|
|

This chapter contains an overall description of the BPX node. For installation information, refer to the BPX Installation Manual. For additional information on BPX operation and configuration, refer to the Release 8.2 System Manual and the Command Reference Manual.
The BPX is a standards based high-capacity (9.6 Gigabit) broadband ATM switch that provides backbone ATM switching and delivers a wide range of user services (Figure 1-1). Fully integrated with the IPX and IGX, the BPX is a scalable, standards-compliant unit. Using a multi-shelf architecture, the BPX supports both narrowband and broadband user services. The modular, multi-shelf architecture enables users to incrementally expand the capacity of the system as needed.

The BPX consists of a single-shelf node with fifteen card slots. Three of these slots are reserved for common equipment cards. The other twelve are general purpose slots used for network interface cards or service interface cards. The cards are provided in sets, consisting of a front card and associated back card. The BPX can be mounted in a STRATM rack enclosure, which provides mounting for co-located AXIS Interface Shelves.
The AXIS interface shelf supports a wide range of economical narrowband interfaces. It converts all non-ATM traffic into 53-byte ATM cells and concentrates this traffic for high speed switching by the BPX. The AXIS provides a broad range of narrowband user interfaces. Release 3 of the AXIS provides T1/E1 and subrate frame relay, FUNI (Frame Based UNI over ATM), T1/E1 ATM, T1/E1 Circuit Emulation Service (CES), and frame relay to ATM network and service interworking for traffic over the ATM network via the BPX.
The IPX may be configured as a shelf and used as a low-cost Frame Relay to ATM interworking concentrator for the BPX. The IPX may also be configured as a co-located shelf and used as an economical ATM service input to the BPX.
Release 8.2 includes the following new features:
The following is a list of previously provided features that are included in Release 8.2 along with the new features previously listed:
For further information on Frame Relay to ATM Interworking and Tiered Networks, refer to Chapter 6 and Chapter 7.
The BPX employs a 9.6 Gbps crosspoint switch matrix for cell-based switching. The switch matrix provides total, non-blocking bandwidth for point-to-point cell switching of up to 20 million point-to-point connections per second between slots for cell-switching. It is designed to easily meet current requirements with scalability to higher capacity for future growth.
The crosspoint switch matrix provides fourteen (including 2 BCC slots), 800 Mbps switch ports, each of which are capable of supporting up to OC-12 transmission rates. A software-controlled polling arbiter supervises polling order and priority. Data flow to and from the switch matrix is supervised by a redundant common controller. Access to and from the crosspoint switch matrix is through multiport network and user access cards.
A BPX node is a self-contained chassis which may be rack-mounted in a standard 19-inch rack or open enclosure. All control functions, switching matrix, backplane connections, and power supplies are redundant, and non-disruptive diagnostics continuously monitor system operation to detect any system or transmission failure. Hot-standby hardware and alternate routing capability combine to provide maximum system availability.
Interworking allows users to retain their existing services, and as their needs expand, migrate to the higher bandwidth capabilities provided by BPX ATM networks. Frame Relay to ATM Interworking enables frame relay traffic to be connected across high-speed ATM trunks using ATM standard Network and Service Interworking
Two types of Frame Relay to ATM interworking are supported, Network Interworking (Figure 1-2) and Service Interworking (Figure 1-3). The Network Interworking function is performed by the AIT card on the IPX and by the BTM card on the IGX. The FRSM card on the AXIS supports both Network Interworking and Service Interworking.
The frame relay to ATM network and service interworking functions are available as follows:
Network Interworking is supported by the FRP on the IPX, the FRM on the IGX, and the. FRSM on the AXIS. The Frame Relay Service Specific Convergence Sublayer (FR-SSCS) of AAL5 is used to provide protocol conversion and mapping.
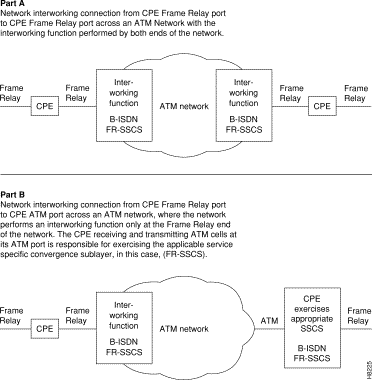
Service Interworking is supported by the FRSM on the AXIS. Translation between the Frame Relay and ATM protocols is performed in accordance with RFC 1490 and RFC 1483.

For additional information about Interworking, refer to Chapter 6.
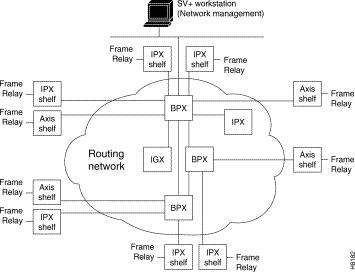
StrataCom networks may be configured as flat (all nodes perform routing and communicate fully with one another), tiered (AXIS, IPX and IGX Interface Shelves are connected to BPX routing hubs where the IPX/IGX Interface Shelves are configured as non-routing hubs), or structured (where a network is divided into a number of domains).
Tiered networks are established by adding interface shelves (non-routing nodes) to an IPX/BPX network (Figure 1-4). AXIS interface shelves and IPX/IGX interface shelves are supported by the BPX routing hubs. Connecting interface shelves to BPX routing hubs, allows the network to support additional T1/E1 frame relay traffic (IPX/IGX Shelves) and T1/E1 frame relay and ATM traffic (AXIS Shelves) without adding additional nodes.
The AXIS Interface Shelf supports T1/E1 frame relay, T1/E1 ATM ports, FUNI, and T1/E1 CES, and is designed to support additional interfaces in the future. The IPX interface shelf supports frame relay ports, as does the IGX (option is available to configure as a shelf).
An IPX/IGX/BPX network can contain 100 nodes and up in a flat network, or 63 nodes per domain in a structured network.
The following are necessary requirements in order to implement tiered networks:
For additional information about Tiered Networks, refer to Chapter 7.
Where greater bandwidths are not needed, the Inverse Multiplexing ATM (IMA) feature provides a low cost trunk between two BPXs. The IMA feature allows BPX nodes to be connected to one another over from 1 to 8 T1 or E1 trunks provided by an AIMNM module on an AXIS Shelf. A BNI port on each BPX is directly connected to an AIMNM module in an AXIS shelf by a T3 or E3 trunk. The AIMNM modules are then linked together by from 1 to 8 T1 or E1 trunks. Refer to the AXIS Reference and the Command Reference manuals for further information.
A virtual trunk may be defined as a "trunk over a public ATM service". The trunk really doesn't exist as a physical line in the network. Rather, an additional level of reference, called a virtual trunk number, is used to differentiate the virtual trunks found within a physical trunk port. Figure 1-5 shows four StrataCom Sub-Networks, each connected to a Public ATM Network via a physical line. The Public ATM Network is shown linking all four of these subnetworks to every other one with a full meshed network of virtual trunks. In this example, each physical line is configured with three virtual trunks.
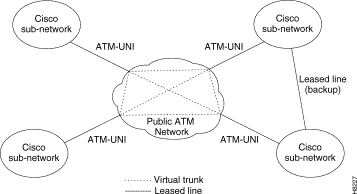
For further information on Virtual Trunking, refer to the Systems Manual and to the Command Reference Manual. For sample configuration information, refer to Chapter 3, "Configuration and Management."
The BPX provides ATM standard traffic and congestion management.
The Traffic Control functions include:
The following standard Congestion Control functions are also supported:
In addition to these standard functions, the BPX provides advanced traffic and congestion management features including:
Network interfaces connect the BPX node to other BPX, IGX, or IPX nodes to form a wide-area network.
The BPX provides T3, E3, and OC3/STM-1 trunk interfaces. The T3 physical interface utilizes DS3 C-bit parity and the 53-byte ATM physical layer cell relay transmission using the Physical Layer Convergence Protocol. The E3 physical interface uses G.804 for cell delineation and HDB3 line coding. The BNI-155 card supports single-mode fiber (SMF), single-mode fiber long reach (SMF-LR), and multi-mode fiber (MMF) physical interfaces.
The design of the BPX permits it to support network interfaces up to 155 Mbps in the current release while providing the architecture to support much higher broadband network interfaces as the need arises.
Optional redundancy is on a one-to-one basis. The physical interface can operate either in a normal or looped clock mode. And as an option, the node synchronization can be obtained from the DS3 extracted clock for any selected network trunk. The BPX node will initially support 32 DS3 or E3 network interfaces.
The StrataCom ATM Interface Shelf (AXIS) interfaces to the Broadband Network Interface (BNI) card, via a T3 or E3 ATM STI interface, respectively. The AXIS provides a concentrator for T1 or E1 frame relay and ATM connections to the BPX with the ability to apply ForeSight across a connection from end-to-end. The AXIS also supports FUNI (Frame Based UNI over ATM) connections.
BPX nodes provide one high-speed and two low-speed data interfaces for data collection and network management. The high-speed interface is an Ethernet 802.3 LAN interface port for communicating with a StrataView Plus NMS workstation. TCP/IP provides the transport and network layer, Logical Link Control 1 is the protocol across the Ethernet port.
The low-speed interfaces are two RS-232 ports, one for a network printer and the second for either a modem connection or a connection to an external control terminal. These low-speed interfaces are the same as provided by the IPX nodes.
A StrataView Plus NMS workstation connects to the Ethernet (LAN) port on the BPX and provides network management via SNMP. Statistics are collected by SV+ using the TFTP protocol. On IPX shelves, frame relay connections are managed via the SV+ Connection Manager. On AXIS shelves, the SV+ Connection Manager manages frame relay and ATM connections, and the Connection Manager is used for AXIS shelf configuration
Each BPX can be configured to use optional low-speed modems for inward access by StrataCom International Support Center for network troubleshooting assistance or to autodial ISC or a customer representative to report alarms remotely. If desired, another option is remote monitoring or control of customer premise equipment through a window on the StrataView Plus workstation.
A BPX network provides network-wide, intelligent clock synchronization. It uses a fault-tolerant network synchronization architecture recommended for Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN). The BPX node internal clock operates as a Stratum 3 clock per ANSI T1.101.
Since the BPX is designed to be part of a larger communications network, it is capable of synchronizing to higher-level network clocks as well as providing synchronization to lower-level devices. Any network access input can be configured to synchronize the node. Any external T1 or E1 input can also be configured to synchronize network timing. A clock output allows synchronizing an adjacent IPX or other network device to the BPX node and the network. In nodes equipped with optional redundancy, the standby hardware is locked to the active hardware to minimize system disruption during system switchovers.
The BPX does not accept clock from an IPX. The BPX can be configure to select clock from the following sources:
System availability is a primary requirement with the BPX. The designed availability factor of a BPX node is (99.99%) based on a node equipped with optional redundancy and a network designed with alternate routing available. The system software, as well as firmware for each individual system module, incorporates various diagnostic and self-test routines to monitor the node for proper operation and availability of backup hardware.
For protection against hardware failure, a BPX node can be equipped with the following redundancy options:
If redundancy is provided for a BPX node, when a hardware failure occurs, a hot-standby module is automatically switched into service, replacing the failed module. All cards are hot-pluggable, so replacing a failed card in a redundant system can be performed without disrupting service.
Since the power supplies share the power load, redundant supplies are not idle. All power supplies are active; if one fails, then the others pick up its load. The power supply subsystem is sized so that if any one supply fails, the node will continue to be supplied with adequate power to maintain normal operation of the node. The node monitors each power supply voltage output and measures cabinet temperature to be displayed on the NMS terminal or other system terminal.
Each BPX node within the network runs continuous background diagnostics to verify the proper operation of all active and standby cards, backplane control, data, and clock lines, cabinet temperature, and power supplies. These background tests are transparent to normal network operation.
Each card in the node has front-panel LEDs to indicate active, failed, or standby status. Each power supply has green LEDs to indicate proper voltage input and output. An Alarm, Status, and Monitor card collects all the node hardware status conditions and reports it using front panel LED indicators and alarm closures. Indicators are provided for major alarm, minor alarm, ACO, power supply status, and alarm history. Alarm relay contact closures for major and minor alarms are available from each node through a 15-pin D-type connector for forwarding to a site alarm system.
BPX nodes are completely compatible with the network status and alarm display provided by the optional StrataView Plus NMS workstation. In addition to providing network management capabilities, it displays major and minor alarm status on its topology screen for all nodes in a network. The StrataView Plus also provides a maintenance log capability with configurable filtering of the maintenance log output by node name, start time, end time, alarm type, and user specified search string.
The BPX system manager can configure alarm thresholds for all statistical type error conditions. Thresholds are configurable for conditions such as frame errors, out of frame, bipolar errors, dropped cells, and cell header errors. When an alarm threshold is exceeded, the NMS screen displays an alarm message.
Graphical displays of collected statistics information, a feature of the StrataView Plus NMS, are a useful tool for monitoring network usage. Statistics collected on network operation fall into two general categories:
These statistics are collected in real-time throughout the network and forwarded to the StrataView Plus workstation for logging and display. The link from the node to StrataView Plus uses a protocol to acknowledge receipt of each statistics data packet. Refer to the StrataView Plus Operations Manual, for more details on statistics and statistical alarms.
Connections in StrataCom cell relay networks are automatically added if there is sufficient bandwidth across the network and are automatically routed when they are added. The user only needs to enter the endpoints of the connection at one end of the connection and the IPX and BPX software automatically set up a route based on a sophisticated routing algorithm. This feature is called AutoRoute and is a standard feature on all StrataCom nodes.
System software automatically sets up the most direct route after considering the network topology and status, the amount of spare bandwidth on each trunk, as well as any routing restrictions entered by the user (e.g. avoid satellite links). This eliminates having to manually enter a routing table at each node in the network. AutoRoute simplifies adding connections, speeds rerouting around network failures, and provides higher connection reliability.
Rather than limiting the user to the four broad classes of service initially defined by the ATM standards committees, OptiClass can provide up to thirty-two classes of service (service subclasses) that can be further defined by the user and assigned to connections. Some of the parameters that may be assigned include:
StrataCom's Frame Relay ForeSight feature is a dynamic closed-loop, rate-based, congestion management feature that yields bandwidth savings compared to non-ForeSight equipped trunks when transmitting bursty data across cell-based networks. This unique, patented, StrataCom feature has been approved as a standard by the ATM Forum as the basis for its closed-loop, rate-based mechanism.
ForeSight permits users to burst above their committed information rate for extended periods of time when there is unused network bandwidth available. This enables users to maximize the use of network bandwidth while offering superior congestion avoidance by actively monitoring the state of shared trunks carrying frame relay traffic within the network.
Fairshare provides per-VC queueing and per-VC scheduling. Fairshare provides fairness between connections and firewalls between connections. Firewalls prevent a single non-compliant connection from affecting the QoS of compliant connections. The non-compliant connection simply overflows its own buffer.
When a BPX receives cells from a port to transmit to a network, the cells are not automatically transmitted at the port access rate to the network trunks. Each VC is assigned its own ingress queue that buffers the connection at the entry to the network. With ForeSight, the service rate can be adjusted up and down depending on network congestion.
When a BPX receives cells from the ATM network for transmission to a port, egress queues provide buffering at the exit point between the BPX network and the ATM Service Interface (ASI) module.
Network queues buffer the data at the trunk interfaces throughout the network according the connections class of service. Service classes are defined by standards-based QoS Classes can consist of the four broad service classes defined in the ATM standards as well as multiple sub-classes to each of the four general classes. Classes can range from constant bit rate services with minimal cell delay variation to variable bit rates with less stringent cell delay.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Thu Jan 18 14:26:37 PST 2001
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2001 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.