|
|

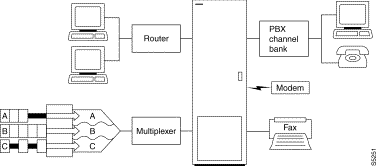 A circuit line is the physical line that carries frame relay, data, voice, or ATM traffic between customer equipment and an IPX, IGX, or BPX node. Each piece of equipment in the illustration above is attached to the node through a circuit line. After a card has been "upped" with the upcd command, a circuit line on that card can be "upped" and configured.
A circuit line is the physical line that carries frame relay, data, voice, or ATM traffic between customer equipment and an IPX, IGX, or BPX node. Each piece of equipment in the illustration above is attached to the node through a circuit line. After a card has been "upped" with the upcd command, a circuit line on that card can be "upped" and configured.
This chapter:
The following table shows the permissible card combinations for CPE-to-IPX and IGX lines.
| Type | Country | Electrical Signal Format | Ones Density Requirement | Multiplexing |
J1 | Japan | Coded Mark Inversion (CMI) |
| 31 channels @ 64kbps each |
E1 | Others | Alternate Mark Inversion (AMI) | High density bipolar 3 (HDB3) | 31 channels @ 64kbps each 1 E1 line on CDP/CVM, 8 E1 lines on UFM) |
T1 | USA ASIA | Alternate Mark Inversion (AMI) | Bipolar Zero Substitution (B8ZS) | 24 channels @ 64kbps each 1 T1 line on CDP/CVM, 8 T1 lines on UFM |
E3 | Europe | Physical Layer Convergence Protocol per AT&T publication; ITU I-361 with HEC for E3 | HDB3 | ITU-T G.804, G.832 |
T3 | USA | Physical Layer Convergence Protocol per AT&T publication TA-TSY-00772 and 000773 for T3 | B3ZS | M13 mode |
| Service | Node Type | Front Card | Back Card |
|---|---|---|---|
ATM | IGX | ALM/A | BC-UAI-1T3 |
Frame Relay | IGX | UFM-4C, UFM-8C | UFI-8T1-DB15, UFI-8E1-DB15, UFI-8E1-BNC |
Frame Relay | IPX/IGX | FRP/FRM | FRI/V.35, FRI/X.21 |
Frame Relay | IPX/IGX | FRP-6, FRP-31/FRM-6, | FRI-T1, FRI-E1 |
Frame Relay | IPX/IGX | FRP-2, FRM-2 | FRI-2-X.21 |
Frame Relay | IGX | UFM-C or UFM-U | UFI-8T1-DB15 |
High Speed Data | IPX/IGX | SDP/HDM | SDI/RS-232 |
Low Speed Data | IPX/IGX | LDP | LDI4/RS-232 |
Voice | IGX | UVM | BC-UVI-2T1EC |
Voice | IPX/IGX | CDP/CVM | BC-T1 |
Frame relay, data, and voice connections require an actived line. Use the commands in the following steps to establish a line. The card must be in the active state before you enter these commands.
Step 1 Use upcln to activate a circuit line in a slot that contains the appropriate circuit line card set.
Step 2 Use cnfcln or cnfln to configure the circuit line.
The upcln and cnfcln commands establish the general parameters for the circuit line. They do not establish specific frame relay, data, or voice parameters. Refer to the appropriate chapter for details of setting up a particular service on a circuit line/ line. For example, the Data Connections chapter describes specific commands for data connections, and the Frame Relay Connections chapter describes specific commands for frame relay connections.
The following describes related commands.
Figure 6-1, Figure 6-2, Figure 6-3, Figure 6-4, and Figure 6-5 show the command sequence for setting up lines for voice, serial data, frame relay, ATM, and FastPADs, respectively. A yes/no decision branch for "Other Side?" and the vt command in the sequence indicates command sequences on local and far nodes. "Multiplex" refers to channelized and unchannelized streams.
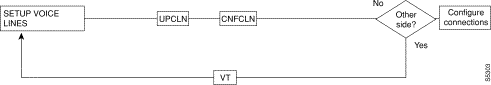
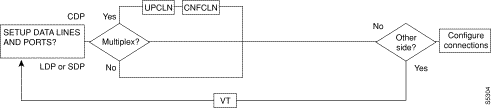
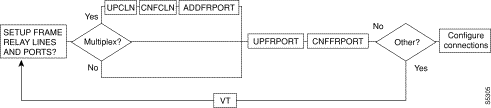
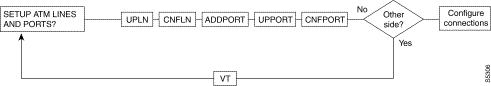
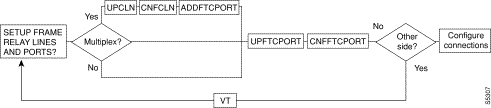
Table 6-3 shows the full command name and starting page for each line command description.
| Mnemonic | Description | Page |
|---|---|---|
cnfln | Configure line (same as cnfcln) | |
dnln | Down line (same as dncln) | |
dsplncnf | Display line configuration (same as dspcln) | |
dsplns | Display lines (same as dspclns) | |
prtlns | Print circuit lines (same as prtclns) | |
upln | Up circuit line (same as upcln) |
Configures a line to be compatible with the device to which it connects. The cnfln command applies to voice, data, frame relay, and ATM lines. See Table 6-2 for a list of the front and matching back cards. Because of the variety of line types and characteristics, the parameters section of this description has three tables to describe the parameters. The system automatically presents the correct options on the command line for each line type. If a parameter is not applicable to a card type, the system displays the parameter in half-tone or the value field of that parameter with dashed lines. Table 6-4 describes the parameters for voice, data, and frame relay parameters. Table 6-5 describes the parameters for the ATM Line Module (ALM/A). Table 6-6 describes the parameters for the ASI line card (BPX node).
For an ALM/A, the cnfln command lets you configure the receive rate and header type and enable payload scrambling. For more details on the features and configurable parameters of the ALM/A, refer to the Cisco IGX 8400 Series Reference and the Cisco IGX 8400 Series Installation manuals. Note that, although the cnfln display shows the transmit rate, you cannot configure it because the ALM/A transmit rate is always the maximum line rate.
configure line
cnfln <line> <parameters>
dspln, dsplncnf
Privilege | 1 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX, BPX |
Lock | Yes |
cnfln 14
Description
Configure voice line 14.
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.2 Mar. 23 1996 09:55 PST
CLN 14 Configuration T1/24 CDP slot: 13
Loop clock: --
Line framing: --
coding: --
CRC: --
recv impedance: --
E1 signalling: --
encoding: --
T1 signalling: --
cable type: --
length: --
56KBS Bit Pos: --
pct fast modem: --
Last Command: cnfcln 14
Next Command:
cnfcln 7 n 2
Configure a frame relay T1 line for the following options: no loop clock and a receive impedance of 75 ohms.
alpha TRM YourID:1 IPX 16 8.2 Mar. 23 1996 09:55 PST
CLN 14 Configuration T1/24 FRPslot: 13
Loop clock: --
Line framing: ESF
coding: ZCS
CRC: --
recv impedance: --
E1 signalling: --
encoding: --
T1 signalling: --
cable type: ABAH
length: 0-133 ft.
56KBS Bit Pos: --
pct fast modem: --
Last Command: cnfcln 7 n 2
Next Command:
cnfln 4.2 7F 0 N
Configure ASI port 4.2 with an idle code 7F and without payload scrambling.
ca19 VT SuperUser BPX 15 8.2 Mar. 23 1996 19:11 GMT
LN 4.2 Configuration T3 [96000 cps] ASI-T3 slot:4
Loop clock: -- Idle code: 7F hex
Line framing: --
coding: --
CRC: --
recv impedance: --
E1 signalling: --
encoding: -- cable type:
T1 signalling: -- length: 0-450 ft.
HCS Masking: Yes
Payload Scramble: No
56KBS Bit Pos: --
pct fast modem: --
Last Command: cnfln 4.2 7F 0 N
Next Command:
cnfln 12
Description
Configure the ALM/A in slot 12.
reach TN SuperUser IGX 16 8.2 July 22 1997 12:39 PDT
LN 12 Config T3/3 [452 cps] ALM slot: 12
Transmit Line Rate: 96000 cps
Receive Line Rate: 452 cps
Header Type: VCC
Payload Scramble Yes
Last Command: cnfln 12 452 vcc y
Next Command:
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
slot or slot.line | Specifies the line. If the back card has one circuit line connector and cable, enter the slot number. If the card has more than one physical line, include a line number. If the card is a UVM, however, enter just the slot number. | |
loop clock | Enables the transmit and receive control leads to use the same clock. Format for the parameter is Y or N | N |
line framing | Configures T1 line framing to be D4 or ESF. Note that UFM-C series is ESF only. | D4 (ESF |
line coding | Configures T1 and E1 coding: |
|
| T1: ZCS B8ZS AMI | ZCS |
| E1:HDB3 ZCS | HDB3 |
line CRC on | Enables CRC-4 detection for E1 lines. Use either Y or N | N |
E1 recv impedance | Parameter Impedance Description 1 75 ohm unbalanced 2 75 ohm balanced 3 120 ohm balanced 4 0-133 ft ABAM cable 5 133-266 ft ABAM cable 6 266-399 ft ABAM cable 7 399-533 ft ABAM cable | 1 |
signaling | E1: Common channel signalling (CCS) or | CAS |
| T1: ABCD or ABAB (with ESF line framing) or AB (with D4 line framing); | AB |
encoding | A-law | A-law |
cable type/length | Parameter Voice Circuits Frame Relay Circuits 1 0-220 ft. MAT cable CSU Network Interface 2 220-440 ft MAT cable 0-133 ft ABAM cable 3 440-655 ft MAT cable 133-266 ft ABAM cable 4 0-133 ft ABAM cable 266-399 ft ABAM cable 5 133-266 ft ABAM cable 399-533 ft ABAM cable 6 266-399 ft ABAM cable 533-655 ft ABAM cable 7 399-533 ft not used 8 533-655 ft not used | 4 |
56kbs bit stuffing | most significant byte (msb) | msb |
pct fast modem | Expected ADPCM fast connections (range 0-100). High speed modems preclude the use of ADPCM. Consequently, channel load requirements increase over that required for a voice channel. The pct fast modem parameters specify the expected channel utilization (%) by a high speed modem. | 20 |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
line | Identifies the line. The line is the slot number of the ALM/A. |
receive rate | Specifies the receive rate for the line. The range for a T3 line is 150 cells per second (cps) through 96000 cps. For an E3 line, the range is 150 cps-96000 cps. |
header type | The header type is either VCC or VPC. The default is VCC. Refer to the IGX-related documentation for an explanation of the header type on the ALM/A. |
payload scramble | Enables or disables payload scramble. The default is No. |
| Parameter | Description | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
line number | Specifies the ASI line to configure | |||
line options | Specifies the ATM line options: | |||
| Parameter | Description | Options | Default |
| Loop clock | Enable loop clocking | Yes/No | No |
| Idle Code | Hex data placed in unused payload of cells. | 0 - FF | 7F |
| Cable | Length and type of cable used for trunk. | 1 = 0 - 225 | 1 |
| HCS Masking | Masking of cell header checksum to disable error checking. | Yes | No | Yes |
| Payload Scramble | Whether or not to scramble (randomize) the cell payload data. Note: for E3, this must always be set to Yes. | Yes | No | No |
Deactivates ("downs") a line. After dnln executes, the line no longer generates framing, and no statistics are gathered. Before you deactivate a line, use delcon to remove all connections on the line.
Down line
dnln <line number>
upcln, dspclns
Privilege | 1-2 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX, BPX |
Lock | Yes |
dnln 12
Deactivate line 12.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
line number | Specifies the line. If the back card has one line, enter the slot number. If the card has more than one line, include a line number. |
Displays the configuration of a line. Table 6-8 shows all possible parameters in the display. The fields that actually contain data depend on the type of line.
| Screen Item | Description | Options |
|---|---|---|
LN configuration | Line type and the number of channels. | T1 |
Loop clock | Specifies whether the receive clock is | Y |
Line framing | Idnetifies the type of T1 line framing | DS4 |
Line coding | Identifies the line coding used by | E1: HDB3, AMI |
CRC | Specifies the CRC checking on E1 lines | Y |
recv impedance | Nominal impedance for the receive line. | 75 ohms balanced or unbalanced 120 ohms balanced |
E1 signalling | Identifies the signalling type used for E1. | CCS or ABCD with CAS |
encoding | Specifies the voice encoding scheme | µlaw |
T1 signalling | Identifies the signalling type used for T1 | ABCD or ABAB (with ESF line framing) or AB (with D4 line framing); CCS is available in timeslot 24 if applicable PBXs need it. |
56 kbps Bit Pos: | Position in word for bit stuffing on 56 kbs data channels. | MSB or LSB |
Pct fast modem |
|
|
Cable type | Specifies the T1 or E1 cable type (used | MAT |
Cable length | Specifies the T1 or E1 cable length in | 0-220 220-440 440-655 0-133 133-266 |
Cnfg | Applies to the UVM: cnfg shows the mode of an individual UVM port. The slot.line identifies the line. | External, Passing, Blocked, or Inserting See the UVM documentation in the Cisco IGX 8400 Series Reference for a description of these modes. |
Transmit Line Rate | Applies to ATM line cards: the display | The value is always the maximum for the line and is in cells per second (cps): 96000 cps for T3 or 80000 cps for E3. |
Receive Line Rate | Applies to ATM line cards: the display | The value is in cells per second (cps). The range is 150-9600 cps for T3 or 150-80000 cps for E3. |
Header Type | Applies to ATM cards: the display | The header type is VCC or VPC. |
Payload Scramble | Applies to ATM cards: the display | The display shows "Yes" or "No." |
display line configuration
dsplcnf <line number>
cnfln (obsolete: cnfcln)
Privilege | 1-6 |
Jobs | No |
Log | No |
Node | IPX, IGX |
Lock | No |
dsplncnf 7.1
Displays configuration for line 1 of the UVM in slot 7. Note that the "cnfg" field shows that the port is configured as "external," so this UVM is terminating all DS0s on the line.
sw109 VT SuperUser IGX 16 8.2 Mar. 20 1997 18:36 PST
LN 7.1 Config T1/24 UVM slot: 7
Loop clock: No
Line framing: D4 cnfg: External
coding: ZCS slot.line: --
CRC: --
recv impedance: --
E1/J1 signalling: --
encoding: --
T1 signalling: AB
cable type: ABAM
length: 0-133 ft.
56KBS Bit Pos: msb
pct fast modem: 20
Last Command: dsplncnf 7.1
Next Command:
dsplncnf 13
Display the configuration of the line card in slot 13. The card in slot 13 is an ALM/A, so fewer parameters appear.
sw142 TN SuperUser IGX 16 8.2 July 31 1997 12:01 PDT
LN 13 Config T3/1 [150 cps] ALM slot: 13
Transmit Line Rate: 96000 cps
Receive Line Rate: 150 cps
Header Type: VCC
Payload Scramble: No
Last Command: dsplncnf 13
Next Command:
dsplncnf 12.1
Display the line configuration for 12.1. The card is slot 12 is an ASI in a BPX node.
ca20 LAN SuperUser BPX 15 8.2 Mar. 23 1996 10:35 PST
LN 12.1 Configuration T3 [96000 cps] ASI-T3 slot:12
Loop clock: -- Idle code: 7F hex
Line framing: --
coding: --
CRC: --
recv impedance: --
E1 signalling: --
encoding: -- cable type:
T1 signalling: -- length: 0-450 ft.
HCS Masking: Yes
Payload Scramble: No
56KBS Bit Pos: --
pct fast modem: --
Last Command: dsplncnf 12.1
Next Command:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
line number | Identifies the line in the format slot or slot.line. If the back card has one line connector and cable, enter the slot number. If the card has more than one physical line, enter a slot and line number. In the case of a UVM, however, enter just the slot number. |
Displays basic configuration and status information for all the lines on the node. The information includes the line number, the type of line, and the line alarm status. The line type shows whether the line is J1, T3, E3, T1, or E1 and shows the number of configured channels. Line status categories include:
♦ Clear—Line OK | Alarm Information Signal |
♦ Loss of Signal | Remote Out of Frame (for T1) |
♦ Out of Frame (for T1) | Remote Out of Packet Frame |
♦ Major—Local CGA (RED) | Minor—Remote CGA (YEL) |
♦ Minor—Bad clock source | Loss of Multiframe (for E1) |
display lines
dspclns
dncln, dsptrks, upcln
Privilege | 1-6 |
Jobs | No |
Log | No |
Node | IPX, IGX |
Lock | No |
dsplns
Display circuit lines on the node.
sw109 VT SuperUser IGX 16 8.2 Mar. 20 1997 18:40 PST
Line Type Current Line Alarm Status
3 T1/24 Clear - OK
5.1 E1/30 Clear - OK
5.2 E1/30 Clear - OK
5.3 E1/30 Clear - OK
5.7 E1/30 Clear - OK
5.8 E1/30 Clear - OK
7.1 T1/24 Clear - OK
11 E1/30 Clear - OK
Last Command: dsplns
Next Command:
Prints the current line configuration and line alarm status for a node. This command uses the same syntax, and prints the same information as is displayed using the dsplns command. See the dspclns command for syntax and output information.
print line configuration
prtlns
dspclns
Privilege | 1-6 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | No |
Node | IPX, IGX, BPX |
Lock | Yes |
prtlns
This command uses the same syntax and prints the same information as is displayed using the dsplns command. See the dsplns command for syntax and output information.
Activates (ups) a line. The upln command makes the line available for configuring and causes statistics gathering to begin. You must execute upln at both ends of the line. Executing upln at only one end of the line eventually causes an alarm. Once both ends of the line are active, you can add connections with the addcon command or optionally configure the line's signal characteristics for the data you intend for the line. See cnfln for information on defining the line characteristics.
A line consists of a cable for transmitting data and the interface circuitry for the line. The cable can be a coaxial wire, fiber optic, or a twisted pair. See Table 6-2 for information on card combinations.
Up line
upln <line number>
cnfcln, dsplns, dspln, dncln
Privilege | 1-2 |
Jobs | Yes |
Log | Yes |
Node | IPX, IGX, BPX |
Lock | Yes |
upln 4.2
Activate line 4.2. After this command executes, the system displays the status of the line using the same information as dsplns displays.
ca19 VT SuperUser BPX 15 8.2 Mar. 23 1996 19:08 GMT
Line Type Current Line Alarm Status
4.1 T3 Clear - OK
4.2 T3 Clear - OK
Last Command: upln 4.2
Next Command:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
line number | Identifies the line number in the form slot for a single-line card or slot.port for a card with more than one line. |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Wed Sep 11 01:55:54 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.