|
|

This internal service makes it possible to consult, at any time, outstanding events affecting the equipment. The outstanding events are classified per family and identified by their ACO Nos.
The syntax of the access code is:
Chapter 1 provides a detailed breakdown of this code.
| Code | Distribution |
01 02 15 16 | Binary ASCII Clear language—distribution of line status (family 04) Clear language—distribution of clears and resets |
· PASSWORD | exists if configured (EE by default) |
· ACO No |
|
The breakdown of the ACO suffix is:
FA: | outstanding event family number whose reports can be observed (see Table 3-2). |
The family number is entered in decimal and displayed in hexadecimal.
· Line No | Number of line concerned. |
The ACO No. may have the following formats:
1. ACO No. absent:
2. Only the FA No. is specified:
3. The FA No. and line No. are specified:
4. FA No. = 99 and line No. is specified:
The outstanding events of the families not depending on any line (family 00, 01, etc.) are not distributed.
In the following cases, the access is refused:
The line number is optional; it makes it possible to limit the generation of outstanding events to the specified line.
| FA (decimal) | FA (hexadecimal) | Family |
00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11
12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 24 25 27 | 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0A 0B
0C 0D 0E 0F 10 11 12 13 14 15
16 17 18 19 1B | Trouble reporting Management Signalling X.25 procedure Link Line, physical level Asynchronous line, protocol level Asynchronous line, command level Asynchronous line, semantic level SDLC procedure VIP procedure Transport procedure - VIP, FRAD, BSC, FRT, FRIP DLC/BSC procedure Multi-link procedures (MLP) X.25 - PSTN procedure ESV securized virtual circuits N4 securized virtual circuits IR securized virtual circuits ISDN, channel D X.29 rerouting Ethernet Bridge and IP router Procedure DLC/MTR - FRAD - RAD, FRT, FRIP Compression procedure Dynamic routing procedure (DLM) Configuration function LM function SNA on frame relay (FRSNA) |
This family contains the trouble reports created following the system reset.
These events concern trouble encountered in remote software implementation by a management center.
These events concern trouble encountered in the processing of call requests from a private network.
These events concern all trouble in connection with the procedures, on the level 2 and 3 (X.25 or, inter-module links or inter-unit links).
These events report when the links go in service and out of order (physical lines, inter-module links or inter-unit links).
These events are produced by all transitions detected in the physical line.
These events are produced by any trouble detected in the asynchronous line.
These events are produced by any syntax errors detected in commands.
These events concern the control of asynchronous link activity (communication, X.29 message reception, triggering of supervision times for the telephone link).
These events concern any trouble relative to the SDLC procedure.
These events concern any trouble relative to the VIP procedure.
These events relate to all problems concerning transport for the procedures VIP, FRAD, BSC, DAR, FRT and FRIP on X.25 network.
These events concern any trouble relative to the DLC/BSC procedure.
These events are produced when any trouble is detected in the Multi Link Protocol (MLP).
These events concern any trouble of an X.25 line with PSTN back-up.
These events are produced when any trouble is detected in the securized ESV procedure (ESV: virtual session entity).
These events are produced when any trouble is detected in the securized N4 procedure (N4: level 4).
These events are produced when any trouble is detected in the securized IR procedure (IR: network interface).
These events are produced when any trouble is detected in the ISDN, channel D procedures (ISDN: Integrated Switched Data Network).
These events are produced when any trouble is detected in X.29 rerouting.
These events concern stabes and anomalies relative to the Ethernet Bridge and IP Router functions.
These events relate to all problems concerning the procedures of the DAR, DLC and MRT of the FRAD, DLC and MTR of the IRT and FRIP.
DLC = | Data Link Control |
MFR = | Multi-Frame |
FRAD = | Frame Relay Assembler/Disassembler |
DAR = | Dynamic Adaptative Routing |
These events are produced when the compression function is switched on or switched off and when any failures are detected.
These events are relative to all trouble related to the dynamic routing procedure of the DLM function.
These events relate to the CONFIGURATOR management function.
These events relate to the LMI function.
These events relate to the SNA statuses and problems on FR.
A message transmitted by the outstanding events function is in Figure 3-1.
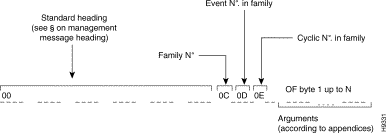
The following types of outstanding events are distributed in clear language:
Outstanding events of family 04
EQUIP No : ------
DATE : --/--/-- TIME --/--/--
HS LINK No : --
Clears or resets received or generated by an equipment item
CLEAR CAUSE --- DIAG --- FUNC No --- LC No ---
RESET CAUSE --- DIAG --- FUNC Nº --- LC Nº ---
Outstanding events are described in the appendices at the back of this section.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Thu Jan 25 13:37:29 PST 2001
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2001 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.