|
|

Cisco WAN Switching software provides the following troubleshooting commands to help you diagnose and correct faults.
| Command | Description | Page |
|---|---|---|
addalmslot | Add alarm slot | |
addextlp | Add external loopback | |
addlnloclp | Add line local loopback | |
addlnlocrmtlp | Add line local remote loopback | |
addloclp | Add local loopback | |
addlocrmtlp | Add local-remote loopback | |
addrmtlp | Add remote loopback | |
clrchstats | Clear channel statistics | |
clrclkalm | Clear clock alarm | |
clrclnalm | Clear circuit line alarm | |
clrclnerrs | Clear circuit line errors | |
clreventq | Clear the events queues | |
clrlnalm | Clear line alarm | |
clrlnerrs | Clear line errors | |
clrlog | Clear log | |
clrmsgalm | Clear message alarm | |
clrportstats | Clear port statistics | |
clrslotalms | Clear slot alarms | |
clrsloterrs | Clear slot errors | |
clrtrkalm | Clear trunk alarm | |
clrtrkerrs | Clear trunk errors | |
clrtrkstats | Clear trunk statistics | |
cnfbus | Configure Bus | |
cnflnalm | Configure line alarm | |
cnfslotalm | Configure slot alarm | |
cnftrkalm | Configure trunk alarm | |
dellnlp | Delete line loopback | |
dellp | Delete loopback | |
dncd | Down card | |
dspalms | Display alarms | |
dspbob | Display Breakout Box | |
dspbuses | Display Buses | |
dspclnerrs | Display circuit line errors | |
dspeventq | Display the event queue names and the data in each. | |
dspfrcbob | Display FRC-2/FRM-2 breakout box | |
dsplog | Display event log | |
dsplnalmcnf | Display line alarm configuration | |
dsplnerrs | Display line errors | |
dsppwr | Display power | |
dspslotalmcnf | Display slot alarm configuration | |
dspslotalms | Display slot alarms | |
dspsloterrs | Display slot errors | |
dspslotstatcnf | Display slot statistics configuration | |
dsptrkerrs | Display individual or all trunk errors. | |
prtclnerrs | Print circuit line errors | |
prtlnerrs | Print line errors | |
prtlog | Print log | |
prttrkerrs | Print trunk errors | |
resetcd | Reset card | |
resetpc | Reset Port Concentrator | |
switchcc | Switch controller card | |
tstcon | Test connection | |
tstconseg | Test connection segment | |
tstdelay | Test delay | |
tstpcs | Test Port Concentrator Shelf | |
tstport | Test port |
Enables the MAJOR and MINOR alarm indicators on an Alarm Relay Card (ARC) or Alarm Relay Module (ARM). It also configures the slot to support external alarms from the Alarm Relay Interface (ARI) back card. You can use this command at any node that can provide external alarm indications to an alarm reporting system. The ARC or ARM can reside in any front slot but usually resides in the right-most slot.
Add alarm slot
addalmslot <slot number>
delalmslot, dspalms
Privilege | 1-4 |
Jobs | No |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX |
Lock | Yes |
addalmslot 16
Enable alarm reporting from slot 16 in a node.
beta TRM YourID:1 IPX 32 8.4 Mar. 3 1996 14:27 MST
Alarm summary (Configured alarm slots: 16)
Connections Failed: None
Groups Failed: None
PLN Alarms: 1 Major
CLN Alarms: None
Cards Failed: 1
Missing Cards: None
Remote Node Alarms: 1 Major
Remote Domain Alarms: None
Last Command: addalmslot 16
Next Command:
Places an external device in loopback mode. The addextlp command applies to existing connections on an SDP, HDM, LDP, or LDM. A "near" loopback causes the NEAR EIA template to be applied. A `far' loopback causes the FAR EIA template to be applied to the data port. The loopback remains in place until removed by the dellp command.
The dspcons command shows which connections are in loopback mode. Specifying an "n" after the channel indicates a near loopback, and an "f" indicates a far loopback. Because addextlp takes the specified connections out of service, use it only when a service disruption is tolerable.
Add External Loop to Connection
addextlp <channel> < n | f >
dellp, dspcons
Privilege | 1-2 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX |
Lock | Yes |
addextlp 5.1 n
Place the device connected to channel 5.1 in near loopback.
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.4 Mar. 16 1996 12:53 PST
Local Remote Remote Route
Channel NodeName Channel State Type Compression Code Avoid COS O
N5.1 beta 25.1 Ok 256 7/8 0 L
9.1.100 gamma 8.1.200 Ok fr 0 L
9.2.400 beta 19.2.302 Ok fr 0 L
14.1 gamma 15.1 Ok v 0 L
Last Command: addextlp 5.1 n
Next Command:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
channel | Specifies the channel to loopback in the format slot.port. |
n /f | Specifies whether the loopback is near or far. An "n" specifies near; an "f" specifies far. For a non-DDS port, the near or far modem is placed in loopback, if it supports this function. For a DDS port, the external DDS device is placed in CSU loopback. Local channels must be configured as OCU in order to place them in external loopback. |
Establishes a local-remote loopback on a trunk or port card in a BPX. Applicable cards are the ASI, BNI, and BXM.
While a line loop is present, software suspends the card self-test and the line diagnostic test that normally run when a line goes into alarm. Suspending these tests prevents background test loops from interfering with the user-specified loop.
Line loops are set for a line on the local node, so you cannot specify a remote node, and no network messaging is supported for setting a line loop of any type on a remote node.
Line loop status is displayed on the dsplns screen for an ASI or a BXM in port mode and the dsptrks screen for a BNI or a BXM in trunk mode. Line loop status is not displayed for connections (dspcons) affected by a line loop. Instead, a warning is printed if the line has connection traffic travelling on it, and an event is logged when a line loop is set or cleared. A line loop on a trunk generates Comm Fail, causing connections to fail and be rerouted.
For both of the dsplns and dsptrks screens, the "]" character appears before the back card type in the "Type" column to indicate that the line local loopback is active.
The line loop state is not saved in BRAM or on a rebuild but is preserved on a switchover. After a rebuild, a line's loop state is cleared.
Exercise caution when you set up loops on a BNI or BXM trunk because looping an added BNI/BXM trunk causes Comm Failure and connection rerouting. BNI/BXM addlnlocrmtlp is not supported because of a lack of useful purpose, and Cisco recommends that you use addlnloclp only when the trunk is upped but not added. On the other hand, the system does not prevent you from looping an added BNI/BXM trunk port.
Add line local loopback
addlnloclp <slot.port>
dellnlp, dsptrks, dsplns, addlnlocrmtlp
Privilege | 1-2 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | BPX |
Lock | Yes |
addlocrmtlp 9.1
The dsplns display appears with the connection highlighted and a prompt for confirmation.
pubsbpx1 TN SuperUser BPX 15 8.4 Feb. 28 1997 01:25 GMT
Line Type Current Line Alarm Status
3.1 OC3 Clear - OK
3.2 OC3 Clear - OK
3.3 OC3 Clear - OK
3.4 OC3 Clear - OK
3.5 OC3 Clear - OK
3.8 OC3 Clear - OK
5.1 T3 Clear - OK
5.2 T3 Clear - OK
9.1 ]OC3 Clear - OK
Last Command: addlnloclp 9.1
Warning - Looping will interrupt data flow on the line
Next Command:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot.port | Specifies the port. |
Establishes a local-remote loopback on a trunk or port card in a BPX. Applicable cards are the ASI, BNI, and BXM.
While a line loop is present, software suspends the card self-test and the line diagnostic test that normally run when a line goes into alarm. Suspending these tests prevents background test loops from interfering with the user-specified loop.
Line loops are set for a line on the local node, so you cannot specify a remote node, and no network messaging is supported for setting a line loop of any type on a remote node.
Line loop status is displayed on the dsplns screen for an ASI or a BXM in port mode and the dsptrks screen for a BNI or a BXM in trunk mode. Line loop status is not displayed for connections (dspcons) affected by a line loop. Instead, a warning is printed if the line has connection traffic travelling on it, and an event is logged when a line loop is set or cleared. A line loop on a trunk generates Comm Fail, causing connections to fail and be rerouted.
For both of the dsplns and dsptrks screens, the "[" character appears before the back card type in the "Type" column to indicate that the line local-remote loopback is active.
The line loop state is not saved in BRAM or on a rebuild but is preserved on a switchover. After a rebuild, a line's loop state is cleared.
Exercise caution when you set up loops on a BNI or BXM trunk because looping an added BNI/BXM trunk causes Comm Failure and connection rerouting. BNI/BXM addlnlocrmtlp is not supported because of a lack of useful purpose, and Cisco recommends that you use addlnloclp only when the trunk is upped but not added. On the other hand, the system does not prevent you from looping an added BNI/BXM trunk port.
Add line local-remote loopback
addlnlocrmtlp <slot.port>
dsptrks, dsplns, dellnlp, addlnloclp
Privilege | 1-2 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | BPX |
Lock | Yes |
addlnlocrmtlp 10.1
The dsptrks screen appears with the loopback highlighted by the "[" character.
pubsbpx1 TN SuperUser BPX 15 8.4 Feb. 28 1997 01:27 GMT
TRK Type Current Line Alarm Status Other End
1.1 T3 Clear - OK pubsaxi1(AXIS)
1.3 T3 Clear - OK pubsipx1/8
4.1 OC3 Clear - OK -
10.1 [OC3 Clear - OK -
Last Command: addlnlocrmtlp 10.1
Next Command:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot.port | The port on the local node. |
The addloclp command places the following types of channels in local loopback mode:
For voice connections, addloclp creates a signal path from a channel or group of channels on an incoming circuit line back to the circuit line. External test equipment can then test the integrity of the path at the T1 DS0 level. Figure 16-1 shows a local loopback on a voice channel.
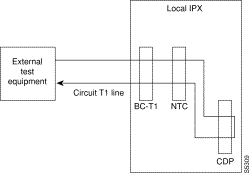
For data connections, addloclp creates a signal path from the incoming data port or set of ports back to these same port(s) through the local voice or data card. External test equipment can then test the integrity of the path. Figure 16-2 illustrates a local loopback on a data connection.
A local loopback can simultaneously exist at both ends of a connection. However, a local loopback and a remote loopback cannot co-exist on a connection. (See the addrmtlp description for more information.)
Prior to executing a loopback, the IPX or IGX performs signal and code conditioning to remove the connection from service. The loopback remains in place until removed by dellp. Only existing connections can be looped back. Use the dspcons command to see which connections are looped back. A flashing right parenthesis ")" or left parenthesis "(" is used in the connections display to indicate a loopback. The direction and location of the parenthesis depends on whether the loopback is local or remote and which end of the connection was used to establish the loopback. A local loopback initiated from the local end of the connection looks like this in the connections display:
Local Channel | Remote Node | Remote Channel |
12.1 | alpha | 15.1 |
A local loopback initiated from the remote end of the connection looks like this:
Local Channel | Remote Node | Remote Channel |
12.1 | alpha | 15.1 |
In frame relay connection loopback mode (DLCI included in command), all packets from the far-end of the connection are dropped. The far-end system software is informed of the loopback. In port loopback mode (port specified without a DLCI), all packets for this port are dropped and each opposite end is informed of the loopback mode. The format slot.port is used in port mode to loop just the port. The data is looped directly in the FRI back card, so no data reaches the MUXBUS or CELLBUS. The format slot.port.DLCI is used in connection (channel) mode to loop a specific channel. Note that this can affect up to 252 connections (channels) in port loopback mode.
Because the addloclp command causes the connection(s) to be removed from service, loopbacks should be used only when a service disruption can be tolerated. Remote loopbacks are established with the addrmtlp command. Both local and remote loopbacks are removed by the dellp command. Loopbacks for data channels can also be initiated by pressing a button on the front of the associated data card.
When a frame relay port or connection is located on a Port Concentrator instead of directly on an FRP or FRM card, the data test path is different. When just the <port> parameter is used, incoming data is looped back out on the Port Concentrator port:
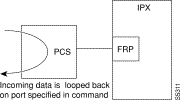
This loop disrupts all frame relay connections on the port that is under test.
When a connection is specified by <port.dlci> parameters, the connection is looped back at the FRM-2 or FRP-2 interface with the IGX or IPX card bus:
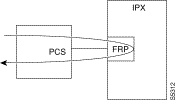
As shown, this test verifies the operation of all components from the Port Concentrator to IPX/IGX interface with the FRP-2 or FRM-2 card.
This tests interrupts only the specified connection on the Port Concentrator port.
Add local loopback to connections on a port
addloclp parameters (see parameters table)
addrmtlp, dellp, dspcons, dspfrport
Privilege | 1-2 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX, BPX |
Lock | Yes |
addloclp 14.1
The connections screen appears with connection 14.1 highlighted. The system prompts to confirm the loopback. To confirm the loopback, enter y.
Next Command:
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.4 Mar. 23 1996 11:03 PST
Local Remote Remote Route
Channel NodeName Channel State Type Compression Code Avoid COS O
5.1 beta )25.1 Ok 256 7/8 0 L
9.1.100 gamma 8.1.200 Ok fr 0 L
9.1.200 gamma 8.1.300 Ok fr 0 L
9.2.400 beta 19.2.302 Ok fr(Grp) 0 L
14.1 )gamma 15.1 Ok v 0 L
Last Command: addloclp 14.1
Next Command:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot | Specifies the slot number of the card containing the port to loop at the local node. |
channel (s) | Specifies the channel or set of channels to loop at the local node. |
port | Where applicable for the connection type, specifies the port. |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot | Specifies the slot number of the card containing the port to loop at the local node. |
port | Specifies the local port to loop at the local node. |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot | Specifies the slot number of the FRP card containing the port to be looped at the local node. |
port | Specifies the local port to loop at the local node. |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot | Specifies the slot number of the FRP card containing the port to loop at the local node |
port | Specifies the local port to loop at the local node. |
DLCI | Specifies the Data Link Connection Identifier (DLCI) number of the channel to loop at the local node. |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot | Specifies the slot number of the ATM card containing the port to loop at the local node |
port | Specifies the local port to loop at the local node. |
vpi.vci | The vpi range is 0 - 7, and the vci range is 1 - 255. An asterisk (*) indicates a virtual path |
Adds support of a local-remote loopback for testing multi-segment connections in a tiered network. The effect is to instruct the remote node to set up a remote loopback. The addlocrmtlp command must be executed prior to using tstcon and tstdelay for multi-segment connections. For interface shelves, you can execute addlocrmtlp on either the interface shelf (after telnetting to it). After testing is complete, remove the local-remote loop by executing dellp. A parenthesis on the screen shows the loop's endpoint.
Add local-remote loopback in a tiered network
addlocrmtlp <channel(s)>
tstcon, tstdelay, dellp, dspcons, dspfrport
Privilege | 1-2 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | BPX, IPX/AF, IPX, IGX |
Lock | Yes |
addlocrmtlp 5.1.3.100
The connections screen appears with the connection highlighted and a prompt for confirmation.
pubsbpx1 TN SuperUser BPX 8.4 July 13 1996 14:41 PDT
Local Remote Remote
Channel NodeName Channel State Type Compress Code COS
5.1.3.100 ( pubsbpx3 7.1.2.49 Ok aftr 0
This Command: addlocrmtlp 5.1.3.100
Loopback these connections (y/n)?
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
channels(s) | The connection endpoint on the local node. |
The addrmtlp command places the following types of channels in remote loopback mode:
For voice connections, addrmtlp loops the information stream from the designated channel or group of channels on an incoming circuit line across the network and loops it back to the circuit line by way of the remote CDP or CVM. External test equipment can then test the integrity of the path at the T1 DS0 level. The following illustrates a remote loopback on a voice channel.
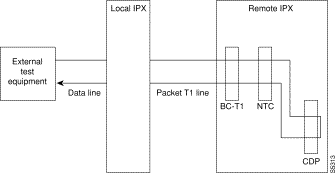
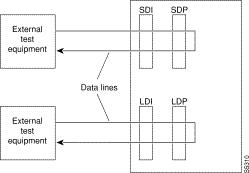
For data connections, addrmtlp transfers the information stream from the designated channels through the network and loops it back to the data port(s) through a remote SDP, HDM, LDM, or LDP. External test equipment can then test the integrity of the path. The following illustrates a data connection remote loopback.
Prior to executing the loopback, the IPX or IGX applies signalling template bit patterns to the A, B, C, and D signalling bits at the remote end to remove the connection from service. The loopback remains in place until removed by the dellp command. Only existing connections (those that have been entered with the add-on command) can be looped back. You cannot establish a remote loopback on a connection that is already looped back, either locally or remotely. (See the addloclp command for more information on local loopbacks.)
Use the dspcons command to see which connections are looped back. A flashing left parenthesis "(" or right parenthesis ")" is used in the connections display to indicate a loopback. The direction and location of the parenthesis depends on whether the loopback is local or remote and which end of the connection was used to establish the loopback. A remote loopback initiated from the local end of the connection looks like this:
Local Channel | Remote Channel | Remote Node |
3.2 | alpha | 12.1 |
A remote loopback initiated from the remote end of the connection looks like this:
Local Channel | Remote Node | Remote Channel |
3.2 | alpha | 12.1 |
For remote loopback of frame relay connections, note that in remote loopback mode, if the transmit minimum bandwidth exceeds the receive minimum bandwidth, then loopback data may be dropped. For this reason, the connection speeds will be checked and the user will receive the following message if there is a problem:
Because the addrmtlp command causes the connection to be removed from service, loopbacks should be used only when a service disruption can be tolerated. Local loopbacks are established with the addloclp command. Both local and remote loopbacks are removed by the dellp command. Loopbacks for data channels can also be initiated by pressing a push-button on the front of the associated data card.
For frame relay remote loops, DLCI MUST be specified; entering only port number only generates an error message.
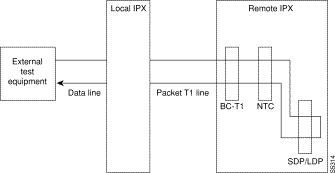
Unlike local loopbacks, remote loopbacks are not supported for frame relay ports; connections must be specified. Data incoming on the frame relay port is looped at the remote end FRM-2 or FRP-2 card.
As shown, this test verifies the operation of IPX/IGX network components up to the interface with the remote-end FRM-2 or FRP-2. This test interrupts data traffic for only the connection specified by DLCI.
If a port concentrator is attached to the FRM-2 or FRP-2, the only difference in the loop is that the port specified to loop data is on the Port Concentrator:
Add remote loopback to connections
addrmtlp (see parameter tables)
addloclp, dellp, dspcons
Privilege | 1-2 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX, BPX |
Lock | Yes |
addrmtlp 5.1
The connections screen appears with connection 5.1 highlighted. The system prompts to confirm the loopback. To confirm it, enter y. A flashing parenthesis ")" appears in the "Remote Channel" column of the connection to indicate that the connection is looped back.
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.4 Mar. 16 1996 12:57 PST
Local Remote Remote Route
Channel NodeName Channel State Type Compression Code Avoid COS O
5.1 beta )25.1 Ok 256 7/8 0 L
9.1.100 gamma 8.1.200 Ok fr 0 L
9.2.400 beta 19.2.302 Ok fr 0 L
14.1 gamma 15.1 Ok v 0 L
Last Command: addrmtlp 5.1
Next Command:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot | Specifies the slot number of the card containing the port to loop at the local node. |
channel (s) | Specifies the channel or set of channels to loop at the local node. |
port | Where applicable for the connection type, specifies the port. |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot | Specifies the slot number of the card containing the port to loop at the local node. |
port | Specifies the local port to loop at the local node. |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot | Specifies the slot number of the FRP card containing the port to loop at the local node |
port | Specifies the local port to loop at the local node. |
DLCI | Specifies the Data Link Connection Identifier (DLCI) number of the channel to loop at the local node. |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot | Specifies the slot number of the card containing the port to loop at the local node. |
channel (s) | Specifies the channel or set of channels to loop at the local node. |
port | Where applicable for the connection type, specifies the port. |
vpi.vci | Specifies vpi/vci. |
Clears the channel utilization statistics for either all frame relay channels or a specified frame relay channel. Statistics generated within the last one minute are not cleared.
Clear channel statistics
clrchstats <channel | *>
dspchstats
Privilege | 1-5 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX |
Lock | Yes |
clrchstats 9.2.400
Clear the statistics of channel 9.2.40.
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.4 Mar. 16 1996 13:24 PST
Channel Statistics for 9.2.400 Cleared: Mar. 16 1996 13:23
MIR: 9.6 kbps Collection Time: 0 day(s) 00:02:42 Corrupted: NO
Frames Avg Size Avg Util Packets Avg
(bytes) (fps) (%) (pps)
From Port: 0 0 0 0
To Network: 0 0 0 0 0 0
Discarded: 0 0 0 0
From Network: 0 0 0 0 0 0
To Port: 0 0 0 0
Discarded: 0 0 0 0 0 0
ECN Stats: Avg Rx VC Q: 0 ForeSight RTD --
Min-Pk bytes rcvd: 0 FECN Frames: 0 FECN Ratio (%) 0
Minutes Congested: 0 BECN Frames: 0 BECN Ratio (%) 0
This Command: clrchstats 9.2.400
OK to clear (y/n)?
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
channel | Specifies the frame relay channel for which to clear statistics. <channel> is specified in the format slot.port.DLCI. An "*" specifies all channels. |
Clears the alarm condition attached to a clock source, either circuit line or trunk. The clock test runs continuously in a node, comparing the frequency of the node's clock source to a reference on the NPC/BCC/CC/control card. If a clock source is found to be outside preset frequency limits, it is declared defective and another clock source is selected. In order for the node to return to the original clock source, the alarm must be cleared using the clrclkalm command. The alarm may be either a "Bad Clock Source" or "Bad Clock Path" alarm.
Clear clock alarm
clrclkalm <line type> <line number>
cnfclksrc, dspclksrcs, dspclns, dspcurclk, dsptrks
Privilege | 1-5 |
Jobs | No |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX |
Lock | Yes |
clrclkalm c 12
Clear a clock alarm on circuit line 12
clrclkalm p 12
Clear a clock alarm on packet line 12
Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
c/p | Specifies the type of line. A "c" is entered for a circuit line, and a "p" is entered for a trunk. |
line number | Specifies the number of the circuit or trunk for which to clear the clock alarm. |
Clears the alarms associated with a circuit line. Since the statistical alarms associated with a circuit line have associated integration times, they can keep a major or minor alarm active for some time after the cause has been rectified. This command allows these alarms to be cleared, allowing any new alarms to be quickly identified. The clrclnalm command can only clear alarms caused by the collection of statistical data. Alarms caused by a network failure cannot be cleared. For example, an alarm caused by a collection of bipolar errors can be cleared, but an alarm caused by a card failure cannot.
Clear circuit line alarm
clrclnalm <line_number> <fail_type>
dspclns, dspclnerrs
Privilege | 1-5 |
Jobs | No |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX |
Lock | Yes |
clrclnalm 14 2
Clear the minor alarm caused by frame slips on circuit line 14.
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.4 Mar. 16 1996 13:10 PST
Line Alarm Configuration
Minor Major
Violation Rate Alarm Time Clear Rate Alarm Time Clear
1) Bpv 10E-7 10 min 3 min 10E-3 10 sec 10 sec
2) Fs .01% 10 min 3 min .1% 10 sec 10 sec
3) Oof .0001% 10 min 3 min .01% 10 sec 10 sec
4) Vpd 2% 5 min 3 min 5% 60 sec 10 sec
5) Tsdp .01% 5 min 3 min .1% 60 sec 10 sec
6) Ntsdp .01% 5 min 3 min .1% 60 sec 10 sec
7) Pkterr .01% 10 min 3 min .1% 125 sec 10 sec
8) Los .0001% 10 min 3 min .01% 10 sec 10 sec
This Command: clrclnalm 14 2
Continue?
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
line number | Specifies the number of the circuit line for which to clear the alarm. |
failure type | Specifies the type of alarm to clear. |
Clears the alarms associated with a circuit line. Since the statistical alarms associated with a circuit line have associated integration times, they can keep a major or minor alarm active for some time after the cause has been rectified. This command allows these alarms to be cleared, allowing any new alarms to be quickly identified. The clrclnalm command can clear only those alarms that the collection of statistical data has caused. Alarms caused by a network failure cannot be cleared by clrclnalm.
Clear circuit line errors
clrclnerrs [<line_number>]
dspclnerrs, prtclnerrs
Privilege | 1-5 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX |
Lock | Yes |
clrclnerrs
Clear circuit line error counts. In response to the prompt, enter "y" to reset all circuit line error counts to "0".
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.4 Mar. 16 1996 13:12 PST
Total Errors
From Code Frame Out of Loss of Frame CRC Out of
CLN Errors Slips Frames Signal BitErrs Errors MFrames AIS-16
14 0 0 0 - 0 - - -
Last Command: clrclnerrs
Next Command:
Clears the alarms associated with a circuit line. Since the statistical alarms associated with a line have associated integration times, they can keep a major or minor alarm active for some time after the cause has been rectified. This command allows these alarms to be cleared, allowing any new alarms to be quickly identified.
The clrclnalm command can only clear alarms caused by the collection of statistical data. Alarms caused by a network failure cannot be cleared. For example, an alarm caused by a collection of bipolar errors can be cleared, but an alarm caused by a card failure cannot.
Clear circuit line alarm
clrclnalm <line_number> <fail_type>
dsplns, dsplnerrs
Privilege | 1-5 |
Jobs | No |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX |
Lock | Yes |
clrlnalm 14 2
Clear the minor alarm caused by frame slips on 14. The 2 indicates frame slips.
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.4 Mar. 16 1996 13:10 PST
Line Alarm Configuration
Minor Major
Violation Rate Alarm Time Clear Rate Alarm Time Clear
1) Bpv 10E-7 10 min 3 min 10E-3 10 sec 10 sec
2) Fs .01% 10 min 3 min .1% 10 sec 10 sec
3) Oof .0001% 10 min 3 min .01% 10 sec 10 sec
4) Vpd 2% 5 min 3 min 5% 60 sec 10 sec
5) Tsdp .01% 5 min 3 min .1% 60 sec 10 sec
6) Ntsdp .01% 5 min 3 min .1% 60 sec 10 sec
7) Pkterr .01% 10 min 3 min .1% 125 sec 10 sec
8) Los .0001% 10 min 3 min .01% 10 sec 10 sec
This Command: clrclnalm 14 2
Continue?
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
line number | Specifies the number of the circuit line for which to clear the alarm. |
failure type | Specifies the type of alarm to clear. |
Clears high water marks for fail handler event queues.
Clear event queues from the fail handler
clreventq
dspeventq
Privilege | 1-6 |
Jobs | No |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX, BPX |
Lock | Yes |
clreventq
Clear the fail handler event queue.
sw151 TN SuperUser IGX 16 8.4 Sep. 12 1996 19:18 GMT
QUEUE LENGTH THROTTLING
NUM NAMES MAX HIGH CURRENT POINT
1 Fail_Xid 26 1 7000
2 Fail_ Q 25 0
3 Mt_Sv_Q[0] 300 9 0 270
4 sv_mt_bufq 9 0
This Command: clreventq
OK to clear HIGH counts(y/n)?
Clears accumulated line error counts for all lines on a node.
Clear line errors
clrlnerrs [<line_number>]
dsplnerrs, prtlnerrs
Privilege | 1-5 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX |
Lock | Yes |
clrlnerrs
Clear the line error counts. In response to the prompt enter "y" to reset all line error counts to "0."
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.4 Mar. 16 1996 13:12 PST
Total Errors
From Code Frame Out of Loss of Frame CRC Out of
CLN Errors Slips Frames Signal BitErrs Errors MFrames AIS-16
14 0 0 0 - 0 - - -
Last Command: clrclnerrs
Next Command:
Clears the event log. When the log is cleared, one entry remains, "Info Log Cleared". Before the event log is cleared, a prompts you to confirm. See the dsplog command for more information on the event log.
Clear event log
clrlog
dsplog
Privilege | 1-5 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX |
Lock | Yes |
clrlog
Clear the event log. When the log is cleared, one entry remains, "Info Log Cleared." Enter "y" to confirm.
sw151 TN SuperUser IGX 16 8.4 Sep. 12 1996 19:19 GMT
Most recent log entries (most recent at top)
Class Description Date Time
Info User SuperUser logged out (Local) 09/12/96 18:18:57
Major LN 5.6 Loss of Sig (RED) 09/12/96 18:12:22
Info User SuperUser logged out (Local) 09/12/96 18:11:17
Info Clock switch to oscillator of SCC 09/12/96 18:10:46
Clear LN 5.6 OK 09/12/96 18:05:11
Minor LN 5.6 Out of Multi-Frames 09/12/96 18:03:27
Info Clock switch to LINE 5.6 09/12/96 18:03:12
Clear LN 5.6 OK 09/12/96 18:02:42
Info Clock switch to oscillator of SCC 09/12/96 17:59:24
Major LN 5.6 Loss of Sig (RED) 09/12/96 17:59:24
Info Clock switch to LINE 5.6 09/12/96 17:59:20
Clear LN 5.6 OK 09/12/96 17:59:20
Major LN 5.6 Loss of Sig (RED) 09/12/96 17:58:51
This Command: clrlog
OK to clear (y/n)?
Clears the minor alarm due to an alarm message received at an alarm collection port.
Clear message alarm
clrmsgalm
dspalms, dsplog
Privilege | 1-5 |
Jobs | No |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX, BPX |
Lock | Yes |
clrmsgalm
Clear a minor alarm due to an alarm message.
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.4 Mar. 23 1996 10:59 PST
Last Command: clrmsgalm
No message alarm set
Next Command:
Clears the statistics for any port on an FRP. This includes the data byte count in the transmit and receive directions and error counts associated with the port. Statistical accumulation then resumes for that port.
Statistics collecting takes place once per minute, so clrportstats may not clear statistics that are less than one minute old.
Clear port statistics
clrportstats <port | *>
dspportstats
Privilege | 1-5 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX |
Lock | Yes |
clrportstats 9.1
Clear the port statistics for port 1 on an FRP card in slot 9. Type "y" to confirm.
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.4 Mar. 23 1996 10:57 PST
Port Statistics for 9.1 Cleared: Mar. 11 1996 15:32
Port Speed: 256 kbps Collection Time: 11 day(s) 19:22:09 Corrupted: YES
Bytes Average (kbps) Util (%) Frames
From Port: 0 0 0 0
To Port: 0 0 0 0
Frame Errors LMI Receive Protocol Stats Misc Statistics
Invalid CRC 0 Status Enq Rcvd 0 Avg Tx Port Q 0
Invalid Alignment 0 Status Xmit 0 FECN Frames 0
Invalid Frm Length 0 Asynch Xmit 0 Ratio (%) 0
Invalid Frm Format 0 Seq # Mismatches 0 BECN Frames 0
Unknown DLCIs 0 Timeouts 0 Ratio (%) 0
Last Unknown DLCI 0 Invalid Req 0 Rsrc Overflow 0
Sig Protocol: None DE Frms Dropd 0
This Command: clrportstats 9.1
OK to clear port statistics (y/n)?
Clears the alarm messages associated with the alarms displayed for the Display Slot Alarms command. Alarm messages are cleared for the specified slot only. These counters should be cleared before beginning any monitoring session. This command prompts the user with a "OK to Clear?" message before actually clearing the counters. Use dspslotalms to observe the slot alarms. Refer to the dspslotalms command for a description of the counters cleared by the clrslotalms command.
Clear slot alarms
clrslotalms parameters
dspslotalms
Privilege | 1-5 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | BPX |
Lock | Yes |
clrslotalms 3
Clear alarm on slot 3
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot number | Specifies shelf slot in the BPX node for which to clear trunk alarms. |
Clears the counters for the error counts displayed for the Display Slot Errors command. Counters are cleared for the specified slot only. These counters should be cleared before beginning any monitoring session. This command prompts the user with a "OK to Clear?" message before actually clearing the counters. Use dspsloterrs to observe the slot errors. Refer to the dspsloterrs command for a description of the counters cleared by the clrsloterrs command.
Clear slot errors
clrsloterrs <slot number | *>
dspsloterrs
Privilege | 1-5 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX, BPX |
Lock | Yes |
clrsloterrs 3
Clear the slot errors in slot 3
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot number | Specifies the shelf slot in the node. |
Clears statistical alarms associated with either a physical or virtual trunk. Since the statistical alarms associated with a trunk have associated integration times, they can keep a major or minor alarm active for some time after the cause has been rectified. The clrtrkalm allows these alarms to be cleared, allowing any new alarms to be quickly identified.
The clrtrkalm command can only clear alarms caused by the collection of statistical data. Alarms caused by a network failure cannot be cleared. For example, an alarm caused by a collection of bipolar errors can be cleared, but an alarm caused by a card failure cannot.
Clear trunk alarm
clrtrkalm <trunk number> <failure type>
dsptrks, dsptrkerrs
Privilege | 1-5 |
Jobs | No |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX, BPX |
Lock | Yes |
clrtrkalm
Statistical trunk alarms are cleared
beta TRM YourID:1 IPX 32 8.4 Mar. 15 1996 15:15 MST
PLN Type Current Line Alarm Status Other End
7 E1/32 Clear - Line OK alpha.10
9 T1/24 Clear - Line OK gamma.10
13 T1/24 Clear - Line OK alpha.14
15 T1/24 Clear - Line OK gamma.15
20 T3/3 Clear - ATM Missing -
Last Command: clrtrkalm
Next Command:
clrtrkalm 7 4
Clear the minor alarm type 4 caused by dropped voice packets on trunk 7. Respond to the "Continue?" prompt with "y" (for yes) to clear and display the remaining alarms.
beta TRM YourID:1 IPX 32 8.4 Mar. 15 1996 15:15 MST
PLN Type Current Line Alarm Status Other End
7 E1/32 Clear - Line OK alpha.10
9 T1/24 Clear - Line OK gamma.10
13 T1/24 Clear - Line OK alpha.14
15 T1/24 Clear - Line OK gamma.15
20 T3/3 Clear - ATM Missing -
Last Command: clrtrkalm 7 4
Next Command:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
trunk number | Specifies the trunk. Note that, for virtual trunks, no virtual trunk parameter is required—just slot.port. The format is either slot (for a single-trunk card) or slot.port. |
failure type | Specifies the type of alarm to clear. |
Clears the statistical error counters at the node for the specified physical or virtual trunk. You should do this before you begin any monitoring session and periodically thereafter to determine exactly when a trunk problem begins. Use dsptrkerrs to observe errors without clearing counters.
Clear trunk errors
clrtrkerrs <trunk_number | *>
dsptrkerrs, prttrkerrs
Privilege | 1-5 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX, BPX |
Lock | Yes |
clrtkerrs *
Clear all trunk errors.
pubsbpx1 TN SuperUser BPX 15 8.4 Sep. 12 1996 19:37 PST
Total Errors
Code Rx Cell Out of Loss of Frame HCS Tx Cell Cell Cell
TRK Errors Dropped Frames Signal BitErrs Errors Dropped Errors Oofs
1.1 0 0 0 0 - 0 0 - -
1.2 0 0 0 0 - 0 0 - -
This Command: clrtrkerrs *
Clears errors on all trunks. Continue (y/n)?
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
trunk number | Specifies the trunk counter to clear. |
Clears the node counters used for the Display Trunk Statistics. Counters are cleared for a physical or virtual trunk. These counters should be cleared before beginning any monitoring session. This is similar to the clrtrkerrs command for errors. This command prompts the user with a "OK to Clear?" message before actually clearing the counters. Use dsptrkstats to observe the trunk statistics. See the dsptrkstats command for a description of the counters cleared by the clrtrkstats command.
Clear trunk statistics
clrtrkstats <trunk number>
dsptrkstats
Privilege | 1-5 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | BPX |
Lock | Yes |
clrtrkstats
Clear the statistics on trunk 3
Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
trunk number | Specifies the trunk. Note that, for virtual trunks, no virtual trunk parameter is required—just slot.port. The format is either slot (for a single-trunk card) or slot.port. |
Selects the active System Bus. It should only be necessary to use this command when a problem is suspected with the currently active System Bus. As a safeguard against bus failure, each IPX node is equipped with redundant System Buses, Bus A and Bus B. Either bus can be configured as the active bus and the remaining bus is reserved as standby. Use the dspbuses command to display the current bus configuration when configuring the buses with the cnfbus command.
Configure active bus
cnfbus <a/b/t>
dspbuses
Privilege | 1-3 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX |
Lock |
|
cnfbus t
Configure the system bus to toggle.
pubsigx1 TN SuperUser IGX 32 8.4 Sep. 12 1996 19:42 GMT
Bus Info
Bus Bandwidth usage in Fastpackets/second (Snapshot)
Allocated = 20000 ( 2%)
Available = 1148000 (98%)
-----------
Bus A: Standby - OK
Bus B: Active - OK
Last Command: cnfbus t
Next Command:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
a | Select Bus A as the active bus. |
b | Select Bus B as the active bus. |
t | Toggles between buses. It changes the standby bus to the active bus and the active bus to the standby bus |
Sets the packet line (trunk) and circuit line alarm values for failures that are statistical in nature. Statistical alarms are declared by the switch software when the cards supporting these lines report too many errors. An alarm is declared if the detected error rate equals the specified "error rate" for the period of time designated by "alarm time". Error rates that exceed the specified error rate cause an alarm in a proportionately shorter period of time. An alarm is cleared when the error rate remains below the rate specified by "error rate" for a period of time designated by "clear time".
Only the thresholds for alarms caused by the collection of statistical data can be configured. Alarms caused by a network failure cannot be configured. For example, the threshold for an alarm caused by a collection of bipolar errors can be configured, but an alarm caused by a card failure cannot. There are six parameters for each alarm type, three each for minor and major alarms respectively. When configuring any one item or more of a minor or major alarm, a value must be entered. The value may be a new value or the current value.
Configure line alarms
cnflnalm <fail_type> <alarm_class> <rate> <alarm_time> <clear_time>
clrclnalm, clrtrkalm, dspclnerrs, dsplnalmcnf, dsptrkerrs
Privilege | 1-3 |
Jobs | No |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX |
Lock | Yes |
cnflnalm 27 1 4 4 3
Set Alarm Type 27, the Minor alarm time threshold, from a default of 5 minutes to 4 minutes. In this example, the cnflnalm command is followed by the alarm type (27), the alarm minor or major (1 for minor, 2 for major), the current rate (which is a default value of.001%, (which is a 4), the new value for Alarm Time of 4 minutes (which is a "4" entry), and the existing Alarm Clear time of "3".
pubsigx1 TN SuperUser IGX 32 8.4 Aug. 20 1996 17:19 GMT
Line Alarm Configuration
Minor Major
Violation Rate Alarm Time Clear Rate Alarm Time Clear
25) Rxbdapd .001% 5 min 3 min .1% 60 sec 10 sec
26) Rxbdbpd .001% 5 min 3 min .1% 60 sec 10 sec
27) Rxhppd .001% 4 min 3 min .1% 60 sec 10 sec
28) Atmhec .1% 10 min 3 min 1% 120 sec 10 sec
29) FSyncErr .01% 10 min 3 min .1% 200 sec 10 sec
30) Rxspdm .01% 4 min 2 min .001% 30 sec 5 sec
Last Command: cnflnalm 27 1 4 4 3
Next Command:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Alarm type | Specifies the alarm type. Following defines the alarm types. (Items with an asterisk, items 18 to 30, pertain to ATM packet lines only. 1. Bpv—Bipolar violations 2. Fs —Frame slip 3. oof—Out of frame 4. Vpd -Voice packets dropped (TX) 5. Tspd—Time stamped packets dropped (TX) 6. Ntspd—Non-time stamped packets dropped 7. Pkterr—Packet error 8. Los—Loss of signal 9. Fer—Frame error 10. CRC—Cyclic Redundancy Check 11. Pkoof—Packet out of frame 12. Oom—Out of multi-frame 13. Ais16 -Alarm information signal—E1/E3 Only 14. Bdapd—Bursty data A packets dropped 15. Bdbpd—Bursty data B packets dropped 16. Badclk—Bad clock 17. Pccpd—PCC packets dropped 18. * Lcv—Line code violations 19. * Pcv1—P-bit parity code violations 20. * Pcvp—C-bit parity code violations 21. * Bcv—PLCP BIP-8 code violations 22. * Rxvpd—Receive voice packets dropped 23. * Rxtspd—Receive time stamped packets dropped 24. * Rxntspd—Receive non-time stamped packets dropped 25. * Rxbdapd—Receive bursty data A packets dropped 26. * Rxbdbpd—Receive bursty data B packets dropped 27. * Rxhppd—Receive high priority packets dropped 28. * Atmhec—Cell header HEC errors 29. * Plcpoof—PLCP out of frame 30. * 30 - Rxspdm - Receive spacer packets dropped |
alarm class | Specifies the class of alarm to configure. The alarm classes are Minor Alarm and Major Alarm. |
Error rates | Specifies the rate at which the error must occur on the line before it is registered. The choices for error rates vary depending on the "alarm type" and the "alarm class". The user choices are called out as Error Rate Options. The default error rates are indicated. With the exception of a Vpd (voice packets dropped) failure, you enter the number corresponding to the desired error rate. For Vpd (voice packets dropped) failures, you enter any dropped packet rate from 1% to 10%. See following for alarm types and error rates. |
| Alarm Type | Alarm Class | Error Rate Options * | Alarm Time | Clear Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| | Option B | | |
| | Option A | | |
3-Oof | 1-minor | 1-1% 2-.1% 3-.01% 4-.001% 5-.0001% (Def.) | 10 Minutes | 3 Minutes |
| 2-major | 1-1% 4-.001% | 10 Seconds | 10 Seconds |
4- Vpd | 1-minor | Any dropped packet | 5 Minutes | 3 Minutes |
| | Option A | | |
| | Option A | | |
7- Pkterr | 1-minor | Any error count | 10 Minutes | 3 Minutes |
| | Option A | | |
| | Option A | | |
| | Option A | | |
| | Option A | | |
| | Option A | | |
| | Option A | | |
| | Option A | | |
| | Option A | | |
| | Option A | | |
| | Option A | | |
| | Option B | | |
| | Option B | | |
| | Option B | | |
| | Option B | | |
| | 1-10% | | |
| | Option A | | |
| | Option A | | |
| | Option A | | |
| | Option A | | |
| | Option A | | |
| | Option A | | |
| | Option A | | |
| | Option A | | |
| Error Rate Options | ||
|---|---|---|
| Option | Alarm Class | Error Rate |
A | 1 - minor | 1 - 1% 2 -.1% 3 -.01% 4 -.001% 5 -.0001% |
2 - major | 1 - 1% 2 -.1% 3 -.01% | |
B | 1 - minor | 1 - 10E-4 2 - 10E-5 3 - 10E-6 4 - 10E-7 5 - 10E-8 |
2 - major | 1 - 10E-2 2 - 10E-3 3 - 10E-4 4 - 10E-5 5 - 10E-6 | |
Alarm time | Specifies the time that the condition must exceed the selected threshold before an alarm is declared. For minor alarms, the "alarm time" is entered as minutes and can range from 3 to 10. For major alarms, the "alarm time" is entered as seconds and can range from 10 to 250. |
Clear time | Specifies the time that the condition must exceed the selected threshold before the alarm is cleared. For minor alarms, the "clear time" is entered as minutes and can range from 3 to 10. For major alarms, the "clear time" is entered as seconds and can range from 10 to 250. |
Configures the alarm parameters for the various card types. Upon command entry, the system displays a screen with a choice of 8 card-alarm types. It then displays "Enter Type" and waits for a number in the range 1-12. Upon entry of the alarm type, the system displays the error rates of the selected type.
Configure slot alarm parameters
cnfslotalm <fail_type> <alarm_class> <rate> <alarm_time> <clear_time>
dspslotalms
Privilege | 1 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | BPX |
Lock | Yes |
cnfslotalm 10
Configure the alarm parameters
pubsbpx1 TN SuperUser BPX 15 8.4.0r Sep. 12 1996 19:43 PST
Slot Alarm Types
1) Standby PRBS Errors 11) Poll Clk Errors
2) Rx Invalid Port Errs 12) CK 192 Errors
3) PollA Parity Errors
4) PollB Parity Errors
5) Bad Grant Errors
6) Tx Bip 16 Errors
7) Rx Bip 16 Errors
8) Bframe parity Errors
9) SIU phase Errors
10) Rx FIFO Sync Errors
This Command: cnfslotalm
Enter Type:
The screen display after selecting alarm type 10:
pubsbpx1 TN SuperUser BPX 15 8.4 Sep. 12 1996 19:47 PST
Slot Alarm Configuration
Minor Major
Violation Rate Alarm Time Clear Rate Alarm Time Clear
1) SPRBS .1% 10 min 3 min 1% 100 sec 100 sec
2) InvP .1% 10 min 3 min 1% 100 sec 100 sec
3) PollA .1% 10 min 3 min 1% 100 sec 100 sec
4) PollB .1% 10 min 3 min 1% 100 sec 100 sec
5) BGE .1% 10 min 3 min 1% 100 sec 100 sec
6) TBip .1% 10 min 3 min 1% 100 sec 100 sec
7) RBip .1% 10 min 3 min 1% 100 sec 100 sec
8) Bfrm .1% 10 min 3 min 1% 100 sec 100 sec
9) SIU .1% 10 min 3 min 1% 100 sec 100 sec
10) RFifo .1% 10 min 3 min 1% 100 sec 100 sec
Last Command: cnfslotalm 10
Next Command:
Configures trunk alarm reporting. When trunks are upped and added to the network, they automatically have their alarm reporting enabled. This command permits alarms from upped trunks to be disabled. This may be useful, for example, for trunks that are connected to the node but not yet in service or if the node is experiencing occasional bursts of errors but is still operational. When the alarms are enabled, they will cause an alarm output from the DTI Group Alarm Connector (if equipped) and an alarm indication from the StrataView Plus terminal.
Configure trunk alarms
cnftrkalm <trunk number> <e|d>
dspalms, dsptrks
Privilege | 1-5 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX, BPX |
Lock | Yes |
cnftrkalm 14 d
Disable a trunk alarm for trunk 14, which has a major alarm. After using this command to disable the alarms, the only indication that the alarms have been disabled is to observe the dspalms screen while a trunk alarm exists. This indicates "disabled" after PLN Alarms. Therefore, when disabling any trunk alarm, be sure to make note of it so that it may be enabled after the trunk failure has been corrected.
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.4 Mar. 16 1996 13:04 PST
From Type Current Line Alarm Status Other End
14 T1/24 Major - Tx NTS Packets Dropped beta.13
Last Command: cnftrkalm 14 d
Next Command:
cnftrkalm 14 e
Enable the alarms after they have been disabled
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
e/d | Enable/disable |
Deletes either a line local or a line local-remote loopback. Applicable cards are the ASI, BNI, and BXM. Applicable loopbacks have been previously set up by addlnloclp or addlnlocrmtlp.
Delete line loopback
dellnlp <slot.port>
addlnloclp, addlnlocrmtlp
Privilege | 1-2 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | BPX |
Lock | Yes |
dellp 9.1
Delete the line loopback on 9.1. In this case, the system removes the loop and displays the dsplns screen.
pubsbpx1 TN SuperUser BPX 15 8.4.0j Feb. 28 1997 02:49 GMT
Line Type Current Line Alarm Status
3.1 OC3 Clear - OK
3.2 OC3 Clear - OK
3.3 OC3 Clear - OK
3.4 OC3 Clear - OK
3.5 OC3 Clear - OK
3.8 OC3 Clear - OK
5.1 T3 Clear - OK
5.2 T3 Clear - OK
9.1 OC3 Clear - OK
Last Command: dellnlp 9.1
Next Command:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot.port | Specifies the port in the format slot.port. |
Deletes an external, local, remote, or local-remote (for tiered nets) loopback form the designated channel, set of channels, or port. After the loopback is deleted, any conditioning applied during the loopback process is removed and service is restored. Local loopbacks are added with the addloclp command, and remote loopbacks are added with the addrmtlp command. External loopbacks are added with the addextlp command. A local loop can be deleted only from the node that added it. However, a remote loop can be deleted from the node at either end of the connection. Local-remote loopbacks are added with the addlocrmtlp command. Note that with local-remote loopbacks, execution of dellp is mandatory after testing is complete, otherwise continuity errors will follow.
Delete loopback from connections or a port
dellp <channel(s)>
addextlp, addloclp, addlocrmtlp, addrmtlp
Privilege | 1-2 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX, BPX |
Lock | Yes |
dellp 4.1.11
Delete the loopback on channel 4.1.11. The connections screen appears with connection 4.1.11 highlighted. The system prompts to confirm deletion of the loopback. To confirm enter "y". Channel 5.1 is no longer looped back and is no longer highlighted, as below.
sw83 TN SuperUser IPX 16 8.4 Jan. 31 1996 19:58 PST
From Remote Remote
4.1.11 NodeName Channel State Type Compress Code COS
4.1.11 sw79 4.1.11 Ok fst 0
4.1.12 sw79 4.1.12 Ok fst 0
4.1.13 sw79 4.1.13 Ok fst 0
4.1.14 sw79 4.1.14 Ok fst 0
4.1.15 sw79 4.1.15 Ok fst 0
4.1.16 sw79 4.1.16 Ok fst 0
4.1.17 sw79 4.1.17 Ok fst 0
4.1.18 sw79 4.1.18 Ok fst 0
4.1.19 sw79 4.1.19 Ok fst 0
4.1.20 sw79 4.1.20 Ok fst 0
4.1.21 sw79 4.1.21 Ok fst 0
4.1.22 sw79 4.1.22 Ok fst 0
4.1.23 sw79 4.1.23 Ok fst 0
This Command: dspcons
Continue?
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
channels | Specifies the channel or set of channels whose loopback is to be deleted. <channel> can be specified in one of three formats as follows: slot.channel voice connection slot.port.vpi.vci ATM connections |
Downs (or deactivates) a card. When you down a card, it is no longer available as a node resource.
A card should be downed before you remove it from a card cage. Before an active card is downed, the node determines if a standby card is available. If no standby card is present, the node gives you an opportunity to abort the command. If a standby card of the same type is available and you execute the command, the standby card is activated. If no standby card is available and you execute the command, a major alarm results. To activate a downed card, use the upcd command.
You cannot down a control card (NPC, NPM, or BCC). To switch a control between active and standby, use the switchcc command.
Down card
dncd <slot number>
dspcds, resetcd, upcd
Privilege | 1-3 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX, BPX |
Lock | Yes |
dncd 9
Down card 9
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot number | Specifies the slot number of the card to be downed. |
Displays major and minor alarms throughout the network and more specific alarms at the local node. The dspalms command displays the following information:
Trunk alarms are differentiated between those trunks that are disabled and those that are not. For more details on each type of alarm, use the display command associated with each failed item as shown below:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
dspcds | Displays cards in the node, with "F" for failures. |
dspclns | Displays circuit lines. |
dspcons | Displays connections. |
dspdmns | Displays the domain and node alarms in the network. |
dsplog | Displays events affecting the node. |
dspnds | Displays unreachable nodes within domains. |
dspnw | Displays alarm status of each domain in network. |
dsptrks | Displays trunks. |
dsppwr | Displays power supply status and internal temperature. |
Display current node alarms
dspalms
dspcds, dspclns, dspcons, dsplog, dspnw, dsptrks, dsppwr
Privilege | 1-6 |
Jobs | No |
Log | No |
Node | IPX, IGX, BPX |
Lock | No |
dspalms
See a summary of all alarms affecting the node
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.4 Mar. 23 1996 10:50 PST
Alarm summary (Configured alarm slots: 16)
Connections Failed: None
Groups Failed: None
PLN Alarms: 1 Major
CLN Alarms: None
Cards Failed: 1
Missing Cards: None
Remote Node Alarms: 2 Majors
Remote Domain Alarms: None
Last Command: dspalms
Next Command:
dspalms
The current alarms on a BPX.
sw53 TN SuperUser BPX 15 8.4 July 21 1996 15:18 GMT
Alarm summary (Configured alarm slots: None)
Connections Failed: 100
Groups Failed: None
TRK Alarms: None
Line Alarms: None
Cards Failed: None
Slots Alarmed: None
Missing Cards: None
Remote Node Alarms: 1 Unreachable, 5 Majors, 5 Minors
Remote Domain Alarms: None
Interface Shelf Alarms: 2 Unreachables, 2 Minors
ASM Alarms: None
Last Command: dspalms
Next Command:
SW MAJOR ALARM
Shows the current state of all inputs from user equipment to the node the state of all outputs from the node to the user equipment. The display is real-time and updated at a user-specified interval. The display refreshes at the designated interval until the Delete key is pressed or until it times out. See the cnfict description for information on configuring data interfaces. When used with Frame Relay T1/E1 applications, dspbob displays the message "This FRP does not support V.35 ports."
If an FRM-2 or FRP-2 card connects to a Port Concentrator Shelf (PCS), up to 44 ports can be specified with the port parameter. In this case, dspbob displays the signal status for ports on the PCS. The PCS relays any changes in signal states to the FRM-2 or FRP-2, so a slight delay occurs when signals are updated.
When used for PCS ports, dspbob has an optional parameter of measuring port clock speed. Selection of this parameter temporarily interrupts all traffic on the logical port. The events that take place upon input of this parameter are:
1. The port is disabled.
2. Two invalid frames are timed as they go out the port.
3. The port is reactivated.
Display breakout box
dspbob <port> [interval] [(measure clock speed) y | n ]
cnfict, dspcon, dspict
Privilege | 1-6 |
Jobs | No |
Log | No |
Node | IPX, IGX |
Lock | Yes |
dspbob 5.1
See the breakout box display for channel 5.1
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.4 Mar. 23 1996 11:29 PST
Port: 5.1
Interface: V35 DCE
Clocking: Normal (255999 Baud)
Inputs from User Equipment Outputs to User Equipment
Lead Pin State Lead Pin State Lead Pin State Lead Pin State
RTS C Off CTS D On
DTR H Off DSR E On
TxD P/S Idle DCD F Off
TT U/W Unused RI J Off
TM K Off
RxD R/T Idle
RxC V/X Active
TxC Y/a Active
This Command: dspbob 5.1
Hit DEL key to quit:
dspbob 9.1
See the breakout box display for frame relay connections
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.4 Mar. 23 1996 11:29 PST
Port: 9.1
Interface: FRI-V35 DTE
Clocking: Normal
Inputs from User Equipment Outputs to User Equipment
Lead Pin State Lead Pin State Lead Pin State Lead Pin State
CTS D Off RTS C On
DSR E Off DTR H On
DCD F Off LT L Off
(TM) n Off (RLB) N Off
This Command: dspbob 9.1
Hit DEL key to quit:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot | Specifies the slot number of the card containing the port whose input and output pins are to be displayed. |
port | Specifies the data port or frame relay port whose input and output pins are to be displayed. |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
interval | Specifies the time in seconds, between updates of the breakout box display. The range is from 1 to 60 seconds. If no interval is specified, the display is updated at five second intervals. Do not use an interval of "1" second in a busy network. |
measure clock speed | For Port Concentrator Shelf only: directs the system to measure the clock speed. If a Port Concentrator port is selected, the last measured clock speed is displayed on the Clocking line. When Measure Clock Speed is entered as an optional parameter, the clock is measured first, and the results are displayed. Clock speed measurement for PCS ports is described in the Cisco WAN Switching System Overview information for the PCS. |
Displays the status of the System Buses on an IPX or IGX node. As a safeguard against bus failure, each node is equipped with redundant System Buses: Bus A and Bus B. Either bus can be configured as the active bus with the other bus as standby. The cnfbus command is used to switch the active bus. Each System Bus contains the following buses: Control Bus, Time Division Multiplex (TDM) bus, clock bus and power bus. In addition to showing which System Bus is active and which is standby, the dspbuses command also shows which sub-bus needs diagnostics or has failed. Bus status is displayed at the bottom of the screen. Table 16-36 shows the possible bus status that dspbuses can display.
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
OK | Bus operation satisfactory |
Failed TDM | A failed TDM Bus |
Failed CNTL | A failed Control Bus |
Needs Diagnostics TDM | The TDM bus needs diagnostics |
Needs Diagnostics CNTL | The Control Bus needs diagnostics |
The remaining MUXBUS or CELLBUS bandwidth available to assign to cards and circuits is displayed. This is primarily used when configuring the AIT card on the IPX or BTM card on the IGX. The user can assign MUXBUS or CELLBUS bandwidth for the IPX or IGX, respectively. Available bandwidth falls into two categories, namely, dedicated and pooled. Dedicated bandwidth is reserved by the system for specific purposes, for example Statistical Reserve for PCC traffic. Pooled bandwidth is available and can be assigned to any use but primarily will be used for an ATM trunk.
MUXBUS or CELLBUS bandwidth is assigned in quantities of "switches", "slices", and "circuits" and the available bandwidth is displayed in three rows accordingly. A single DS0 circuit occupies 333 packets/second of MUXBUS or CELLBUS bandwidth. A "slice" of bandwidth is equivalent to three DS0 circuits for a total of 1000 packets/second. A switch is 8 slices for a total of 8000 packets/second of bus bandwidth. In a newly installed node with no cards and no circuits installed, the total bus bandwidth that is available to be assigned is listed in the right column of the following table, which is the sum of the dedicated and pooled bandwidth. As cards and circuits are added to the node, the available bandwidth decreases accordingly.
| Unit of BW | Quantity | MUXBUS/CELLBUS Capacity |
|---|---|---|
switch | 8 slices or 8000 packets/sec. | 20 |
slice | 3 DS0's or 1000 packets/sec. | 160 |
DS0 | 333 packets/sec. | 480 |
Display status of buses
dspbuses
cnfbus
Privilege | 1-6 |
Jobs | No |
Log | No |
Node | IPX, IGX |
Lock | No |
dspbuses
Display status and bandwidth available. The status of Bus A and Bus B is displayed. In this example, both buses are OK and B is the active Control bus (normal operation is for bus A to be the active bus).
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.4 Mar. 16 1996 13:34 PST
Bus Info
Available MUXBUS bandwidth (snapshot)
Dedicated Pooled Units
--------- ------ -----
0 13 8000 pkts/sec
5 104 1000 pkts/sec
22 312 ds0 circuits
Bus Status
-----------
Bus A: Standby - OK
Bus B: Active - OK
Last Command: dspbuses
Next Command:
Displays the accumulated error count since the last time errors were reset. Table 16-38 lists the types of circuit line errors. The clrclnerrs command clears the error counters for circuit lines.
| Type | Explanation |
|---|---|
Bipolar errors | Number of times two consecutive pulses have the same polarity (AMI coding only). |
Frame slips | Number of times a frame is discarded to re-establish synchronization. |
Out of frames | Number of times a loss of-frame synchronism is detected on this circuit line. |
Loss of signal | Number of times the signal level at the circuit line input went below the minimum acceptable level. |
Frame bit errors | Number of times the frame bit failed to alternate (frame error). |
CRC errors | Number of times the generated CRC character did not match the received CRC character (applies only if CRC checking is enabled). |
Out of MFrames | Number of times a multiframe synch error was detected (E1 lines only). |
AIS - 16 | Number of times the Alarm Information Signal (Blue signal) was received. |
Display circuit line errors
dspclnerrs [slot | slot.line]
clrclnerrs, prtclnerrs
Privilege | 1-6 |
Jobs | No |
Log | No |
Node | IPX, IGX |
Lock | No |
dspclnerrs
Display a summary of all circuit line errors.
sw151 TN SuperUser IGX 16 8.4 June 20 1996 12:45 GMT
Total Errors
Code Frame Out of Loss of Frame CRC Out of
CLN Errors Slips Frames Signal BitErrs Errors MFrames AIS-16
9 0 - 0 0 - 0 - -
5.1 0 - 0 0 - 0 - -
12 0 0 0 0 - 0 - -
5.2 0 - 0 0 - 0 - -
Last Command: dspclnerrs
Next Command:
dspclnerrs 5.1
Display the circuit line errors for line 5.1 on the UFM card in slot 5. A UFM
sw151 TN SuperUser IGX 16 8.4 June 20 1996 12:38 GMT
Circuit Line 5.1 Status:Major - Out of Frm (RED) Clrd: 06/20/96 12:08:38
Type Count ETS Status Type Count ETS Status
Bipolar Err 0 0 Loss of Sig (RED) 0 -
Frame Slips - - AIS (BLU) 0 -
Out of Frms 0 0 Out of Frms (RED) 2 -
Loss of Sig 0 0 Frm Err Rate(RED) - -
Frame BitErrs - - AIS-16 (RED) - -
CRC Err 0 0 Rmt Oof (YEL) 0 -
AIS-16 - - Out of MFms (RED) -
Out of MFms - - Rmt Oom (YEL) - -
Local CGA (RED) - -
Remote CGA (YEL) - -
Last Command: dspclnerrs 5.1
Next Command:
SW MAJOR ALAR
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot or slot.line | For most circuit lines, the slot number is the line number. For the UFM card, one of eight line numbers is necessary to use this optional parameter. With no optional parameter specification, a summary screen for all circuit line errors appears. |
Display information about any configured event queues from the fail event handler.
Display event queue
dspeventq
clreventq
Privilege | 1-6 |
Jobs | No |
Log | No |
Node | IPX, IGX, BPX |
Lock | No |
dspeventq
Display the contents of the fail event handler on the current node.
swstorm TN SuperUser BPX 15 8.4 Jan. 24 1996 11:00 GMT
QUEUE LENGTH THROTTLING
NUM NAMES MAX HIGH CURRENT POINT
1 Fail_Xid 4 1 14000
2 Fail_ Q 4 0
Last Command: dspeventq
Next Command:
Displays the current state of the signals on the FRM-2 or FRP-2 physical port. The display is real-time and updated according to the interval parameter. The display refreshes at a user-specified interval until either the Delete key is pressed or until a timeout occurs.
This command does not show inputs from the user equipment. It shows inputs from the Port Concentrator module to the FRI-2.
For the Inputs from the User Equipment, the display shows the signals as either On, Off, Active, or Inactive For the Outputs to User Equipment, the display shows the signals as either On, Off, Active, or Inactive. X.21 State Names and Leads for DTC and DCE interfaces are also displayed as ON or OFF.
Display FRC/FRM breakout box
dspfrcbob <slot.pot> <interval>
dspbob, dspfrcport
Privilege | 1-3 |
Jobs | No |
Log | No |
Node | IPX, IGX |
Lock | Yes |
dspfrcbob 5.2
Display the signals states for port 2 in slot 5.
bootzilla LAN SuperUser IPX 32 8.4 Apr. 4 1996 15:09 GMT
Physical Port: 5.2
Interface: FTI-X21 DCE
Clocking: Normal (512224 bps)
Inputs from User Equipment Outputs to User Equipment
Lead Pin State Lead Pin State Lead Pin State Lead Pin State
C 3/10 On I 5/12 On
T 2/9 Active R 4/11 Active
X.21 State Name DTE Lead T C DCE Lead R I
1 Ready 1 OFF 1 OFF
13 S Send Data D ON 1 OFF
13 R Receive Data 1 OFF D ON
13 Data Transfer D ON D ON
This Command: dspfrcbob 6.2 1
Hit DEL key to quit:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot.pot | Specifies the slot and port of an FRM-2/FRC-2 physical port. Port range is 1-4. |
interval | Specifies the screen update interval in seconds. The default is 5 seconds. |
Displays the event log for a node. Events affecting the node are displayed in chronological order with the most recent events at the top of the log. Events from the FastPAD are integrated into the log. The display includes a description of the event, the date and time of the event, and the alarm class of the event. A "Continue?" prompt is displayed if more than one screen is required to display all the log entries. Events generating alarms are marked "Major" or "Minor", and events clearing alarms are marked "Clear". Specific events are logged only within a domain. Events occurring in other domains are not reported at all.
Display event log
dsplog
clrogs
Privilege | 1-6 |
Jobs | No |
Log | No |
Node | IPX, IGX |
Lock | No |
dsplog
Display the event log for the node.
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.4 Mar. 16 1996 13:35 PST
Most recent log entries (most recent at top)
Class Description Date Time
Info User YourID logged in (Local) 03/16/95 13:31:41
Info Standby NPC 2 Update Completed 03/16/95 13:31:14
Major PLN 14 Tx NTS Packets Dropped 03/16/95 13:27:50
Info CDP 7 Inserted 03/16/95 13:27:41
Info NPC 2 Restarted due to a NPC Switchover 03/16/95 13:27:39
Info Clock switch to oscillator of gamma via PLN 10 03/16/95 13:27:31
Info CDP 7 Removed 03/16/95 13:27:31
Info NPC 2 Removed - Activated NPC 1 03/16/95 13:27:31
Clear PLN 14 Line OK 03/16/95 13:27:30
Major PLN 14 Tx NTS Packets Dropped 03/16/95 13:27:05
Clear PLN 14 Line OK 03/16/95 13:26:55
This Command: dsplog
Continue?
Displays alarm configuration by alarm type. Each alarm type includes:
The alarm threshold, alarm time, and alarm are set in the cnflnalm command. See the cnflnalm command for descriptions of these parameters.
Display line alarm configuration
dsplnalmcnf
cnflnalm, dspclnerrs, dsptrkerrs
Privilege | 1-6 |
Jobs | No |
Log | No |
Node | IPX, IGX |
Lock | No |
dsplnalmcnf
View the line alarm threshold configurable for a node. Following are system responses:
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.4 Mar. 23 1996 10:51 PST
Line Alarm Configuration
Minor Major
Violation Rate Alarm Time Clear Rate Alarm Time Clear
1) Bpv 10E-7 10 min 3 min 10E-3 10 sec 10 sec
2) Fs .01% 10 min 3 min .1% 10 sec 10 sec
3) Oof .0001% 10 min 3 min .01% 10 sec 10 sec
4) Vpd 2% 5 min 3 min 5% 60 sec 10 sec
5) Tsdp .01% 5 min 3 min .1% 60 sec 10 sec
6) Ntsdp .01% 5 min 3 min .1% 60 sec 10 sec
7) Pkterr .01% 10 min 3 min .1% 125 sec 10 sec
8) Los .0001% 10 min 3 min .01% 10 sec 10 sec
This Command: dsplnalmcnf
Continue?
---------------
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.4 Mar. 23 1996 10:51 PST
Line Alarm Configuration
Minor Major
Violation Rate Alarm Time Clear Rate Alarm Time Clear
9) Fer .01% 10 min 3 min .1% 200 sec 10 sec
10) CRC .01% 10 min 3 min .1% 200 sec 10 sec
11) Pkoof .01% 10 min 3 min .1% 200 sec 10 sec
12) Oom .001% 10 min 3 min .1% 10 sec 10 sec
13) Ais16 .0001% 10 min 3 min .01% 10 sec 10 sec
14) Bdapd .001% 5 min 3 min .1% 60 sec 10 sec
15) Bdbpd .001% 5 min 3 min .1% 60 sec 10 sec
16) Badclk .1% 10 min 3 min 1% 50 sec 10 sec
This Command: dsplnalmcnf
Continue?
----------------
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.4 Mar. 23 1996 10:52 PST
Line Alarm Configuration
Minor Major
Violation Rate Alarm Time Clear Rate Alarm Time Clear
17) Pccpd .001% 5 min 3 min .1% 60 sec 10 sec
18) Lcv 10E-6 10 min 3 min 10E-2 10 sec 10 sec
19) Pcvl 10E-6 10 min 3 min 10E-2 10 sec 10 sec
20) Pcvp 10E-6 10 min 3 min 10E-2 10 sec 10 sec
21) Bcv 10E-6 10 min 3 min 10E-2 10 sec 10 sec
22) Rxvpd 1% 5 min 3 min 4% 60 sec 10 sec
23) Rxtspd .01% 5 min 3 min .1% 60 sec 10 sec
24) Rxntspd .01% 5 min 3 min .1% 60 sec 10 sec
This Command: dsplnalmcnf
Continue?
----------------
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.4 Mar. 23 1996 10:52 PST
Line Alarm Configuration
Minor Major
Violation Rate Alarm Time Clear Rate Alarm Time Clear
25) Rxbdapd .001% 5 min 3 min .1% 60 sec 10 sec
26) Rxbdbpd .001% 5 min 3 min .1% 60 sec 10 sec
27) Rxhppd .001% 4 min 3 min .1% 60 sec 10 sec
28) Atmhec .1% 10 min 3 min 1% 120 sec 10 sec
29) Plcpoof .01% 10 min 3 min .1% 200 sec 10 sec
30) Rxspdm .01% 4 min 2 min .001% 10 sec 5 sec
Last Command: dsplnalmcnf
Next Command:
Displays the accumulated error count since the last time errors were reset. The following lists the error types displayed. The clrlnerrs command clears the error counters for circuit lines by resetting all error counts to 0.
Type | Explanation |
|---|---|
Bipolar errors | Number of times two consecutive pulses have the same polarity (AMI coding only). |
Frame slips | Number of times a frame is discarded to re-establish synchronization. |
Out of frames | Number of times a loss of-frame synchronism is detected on this circuit line. |
Loss of signal | Number of times the signal level at the circuit line input went below the minimum acceptable level. |
Frame bit errors | Number of times the frame bit failed to alternate (frame error). |
CRC errors | Number of times the generated CRC character did not match the received CRC character (applies only if CRC checking is enabled). |
Out of MFrames | Number of times a multiframe synch error was detected (E1 lines only). |
AIS - 16 | Number of times the Alarm Information Signal (Blue signal) was received. |
Display line errors
dsplnerrs [line_number]
clrclnerrs, prtclnerrs
Privilege | 1-6 |
Jobs | No |
Log | No |
Node | IPX, IGX |
Lock | No |
dsplnerrs
Display the circuit line errors for all lines.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
line number | Specifies the circuit for which to display a detailed description of the error counts. Otherwise, a summary screen for all circuit lines is displayed |
The dsppwr command displays the current status of the power supplies and the temperature in the cabinet.
Display power
dsppwr
resetcd
Privilege | 1-6 |
Jobs | No |
Log | No |
Node | IPX, IGX, BPX |
Lock | No |
dsppwr
Display the power status and temperature inside the current IPX.
pubsipx1 TN SuperUser IPX 16 8.4 Nov. 8 1996 04:24 PDT
Power Supply Status Cabinet Temperature
Monitor Status Revision 26 78
Installed Active FP
C 60 | | 140 F
e | | a
Power Supply Type +5v +12v -12v -48v Temp n 50 |--| 122 h
t | | r
A Empty i 40 | | 104 e
B Empty g | | n
C AC 400W IPX Ok Ok Ok Ok r 30 | | 86 h
D AC 400W IPX Ok Ok Ok Ok a | | e
d 20 | | 68 i
e \Q--' t
Last Command: dsppwr
Next Command:
dsppwr
Display the power status and temperature inside the current IGX.
sw151 TN SuperUser IGX 16 8.4 Aug. 23 1996 11:50 GMT
Power Supply Status Cabinet Temperature
Monitor Rev AK, Ser # 247582 - Status: Active 30 86
AC Supply Status C 60 | | 140 F
A 1 875W OK e | | a
B 1 875W OK n 50 |--| 122 h
C 1 Empty t | | r
D 2 Empty i 40 | | 104 e
E 2 Empty g | | n
F 2 Empty r 30 | | 86 h
a | | e
d 20 | | 68 i
e \Q--' t
Last Command: dsppwr
Next Command:
dsppwr
Display the power status and temperature inside the current BPX.
bootzilla TN SuperUser BPX 15 8.4 May 17 1996 11:06 GMT
Power Status Cabinet Temperature
ASM Status: Active 21 69
Power voltage A/B: 0 / 49 V C 60 | | 140 F
e | | a
PSU Ins Type Rev SerNum Failure n 50 |--| 122 h
A N N/A N/A N/A N/A t | | r
B Y ???? 00 ...... None i 40 | | 104 e
g | | n
Fan Status r 30 | | 86 h
a | | e
FAN 1 2 3 d 20 | | 68 i
0000 3300 3240 RPM e \Q--' t
Last Command: dsppwr
Next Command:
Displays the slot alarm configuration for the BPX.
Display slot alarm configuration.
dspslotalmcnf [slot]
dspslotalms
Privilege | 1-6 |
Jobs | No |
Log | No |
Node | BPX |
Lock | No |
dspslotalmcnf 7
Display the slot alarm configuration for the BPX.
D1.jea TRM SuperUser BPX 15 8.4 Mar. 30 1996 12:04 GMT
Slot Alarm Configuration
Minor Major
Violation Rate Alarm Time Clear Rate Alarm Time Clear
1) SBus .01% 10 min 3 min .1% 10 sec 10 sec
2) InvP .01% 10 min 3 min .1% 10 sec 10 sec
3) PollA .01% 10 min 3 min .1% 10 sec 10 sec
4) PollB .01% 10 min 3 min .1% 10 sec 10 sec
5) BGE .01% 10 min 3 min .1% 10 sec 10 sec
6) TBip .01% 10 min 3 min .1% 10 sec 10 sec
7) RBip .01% 10 min 3 min .1% 10 sec 10 sec
8) Bfrm .01% 10 min 3 min .1% 10 sec 10 sec
9) SIU .01% 10 min 3 min .1% 10 sec 10 sec
Last Command: dspslotalmcnf 7
Next Command:
Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot number | Specifies the slot number of the card to be displayed. |
Displays statistical alarms associated with the SIU on each BPX card. It displays a single line for each slot in a local BPX node occupied by a card. Both the card type and current card alarm status is listed. If a card is operating normally, a "Clear - Slot OK" is displayed. If fault conditions persist to cause the slot errors (described in the Display Slot Errors command) to exceed a preset threshold, this will be displayed under column labeled Current Card Alarm Status. The clrslotalms command clears these alarm messages if the alarm condition has retired.
Display slot alarms
dspslotalms
dspsloterrs
Privilege | 1-6 |
Jobs | No |
Log | No |
Node | BPX |
Lock | No |
dsplotalms 1
Display the status of the card in slot 1.
D1.jea TRM SuperUser BPX 15 8.4 Mar. 30 1996 12:00 GMT
Slot Type Current Slot Alarm Status
7 BCC Clear - Slot OK
11 BNI-T3 Clear - Slot OK
Last Command: dspslotalms
Next Command:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot number | Specifies the slot number of the card to be displayed. |
Displays statistical alarms associated with the SIU on each BPX card. The dspsloterrs command displays a single line for each slot in a local BPX node occupied by a card. If a card is operating normally, a "Clear - Slot OK" is displayed. If error-producing conditions persist and cause the slot errors to exceed a preset threshold, this fact is displayed under the column labeled Current Card Alarm Status. The clrslotalm command clears the alarm messages if the alarm condition has been corrected. Table 16-45 shows the errors displayed.
| Error | Description |
|---|---|
Standby Bus Errors | Indicates a background test over the standby bus produced an error. |
Invalid Port Errors | Indicates port number was out of the range 1 - 3. |
Polling Bus A Errors | Parity error occurred on this polling bus. |
Polling Bus B Errors | Parity error occurred on this polling bus. |
Bad Grant Errors | Error indicates arbiter did not issue a grant to send data before a time-out. |
Tx BIP-16 Errors | Data frame transmitted had a checksum error. |
Rx BIP-16 Errors | Data frame received with a checksum error. |
SIU Phase Errors | Serial Interface Unit on the card did not detect the frame synch properly. |
Bframe Errors | Errors detected in the BPX frame on the StrataBus or in a memory operation. |
Display slot errors.
dspsloterrs
dspslotalms
Privilege | 1-6 |
Jobs | No |
Log | No |
Node | BPX |
Lock | No |
dspsloterrs 7
Display the slot alarm configuration for the BPX
D1.jea TRM SuperUser BPX 15 8.4 Mar. 30 1996 12:01 GMT
BCC 7 Status: Clear - Slot OK Clrd: Date/Time Not Set
Type Count ETS Status Type Count ETS Status
Stby PRBS Errs 0 0
Rx Invld Prt Errs 0 0
Poll Bus A Parity 0 0
Poll Bus B Parity 0 0
Bad Grant Errs 0 0
Tx BIP-16 Errs 0 0
Rx BIP-16 Errs 0 0
SIU Phase Errs 0 0
Bfrm. Par. Errs 0 0
Last Command: dspsloterrs 7
Next Command:
----------------
swstorm TN SuperUser BPX 15 8.4 July 21 1996 15:40 GMT
Summary of Slot Errors
Invld Poll Poll Tx Rx B- Rx
Stdby Rx A Bus B Bus Bad BIP- BIP- SIU Frame FIFO Poll CK-
PRBS Port Par Par Grant 16 16 Phase Par Sync Clk 192
Slot Errs Errs Errs Errs Errs Errs Errs Errs Errs Errs Errs Errs
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4 15K 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
7 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 8660 3366 0 0 0
13 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Last Command: dspsloterrs
Next Command:
SW MAJOR ALARM
Displays the enabled statistics for the specified slot.
Display statistics enabled for a slot.
dspslotstatcnf [slot]
dspslotalmcnf
Privilege | 1-6 |
Jobs | No |
Log | No |
Node | BPX |
Lock | No |
dspslotstatcnf 7
Display thresholds for slot 7
D1.jea TRM SuperUser BPX 15 8.4 Mar. 30 1996 12:03 GMT
Statistics Enabled on Slot 7
Statistic Samples Interval Size Peaks Owner
----------------------------------- ------- -------- ---- ----- ----------
Standby PRBS Errors 60 0 4 NONE Automatic
Rx Invalid Port Errors 60 0 4 NONE Automatic
Polling Bus A Parity Errors 60 0 4 NONE Automatic
Polling Bus B Parity Errors 60 0 4 NONE Automatic
Bad Grant Errors 60 0 4 NONE Automatic
Transmit Bip 16 Errors 60 0 4 NONE Automatic
Receive Bip 16 Errors 60 0 4 NONE Automatic
Bframe parity Errors 60 0 4 NONE Automatic
SIU phase Errors 60 0 4 NONE Automatic
Last Command: dspslotstatcnf 7
Next Command:
Displays the accumulated line error counts, by failure type, for the specified trunk(s). If no trunk number is entered, a one-line summary of errors for all trunks at the local node is displayed. Table 16-46 shows the types of errors that are displayed with a brief description of each type. If a specific trunk number is entered with the command, a detailed analysis, including error threshold (ETH), is displayed. Disabled trunks have their trunk number displayed in dim, reverse video on the screen. The clrtrkerrs command resets all error counts to 0.
| Line Type | Error | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
All except ATM | Bipolar errors | Number of times two consecutive pulses have the same polarity (AMI coding only). |
| Frame slips | Number of times a frame is discarded to re-establish synchronization. |
| Out of frames | Number of times a loss of-frame synchronism is detected on this circuit line. |
| Loss of signal | Number of times the signal level at the circuit line input went below the minimum acceptable level. |
| Frame bit errors | Number of times the frame bit failed to alternate (frame error). |
| CRC errors | Number of times the generated CRC character did not match the received CRC character (applies only if CRC checking is enabled). |
| Out of MFrames | Number of times a multiframe synch error was detected (E1 lines only). |
| AIS - 16 | Number of times the Alarm Information Signal (Blue signal) was received. |
Only ATM | Out of Frames | Number of times a momentary loss of-DS3 frame alignment was detected. |
| Loss of sync (XX) | Number of times a loss of-DS3 frame alignment lasting more than XX seconds was detected. |
| Packet Error | Number of CRC errors for a packet address. |
| Line Code Errors | Number of B3ZS code errors detected. |
| P-bit Parity Errors | Number of parity errors for the DS3 parity bit (P-bit) sequence. |
| C-bit Parity Errors | Number of parity errors for the DS3 control bit (C-bit) sequence. |
| Comm Fails | Number of BCC failed to communicate to the other node. |
| Loss of signal | Number of times the signal level at the trunk line input went below the minimum acceptable level. |
Only ATM | AIS (BLU) | Number of times the Alarm Information Signal (Blue signal) was received. |
| Out of MFrames | Number of times a loss of-frame synchronism in the DS3 multiframe alignment was detected. |
| Remote Oof | Number of times the DS3 remote alarm (indicating remote end was out of frame alignment) was received. |
Display trunk errors
dsptrkerrs [slot | slot.port]
or
dsptrkerrs <slot.port> (for virtual trunks)
clrtrkerrs, prttrkerrs
Privilege | 1-6 |
Jobs | No |
Log | No |
Node | IPX, IGX, BPX |
Lock | No |
dsptrkerrs
Display a summary of all trunk errors at the local node.
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.4 Mar. 16 1996 13:13 PST
Total Errors
Code Rx Pkts Out of Loss of Frame CRC Tx Pkts Packet Packet
PLN Errors Dropped Frames Signal BitErrs Errors Dropped Errors Oofs
10 - - 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
14 0 0 0 - 0 - 218M 0 -
Last Command: dsptrkerrs
Next Command:
dsptrkerrs 16
Display a detailed description of the errors for trunk 16
D2.ipx4 TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.4 Aug. 4 1996 16:34 PST
Packet Line 16 Status: Clear - Line OK Clrd: Date/Time Not Set
Type Count ETS Status Type Count ETS Status
Bipolar Err 0 0 Comm Fails 0 -
Out of Frms 0 0 Loss of Sig (RED) 1 -
Loss of Sig 0 0 AIS (BLU) 0 -
Frame BitErrs 0 0 Out of Frms (RED) 0 -
Tx Voice Pkt Drp 0 0 Rmt Oof (YEL) 0 -
Tx TS Pkt Drp 0 0 Packet Oofs (RED) 1 -
Tx Non-TS Pkt Drp 0 0 Rmt Alarms (YEL) 0 -
Tx NPC Pkt Drp 0 0
Tx Bdata A Pkt Drp 0 0
Tx Bdata B Pkt Drp 0 0
Packet Err 4 1
Packet Oofs 0 0
Last Command: dsptrkerrs 16
Next Command:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Specifies the trunk for which to display detailed description of its statistical error counts. Otherwise, a summary screen for all trunks is displayed. |
Prints the accumulated error count since the last time errors were reset. This command uses the same syntax and prints the same information as is displayed using the dspclnerrs command. The clrclnerrs command clears the error counters for circuit lines by resetting all error counts to 0.
Print circuit line errors
prtclnerrs
clrtrkerrs, prttrkerrs
Privilege | 1-6 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | No |
Node | IPX, IGX |
Lock | Yes |
prtclnerrs
Print a summary of all trunk errors at the local node.
None available as command produces hardcopy.
Prints the accumulated error count since the last time errors were reset. This command uses the same syntax and prints the same information as is displayed using the dsplnerrs command. The clrlnerrs command clears the error counters for circuit lines by resetting all error counts to 0.
Print line errors
prtlnerrs
dsplnerrs
Privilege | 1-6 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | No |
Node | IPX, IGX, BPX |
Lock | Yes |
prtlnerrs
Print errors for all upped lines on a node.
None available as command produces hardcopy.
Prints the event log for a node. Events affecting the node are displayed in chronological order with the most recent events at the top of the log. The printout includes a description of the event, the date and time of the event, and the alarm class of the event. This command uses the same syntax and prints the same information as is displayed using the dsplog command. See the dsplog command for output information.
Print event log
prtlog
dsplog
Privilege | 1-6 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | No |
Node | IPX, IGX, BPX |
Lock | Yes |
prtlog
Print the event log for a node.
None available as command produces hardcopy.
Prints a summary of the trunk error counts for both physical and virtual trunks on the local node. This is the same information as is displayed using the dsptrkerrs command. See the dsptrkerrs command for output information.
Print trunk errors
prttrkerrs
dsptrkerrs
Privilege | 1-6 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | No |
Node | IPX, IGX, BPX |
Lock | Yes |
prttrkerrs
Print a summary of trunk errors.
None available as command produces hardcopy.
Resets the hardware and software for a specified card. A hardware reset is equivalent to physically removing and reinserting the front card of a card group and causes the card's logic to be reset. When you reset the hardware of an active card other than a controller card (an NPC, NPM, or BCC), a standby card takes over if one is available. A failure reset clears the card failures associated with the specified slot. If a slot contains a card set, both the front and back cards are reset.
Do not use the reset command on an active NPC, NPM, or BCC because this causes a temporary interruption of all traffic while the card is rebooting. (Resetting a controller card does not destroy configuration information.) Where a redundant NPC, NPM, or BCC is available, the switchcc command is used to switch the active controller card to standby and the standby controller card to active. If a standby card is available, resetting an active card (except for a NPC, NPM, or BCC) does not cause a system failure. H/F Resetting of an active card that has no standby does disrupt service until the self-test finishes.
Reset card
resetcd <slot_num> <reset_type>
resetcd
Privilege | 1-3 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX, BPX |
Lock | Yes |
resetcd
Reset the card in slot 23
No display produced.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot number | Specifies the card number to be reset. |
H/F | Specifies whether the hardware or failure history for the card is to be reset. An "H" specifies hardware; an "F" specifies failure history. |
The resetpc command resets a PCS attached to a specified FRM-2 or FRP-2 physical port. Concentrated links, logical ports, and all connections are temporarily suspended while the PCS hardware performs a warm boot.
Once the PCS re-establishes communication with the FRM-2 or FRP-2, logical ports are reconfigured and connections repaired. A series of messages describing each of the concentrated links failing and being re-established is generated.
Reset Port Concentrator
resetpc <slot.port>
tstpcs, dsppcs
Privilege | 1-3 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX, BPX |
Lock | Yes |
resetpc 2.3
Reset the card in slot 23
No display produced. (Use dsppcs to check status.)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot.port | Specifies the card and port number to be reset. |
Switches the standby BCC or NPC (or NPM) card to active and the active card to standby. If a standby BCC is not available, the command is not executed. If a standby BCC is available but not ready to go active, a prompt asks you to confirm or abort the switch. This command was previously called switchpcc. Executing switchcc has the following effect:
Immediately after the switch, the controller card that was previously active reverts to a download mode. This is indicated by the flashing front panel FAIL lamp. The system software image that is always stored in ROM is downloaded to RAM in the event that the system software was corrupted.
After this is completed, the configuration database is downloaded from the newly active controller card to complete the download. This process takes a number of minutes so this controller card not available for standby operation until this download process is completed. The switchcc command results in a very brief interruption of all traffic. Consequently, you should use switchcc only when the network can tolerate a brief interruption.
Switch control card
switchcc [f]
dspcd, dspcds
Privilege | 1-3 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | No |
Node | IPX, IGX, BPX |
Lock | Yes |
switchcc
Change the active NPC/BCC to standby, and the standby NPC/BCC to active
No display produced.
The tstcon command tests the integrity of an IPX or IGX data path by inserting node-generated test data. The connection service is affected for only a few seconds during the test. One channel at a time is tested to minimize disruption. Because service is disrupted for a short time, no conditioning is applied during the test.
The tstcon command can also test an IPX that has been configured as an interface shelf (IPX/AF) in a tiered network but only after a local-remote loopback has been set up with the addlocrmtlp command. After testing is complete, the loopback established with addlocrmtlp must be removed by dellp.
Table 16-50 shows the test results that are reported.
| Result | Description |
|---|---|
Completed | total number of tests that were run. |
Aborted | number of tests that did not run because the connection was not testable because of loopbacks or missing or failed hardware. |
Failures | number of tests that failed. |
Repaired | number of connections that failed a previous test and have passed the current test. |
If a failure is detected, the fault is isolated to a replaceable IPX or IGX, and the standby module (if available) automatically goes into service. During fault isolation, conditioning is applied to both ends of the connection. Only existing connections can be tested. If you enter a range of channels (with connections and some without), the unconnected channels are skipped. The tstcon command can be entered from the node at either end of the connection. Unlike the addloclp and addrmtlp commands, the tstcon command does not require external test equipment. Connections cannot be tested with the tstcon command if they are currently looped back with either the addloclp or addrmtlp commands. Example commands and arguments appear in Table 16-51.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
tstcon * | test all connections. |
tstcon * f | test all frame relay connections. |
tstcon * v x | test all voice connections, abort on first failure. |
tstcon 1.3 | test connection on channel 1.3. |
tstcon 4.2.200 | test connection on channel 4.2.200. |
tstcon 1.13-16 | test connections on channels 1.13-16. |
tstcon 3.21-24 x | test connections on channels 3.21-24, abort on first failure. |
tstcon 3.11-20 v | test voice connections only on channels 3.11-20. |
tstcon 3.11-20 v x | test voice connections only on channels 3.11-20, abort on first failure. |
tstcon 3.21-22 v 5 | test voice connections only on channels 3.21-22 and repeat the test 5 times. |
tstcon 3.14-15 d x 5 | test data connections only on channels 3.14-15: repeat test 5 times, but abort on failure. |
For V.35 ports configured for DTE, the following three bulleted items apply:
Test connections
testcon <channel(s)> [-nolp] [type] [failure abort] [repeat count]
dspcons, dspcons
Privilege | 1-2 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX |
Lock | Yes |
tstcon 9.1.100
Test connection 9.1.100. The connections screen appears with the connection for channel 9.1.100 highlighted. The system prompts to confirm the test. A "T" after channel under test indicates that the test is currently running on that channel. When the first test is completed, a message appears indicating the results of the tests. As each test is completed, the T moves to the next channel to be tested and the message is updated to include the cumulative results of the tests. When the test is completed for all the specified connections, the "T" disappears and the message indicates the total number of tests and the cumulative results of the test.
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.4 Mar. 23 1996 11:04 PST
Local Remote Remote Route
Channel NodeName Channel State Type Compression Code Avoid COS O
5.1 T beta )25.1 Ok 256 7/8 0 L
9.1.100 gamma 8.1.200 Ok fr 0 L
9.1.200 gamma 8.1.300 Ok fr 0 L
9.2.400 beta 19.2.302 Ok fr(Grp) 0 L
14.1 gamma 15.1 Ok v 0 L
Last Command: tstcon 9.1.100
Tests: Completed = 1, Aborted = 0, Failed = 1, Connections Repaired = 0
Next Command:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
channels | Specifies the specifies the channel or set of channels whose connections are to be tested. An "*" specifies all connections. Channel is specified in one of the following formats: slot.channel voice connection |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
-nolp | No automatic loopback. This parameter applies only to local-remote loopbacks and is mandatory for testing a multi-segment connection in a tiered network. |
type | Restricts the test to the designated connection type. Valid connection types are listed below. If no connection type is designated, all connections are tested. v Tests only voice connections. |
x | Aborts the test as soon as a failure is detected. If an "x" is not entered, all specified connections are tested regardless of the test results for each individual connection. |
repeat count | Specifies the number of times the test is to be repeated. The range is from 1 to 50. If no test count is specified, the test is run once. |
Externally tests the integrity of a connection by inserting OAM segment loopback cells. The connection service is affected for only a few seconds while the data path is tested. To minimize this disruption, only one connection at a time is removed from service. Because service is disrupted for a short time, no conditioning is applied during the test.
The tstconseg command can also test the connection to an IPX that has been configured as an interface shelf (IPX/AF) in a tiered network but only after a local-remote loopback has been set up with the addlocrmtlp command. After testing is complete, the loopback established with addlocrmtlp must be removed by dellp.
Table 16-54 shows the possible test results.
| Result | Description |
|---|---|
Completed | total number of tests that were run. |
Aborted | number of tests that did not run because the connection was not testable because of loopbacks or missing or failed hardware. |
Failures | number of tests that failed. |
Repaired | number of connections that failed a previous test and have passed the current test. |
Test connection segment
tstconseg <channel> <iteration count> [A | a]
dspcons, dspcons
Privilege | 2 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | BPX |
Lock | Yes |
tstconseg 11.2.10.17
Test connection segment 11.2.10.17. The connections screen appears with the connection for channel 11.2.10.17 highlighted. The system prompts to confirm that the test should begin. A "T" after the channel under test indicates the test is currently running on that channel. When the first test is complete, a message appears indicating the results of the tests. As each test is completed, the T moves to the next channel to be tested and the message is updated to include the cumulative results of the tests. When the test is completed for all the specified connections, the "T" disappears and the message indicates the total number of tests and the cumulative results of the test.
nmsbpx23 TN SuperUser BPX 15 8.4 Aug. 16 1996 12:37 PST
Local Remote Remote Route
Channel NodeName Channel State Type Avoid COS O
11.2.10.17 nmsbpx23 11.1.11.17 Ok atfst
This Command: tstconseg 11.2.10.17 1
Perform a tstconseg on this connection (y/n)?
----------------
nmsbpx23 TN SuperUser BPX 15 8.4 Aug. 16 1996 12:38 PST
External Connection Segment Test
Status: Test Complete
Connection ID Test Count Failure Count Success Count
11.2.10.17 1 1 0
Last Command: tstconseg 11.2.10.17 1
Next Command:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
channel | Specifies the slot.port.vpi.vci of the channel to be tested. |
iteration | Number of times to repeat the test. |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
A|a | Specifies that the test be aborted if an error occurs (not case sensitive). |
Puts the remote end of the connection into a loopback state, requests the FRP (frame relay) or ASI (ATM) to generate a test packet, calculates the round trip delay (RTD), and displays the round trip delay. This delay includes the FRP or ASI and trunk queuing and processing delays throughout the network. The measured delay using tstdelay differs from the ForeSight RTD, which uses a high-priority packet and does not include processing and queuing delays. Using the tstdelay command requires that the FRP is at least a Model D. This test interrupts transmission on the connection during the test. Test results appear at the bottom of the screen (this may include a timeout message, as in Example 1).
Testing an IPX that has been configured as an interface shelf (IPX/AF) requires execution of addlocrmtlp prior to tstdelay and a tstdelay parameter that applies only to tiered networks (see optional parameter table). After testing is complete, the loopback established with addlocrmtlp must be removed by dellp.
Test Frame Relay connection delay
tstdelay <slot.port.DLCI> [count] | tstdelay <slot.port.vpi.vci> [-nolp] [count] [y]
addlocrmtlp, dellp, dspcons, dspcons
Privilege | 1-2 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX, BPX |
Lock | Yes |
tstdelay 9.1.100
Test the delay on frame relay channel 9.1.100.
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.4 Mar. 23 1996 11:05 PST
Conn: 9.1.100 gamma 8.1.200 fr
MIR CIR VC Q Depth PIR Cmax ECN QThresh QIR FST
9.6/9.6 9.6/9.6 5/5 256/256 10/10 65535/65535 9.6/9.6 n
% Util: 100/100
Owner: LOCAL Restriction: NONE COS: 0 Status: Failed Test
Group: NONE Priority: H TestRTD: 0 msec
Path: alpha 14--13beta 15--15gamma
Pref: alpha 14--13beta 15--15gamma
alpha 9.1.100 gamma 8.1.200
FRP: OK FRP: OK
FRI: OK FRI: OK
Last Command: tstdelay 9.1.100
Test delay timed out
Next Command:
tstdelay 9.1.1.1
Test the delay on ATM connection 9.1.1.1. The first prompt that follows initial command entry is for whether the ForeSight RTD should be included. The second prompt is for confirming that the test should proceed.
bpx1 TN SuperUser BPX 15 8.4 Jan. 31 1996 13:45 PST
Conn: 9.1.1.1 ]bpx6 11.1.1.1 abr Status: OK
SCR MBS MCR ABR PCR UPC FST CLP % util
4000/4000 1000/1000 4000/4000 4000/4000 y y y 100/100
Owner: REMOTE Restriction: NONE COS: 0
Group: NONE ForeSightRTD: 40 msec TestRTD: 10 msec
Path: bpx1 1.3-- 3.3bpx6
Pref: Not Configured
bpx1 ASI-T3 : OK bpx6 ASI-T3 : OK
Line 9.1 : OK Line 11.1 : OK
OAM Cell RX: Clear
Last Command: tstdelay 9.1.1.1 n
Round trip delay is 10 msec.
Next Command:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
channel | Specifies the channel of the connection to be tested. It can be a frame relay connection specified as slot. port. DLCI or an ATM connection specified as slot.port.vpi.vci. |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
-nolp | No automatic loopback. This parameter applies only to local-remote loopbacks and is mandatory for testing a multi-segment connection in a tiered network. |
repeat count | Specifies the number of times the test is to be repeated. The range is from 1 to 50. If no test count is specified, the test is run once. |
ForeSight RTD (y/n) | Specifies that the ForeSight RTD is included and applies to ATM connections only. |
The tstpcs command tests the data path for PCS ports for a selected module. The port parameter specifies the particular PCS module. The port parameter specifies an FRM-2 or FRP-2 physical port to which one of the PCS modules connects.
Upon command entry, each of the 11 ports for the PCS goes into a loop state. In this state, data goes to each port and loops back to the PCS module. Test frames go to a port and are checked for integrity when they return. The test frames also go out on the port.
During this test, any frame relay connection data received by the FRM-2 or FRP-2 destined for one of the ports is discarded. The other three Port Concentrator modules are unaffected. After the test, the port is returned to its previous configuration.
The PCS tests available RAM, and sets each of the 11 ports into a loop mode. Ten frames of data are sent to each port and checked to make sure the same frames are received in entirety and order.
During a test, the dsppcs screen shows "Testing" then either "Passed" or "Failed." The test takes about 15 seconds.
Test Port Concentrator Shelf
tstpcs <slot.port>
dsppcs, resetpc
Privilege | 1-2 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX |
Lock | Yes |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot.port | Slot is the location of an FRM-2 or FRP-2 card. Port selects the physical port to which one of the Port Concentrator modules is connected. The range for port is 1-4. |
Executes a port loopback test on the specified data port. Using tstport without the optional parameter performs an internal test. The loopback for the internal test is performed on the IPX or IGX back card and is used to test just the IPX or IGX front and back cards. The test disables the communications for that port and the back card is placed into a loopback mode. The applicable card sets for the tstport command are the FRP, FRM, SDP, HDM, LDP, and LDM. The card under test sends several frames of data to the port on the interface card, loops them back, and checks their integrity.
If connections exist on the port being tested, the dspcons screen appears. If no connections are present, the dspfrport screen appears. A flashing `T' in the connections screen indicates those connections affected by the test. Either a "(" character or a ")" character indicates the loopback in the dspfrport. If a local or remote test fails, the port itself is automatically tested (internal) to determine if the IPX or IGX caused the failure. The following are example command lines:
tstport 5.3 | internal loopback port test—this is the default loopback |
tstport 5.3 n | near external port loopback test |
tstport 5.3 f | far external port loopback test. |
For a frame relay port or an LDP or LDM port, an external loopback may be placed at the near (local) or far (remote) modem during the test. For a DDS port, the external loopback is a CSU or DSU loopback at the remote DSU device. If an external port loopback test fails, the internal port loopback test is executed to determine if the IPX or IGX caused the failure. The cnfict command can be used to specify the interface control lead template used to condition the output control leads during loopback.
The local and remote modem tests that test the near end and far end modems or NTUs require the IPX or IGX back card to operate as a DTE, so the modem acts as a DCE in this case. The back card asserts the local or remote loopback pin of the V.35 port. For X.21 ports, which do not have a loopback pin defined, the back card sends a loopback command in the data stream to cause the NTU to go into loopback mode. The test then begins.
The loopback test operation sends several frames of test data, receives them back, compares them, and verifies their integrity. The loopback pin subsequently returns to the inactive state, and the modems return to normal operation. The local or remote test works with only those modems that recognize a local and remote loopback command.
Before starting a test, the user must be sure the cabling is correct for the specific equipment. The test conventions are described in CCITT V.54 and X.21 specifications. Only the near (n) and far (f) options are available for the Model C SDP. If the near or far tests fail, no internal test is executed on the SDP to isolate the problem. The SDP is not failed due to a tstport failure.
Test port
tstport <slot.port> [n | f]
cnfict, dspcons, dspfrport
Privilege | 1-2 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX |
Lock | Yes |
tstport 9.1
Perform an internal port test on a frame relay port.
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.4 Mar. 23 1996 11:27 PST
Conn: 9.1.100 gamma 8.1.200 fr
MIR CIR VC Q Depth PIR Cmax ECN QThresh QIR FST
9.6/9.6 9.6/9.6 5/5 256/256 10/10 65535/65535 9.6/9.6 n
% Util: 100/100
Owner: LOCAL Restriction: NONE COS: 0 Status: Failed Test
Group: NONE Priority: H TestRTD: 0 msec
Path: alpha 14--13beta 15--15gamma
Pref: alpha 14--13beta 15--15gamma
alpha 9.1.100 gamma 8.1.200
FRP: OK FRP: OK
FRI: OK FRI: OK
Last Command: tstport 9.1
No external clock is detected for DTE
Next Command:
tstport 32.1 n
Perform a local (near end) loopback test on port 32.1 (requires port to be configured as DTE).
tstport 32.1 f
Perform a remote (far end) loopback test on port 32.1 (requires port to be configured
as DTE).
tstport 9.1
Perform a test of an FRP port.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
slot | Specifies the slot number of the FRP, FRM, LDP, LDM, HDM, or SDP. |
port | Specifies the number of the port to test. The range is 1-4. |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
n/f | Specifies that an external loopback test should run at the near or far-end modem. An "n" specifies a "near-end" test. An "f" specifies a "far-end" test. Without one of these optional parameters, the test runs internally. |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Thu Jan 18 13:09:43 PST 2001
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2001 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.