 prior to this procedure and return to default values after this procedure
Step 2 On IGX to have firmware upgraded, issue command cnffunc 15 d to disable the UXM from resetting automatically after the firmware is burned in.
Step 3 On each IGX-UXM with IMA to be upgraded, burn firmware A.B.E or later to each UXM with IMA trunks.
Step 4 Simultaneously reset the card at each end of each IMA trunk to minimize trunk outage.
Step 5 Upgrade 9.1 nodes to 9.2 via loadrev and runrev.
Step 6 Issue the command cnffunc 15 e after each IGX is upgraded to 9.2.20 or later.
To enable BXM cards to utilize 9.2 features, all BXM cards must be upgraded to 9.2 firmware release.
The following steps should be taken:
Step 2 Upgrade BCC software to 9.2
Note See the Compatibility Matrix for the tested/supported versions of other firmware and software that work with this release.
Please consult your Support Representative before performing any software upgrade.
The TSC is upgraded to CoS VSI Version capable release [IOS 12.05(T)]. This image is VSI bilingual, meaning it understands both VSI Version 1 and Version 2.
Step 2 Upgrade the BXMs
All the BXM cards in the node are upgraded to Revision E, which is VSI Version 2 and CoS capable. After each BXM card is downloaded with the Revision E image, it temporarily experiences VSI outage until the BCC software is upgraded to the 9.2.20 image. The VSI outage during the upgrade is caused by the Revision E firmware not being backward compatible with VSI Version 1 features.
Note that from the TSC perspective, after a BXM is upgraded to Revision E image the interfaces that used to be on the card will "disappear." The TDP sessions that were on the interfaces will be lost. When all the BXMs are upgraded to the Revision E while still running Release 9.1 software on the BCC, the node will experience a complete outage of MPLS traffic. Autoroute will have a hitless upgrade.
Step 3 Upgrade the BCC
As the BCC is upgraded from software Release 9.1 to Release 9.2.20, the BCC recognizes the Revision E BXMs and downloads the VSI partition configuration. This causes the BXMs to issue ifc cfg traps to the TSC, allowing the TSC to rediscover all the BPLS interfaces on the BPX. The TDP sessions are reestablished and BPLS traffic starts flowing again through the BPX.
Version Interoperating upgrades are supported from the 9.1 to 9.2 releases of switch software, with Secondary Revision Incorporation for Network Lowest Revision. This will lessen the risk of new features being enabled in a mixed network after the downgrade.
The "Secondary Revision" field in the node is used for the determination of the network lowest revision. Previous to this change, software used only the node's primary revision. The interoperability functionality uses network lowest revision for:
For a complete list of firmware versions supported, see the Compatibility Matrix document, which is included in this release package.
All processor cards must be configured with a minimum of 32 MB of RAM. This includes BCCs and NPMs. NPMs require at least 1 MB of BRAM. To verify the BRAM size on IGX 8400 nodes, use the dspcd command.
Note If any control cards contain less than 32 MB of DRAM (these would be NPMs) then they must be replaced with cards containing at least 32MB of DRAM prior to upgrading to Release 9.2. The physical upgrade of the nodes with these control cards must be done according to the upgrade procedure defined below.
As specified below, the correct version of CC boot firmware must be installed on the cards prior to a software upgrade to Release 9.2.
When upgrading the boot code on the NPM, perform the following steps:
Step 2 Execute the switchcc command and wait until the NPM(1) becomes standby. NPM(2) is now active.
Step 3 Execute the dncd command on the standby NPM(1) and physically reset (remove and reinsert) NPM(1). Wait until NPM(1) becomes standby
Step 4 Burn the boot code on the active NPM(2)
Step 5 Execute the switchcc command and wait until the NPM(2) becomes standby. NPM(1) is now active.
Step 6 Execute the dncd command on the standby NPM(2) and physically reset NPM(2)
Each redundant pair of BCC cards in a given BPX 8600 node must be of the identical type and memory configuration. That is, for example, if the active card is a BCC-3-32, then so must be the standby. BCC-3 cards with 32MB of RAM cannot be mixed with BCC-3 cards with 64MB of RAM.
Each redundant pair of NPM cards in a given IGX 8400 node must be of the identical type and memory configuration. That is, for example, if the active card is an NPM-32, then so must be the standby. NPM cards with 32MB of RAM cannot be mixed with NPM cards with 64MB of RAM. Also, NPM-64 cards cannot be mixed with NPM-64B cards.
This is a requirement for all software upgrade and downgrade procedures. It does not apply to the physical card upgrade procedure, as described below.
When performing a Control Card (CC) upgrade, the following procedure must be used. This applies to all processors: BCCs, and/or NPMs.
Step 2 Replace with a new CC front card. (For a BCC, also replace the backcard).
Step 3 Wait for the standby updates on the newly installed standby CC to complete.
Step 4 Issue a switchcc command to utilize the newly installed CC.
Step 5 Verify that the network is stable.
Step 6 Remove the current standby CC front card. (For a BCC, also remove the backcard).
Step 7 Replace with a new CC front card that is identical to the current active CC. (For a BCC, also replace the backcard).
Step 8 Wait for the standby updates on the newly installed standby CC to complete.
Step 9 The CC physical upgrade is now complete.
Step 10 With the secondary card in the standby state, cause a switchover using the switchcc command. This will test that the hardware is working correctly.
Note After Step 2, the node will contain a mix of an old type CC and the new type CC. This condition is only permitted while the standby updates to the new CC are in progress, which will take less than one hour. The time during which this mixture of CC types exists must be kept to a minimum, by immediately replacing the second old type CC with the matching one of the new type.
The following feature is not supported in this release:
Out of band communication to non-gateway nodes from the CWM workstation is not supported.
2. OAM loopback in IGX and BPX
Note These features are currently in trials at several customer sites and will be generally available upon successful completion of these trials. If you would like to participate in the trials, please contact your Account Manager/Systems Engineer.
1. Because of the hardware limitation, BXM hardware is not able to recognize all user programmed cell transmission rates. Rather only discrete transmission rates can be used instead.
The equation below shows what the BXM hardware actually transmits given a user configured cell rate. The transmitted cell rate is always less than or equal to the configured cell rate. To prevent any cell loss, the transmitted cell rate must be equal to the configured rate. To do so, a cell rate must be chosen from the table below.
The rate table below lists the highest 200 cell rates supported be BXM such that if used, will result in no cell loss (given cell traffic is less than configured cell rate). Additional rates can be calculated using 1470588/[n + (1/256)], where n is an integer.
The logic to calculate the actual cell transmission rate in a BXM card is as followed:
if (configured cell rate == full line cell rate) then
transmitted cell rate = full line cell rate
transmitted cell rate = from equation below or from table below
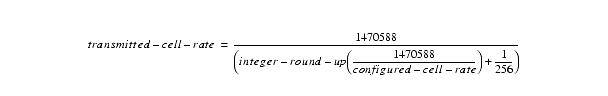
If a trunk is configured at 100,000 cps, the actual transmitted cell rate is then 98,013 cps, any traffic sent over 98,013 cps would be discarded.
If a trunk is configured at 98,013 cps, then the actual transmitted cell rate is 98,013 cps with no cell loss.
Therefore, only rates in the table should be used. Otherwise, cell loss may be experienced. The table will not be exhausted at the end but still go on with the computing from the above equation.
2. On the BPX with MGX 8220 feeder(s), regardless of the setting of the Node Parameter "42 Enable Feeder Alert", a feeder alert message will be sent to all MGX 8220 feeders immediately before a hitless rebuild takes place. The feeder alert message will temporarily disable the LMI polling from the MGX 8220 feeders. The MGX 8220 polling will resume as soon as the BPX is ready to exchange LMI messages.
3. The amount of traffic allowed on a VP Tunneling connection is 1/2 bandwidth of that connection. The minimum bandwidth must be 100 cells per second. For example, CBR connection with peak cell rate 1000 cps then can pass traffic up to 500 cps.
4. For IMA trunks, the configuration is blocked if the converted cps (cells per second) of the number of links to be decremented is MORE than the transmit rate. (CSCdm71616)
5. Card errors (0x25170076) occur on BXM when only one Virtual Trunk is configured in a physical port. To avoid this situation, configure at least 2 Virtual Trunks on any physical port that you have VTs on. When performing the configuration, make sure to configure the VTs one directly after the other. (CSCdm69974)
1. For UVM cards, there will be no new revisions of Model A firmware. When attempting to download Model A firmware to a UVM, software will give the user an error message indicating that the firmware does not match the card type. Note that there is no problem with continuing to use existing UVM cards running the old firmware. (CSCdp08741)
2. For a virtual trunk on a BXM/UXM, the Transmit Trunk Rate (the transmit rate of the virtual trunk) is configurable to match the PCR value of the subscribed public VPC service. In this release, the actual shaping rate for a virtual trunk is higher than the configured Transmit Trunk Rate (CSCdm80482). The actual virtual trunk shaping rates are 1/(n x 680 x 10-9) cells per second, where n is an integer from 1 to 29,411. In this release, the user configured Transmit Trunk Rate is rounded to the next higher (as opposed to lower) actual shaping rate for shaping.
To configure a virtual trunk so that the actual shaping rate is no greater than the PCR value of the subscribed public VPC service, the following steps can be taken:
Step 2 Configure the Transmit Trunk Rate for the virtual trunk to be less than 1/(n x 680 x 10-9) cps but greater than 1/((n+1) x 680 x 10-9) cps. For example, if the PCR value of the subscribed public VPC service is 10 Mbps or 23,585 cps, configure the Transmit Trunk Rate for the virtual trunk to be less than 1/(63 x 680 x 10-9)=23,342.67 cps but greater than 1/(64 x 680 x 10-9)=22,977.94 cps.
3. There is a new traffic class added in release 9.2.20 that causes a trunk parameter conflict with pre-9.2.20 node. The conflict fails adding trunks between 9.2.20 BTM/ATM nodes and pre- 9.2.20 BTM/ATM nodes.
All ATM traffic classes are set for BTM/ALM trunks and is hidden to user. Introducing of rt-VBR traffic class in 9.2.20 makes it different from pre-9.2.20 BTM/ALM trunk traffic class. The user can not change ATM traffic class for BTM/ALM trunk.
This problem exists with a new BTM/ALM trunk on an upgraded 9.2.20 node and does not exist with an upgraded BTM/ALM trunk since the rt-VBR traffic class is not set while upgrading. (CSCdm64345)
4. The cloud port to which a virtual trunk is connected should have ILMI polling disabled. Otherwise, it could lead to a virtual trunk being clear on one end and declaring Virtual Trunk Path Failure at the other end. (CSCdm52909)
5. In a BPX that contains BCC cards with 64MB, there is no limitation. All 12 available slots can contain BXM or Enhanced-BXM cards.
In a BPX that contains BCC cards with 32MB, a maximum of 10 legacy BXM cards are allowed. If some Enhanced-BXM cards are used in place of BXM cards, then each Enhanced-BXM will count as two BXM cards.
6. Due to performance reasons, AIS status of connections is not sent to the standby BCC. After switchcc, it may take few minutes to update the AIS status of connections. If dspcon does not show the proper status of AIS or dspalms screen shows incorrect number of AIS, (after switchcc) wait for few minutes so that the status gets updated. (dspalms and dspcon commands show the status of AIS).
7. Hitless Rebuild has similar limitations to that of a "switchcc" and full rebuild:
Some statistics that are collected by Cisco WAN Manager will be re-enabled automatically. These include:
All other statistics have to be re-enabled for collection after a hitless rebuild takes place. These mainly include the user statistics.
8. UVM cards in y-redundancy will mismatch if one is burned with Idle Code Suppression Firmware and the other is not.
When installing/burning Idle Code Suppression Firmware on UVM pairs, the y-redundancy must be removed, firmware in both UVM cards burned, and then the y-redundancy can be restored.
9. Mismatch is reported when replacing a BXM card with another BXM card that has different Port Group, even though both BXM cards have identical channel numbers.
10. When upgrading from release 9.1 to 9.2, the 9.1 statistics on UXM cards are supported to maintain compatibility. However, once you configure a statistics level in 9.2, you can not revert back to 9.1 statistics.
There is no 9.1 statistics support for BXM/UXM cards that were shipped with 9.2 firmware since the BXM/UXM card has the default level 1 statistics.
Therefore, when using an UXM card with 9.2, a user must either:
11. The BXM and UXM channel statistics level feature gives these cards the capability of collecting more than 4 statistics per connection. However, it is the controller card's limitations, available memory and performance, that indicates how many statistics can actually be collected from the cards and then reported to the Cisco WAN Manager (CWM).
The BCC-64 can collect at most three (3) interval statistics per connection when there are 16,000 AutoRoute (AR) connections configured on the node. (Interval statistics are those statistics that are reported to the CWM. They are often referred to as TFTP statistics).
You can collect approximately 48,000 statistics (3 x 16,000) on the BCC-64. This is approximate because there are many variables that will affect this value such as: are peaks enabled, how many buckets are collected, are all connection of the same type, are trunk, line or port stats enabled, etc.
With this approximation of 48,000 statistics on the BCC-64, this then means that as a rough estimate you could enable 32 stats on 1,500 connections, 48 stats on 1,000 connections or 9 stats on 5,000 connections, etc. The approximation formula being:
max_stats_per_connection = 48,000 / number_of_connections.
12. In release 9.1, the UXM card ran a proprietary IMA communication protocol. This protocol matched that used on the MGX 8220 4 IMATM-B cards and hence could be connected together to form a trunk. In release 9.2, we now support standards compliant IMA on the UXM card and the standards compliant IMATM-B on MGX 8220 5.0 is not yet released. Hence, when the network is upgraded to 9.2.20, the UXM will be running compliant IMA protocol and the IMATM-B will still be running the proprietary IMA communication protocol. They will no longer communicate and the trunk will fail. This will be fixed in the MGX 8220 5.0 release containing IMATM-B. However, it should be noted that an upgrade at that time will also incur some amount of downtime as there will be a difference in timing between the MGX 8220 upgrade and the switch software upgrade. There should be no effect to UXM-IMA trunks connected to other UXM-IMA trunks in 9.1 to 9.2 interoperability mode.
13. We allow the transmit rate on an IGX IMA trunk to be altered at the local node with any trunk outage. It is possible that the transmit rates are different at the two ends of an IMA trunk. After this trunk is deleted, we cannot add it back unless the transmit rates are the same.
14. When doing a grouped upgrade from release 9.1 to 9.2, the software error 1427 may be logged on the BPX/IGX node during non-graceful upgrade. This error can be ignored since it is harmless to the network.(CSCdm14613)
15. Reconfiguring trunk parameters may cause connection to be rerouted if the changed bandwidth load is smaller than what was used by the connections that use the trunk.
16. If LMI/ILMI is provided by the BCC:
The maximum possible number of ports on the BPX 8600 that can be configured with LMI/ILMI enabled is 52. However, each BPX will support up to a total of 16 feeder trunks and each feeder trunk will have LMI enabled. That is, if a BPX 8600 is configured with only 2 feeder trunks, then only (52 - 2) = 50 ports can have LMI/ILMI enabled.
If LMI/ILMI is provided by the BXM firmware:
17. Virtual Path Connections with cells whose VCI values are above 4095 will be transmitted correctly if and only if the path is exclusively through BXM trunks and terminates at BXM ports.
18. The feature of CIR=0 for Frame Relay connections is not supported for connections terminating between FRM cards in IPX/IGX nodes and FRSM cards in an MGX 8220 shelf.
19. SVC Connections are derouted after decreasing the allocated bandwidth (increasing Stat Reserve). It is the design intent that increasing the statistical reserve will cause SVC conns to deroute and not be rerouted.(See bug CSCst92308).
20. For the loadrev operation, it is important that the Cisco WAN Manager/TFTP buffers are maintained at their default size.
21. Due to a hardware limitation, the BNI trunk will send 13 -15% more traffic than what it is configured for when the trunk is configured for less speed (cps) than the maximum port speed. This is especially important when the BNI trunk is connected to IM-ATM pairs, which carry less than T3 bandwidth.
22. When using the shift/no-shift feature on a BPX 8600 node's port card, controlled via the cnfport command, the other end of the connection must have the same setting. Otherwise, there will be a loss of continuity.
23. If the Stat Reserve field on a trunk is dramatically increased to a value which represents a significant majority of the total trunk bandwidth, then, if connections are present on the trunk, the dspload command will show negative values. This is to signify that the trunk is oversubscribed. The trunk load values will eventually reach 0, or a small positive number after all the necessary connections are routed off that trunk. (CSCdi84878)
24. When deleting trunks, there is a known limitation with the switch software. The deltrk command should always be executed on the node that remains as part of the network, rather than from the node which ends up being removed from the network. This is to ensure that all the necessary updates are sent to the rest of the network. (CSCdi85134). Also, If the command is not used as recommended here, a software error 419 could occur (CSCdi91285).
25. Due to Trunk Based Loading, any commands having to do with trunk loading and the load model (dspload chklm dsplm, etc.) need to be done only after waiting a certain period of time. This time is directly a function of the trunk load update interval time (as configurable) plus the conditional update latency time.
26. The external ABR segment control loop on ForeSight (ABRFST) is an option at the User Interface, but is not supported in hardware. The user should not enable this option on ForeSight connections (CSCdi92451). In any case, there is no coupling between the loops.
27. On a heavily loaded BPX 8600 node, during connection re-routing, the status of a particular connection is indicated as OK even though the line status of the other end of the connection is listed as failed. The connection is in fact OK, because the conditioning of the connection (to update the status for both ends) is done by a low-priority process so that the re-routing of the connections can be given high priority. The status will be eventually updated. (CSCdj10762)
28. A node whose number is greater than 63 cannot have a clrcnf operation performed on it. This is as designed. A clrallcnf can be done, or the node must be renumbered to less than 63 before running clrcnf. (CSCdj14920)
29. The interface between a BXM feeder trunk and an MGX 8220 feeder is always considered to be an NNI interface. (CSCdj16808)
30. When adding more than 4000 connections on a BPX node, the VC polling rate must be changed to a higher interval, to accommodate the additional time needed to poll for the statistics for each VC. The cnfsysparm command, parameter 24 must be changed according to the following:
31. Given a connection that terminates on an IGX 8400 FRM at one end and an ASI on the other end, tstdelay initiated at the FRM end may not work if the ASI firmware is below the appropriate revision and does not support OAM cells as opposed to supervisory cells. This is because the updated BTM on the IGX will always generate OAM cells. Please check the Compatibility Matrix.
32. Because the detailed card error event log is not retained within BRAM, this information will be lost should a processor rebuild occur. Therefore, when issuing a dspcderrs command on a particular slot, the display will not show the detailed card error information should rebuild event occur. This functionality has not been modified from previous releases.
33. When a physical-layer failure (for example, LOS) is detected on the BXM, a Major Alarm is generated, and any connection routed over that port is downed (Fail state). The software sends a command to the remote end of the connection to generate AIS in the egress direction. (CSCdj30543).
Since the connection is in a failed state, AIS is generated in the upstream direction (in addition to the downstream direction). Although this does conform to the letter of the I.610 standard, this is not necessarily what a user would expect to see, because it interferes with the RDI response from the end-to-end connection termination point. (A fault in the downstream direction causes a fault in the upstream direction.)
Reason for the current implementation:
The BNI can not generate AIS. If there is a fault at a BNI trunk, the current mechanism is to cause AIS to be generated by the BXM port by downing the connection. Since the BXM can only generate OAM cells from the RCMP, and the RCMP is in the ingress path, the cells must be backward routed to the egress (egress QE). Also, since end-to-end OAM cells are required, the ingress QE must be configured to drop ALL cells in the ingress path. This creates a break in continuity in the opposite direction, and AIS cells must also be generated at the other end of the same connection, in the upstream direction of the original fault.
34. There are problems in the downgrade mechanism which can cause database corruption. If downgrade is performed immediately after upgrading, the Stby_Info revision fields are not yet filled in on the new active CC. They don't get filled in until the upcard response from the new locked CC. This causes restart instead of a switchcc. If the locked CC is reset, then downgrade immediately, a restart will occur instead of a switchcc. (CSCdj30811).
35. In order to test/simulate the Y-redundant switchover of ASI T3 or E3 pairs the resetcd command must be used, or by pulling out the active card. It will not be correctly simulated by doing a dncd (down card) on the active card. Using dncd will cause cell discards. (CSCdj08923).
36. BXM cards can support 32K PVC's only when no stats are collected. If collecting 4 stats per PVC is desired, the number of PVC's per BXM card drops to 16K. (CSCdj31773).
37. UBR traffic gains an advantage over ABR traffic when UBR and ABR PVC's are combined on the same network. This is because UBR and ABR PVC's share the same QBIN (Class of Service Queue) on the BXM card. ABR PVC's use a flow control mechanism, VSVD, which ensures that traffic sources slow down when the QBIN usage exceeds the EFCI threshold. However, UBR PVC's do not have this throttling mechanism. Therefore, ABR will throttle back whereas UBR will not. This unfair advantage is not considered a problem, since the decision to share a QBIN for ABR and UBR traffic was intentional. Any best-effort service that one would route over UBR can be routed over ABR(VSVD), with the additional benefit of protecting resources in the network. If UBR and ABR PVC's are required then:
Option 1 - Consider adding all best-effort PVC's as UBR, or
Option 2 - Isolate the ABR and UBR paths by using cnfpref command to ensure that ABR and UBR PVC's do not share the same queues.
Option 3 - To provide UBR service on a connection, rather than setting up a UBR connection, do the following:
Step 2 Enable VSVD
Step 3 Disable FCES (Flow Control External Segment)
Step 4 Disable DEFAULT EXTENDED PARAMETERS
Step 5 Choose policing option "4" to allow access as UBR.1 (PCR policing only). This connection has ABR VSVD in the network and allows UBR.1 access. The MCR for such ABRSTD connection may be set at the minimum acceptable value of 6 cell per second (explained later why doing so).
To provide ABR service on a connection, set up an ABRSTD connection, enable VSVD and enable FCES to allow RM cells to be passed to and from customer equipment. The MCR for such ABRSTD connection can be set at any user desired value.
When the network is experiencing congestion, all the affected ABRSTD connections, regardless of the services (ABR or UBR) they are carrying, will all be throttled back at the VSVD points at the network edge. During network congestion, connections carrying UBR services are virtually stopped (to a through put of mere 6 cps) while connections carrying ABR services can send at a much higher, user desired MCR. This option would avoid that UBR service gains an unfair advantage over ABR service while sharing the same CoS queue.
38. Combining FBTC and non-FBTC connections within a Class of Service can cause FBTC connections to not receive a fair share of bandwidth. For example, if VBR connections are added at a terminating port, and some of these VBR connections have FBTC enabled while other VBR connections have FBTC disabled, the VBR connections with FBTC disabled may obtain all of the excess bandwidth before the connections with FBTC enabled receive any of the excess bandwidth. The same holds true for ABR or UBR connections. This only is relevant where FBTC and non-FBTC connections share a QBIN, either at a port or at a trunk.
39. The maximum number of VC Parameters supported: 749 for BCC-32 MB, 2,999 for BCC-64 MB. (CSCdj48589).
VC Parameters are Virtual Circuit Parameters combinations/sets. One set of VC Parameter is used for each unique Virtual Circuit that has been provisioned. Identically provisioned Virtual Circuits (exclusive of endpoints) use the same set of parameters. Thus, on a 32MB BCC, a total of 749 uniquely configured Virtual Circuits can be provisioned.
40. Care must be taken when changing the Deroute Delay parameter, which is controlled by the cnftrk command. This parameter defaults to zero, but if it is set to anything but zero, connection re-routing due to a trunk failure will be delayed as provided by the parameter.
1. The logical line and logical port databases can be corrupted when an IGX has Frame Relay lines as well as ATM lines, and a rebuild or Control Card switch over occurs. This corruption is evident by the appearance the software errors 549, 886, and 2071 on a switchover or rebuild, or if a software error 928 occurs while upping an ATM line. If such a corruption is found, the database can be cleaned up. Refer to the workaround of CSCdm54814.
2. When adding a node into an existing network, ensure that its node number is unique prior to actually adding it into the network. Use the rnmnd command (which is a Service-level command), and renumber the individual node while it is still stand-alone. This will make the joining of this node much simpler, and will avoid the problem of node renumbering an active network, as described below.
3. There is a problem with node renumbering. Node renumbering (the rnmnd command) should be executed only during a stable network environment and only if absolutely necessary. A stable network environment would be, for example, one in which no connection was added for the past 30 minutes and no topology change was made in the last hour and there are no alarms or node unreachabilities. Node renumbering must only be done when the network is stable to reduce the possibility of certain temporarily blocked messages during the node renumbering process being delivered to the wrong nodes. This would occur after the completion of the node renumbering process. It is recommended that a node be renumbered prior to being added to the network.
4. The settling time for network wide updates can take a long time in certain situations. Specifically, the settling time for updates due to network wide topology changes and connections in a large network when a processor switchover occurs can take a long time. The time is proportional to the number of nodes as well as the number of connections. A general estimate would be 30 seconds per node. During the period of transitions (when the updates are occurring) some network operations such as adding connections might, in some cases, take somewhat longer to complete.
5. When using Cisco WAN Manager, there could be a problem with communicating with a node that just had a processor switchover. The problem is within the SPARCstation itself and its caching of EtherNet addresses. It can be solved by execution the following command on the workstation as the superuser: # arp -d <node_name>
6. Users may not use the command addcon slot.1-24 v to add 24 voice connections to a CVM/UVM card at once. Instead, they must separate this activity into two or more commands, so that no more than 16 connections are added at once. This is only an issue for voice connections. Data connections can be added using the "1-24" syntax. This also applies when the CVM/UVM circuit line is an E1, in which case "1-32" would apply. (CSCdj14319)
7. Statistics collection must be disabled prior to the start of an upgrade, prior to the issuing of the first loadrev command. Stats should be disabled from Cisco WAN Manager (Stats collection manager).
8. Statistics sampling must be disabled prior to the start of an upgrade (using off1/off2), prior to the issuing of the first loadrev command. Stats sampling state machine should be disabled from the Command Line Interface.
9. When a switchcc is executed on a BPX 8600 configured with two BCC-4 cards and contains a BXM-622 trunk card, there may be a bad clock path problem reported. It is indicated as a Minor Alarm - bad clock path. This is a transitory problem, although the alarm indication persists. To clear this, execute the clrclkalm command.
10. Currently, T3-3 and T3-2 backcards are not interchangeable between ASI and BNI front cards, as this has been the case since the introduction of these cards. The back cards must be configured using cnfbkcd (with setnovram) so as to avoid backcard mismatch. (CSCdj41999)
In order to take advantage of the dual SIU when upgrading to the BCC-4, the BPX 8600 node must have a new back plane which has dual traces for incorporating with the BCC-4.
The command dspbpnv can be issued to verify if the node has the new backplane or the old backplane. The following table details the bit fields for the BCC Backplane NOVRAM format, the display of word 2 describes the back plane type:
With regards to statistics collection, the peak statistics collection intervals are controlled to be only those values for which peaks can be accurately collected The rules for peak intervals are as follows:
There are additional commands to control trunk and line loopbacks in this release:
On the node on which it is executed, creates a loop back within the port such that the cells do not leave the card.
On the node on which it is executed, creates a loop such that incoming cells are looped back to the other end.
Removes the loopback added by either of the above two commands.
The card synchronization (Hitless-Switchcc) feature can be turned on/off using the on3/off3 command (which is a StrataCom-level command). For example, enter at the command line:
This will enable the card synchronization feature.
This will disable the card synchronization feature.
In order for the feature to work, the line statistics sampling should always be enabled (using the on2 1 command) and the front card installed must support the card synchronization feature. The dspcd command provides an easy way to determine whether the front card supports this new feature. If the front card supports the feature, the following message is shown on the dspcd screen:
Front card supports card synchronization
Additionally, the following debug commands are added to allow synchronization between the interface card and the CC database:
<slot_number> for a particular slot that supports the card synchronization feature.
* for all cards that support the card synchronization feature.
This command displays the number of connections reconciled during the synchronization process after a switchcc command for different slots.
<slot_number> for a particular slot that supports the card synchronization feature.
* for all slots supporting this feature.
For a complete list of firmware revisions supported, see the Compatibility Matrix document, which is included in this release package.
This release will run with Release 4.0.0x, 4.1.0x, or 5.0.0x of the MGX 8220.
IGX Firmware
Latest tested versions of firmware and software:
The following is the list of known anomalies in this Switch Software delivery. Included with each is a brief discussion of the problem. A more in depth discussion is available in the release note enclosure of the problem record in Bug Navigator
| Bug ID | Description |
|---|---|
|
UVM connections do not show slot number in the event log, and show the incorrect channel number if the connection terminates on the second line. The defect will be observed for any event log entry for a connection terminated on a UVM card. The format of the connection in the event log is displayed as slot.channel, rather than slot.line.channel. The channel displayed is the internal database channel (plus one for display). It is correct, but is not the format expected by the user. The channel displayed is the actual channel used for the connection, plus one. The UVM has 31 channels for each line. Thus subtract 31 from the channel displayed in the event log for any connection terminating on line 2 of a UVM to get the expected channel for line 2. Events for connection: Will be displayed as: slot.line.channel slot.(((line - 1) * 31) + channel) 9.1.1 9.1 (same if line 1 is T1 or E1) 9.1.24 9.24 (max if line 1 is T1) 9.1.31 9.31 (max if line 1 is E1) 9.2.1 9.32 (same if line 2 is T1 or E1) |
|
|
There is no UAS alarming. Spec requires that when we have more than 10 consecutive SES then we should enter UAS. Because this is currently not implemented, no UAS alarm is generated in this situation. This requires that both firmware and switch software fixes to the following bugs must be present to fix this problem. CSCdk48827 - Firmware bug to fix the thresholds for SES to kick in. This is fixed in firmware image BXMMCB or later images. CSCdk48816 - The software portion of this problem to alarm based on UAS. Without the software fix to this bug, customer cannot upgrade firmware beyond MBY because when we enter UAS, per specification, we stop counting Bip8 ES and SES - as such we will not have alarming on ES as well as no alarming on SES. MBY provides a temporary fix to keep the ES alarming on by raising this threshold. Work around is to continue to use MBY which will prevent SES alarming to kick in. The side effect is that this will prevent the customer from using the features introduced in the MC firmware. |
|
|
ASI-T3 or ASI-E3 cards using T3-3 or E3-3 backcards show lines as Clear-OK when the line actually should show LOS. (No loopback or other line attached) Use cnfbkcd to change the backcard to a T3-2 or E3-2 and the line will show LOS status correctly. |
|
|
dspport command is not available to level 6 user ids. After upgrade from 7.x software to 8.1+ software. The privileged level of the dspport command was changed in release 8.1 to level 2 from level 6. This difference was first noticed by offsite user after upgrade from 7.4 to 8.5.05. User who running 8.x.x software hasn't noticed this difference until opening of this problem. |
|
|
NPM 2 restarted due to a Watchdog Timeout Happens when you run resetsys command to reset all the cards (except the active NPM card) on an IGX node with lot of active connections. When the standby NPM comes up, the event log mentions that: "NPM 2 Restarted due to a Watchdog Timeout" where 2 refers to the slot number of the standby NPM card. This does not affect any functionality except for the above log. Instead of running the resetsys command, individually reset the cards using resetcd command. |
|
|
After upgrading from to 9.1 or a switchcc in 9.1, there is some connection database corruption. You can dspcon on one end but dspcon on the other end shows the connection does not exist. dspchstats on one end ok but the other end shows the connection does not exist. Cards previously without connections, may have new connections. The active CC has conns to a remote node. After a switchcc extra connections appear. These connections appear on a slot which matches to remote node's slot number. There is an extra logical endpoint for the connection. dcct of the connection shows the OE LCN non-zero, even though the connection actually terminates on another node. The OE LCN field should be set to a non-zero value only for dax conns. This is a side affect of CSCdk06460 where the LCN and OE LCN fields are not initialized during an addcon. |
|
|
(1) When adding a new VT on a BXM port already supporting VTs, some unnecessary channel programming takes place. (2) When deleting a VT on a BXM port the still supports other VTs, the directed networking channels get assigned to the VI of the deleted trunk. If this VI gets reassigned to a different port, Comm Breaks could happen. (3) A direct routing loop is not stopped for BXM VTs, as a VT transmitting a specific VPI/VCI can also receive it. This will fill up the VT with hipri traffic, when a routing loop is created where the neighbor sends this VPI/VCI back. (1) addtrk of multiple VTs on a single BXM port. (2) deltrk of one of several VTs of a single BXM port, and reassigning the VI to another port by dntrk of the VT and uptrk and addtrk of a new trunk on a different port of the same card. (3) Inconsistency of topology information of two neighbor nodes. (1) None, but the problem is not serious. (3) The operator can resolve this situation by removing the routing loop. Routing loops occur when nodes do not have the same topology information. The topology information can be made consistent by use of the updates 1 or the recovertopo command. Another note for (3) There exists a theoretical chance of a trunk loopback generating a large stream of cells. However, so far all attempts to demonstrate this have failed. |
|
|
Using the 'dspchstats' on a BXM there are missing value's During 9.1.08 system software testing the lab personnel discovered that the BXM statistics usually recorded in an enhancement in switch software 8.4.09 has been removed. |
|
|
1.) A hitless rebuild was done on a slave node while the master rerouting some connections. 2.) There is a remote chance that, when the rebuild occurs slave has not finished routing on its side. The connections remain as derouted on the slave side but are routed on the master. 1.) Rebuild the slave when connections are being routed from the master side. |
|
|
When a user ID is deleted from the user database, subsequent users are shifted and use of the same privilege level as the immediately following user. Network of 9.1.09 where issue was discovered. Lab network at 9.1.09, 9.1.10, and 9.2.00 with problem. Not observed in lab environment at 8.4.21. In order to prevent the shifting, a dummy user ID needs to be created any time an existing user ID is deleted. The dummy ID will fill the spot vacated by the deleted user ID and user IDs below the deletion will shift back to their normal positions. |
|
|
Software error 446 may be logged during switchcc. This happens if the node is just about to kick off conditional update. |
|
|
No symptoms observed. The theoretical issue is that high volumes of data traffic on VSI queues could squeeze out the high priority networking traffic. At the very least, all VSI data is being prioritized over all AR data. Poor performance for AR queues if the VSI queues are experiencing heavy load. These software errors are a result of a recent code check in which is believed to not have ever made it to the field. |
|
|
Software error 3005 BAD_BW_DEFAULTS is seen on two bpx nodes. An ATFR or ATFST connection was created using Cisco WAN Manager or SNMP with the cell-routing restricted property set. During a later re-configuration that restriction was lifted causing the 3005 software error and the change of the connection type to FPVBR. Delete and re-add connection without cell-routing restriction. |
|
|
cnftrk failed to increase trunk receive rate. dspbuses shows the bus bandwidth has 100% allocated. The problem occured to Y-red FRMs in the lower shelf of IGX. Use getubus <slot> 0 to free up incorrect UBUs allocated to the slot. Since the system has run out of UBU, any operation required new allocation of UBU, such as adding a new trunk, will be failed. |
|
|
The BXM-T3 line is configured to be in the Direct-mapping (HEC) mode and the CAC override is Disable at the port. When attempting to add a single connection to a BXM-T3 line with a PCR=104268cps, the system rejects and return an error "CAC override disabled on port". This indicates that the request will over subscribe on the line but in fact it is NOT CAC override is Disabled. BXM-T3 line is set for Direct-mapping (HEC). Attempt to add connection with PCR=104268. |
.
The following is the list of fixed anomalies in the 9.2.23 Switch Software delivery. Included with each is a brief discussion of the problem.
| Bug ID | Description |
|---|---|
|
SWERR 3005 BAD_BW_DEFAULTS seen on two bpx nodes atfr or atfst connection was created using Cisco Wan Manager or SNMP with the cell-routing restricted property set. During a later re-configuration that restriction was lifted causing the 3005 software error and the change of the connection type to fpvbr. Delete and re-add connection without cell-routing restriction. |
|
|
Full rebuild after a 1000001 abort No special conditions - can happen with any marginal control card |
The following is the list of fixed anomalies in the 9.2.22 Switch Software delivery. Included with each is a brief discussion of the problem.
| Bug ID | Description |
|---|---|
|
CMUPDATE state machine uses a lot of CPU time after node rebuild in a large net. Large network and node has many thousand (around 10000) connections spread to many nodes. Turn off routing state machine to provide more CPU for CMUPDATE state machine. |
|
|
Node does not clear Comm Break with some nodes although it could send messages to them. Node is in Comm Break with several nodes, and some close by (in terms of hop count) nodes go continuously in and out of Comm Break. As a result node never sends a Comm Break test message to nodes farther away. Clear up the situation of nodes going in and out of Comm Break. Could be a flaky trunk, or nodes are busy with something else. A final resort would be to give the command: droppkts 100 <originating node> 60 on the nodes going in and out of Comm Break where <originating node> is the name of the node trying to clear Comm Break. After one wants to attempt again to clear Comm Break with a node type: |
|
|
tftp file for PHYSLINE object stats reports all ports as zero. The port value could be non-zero but garbled up value. Enable Physline stats and we have multiple physlines (i.e trunks/lines) up on the same card. |
The following is the list of fixed anomalies in the 9.2.21 Switch Software delivery. Included with each is a brief discussion of the problem.
| Bug ID | Description |
|---|---|
|
A user with privilege level SuperUser cannot execute the "dspqs" command. The user has to be of privilege level StrataCom or Service to execute the "dspqs" command. Ensuring that there are no standby database updates pending is an important step in executing a graceful switchcc. One can determine this fact through the "dspqs" command. |
|
|
Unable to add a PVC on a BXM card at less than 50cps/19.2kbps. The current BXM has a limit for smallest SCR/CIR, not allowing a PVC to have a SCR/CIR less than 50cps/19.2kbps with policing. The system software was restricting SCR/PIR to no lower than 50 CPS (where 6 CPS could be supported). This Command: addcon 9.3.44.444 nodename 9.2.44.444 abrfst 40 PCR(0+1) value out of range (local end). Valid range 50 - 96000. If the user entered PCR < 50 cells, switch software CLI checks for the entered policing value. If it is off (Value = 5), then it proceeds further to add the connection. Else, it blocks. This is true for CBR, VBR, ATFR, ABRFST & ATFST connections. In the case of ABRSTD with VSVD disabled, it allows to add connection only in the following cases. 2) PCR < 50 cps and the endpoint on a feeder trunk. For all other cases, it displays the following error message and blocks. "For ABRTSD with VSVD: OFF connections, PCR should be at least 50 cps" In all the above cases, if it is not a DAX connection and the remote card is a BXM/UXM interface, then the slave will check if PCR < 50 and policing is off. If not, it sends a cm error message to the master. The cm message: BAD_PIR_AT_SLV In the case of ABRSTD with VSVD=OFF, the slave allows to add the connection if PCR < 50 cps and the endpoint is on a feeder trunk. |
|
|
A user can disable CAC override (atmPortCACOverride) even though the port is oversubscribed. |
|
|
For ABR Queue, cnfportq or cnftrkparm does not allow to set CLP_LO higher in value than CLP_HI. Configuring ABR Queue (BXM/UXM) by using cnfportq for port and cnftrkparm for trunks. Do not configure CLP_LO higher than the CLP_HI value for ABR queue. |
|
|
Modem upgrade failed due to a immediate downgrade for a non-DAX UVM connection. The failure rate may be as low as 10%, or as high as 95%. This happens randomly and is caused by a race condition. 2. If the failure rate is very high, try using the Fax Relay feature: a. Enable fax-relay on the channel or channels with the command cnfchfax. b. Disable V.25 modem detection on the channels with the command cnfvchparm. 3. Upgrade software to release 9.1.07 or above. This problem is caused by a race condition in SW. It occurs only about 10% of the modem sessions in the lab. In a customer environment the failure rate has been observed as high as 95%. |
|
|
Extra connection statistics are reported in statistics file, or the Cisco Wan Manager rejects the statistics file indicating that it is corrupted. This problem will occur when the user has an access device configured that is supporting connection other than the voice connections, and the Cisco Wan Manager's Stats Collection Manager has statistics of the subtypes FastPad Voice, FastPad Switched Voice, FastPad Data, or FastPad Frame Relay enabled. Do not enable statistics for the subtypes listed above when there are access devices other than FastPADs configured in the network. |
|
|
If a software loop is added to a BNI trunk by "addlnlocrntlp" command. The software loop will become ineffective after a node rebuild or the BNI card is reseated. If a sim-fdr is added on a software looped BNI trunk. The sim-fdr will become unreachable. (1) A BNI trunk is upped and added a software loop by "addlnlocrmtlp" (2) Either node is rebuild or BNI card reset. Delete the previous added software loop and re-add the software line loop on the BNI trunk. |
|
|
The cnfport command is not allowed on BME card ports. This command is used to change the "Shift" and "CAC Override" defaults for the port. Although this was not a part of the original design, a valid reason has been presented to allow configuration of these two fields. No special conditions. If the command "cnfport" is executed on a BME card ports, the message "BME ports are not configurable" will appear on the user interface screen and changes will not be allowed. None. The cnfport command will be unblocked for BME ports when this software change is integrated. It is recommended that only the "Shift" and "CAC Override" fields be modified (if desired) and to leave all other values at their default. |
|
|
When a backcard to an active BCC is removed or inserted, no entry is logged into the event log. When the backcard to a standby BCC is removed or inserted, an entry is logged into the event log. |
|
|
ALM/A VPC connections discard 100% of traffic when routed over ALM/B trunks after a SWSW upgrade from 8.2.59 to 9.1.09. ALM/A VPC connections routed over ALM/B trunks; 9.1.09 and higher software. |
|
|
Executing the following commands one after the other causes software error 9091 1) resetcd both cards of a yred pair. 2) As soon as they come up OK in dspcds, add a conn. 3) As soon as the conn shows OK, perform tstdelay. This software error occurs when we execute tstdelay soon after we add a conn, after noticing in dspcons that the status is OK. It is to be noted that dspcons only displays if the route for that conn is established. The programming of the conn takes a little more longer. Not to execute the tstdelay soon after adding the connection but to wait a couple of minutes. Especially this long if there are a lot of connections in the node for which the cards may take a little longer to program the conns. |
|
|
Addcon is being allowed to oversubscribe the receive bandwidth of the port. Addcon command was given on a port with CAC override disabled. Manually calculate the available receive bandwidth of the port before adding/configuring a connection. |
|
|
When you do dspnds -d, the columns wrap and the display is a mess. You have to do a clrscrn to get rid of all the junk before you can display anything else correctly. The problem is that prior to 9.1, the command displayed the node name followed by IPX, IGX, or BPX. Now, the command displays the node name followed by the longer part number (84xx or 86xx). |
|
|
Printer output not properly formatted in 9.1.09. Headers not printed properly for every print operation. |
|
|
switchyred causes data transfer stops for 1 to 4 min. The secondary should be active before the rebuild. The data transfer stops/tstdelay fails for 1-4 min. after switchyred. dspchstats shows no data can be received from bpx node, dspcon shows route is OK and no alarm at all. Issue switchyred such that primary card is active before rebuild. |
|
|
It is not yet clear but possibly when we have trunks or ports on a BXM card and either BXM gets reset or BCC switchcc/rebuild happens. Note: This bug does not cause any harm. 8096 is STAT_UNEXPECTED_VAL. Basically, this is logged when we do not have statistics block available. This error may be ignored, if we are in the middle of condition mentioned above. |
|
|
Software error 919 was logged. Jobs were running on the node, to reset the card (for which the error was logged) periodically. |
|
|
On burnfwrev, dspcds shows UXM card as active when it is getting programmed. On burning a UXM card through CBUS, dspcds displays card as still active. Check dspfwrev whenever burning f/w to be certain that card is getting programmed. |
|
|
Software error 986 on configuring a virtual trunk. The following sequence can lead to the software error. - Upport 6.1 on a UXM and enable ilmi - Change the protocol from ilmi to lmi on port 6.2 Also if you delete a feeder trunk and up and configure a virtual trunk you may find this problem. The software error 986 logged in this case doesn't have any harmful effects. |
|
|
Software error 31 and software error 52 (software watchdog abort) logged. Command addlocrmtlp causes the remote node to abort when the remote end of the connection is a BPX feeder and the connection is a VPC. The local end of the connection may be a BXM or ASI port. The problem only occurs when command addlocrmtlp is initiated from a BPX, for example, an UXM to BPX feeder VPC connection will not trigger the problem in a mixed network. 1. Use VCC connections for troubleshooting when possible 2. Make sure a stand by BCC in STANDBY state is available on the remote node as an abort/switchover will occur. |
|
|
hitless database will not get updated even node has done hitless rebuild due to an abort. Cause an abort and do dsphitless. Current hitless rebuild count shows 0. |
|
|
tstdelay command given for an ATM connection, reports with the message "State Table Hung". Test was getting aborted due to some card failure events reported for that card. None. Interpret the message "State Table Hung" as "Test delay aborted". |
|
|
switchyred causes LOS for 10 secs. I cause LOS on the protection line. The working is active and the last user request= W->P. When I do a switchyred 11 on BPX node, the active working line experienced LOS for about 10 sec. |
|
|
APS: switch back to working line incorrectly. 1) switchapsln 11.8 5 (-> switch from W->P) 2) switchapsln 11.8 6 (-> switch from P->W) 3) switchapsln 11.8 5 (-> will not switch. Last user request shows manual W->P)PS 4) Disconnect RX of 11.8 (-> switch to the Protection line due to LOS on the working line) 5) Reconnect RX of 11.8 (-> switch back to the working line). The problem is why does it switch back to the working line after LOS is clear on |
|
|
AIS cell generated even when remotely looped connection was in OK state addrmtlp on a failed routed connection, failed because of LOS on the remote-end line connection on this-end, non LOS end from where addrmtlp is executed, get into OK state but still it generates AIS cells |
|
|
Software errors 900 or 1427 were observed in the network. Node sending messages to Cisco Wan Manager timed out on the application level, while network handler was still sending the message. |
|
|
On trying to delete members in an IMA trunk, you get a message saying "Cannot reduce trunk xmt rate by cps to delete members". You get this message even when the remaining members have enough bandwidth to support the transmit rate configured for the trunk (In case of IMA Virtual trunks, sum of transmit rates configured for all the virtual trunks). You might also get the message "Cannot reduce trunk xmt rate below min. rcv rate (cps) to delete members". You get the first message when members in an IMA trunk are deleted with the trunks transmit rate less than the bandwidth of the members being deleted. You get the second message when the transmit rate is more than the bandwidth of the members being deleted, but transmit rate minus bandwidth of members being deleted is less than the statistical reserve. First increase the transmit rate of the trunk to be such that even if you reduce the bandwidth of the members being deleted from it, you still have more bandwidth than the statistical reserve. Now delete the member(s). |
|
|
dspcds does not show up as mismatch for the BXM card When active VSI supported BXM is replaced by the BXM card which does not support VSI. |
|
|
Software error 1415 is logged on a Standby. Standby gets an update to delete a trunk that is already deleted. The software error does not indicate a problem, as after the software error is logged both the Standby and Active are in sync regarding this trunk. |
|
|
Prompt string for trunk various load type string overflows screen. |
|
|
addyred fails for the active BXM card in 9.2. When a node with 8.4.21 image, which has active BXM card, is upgraded to 9.2 then addred is not possible for this BXM card. |
|
|
1) Even when there is a VPC conn on an ALM-A card, the line mode is allowed to be changed to VCC. 2) Even when there is a VPC conn (non -dax) on an ALM-A card, the user is allowed to add a VCC conn with the same VPI |
|
|
AXIS feeder may be shown as MXG feeder. This could happen after a node rebuild/processor switchover. Delete the shelf and add it back again. Another option is to patch the Fdr_Info database for the affected feeder with the correct revision number. There is a very small possibility that this issue can happen during an upgrade from 9.1 or 9.2 releases before 9.2.21. This should not affect user traffic though the feeder might become unreachable. This can be fixed by the options mentioned in the workaround. For upgrades from 9.2.21 or later, this issue will not happen again. |
|
|
Unable to add 3 segment conns using CM GUI When we have feeder connected to BXM card of BPX routing node and for, BXM trunk configuration: ILMI/LMI protocol is enabled as CARD based. Before adding Feeder shelf to BXM trunk, configure BXM trunk (cnftrk command) with "Protocol by the Card" as NO and then, add shelf. If you want card based ILMI/LMI, run cnftrk again to reconfigure option. If you have already added shelf to BXM trunk and ILMI/LMI protocol is card based from very beginning of upping the trunk, configure trunk to have "Protocol by the Card" as NO, then reconfigure it back to card based protocol. |
|
|
Addyred fails on LDM with warning about incorrect values (mismatch) for RCMP entries. Condition: |
|
|
Channels on AXIS have alarms while corresponding connections on BPX are O.K. 1. The connection on BPX feeder trunk is local. 2. BPX feeder trunk loses signal and recovers. |
|
|
Some connections that are shown by dspcons cannot be displayed by dspcon, nor can they be deleted with delcon or modified with cnfcon. Upgrade from 9.1 to 9.2.20. Last port of a BXM card has to be an active routing trunk. Simple work around: Cause full rebuild on affected node Workaround nor requiring rebuild: This problem only occurs when the last port of a BXM trunk is a routing trunk. The memory of the port lccb of this trunk needs to be patched to remove the dual allocation of some connection. The main problem is for the trunk on the last port. But if later on one of the other trunks would be downed (deleted and then downed). A problem could develop for some of the newly freed lcns as well. We therefore strongly suggest not to down any trunks until the software revision was upgraded to 9.2.21 or above |
|
|
BXM E3 and T3 cards show up as wrong type in Cisco WAN Manager. |
The following is the list of fixed anomalies in the 9.2.20 Switch Software delivery. Included with each is a brief discussion of the problem.
| Bug ID | Description |
|---|---|
|
01.) Connections fail when there is a loss of signal on the UXM feeder trunk as expected. 02.) When the LOS is no longer present, the connections still remain failed, but there is data continuity. 01.) LOS on the UXM feeder trunk can cause this situation 01.) Rebuilding the problem slot will clear the incorrect status. |
|
|
Card error (N Fatal from 0x17:0x25010022) is logged on standby of Y-red pair when the card is reset/node rebuild. This happens only on standby of Y-red BXM pairs which support VSI and only when the card is rebuilt along with other cards simultaneously. |
|
|
Connections are deleted without user intervention and software errors 532 logged with 000000FF in the data field. The software errors are logged prior to the logging of the connection deletions in the event log. The source node for the deletions (the one with the software error 532s) is an IGX or IPX. The connections deleted terminate on FRM or FRP cards on the source node. This problem has only observed a few times, but was observed multiple times on at least one node. It is very likely that an operation performed on the node triggered the problem, but this operation has not been identified. The conditions for this problem need to be identified before a workaround can be provided. To help characterize the problem, please collect the following: 4. dsplog (showing auto deletions and prior activities) 5. Anything that does not look 'normal'. 6. Input from the customer regarding activities performed on the node. Issuance of the 'switchcc' command will probably not restore the connections, but may be necessary to resolve inconsistencies that prevent adding the connections again. The connections were probably deleted to resolve an inconsistency. Unfortunately the auto deletion is not complete, and logical endpoint data from the auto deleted connections may prevent adding connections after the auto deletion. The logical endpoint data is rebuilt after a CC switch, thus removing the inconsistency. Further Information: If this problem is observed, please determine what operations were performed on the node at the time the problem was observed. The auto deletion condition has not been identified, and the problem has not been reproducible in the lab. Inconsistencies induced into the connection data bases have not produced the characteristics observed in the field (primarily the swerr 532). The induced inconsistencies have shown that the auto deletions of the connections may be incomplete, and a switchcc is often required after the auto deletion to restore the logical endpoint structure. |
|
|
Wrong value returned in SNMP for atmOtherEndptDesc of a connection terminated on a remote BTM feeder trunk. The port number should be 255 not 256. When query from BPX side in SNMP. NMS needs to interpret port number 256 as 255 for this kind connection. |
|
|
Unable to configure a UFM-C E1 line to unchannelized with 9.1.x SWSW. Cannot set E1 line framing to OFF Cannot set line Signalling to None. Customer environment not relevant. Affects 9.1.03 and 9.1.06 and probably all releases of 9.1. |
|
|
When a connection is ended on a BXM port and MCR is less than 6. Don't set MCR less than 6 if a connection is ended on a BXM port. |
|
|
Hardware watchdog aborts on all versions of release 9.1 on an NPM-32. When software attempts to access memory in the 32-64Mb range on an NPM-32 an access error interrupt will not be generated, the CPU will freeze until a hardware watchdog occurs. A switchover will occur if a standby NPM is available. A rebuild will occur if a standby NPM is not available. NPM-32 with the SNMP Get community string configured. Certain SNMP operations are causing switch software to access non existent memory. |
|
|
No OAM loopback configuration is displayed while cnfoamlpbk is in progress or upon completing cnfoamlpbk command. Occurs while performing cnfoamlpbk command Need to type dspoamlpbk command before and after cnfoamlpbk. |
|
|
The physical portion of a BXM trunk, a physline, is allowing a BNI card's physical based CRXL statistic to be enabled. The BXM's CRXL statistic is a logical statistic based and not the same as a BNI card's CRXL statistic. This will occur when the customer enables the statistic "BNI: Total Cells Rx (Phys)" and there are BXM trunks up on the node. The physical portion of the BXM trunk, the physline, will enable this BNI-only statistic. Ignore the BNI-only statistic that is being reported for the BXM trunk. |
|
|
For the following conditions, the user either cannot add yred or is reported with false mismatch alarm. The user does not get any benefit by upgrading to the enhanced UXM card because of the mismatch. 1. Can not configure yred for mixed UXM cards if in standby mode. Can not configure yred if in active mode and the primary card is enhanced while secondary is non-enhanced. 2. The switch issues false mismatch alarm under any of the following conditions: * For standby yred UXM card pair, when change the secondary card from non-extended card to extended card. * For mixed yred UXM card pair, when upgrade from release 9.1 to release 9.2. * For active non-yred card, when change from extended card to non-extended card. * For active yred card pair, when change the secondary card from extended card to non-extended card. |
|
|
Card error (N Fatal from 0x17:0x25010022) is logged on standby of Y-red pair when the card is reset/node rebuild. This happens only on standby of Y-red BXM pairs which support VSI and only when the card is rebuilt along with other cards simultaneously. |
|
|
It takes too much time for the virtual trunk to declare/clear Virtual Trunk Path Failure when the VPC connection at the cloud becomes bad/good even if ILMI is configured on the cloud port with trap enabled. This happens when a UXM virtual trunk is connected to a BXM cloud port and ILMI at the cloud port is configured to be on the BXM card. When a UXM virtual trunk is connected to a BXM cloud port, do not configure ILMI protocol on the BXM card at the cloud port. Have protocol on the BCC. |
|
|
There's not enough space for cnfpref command when the path is 10 hops long |
|
|
Software error 55 after graceful upgrade due to sampling of the card even when it was not active. |
|
|
Command "dcdrtbl" causes software errors 532 and 55 |
|
|
Software error 2000 (SNMP_INVLD_OBJ) logged on BPX. The SNMP get operation on BPX for trunk parameters with the remote node IGX and other end slot greater than 32 cause this error. |
|
|
Certain counter values in CiscoView are undefined in CLI and display incorrect values. SNMP Agent on switch is returning bad values. Observed on node with BXM viewing dspportstats, verifying CiscoView values, and walking switch MIB values. |
|
|
The node performed the hitless rebuild but the log shows that the MGX 8220 shelves all went into and out of alarm. Logging onto the MGX 8220 shelves and displaying their logs indicate that the MGX 8220 shelf reported LMI failure in addition to the LCNs going into and out of alarm. This problem will only happen when the BPX node has a lot of connections (e.g. 10,000+) terminating on it and has a lot of MGX 8220 shelves (e.g. 8+) attaching to it. The MGX 8220 reports LMI failure because the BPX is busy rebuilding the connections and is not responding to the MGX 8220 LMI polling in time. |
|
|
Software error 121 (CB_TMOUT_FLUSH) is logged when there standby UXM cards performing selftest, and a hitless rebuild or switchcc is done. |
|
|
Node experiences 3M and 1M3 due to flooding on ILMI/LMI channel or an IP relay channel. When we have feeder added (PAR feeder type) and we have added connection with VPI, VCI 3.8 or 3.31 (which are used by ILMI/LMI and IP relay channels). The added feeder could be MGX 8220, PAR, popeye. Do not add connection with VPI, VCI 3.8 or 3.31 when we have feeder added. |
|
|
The various Qbin depths does not change with the new transmit rate value for non-added trunk. Various Qbin depths are not reflected with the transmit rate change for non-added physical/virtual. |
|
|
Software error 129 seen on the active BCC when dspswlog is issued when the standby BCC is in cleared state. When Standby BCC is in cleared state. This happens for a very small interval soon after a switchcc. Wait for sometime after switchcc, until the card comes out of the cleared state. |
|
|
User id updates may not stop when one user id is marked with a corrupted password. This can take up bandwidth for control messages. No easy one. Patch memory of the user id database on the node with the number to clear the corrupted password flags. |
|
|
Trunk errors not reported under "dsptrkerrs" after the upgrade from 8.4.14 to 9.1.09 Trunk errors were reported on heavily loaded NTM trunks with Bursty Data B traffic prior to the upgrade. Since the IPX/IGX upgrade to 9.1.09 no error are registered. Delete, down, up, and re-add the trunk in question. Merely deleting and re-adding will be insufficient. If delete and add trunks are not desirable, a procedure to patch memory are described in the workaround enclosure. This procedure applies to all platforms. This problem affects BPX, IGX and IPX trunks, lines AUTO statistics collections after upgrade from 8.4 to 8.5 or 8.4 to 9.1 or 8.5 to 9.1. |
|
|
This DDTS report is for new functionality. There are several new versions of BXM cards that are known as "enhanced" cards. In robust messages that are sent from switch software to Cisco WAN Manager, the new card types need to be sent. |
|
|
Statistics counter value is displayed for atmPortStatBcmRxs. Command 'walk atmPortStatEntry' was given for a BXM port from an SNMP tool e.g. snmptalk. Ignore this counter value, as atmPortStatBcmRxs is not valid for BXM port statistics. |
|
|
The dsptrkstats command, when executed on a BXM trunk, displays the full physical port bandwidth for the "trunk speed" rather than the configured bandwidth. This will occur when the command, dsptrkstats, is run on a BXM trunk. This is a cosmetic defect. The trunk speed is really the value that the customer has configured, however, this command is displaying the full physical line interface rate. |
|
|
LDM and CVM connections cannot be modified by the Cisco Wan Manager (CWM) GUI. Specifically, preferred route and COS cannot be changed and the connections cannot be deleted. LDM and CVM connections which have been added to an 8.4 network and upgraded to 9.1.12 cannot be modified nor deleted by CWM GUI. Command line access works fine. Connections deleted and re-added or which are added in 9.1 work fine. Delete (via CLI) and re-add (via CLI or CWM) the connections after the upgrade is complete to restore full management capability. |
|
|
In the Robust ATM Connection Object message sent from Switch Software to StrataView, certain connection object subtypes are not being sent. In particular, the following are not being sent. Instead, they are being mapped to other subtypes. The mappings need to be removed so that the additional details will be available to StrataView. There is no workaround needed for this situation. It will not affect most customers. The additional information is sometimes useful to StrataView. |
|
|
The BPX node reported that the firmware upgrade was completed, but the actual burnt firmware failed. Due to a bad flash, the firmware upgrade aborted. The firmware upgrade can also abort when we try to burn a certain kind of firmware over a very old and incompatible firmware. In such cases the firmware burn would abort but switch software would report incorrectly that the burning of firmware has been completed. Usually burning of firmware takes 2 to 3 minutes. If swsw reports the burn to be complete within 20 to 30 seconds these are signs that something is wrong. Also there must be no card errors while the burnfw is taking place. |
|
|
Software error 2085 is logged on standby. Standby does not get TRUNK_CNFG update in time, when we up a trunk and we have line stats machine triggered at that moment. Note: This bug fix also, includes changes made for 9.2 rev up for bug # CSCdm53376 See this bug release notes for more information. |
|
|
cnftrk does not prompt for Header type (like STI/UNI) BTM and AIT trunks. Henceforth it does not prompt for selecting gateway type (like BAM, CAM, SAM). When we have BTM or AIT trunks and we do "cnftrk" on those trunks. |
|
|
Standby controller card kept being reset and was in a continuous state of updating. When TFTP statistics are enabled, and the global that controls when a file interval is completed gets clobbered it may lead to this situations. We currently do not know what conditions lead to the clobbering of the global. 1. Disable and then re-enable all TFTP interval stats 2. Patch the Rt_Interval_In_Prog global to the correct value. Rt_Interval_In_Prog is used to control the completion of a file interval by comparing it with the current time. It is displayed in "Rt Interval:" by dspstatparms command. When Rt Interval is clobbered and has a value much smaller than the current time, the system will try to finish too many file intervals, which may prevent standby updates from completing. Code has been put in to correct Rt Interval automatically when it is clobbered. Software error 2095 is logged with the correction, one stat file is lost and a new file interval is started. |
|
|
Standby controller card logs several software error 886's and 2071's during an upgrade for circuit lines. The software errors are logged, and the supporting data structures for statistical alarming are not allocated. These errors can and will fill the standby's software error log. These software errors are a result of a recent code check in which is believed to not have ever made it to the field. |
|
|
Unable to bring up a UNI IMA Trunk between IMATM and UXM. |
|
|
tstber in manual mode stops receiving after nearly 1 1/2 hours. When auto tstber also runs at the interval set in cnftstparms for self test. Disable self test using cnftstparms if you need to run tstber in auto mode continuously. |
|
|
Can't configure cnfasm parameters 8-12 from Y-> N. "cnfasm 8", "cnfasm 9", "cnfasm 10", "cnfasm 11", "cnfasm 12", "cnfasm 13" won't work for all BPX 9.2.10 nodes. |
|
|
ABR traffic class gets dropped from BXM/UXM/BNI trunks. An non-graceful upgrade from 9.2.10 to 9.2.20 with ABR traffic class set for the trunk. This is for both, IGX and BPX. This is because, we store the traffic class bits incorrectly in BRAM and it shows up when the 10th traffic class RT_VBR is introduced into 9.2.20 |
|
|
The following symptoms are all related to this defect: - An error and abort 3000000 is logged under seemingly normal circumstances, followed by various memory errors such as 502, 589, 504, 501 - A 1000003 abort is logged from the Root process on the standby after a switchover, or on the active after a hitless rebuild. - After a switchover, the standby is continuously reset, the IGX indicates a watch dog timeout, the BPX indicates a system reset. - The active card continuously resets after a hitless rebuild on a node that does not have redundant controller cards. The hitless rebuild could be caused by the user via the resetcd command or it could be a true hitless scenario. - Other unknown problem can occur due to this defect, this release note will be updated as investigation reveals them. The following conditions are needed for this problem to occur. 1) The node needs to have a large configuration, that causes non-hitless memory allocations to overflow into the hitless memory region. Overflows can be detected by using the service level command (dspprf r t). The column to the far right indicates the number of overflows that have occurred. On a 64M controller card, when the overflow count for the second pool region (PL02) is non zero, that indicates that a non-hitless memory allocation has overflowed into the hitless region. On a 32M controller card, when the overflow count for the first poll region (POOL) is non zero, that indicates that a non-hitless memory allocation has overflowed into the hitless region. BEWARE: The overflow counts can be cleared. If the command (dspprf r t c) is issued the overflow counts will have been cleared, and you will not know if you have overflowed into the hitless memory regions. However, you can tell if and when the command has been cleared, by the "Last Cleared" time stamp at the top of the screen. If it is a value other than "Date/Time Not Set" then it has been cleared. If your node does not have memory overflows into the hitless region, then these problems cannot occur. 2) The first memory block in the hitless region is an overflow memory block of size 1. The service level command (dspalloclocal #region#) will display data for the locally managed regions -- our hitless regions. #region# can be 5 for region HITLESS1 (on 32 and 64M CC's), or it can be 15 for region HITLESS2 (on 64M CC's). The memory blocks listed are in the order that they are in memory. Therefore if the first entry (top left corner) of the first page of dspalloclocal's display is a size 1 overflow block this problem can occur. To determine if this block is a overflow block invoke the service level command (dm) on the address under the "cntl" column. The value should be a 0xC0 or an 0x80. If it is an 0x80, then this is an overflow allocation. 3) An overflow block of size 1 follows an overflow block of any other size, or it follows a memory hole (unallocated memory). The dspalloclocal screens can be searched for overflow blocks of size 1, using the method explained in (2) above. If the preceding block is an overflow block of any size, then these problems can occur. NOTE: There are several 10's of thousands of possible memory blocks, this scan can take a long time. 4) The final key is if the card undergoes any hitless rebuild, whether invoked by the user or not. Any hitless rebuild, that occurs when the node has the first memory block as a size one overflow or a size one overflow following any other size overflow, will cause one of the before mentioned problems. |
|
|
1) The active controller card can abort due to a memory limitation error logging 3000000 errors and aborts, followed by various other memory errors such as 502, 589, 504 or 501's. If there is a secondary controller card it will switch over, and can possibly lead to impact #2 listed below. If there is no secondary controller card, or the secondary controller card is not in "Standby" state, then the active card will undergo a hitless rebuild and can lead to impact #3 listed below. 2) The standby CC can undergo an unknown number of watchdog timeout (WDTs) continuously resetting itself. This will be evident by the active's log indicating that the standby card is reset due to a WDT (IGX) or a system reset (BPX). This is also evident by the dspcds screen showing the standby CC cycling between missing and downloading. 3) If there is no standby CC available to take over when the active undergoes a hitless rebuild, the active CC can: - lock up, not responding to any login attempts, appearing as UNREACHABLE by other nodes in the network. - Undergo an unknown number of watchdog timeouts, and continuously restart. 1) Avoid causing a user hitless rebuild via the resetcd command. 2) If the standby or active card becomes unresponsive or continuously resets itself it can be resolved immediately by pulling and reseating the controller card that is having these problems. Or the customer can wait for an unspecified amount of time until the memory cleans itself up. However, we've seen the card resets last for longer than a day, before someone pulled the card to reset it. When we are freeing overflow memory during a hitless rebuild and an overflow block of size 1 is the first block of hitless memory or the block of size 1 follows a memory hole or another overflow block, the memory step counter increments incorrectly and we jump forward an incorrect number. In this jump, we can skip other blocks of overflow memory that should be freed but are not, causing a memory leak which can then eventually cause a 3M abort. Or this jump can take us to a memory block that is apart of a larger memory allocation, and therefore has no forward jump counter, at which point we sit and continuously process that memory block, causing an infinite loop and eventually a WDT. Or this jump can take us to a memory block that is no longer in use, but still has its old value in it that can then cause a 1m3 abort because we are processing obsolete data. More investigation into exactly how these scenarios can be achieved as well as any other problems are being done, and this release note will be updated accordingly. |
|
|
Software error 633, traffic class displayed on cnftrk not cleaned up properly and "VC Shaping" configuration not shown in dsptrkcnf/cnftrk screen. |
|
|
The command cnftrk on UXM feeder trunk when executed currently allows the channel count to go below the used channel count on the UXM feeder trunk. This has been blocked. Executing the cnftrk command and lowering the channels to a value less than the used value. |
|
|
The traffic types displayed on cnftrk/dsptrkcnf have garbage. |
|
|
The default service class template is set to 2 (instead of 1) if upgrading from 9.1.00 to 9.2.10. This happens only when upgrading from 9.1.00 to 9.2.10 (directly, 9.1 -> 9.2.10 OR via 9.2.00, 9.1.00 -> 9.2.00 -> 9.2.10). This will have an impact only if VSI is used in the network. Different scenarios: 1. If VSI is used in 9.1.xx and the network is upgraded to 9.2.10, then this is a show stopper - the VSI conns can loose continuity. All interfaces will have templates set to 2 (PNNI template) instead of 1 (MPLS template). MPLS network SHOULD NOT be upgraded from 9.1 to 9.2.10 - instead it should be upgraded to 9.2.20 (which will have this fix). 2. In all upgrade paths from 9.1 to 9.2.xx (xx < 20), the default template will be set to 2 for all interfaces. The template assignment can be modified using the cnfvsiif command if VSI is going to be used. |
|
|
Unable to addtrk or loss of continuity on UXM conns (may affect ports or trunks) |
The following is the list of fixed anomalies in the 9.2.10 Switch Software delivery. Included with each is a brief discussion of the problem.
| Bug ID | Description |
|---|---|
|
The MIB variable slotCardStatus does not show proper value. The IPX/IGX/BPX SNMP agent reports the above MIB variable as active when there is no backcard installed. |
|
|
AIS alarm counts are not displayed for E3 lines and trunks when using the commands dsplnerrs line_num and dsptrkerrs trk_num. The problem occurs on BPX nodes using E3 lines or trunks. No workaround is available; however, the AIS alarm status is correctly displayed. |
|
|
Discrepancy in the "dspchstats" when comparing the two end points of a given PVC. More traffic appears on one side than the source sends. |
|
|
The connection got deleted because the update message sent from Master node is inconsistent with the Slave node. Software error 614 was logged. |
|
|
The command dsplnalmcnf only shows the line alarm configuration, it does not show the trunk (packet line) alarm configuration. The customer must use a round about way to view the trunks statistical alarm configuration as detailed in the workaround. We can use a round about method to display the current line and trunk statistical alarm configuration. This can be done by invoking cnflnalm. Then from the list of alarms, choose one that is only relevant to trunks (i.e. Tx NTS C Dscd). You will then be prompted for the "Alarm Class?" immediately hit the <DEL> key to cancel the command. The screen now has the configuration for 8 statistical alarms, one of those is the alarm you specified. |
|
|
Only for the UXM and BXM can NMS get the information of slotBackNumPort from the MIB. |
|
|
BIP8 errors are received at 10E-3 and the line/trunk is in MINOR alarm. The line/trunk MAJOR alarm threshold is configured at 10E-3 (cnflnalm command). When BIP8 errors are received on an E3 line or trunk at a rate of 10E-3, the line or trunk will not go into a MAJOR alarm state. The line/trunk will instead go into a MINOR alarm. Change the MAJOR alarm threshold for BIP8 to 10E-4 using the cnflnalm command. |
|
|
Software error 52 in dspswlog with VT_1 as running process One-time occurrence of a watchdog timeout on a BCC while VT'd in from another node |
|
|
The wrong error message is reported: "SVC caching: timeslot(DS0) for this channel already in use". Number of LCNs (channels) is used up on the remote BXM port while adding a connection. 1. Verify the error condition by adding the same connection to the BXM port as a master end. Message "No channels left on this line" indicates the problem. 2. Allocate more channels on the port use command cnfrsrc so you can add the connection to the port. |
|
|
After an ARP request is received by the switch with the network id of the senders address different than the network id of the switch subsequent walks of the ARP table will cause a 1000003 abort. Remove walks of the switch ARP table or set the SNMP get community string to NOACCESS. |
|
|
Some connections are deleted after network flood is cleared. In the lab where faulty hardware is used to simulated flood, after flooding is cleared, there are some connections being deleted. This problem is caused by the network messages that are circulated in the queue using the faulty hardware. Network messages were corrupted causing the switch to interpret the network message incorrectly and the connections are deleted. |
|
|
dsplogcd 112 5 cmd entered and screen freezed The card is BXM-T3/E3 and sonet mode attribute has bad value. Use "dspcmi p" to examine the value. It is bad if the value exceeds 6. Patch sonet mode to 0. Please contact Cisco for the operation. |
|
|
The OAM loopback test may be failing on a DAX conn with endpoints at 2 cards on the same node. When the OAM capability is disabled on one card, the OAM loopback failure condition is also cleared at the other card which still has the OAM capability enabled. |
|
|
The response of an SNMP query of the object atmPortIfType is wrong. oc12-smf(10) is returned for a BXM T3/E3 card. |
|
|
dspstatsinfo is counting a connection terminated at a feeder trunk. If there are connections terminated at feeder trunk, they are included in the summary of the connection count. |
|
|
3-byte frames routed over a UXM trunk on a frame forwarding connection between a UFMU and a UFM port are not being received by the other end. If transmitting 3 bytes frames on a frame forwarding connection between a UFMU and a UFM port, routed over a UXM trunk, the frames get corrupted at the UXM card on the transmitter node and hence are discarded by the receiver node. Do not transmit frames of size less than 5 bytes on a frame forwarding connection between two UFMU connections routed over a UXM trunk |
|
|
For the following conditions, the user either cannot add yred or is reported with false mismatch alarm. The user does not get any benefit by upgrading to the enhanced UXM card because of the mismatch. 1. Cannot configure yred for mixed UXM cards if in standby mode. Cannot configure yred if in active mode and the primary card is enhanced while secondary is non-enhanced. 2. The switch issues false mismatch alarm under any of the following * For standby yred UXM card pair, when change the secondary card from non-extended card to extended card. * For mixed yred UXM card pair, when upgrade from release 91 to release 92. * For active non-yred card, when change from extended card to non-extended card. * For active yred card pair, when change the secondary card from extended card to non-extended card. |
|
|
dspchstats command does not show OAM Rx: AIS when line is failed in 9.2.1F. This works properly in 9.1.09. On an FR-ATM conn (Axis-BPX), fail the FRSM line. This should show AIS for connections on the BPX on the dspcon and dspchstats screens. |
|
|
If old 9.1 firmware is burned into a new enhanced BXM card, then the card will not function. The user interface should be able to verify that the version of firmware is correct for the card before allowing it to be burned. Be careful when choosing the correct version of BXM firmware before burning it. |
|
|
Unable to add connections. Addcon command errors such as "Local resources unavailable or Network Expansion not allowed" or "Local channel unavailable" may be displayed. Commands such as "dcct t" will produce swerrs 374 and 752. (For 9.2, this only occurs on BPX; IGX works OK) Command "dvc #" (where # is a number between one and the maximum number of VCs supported by the switch) for an unused VC shows "VC #0" on a BPX running release 9.1. Only VC 0 should have "VC #0". A VC with an invalid VC index may also have an invalid connection type for an uninitialized VC. If the first "dvc #" screen has "VC #0", "Exists : 0", and "Con Type : ADPCM", attempting to display the second screen will probably cause a 1000003 abort. Do not use "dvc" on an IGX. It will probably cause a 1000003 abort without displaying the first screen. This problem is observed after a non-graceful upgrade from release 8.4 to release 9.1 or on BPX from release 9.1 to release 9.2. There is not a problem with - graceful upgrades, or - non-graceful upgrades from releases 8.2.xx (xx = 55 or higher) or 8.5, or - non-graceful upgrades of IGX from release 9.1 to release 9.2. The problem is that VCs which were used for connections that were deleted in the previous release will have a VC number 0. There is not a problem with VCs which are used for connections, or which have never been used. Audit the standby BCC. If the standby BCC does not have the "VC #0" set for VCs other than 0, and other standby databases are updated, perform a switchcc. Do not reset the standby BCC prior to the switchcc, as this will send the invalid active BCC "VC #0" over to the standby BCC for used VCs. Unused VCs will not be updated the standby CC. If the active BCC is in better condition than the standby, the standby BCC may be reset prior to the switch. The used VCs with index 0 will be auto deleted during database cleanup performed after the switch. Do not use "dvc" to audit an NPM/C. Prior to performing the switchcc, enable connection logging to the event log (cnffunc) so that any connections that are deleted as part of the database cleanup can be identified. If a non-graceful upgrade was performed because a standby CC was not available, loadrev the 9.1 release into flash, then rebuild the node a second time in 9.1 (the first rebuild was the non-graceful upgrade). (Use 9.2 instead if that's the release you are using) Further: The SW initializes the VC number for all VCs when the node rebuilds. In the case of a non-graceful upgrade, SW maps the BRAM from the old release to the new release after the rebuild. The VCs are mapped one at a time. A VC is mapped by clearing all fields (all fields initialized to 0), then mapping the values from BRAM. This mapping is performed for all connections that exist in BRAM. Connections that do not exist in BRAM have their LCON index set to 65535 (-1), but the other fields are not mapped from BRAM. VCs which have never existed (never been used for a connection) are not processed by the BRAM mapping software. Thus the VC number initialized by the rebuild initialization SW is not cleared by the BRAM mapping SW. |
|
|
APS activated alarm trap #20101 seen for T3 trunk. A T3 trunk was modified using cnfrsrc command. The trunk object structure in the BPX has some fields reversed from the definition in the external interface specification. Cisco WAN Manager is coded according to the specification and so it interprets the max_channels_per_port field as the APS slot/port fields. |
|
|
Software error 9082 was seen after upgrade A race condition. The channels on the card were not reorganized the 9.2 way before reprogramming messages were sent to the card. |
|
|
This problem occured when HDM fails the self test continuously due to the bad hardware. Disable the HDM selftest by executing the cnftstparm command. |
|
|
A cnfrsrc on the trunk connecting a Tag Switching Controller to BPX does not allow the MAX PVC LCNs to be more than 10. 1) disable VSI partition on trunk 3.3 Got "PVC Channels(256) Can not exceed (10)" message The underlying problem could be that there is an APS channels halved attribute mismatch. |
|
|
Whenever NMS like CiscoView inquires about UXM back card and whenever we have E1 backcard with BNC type of connectors, we send UAI-E1 as enumerated value. Now, NMS inquires about port and finally get as DB-15 as connector type. If we have BNC type of connector, we end up in giving wrong back card - connector info to NMS. UXM with E1 back card and BNC type of connectors Use CLI to find out type of connector ("dspcd <slot>") or do not reply for SNMP query for UXM with E1 backcard with BNC connectors. |
|
|
SNMP walk will show some revision for ARM backcard. |
|
|
dspblkdfuncs did not list VT as being blocked as blocked for all but 9.2 - (VT not listed at all) |
|
|
switchcc was performed on a bpx having connections. The bpx was previously upgraded from rel 9.1.09 and the connection (due to which the error was logged) was added in release 9.1.09. |
|
|
Software errors 514, 589 on delyred following switchyred with a BXM and another BXM supporting more number of channels (BXM-E) forming the yred pair. This software error occurs when you addyred two BXM cards, replace the secondary with another that supports more number of channels (BXM-E), switchyred and then delyred. In a redundant BXM setup, do not replace the secondary with a BXM that supports more number of channels (BXM-E), and do switchyred. As a workaround replace the primary instead. |
|
|
Minor alarm regarding high CPU usage gets logged after rebuild or switchcc of a loaded node, and never clears. Ignore. There are no bad side effects except for the minor alarm indication. |
|
|
"Connection Channels" field is missing from dsptrkcnf and cnftrk screen. |
|
|
Software errors 514, 589 and 502. Under rare circumstances the first fragment of a message did not match the following received fragment causing buffer overwrites. |
|
|
1) The active, or standby has non-zero interval statistics counts (as displayed by dspstatparms) thereby indicating that TFTP interval stats are enabled. However, TFTP interval stats are not enabled as indicated by dspstatparms' "Object Count" field showing zero objects, and the "Interval Stats:" field indicates DISABLED. This is being referred to as stats being partially enabled. 2) The standby controller card logs a software error 2000000 and then resets itself once. 3) The standby controller card logs the software error 2000000 and then resets itself at the regular interval of 5, 10, 15, 30 or 60 minutes. 4) After a controller card switch over, the new-active controller card logs the software error 2000000 and then reset itself. 5) After a controller card switch over, the new-active controller card fills the software error log with software error 136's. The steps leading up to the various symptoms listed above are similar, but not quite the same. They are explained as follows: 1) The partial enabling of TFTP stats will occur if: a) The customer has a redundant controller card. b) TFTP interval statistics are enabled. c) The active controller card does a hitless rebuild At this point the standby will have TFTP interval stats partially enabled, when they have actually been disabled. d) A controller card switch over is done. At this point both the active and the standby will have TFTP interval stats partially enabled, when they have actually been disabled. 2) The single 2000000 and standby rest will occur if: a) The customer has a redundant controller card. b) TFTP interval statistics are enabled. c) The active controller card does a hitless rebuild d) A controller card switch over is done. e) The same set of TFTP interval statistics are enabled, as done in step b. When the active creates its TFTP interval stats file at the end of its file interval, it will send a message to the standby to do the same. However, when the standby stumbles across some of the TFTP interval stats that where partially enabled (see FURTHER PROBLEM DESCRIPTION below), the 2000000 is logged and the standby controller card is reset. However, when the standby resets all of the partially enabled TFTP statistics are deleted. Note that the active has its global statistic data structure indicating that stats are enabled, so when the standby update mechanism enables the statistics on the standby it will obtain acceptable initializers from the statistic global data structure and the problem "corrects itself". 3) The standby "2000000 and reset" scenario will occur if: a) The customer has a redundant controller card. b) TFTP interval statistics are enabled. |
|
NOTE: Statistics were not re-enabled. In this case the active has its global statistic data structure cleared, but it incorrectly has statistics enabled (See FURTHER PROBLEM DESCRIPTION below). Periodically, the active will send an update to the standby to roll its statistic buckets. At this time, the incorrectly initialized statistics will log a software error 2000000 and then restart the standby. These restarts will occur at approximately the bucket interval rate. We say approximately, because it generally takes longer than 5 or 10 minutes for the secondary card to become fully updated. 4) The scenario for the active controller card logging a software error 2000000 and then resetting itself will occur under the following conditions: a) The customer has a redundant controller card. b) TFTP interval statistics are enabled. c) The active controller card does a hitless rebuild d) A controller card switch over is done. e) Prior to a statistics bucket interval completion, another controller card switch over is done. Prior to the last switch over the standby has incorrectly initialized statistics. Some of the initialized values are zeros. When we switch over, the card starts using some of the fields and logs the 2000000 and then restarts. However, after the restart, the situation has cleaned itself up. 5) The scenario for the active controller card filling its log with 136 errors is the same as for scenario 4. The difference here is that symptom 4 was discovered in an earlier release, but the root cause was not tracked down, so instead preventative code was added to avoid the 2000000 and restart, and simply log a 136 and continue. This scenario will not clean itself up. The 136 software errors will be logged at a high frequency until the work around is enacted. 1) Symptoms 1, and 3 can be resolved by doing the following: b) Disable the statistics. At this point, dspstatparms should indicate that interval statistics are disabled, and the statistic tally counts should also be zero. c) Reset the standby controller card. Realistically the standby should have disabled all of these statistics, but to make absolutely certain I recommend that the standby controller card be reset. 2) Symptom 2 corrects itself, however, I would still recommend following work around #1 to be absolutely certain. 3) Symptom 4 also corrects itself. However, to avoid symptom 4 from occurring in the first place, the following preventative steps can be done. a) After any hitless rebuild, validate that the standby agrees with the active regarding the state of statistics. If the standby has a non zero statistic count, while the active has a zero statistic count, then follow the steps for work around #1. b) Prior to doing a manual controller card switch over, follow the instructions for step a) above. |
|
|
After upgraded from 8.4 to 9.1 or from 9.1 to 9.2 Cisco WAN Manager can not see switch software FRM, VOICE and DATA connections anymore. Only FRM to ATM endpoint connections showed. Problem exists on upgrade to Release 9.1 switch software from Release 8.2, Release 8.4 or Release 8.5, or to Release 9.2 from Release 9.1. 1. Delete connections and re-add After upgrade from 8.2, or 8.4, or 8.5 to 9.1 Cisco WAN Manager can not see SWSW FR-FR connections, voice connections, and data connections anymore. Only FR to ATM endpoint connections are not affected. |
|
|
APS Annex B connection is not defaulted to bi-directional. Use cnfapsln to configure the line to bi-directional Even though the default says uni-directional, BXM firmware will only use bi-directional internally for Annex B. |
|
|
Software error 1433 was sometimes logged on the Standby. Customer typed command 'dspstbyclk'. The only side effect of this bug is the logging of software error 1433. |
|
|
Adding additional trunk from the neighbor node with the port number greater than 8, and the neighbor node is running release 9.1 while this node is running 9.2 before the fix. |
|
|
After a line or trunk alarm is modified, the alarm information is displayed on the top line of the screen, overwriting the "Line/Trunk Alarm Configuration" text. None is needed. The command works correctly, it is just the display that is incorrect. |
|
|
32K channels of BXM-E card not available until "resetcd h" is done Replace the regular BXM active card with an Enhanced BXM card Bring up the BXM-E card in standby state |
|
|
The most common symptom is that when TFTP interval statistics are enabled the software error log is filled with software error 2068's and 504's. However due to the nature of this defect, it is hypothesized that this could also lead to the aborts 1000003 and 2000000. This occurs under the following conditions: 2) The customer has TFTP interval statistics enabled on the UXM ports. After this point, the hypothesized effects could occur. If the customer then enables TFTP interval statistics again (which the SCM will do automatically when it discovers TFTP interval statistics have been disabled after the hitless rebuild) the software error log will fill with the 2068's and 504's -- but it will then clean itself up. Meaning that there is no longer a threat of the aborts and no further 2068's or 504's will logged (unless another hitless rebuild occurs). Do not enable TFTP interval statistics on UXM ports, or disable the hitless rebuild functionality. The problem is that the handle (pointer) to the linked list of memory used for monitoring TFTP interval statistics is not being correctly initialized on a hitless rebuild. After a hitless rebuild, the handle is referencing memory that is no longer allocated. Initially it has it will still have its old data (we do not clear out all memory on a rebuild) so it appears that we are pointing at valid memory. However, because this data is not allocated, it can be allocated for something else related to statistics at which point we now have two different handles to the same memory. If the allocation changes the data format, which is almost guaranteed. It is hypothesized that incorrect handle could, in the worst case, abort because the old data is no longer maintained, or simply cause one of several other possible statistics related errors. Similarly, the old handle could change the memory, clobbering the memory because it does not really own the memory, which could then cause the real memory owner to abort, or cause any other possible statistics related error. When TFTP statistics are enabled after a hitless rebuild we first check to make sure that all existing TFTP statistics are disabled, however, these handles appear to be pointing at existing statistics. When we go to free them, we first log a 2068 because this does not coincide with our internal statistics accounting, then we log a 504 because we are attempting to free memory that has not been allocated yet. Finally, after all of this has occured, we will correctly initialized the handle and then start the enabling process correctly. |
|
|
Forced or manual APS switch causes a switch to opposite line then requested. Switch software and BXM firmware may get out of sync. Performing an APS switch to a line which is already active. Perform an APS clear switch on the line (switchapsln option 1). This should get swsw and BXM firmware back in sync. BXM Firmware cannot handle getting a command to switch to a line which is already active and requests that swsw block such a switch. |
|
|
Software errors 509 and 101 logged This occurs when firmware debug command response from the card is processed immediately after the node rebuilds or after a switchover. There is a very remote chance for this error condition to occur. |
|
|
Adding, deleting, or displaying an APS line This is the result of a display problem in the code. There is no affect on BPX operation. |
|
|
Software error 116 (BAD_OBJ_RESP) seen close in time to when UXM cards were being reset or during switchccs or rebuilds. |
|
|
dspswlog has SWERR 501, possible ABORT 3000000 (3M). dspprf r t shows overflows from DYNM region. dspprf m t shows high memory usage in TRNS process. nwstats shows a very high number of received bandwidth updates (fcode 80 has one of the highest message counts). When the bandwidth for a connection is increased the nodes along the connection path are locked until the process is completed. If there are multiple nodes attempting to increase connection bandwidth at the same time there may be a collision if the connection paths go through the same node. A collision is when a node attempts to lock a node that is already locked. When this occurs, the locked node sends a message saying that it is already locked, and the locking node aborts the lock on all nodes along the connection path. If there are changes that affect adaptive voice connections a node will broadcast a message to abort a lock. The memory leak occurs whenever a node is locked for a bandwidth change, and receives a message to abort the lock. It is possible that this could happen while bandwidth is changed due to user configuration (frame relay connection configuration) or FAX/modem upgrade, but it is unlikely due to the low rate of change and the low probability that a locked node will receive a second request to lock. The memory leak is most likely to be observed in networks which have PCM, ADPCM, or LDCELP connections, and have adaptive voice enabled (cnfswfunc) because the bandwidth lock abort message is broadcast to all nodes. Use cnfswfunc to disable 'Adaptive Voice'. Switch CC after disabling adaptive voice to free any leaked memory. If adaptive voice cannot be disabled, monitor the network for memory accumulation and switch CC if memory accumulation is observed. Use existing memory accumulation maintenance guidelines to determine when a switch CC should be performed. Existing audit scripts for SW release 8.4.xx will need to be modified for changes to the memory display screens. The SWSW will be changed to not leak memory when a node which is locked for a bandwidth update change receives a message to abort the bandwidth update lock. |
|
|
Software error 9000, indicating an improperly aborted selftest, after uptrk or upln on a UXM. Turn off the selftest or wait for it to finish when activating the card. |
|
|
CMGUI for the ATM ports of a BXM card is not available. The message "No ports on this card" is printed on selecting the pop-up port for the card. BXM card is a yred card and the command "switchyred" was given for this card to change the status of the primary card to standby. switchyred back to the primary card (if possible) should solve the problem. |
|
|
In case of Controller Card Redundancy, hitless rebuild may cause switchover and new standby card may never come out of hitless rebuild. During Hitless Rebuild if some null pointer/ memory corruption is detected, which in turn again triggers hitless rebuild and so on. |
|
|
BXM cards went to mismatch when upgraded BPX nodes from 9.1 to 9.2.01. The cards upgraded firmware from MCC to MDA were OK in 9.1.08 until upgraded to 9.2.01. Provided the memory patched to correct the pg_max_lcns = 16352; (16320) |
|
|
300000 Abort logged on the standby BCC of a BPX node with 16K connections If a full rebuild is done on a BPX node having a card with all 16,000 connections on the same card. Not to have 16K connections on the card. With 15K connections on the card and no other connection on the node, this symptom has not been seen. |
|
|
This problem is likely to manifest after a switchcc or an upgrade and results in loss of continuity to a large number of connections. The best way is to clean up the database manually (change memory) Other things are more drastic and not fool-proof, including deltrk / addtrk, and node rebuild. |
|
|
There are several symptoms of this defect as follows: - After a rebuild or switch over software error 549, 886 and 2071's are logged. - One or more software error 928's are logged when a UXM line is upped. - The switch indicates that "Maximum number of logical ports exceeds" but there are fewer than 65 UXM lines up. - A UXM line disappears from the 'dsplns' output after a rebuild or switch over. This can occur on an IGX that has frame relay lines (FRM, UFM, etc.) as well as ATM lines (UXM), a rebuild is done and then lines are deleted. See Further Description for more information on how this can come about. This problem is essentially caused by the logical line and logical port databases getting out of synch with each other (see Further Description). The defect resolution for CSCdm43412 has corrected the code so that these databases can no longer get out of synch. However, once the databases are out of synch, they will remain out of synch and cause the symptoms mentioned above until the databases are cleaned up as follows: 1) Do a dsplns to obtain a listing of all of the IGX's lines. 2) Filter out all of the lines that are not UXM lines. 3) Do a 'dsplogcd 10 slot' for each slot that has these lines, and obtain the logical port number from page 3's output. Find the logical port number for each line 4) Sort the logical ports in ascending order to make the next step easier. ---Now comes the tedious part, finding the corrupted logical port entries--- 5) For each logical port entry (1-64) that IS NOT being used for a line, do the following steps. 6) If the slot is 33, but the port state is other than 0, then we have an entry that will eventually cause a 928. Note all such logical port entries. 7) If the slot is not 33, then we have an orphaned logical port, which will never be deallocated, and will decrease the total number of ports that can be upped on the switch. Note all such logical port entries. ---- Now comes the cleanup ----- Background: When we allocate a UXM line, we start at the first logical port entry and search for the first available, logical port. The logical port is available if its slot value is a 33 and its state is 0, inactive. We will need to up lines so that there are no "free-log-port-holes" in the logical port database. I.E. Suppose you had 3 line up and they used logical ports 1, 3 and 6. Moreover, suppose you had 4 corrupted logical port entries (an orphan or one that will cause a 928) and these 4 corrupted logical ports where at 2, 7, 8 and 9. Then the "used" logical port entries would be 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8 and 9 and "free-log-port-holes" would be at 4 and 5. This means that the next two lines that are upped will use 4 and then 5, respectively. To be able to clean up corrupted entries 7, 8 and 9, we will need to up two lines to fill the "free-log-port-hole". To cleanup we need to get the on-line and BRAM databases in synch, which can be done as follows: |
|
8) Up lines to fill the free logical port holes. 9) Starting with the largest corrupted logical port entry we found and working backwards, do the following: a) Invoke 'dlprt' on the logical port entry, and obtain the memory address of the logical port entry from the field "Address:" b) The memory location for the slot field is (address + 42), do a patch memory to change the value to a 0x21 (33). This sets the slot to NULL_CD. c) The memory location for the port state is (address + 4), do a patch memory to change the value to a 0x00. This sets the port state to 0 (inactive). d) Up a line -- it should use this logical port entry. Validate that it uses this entry by doing a 'dlprt' on the entry. The slot and port should match what the line just upped. e) down the line you just upped. This will remove the software and BRAM entries for this line and logical port entry, and update the standby so that its software and BRAM are also up to date. This logical port entry has now been cleaned. f) Repeat the above steps for each corrupted logical port entry, working from the largest to the smallest corrupted logical port entry. Prior to the fix for CSCdm43412 we could get the logical line and logical port databases out of sync, as follows: Then when a rebuild, or switchover occurs the UXM's logical ports will get out of sync. as follows: Now if we do a down line on 13.4 it will also deallocate the logical port #2, which really belongs to line 13.2. We are now in a state where 13.2 has its logical line entry, but its logical port entry is no longer there. Moreover, the logical port entry #1 has no corresponding logical line entry. Now if we load an image that has the fix for CSCdm43412 in it, when we rebuild or switch over we will correctly set the logical ports, however, for line 13.2, it no longer has a logical port entry. So software will log a 549, and later 886's and 2071's will be logged, for the same reason. Moreover when an upln is done we attempt to retrieve the first available logical port entry, as indicated by its slot being NULL_SLOT (33). We will stumble across the logical port entry that was incorrectly de-allocated when we downed line 13.4 earlier, but we also check the corresponding configured bit -- it should be cleared -- but the bit is set because this entry was not correctly de-allocated. The result is that a 928 gets logged. |
The following is the list of fixed anomalies in the 9.2.01 Switch Software delivery. Included with each is a brief discussion of the problem.
| Bug ID | Description |
|---|---|
|
False power supply over voltage or under voltage alarms reported A bogus minor alarm is generated on IGXs running 8.2.10 for power supplies with hardware revisions AR and AS. The commands dspalms and dsppwr show the problem. Run the command 'off2 8'. This will disable all monitoring of the power supply, not just voltage. Fail status, temperature, and voltage will not be collected if "Power Supply Monitor" is disabled. Another workaround is to downgrade to a power supply with a hardware revision below AM (but NOT AM). With this fix in place, voltages and alarms are properly reported for nodes with PEMs installed in all PEM slots; however, a minor alarm will be reported for an empty PEM slot. Please see DDTS document CSCdm14418 for further information. |
|
|
The clrcnf command does not utilize a double confirmation prompt prior to acting on the users instructions. The warning message is also based on an understanding of the node/switch management operations. Do not issue the clrcnf command unless there is the desire to erase the database and cause the node/switch to be removed from operations. An enhanced display screen with flashing lights and detailed operational messages in used in conjunction with a double confirmation prompting input request. |
|
|
Software error 921 may be logged when accessing atmTrunkStatsTable using SNMP get operation on an AIT/BTM/ALM trunk. The above software error is logged when the above MIB variable is being accessed via an SNMP get operation on IGX/IPX node. |
|
|
A software error 526 appears if a card failure event log string is longer than what can fit on the display screen. This problem can be created if a dspswlog is done for the screen on which the long string is present. |
|
|
The protocol type value for an FRP port in the Cisco WAN Manager database is 0. Whenever a FRP port is added to the node, the Cisco WAN Manager data base is updated and receives a message with the protocol type field in it. This field can have the value 1. |
|
|
E1 CCS Frame relay lines continue to send Yellow alarm to the remote end after a failure (red alarm) due to cnfclnsigparm 9 being set to 'YES'. When an E1 configured for CCS fails and cnfclnsigparm 9 is set to Y. The E1 line will send yellow alarm to the remote end and will continue to do so even after LOS Red alarm is cleared. Issue cnfclnsigparm 9 N to disable: 9 CDP & CIP Condition CCS Lines? [YES] |
|
|
The modem session for an UVM connection failed. The modem session always fails for a local (dax) UVM connection. About 5% chance of failure for an inter-node connection. |
|
|
Software tries to access the invalid memory entry cause the ABORT when user executes the dth command. While doing the dth command, and the memory is corrupt thus cause the switch abort. Software error 1000003 is logged. Make sure you clean up the unexpected event first. Do cth then dth. |
|
|
If a connection is added from a node to some other node which had just done a switchcc, the connection gets deleted. The slave endpoint of the connection should be on a node which just did a switchcc. Connection additions should be done approximately 10 minutes after switchcc. |
|
|
When trying to execute the command hipri, get the error messages. Correct the earlier error and then execute it, it may come up with another error and so on. Need to execute the hipri command when it's supposed to work. Login into the control port with the proper privileged level and then execute the command hipri as the first command immediately after login. This really isn't the workaround, just the way it's supposed to be. |
|
|
'dspprf' shows IDLE very low when many UVM cards in IGX chassis with switch software 9.1.04 When turning off either 'off2 1' or 'off2 10' or 'off1 16' parameters the idle time rises to over 70%. Disabling Modem Test (off1 16) will disable modem upgrade detection capability on the node. |
|
|
The A-Bit status of a connection is not correctly displayed on LMI failure at the user end over a frame relay NNI link. Environment is not an issue as this happens on the customers network and in the LAB with just a single node. This problem has only been seen on 9.1.03 and 9.1.04, although it is suspected in all releases of 9.1, 8.2 and 8.5 have been tested and work correctly. |
|
|
Trunk Capacity is not displayed correctly on a DSPLOAD of an IMA group. Trunk on UXM and IMA T-1 Back cards. One end of the IMA trunk shows a reduction in available receive bandwidth though all physical lines are clear of alarms. Connections fail if their bandwidth requirements exceed the available bandwidth on the reduced side. This has been observed when IMA physical line failure and repair events occur in rapid succession. Three possible workarounds are available: 1. Call TAC and have them issue manual updates 2 command. 2. Delete and re-add the trunk, if possible. 3. Set the number of retained links equal to the total number of physical lines in the IMA trunk group. If the loading problem was encountered, workaround 1 or 2 must be done first. |
|
|
Slow response and time-outs when telnetting from CAT5000 or NMS workstation to IGX switch LAN port running 9.1.04. Most of telnet sessions disconnect after 5 minutes. Average delay is between 3-4 seconds for telnet connect. Relatively new switch without large quantity of traffic running on it. telnet, tcp, nwip, and snmp are set to defaults. Lan is configured with IP, subnet, gateway, and default port number. Switchcc does not increase telnet connect time. Telnet from a NMS workstation with acceptable telnet delay set above 4 seconds. |
|
|
When issuing a 'tstconseg' on a connection endpoint, the software passes a returned F5 OAM Segment loopback with a correlation tag different from what was sent. This is in violation of ATM Forum specification UNI 3.1 section 3.5.3.2 But CLI indicates test passed. 'tstconseg' on a connection endpoint Non-compliant with ATM forum, ITU and Belcore specifications. |
|
|
The addcon command using the avoid satellite links in 8.5 and 9.1 needs to have all the optional parameters entered as stars before the *s can be used. addcon 8.1.100 igx32-1 9.1.100 4 * * * * * * * * *s Shouldn't need the starts for optional parameters. Use the full command for specifying restrictions (with the *'s for the optional parameters). |
|
|
A vague error message ("BW PARAMS: Unknown response (xx)") is returned to user when a connection's remote PCR value is configured to a value higher than the maximum port speed. |
|
|
There is no obvious symptom when this problem occurs. This problem consumes more trunk bandwidth than what the connection needs. This problem occurs to the G729 connection only. The problem occurs when a FAX session is terminated from active state. When a G729 connection upgrade to the FAX session its bandwidth is configured to be 64Kps. When the FAX session is over, the connection's bandwidth should be configured back to 8Kps. But due to the software bug the connection's bandwidth remains in 64Kps. There will be no any problem to the connection when this problem occurs. The only problem is that the system bandwidth is not used efficiently. |
|
|
Most of time no specific symptom shows up. Sometime channel configuration may be corrupted. When a channel configuration changes this problem may occur. But if the default channel configuration is used then there is no problem. |
|
|
When the customer enables TFTP interval statistics with an invalid configuration the switch logs a 2065 and the SCM receives the following error string: Node=l2a Undefined TFTP Error num=28 text=021, Bucket interval (5m/300s) is not a multiple of Invalid obj type polling interval(900s) This will occur when the customer attempts to enable statistics with an invalid bucket interval. Bucket intervals must be a multiple of the switches largest polling interval. i.e If the switches largest polling interval is 15 minutes and 5 minute buckets are enabled, then that would trigger this error. This has minimal customer impact. The switch is logging a software error because it cannot correctly formulate the return error string. This then means that instead of telling the customer which object type has the largest polling interval it will say "Invalid obj type". However, it still specifies how large the largest polling interval is, therefore the customer still has enough information to correct the problem. |
|
|
Both the BPX routing node and the IGX feeder node are at 9.1 level. After upgrading the IGX feeder node to 9.2, the LMI communication between the 9.1 BPX routing node and 9.2 IGX feeder node is broken. The problem only occurs when the feeder node is a 9.2 IGX and the routing node is a 9.1 BPX. Upgrade the BPX routing node to 9.2 before upgrading the IGX feeder node to 9.2. |
|
|
Upping the 32nd log interface results in BXM cards going into failed state. BXM supports only 31 Log Interfaces per card. But software allows 32 logical interfaces (31 virtual trunk and 1 port). Bringing up the 32nd log interface will result in card going into failed state. Bring down the last port/trunk which was upped and reset the card. Make sure that we do not configure more than 31 log interface per card. |
|
|
There may exist dangling lcns, which indicate one less connection to add on the card. There are two conditions when this may happen: 1. If addcon fails with "Warning: Inconsistent shift mode" 2. After executing the command rbldcondb, if there are software errors 614 & 612. |
|
|
Processor card repeatedly sends message 0x52 to the UXM card for all the dax connections. Condition: Dax connections are added on an IGX node, with %Util less than 100. Switchover is performed. Dax connections cannot have %Util less than 100. Do not add dax connections with %Util less than 100. |
|
|
Software error 526 appears in the error table. This can be caused by running certain user commands, such as dsptrkerrs. The problem occurs when the command is run on a trunk or physical line with a long address, so the address does not fit in the space available. This causes a minor alignment problem in the display. The software error 526 is not an indication of any problem beyond the display misalignment. Just clear the error table. |
|
|
When a failed UFM card is exchanged with another UFM, this problem occured. |
|
|
When switching controller cards, some connections for which this node is a VIA or SLAVE node may reroute. Occurrence is related to the presence of Virtual Path Cons (VPC). When a switchcc is done on a slave or via node for a VPC, there is a chance that one unrelated con could reroute for every VPC. There is also a chance that the VPC may reroute. Graceful upgrade of a node can cause this to happen, too. VPCs may have conids that are duplicates of conids assigned to VCCs. The VPC conid space is managed separately from the VCC space. Trunk translate verification of the neighbor update message currently tries to match the trunk xlat entry from the VCC space against the con info for the VPC. This inevitably does not match, and the VCC con is rerouted. When there is no VCC con with a conid matching the VPC, no con is rerouted, though a swerr 331 occurs if the Neighbor Update Debug switch is on. |
|
|
Traffic going out of the vsi feeder endpoint will be mapped to the wrong vpi/vci. A connection is added from a VSI feeder endpoint to any other endpoint. Traffic is passing from the other endpoint to the VSI feeder endpoint. |
|
|
Command cnfcon gives the following error message: "Extraneous value entered, ignore and continue (y/n)? " Command cnfcon was given for an ATM non-dax connection, such that all the parameters were entered on the command line at the same time, rather than entering one by one. None. However the problem is harmless unless you need to give cnfcon in a script file. Just press 'y' and enter the value of the parameter 'Trunk Cell Routing Restrict' if/when prompted. Command would work fine. |
|
|
After a graceful upgrade from 9.1 to 9.2, connections throughout the network were manually downed and then upped using the UI commands dncon and upcon. Most of these tests completed successfully. However, on one node, not all of the conns were successfully upped, and a software error 514 was logged. It is not clear whether there could be a problem with either the dncon or upcon command. Use them only when necessary. |
|
|
The port got the wrong value FFFFFFFF. This value is out of range of the port number allow. Condition: This happen when a trunk is deleted. It happen for 9.2.0I in regression network |
|
|
Software error 1000003 logged. |
|
|
After upgrading from 9.1 to 9.2 The feeders are in loop. The problem only happens after an upgrade from 9.1 to 9.2 on a BPX/IGX node with feeder(s) attached. |
|
|
Upon upgrade (9.1.09 to 9.2.0J) some connections were seen by the dspcons command but not seen using the dspcon command. If the problem is that of dangling logical endpoints. They can be deleted by deleting and re-adding the connection |
|
|
Free the memory for IP relay message. This problem is seen when Cisco WAN Manager continuously ping the SES feeder over an UXM feeder trunk. The memory allocated for these message was not free correctly. The problem will not occur if there is no ping message from Cisco WAN Manager to the SES feeder. |
|
|
YRED UXM/IMA trunk cards came up as mismatch after graceful upgrade from 9.1 to 9.2. UXM cards are burned with 9.2 UXM firmware before the upgrade. IMA compliance is a new attribute in 9.2. When the switch is gracefully upgraded to 9.2, only non YRED IMA trunk cards inherit the new attribute while the YRED pair will flag the mismatch condition. Delete the YRED pair before the graceful upgrade Re-add YRED after the graceful upgrade. |
|
|
Software error 4225, 614, 534, 612, 4208, and 3058 are logged. As mentioned in the Eng-note and Description, the 4225 error caused the rest of the errors to be logged. The 4225 error was logged on a node which has jobs that do switchcc, full/hitless rebuilds, delcon/addcon, and rrtcon. |
|
|
Card error 0x25010022 appears. A BXM with APS 1+1 trks/lines configured reports card errors when node rebuilds. None needed, should self correct, and program correctly when active card is configured. Description: The standby card is being configured and programs the active card's card redundancy channel before that card is ready, causing card errors. |
|
|
To configure HCF shift to "on" or "off" on a port, the connections must be deleted and the port downed and upped. Delete all the connections, down the port, change the parameter, up the port, and re-add all the connections. |
|
|
The "Trunk cell routing restriction" may not be prompted for ATM connections when executing the addcon command. This happens only on IGX and occurs intermittently (may or may not happen). If connection is being added between IGX-BPX, execute the addcon from the BPX side. For an IGX-IGX connection, there is no workaround. The trunk cell routing restriction will be set to FALSE except for VPC connections. |
|
|
When we have vtrk up on one port and then we up a trunk (vtrk) with multiple ports grouped i.e. IMA trunk, we can add the above port and IMA port group by "cnftrk" command. This should not be allowed as the port where we upped the vtrk before upping an IMA trunk, belongs to different trunk. Do not add ports in "cnftrk"-> IMA port group option, with vtrks |
|
|
addcon for a dax path connection fails with error "Local channel unavailable". Tried to add a dax path connection as follows: >addcon a.b.c.* <node_name> x.y.z.* Where a connection such as x.y.c.d already existed where c is not equal to z and d can have any value. - Delete the connection x.y.c.d if possible or - Change the vpi of a.b.c.* to a value say 'n' such that connection x.y.n.d does not exist, where 'd' could be any number. |
|
|
Software error 55 (BAD_CD_TYPE), after using addalmslot on an ARM card. There are more subtle problems, such as line statistics not being polled / responded to properly, and other statistics related errors occurring. The database becomes corrupted for a slot (usually 4, but could be 12,20, or 28) The corruption can be seen by doing dspcmi l <slot> Don't use addalmslot; or, don't use above mentioned slots. If those slots must be used, then activate the slots after addalmslot has been done. |
|
|
In a T1 (CCS) environment, IGX cannot notify PBXs of a connection failure within the network. In a T1 (CCS) environment -- in which T1 channels do not use Robbed Bit Signalling (RBS), and channels status information is conveyed between PBXs in a d-channel -- IGX cannot notify the PBXs of a connection failure within the network since the d-channel is carried transparently through the IGX network. In a voice E1 CCS environment, there is an super-user IGX command to handle this situation: cnfclnsigparm, option 9. If the option is enabled, IGX generates an alarm for a whole circuit lines if any channel connection in that line is failed in the IGX network. |
|
|
Comm. fail or no continuity on connections after switchcc or hitless rebuild. Condition: The comm. fail happens because a blind channel LCN was reallocated to a routing channel on a BXM card when the node is in switchcc or hitless rebuild mode. BXM routing channel rebuild is done a little later after local rebuild is done which leaves a window of possible LCN reallocation and may cause either comm. fail or no continuity on connections. Avoid rerouting or adding connections while the node is in switchcc or hitless rebuild. |
|
|
After upgrading from 9.1 to 9.2.00 some BXM trunks go briefly into Comm Fail. There is definitely a race condition here. Otherwise the rule is that a trunk s.p goes into Comm Fail, if trunk s.(p-1) exists. All Comm Fails are caused by data mismatches due to a change in 9.2 that moves up transparent channel programming by one channel. |
|
|
The maximum route cost of a connection could be incorrect after a graceful upgrade from release 9.1 to 9.2. This problem only happens during 9.1 to 9.2 graceful upgrade. Re-configure the maximum route cost of a connection by using the CLI cnfrtcost. |
The SNMP IGX/BPX switch SNMP MIB is being provided with the delivery of Release 9.2.20 Switch Software. The MIB is in standard ASN.1 format and is located in the ASCII text files agent.m, ilmi.m, ilmi_ctl.m, ilmiaddr.m, switch.m, swtraps.m, and errors.m which are included in the same directory as the Switch Software images. These files may be compiled with most standards-based MIB compilers.
The following Switch MIB changes were introduced in Release 9.2.
This table provides the manager a detailed view of the ATM ports available on the switch.
The following objects are under the branch of shelf information:
The default values for BXM and Enhanced-BXM cards are the same.
BXM Firmware version M.E.C. supports all the existing interfaces and models of BXM hardware. Following table outlines various levels of hardware revisions supported for BXM firmware version M.E.C.
There are no new features in release MEC.
There are no new features in release MEB
1. VSI version 2.2 (single partition)
2. ITUT Annex B and configurable SD and SF thresholds for SONET Linear APS on BXM-OC3 and BXM-OC12 (1+1, 2 card, 1:1).
The current default thresholds are as follows:
1. Support for Virtual Trunking
2. Support for BXM Multi-Level Channel Statistics
3. SONET Linear APS on BXM-OC3 and BXM-OC12 (1+1, 2 card, 1:1)
4. Support for card based LMI and ILMI
1. The OC-3 MultiMode Fiber backcards do not support Y-cable redundancy.
2. Upgrade from VSI 1.1 to VSI 2.2 is supported in this release. It is not a graceful upgrade. See the upgrade section on page 9 .
3. Customers currently operating MPLS with the 9.1 switch software and MCx firmware should note that either they can run 9.1 with MCx or 9.2.10 or above with firmware MEA. They can not intermingle software and firmware releases for MPLS as they run different VSI versions.
BXM cards with MCB/MDA firmware or later can be smoothly migrated to the MEC version of firmware by using y-cable redundancy. To upgrade a BXM card pair in y-red configuration, first upgrade the standby card with the MEC firmware version and wait for all the configuration to be downloaded into the card. Do a switchyred to switch to the card with firmware MEC and burn the other card also with MEC firmware. Follow the standard firmware upgrade procedure for downloading and burning the firmware into the cards.
1. RAS features: OAM loopback test and traffic generation capability
VSI 1.0 is obsoleted by VSI 2.2 in this release.
1. MEC is fully compatible with 9.1 and 9.2 Switch Software. It has not been tested for compatibility with 8.4 or 8.5 Switch Software.
2. Burn firmware should not be interrupted. Card resets in the middle of burn firmware will result in the BXM being maintained in the core state (Identified by blinking yellow LED), or failed state (Identified by a solid red led). In this case the dspcds screen will report the card as FAILED. This state can be recovered by reburning the firmware into the card.
3. Protection Switching based on BER on BXM may not comply to standards. The GR-253 & ITU-T G.783 requires that switching be completed within 60 msec from the time the error starts. BXM is unable to detect BER threshold crossing until the next poll, which occurs every 250 msec. Thus, switching time may be up to 250 msec under certain circumstances.
4. In APS 1+1 default configuration, both backcard LEDs show green when primary card is active and selection is from PROT line. When primary card is active and it is selecting from PROT, PROT backcard should be green, since it is carrying traffic. WORK backcard should also be green since that is the physical path for the primary (and active) card to pass traffic. So backcard LED green means the backcard is directly or indirectly carrying traffic and pulling the backcard will cause traffic disruption. (CSCdm53430)
5. In APS 1+1 default configuration and a manual W->P is on and a switchyred is issued, a manual W->P event is logged. By default, on switchyred the new active card comes up in "clear" state. But in this case since there is a manual W->P on, the APS line switches to PROT and the switching is logged. (CSCdm53404)
6. In APS 1+1 default configuration if the selected line is PROT and last user request is clear and a switchyred is issued, line switches to WORK. If the last user request is "clear", full automatic APS switching is in effect with the working line being active by default. When there is no last user switch request to switch to any particular line, the working line will become active. (CSCdm53420)
7. When APS Annex B is added to local end which has the Secondary card active, the APS trunk goes into Comm Failure for few seconds and then clears. If Secondary card is active, then do a switchyred to make Primary card active and then add APS Annex B. (CSCdm46359)
The following is the list of known anomalies for the MEB BXM firmware:
|
The following is the list of bugs fixed in release MEC:
|
The following is the list of bugs fixed in release MEB:
|
The following is the list of bugs fixed in release MEA:
|
The following is the list of bugs fixed in release MDA:
|
These release notes define the UXM functionality of Firmware version ABE which will operate with 9.1 and 9.2 Switch Software Releases
UXM firmware will operate under 9.1.XX software, so it can be loaded prior to upgrading Switch Software.
UXM firmware ABE introduces the following features:
1. Dynamic queue control to vary the queue performance as IMA trunks change throughput
2. Compatibility with AXIS IMATM-B cards
UXM firmware ABD introduces the following features:
1. Support for XLR backcard (2 ports)
UXM firmware ABA introduces the following features:
1. Support for Virtual Trunking
2. VC Traffic Shaping on ports only
3. Standards compliant IMA on E1 and T1 interface cards
4. Enhanced Multi-Level Channel Statistics, enables more statistics on each connection
5. Ports and trunks on the same card
1. On the UXM, for the OC-3 MultiMode Fiber backcards, no Y-Redundancy/hot standby is supported.
2. Traffic Shaping is a new feature on UXM card. The VC/VP traffic shaping shapes each individual connection by scheduling the cells using the WFQ (weighted Fair Queueing) technique to ensure appropriate conformance dictated by the service provider. In general, traffic shaping provides a tight control on each connection's CDV in order to meet carrier requirement. Also, it prevents any connection from dominating bandwidth resources. On UXM, the traffic shaping is on per port basis. Once the traffic shaping is turned on, then all connections added after will have traffic shaping on. For details, please refer to 9.2 feature description and commands.
Before upgrading to this release when UXM cards are to be used, certain legacy cards firmware must be upgraded. See the Compatibility Matrix for cards affected and the exact versions to be used.
Note Standards compliant IMA is not compatible with the proprietary IMA protocol used in revision A firmware. Both ends of an IMA trunk must have the same protocol.
For upgrades from firmware versions prior to ABA follow steps 1 through 3 else just burn ABB and perform step 3. Failure to follow this procedure may result in the card not operating. The card should be returned to Cisco if this occurs:
Step 2 When the boot code has been loaded burn the firmware.
Step 3 When Yred trunks are used the red alarm in/out values must be configured to 1.25/1.5 seconds or greater else INVMUX failures will occur and trunk failures will be observed during a Yred switchover. This is due to the IMA protocol and may cause re-route of connections. Use the cnftrkparm command
OAM Loopback Connection Connectivity Testing for Reliability and Serviceability
Auto link disable on IMA groups is no longer available as the ATM forum standard does not permit it.
1. Multi level Stats has to be configured as the card is initially configured in the down state. The higher levels of statistics make more information on each connection. As a result the maximum number of connections is limited as defined below
Lvl 2 = 8126 conns (UXM-E), 4030 conns (UXM)
Lvl 3 = 4030 conns (UXM-E), 1982 conns (UXM)
2. There is no 9.1 stats support for UXM cards that were shipped with 9.2 firmware since the UXM card has the default level 1 stats.
There is 9.1 stats support for UXM-E cards that were shipped with 9.2 firmware since the UXM-E card has the default level 2 stats. Level 2 stats include all of the needed to be 9.1 compatible.
Therefore, when using an UXM with 9.2, a user must either:
3. The UXM-IMA and MGX 8220 IMATM are not compatible if the IMA group contains only one T1 or E1 line. Since on the IGX-UXM trunk, the IMA protocol is invoked only if an IMA trunk consists of multiple physical lines, therefore, for a trunk with a single T1 or E1 line, the IMA protocol is not invoked. This implementation is different with MGX 8220 IMATM because the MGX 8220 shelf invokes the IMA protocol regardless of the number of T1/E1 lines in the IMA group.
4. UXM IMA trunk groups must use common clock. Independent clocking is not permitted.
5. On the UXM, for the OC-3 Multi-Mode Fiber backcards, no Y-Redundancy/hot standby is supported.
6. It is not recommended to combine ABR and UBR PVC's on the same network. ABR and UBR PVC's share the same QBIN (Class of Service Queue) on the BXM card. However, ABR (VSVD) uses a flow control mechanism which ensures that the traffic source slows down when the QBIN usage exceeds the EFCI threshold. However, UBR does not have a mechanism to slow down. Thus, UBR traffic gains an unfair advantage over ABR. This implementation is not considered a problem, since the decision to share a QBIN for ABR and UBR traffic was intentional, since any best-effort service that one would route over UBR can be routed over ABR (VSVD), with the additional benefit of protecting resources in the network. If there is a real requirement to use UBR PVC's instead of ABR (VSVD), then either (1) add all best-effort PVC's as UBR, or (2) isolate the ABR and UBR paths by using cnfpref and separating ABR and UBR endpoints.
7. Combining FBTC and non-FBTC connections within a Class of Service can cause FBTC connections to not receive a fair share of bandwidth. For example, if VBR connections are added at a terminating port, and some of these VBR connections have FBTC enabled while other VBR connections have FBTC disabled, the VBR connections with FBTC disabled may obtain all of the excess bandwidth before the connections with FBTC enabled receive any of the excess bandwidth. The same holds true for ABR or UBR connections. This only is relevant where FBTC and non-FBTC connections share a QBIN, either at a port or at a trunk.
Note When Yred trunks are used the red alarm in/out values must be configured to 1.75/2.0 seconds or greater else INVMUX failures will occur and trunk failures will be observed during a Yred switchover. This is due to the IMA protocol and may cause re-route of connections.
For a complete list of firmware revisions supported, see the Compatibility Matrix document, which is included in this release package.
UXM model B uses standards compliant IMA protocol. This is not compatible with the previous proprietary IMA protocol in Model A firmware.
UXM boot code revision AB06 has no known compatibility issues with any released version of UXM hardware or firmware.
UXM firmware revision ABA requires UXM boot code revision AB06 be burned into the UXM card prior to burning ABA firmware.
There are no known anomalies in this release.
| Bug ID | Description |
|---|---|
|
SYMPTOM : 0B card error occurs, card resets and continues. |
|
OAM loopback test fails. OAM cells are discarded SYMPTOM: OAM RAS failures are indicated. CIRCUMSTANCES : Large bursts of OAM cells on 400+ connections |
|
When IMA trunks are cross connected in a group the trunk fails to come up. CIRCUMSTANCES: On any IMA trunk of a group greater than 1with the lines cross connected FREQUENCY: Repeatable |
|
SYMPTOM : Data rate of cells transmitted to the trunk when configured as a virtual trunk exceeds the maximum rate configured. CIRCUMSTANCES: On a virtual trunk when transmit data rate exceeds defined max. Actual rate depends on the configured rate. |
|
|
SYMPTOM : Data is discarded if AAL-5 data on some connections and not others. Other data types can have the data stream re-sequenced. |
|
SYMPTOM: VI rates are set incorrectly when a corrupted back card message is received. |
| Bug ID | Description |
|---|---|
Intermittent OB error 0c02 after hitless rebuild or switchcc UXM experiences hardware error as below: Frequency is about 1:50 "switchcc" or 'resetcd <NPM slot #> r' [hitless rebuild] with the UXM loaded with more than 1000 connections and stats collection turned on. |
|
OAM status inconsistency after y-redundant switchover of UXM Status of connections which traverse a UXM all show "Status: OAM-F" after a y-redundant switchover of that UXM. There is a primary and a secondary UXM configured to be a y-redundant pair.'cnfoamlpbk' is enabled. After the y-redundant switchover, all connections which traverse the card enter "Status: OAM-F" about 10 minutes after the y-redundant switchover. Frequency is intermittent, but always after a y-redundant switchover. User traffic is unaffected. |
| Bug ID | Description |
|---|---|
|
RAS OAM.loopback shows failed at one end but OK in the other end. |
|
|
With more than 2000 connections routed across [or terminating on] a UXM, the UXM may produce a software error 103 and be automatically reset in about 1:5 'switchcc' or 'rrtcon *' commands. The failure rate increases to about 1:3 'switchcc' or'rrtcon *' commands as the number of connections routed across [or terminating on] the UXM exceeds 7000. When the UXM is reset, all connections are rerouted or temporarily down until rerouted. The UXM recovers, however, it may take several minutes to reroute all connections after the UXM is reset. The UXM under test was running FW with baseline revision ABA. Software revision was baseline 9.2.01. For the test case, there were two ports and one trunk on the UXM of OC3 rate each, and traffic on the trunk was about 10% of a full OC3 rate. The connection types were mixed: 700 Interworking Gateway - terminating on a UFM. 1000 CBR - using default settings 500 VBR - using default settings 500 ABR - using default settings. A fix for the problem is found in UXM firmware revision ABC. |
|
|
UXM card sends up a card error: 0B with a 0C02 parameters. |
| Bug ID | Description |
|---|---|
|
UXM trunk card went UNAVAILABLE after a graceful upgrade from 9.1 to 9.2. |
|
|
Connection terminating on a UXM or traversing a UXM trunk may fail the OAM loopback test [refer to 'cnfoamlpbk' command] and begin showing status 'OAM-F'. All connections traversing the problem UXM which have the OAM loopback test enabled will show status 'OAM-F' and fail all 'tstdelay' tests. Connections traversing a problem UXM trunk which do not have the OAM loopback test enabled will show status 'OK', however, will fail 'tstdelay'. Connectivity for real user traffic is unaffected in either case. The failure condition occurs and will pursist after the problem UXM experiences a short-term, large burst of OAM packets. With 400 connections from each of 20 port cards which support the OAM loopback test, traversing a UXM trunk, and then terminating on 20 additional port cards on the other side of the trunk, the OAM loopback test enabled, traversing a UXM trunk, and then terminating on 20 additional port cards on the other side of the trunk, the failure will occur within a few hours of operation. Failure will occur within a few hours with following setup if all terminating port cards have OAM loopback test enabled: >15 UFM cards @ 400 conns each -> UXM trunk -> >15 UFM cards @ 400+ conns each '>15' greater than 15 terminating cards. The failure is unlikely to occur when there are fewer than 10 terminating port cards with connections which traverse a UXM trunk even though OAM loopback is enabled on all cards. With more than 15 or 20 terminating cards, there is a possibility of a short-term burst of OAM packets through the UXM trunk. This short- term burst of OAM packets may cause an internal OAM queue error condition. Previous versions of firmware could not recover from this error condition and stop passing traffic. It is necessary to reset the UXM in order to recover from the overflow condition. |
FRP/FRM Model J & K (previously known as Model D & E)
Support for OAM RAS and Traffic Generation
This firmware is also compatible with older switch software release for the FRM. This firmware will work on all hardware revision though using the latest hardware revision is recommended.
Note The OAM RAS and Traffic Generation capability will only work with the switch software 9.2 release.
The command burnfwrev is sufficient to upgrade.
| Bug ID | Description |
|---|---|
|
When a 17 or less byte frame is received from the network and the DE bit is set on a CGW connection, the frame is interpreted as a supervisory frame and discarded. Because it is interpreted as a supervisory frame the dspchstats will not be incremented for this frame. Always occurs with short frames when DE bit is set on CGW conns. Note: This may occur if DE is enabled and the connection is above the CIR. This bug is only applicable to FW images with bug fix for CSCdk15283 (UXM CGW conns FST RA's are not timing out): FDZ/FEZ through FJA/FKA. This bug is N/A to SGW conns. rxfpproc.asm - only check for SPV bit if SGW conn (fix adds one line & a jmp label) |
|
|
Due to bug fix CSCdk15283 CGW Supervisory FastPackets were not correctly recognized and were being discarded, thus effectively disabling Foresight. |
|
|
addloclp on port doesn't loop data back to external equipment in FW revs since FDZ (a result of bug fix CSCdj71238) True simultaneous bi-directional looping (of CPE traffic to itself and of net traffic to itself) cannot be done through the hardware as is done in the Line Model. The solution to obtain both loops is to setup the SCC back to auto-echo mode (external CPE loopback, as it was in pre-Rev Z) and to loop all network traffic as if each of the conns were in remote loopback (by checking the port state). Because the network looping is not being done in the backcard (as was done for the Line) the following differences with the Line operation WHEN IN THE "addloclp port" STATE must be noted: 1. dspportstats shows no traffic (as it was in Port pre-Rev Z FW). 2. dspchstats only shows Rxd & Txd fastpacket stats (as if the conns were in individual remote loop) and not the Rxd & Txd frames & bytes (as with the Line Model in the addloclp port state). |
|
Other end of E1/T1 line gets 1 OOF error when up/dn port done |
|
|
Executing upfrport causes 1 OOF & 1 CRC err on other end of circuit line. Executing dnfrport causes 1 OOF on other end of circuit line. [This was due to a FW work-around for a HW lockup problem associated with the ATT Spyder chip and a PLD. A timing problem was fixed in the PLD in HW rev B which caused a Spyder dead HW error about every 10th upfrport/dnfrport.] Every time a upfrport/dnfrport is executed. The FW now checks if HW rev B or greater exists in the backcard and skips the FW work-around. Thus, this bug is fixed for all HW revs >= B. dma_ctrl.c - skip FW work-around for Spyder (framer) lockup if not HW rev A or P01. Note: with old HW would previously get the following hardware error, 0B 00 06 99 01 D2 01 03 01 00 00 00 11 (11 = SPYDER_DEAD code). |
UFM Model C Firmware ZCA, and UFMU Model C Firmware YCA
Support for OAM RAS and Traffic Generation
This firmware is compatible with all supported switch software releases for UFM.This firmware will work on all hardware revision though using the latest hardware revision is recommended.
Note The OAM RAS and Traffic Generation capability will only work with the switch software 9.2 release that supports OAM.
The command burnfwrev is sufficient to upgrade
| Bug ID | Description |
|---|---|
Corrupt display when doing a dspchstats on the UFM When doing a test delay on a service interworking connection the dspchstats shows incorrect values. This also causes packet drops to happen in the egress direction. Always happens after a tstdelay is performed on a service interworking connection. |
For service and support for a product purchased from a reseller, contact the reseller. Resellers offer a wide variety of Cisco service and support programs, which are described in the section "Service and Support" in the information packet that shipped with your chassis.
Note If you purchased your product from a reseller, you can access Cisco Connection On-line (CCO) as a guest. CCO is Cisco Systems' primary, real-time support channel. Your reseller offers programs that include direct access to CCO's services.
For service and support for a product purchased directly from Cisco, use CCO.
Cisco Connection Online (CCO) is Cisco Systems' primary, real-time support channel. Maintenance customers and partners can self-register on CCO to obtain additional information and services.
Available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, CCO provides a wealth of standard and value-added services to Cisco's customers and business partners. CCO services include product information, product documentation, software updates, release notes, technical tips, the Bug Navigator, configuration notes, brochures, descriptions of service offerings, and download access to public and authorized files.
CCO serves a wide variety of users through two interfaces that are updated and enhanced simultaneously: a character-based version and a multimedia version that resides on the World Wide Web (WWW). The character-based CCO supports Zmodem, Kermit, Xmodem, FTP, and Internet e-mail, and it is excellent for quick access to information over lower bandwidths. The WWW version of CCO provides richly formatted documents with photographs, figures, graphics, and video, as well as hyperlinks to related information.
You can access CCO in the following ways:
For a copy of CCO's Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ), contact cco-help@cisco.com. For additional information, contact cco-team@cisco.com.
Note If you are a network administrator and need personal technical assistance with a Cisco product that is under warranty or covered by a maintenance contract, contact Cisco's Technical Assistance Center (TAC) at 800 553-2447, 408 526-7209, or tac@cisco.com. To obtain general information about Cisco Systems, Cisco products, or upgrades, contact 800 553-6387, 408 526-7208, or cs-rep@cisco.com.

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Tue Jul 15 00:51:51 PDT 2003
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.