|
|

| Parameter No. | Synchronous X.25 connection or B-channel (ISDN) | Parameter No. | Synchronous X.25 connection or B-channel (ISDN) |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Profile number | 27 | Not significant |
1 | Type of Link | 28 | Speed |
2 | Type of Connection | 29 | Max.No.Buffers/Frame |
3 | Scanning direction | 30 | Not significant |
4 | No. of 1st group of incoming LCs | 31 | Initial transmission credit |
5 | No. of 1st incoming LC | 32 | Time-out T1 |
6 | No. of groups of incoming LCs | 33 | Time-out T0 |
7 | No. of incoming LCs | 34 | Frame repetitions |
8 | No. of 1st group of mixed LCs | 35 | Frame window width |
9 | No. of mixed LCs | 36 | Frame module |
10 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 37 | Primary address |
11 | No. of mixed Lcs | 38 | Secondary address |
12 | No. of 1st group of outgoing LCs | 39 | Restart time-out |
13 | No. of 1st outgoing LC | 40 | Reset time-out |
14 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 41 | Clear time-out |
15 | No. of outgoing LCs | 42 | No. of retransmissions |
16 | Behavior of not-used PVC | 43 | Restart/reset/clear elimination |
17 | Billing type | 44 | X.25 type of signalling |
18 | Receive filtering | 45 | 1 or 2 addr. in packet |
19 | Send filtering | 46 | Local calling subscriber No. |
20 | Interface state/interface superv. | 47 | Subaddress transparency |
21 | Interface state/interface superv. | 48 | CUG facility |
22 | Interface scanning period | 49 | RC acceptance (Tx) |
23 | No. of interface scanning TOs | 50 | Reserved |
24 | Interface state/interface superv. | 51 | Transit time |
25 | Interface state/interface superv. | 52 | PDN link |
26 | Int.signals forced | 53 | PDN address No. |
54 | Tx fast sel.subscr. | 81 | Call return authorized |
55 | Rx. fast sel.subscr. | 82 | Reserved |
56 | Throughput class negotiation | 83 | Facility marker CTRL |
57 | Default TX throughput class | 84 | React.on called add.mod.notific. |
58 | Default RX throughput class | 85 | Clear TX format |
59 | Max. TX throughput class | 86 | Bit D management |
60 | Max. RX throughput class | 87 | Type of line |
61 | Packet size negot.subscription | 88 | Facility unknown |
62 | Default TX packet size | 89 | Address conversion |
63 | Default RX packet size | 90 | No. of PVCs |
64 | Max. TX packet size | 91 | Position of first PVC |
65 | Max. RX packet size | 92 | Reserved |
66 | Min. TX packet size | 93 | Type of LAP |
67 | Min. RX packet size | 94 | Securized VCs |
68 | Tx window size negot.subscription | 95 to 123 | Reserved |
69 | Default TX window size | 124 | Consultation |
70 | Default RX window size | 125 | Low threshold |
71 | Max. TX window size | 126 | High threshold |
72 | Max. RX window size | 127 | Reserved |
73 | Transfer request | 128 | Cost and use of support |
74 | Call confirm.format | 129 | Remote equipt class 22 position |
75 | X.29 rerouting | 130 | Behavior |
76 | Reserved | 131 to 145 | Reserved |
77 | Reserved |
|
|
78 | Compression/scrambling |
|
|
79 | Reserved |
|
|
80 | Call request timing |
|
|
| Parameter No. | Asynchronous X.25 connection | Parameter No. | Asynchronous X.25 connection |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Profile number | 38 | Automatic call number |
1 | Type of Link | 39 | NUI management |
2 | Type of Connection | 40 | Type of terminal |
3 | Scanning direction | 41 | X.25 parity |
4 | No. of 1st group of incoming LCs | 42 | No. of significant bits exchanged |
5 | No. of 1st incoming LC | 43 | Auto data rate recogn. |
6 | No. of groups of incoming LCs | 44 | X.25 type signalling |
7 | No. of incoming LCs | 45 | 1 or 2 addr. in packet |
8 | No. of 1st group of mixed LCs | 46 | Local calling subscriber No. |
9 | No. of mixed LCs | 47 | Subaddress transparency |
10 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 48 | CUG facility |
11 | No. of mixed LCs | 49 | RC acceptance (Tx) |
12 | No. of 1st group of outgoing LCs | 50 | Reserved |
13 | No. of 1st outgoing LC | 51 | Transit time |
14 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 52 | PDN link |
15 | No. of outgoing LCs | 53 | PDN address No. |
16 | Reserved | 54 | Tx fast sel.subscr. |
17 | Billing type | 55 | Rx. fast sel.subscr. |
18 | Receive filtering | 56 | Throughput class negotiation |
19 | Send filtering | 57 | Default TX throughput class |
20 | Interface state/interface superv. | 58 | Default RX throughput class |
21 | Interface state/interface superv. | 59 | Max. TX throughput class |
22 | Interface scanning period | 60 | Max. RX throughput class |
23 | Filtering/conf. of signal transition | 61 | Packet size negot.subscription |
24 | Interface state/interface superv. | 62 | Default TX packet size |
25 | Interface state/interface superv. | 63 | Default RX packet size |
26 | Int.signals forced | 64 | Max. TX packet size |
27 | Flow control | 65 | Max. RX packet size |
28 | Parity | 66 | Min. TX packet size |
29 | Max.No.Buffers/Frame | 67 | Min. RX packet size |
30 | Not significant | 68 | Tx window size negot.subscription |
31 | Initial transmission credit | 69 | Default TX window size |
32 | Inactivity time-out | 70 | Default RX window size |
33 | No. of bytes received in buffer | 71 | Max. TX window size |
34 | Block of character mode | 72 | Max. RX window size |
35 | No. of stop bits | 73 | Transfer request |
36 | Type of physical connection | 74 | Call confirm.format |
37 | Not significant | 75 | X.29 rerouting |
76 | Reserved | 92 | Conn. to HP equipment |
77 | Reserved | 93 | Type of call |
78 | Compression/scrambling | 94 | Securized VCs |
79 | Reserved | 95 to 123 | Reserved |
80 | Call request timing | 124 | Consultation |
81 | Call return authorized | 125 | Low threshold |
82 | Reserved | 126 | High threshold |
83 | Facility marker CTRL | 127 | Reserved |
84 | React.on called add.mod.notific. | 128 | Cost and use of support |
85 | Clear TX format | 129 | Remote equipt class 22 position |
86 | Bit D management | 130 | Behavior |
87 | Msg Txm superv, time-out | 131 to 145 | Reserved |
88 | Mixed flow control |
|
|
89 | Address conversion |
|
|
90 | Error threshold (ECP) |
|
|
91 | Txm time-out NACK (ECP) |
|
|
| Parameter No. | SDLC connection | Parameter No. | SDLC connection |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Profile number | 38 | Processing unknown packets |
1 | Type of Link | 39 | Not significant |
2 | Type of Connection | 40 | QLLC segment length (PSH) |
3 | Scanning direction | 41 | Protocol type |
4 | No. of 1st group of incoming LCs | 42 | No. of transmissions |
5 | No. of 1st incoming LC | 43 | Restart/reset/clear elimination |
6 | No. of groups of incoming LCs | 44 | X.25 type signalling |
7 | No. of incoming LCs | 45 | 1 or 2 addr. in packet |
8 | No. of 1st group of mixed LCs | 46 | Local calling subscriber No. |
9 | No. of mixed LCs | 47 | Subaddress transparency |
10 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 48 | CUG facility |
11 | No. of mixed LCs | 49 | RC acceptance (Tx) |
12 | No. of 1st group of outgoing LCs | 50 | Reserved |
13 | No. of 1st outgoing LC | 51 | Transit time |
14 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 52 | PDN link |
15 | No. of outgoing LCs | 53 | PDN address No. |
16 | Coding (NRZ/NRZ1) | 54 | Tx fast sel.subscr. |
17 | Billing type | 55 | Rx. fast sel.subscr. |
18 | Receive filtering | 56 | Throughput class negotiation |
19 | Send filtering | 57 | Default TX throughput class |
20 | Interface state/interface superv. | 58 | Default RX throughput class |
21 | Interface state/interface superv. | 59 | Max. TX throughput class |
22 | Interface scanning period | 60 | Max. RX throughput class |
23 | Filtering/conf. of signal transition | 61 | Packet size negot.subscription |
24 | Interface state/interface superv. | 62 | TX packet size |
25 | Interface state/interface superv. | 63 | RX packet size |
26 | Int.signals forced | 64 | Max. TX packet size |
27 | Not significant | 65 | Max. RX packet size |
28 | Speed | 66 | Min. TX packet size |
29 | Max.No.Buffers/Frame | 67 | Min. RX packet size |
30 | Not significant | 68 | Tx window size negot.subscription |
31 | Initial transmission credit | 69 | Default TX window size |
32 | Frame repeats time-out T1 | 70 | Default RX window size |
33 | Interpolling wait time-out | 71 | Max. TX window size |
34 | No. of Frame repetitions | 72 | Max. RX window size |
35 | Frame window width | 73 | Transfer request |
36 | Frame modulo | 74 | Call confirm.format |
37 | Polling counter | 75 | Reserved |
76 | Reserved | 92 | Not significant |
77 | Reserved | 93 | Not significant |
78 | Compression/scrambling | 94 | Securized VCs |
79 | Reserved | 95 to 123 | Reserved |
80 | Call request timing | 124 | Consultation |
81 | Call return authorized | 125 | Low threshold |
82 | Reserved | 126 | High threshold |
83 | Facility marker CTRL | 127 | Reserved |
84 | React.on called add.mod.notific. | 128 | Cost and use of support |
85 | Clear TX format | 129 | Remote equipt class 22 position |
86 | Bit D management | 130 | Behavior |
87 | Type of line | 131 to 145 | Reserved |
88 | Facility unknown |
|
|
89 | Address conversion |
|
|
90 | No. of clusters |
|
|
91 | Position of first cluster |
|
|
| Parameter No. | VIP connection | Parameter No. | VIP connection |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Profile number | 38 | Reserved |
1 | Type of Link | 39 | Screen msg restransm time-out |
2 | Type of Connection | 40 | Printer msg. time-out |
3 | Scanning direction | 41 | Screen message blocking |
4 | No. of 1st group of incoming LCs | 42 | No. of retransmissions |
5 | No. of 1st incoming LC | 43 | Print management |
6 | No. of groups of incoming LCs | 44 | X.25 type signalling |
7 | No. of incoming LCs | 45 | 1 or 2 addr. in packet |
8 | No. of 1st group of mixed LCs | 46 | Local calling subscriber No. |
9 | No. of mixed LCs | 47 | Subaddress transparency |
10 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 48 | CUG facility |
11 | No. of mixed LCs | 49 | RC acceptance (Tx) |
12 | No. of 1st group of outoging LCs | 50 | Reserved |
13 | No. of 1st outgoing LC | 51 | Transit time |
14 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 52 | PDN link |
15 | No. of outgoing LCs | 53 | PDN address No. |
16 | Reserved | 54 | Tx fast sel.subscr. |
17 | Billing type | 55 | Rx. fast sel.subscr. |
18 | Receive filtering | 56 | Throughput class negotiation |
19 | Send filtering | 57 | Default TX throughput class |
20 | Interface state/interface superv. | 58 | Default RX throughput class |
21 | Interface state/interface superv. | 59 | Max. TX throughput class |
22 | Interface scanning period | 60 | Max. RX throughput class |
23 | Filtering/conf. of signal transition | 61 | Packet size negot.subscription |
24 | Interface state/interface superv. | 62 | Message length (Tx) |
25 | Interface state/interface superv. | 63 | Message length (Rx) |
26 | Int.signals forced | 64 | Max. TX packet size |
27 | Not significant | 65 | Max. RX packet size |
28 | Speed | 66 | Min. TX packet size |
29 | Max.No.Buffers/Frame | 67 | Min. RX packet size |
30 | Not significant | 68 | Tx window size negot.subscription |
31 | Initial transmission credit | 69 | Default TX window size |
32 | Transit polling time-out | 70 | Default RX window size |
33 | Interpolling wait time-out | 71 | Max. TX window size |
34 | Max. no. of unanswered calls | 72 | Max. RX window size |
35 | Frame window width | 73 | Transfer request |
36 | Reserved | 74 | Call confirm.format |
37 | EOT response | 75 | Reserved |
76 | Reserved | 92 | Not significant |
77 | Reserved | 93 | Not significant |
78 | Compression/scrambling | 94 | Securized VCs |
79 | Reserved | 95 to 123 | Reserved |
80 | Call request timing | 124 | Consultation |
81 | Call return authorized | 125 | Low threshold |
82 | Reserved | 126 | High threshold |
83 | Facility marker CTRL | 127 | Reserved |
84 | React.on called add.mod.notific. | 128 | Cost and use of support |
85 | Clear TX format | 129 | Remote equipt class 22 position |
86 | Bit D management | 130 | Behavior |
87 | Type of line | 131 to 145 | Reserved |
88 | Facility unknown |
|
|
89 | Address conversion |
|
|
90 | No. of controllers |
|
|
91 | Position of first controller |
|
|
| Parameter No. | BSC 3270 connection | Parameter No. | BSC 3270 connection |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Profile number | 38 |
|
1 | Type of Link | 39 |
|
2 | Type of Connection | 40 |
|
3 | Scanning direction | 41 | "No response" time-out |
4 | No. of 1st group of incoming LCs | 42 | No. of transmissions |
5 | No. of 1st incoming LC | 43 | Type of TPAD connection |
6 | No. of groups of incoming LCs | 44 | X.25 type signalling |
7 | No. of incoming LCs | 45 | 1 or 2 addr. in packet |
8 | No. of 1st group of mixed LCs | 46 | Local calling subscriber No. |
9 | No. of mixed LCs | 47 | Subaddress transparency |
10 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 48 | CUG facility |
11 | No. of mixed LCs | 49 | RC acceptance (Tx) |
12 | No. of 1st group of outoging LCs | 50 | Reserved (RC Rx acceptance) |
13 | No. of 1st outgoing LC | 51 | Transit time |
14 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 52 | PDN link |
15 | No. of outgoing LCs | 53 | PDN address No. |
16 | To time-out | 54 | Tx fast sel.subscr. |
17 | Billing type | 55 | Rx. fast sel.subscr. |
18 | Receive filtering | 56 | Throughput class negotiation |
19 | Send filtering | 57 | Default TX throughput class |
20 | Interface state/interface superv. | 58 | Default RX throughput class |
21 | Interface state/interface superv | 59 | Max. TX throughput class |
22 | Interface scanning period | 60 | Max. RX throughput class |
23 | Filtering/conf. of signal transition | 61 | packet size negot.subscription |
24 | Interface state/interface superv. | 62 | Length of message (Tx) |
25 | Interface state/interface superv. | 63 | Length of message (Rx) |
26 | Int.signals forced | 64 | Max. TX packet size |
27 | Not significant | 65 | Max. RX packet size |
28 | Speed | 66 | Min. TX packet size |
29 | Max.No.Buffers/Frame | 67 | Min. RX packet size |
30 | Not significant | 68 | Tx window size negot.subscription |
31 | Initial transmission credit | 69 | Default TX window size |
32 | Val. line superv. time-out | 70 | Default RX window size |
33 | Val. interpoll. time-out | 71 | Max. TX window size |
34 | No. of unanswered polls | 72 | Max. RX window size |
35 | Frame window queue (Rx) | 73 | Transfer request |
36 | Type of coding | 74 | Call confirm.format |
37 | Type of parity | 75 | Reserved |
76 | Reserved | 92 | Not significant |
77 | Reserved | 93 | Type of LAP |
78 | Compression/scrambling | 94 | Securized VCs |
79 | Reserved | 95 to 123 | Reserved |
80 | Call request timing | 124 | Consultation |
81 | Call return authorized | 125 | Low threshold |
82 | Reserved | 126 | High threshold |
83 | Facility marker CTRL | 127 | Reserved |
84 | React.on called add.mod.notific. | 128 | Cost and use of support |
85 | Clear TX format | 129 | Remote equipt class 22 position |
86 | Bit D management | 130 | Behavior |
87 | Type of line | 131 to 145 | Reserved |
88 | Facility unknown |
|
|
89 | Address conversion |
|
|
90 | No. of controllers |
|
|
91 | Position of first controller |
|
|
| Parameter No. | BSC 2780/3780 connection | Parameter No. | BSC 2780/3780 connection |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Profile number | 38 | Type of paired equipment |
1 | Type of Link | 39 | Time-out to restransmit an ENQ |
2 | Type of Connection | 40 | "Author. response" time-out |
3 | Scanning direction | 41 | "No response" time-out |
4 | No. of 1st group of incoming LCs | 42 | No. of retransmissions |
5 | No. of 1st incoming LC | 43 | Type of protocol |
6 | No. of groups of incoming LCs | 44 | X.25 type signalling |
7 | No. of incoming LCs | 45 | 1 or 2 addr. in packet |
8 | No. of 1st group of mixed LCs | 46 | Local calling subscriber No. |
9 | No. of mixed LCs | 47 | Subaddress transparency |
10 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 48 | CUG facility |
11 | No. of mixed LCs | 49 | RC acceptance (Tx) |
12 | No. of 1st group of outoging LCs | 50 | Reserved |
13 | No. of 1st outgoing LC | 51 | Transit time |
14 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 52 | PDN link |
15 | No. of outgoing LCs | 53 | PDN address No. |
16 | To time-out | 54 | TX fast sel.subscr. |
17 | Billing type | 55 | RX fast sel.subscr. |
18 | Receive filtering | 56 | Throughput class negotiation |
19 | Send filtering | 57 | Default TX throughput class |
20 | Interface state/interface superv. | 58 | Default RX throughput class |
21 | Interface state/interface superv. | 59 | Max. TX throughput class |
22 | Interface scanning period | 60 | Max. RX throughput class |
23 | No. of interface scanning TOs | 61 | Packet size negot.subscription |
24 | Interface state/interface superv | 62 | Length of message (Tx) |
25 | Interface state/interface superv | 63 | Length of message (Rx) |
26 | Int.signals forced | 64 | Max. TX packet size |
27 | Line clock | 65 | Max. RX packet size |
28 | Speed | 66 | Min. TX packet size |
29 | Max.No.Buffers/Frame | 67 | Min. RX packet size |
30 | Not significant | 68 | Tx window size negot.subscription |
31 | Initial transmission credit | 69 | Default TX window size |
32 | Value of diconn. time-out | 70 | Default RX window size |
33 | Supervision mode time-out | 71 | Max. TX window size |
34 |
| 72 | Max. RX window size |
35 | Frame width queue | 73 | Transfer request |
36 | Type of coding | 74 | Call confirm.format |
37 | Type of parity | 75 | Reserved |
76 | Reserved | 92 | Not significant |
77 | Reserved | 93 | Type of LAP |
78 | Compression/scrambling | 94 | Securized VCs |
79 | Reserved | 95 to 123 | Reserved |
80 | Call request timing | 124 | Consultation |
81 | Call return authorized | 125 | Low threshold |
82 | Reserved (address conversion) | 126 | High threshold |
83 | Facility marker CTRL | 127 | Reserved |
84 | React.on called add.mod.notific. | 128 | Cost and use of support |
85 | Clear TX format | 129 | Remote equipt class 22 position |
86 | Bit D management | 130 | Behavior |
87 | Type of line | 131 to 145 | Reserved |
88 | Facility unknown |
|
|
89 | Address conversion |
|
|
90 | No. of controllers |
|
|
91 | Position of first controller |
|
|
| Parameter No. | ESV/N4 connection | Parameter No. | ESV/N4 connection |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Profile number | 38 | Not significant |
1 | Type of Link | 39 | Not significant |
2 | Type of Connection | 40 | Reserved |
3 | Scanning direction | 41 | Reserved |
4 | No. of 1st group of incoming LCs | 42 | Reserved |
5 | No. of 1st incoming LC | 43 | Reserved |
6 | No. of groups of incoming LCs | 44 | X.25 type signalling |
7 | No. of incoming LCs | 45 | 1 or 2 addr. in packet |
8 | No. of 1st group of mixed LCs | 46 | Local calling subscriber No. |
9 | No. of mixed LCs | 47 | Subaddress transparency |
10 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 48 | CUG facility |
11 | No. of mixed Lcs | 49 | RC acceptance (Tx) |
12 | No. of 1st group of outoging LCs | 50 | Reserved |
13 | No. of 1st outgoing LC | 51 | Transit time |
14 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 52 | PDN link |
15 | No. of outgoing LCs | 53 | PDN address No. |
16 | Reserved | 54 | Tx fast slec.subscr. |
17 | Billing type | 55 | Rx. fast sel.subscr. |
18 | Not significant | 56 | Throughput class negotiation |
19 | Not significant | 57 | Default TX throughput class |
20 | Number of retransmissions | 58 | Default RX throughput class |
21 | Not significant | 59 | Max. TX throughput class |
22 | Not significant | 60 | Max. RX throughput class |
23 | Ref. freezing time-out | 61 | packet size negot.subscription |
24 | Not significant | 62 | Length of msg. (Tx) |
25 | Not significant | 63 | Length of msg. (Rx) |
26 | Not significant | 64 | Max. TX packet size |
27 | Not significant | 65 | Max. RX packet size |
28 | Not significant | 66 | Min. TX packet size |
29 | Not significant | 67 | Min. RX packet size |
30 | Not significant | 68 | Tx window size negot.subscription |
31 | Not significant | 69 | Default TX window size |
32 | Not significant | 70 | Default RX window size |
33 | Not significant | 71 | Max. TX window size |
34 | Not significant | 72 | Max. RX window size |
35 | Transport window size | 73 | Transfer request |
36 | Not significant | 74 | Call confirm.format |
37 | Not significant | 75 | Reserved |
76 | Reserved | 92 | Not significant |
77 | Reserved | 93 | Not significant |
78 | Reserved | 94 | Securized VCs |
79 | Reserved | 95 to 123 | Reserved |
80 | Reserved | 124 | Consultation |
81 | Call return authorized | 125 | Low threshold |
82 | Reserved (address conversion) | 126 | High threshold |
83 | Facility marker CTRL | 127 | Reserved |
84 | React.on called add.mod.notific. | 128 | Cost and use of support |
85 | Clear TX format | 129 | Remote equipt class 22 position |
86 | Bit D management | 130 | Behavior |
87 | Type of line | 131 to 145 | Reserved |
88 | Facility unknown |
|
|
89 | Address conversion |
|
|
90 | No. of PVCs |
|
|
91 | Position of first PVC |
|
|
| Parameter No. | IR connection | Parameter No. | IR connection |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Profile number | 38 | Not significant |
1 | Type of Link | 39 | Not significant |
2 | Type of Connection | 40 | Reserved |
3 | Scanning direction | 41 | Reserved |
4 | No. of 1st group of incoming LCs | 42 | Reserved |
5 | No. of 1st incoming LC | 43 | Reserved |
6 | No. of groups of incoming LCs | 44 | X.25 type signalling |
7 | No. of incoming LCs | 45 | 1 or 2 addr. in packet |
8 | No. of 1st group of mixed LCs | 46 | Local calling subscriber No. |
9 | No. of mixed LCs | 47 | Subaddress transparency |
10 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 48 | CUG facility |
11 | No. of mixed Lcs | 49 | RC acceptance (Tx) |
12 | No. of 1st group of outoging LCs | 50 | Reserved |
13 | No. of 1st outgoing LC | 51 | Transit time |
14 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 52 | PDN link |
15 | No. of outgoing LCs | 53 | PDN address No. |
16 | Reserved | 54 | Tx fast slec.subscr. |
17 | Billing type | 55 | Rx. fast sel.subscr. |
18 | Waiting time-out (for 1st packet) | 56 | Throughput class negotiation |
19 | Not significant | 57 | Default TX throughput class |
20 | Number of calls | 58 | Default RX throughput class |
21 | "Slow call" time-out | 59 | Max. TX throughput class |
22 | "Wait for reconn." time-out | 60 | Max. RX throughput class |
23 | Ref. freezing time-out | 61 | Packet size negot.subscription |
24 | Not significant | 62 | Length of msg (Tx) |
25 | Not significant | 63 | Length of msg (Rx) |
26 | Not significant | 64 | Max. TX packet size |
27 | Not significant | 65 | Max. RX packet size |
28 | Not significant | 66 | Min. TX packet size |
29 | Not significant | 67 | Min. RX packet size |
30 | Not significant | 68 | Tx window size negot.subscription |
31 | Not significant | 69 | Default TX window size |
32 | Not significant | 70 | Default RX window size |
33 | Not significant | 71 | Max. TX window size |
34 | Not significant | 72 | Max. RX window size |
35 | Not significant | 73 | Transfer request |
36 | "Fast select" utilization | 74 | Call confirm.format |
37 | Not significant | 75 | Reserved |
76 | Reserved | 92 | Not significant |
77 | Reserved | 93 | Not significant |
78 | Reserved | 94 | Securized VCs |
79 | Reserved | 95 to 123 | Reserved |
80 | Reserved | 124 | Not significant |
81 | Call return authorized | 125 | Not significant |
82 | Reserved (address conversion) | 126 | Not significant |
83 | Facility marker CTRL | 127 | Not significant |
84 | React.on called add.mod.notific. | 128 | Not significant |
85 | Clear TX format | 129 | Not significant |
86 | Bit D management | 130 | Not significant |
87 | Type of line | 131 to 145 | Not significant |
88 | Facility unknown |
|
|
89 | Address conversion |
|
|
90 | No. of PVCs |
|
|
91 | Position of first PCV |
|
|
| Parameter No. | FRTE/FRSW Physical Connection | Parameter No. | FRTE/FRSW Physical Connection |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Profile number | 38 | Not significant |
1 | Type of Link | 39 | Not significant |
2 | Type of Connection | 40 | Reserved |
3 | Not significant | 41 | Reserved |
4 | Not significant | 42 | Reserved |
5 | Not significant | 43 | Reserved |
6 | Not significant | 44 | X.25 type signalling |
7 | Not significant | 45 | 1 or 2 addr. in packet |
8 | Not significant | 46 | Local calling subscriber No. |
9 | Not significant | 47 | Subaddress transparency |
10 | Not significant | 48 | CUG facility |
11 | Not significant | 49 | RC acceptance (Tx) |
12 | Not significant | 50 | Reserved |
13 | Not significant | 51 | Transit time |
14 | Not significant | 52 | PDN link |
15 | Not significant | 53 | PDN address No. |
16 | Time-out Ta | 54 | Not significant |
17 | Billing type | 55 | Reserved |
18 | Receive filtering | 56 | Not significant |
19 | Transmission filtering | 57 | Not significant |
20 | Interface state/interface superv. | 58 | Not significant |
21 | Interface state/interface superv. | 59 | Not significant |
22 | Interface scanning period | 60 | Not significant |
23 | Filtering/conf. of signal transition | 61 | Not significant |
24 | Interface state/interface superv. | 62 | Not significant |
25 | Interface state/interface superv. | 63 | Not significant |
26 | Int.signals forced | 64 | Not significant |
27 | Not significant | 65 | Not significant |
28 | Parity | 66 | Not significant |
29 | Max.No.Buffers/Frame | 67 | Not significant |
30 | Not significant | 68 | Not significant |
31 | Initial transmission credit | 69 | Not significant |
32 | Inactivity time-out | 70 | Not significant |
33 | No. of bytes received in buffer | 71 | Not significant |
34 | Block of character mode | 72 | Not significant |
35 | No. of stop bits | 73 | Not significant |
36 | Type of physical connection | 74 | Not significant |
37 | Not significant | 75 | Reserved |
76 | Reserved | 92 | Type of LMI |
77 | Reserved | 93 | Not significant |
78 | Reserved | 94 | Not significant |
79 | Reserved | 95 to 123 | Reserved |
80 | Not significant | 124 | Not significant |
81 | Not significant | 125 | Not significant |
82 | Not significant | 126 | Not significant |
83 | Not significant | 127 | Not significant |
84 | Not significant | 128 | Not significant |
85 | Not significant | 129 | Not significant |
86 | Not significant | 130 | Not significant |
87 | Not significant | 131 to 145 | Not significant |
88 | Not significant |
|
|
89 | Not significant |
|
|
90 | Not significant |
|
|
91 | Not significant |
|
|
| Parameter No. | Connection Logical line FR Network (FRT, FRIP, FRI) | Parameter No. | Connection Logical line FR Network (FRT, FRIP, FRI |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Profile number | 37 | Primary address |
1 | Type of Link | 38 | Secondary address |
2 | Type of Connection | 39 | Not significant |
3 | Scanning direction | 40 | Not significant |
4 | No. of 1st group of incoming LCs | 41 | Not significant |
5 | No. of 1st incoming LC | 42 | No. of retransmission |
6 | No. of groups of incoming LCs | 43 | Elim. diagn. code |
7 | No. of incoming LCs | 44 | Type signalling |
8 | No. of 1st group of mixed LCs | 45 | Add no. in packets |
9 | No. of mixed LCs | 46 | Local calling subscriber No. |
10 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 47 | Subaddress transparency |
11 | No. of mixed Lcs | 48 | CUG facility |
12 | No. of 1st group of outoging LCs | 49 | RC acceptance (Tx) |
13 | No. of 1st outgoing LC | 50 | Reserved |
14 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 51 | Transit time |
15 | No. of outgoing LCs | 52 | PDN link |
16 | Not significant | 53 | PDN address No. |
17 | Billing type | 54 | Tx fast slec.subscr. |
18 | Receive filtering | 55 | Rx. fast sel.subscr. |
19 | Transmission filtering | 56 | Throughput class negotiation |
20 | Not significant | 57 | Default TX throughput class |
21 | Not significant | 58 | Default RX throughput class |
22 | Not significant | 59 | Max. TX throughput class |
23 | Not significant | 60 | Max. RX throughput class |
24 | Not significant | 61 | Packet size negot.subscription |
25 | Not significant | 62 | Length of message (Tx) |
26 | Not significant | 63 | Length of message (Rx) |
27 | Not significant | 64 | Max. TX packet size |
28 | Not significant | 65 | Max. RX packet size |
29 | Max.No.Buffers/Frame | 66 | Min. TX packet size |
30 | Not significant | 67 | Min. RX packet size |
31 | Initial transmission credit | 68 | Tx window size negot.subscription |
32 | Val. line supervision time-out T1 | 69 | Default TX window size |
33 | Val. interpoll time-out T0 | 70 | Default RX window size |
34 | No. of unanswered polls | 71 | Max. TX window size |
35 | Frame window | 73 | Transfer request |
36 | Frame module type | 74 | Call confirm.format |
75 | X.29 rerouting | 92 | Not significant |
76 to 77 | Reserved | 93 | Type of LAP |
78 | Compression/scrambling | 94 | Securized VCs |
79 | Reserved | 95 to 123 | Reserved |
80 | Call request timing | 124 | Not significant |
81 | Call return authorized | 125 | Not significant |
82 | Reserved (address conversion) | 126 | Not significant |
83 | Facility marker CTRL | 127 | Not significant |
84 | React.on called add.mod.notific. | 128 | Not significant |
85 | Clear TX format | 129 | Not significant |
86 | Bit D management | 130 | Not significant |
87 | Type of line | 131 to 145 | Not significant |
88 | Facility unknown |
|
|
89 | Calling-called conversion |
|
|
90 | No. of PVCs |
|
|
91 | Position of first PVC |
|
|
| Parameter No. | HDLC connection | Parameter No. | HDLC connection |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Profile number | 38 | Not significant |
1 | Type of Link | 39 | Not significant |
2 | Type of MCX Connection | 40 | Not significant |
3 | Scanning direction | 41 | "Frame ignored" threshold T4 |
4 | No. of 1st group of incoming LCs | 42 | Not significant |
5 | No. of 1st incoming LC | 43 | Not significant |
6 | No. of groups of incoming LCs | 44 | Type signalling |
7 | No. of incoming LCs | 45 | Add nbr. in packets |
8 | No. of 1st group of mixed LCs | 46 | Local calling subscriber No. |
9 | No. of mixed LCs | 47 | Subaddress transparency |
10 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 48 | CUG facility |
11 | No. of mixed Lcs | 49 | RC acceptance (Tx) |
12 | No. of 1st group of outoging LCs | 50 | Reserved |
13 | No. of 1st outgoing LC | 51 | Transit time |
14 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 52 | PDN link |
15 | No. of outgoing LCs | 53 | PDN address No. |
16 | Reserved for VC break time-out | 54 | Tx fast slec.subscr. |
17 | Billing type | 55 | Reserved (Subscr.fast Sel.rec) |
18 | Receive filtering | 56 | Throughput class negotiation |
19 | Send filtering | 57 | Default TX throughput class |
20 | Interface state/interface superv. | 58 | Default RX throughput class |
21 | Interface state/interface superv. | 59 | Max. TX throughput class |
22 | Interface scanning period | 60 | Max. RX throughput class |
23 | Filtering/conf. of signal transition | 61 | Packet size negot.subscription |
24 | Interface state/interface superv. | 62 | Packet length (Tx) |
25 | Interface state/interface superv. | 63 | Packet length (Rx) |
26 | Int.signals forced | 64 | Max. TX packet size |
27 | Not significant | 65 | Max. RX packet size |
28 | Speed | 66 | Min. TX packet size |
29 | Max.No.Buffers/Frame | 67 | Min. RX packet size |
30 | Not significant | 68 | Tx window size negot.subscription |
31 | Initial transmission credit | 69 | Default TX window size |
32 | CRC count | 70 | Default RX window size |
33 | No. of flags (Tx) | 71 | Max. TX window size |
34 | Not significant | 72 | Max. RX window size |
35 | Frame window width | 73 | Transfer request |
36 | Start of frame regr.thresh.T1 | 74 | Call confirm.format |
37 | Not significant | 75 | Reserved |
76 | Reserved | 92 | Not significant |
77 | Reserved | 93 | Type of LAP |
78 | Compression | 94 | Securized VC |
79 | Reserved | 95 to 123 | Reserved |
80 | Call request timing | 124 | Consultation |
81 | Call return authorized | 125 | Low threshold |
82 | Reserved (address conversion) | 126 | High threshold |
83 | Facility marker CTRL | 127 | Reserved |
84 | React.on called add.mod.notific. | 128 | Cost and use of support |
85 | Clear TX format | 129 | Remote equipt class 22 position |
86 | Bit D management | 130 | Behavior |
87 | Type of line | 131 to 145 | Reserved |
88 | Facility unknown |
|
|
89 | Calling-called conversion |
|
|
90 | No. of DLCIs |
|
|
91 | Position of first DLCI |
|
|
| Parameter No. | Connection FRA subscriber type | Parameter No. | Connection FRA subscriber type |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Profile number | 38 | Not significant |
1 | Type of Link | 39 | Positioning threshold T2 (FECN/BECN) |
2 | Type of Connection | 40 | "DE ignored" threshold T4 |
3 | Scanning direction | 41 | "Frame ignored" threshold T4 |
4 | No. of 1st group of incoming LCs | 42 | Not significant |
5 | No. of 1st incoming LC | 43 | Not significant |
6 | No. of groups of incoming LCs | 44 | Type signalling |
7 | No. of incoming LCs | 45 | Add. nbr. in packets |
8 | No. of 1st group of mixed LCs | 46 | Local calling subscriber No. |
9 | No. of mixed LCs | 47 | Subaddress transparency |
10 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 48 | CUG facility |
11 | No. of mixed Lcs | 49 | RC acceptance (Tx) |
12 | No. of 1st group of outoging LCs | 50 | Reserved |
13 | No. of 1st outgoing LC | 51 | Transit time |
14 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 52 | PDN link |
15 | No. of outgoing LCs | 53 | PDN address No. |
16 | Reserved for VC break time-out | 54 | Tx fast sel.subscr. |
17 | Billing type | 55 | Reserved (Subscr.fast Sel.rec) |
18 | Receive filtering | 56 | Throughput class negotiation |
19 | Send filtering | 57 | Default TX throughput class |
20 | Interface state/interface superv. | 58 | Default RX throughput class |
21 | Interface state/interface superv. | 59 | Max. TX throughput class |
22 | Interface scanning period | 60 | Max. RX throughput class |
23 | Filtering/conf. of signal transition | 61 | Packet size negot.subscription |
24 | Interface state/interface superv. | 62 | Length of msg (Tx) |
25 | Interface state/interface superv. | 63 | Length of msg (Rx) |
26 | Int.signals forced | 64 | Max. TX packet size |
27 | Not significant | 65 | Max. RX packet size |
28 | Speed | 66 | Min. TX packet size |
29 | Max.No.Buffers/Frame | 67 | Min. RX packet size |
30 | Not significant | 68 | Tx window size negot.subscription |
31 | Initial transmission credit | 69 | Default TX window size |
32 | CRC count | 70 | Default RX window size |
33 | No. of flags (Tx) | 71 | Max. TX window size |
34 | No. of unanswered polls | 72 | Max. RX window size |
35 | Frame window width | 73 | Transfer request |
36 | Start of frame regr.thresh.T1 | 74 | Call confirm.format |
37 | Not significant | 75 | Reserved |
76 | Reserved | 92 | Not significant |
77 | Reserved | 93 | Type of LAP |
78 | Compression | 94 | Securized VC |
79 | Reserved | 95 to 123 | Reserved |
80 | Call request timing | 124 | Consultation |
81 | Call return authorized | 125 | Low threshold |
82 | Reserved (address conversion) | 126 | High threshold |
83 | Facility marker CTRL | 127 | Reserved |
84 | React.on called add.mod.notific. | 128 | Cost and use of support |
85 | Clear TX format | 129 | Remote equipt class 22 position |
86 | Bit D management | 130 | Behavior |
87 | Type of line | 131 to 145 | Reserved |
88 | Facility unknown |
|
|
89 | Calling-called conversion |
|
|
90 | No. of DLCIs |
|
|
91 | Position of first DLCI |
|
|
| Parameter No. | ISDN Channel D | Parameter No. | ISDN Channel D |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Profile number (number 47) | 38 | SO inactivation time-out |
1 | Type of Link | 39 | Time-out monit. a transm.line |
2 | Country | 40 | No. of buffers for DMA |
3 | Reserved | 41 | Priority access to channel D |
4 | Reserved | 42 | No. of TEIs per SAPI0/Interf. |
5 | Reserved | 43 | No. of TEIs per SAPI16/Interf. |
6 | Reserved | 44 | TEI allocation at start-up |
7 | Reserved | 45 | Automatic TEI allocation |
8 | Reserved | 38 | SO inactivation time-out |
9 | Reserved | 39 | Time-out monit. a transm.line |
10 | Reserved | 40 | No. of buffers for DMA |
11 | Reserved | 41 | Priority access to channel D |
12 | Reserved | 42 | No. of TEIs per SAPI0/Interf. |
13 | Reserved | 43 | No. of TEIs per SAPI16/Interf. |
14 | Reserved | 44 | TEI allocation at start-up |
15 | Reserved | 45 | Automatic TEI allocation |
16 | Reserved | 46 | SAPI0 transmission window |
17 | Reserved | 47 | SAPI16 transmission window |
18 | Reserved | 48 | TO waiting for response outgoing call (T3030 |
19 | Reserved | 49 | TO waiting for response of a disconnect request (T305) |
20 | Reserved | 50 | TO waiting for response on a clear request (T308) |
21 | Reserved | 51 | TO Monit. the time between an already received incoming call and an alarm on a connection (T310) |
22 | Reserved | 52 | TO waiting for response on a connect request (T313) |
23 | Reserved | 53 | TO Monit. the time between an N2 clear and an establishment of N2 (T309) |
24 | Reserved | 54 | TO waiting for response of a recording request (T309) |
25 | Reserved | 55 | Reserved |
26 | Reserved | 56 | Number of B-channels |
27 | Reserved | 57 | Established mode of channel B1 |
28 | Reserved | 58 | Established mode of channel B2 |
29 | Reserved | 59 | TO monit.for the time between a received alarm and a received connection |
30 | Reserved | 60 | TO monitoring "no virtual circuits establishment" |
61 | TO monit.to move into service after having received a "service interrupted" on a B-channel |
|
|
62 | Called sub-address |
|
|
63 | MSN behavior |
|
|
64 | SO interface number (position in C10) |
|
|
65 to 93 | Not significant |
|
|
94 | Securized VC |
|
|
95 to 123 | Reserved |
|
|
124 | Consultation |
|
|
125 | Low threshold |
|
|
126 | High threshold |
|
|
127 | Reserved |
|
|
128 | Cost and use of support |
|
|
129 | Remote equipt class 22 position |
|
|
130 | Behavior |
|
|
131-145 | Reserved |
|
|
| Parameter No. | BSC-Transparent connection | Parameter No. | BSC-Transparent connection |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Profile number | 38 | Type of coding |
1 | Type of Link | 39 | Not significant |
2 | Type of Connection | 40 | Not significant |
3 | Scanning direction | 41 | Refusal threshold |
4 | No. of 1st group of incoming LCs | 42 | BSC-transparent |
5 | No. of 1st incoming LC | 43 | Underrun management |
6 | No. of groups of incoming LCs | 44 | X.25 type signalling |
7 | No. of incoming LCs | 45 | 1 or 2 addr. in packet |
8 | No. of 1st group of mixed LCs | 46 | Local calling subscriber No. |
9 | No. of mixed LCs | 47 | Subaddress transparency |
10 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 48 | CUG facility |
11 | No. of mixed Lcs | 49 | RC acceptance (Tx) |
12 | No. of 1st group of outoging LCs | 50 | Reserved (RC Rx acceptance) |
13 | No. of 1st outgoing LC | 51 | Transit time |
14 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 52 | PDN link |
15 | No. of outgoing LCs | 53 | PDN address No. |
16 | Reserved | 54 | Tx fast slec.subscr. |
17 | Billing type | 55 | Rx. fast sel.subscr. |
18 | Receive filtering | 56 | Throughput class negotiation |
19 | Send filtering | 57 | Default TX throughput class |
20 | Interface state/interface superv. | 58 | Default RX throughput class |
21 | Interface state/interface superv. | 59 | Max. TX throughput class |
22 | Interface scanning period | 60 | Max. RX throughput class |
23 | Filtering/conf. of signal transition | 61 | Packet size negot.subscription |
24 | Interface state/interface superv. | 62 | Length of msg (Tx) |
25 | Interface state/interface superv. | 63 | Length of msg (Rx) |
26 | Int.signals forced | 64 | Max. TX packet size |
27 | Junction clock | 65 | Max. RX packet size |
28 | Speed | 66 | Min. TX packet size |
29 | Max.No.Buffers/Frame | 67 | Min. RX packet size |
30 | Not significant | 68 | Tx window size negot.subscription |
31 | Initial transmission credit | 69 | Default TX window size |
32 | Not significant | 70 | Default RX window size |
33 | Un necessary SYN | 71 | Max. TX window size |
34 | Frame envelope | 72 | Max. RX window size |
35 | Not significant | 73 | Transfer request |
36 | Not significant | 74 | Call confirm.format |
37 | Type of parity | 75 | Reserved |
76 | Reserved | 92 | PAD character deletion |
77 | Compression/scrambling | 93 | Type of LAP |
78 | Reserved | 94 | Securized VCs |
79 | Reserved | 95 to 123 | Reserved |
80 | Call request timing | 124 | Consultation |
81 | Call return authorized | 125 | Low threshold |
82 | Reserved | 126 | High threshold |
83 | Facility marker CTRL | 127 | Reserved |
84 | React.on called add.mod.notific. | 128 | Cost and use of support |
85 | Clear TX format | 129 | Remote equipt class 22 position |
86 | Bit D management | 130 | Behavior |
87 | Type of line | 131 to 145 | Reserved |
88 | Facility unknown |
|
|
89 | Address conversion |
|
|
90 | No. of controllers |
|
|
91 | Position of first controller |
|
|
| Parameter No. | Asynchronous X.28+ connection | Parameter No. | Asynchronous X.28+ connection |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Profile number | 38 | Automatic call number |
1 | Type of Link | 39 | NUI management |
2 | Type of Connection | 40 | Type of terminal |
3 | Scanning direction | 41 | X.25 parity |
4 | No. of 1st group of incoming LCs | 42 | No. of significant bits exchanged |
5 | No. of 1st incoming LC | 43 | Auto data rate recogn. |
6 | No. of groups of incoming LCs | 44 | X.25 type signalling |
7 | No. of incoming LCs | 45 | 1 or 2 addr. in packet |
8 | No. of 1st group of mixed LCs | 46 | Local calling subscriber No. |
9 | No. of mixed LCs | 47 | Subaddress transparency |
10 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 48 | CUG facility |
11 | No. of mixed Lcs | 49 | RC acceptance (Tx) |
12 | No. of 1st group of outoging LCs | 50 | Reserved |
13 | No. of 1st outgoing LC | 51 | Transit time |
14 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 52 | PDN link |
15 | No. of outgoing LCs | 53 | PDN address No. |
16 | Reserved | 54 | Tx fast slec.subscr. |
17 | Billing type | 55 | Reserved (Subscr.fast Sel.rec) |
18 | Receive filtering | 56 | Throughput class negotiation |
19 | Send filtering | 57 | Default TX throughput class |
20 | Interface state/interface superv. | 58 | Default RX throughput class |
21 | Interface state/interface superv. | 59 | Max. TX throughput class |
22 | Interface scanning period | 60 | Max. RX throughput class |
23 | Filtering/conf. of signal transition | 61 | Packet size negot.subscription |
24 | Interface state/interface superv. | 62 | Default TX packet size |
25 | Interface state/interface superv. | 63 | Default RX packet size |
26 | Int.signals forced | 64 | Max. TX packet size |
27 | Flow control | 65 | Max. RX packet size |
28 | Parity | 66 | Min. TX packet size |
29 | Max.No.Buffers/Frame | 67 | Min. RX packet size |
30 | Not significant | 68 | Tx window size negot.subscription |
31 | Initial transmission credit | 69 | Default TX window size |
32 | Inactivity time-out | 70 | Default RX window size |
33 | No. of bytes received in buffer | 71 | Max. TX window size |
34 | Block of character mode | 72 | Max. RX window size |
35 | No. of stop bits | 73 | Transfer request |
36 | Type of physical connection | 74 | Call confirm.format |
37 | Not significant | 75 | X.29 rerouting |
76 | Reserved | 114 | Reserved |
77 | Reserved | 115 | Padding |
78 | Compression/scrambling | 116 | X. ON character (DCE to DTE) |
79 | Reserved | 117 | X. OFF character (DCE to DTE) |
80 | Call request timing | 118 | Escape |
81 | Call return authorized | 119 | Action after escape |
82 | Reserved | 120 | X. ON character (DTE to DCE) |
83 | Facility marker CTRL | 121 | X. OFF character (DTE to DCE) |
84 | React.on called add.mod.notific. | 122 | Connection mode |
85 | Clear TX format | 123 | Reserved |
86 | Bit D management | 124 | Reserved |
87 | Msg Txm superv, time-out | 125 | Reserved |
88 | Not significant | 126 | M bit management |
89 | Not significant | 127 | Reserved |
90 | Error threshold (ECP) | 128 | Reserved |
91 | Txm time-out NACK (ECP) | 129 | Reserved |
92 | Conn. to HP equipment | 130 | Reserved |
93 | Type of call | 131 | Reserved |
94 | Securized VCs | 132 | Reserved |
95 | Reserved | 133 | Flux control by signals |
96 | Reserved | 134 | Reserved |
97 | Reserved | 135 | Reserved |
98 | Reserved | 136 | Reserved |
99 | Reserved | 137 | Reserved |
100 | Reserved | 138 | Reserved |
101 | Reserved | 139 | Reserved |
102 | Echo mask | 140 | Reserved |
103 | Reserved | 141 | Reserved |
104 | Reserved | 142 | Reserved |
105 | Full/half duplex | 143 | Reserved |
106 | Character coding |
|
|
107 | Type of terminal |
|
|
108 | Predefined terminal |
|
|
109 | Manual or automatic call |
|
|
110 | Automatic cleardown |
|
|
111 | Send on time-out |
|
|
112 | Data transfer time-out |
|
|
113 | Reserved |
|
|
| Parameter No. | Virtual Router | Parameter No. | Virtual Router |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Profile number | 38 | not significant |
1 | Not significant | 39 | Threshold S2 |
2 | Not significant (except MCX) | 40 | Threshold S3 |
3 | Scanning direction | 41 | Threshold S4 |
4 | No. of 1st group of incoming LCs | 42 | Not significant |
5 | No. of 1st incoming LC | 43 | Not significant |
6 | No. of groups of incoming LCs | 44 | X.25 type signalling |
7 | No. of incoming LCs | 45 | No. of addresses in packets |
8 | No. of 1st group of mixed LCs | 46 | Local calling subscriber No. |
9 | No. of mixed LCs | 47 | Subaddress transparency |
10 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 48 | CUG facility |
11 | No. of mixed Lcs | 49 | Reserved (RC Rx acceptance) |
12 | No. of 1st group of outoging LCs | 50 | Reserved (RC rec. accepted) |
13 | No. of 1st outgoing LC | 51 | Transit time |
14 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 52 | PDN link indication |
15 | No. of outgoing LCs | 53 | PDN address No. |
16 | Reserved | 54 | Tx fast Selc. subscription |
17 | Billing type | 55 | Tx fast Selc. subscription |
18 | Not significant | 56 | Throughput class negotiation |
19 | Not significant | 57 | TX Default throughput class |
20 | TO ARP superv. | 58 | RX Default throughput class |
21 | ARP time to live TO | 59 | Tx Max. throughput class |
22 | ARP proxy | 60 | Rx Max. throughput class |
23 | Intermediate routing | 61 | packet size negot.subscription |
24 | TO Tx Root 0.0.0.0 | 62 | Default TX packet size |
25 | IP time to live | 63 | Default RX packet size |
26 | Type of routing | 64 | Max. TX packet size |
27 | Algorithm number | 65 | Max. RX packet size |
28 | Reserved | 66 | Min. TX packet size |
29 | Reserved | 67 | Min. RX packet size |
30 | Reserved | 68 | Tx window size negot.subscription |
31 | Reserved | 69 | Default TX window size |
32 | Reserved | 70 | Default RX window size |
33 | Reserved | 71 | Max. TX window size |
34 | Not significant | 72 | Max. RX window size |
35 | Reserved | 73 | Transfer request |
36 | Threshold S1 | 74 | Call confirm. Tx format |
37 | not significant | 75 | Reserved |
76 | Not significant | 88 | Facility unknown |
77 | Not significant | 89 | Calling/called Address conv. |
78 | Reserved | 90 | No. of SVCs |
79 | Reserved | 91 | Position of first SVC (C17) |
80 | Call supver. timing | 92 | SVC position not conf. (C8) |
81 | Call return authorized | 93 | Not significant |
82 | Reserved (call.conv.) | 94 | Securized VCs |
83 | Facility marker Control | 95 to 145 | Reserved |
84 | CLAMN reaction |
|
|
85 | Clear format sent |
|
|
86 | D bit management |
|
|
87 | Not significant |
|
|
| Parameter No. | FRSNA connection | Parameter No. | FRSNA connection |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | Profile number | 54 | Tx fast slec.subscr. |
1 | Type of Link | 55 | Reserved (Subscr.fast Sel.rec) |
2 | Type of Connection | 56 | Throughput class negotiation |
3 | Scanning direction | 57 | Default TX throughput class |
4 | No. of 1st group of incoming LCs | 58 | Default RX throughput class |
5 | No. of 1st incoming LC | 59 | Max. TX throughput class |
6 | No. of groups of incoming LCs | 60 | Max. RX throughput class |
7 | No. of incoming LCs | 61 | Packet size negot.subscription |
8 | No. of 1st group of mixed LCs | 62 | Default TX packet size |
9 | No. of mixed LCs | 63 | Default RX packet size |
10 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 64 | Max. TX packet size |
11 | No. of mixed Lcs | 65 | Max. RX packet size |
12 | No. of 1st group of outoging LCs | 66 | Min. TX packet size |
13 | No. of 1st outgoing LC | 67 | Min. RX packet size |
14 | No. of groups of outgoing LCs | 68 | Tx window size negot.subscription |
15 | No. of outgoing LCs | 69 | Default TX window size |
16 | Initiative of XID transmission | 70 | Default RX window size |
17 | Not significant | 71 | Max. TX window size |
18 | Not significant | 72 | Max. RX window size |
19 | Virtual line credit | 73 | Transfer request |
20 | Not significant | 74 | Call confirm.format |
21 | Not significant | 75 | Reserved |
22 | Address station | 76 | Reserved |
23 | Callback time-out | 77 | Compression/scrambling |
24 | Not significant | 78 | Compression/scrambling |
25 | Not significant | 79 | Reserved |
26 | NLPID | 80 | Call request timing |
27 | L2PID | 81 | Call return authorized |
28 | L3PID | 82 | Reserved |
29 | DSAP | 83 | Facility marker CTRL |
30 | SSAP | 84 | React.on called |
31 | SABME transmission initiative |
| add.mod.notific. |
32 | Not significant | 85 | Clear Tx format |
33 | Time-out T2 | 86 | Bit D management |
34 | No. of frame repetition | 87 | Type of line |
35 | Frame window TW in transm. | 88 | Facility unknown |
36 | Frame modulo type | 89 | Address conversion |
37 | Inactivity time-out | 90 | No. of controllers |
38 | Acknowledgment counter N3 | 91 | Position of first controller |
39 | Dynamic window counter NW | 92 | PAD character deletion |
40 | Not significant | 93 | Type of LAP |
41 | Refusal threshold | 94 | Securized VCs |
42 | BSC transparent | 95 to 123 | Reserved |
43 | Frame window RW in reception | 124 | Consultation |
44 | X.25 type signalling | 125 | Low threshold |
45 | 1 or 2 addr. in packet | 126 | High threshold |
46 | Local calling subscriber No. | 127 | Reserved |
47 | Subaddress transparency | 128 | Cost and use of support |
48 | CUG facility | 129 | Remote equipt class 22 position |
49 | RC acceptance (Tx) | 130 | Behavior |
50 | Reserved (RC Rx acceptance) | 131 to 145 | Reserved |
51 | Transit time |
|
|
52 | PDN link |
|
|
53 | PDN address No. |
|
|
Profile number (See Appendix A).
Type of link.
This parameter determines the behavior of the equipment with respect to the X.25 procedure (level 2 connection mode and cause and diagnostic code management).
1 = DTE | : Interface with public network |
2 = DCE | : Interface with a subscriber |
3 = DSE | : Interface with another MCX. |

Type of link.
| Primary
| Secondary
| ||||
| Line X | Profile 18 | Profile 17 | Line Y | ||
| Protocol | Type | C12RXP1 | C12RXP1 | Type | Protocol |
SDLC | T4 | 16 | 17 | T2.0 | SDLC |
SDLC | T4 | 18 | - | T2.0/T2.1 | X.25 |
X.25 | T4 | - | 19 | T2.0 | SDLC |
SDLC | T4 | 20 | 21 | T2.1 | SDLC |
SDLC | T2.1 | 22 | 23 | T2.1 | SDLC |
X.25 | T2.1 | - | 24 | T2.1 | SDLC |
SDLC | T4 | 25 | 26 | T4 | SDLC |
| NIXD | 27 | 28 | T2.0 |
|
X.25 | NIXD | - | 29 | T2.0 |
|
| RWSI | 30 | 31 | T2.0 |
|
X.25 | RWSI | - | 32 | T2.0 |
|
X.25 | T4 | - | 34 | * | SDLC |
NIXD: | Nixdorf protocol |
RWSI: | Remote WorkStation Interface Protocol |
| * Reserved for special use (0.1.P terminals with T2.0 simulation) |
Type of link.
6 = controller
7 = Host.
Type of link.
8 = BSC controller: TPAD
9 = BSC Host: HPAD.
Type of link.
10 = secondary BSC
11 = primary BSC.
Type of link.
2 = DCE: The PAD is a subscriber of the switch.
Type of link.
0 = user
1 = network (subsequent use).
Type of connection/network
The value of the parameter indicates the network.
00 = | X.25 | (X.25 standard) |
04 = | TRANSPAC | (France) |
08 = | TELENET | (USA) |
12 = | TYMNET | (USA) |
16 = | INFOSWITCH | (Canada) |
20 = | DATAPAC | (Canada) |
24 = | DN1 | (Netherlands) |
28 = | PSS | (Great Britain) |
32 = | DATEX-P | (Germany) |
36 = | DCS | (Belgium) |
40 = | ITAPAC | (Italy) |
44 = | AUSTPAC | (Australia) |
52 = | UNINET | (USA) |
60 = | TELEPAC | (Switzerland) |
64 = | IBERPAC | (Spain) |
68 = | DATAPAK | (Sweden) |
72 = | HELPAC | (Greece) |
76 = | ENTEL | (Argentina) |
92 = | DATEX-P | (Austria) |
240 = | VIRTUAL ROUTER (only C24 (FastPad)) |
|
Type de connection.
20 = HDLC
21 = Frame relay (subscriber).
Country.
0 = France
2 = Switzerland.
Scanning direction of outgoing logical channel numbers.
0 = decreasing
1 = increasing.
In case of an asynchronous line, this parameters are reserved.
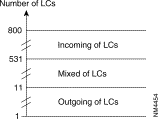
With the following table, the values of the parameters 4 to 15 can be found when configuring the logical channels.
| Configuration of the logical channels | Notation | Division to accomplish | Parameters affected | |
No.r of 1st incoming | A | A: 256 = GA Remainder LCA | P4 = GA | P5 = LCA |
No. of incoming | B | B: 256 = GB Remainder LCB | P6 = GB | P7 = LCB |
No. of 1st mixed | C | C: 256 = GC Remainder LCC | P8 = GC | P9 = LCC |
No. of mixed | D | D: 256 = GD Remainder LCD | P10 = GD | P11 = LCD |
No. of the 1st outgoing | E | E: 256 = GE Remainder LCE | P12 = GE | P13 = LCE |
No. of outgoing | F | F: 256 = GF Remainder LCF | P14 = GF | P15 = LCF |
with
C = A + B
E = C + D
The values GA to GF are the results of the divisions and the values LCA to LCF correspond to the remainders of the divisions.
The value 256 corresponds to the number of logical channels per group.
| Configuration of the logical channels | Notation | Division to accomplish | Parameters affected | |
No. of 1st outgoing LC | 1 | 1: 256 = 0 Remainder 1 | P12 = 0 | P13 = 1 |
No. of outing LCs | 10 | 10: 256 = 0 Remainder 10 | P14 = 0 | P15 = 10 |
No. of 1st mixed LC | 11 | 11: 256 = 0 Remainder 11 | P8 = 0 | P9 = 11 |
No. of mixed LCs | 520 | 520: 256 = 2 Remainder 8 | P10 = 2 | P11 = 8 |
No. of 1st incoming LC | 531 | 531: 256 = 2 Remainder 19 | P4 = 2 | P5 = 19 |
No. of incoming LCs | 270 | 270: 256 = 1 Remainder 14 | P6 = 1 | P7 = 14 |
With the following table, the mixed logical channels can be configured.
| Use of LC0 | No Use of LC0 | ||||
| DTE | DCE | DTE | DCE | ||
| Parameters designation | N° PAR. | Profile 0 Profile 4 Profile 20 Profile 40 | Profile 1 Profile 2 Profile 5 Profile 21 Profile 41 | Profile 0 Profile 4 Profile 20 Profile 40 | Profile 1 Profile 2 Profile 5 Profile 21 Profile 41 |
1st group of incoming LCs | 4 | $ | N | $ | N |
1st incoming LC | 5 | 0 | R | 1 | R+1 |
1st mixed LC | 9 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
Nber of groups of mixed LCs | 10 | N | N | N | N |
Nber of mixed LCs | 11 | R | R | R | R |
1st group of outgoing LCs | 12 | N | $ | N | $ |
1st outgoing LC | 13 | R | 0 | R+1 | 1 |
LC | Logical channel. |
0 | Value = 0. |
1 | Value = 1. |
$ | Default value. |
X | Number of mixed LCs to configure. |
N | Number of groups of necessary mixed LCs. |
If X < 256 then N = 0 and R = X.
Number of the first group of incoming logical channels (call received by the FastPad).
0 to 15 (modulo 256).
Number of the first incoming logical channel.
0 to 255.
Number of groups of incoming logical channels.
0 to 15 (modulo 256).
Number of incoming logical channels.
0 to 255.
Number of the first group of mixed logical channels (call transmitted or received by the FastPad).
0 to 15 (modulo 256).
Number of the first mixed logical channel.
0 to 255.
Number of groups of mixed logical channels.
0 to 15 (modulo 256).
This number allows the dimensioning of the total number of inter-Router connections (SVCs configured or not significant).
Number of mixed logical channels.
0 to 255.
This number allows the dimensioning of the total number of inter-Router connections (SVCs configured or not configured).
Number of the first group of outgoing logical channels (call transmitted by the FastPad).
0 to 15 (modulo 256).
This number above equal to parameter 10.
Number of the first outgoing logical channel.
0 to 255.
This number above be equal to parameter 11.
Number of groups of outgoing logical channels.
0 to 15 (modulo 256).
Number of outgoing logical channels.
0 to 255.
Type of coding.
0 = NRZ (default)
1 = NRZI.
Behavior of a not-used PVC.
0 = | Sending of PVC RESET not utilizable on reception of data or reset packet. |
7 = | Data or reset packets received in non-utilizable PVC state are ignored. |
Periodical disconnection of an SVC link (time-out TA).
0 = Ta not activated
1 to 254 (in step of 1 mn).
transmission of XID frame.
0 = transmission of XID frame by the remote (default)
1 = transmission of XID frame by the FastPad.
Billing.
0 = no billing
1 = overall billing
2 = detailed billing.
Behavior of FastPad when clear or reset cause packets are received.
0 = | transparent |
1 = | cause forced to zero |
2 = | cause forced to zero if cause code is lower than 128 |
3 = | cause forced to the "network trouble" value if received cause codes relates to "local procedure error" or "invalid facility request". |
| Otherwise, transparent mode. |
| Clears generated internally and resulting from the reception of a restart have a network trouble cause. |
Parameters 18 and 19 allow the configuration of phase identification.
| Parameter | Most sign. nibble | Least sign. nibble |
18 | 3rd phase | 1st phase |
19 | 4th phase | 2nd phase |
Each nibble may have one of the following values:
0 = | not defined |
1 = | Terminal Facility Identifier (TFI) without parity (sp) |
2 = | TFI with even parity (ep) |
3 = | ENQ |
4 = | ter? |
When we have the following list: "TFI(np), TFI(ep), ENQ and ter?", this gives the following values:
P18 = 3 * 16 + 1 = 49
P19 = 4 * 16 + 2 = 66
"Waiting" time-out of the 1st data packet following the call confirmation (only when "fast select" is not used; parameter 54 is zero).
1 to 254.
Default: 12.
Behavior of the FastPad in sending of clear or reset cause packets.
0 = no modification of causes
1 = cause forced to DTE.
See parameter 18.
See parameter 18.
Reserved parameter.
Interface state/interface superv. which enables the link to be "in service" and monitored.
| Physical signals CT | ||
| Parameters 20-21 | Parameters 24-25 | Description |
0 1 0
1 | 0 0 1
1 | Signal not monitored and not significant to put into service Signal monitored (evt. outstanding event) and not significant to put into service Signal monitored but info" position (contacts opened) Signal monitored but in"ON" position (contacts closed) |
The FastPad detects changes of state of the interface circuits by periodic scanning (period defined by parameter 22) of the interface.
| Bit 5 | P20 | P24 | ||
SYN | NS | Not significant | 0 | Activity not monitored |
SYN | 0 | Activity present | 1 | Activity monitored |
| 1 | Activity absent | 1 | Activity monitored |
| 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | bit |
128 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
|
27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 |
|
NS | NS | 108 | SYN | 105 | NS | NS | NS | DCE |
NS | NS | 106 | SYN | 109 | NS | NS | NS | DTE |
NS = | 0 = Not significant |
|
106 = | 1 = 106 OFF | 105 = 1 = 105 OFF |
106 = | 0 = 106 ON | 105 = 0 = 105 ON |
108 = | 1 = 108 OFF | 109 = 1 = 109 OFF |
108 = | 0 = 108 ON | 109 = 0 = 109 ON |
| 128 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |
| 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | |
NS | NS | NS | NS | CTE | 141 | 140 | 111 | DCE |
NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | 117 | 142 | 107 | DTE |
NS = 0 = Not significant | 140 = 1 = 140 OFF |
CTE = 1 = defined value | 140 = 0 = 140 ON |
141 = 1 = 141 OFF | 111 = 1 = 111 OFF |
141 = 0 = 141 ON | 111 = 0 = 111 ON |
142 = 1 = 142 OFF | 107 = 1 = 107 OFF |
142 = 0 = 142 ON | 107 = 0 = 107 ON |
117 = 1 = 117 OFF | 117 = 0 = 117 ON |
Case of a synchronous line where the following monitored signals must all be present so that this line goes to the ON state.
Interface state/interface superv., which enables the link to be in service.
These two parameters must be given in decimal form in the configuration.
The "in service" condition is defined by the value "1" of the corresponding bit of that interface signal.
For a Videotex/PSTN line, parameter 20 should not be changed.
| 128 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |
| 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | |
NS | NS | 108 | NS | 105 | NS | NS | NS | DCE |
NS | NS | 106 | NS | 109 | NS | NS | NS | DTE |
NS = 0 = Not significant |
|
106 = 1 = 106 OFF | 105 = 1 = 105 OFF |
106 = 0 = 106 ON | 105 = 0 = 105 ON |
108 = 1 = 108 OFF | 109 = 1 = 109 OFF |
108 = 0 = 108 ON | 109 = 0 = 109 ON |
| 128 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |
| 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | |
NS | NS | NS | NS | CTE | 141 | NS | 111 | DCE |
NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | 117 | NS | 107 | DTE |
NS = 0 = Not significant | 140 = 1 = 140 OFF |
CTE = 1 = defined value | 140 = 0 = 140 ON |
141 = 1 = 141 OFF | 111 = 1 = 111 OFF |
141 = 0 = 141 ON | 111 = 0 = 111 ON |
142 = 1 = 142 OFF | 107 = 1 = 107 OFF |
142 = 0 = 142 ON | 107 = 0 = 107 ON |
117 = 1 = 117 OFF | 117 = 0 = 117 ON |
| ENABLING CONDITION | PAR. 20 | PAR. 21 | SUPERVISION OF | PAR. 24 | PAR. 25 | |
TTY - Direct | 105-108 | 40 | 0 | Nothing | 0 | 0 |
TTY - PSTN | 107-106 | 32 | 1 | 109 | 8 | 0 |
TTY - DL or | 107-106-109 | 40 | 1 | Nothing | 0 | 0 |
TTY - Slaved line | 105 | 8 | 0 | Nothing | 0 | 0 |
LSCP - Direct or | 108 | 32 | 0 | 105 | 8 | 0 |
LSCP - DL or | 107-106 | 32 | 1 | 109 | 8 | 0 |
LSCP - Slaved line or | None | 0 | 0 | 105 | 8 | 0 |
DL = Dedicated line
LSCP = Low speed computer port
LSCPA = Low speed computer port with automatic calling.
Number of calls.
1 to 254.
"Slow call" time-out.
1 to 254 s (in step of 1 s).
Number of re-transmissions.
1 to 254.
Transparency of Teletel rerouting requests with parameter DR2 = 0 (address towards rerouted end).
Yes = | a rerouting request (DR) with the length of the parameter DR2 = 0 (.....8200.....) is regarded as a data packet and transmitted transparently. |
No = | in the same case, the rerouting request (DR) is refused. |
Scan time to detect the transition of the interface signals.
1 to 254 | (step of 200 msec) |
255 = | No scan time (used specially for modem return C12, profile 36). |
"Wait for reconnection" time-out.
1 to 254 s (in 10 s step).
Operation in ARP proxy.
0 = no
1 = Yes (default route ignored)
2 = Yes (default route taken).
Reserved parameter.
DR2 mnemonic transparency.
0 = no (default value)
1 = yes.
Filtering and confirmation of interface signal state changes (parameters 20 and 21).
1 to 250 = number of times the period defined by parameter 22 expires.
Declaration of "enabled" state of a synchronous line after 6 seconds' stabilization of the interface.
Param. 22 = 3 (0.6 s)
Param. 23 = 10 expirations.
Reference freezing time-out.
1 to 254 s (in 10 s step).
The multiplication of the values of parameters 22 and 23 defines the time to wait after ringing off a telephone line (duration, the signal 108/1 or 108/2 is "open").
3xP22xP23.
Authorization of intermediate routing.
0 = no
1 = yes.
Reserved parameter.
Position of the reconnection address.
Number of the parameter defined in C8R0.
The value of this parameter corresponds to the position of the address defined in C8 towards which is retransmitted the reconnection call with:
The configured call data are transmitted with the reconnection call. The corresponding facilities are not processed.
See parameters 20 and 21.
Definition of the interface signals on the link to monitor.
These two parameters must be given in decimal form in the configuration.
The FastPad scans periodically the changes of state of the interface signals (scanning interval defined in parameter 22).
The monitoring conditions are defined by the value "1" of the corresponding bit of that interface signal.
Asynchronous case: see P20 and P21.
Example: see parameters 20 and 21 and the previous table.
Reconnect address by means of:
0 = no
1 = yes (taking into account P24).
Value of TTL (Time To Live) equal to life of an IP datagram.
1 to 254.
Forcing of interface circuits.
The circuits present on the output of the interface are chosen in accordance with the following format:
| 128 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |
| 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | |
NS | NS | NS | 117 | 142 | 109 | 107 | 106 | DCE |
NS | NS | NS | 141 | 140 | 105 | 111 | 108 | DTE |
Circuit OFF = 1
Circuit ON = 0.
The flow control, LSCP and PSTN state machines have priority over the states defined by parameter 26.
For circuits 109, 107 and 106 to be present on the interface on the FastPad.
Parameter 26 = 7.
Transmission of the protocol identification.
0 = transmission (Balzac)
1 = no transmission.
Type of routing.
0 = routing of IP address ranges
1 = routing of IP address ranges and use of default route
Reserved parameter.
Flow control.
Value | Parity XON-XOFF | Parity Indicator | Control Mode |
0 | EP | EP | Norm |
1 | EP | NP | Screen/keyboard norm |
2 | NP | EP | Norm |
3 | NP | NP | Screen/keyboard norm |
4 | 0P | OP | Norm |
5 | EP | EP | Screen/keyboard norm |
6 | NP | NP | Norm |
7 | OP | OP | Screen/keyboard norm |
EP: Even Parity | OP: Odd Parity | NP: No Parity
|
Sampling of compression rate measurement.
1 to 255.
16.
Reserved parameter.
Value of line clock is provided by the FastPad.
2 = | 600 bit/s |
3 = | 1200 bit/s |
6 = | 2400 bit/s |
7 = | 3200 bit/s |
8 = | 4800 bit/s |
10 = | 9600 bit/s |
9 = | 14,4 kbit/s |
11 = | 19,2 kbit/s |
12 = | 38,4 kbit/s |
13 = | 48 kbit/s |
14 = | 56 kbit/s |
15 = | 64 kbit/s |
16 = | 72 kbit/s |
17 = | 128 kbit/s |
18 = | 144 kbit/s |
19 = | 256 kbit/s |
20 = | 512 kbit/s |
21 = | 1 Mbit/s |
22 = | 2 Mbit/s. |
Parity.
3 = even 1 = odd |
| These values are significant if |
0 = transparent |
|
|
5 = odd (8 bits) 7 = even (8 bits) |
| These values are significant is |
Compression dictionary RESET threshold.
0 to 100 in percent.
90.
Number of remote IP ranges C31R14
0 to 200.
Reserved parameter.
Maximum number of buffers per frame. This system parameter makes it possible to supply the FastPad with memory resource buffers according to the length of the received frames. The elementary buffer (memory) allows the reception of frames made up of 128 data bytes.
from 1 to 64.
1 = | 128-bytes frames |
2 = | 256-bytes frames |
4 = | 512-bytes frames |
8 = | 1024-bytes frames |
16 = | 2048-bytes frames |
32 = | 4096-bytes frames |
64 = | 8192-bytes frames. |
Row of first range of addresses in (C31R14).
1 to 200.
Reserved parameter.
Row of default route in C31 R15 (1 route per Router Function).
1 to 4.
Reserved parameter.
Initial line transmission credit. This parameter makes it possible to load the line with anticipated frame transmissions.
1 to 3.
Transmission of consecutive frames with a single inter-frame flag. In this case the value of parameter 31 is 3.
IP/ Prim. WAN address number in C31 R7 (1IP Primary WAN address per Router function).
1 to 6.
Reserved parameter.
Value of frame retransmission time-out link (X.25 parameter T1).
2 to 250 (unit = 100 ms).
Frame repeats time-out T1.
Frame repeats time-out T1.
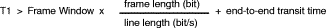
Value of line inactivity time-out in transfer state. When the time-out expires, the call is cleared.
0 = no time-out.
1 to 250 (unit = 10 s).
Value of inactivity time-out of the alarm function. At its expiration, the call is cleared.
0 = no time-out
1 to 250 (unit = 10 s).
Value for time-out of response survey of transmit polling.
1 to 250 (unit 100 ms).
Value of line supervision time-out.
Side TPAD (controller BSC): not significant.
Side HPAD (Host BSC): this value must be higher than the polling time-out fixed by the host (unit: 10 s).
Value of disconnection time-out.
10 to 250 s (unit 10 s).
CRC count.
0 = yes
1 = no (transparent).
Number of compression VCs of most significant module 0.
0.
Country version.
0 to 99
Number of primary or secondary interfaces on LAN side.
0 to 6.
Value of frame acknowledge transmission time-out T0.
1 to 250, T0 = T1 (Par. 32)/2
(unit = 100 ms).
This parameter indicates the number of bytes received by the FastPad in the receive buffers.
1 to 128.
Value of interpolling wait time-out (retransmission of polling frame on expiry of time out).
1 to 250 (100 ms units).
Profile 50 VIP controller:
Value of interpolling wait time-out (retransmission of polling frame on expiry of time-out).
Profile 51 VIP Host:
Value of interpolling wait time-out for printer
1 to 128 (100 ms units).
Value of polling intersequence time-out.
TPAD side: | 0.1 to 25 s (100 ms units). |
HPAD side: | Not significant. |
Value of time-out, supervision mode.
10 to 250 s (10 s units).
Number of "flags" (transmission).
1 to 15.
Number of compression VCs of least significant module 0.
0 to 10 with 512 kbyte of RAM
0 to 100 with 2 Mbyte of RAM
0 to 230 with 4 Mbyte of RAM.
Protocol type.
0 = LAP-D
1 = LAP-B (subsequent user).
Unnecessary SYN.
0 = The frame is preceded by 2 SYNs during transmission (normal case).
2 = The frame is preceded by 4 SYNs during transmission.
Row of first definition of primary interface on LAN side LAN in C31 R8, and R11.
0 to 20.
Sampling time used for counters to data rates.
1 to 180 (step of 10 seconds).
Value of time-out T2 on frame acknowledgment transmission.
1 to 127 (step of 100 ms) T2 < T1
Maximal number of times a transmitted information frame is repeated (X.25 parameter N2).
2 to 250.
Type of reception for information messages received from the FastPad.
The character mode means that the reception of a character leads to immediate management of the character.
The block mode means that the complete reception of the block leads to the management of the message carried by this block.
Not significant, depending on chosen X.3 parameters, the most suitable mode is dynamically selected. However, the following modes can be forced:
3 = | Block mode. |
7 = | Character mode. |
11 = | Block mode transmission time-out, calculated according to the line speed. |
15 = | Character mode with transmission time-out, calculated according to the line speed. |
Maximum number of unanswered polls.
1 to 250.
Number of "no responses" to polling.
1 to 20.
Number of compression VCs of most significant module 1.
0.
Type of access.
0 = basic access
1 = primary access (subsequent user).
(subsequent user, do not modify)
Frame envelope.
0 = CT105 (DTE) or CT109 (DCE) is on (see P26).
1 = CT105 (DTE) or CT109 (DCE) envelopes the transmitted frames.
Sampling time used for counters relative to logical channels and for counters relative to status of interface and of frame level.
1 to 180 (step of 10 seconds).
Width of frame window as defined in X.25.
1 to 7 | if modulo 8 |
1 to 30 | if modulo 128. |
Frame of windows width.
1 to 7: modulo 8
Number of stop bits in 1 byte.
4 = | 1 stop bit |
12 = | 2 stop bits. |
Number of buffers in the VIP window.
1 to 40.
Reception queue width.
The sum of P35 and P69 (packet window default value) must be more than P29 (maximum frame size).
Frame width receive queue BSC.
1 to 20.
Percentage of line speed for transmit data rate threshold calculation.
0 to 100.
Size transport window.
1 to 15.
Width of frame window.
0 to 100 ; 0 = no check.
Number of compression VCs of Least significant module 1.
0 to 10 with 512 kbyte of RAM
0 to 100 with 2 Mbyte of RAM
0 to 230 with 4 Mbyte of RAM.
Scan time needed to detect connection to the network.
0 to 255 (step of 200 msec).
Frame window in transmission.
1 to 127 (modulo 128).
Modulo used for numbering of information frames.
8 = | modulo 8 |
128 = | modulo 128. |
Same as synchronous case.
8 = modulo 8
The SDLC does not support modulo 128.
Type of connection to MCX interfaces.
0 = | Modem access on the PSTN with automatic calling |
1 = | Modem access on dedicated line |
2 = | Direct access (without modem) |
3 = | Direct access with control by 105/106 (par. 20, 21, 24, 25, 26 in class 12 and par. 5, 12 in class 13) |
4 = | V.25bis PSTN access by modem. |
Flow control circuits may be elected to be the "in-service" criterion.
Type of coding.
0 = EBCDIC
1 = ASCII
Fast select utilization.
0 = no
1 = yes.
Number of compression VCs of most significant module 2.
0.
When frame relay is used: the "start of frame regrouping" threshold (= threshold 1).
1 to 33.
Number of filter repeats.
0 to 255.
Percentage of line speed for receive data rate threshold calculation.
0 to 100.
Behavior of TPAD after sending of text to cluster controller.
0 = TPAD sends Statistics polling
1 = TPAD sends Controller polling.
Address of primary for transmission of command frames.
1 for DTE
30 for DCE.
Type of parity.
0 = no parity
1 = odd parity
2 = Reserved
If P36 = 1 then P37 = 1.
Reserved parameter.
EOT response or not from the HPAD on polls of the HOST and in case the virtual circuit with the TPAD has not been established.
0 = | no EOT response on the polls |
1 to 255 = | EOT response on the polls (255 = default value). |
This parameter is only significant in a configuration where a HPAD faces a VIP Host.
Polling counter, when the station does not reply (slow polling).
1 to 255.
Value of the S0 interface activation time-out.
1 to 150 (step of 200 ms).
Number of compression VCs of least significant module 2.
0 to 10 with 512 kbyte of RAM
0 to 100 with 2 Mbyte of RAM
0 to 230 with 4 Mbyte of RAM.
Remark: For the LMX, the utilization limit is 80 VCs, with compression by module.
Percentage of number of LCs configured for calculating the threshold of busy logical channels.
0 to 100.
Address of secondary for transmission of command frames.
1 for DCE
3 for DTE.
The automatic call number makes it possible to associate a network address, utilities/facilities, and call user data with an asynchronous terminal (e.g. LSCP-A).
This number corresponds to the parameters of recurrences of class 8 (automatic calling table).
P38 = 1
1: means first automatic call defined in C8 par. 0 of all the recurrences.
1 to 200.
0 = service not required.
Percentage of number of buffers free after the initialization of the equipment for calculating the threshold of busy buffers.
0 to 100.
Processing of unknown packets.
0 = Clear the VC (default value profile 17)
1 = Ignored.
Type of paired equipment.
The 1st element mentioned represents the FastPad equipment.
0 = Terminal-Terminal (T-T)
1 = Terminal-CPU (T-CPU)
2 = CPU-CPU (CPU-CPU)
3 = CPU-Terminal (CPU-T).
Value of the S0 interface inactivation time-out.
0 to 5 (step of 200 ms).
Reserved parameter.
Value of supervision time-out for the response of a restart transmitted on the line. The restart is repeated if there is no response by the expiry of the time-out (unit = 10 s).
After N repetitions, the link is reset at the frame level (transmission of a DISC frame).
1 to 250.
Positioning threshold of the FECN and BECN bits (threshold 2).
Threshold 2 > threshold 1 (P36).
Value of screen message retransmission time-out.
1 to 250 (unit = 10 s).
Management of NUI (Network User Identifier) with respect to the operator and to the format of the call request packet transmitted to the network line.
0 = | NUI not checked by the FastPad |
1 = | NUI obligatory. The FastPad checks the value (password) assigned to it |
2 = | After checking the NUI acquired, the FastPad translates it into an NUA in accordance with the values chosen in class 6. |
3 = | NUI optional but reverse charging facility set in call request if NUI missing. |
4 = | NUI obligatory and not controlled by the FastPad. Transported in the X.25 facility. |
5 = | NUI optional. If present: see "4" if absent: communication established with reverse charging facility. |
6 = | NUI inhibited. Communication established with reverse charging facility |
10 = | NUI ON or NUI OFF obligatory on PSTN line before any call setup. |
Condition for sending a WACK to the Host.
0 = | on detection of a start print bit at 1 |
1 = | on network congestion; in this case, the sum of parameters P35 (queuing width) and P69 (packet window size default value) must come out higher than P29 (maximum frame size). |
Value of time-out of retransmission of ENQ in case of simultaneous BID.
1 to 255 (step of 100 ms).
Time-out monitoring a transmitting line.
0 to 5 (step of 200 ms).
NW, dynamic window counter allowing work window incrementation.
The value 4 is recommended, 2 to 10.
Value of supervision time-out for the response to a reset transmitted on a logical channel of the link. After the first expiry of the time-out, the reset packet is repeated. After n reset retransmissions, the logical channel is cleared.
1 to 250 (unit = 10 s).
Type of terminal connected to the link.
0 = standard TTY terminal
1 = VDX terminal with Minitel type function key
2 = LSCP (Low Speed Computer Port)
3 = LSCPA (Low Speed Computer Device with Automatic calling).
QLLC segment length for PSH procedure.
7 = 128
8 = 256
Threshold 3 > Threshold 2 (P39).
Values of printer message retransmission time-out.
1 to 250 (unit = 10 s).
Value of time-out T2, authorized response time.
1 to 255 (unit = 100 ms).
Possibility not to respond to polling/select of the host when the X.25 link is interrupted.
0 = Yes, independent of the state of the VC
1 = Yes when connected (1 station per controller); only in case of BSC3275
Number of available buffers for DMA (Direct Memory Access).
1 to 8.
Value of supervision time-out for the response to a clear transmitted on the link. After the first expiry of the time-out, the clear is repeated. After N retransmissions of the clear packet, the logical channel is assumed to be cleared.
1 to 250 (unit = 10 s).
Parity X.25 (VDX).
0 = transparent mode
1 = eighth bit forced to 0.
SDLC-type protocol.
0 = PSH
1 = QLLC.
Value of "no response" time-out.
0,1 s to 25 s (unit = 100 ms).
Value of "no response" time-out (T3).
0,1 to 25 s (unit = 100 ms).
Refusal threshold (as of a number of frames waiting for transmission equal to this threshold, all news frames are lost. No flow control is possible through Transparent-BSC).
0 to 254.
Priority access to channel D.
0 = priority 8
1 = priority 10.
After reception of a screen message, transmitted by a VIP station, the message flow from that station to the screen, is blocked.
The station is released when a screen message is received from the Host or when the protection time-out expires.
0 = | no blocking |
1 to 255 = | duration of the blocking of the screen flow (step of 10 s). |
This parameter is only significant in a configuration where a TPAD channel faces VIP terminals.
When this threshold is exceeded, all received frames are ignored (threshold 4).
HDLC-T: | Threshold 4 > Threshold 1 (P36) + Threshold 2 (P39) |
Frame relay subscriber: | Threshold 4 > Threshold 3 (P40) |
Value of reset, restart and clear packet retransmission counter. This counter is incremented upon the expiry of the reset, restart and clear transmission supervision time-outs.
1 to 250.
Number of significant bits in characters exchanged between the terminal and the FastPad.
8 (7 bits + possible parity defined in X.3 parameters of class 13).
Number of call request packet retransmissions.
0 to 99.
Number of message retransmissions.
1 to 7.
Number of retransmissions.
1 to 20.
Number of TEIs per SAPI0 and per interface (*).
(*) | TEI = | Terminal Equipment Identification |
| SAPI = | Service Access Point Identification (0 = signalling, 16 = packet in D-channel). |
0 and 1.
(subsequent user, do not modify)
0 = no
1 = mixed.
The value 1 must be configured if coding is ASCII with parity and if frames to Transparent-BSC format can be received on the connection.
Elimination of diagnostic code from clear and restart packets sent by the FastPad. The feature ensures compatibility with older X.25 systems.
0 = transparent mode
1 = elimination of diagnostic code.
Window frame in reception.
1 to 127 (modulo 128).
Use of terminal's automatic data rate recognition.
The recognition range is 300 to 9600 bit/s.
0 = | no recognition (in this case, the terminal's rate must be the one chosen by the X.3 parameter) |
1 = | automatic data rate recognition |
2 = | automatic data rate and parity. |
Under unmanagement.
1 = | the double SYNs of a normal BSC frame and the DLE SYNs of a transparent-BSC data frame are eliminated on reception and no transmitted on the network. |
0 = | these characters are carried to the other end (except for DLE SYN). |
Type of protocol.
0 = 2780
1 = 3780.
Type of TPAD connection.
0 = automatic
1 = DATA.
Number of TEIs per SAPI 16 and per S0 interface
Number of PLLs.
0 to 4.
"Local management" or "transparency" for printer messages.
0 = standard: local management of status messages from the printer.
1 = transparent management, end to end acknowledgment.
Type of X.25 signalling. This parameter defines the signalling processing behavior of the connected line. It is independent of the type of link operation parameter (DTE, DCE, DSE).
0 = X.25 network
1 = X.25 subscriber
2 = X.75.
TEI allocation at start-up.
0 = No (Switzerland)
1 = Yes (France).
Number of addresses in call request packets sent or received.
1 = | one address in call request packets |
| One of the two fields (calling address for packets from subscriber) contains only the suffix (after DNIC-Z0-AB) |
2 = | two addresses in call request packets |
| Both address fields of each of the two types of call request (calling, called) contain complete addresses. |
Automatic TEI allocation.
0 = No
1 = Yes.
This is the AB number of a subscriber connected to a link. The subscriber's number is significant only if the signalling is of the subscriber type (P44 = 1).
This number is added in the calling address for a incoming call.
0 to 98.
Subscriber number (AB) corresponding to the router function.
00 to 98.
SAP I0 transmission window.
1 up to 7.
Transparency of sub-address restored on the subscriber line.
This configuration parameter indicates the sub-address of the called address field of the call request packet received on a PDN line must be retransmitted on the outgoing line.
0 = | call sub-address is not transmitted. |
| This sub-address is not transmitted in the outgoing call request packet. |
1 = | The sub-address of the called party is transmitted on the outgoing line. |
SAPI16 transmission window.
1 to 7.
This parameter specifies the behavior of the FastPad with respect to the closed user group facility. 28 pairs of CUGs (Closed User Group) can be configured for each line (C18R0 to R35).
0 = | Not subscriber: clearing if presence of CUG |
1 = | Transparent: CUG not tested |
2 = | Subscriber: clearing of CUG is absent or if CUG is incorrect |
3 = | Subscriber + filtering: same behavior as value 2 but the CUG facility is eliminated from the call request packet sent to the subscriber. |
Value of the time-out waiting for response of an outgoing call (T303).
1 to 255 s (step of 1 s)
Reverse charging acceptance.
This parameter specifies the behavior of the FastPad with respect to the reverse charging facility.
0 = subscriber does not accept reverse charging calls
1 = subscriber accepts reverse charging calls.
Value of the time-out waiting for a response on a disconnect request (T305).
1 to 255 s (step of 1 s)
(Reserved).
Value of the time-out waiting for a response on a clear request (T308).
1 to 255 sec (step of 1 s); for VN2 the value is 4 sec.
Transit delay.
0 = transparent
1 = filtering (see table)
2 = clearing.
| Origin = network line | Origin = subscriber line | |
| Call | Transp. | Transp. |
Config. call |
| CLEAR 03.41 |
|
| to near-end |
Clearing | CLEAR 05.41 | CLEAR 11.41 |
|
| to far-end |
Value of the time-out monitoring the time between an already received incoming call and an alarm or the connection (T310).
1 to 255 s (step of 1 s)
PDN (Public Data Network) line indicator, configured in the two-address mode. This parameter indicates whether the link is connected directly to a public data network.
0 = no PDN Line
1 = PDN line with compacting/decompacting
2 = Reserved (Muse)
3 = Reserved (TRANSPAC)
4 = PDN line with address transport.
Value of the time-out waiting for response on a connect request (T313).
1 to 255 sec (step of 1 sec); for VN2 the value is 4 sec.
Access number in PDN line table.
This parameter indicates the position in the table of PDN link addresses. It is significant only if the link is a PDN line (parameter 52) and is configured in the two-address mode (parameter 45).
0 = first PDN line used
9 = tenth PDN line used.
Value of the time-out monitoring the time between an N2 clear and an establishment of N2 (T309).
60 to 180 sec (step of 1 sec); for VN2 the value is 60 sec.
Fast select facility for transmission.
Subscription of fast select facility for transmission by the FastPad.
0 = not subscriber
1 = subscriber
2 = transparency.
"Fast select" subscription.
0 = no facility
1 = with facility.
Value of the time-out waiting for response of a registration request (T399)
1 to 255 sec (step of 1 sec)
The value is 10 sec for VN2.
Tolerance on call data is a received call request packet not containing the "fast select" facility.
2 = authorized call data length up to 128 bytes.
Other value = authorized length up to 16 bytes.
Throughput negotiation facility subscription.
This parameter indicates whether the subscriber connected to the link has subscribed to the throughput class negotiation facility.
0 = not subscriber
1 = subscriber.
Number of B-channels.
0 to 2.
Default throughput class in transmit direction (FastPad to exterior).
3 | for | 75 | bit/s |
4 | for | 150 | bit/s |
5 | for | 300 | bit/s |
6 | for | 600 | bit/s |
7 | for | 1200 | bit/s |
8 | for | 2400 | bit/s |
9 | for | 4800 | bit/s |
10 | for | 9600 | bit/s |
11 | for | 19200 | bit/s |
12 | for | 48000 | bit/s |
13 | for | 64000 | bit/s |
14 | for | 128000 | bit/s |
15 | for | 192000 | bit/s |
Establishment mode of channel B1.
0 = without signalling (subsequent use)
1 = with signalling.
Default throughput class in receive direction (exterior to FastPad).
3 | for | 75 | bit/s |
4 | for | 150 | bit/s |
5 | for | 300 | bit/s |
6 | for | 600 | bit/s |
7 | for | 1200 | bit/s |
8 | for | 2400 | bit/s |
9 | for | 4800 | bit/s |
10 | for | 9600 | bit/s |
11 | for | 19200 | bit/s |
12 | for | 48000 | bit/s |
13 | for | 64000 | bit/s |
14 | for | 128000 | bit/s |
15 | for | 192000 | bit/s |
The final choice of throughput classes for the transmit and receive directions of a link is made on the call confirmations.
Establishment mode of channel B2.
0 = without signalling (subsequent use)
1 = with signalling.
Maximum throughput class in transmit direction.
3 | for | 75 | bit/s |
4 | for | 150 | bit/s |
5 | for | 300 | bit/s |
6 | for | 600 | bit/s |
7 | for | 1200 | bit/s |
8 | for | 2400 | bit/s |
9 | for | 4800 | bit/s |
10 | for | 9600 | bit/s |
11 | for | 19200 | bit/s |
12 | for | 48000 | bit/s |
13 | for | 64000 | bit/s |
14 | for | 128000 | bit/s |
15 | for | 192000 | bit/s |
Value of the audible time-out monitoring the time between a received alarm and a received connection.
1 to 255 sec. in step of 10 sec.
Maximum throughput class in receive direction.
3 | for | 75 | bit/s |
4 | for | 150 | bit/s |
5 | for | 300 | bit/s |
6 | for | 600 | bit/s |
7 | for | 1200 | bit/s |
8 | for | 2400 | bit/s |
9 | for | 4800 | bit/s |
10 | for | 9600 | bit/s |
11 | for | 19200 | bit/s |
12 | for | 48000 | bit/s |
13 | for | 64000 | bit/s |
14 | for | 128000 | bit/s |
15 | for | 192000 | bit/s |
Value of the time-out monitoring "no virtual circuits established"
1 to 255 seconds in step of 10 sec.
Subscription to packet size negotiation facility.
0 = no subscriber
1 = subscriber.
Value of the time-out waiting to move into service after having received a "service interrupted" on a B-channel.
1 to 255 sec. in step of 10 sec.
This parameter must be consistent with the length of the frame switched to the line (parameter 29).
Default value of packet size for transmit direction (FastPad to exterior network or subscriber connected to the FastPad).
4 | for | 16 | bytes |
5 | for | 32 | bytes |
6 | for | 64 | bytes |
7 | for | 128 | bytes |
8 | for | 256 | bytes |
9 | for | 512 | bytes |
10 | for | 1024 | bytes |
11 | for | 2048 | bytes |
12 | for | 4096 | bytes |
13 | for | 8192 | bytes. |
Default value of packet length with QLLC procedure for transmission from the FastPad to exterior (transmit).
4 | for | 16 | bytes |
5 | for | 32 | bytes |
6 | for | 64 | bytes |
7 | for | 128 | bytes |
8 | for | 256 | bytes |
9 | for | 512 | bytes |
10 | for | 1024 | bytes |
11 | for | 2048 | bytes |
12 | for | 4096 | bytes |
13 | for | 8192 | bytes. |
Tx VIP message length.
4 | for | 16 | bytes |
5 | for | 32 | bytes |
6 | for | 64 | bytes |
7 | for | 128 | bytes |
8 | for | 256 | bytes |
9 | for | 512 | bytes |
10 | for | 1024 | bytes |
11 | for | 2048 | bytes |
12 | for | 4096 | bytes |
13 | for | 8192 | bytes. |
BSC message length (transmission).
> 10 |
|
|
|
10 | for | 1024 | bytes |
11 | for | 2048 | bytes |
12 | for | 4096 | bytes. |
BSC message length (transmission).
7 to 10 |
|
|
|
7 | for | 12 | bytes |
8 | for | 256 | bytes |
9 | for | 512 | bytes |
10 | for | 1024 | bytes. |
Check on presence of called sub-address.
1 = refused when sub-address is not present
0 = acceptation in all cases.
This parameter must be consistent with the length of the frame switched to the line (parameter 29).
Default value of packet size for transmission from the exterior (network or subscriber connected to the FastPad) to the FastPad.
4 | for | 16 | bytes |
5 | for | 32 | bytes |
6 | for | 64 | bytes |
7 | for | 128 | bytes |
8 | for | 256 | bytes |
9 | for | 512 | bytes |
10 | for | 1024 | bytes |
11 | for | 2048 | bytes |
12 | for | 4096 | bytes |
13 | for | 8192 | bytes. |
Default value of packet length with QLLC procedure for transmission from exterior to the FastPad.
4 | for | 16 | bytes |
5 | for | 32 | bytes |
6 | for | 64 | bytes |
7 | for | 128 | bytes |
8 | for | 256 | bytes |
9 | for | 512 | bytes |
10 | for | 1024 | bytes |
11 | for | 2048 | bytes |
12 | for | 4096 | bytes |
13 | for | 8192 | bytes. |
Rx VIP message length.
4 | for | 16 | bytes |
5 | for | 32 | bytes |
6 | for | 64 | bytes |
7 | for | 128 | bytes |
8 | for | 256 | bytes |
9 | for | 512 | bytes |
10 | for | 1024 | bytes |
11 | for | 2048 | bytes |
12 | for | 4096 | bytes |
13 | for | 8192 | bytes. |
BSC message length reception.
> 7 |
|
|
|
7 | for | 128 | bytes |
8 | for | 256 | bytes |
9 | for | 512 | bytes |
10 | for | 1024 | bytes |
11 | for | 2048 | bytes |
12 | for | 4096 | bytes. |
BSC message length reception.
4 to 7 |
|
|
|
4 | for | 16 | bytes |
5 | for | 32 | bytes |
6 | for | 64 | bytes |
7 | for | 128 | bytes. |
MSN behavior (MSN = Multiple Subscriber Number).
0 = call acceptation
1 = check of the destination number.
This parameter must be consistent with the length of the frame switched to the line (parameter 29).
Maximum packet size transmitted by the FastPad.
4 | for | 16 | bytes |
5 | for | 32 | bytes |
6 | for | 64 | bytes |
7 | for | 128 | bytes |
8 | for | 256 | bytes |
9 | for | 512 | bytes |
10 | for | 1024 | bytes |
11 | for | 2048 | bytes |
12 | for | 4096 | bytes |
13 | for | 8192 | bytes. |
S0 interface number (position in class 10).
0 to 35.
This parameter must be consistent with the length of the frame switched to the line (parameter 29).
Maximum packet size received by the FastPad.
4 | for | 16 | bytes |
5 | for | 32 | bytes |
6 | for | 64 | bytes |
7 | for | 128 | bytes |
8 | for | 256 | bytes |
9 | for | 512 | bytes |
10 | for | 1024 | bytes |
11 | for | 2048 | bytes |
12 | for | 4096 | bytes |
13 | for | 8192 | bytes. |
This parameter is used in the case of a multiple backup.
Time-out between two successive attempts on a given ISDN number.
1 to 254.
5 s.
This parameter must be consistent with the length of the frame switched to the line (parameter 29).
Minimum packet size received by the FastPad.
4 | for | 16 | bytes |
5 | for | 32 | bytes |
6 | for | 64 | bytes |
7 | for | 128 | bytes |
8 | for | 256 | bytes |
9 | for | 512 | bytes |
10 | for | 1024 | bytes |
11 | for | 2048 | bytes |
12 | for | 4096 | bytes |
13 | for | 8192 | bytes. |
This parameter is used in the case of a multiple backup.
Time-out between two successive attempts cycles.
1 to 254.
10 s.
This parameter must be consistent with the length of the frame switched to the line (parameter 29).
Minimum packet size received by the FastPad
4 | for | 16 | bytes |
5 | for | 32 | bytes |
6 | for | 64 | bytes |
7 | for | 128 | bytes |
8 | for | 256 | bytes |
9 | for | 512 | bytes |
10 | for | 1024 | bytes |
11 | for | 2048 | bytes |
12 | for | 4096 | bytes |
13 | for | 8192 | bytes. |
This parameter is used in the case of a multiple backup.
Number of attempt cycle.
1 to 255.
3.
Transmit window size facility.
0 = not subscriber
1 = subscriber.
This parameter is used in the case of a multiple backup.
Duration of multiple backup.
1 to 100 (unit = 1s).
100.
Default value of packet window for transmission from FastPad to exterior (network or subscriber connected to the FastPad).
1 to 7.
This parameter is used in connection with PLLs.
Time-out 0VC on PLL. This parameter is global to the interface.
0 = not managed 1 to 250 (step of 1s)
0
Default value of packet window for transmission from exterior to the FastPad.
1 to 7.
This parameter is applied when PLLs are used.
Activation of PLLs on start-up.
0 = No
1 = Yes
0.
Maximum value of packet window for transmission from the FastPad to exterior.
1 to 7.
High layer compatibility (HLC).
One byte coded in 8 bits (bit 0 = least significant bi).
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 bit
Reserved | |
| |___HLC I.E transmission
HLC I.E _____ | 0 = no
analysis 1 = yes
0 = no
1 = yes
00 = | no transmission and analysis of HLC I.E. |
01 = | transmission and no analysis of HLC I.E. |
02 = | no transmission and analysis of HLC I.E. |
03 = | transmission and analysis of HLC I.E. |
02.
Maximum value of packet window for transmission from exterior to the FastPad.
1 to 7.
Coding type of High Layer Information Elements.
One bit coded in 8 bits (bit 0 = least significant bit).
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | bit |
| | | |______ ___ Presentation
| | | 1 | 0 | bit
| | |
| | | 01 = Method of protocol profile
| | | The other values are reserved
| | |_______________________ __Interpretation
| | 4 | 3 | 2 | bit
| | : 0 : 0 : 0 : = Coding of services:
| | : : : : audiography,
| | : : : : AudioVideotex
| | : : : : and no standardized
| | : : : : application (value not
| | : : : : defined in the ETS 300
| | : : : : 102).
| | : : : :
| | : 1 : 0 : 0 : = Teleservice by parameter
| | 73.
| |
| | The other values are reserved
| |
| |_____________________________________Coding standard
| 6 | 5 | bit
| : 0 : 0 : = ITU-T standard
| : 1 : 0 : = National standard
|
| The other values are reserved
|
|____________________________________________ _Value fixed at 1
In VN3, the values of parameters 72 are:
· 145 (91 hexa): | ITU-T standard |
· 193 (C1 en hexa): | National standard* |
· 209 (D1 en hexa): | National standard |
*The values of tests 2, 3 and 4 are not defined in the ETS 300102. | |
Request call transfer to a backup subscriber when the called subscriber is busy.
0 = transparent
1 = filtering
2 = clearing.
Definition of the teleservice. There are to 2 teleservice groups according to the coding standard:
1) | Teleservice with ITU-T coding standard: | |
| 129 (81 hexa): | Telephony |
| 132 (84 hexa): | Facsimile group 2/3 |
| 161 (A1 hexa): | Facsimile group 4 Class 1 |
| 164 (A4 hexa): | Teletex and telecopy group 4 Class 2/3 |
| 168 (A8 hexa): | Teletex service basic and processable mode of operation |
| 177 (B1 hexa): | Teletex service basic mode of operation |
| 178 (B2 hexa): | Syntonic Videotex |
| 179 (B3 hexa): | International Interworking for videotex service |
| 181 (B5 hexa): | Telex service |
| 184 (B8 hexa): | Messages handling systems (MHS) |
| 193 (C1 hexa): | OSI application |
| 224 (E0 hexa): | Audiovisual. |
2) | Teleservices with national coding standard | |
| 128 (80 hexa): | Unknown teleservice |
| 192 (C0 hexa): | Audiography |
| 200 (C8 hexa): | Audiovideotex |
| 255 or 127 (FF hexa): | Application not standardized |
193 = OSI application.
Format of call confirmation transmitted by the FastPad.
0 = complete X.25 format (facilities and addresses)
1 = reduced X.25 format, the (calling, called) address length field is zero (facilities, no address)
2 = reduced format (no facility, no address)
3 = complete X.25 format (facilities and addresses + transparency on addresses).
Low layer compatibility (LLC).
One byte coded in 8 bits (bit 0 = least significant bit).
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 bit
Reserved | |
| |___LLC I.E transmission
LLC I.E analysis 0 = no
0 = no 1 = yes
1 = yes
00 = | no transmission and analysis of LLC I.E |
01 = | transmission and no analysis of LLC I.E |
02 = | no transmission and analysis of LLC I.E |
03 = | transmission and analysis of LLC I.E |
02
Remark: The content of the LLC I.E can not be configured. If the analysis of this I.E is required, only the following compatibilities are accepted:
· LEV1: | ITU-T X.31 throughput adaptation | |
| LEV2: | ITU-T X.25 level 2 LAPB (SLP) |
| LEV3: | ITU-T X.25 packet level |
· LEV1: | ITU-T X.31 throughput adaptation | |
| LEV2: | ITU-T X.25 level 2 multilink (MLP) |
| LEV3 = | ITU-T X.25 packet level. |
Subscription X.29/Teletel rerouting.
0 = no (default values of synchronous profiles)
1 = reroutable calls.
Reserved.
Reserved.
Subscription to compression
Facility direction
Facility obligatory/optional
Scrambling
Implementation of service with or without negotiation.
| Value | Subscriber | Direction | Obligatory/ Optional | Scrambling | Negotiation |
0, 4, 64, | NO | - | - | - | - |
1 | YES | Network to | Optional | NO | YES |
2 | YES | Subscriber to | Optional | NO | YES |
3 | YES | Bi-directional | Optional | NO | YES |
5 | YES | Network to | Obligatory | NO | YES |
6 | YES | Subscriber to | Obligatory | NO | YES |
7 | YES | Bi-directional | Obligatory | NO | YES |
65 | YES | Network to | Optional | YES | YES |
66 | YES | Subscriber to | Optional | YES | YES |
67 | YES | Bi-directional | Optional | YES | YES |
69 | YES | Network to | Obligatory | YES | YES |
70 | YES | Subscriber to | Obligatory | YES | YES |
71 | YES | Bi-directional | Obligatory | YES | YES |
129, 133 | YES | Network to | - | NO | NO |
130, 134 | YES | Subscriber to | - | NO | NO |
131, 135 | YES | Bi-directional | - | NO | NO |
193, 197 | YES | Network to | - | YES | NO |
194, 198 | YES | Subscriber to | - | YES | NO |
195, 199 | YES | Bi-directional | - | YES | NO |
N = Network
A = Subscriber
Time-out associated with packet grouping.
0 = | service not implemented |
1 to 15 = | value time-out in units of 100 ms. |
Value of supervision time-out for response to a call request packet sent on the link. A clear packet is sent if there is no response after this period.
1 to 250 (unit 10 s).
Call-return authorized.
0 = not authorized
2 = authorized with DNIC.ZO.
Type of access to output line.
0 = multiple access (sending of ringback is line is configured for ringback)
1 = single access (sending of clear even if line is a ringback subscriber).
Supervision of markers.
This parameter specifies the behavior of the FastPad with respect to facility markers. The FastPad accepts all correct incoming markers.
For transmission to the exterior, there are three possibilities.
0 = | transparency: the FastPad transmits facility markers |
1 = | blocking: the FastPad ignores markers received from the exterior, which are therefore not retransmitted |
2 = | filtered: the FastPad filters received markers on the basis of their values and of the protocol elements transmitted (call, call confirmation, or clear). |
| The filtering is as follows: |
Markers  | Network of caller | Network of called party | DTE |
Packets received | 0000 | 00FF | 000F |
Call | Transp. | CLEAR 03.42 | Transp. |
Confirm. Call | CLEAR 03.42 | Transp. | Transp. |
Clear | Irrelevant | Irrelevant | Transp. |
Markers  | Network of caller | Network of called party | DTE |
Packets received  | 0000 | 00FF | 000F |
Call | CLEAR 03.42 | Transp. | Transp. |
Confirm. Call | Transp. | CLEAR 03.42 | Transp. |
Clear | CLEAR 03.42 | CLEAR 03.42 | Transp. |
Notification of change of called address.
This parameter specifies the behavior of the FastPad with respect to the "Called Line Address Modification" (CLAM) facility in the call confirmation packet.
0 = | No consistency check of received call confirmation (presence of facility and existence of called address). The FastPad does not transmit the facility. |
1 = | The facility is transmitted in clear and call confirmations if the clear and call confirmation formats are complete. |
| If not, the FastPad transmits a clear. |
2 = | The facility is not transmitted, but the FastPad checks that the called address is present in the received call confirmation. If not, the FastPad sends a clear. |
3 = | The facility is transmitted in clear and call confirmations if the formats are complete; otherwise, the FastPad transmits a clear. |
| There is a consistency check to the presence of the called address in the call confirmation; a clear is transmitted if it is missing. |
Format of clear transmitted by the FastPad.
In reception, the FastPad accepts all clear packet formats. The format in which it transmits clear packets depends on this configuration parameter.
0 = | Complete X.25 format (address and facility) |
1 = | Reduced X.25 format |
2 = | Reduced format; the clearing to 5 bytes indicate the cause and the diagnostic |
3 = | Complete X.25 format (facilities and addresses + transparency on addresses). |
Management of D bit.
0 = transparent
1 = clearing
2 = management.
Type of line.
0 = X.25 on dedicated line
2 = X.25 on PSTN.
(exceptionally modifiable)
Supervision time-out for transmission of messages sent to an asynchronous terminal.
0 | = no time-out |
1 to 250 | = 1 to 250 seconds. |
Behavior with respect to unknown facilities.
0 = transparent mode (no conversion)
1 = facility filtered
2 = communication released
3 = transparent for reception, filtered for transmission
4 = transparent for reception, cleared for transmission
5 = filtered for reception, transparent when transmission
6 = filtered for reception, cleared when transmission
7 = cleared for reception, transparent for transmission
8 = cleared for reception, filtered for transmission
Mixed flow control.
0 = no
1 = yes.
This parameter manages the address conversion in accordance with the following values:
| 128 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
| 0 | 0 |
|
|
| | | | | | | 0 = no conversion
| | | | | | | 1 = Calling address
| | | | | | | conversion on in-
| | | | | | | coming call
| | | | | | | request into the
| | | | | | | FastPad.
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | 1 = called address coversion
| | | | | | on incoming call request
| | | | | | into the FastPad.
| | | | | |
| | | | | 1 = Calling address conversion on
| | | | | outgoing call request from the FastPad.
| | | | |
| | | | 1 = Called address conversion on outgoing call request
| | | | from the FastPad.
| | | |
| | | 0 = Transparency | on incoming call
| | | 1 = Conversion + | request into the FastPad
| | | Clear* |
| | |
| | 0 = Transparency | on outoing call request
| | 1 = Conversion + | from the FastPad.
| | Clear* |
| |
| 0 = Called address conversion depends on bit 21
| 1 = Called address check and insertion.
* COM cleared if address to be convertedd is not in coversion table.
Step 2 "Calling and Called" address conversion on incoming call with clearing if conversion impossible in C9, R11. Parameter 89 = 19.
Number of permanent virtual circuits.
0 to 29 ; PVCs are configured beginning with LC0.
Number of clusters.
1 to 30 for a "Front end" link.
1 to 8 for a "Remote" link.
0.
Number of polled stations.
1 to 32.
Number of controllers.
1 to 10.
Number of controllers.
See appendix G.
Number of DLCIs.
1 to 32 (value = 1 for HDLC).
Error threshold for the error correction procedure.
1 to 254.
Number of configured SVCs (inter-router connections).
0 to 200.
Position of first PVC in C17.
1 to 250.
Position of first cluster in the class 19.
1 to 100.
Position of first controller in class 19.
1 to 100.
Position of the controller in class 19.
1 to 100.
Position of 1st DLCI in class 17.
1 to 200.
Transmission time-out NACK for the error Correction Procedure.
1 to 254 in step of 100 msec.
Mixed flow control.
0 = yes
1 = no.
Position of first SVC in Class 17.
1 to 250.
(Not significant in synchronous case).
Connection to Hewlett Packard equipment.
0 = standard asynchronous equipment
1 = Hewlett Packard Host computer
2 = Hewlett Packard terminal.
Deletion of a PAD character.
0 = no
1 = a PAD character is eliminated at the end of each frame (exception use).
LMI signalling.
0 = no LMI.
1 = subscriber LMI (FRTE or FRCE).
2 = network LMI (FRCE).
0
Type of LAP.
0 = LAP B
1 = LAP A.
Type of call.
0 = | standard case, PAD or video-PAD |
| mnemonics obligatory preceded by a "." |
| digital call command authorized |
| X.28 command authorized. |
| call data and password for VDX controlled by remote host |
1 = | used for VDX (Minitel) |
| mnemonics optionally preceded by a "." |
| digital call command not authorized. |
| X.28 command not authorized. |
| call data and password for VDX controlled by the server. |
2 = | used for VDX (TELETEL) |
| mnemonics optionally preceded by a "." |
| digital call command authorized. |
| X.28 command not authorized. |
| call data and password for VDX controlled by the server. |
3 = | used for Minitel |
| mnemonics optionally preceded by a "." |
| digital call command not authorized. |
| X.28 command not authorized. |
| call data and password for VDX controlled locally (C7R3). |
Securized VC.
(See Chapter 3.11 on local calls)
Possible values:
0 = | no securized VC. |
| The VCs are considered normal VCs, the equipment does not handle it differently. |
1 = | securized subscriber. |
| All calls transmitted by the subscriber are securized. It is also possible to receive calls from securized subscribers on a securized VC. |
2 = | securization not allowed |
| Securization not allowed for the subscriber. Each attempt to establish a securized VC provokes a 'clear' of the connection. |
3 = | filtered securization. |
| Line to the subscriber: the call is securized in case of reception of a securized call. |
| Line to the network: if the call comes from a subscriber connected to the unit, the securization is ignored; if the call comes from the network, it is cleared. |
0 = | Load | OOS | Signalling | HS | Totalizer | OOS | Compression | OOS |
1 = | Load | INS | Signalling | OOS | Totalizer | OOS | Compression | OOS |
2 = | Load | OOS | Signalling | INS | Totalizer | OOS | Compression | OOS |
3 = | Load | INS | Signalling | INS | Totalizer | OOS | Compression | OOS |
4 = | Load | OOS | Signalling | OOS | Totalizer | INS | Compression | OOS |
5 = | Load | INS | Signalling | OOS | Totalizer | INS | Compression | OOS |
6 = | Load | OOS | Signalling | INS | Totalizer | INS | Compression | OOS |
7 = | Load | INS | Signalling | INS | Totalizer | INS | Compression | OOS |
8 = | Load | OOS | Signalling | OOS | Totalizer | OOS | Compression | INS |
9 = |
| INS | Signalling | OOS | Totalizer | OOS | Compression | INS |
10 = |
| OOS | Signalling | INS | Totalizer | OOS | Compression | INS |
11 = | Load | INS | Signalling | INS | Totalizer | OOS | Compression | INS |
12 = | Load | OOS | Signalling | OOS | Totalizer | INS | Compression | INS |
13 = | Load | INS | Signalling | OOS | Totalizer | INS | Compression | INS |
14 = | Load | OOS | Signalling | INS | Totalizer | INS | Compression | INS |
15 = | Load | INS | Signalling | INS | Totalizer | INS | Compression | INS |
OOS = | Out of service |
|
|
|
|
| ||
INS = | In service |
|
|
|
|
| ||
Activation/deactivation of "load", "signalling", totalizing and compression headings of "Loads statistics" management function.
Possible values:
Sampling time used for the counters of the COMPRESSION heading.
1 to 180 (step of 10 seconds)
Reserved
Acknowledgment of packet 1 for 1.
0 = no
1 = yes.
Reserved.
Echo mask.
0 = The value of the X.3 parameter number ZO of class 13 imposes the echo mask.
Reserved.
This parameter defines whether the line is in full duplex (with echo) or half duplex (without echo).
The echo of a "transfer" mode character is also defined by the X.3 parameter Number 2 in Class 13.
0 = FULL DUPLEX
1 = HALF DUPLEX.
| C12P105 VALUE | C13P2 VALUE | TRANSFER | OTHER |
0 | 0 | Without echo | With echo |
0 | 1 | With echo | With echo |
1 | 0 or 1 | Without echo | Without echo |
This parameter defines the type of character coding (conversion to lower case or not).
0 = ASCII characters, no conversion.
Definition of type of terminal.
127 = Type of terminal defined in classes 12 and 13.
Use of a predetermined type of terminal. The type of terminal may be entered on connection in the form of a mnemonic or predefined.
1 = Type of terminal predefined.
Manual or automatic call.
0 = | Manual connection command. |
1 = | Automatic connection on establishment of physical path between terminal and PAD. |
| The user cannot enter a connection command. |
Automatic hang-up on PSTN line on clearing of the VC. This hang-up results in the "dropping" of interface signals 106, 107 and 109 for 3 seconds. After 3 seconds, the configured interface signals go high in order to be ready to receive another PSTN call.
1 = Automatic hang-up after clearing of VC.
Type of private network management. This parameter specifies the fields that must be backed up (or restored) in (or from) the address extension facility.
| 128 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
| 0 | 0 |
|
|
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Called address
| | | | | | | 0 = no
| | | | | | | 1 = yes
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | Calling address
| | | | | | 0 = no
| | | | | | 1 = yes
| | | | | CUG
| | | | | 0 = no
| | | | | 1 = yes
| | | | NS
| | | NS
| | NS
| NS
NS
The values used are:
0: | no processing |
3: | backup (or restitution) called and calling address |
7: | backup (or restitution) called address, calling address and internal CUG |
15: | backup (or restitution) called address, calling address, internal CUG and RC |
Activation/deactivation of two data forwarding time-outs defined by parameters C12P112 and C13P4.
When the time-outs are activated, the data are sent upon the expiry of one of the two time-outs.
1 = Activation of time-outs.
Type of behavior to be adopted on X.25 fields. It corresponds to a row in C26 "X.25 field modification table".
0 =no behavior
1 to 20 = row in C26 (1 point on parameter 0 in C26, ..., 20 on parameter 19).
Value of data forwarding time-out.
This time-out is activated on reception of the first character. On expiry of the time-out, the PAD sends the received characters to the network. The time-out is restarted upon reception of the first character to follow.
1 to 255 (step of 50 ms).
Reserved.
Activation/deactivation of "padding" parameters:
C13P9: | "padding" after CR |
C13P14: | "padding" after LF |
1 = Activation of "padding".
Defines the X.ON character in the DCE 
DTE direction.
17 = DC1 character.
Defines the X.OFF character in DCE 
DTE direction.
19 = DC3 character.
This parameter defines the element (character or sequence of characters) allowing Changeover from "transfer" mode to "command" mode.
This parameter is taken into account only when the parameter C13P1 = 1.
Otherwise, the escape character is defined by parameter C13P1.
1 = Escape character: (CR) @ (CR).
Defines the behavior of the PAD after execution of a command.
1 = The PAD remains in commands mode.
Defined X.ON character in the DTE 
DCE direction.
17 = DC1 character.
Defined the X.OFF character in the DTE 
DCE direction.
19 = DC3 character.
Activation/deactivation of parameters 1, 13 and 15 of class 13 as well as parameter C12P106.
1 = | Transparent mode. Parameters 1, 13 and 15 of C13 are not taken into account (case of escape, no LF insertion after CR) |
2 = | Virtual terminal mode. Parameters 1, 13 and 15 of C13 are not inhibited. |
Reserved
Consolidation function.
This parameter defines the number of times that the "traffic/configured threshold" comparison must be made before possible "overflow/backup".
0 to 249
255 = no consolidation.
Configuration of lower threshold relative to the line speed declared in P28.
This threshold is used in connection with overflow backup.
0 to 100 (in percentage).
Configuration of upper threshold relative to the line speed declared in P28. This threshold is used in connection with overflow backup.
0 to 100 (in percentage).
DLM functioning mode.
0 = | Passive: | transmission of outstanding events only (no action taken) |
1 = | Active: | transmission of outstanding events and action configured in P130. |
Load calculation integration time-out.
1 to 250 (step of 10 s).
Cost and use of the network.
0 = Direct (case of dedicated line)
1 = Overflow backup (SL case).
Spacing of outstanding load events.
1 to 250 (step of 10 s).
Position of remote equipment in class 22.
This parameter is used mainly for MLP but also for the management of the automatic return of backup and the load changeover.
0 to 250 (see C22).
Backup behavior.
00 = | no |
01 = | backup and automatic return of backup, |
03 = | backup and automatic return of backup in MLP, |
05 = | load changeover and automatic return of backup, |
10 = | load overflow and automatic backup in MLP, |
11 = | load overflow and automatic backup in MLP and automatic return of backup. |
Overflow and changeover must be configured on only one end of the link.
Cannot be applied to a frame-relay PLL.
Maximum number of information packets (LSPDU) that a DAR can store in its data base.
1 to 250.
50
Reserved
Configuration of DAR operation
0 = | Passive DAR (default value) |
1 = | Distribution of inter-DAR topology information without route calculation. |
2 = | Active DAR (distribution and calculation of routes). |
Distribution period for topology information (LSPDU) exchanged between DARs.
1 to 250 (in step of 10 s).
3
Calculation period for routes with shortest path used by the DAR.
In order for the calculation of routes to be carried out with the latest information (LSPDU) coming from all the switches of the domain, it is preferable for the value of P135 to be at least twice as high as the distribution period of the LSPDUs (P134).
1 to 250 (in step of 10 s).
6
Storage time for an LSPDU in the DAR data base.
Whenever the DAR performs a route calculation, it decrements the life assigned to each LSPDU of the data base.
When the value is zero, the LSPDU is cleared from the data base.
1 to 250 (in step of 10 s).
120
Expiration thresholds for LSPDUs exchanged, associated with the life of the LSPDU below which the DAR transmitting the LSPDU must redistribute a new LSPDU in the domain. This mechanism avoids clearing the LSPDU transmitted at low frequencies.
1 to 250 (in step of 10 s).
6
Management on M bit.
3 = M bit is equal to 1 in full packets.
Duration of locking of route calculation following an exception LSPDU.
This mechanism avoids the DAR having to carry out several times the same route calculation following a change in topology.
1 to 250 (in step of 1 s).
2
Reserved.
Flow control by signals.
8 = use of flow control by signals.
The backup mode of the FastPad200Y/FastPad500Y is a service for the user on a subscription basis.
A configuration parameter has to be specified to indicate to the unit that it can be backed up for 12 (C2R2P7 = 2) or 24 (C2R2P7 = 3) lines. Also, outstanding events can be generated for this facility.
This service automatically replaced the configured lines by the backup lines when one of the modules has a hardware failure.
When a switch over is made, the backup lines have the same characteristics as the lines in the normal mode.
Being in the backup mode, return to the normal mode can only be accomplished by the operator.
Therefore he has to execute a "unit reset", a "file transfer" function of OPALE or NMX. It is also possible, with the configuration function, to execute an "ITO" reset (see chapter 2, paragraph 3.4).

For the user there are a total of 12 lines available: 0 up to 5 and 12 up to 17. The 12 backup lines are used when a module has a hardware failure.
| Potential Lines | Lines and module No. | User Lines | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
| 0 | (0) | 0 |
2 |
| 2 | (0) | 2 |
3 |
| 3 | (0) | 3 |
4 |
| 4 | (0) |
|
5 |
| 5 | (0) |
|
6 | backup | 6 | (0) |
|
7 | backup | 7 | (0) |
|
8 | backup | 8 | (0) |
|
9 | backup | 9 | (0) |
|
10 | backup | 10 | (0) |
|
11 | backup | 11 | (0) |
|
12 |
| 0 | (1) | 12 |
13 |
| 1 | (1) | 13 |
14 |
| 2 | (1) | 14 |
15 |
| 3 | (1) | 15 |
16 |
| 4 | (1) | 16 |
17 |
| 5 | (1) | 17 |
18 | backup | 6 | (1) |
|
19 | backup | 7 | (1) |
|
20 | backup | 8 | (1) |
|
21 | backup | 9 | (1) |
|
22 | backup | 10 | (1) |
|
23 | backup | 11 | (1) |
|
When a module has a hardware failure, the 6 user lines of the module to be "backed up", are interrupted for a moment and then replaced by the lines of the "backup" module.
Example: module 1 has a failure:
| Potential Lines | Lines and module No. | User Lines | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
| 0 | (0) | 0 |
2 |
| 2 | (0) | 2 |
3 |
| 3 | (0) | 3 |
4 |
| 4 | (0) | 4 |
5 |
| 5 | (0) | 5 |
6 |
| 6 | (0) | 12 |
7 |
| 7 | (0) | 13 |
8 |
| 8 | (0) | 14 |
9 |
| 9 | (0) | 15 |
10 |
| 10 | (0) | 16 |
11 |
| 11 | (0) | 17 |
12 | out of order | 0 | (1) |
|
13 | out of order | 1 | (1) |
|
14 | out of order | 2 | (1) |
|
15 | out of order | 3 | (1) |
|
16 | out of order | 4 | (1) |
|
17 | out of order | 5 | (1) |
|
18 | out of order | 6 | (1) |
|
19 | out of order | 7 | (1) |
|
20 | out of order | 8 | (1) |
|
21 | out of order | 9 | (1) |
|
22 | out of order | 10 | (1) |
|
23 | out of order | 11 | (1) |
|
 ne Example
ne Example
For the user there are a total of 24 lines available: 0 up to 5, 12 up to 17 and 24 up to 35. The backup lines are used when one (and only one) module has a hardware failure.
Example: Module 2 has a failure
| Potential Lines | Lines and module No. | User Lines | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
| 0 | (0) | 0 |
2 |
| 2 | (0) | 2 |
3 |
| 3 | (0) | 3 |
4 |
| 4 | (0) | 4 |
5 |
| 5 | (0) | 5 |
6 | backup | 6 | (0) |
|
7 | backup | 7 | (0) |
|
8 | backup | 8 | (0) |
|
9 | backup | 9 | (0) |
|
10 | backup | 10 | (0) |
|
11 | backup | 11 | (0) |
|
12 |
| 0 | (1) | 12 |
13 |
| 1 | (1) | 13 |
14 |
| 2 | (1) | 14 |
15 |
| 3 | (1) | 15 |
16 |
| 4 | (1) | 16 |
17 |
| 5 | (1) | 17 |
18 | backup | 6 | (1) |
|
19 | backup | 7 | (1) |
|
20 | backup | 8 | (1) |
|
21 | backup | 9 | (1) |
|
22 | backup | 10 | (1) |
|
23 | backup | 11 | (1) |
|
24 |
| 0 | (2) | 24 |
25 |
| 1 | (2) | 25 |
26 |
| 2 | (2) | 26 |
27 |
| 3 | (2) | 27 |
28 |
| 4 | (2) | 28 |
29 |
| 5 | (2) | 29 |
30 |
| 6 | (2) | 30 |
31 |
| 7 | (2) | 31 |
32 |
| 8 | (2) | 32 |
33 |
| 9 | (2) | 33 |
34 |
| 10 | (2) | 34 |
35 |
| 11 | (2) | 35 |
When a module has a hardware failure, the 6 or 12 user lines of the module to be "backed up", are interrupted for a moment and then replaced by the 6 or 12 lines of the "backup" module.
| Potential Lines | Lines and module No. | User Lines | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
| 0 | (0) | 0 |
2 |
| 2 | (0) | 2 |
3 |
| 3 | (0) | 3 |
4 |
| 4 | (0) | 4 |
5 |
| 5 | (0) | 5 |
6 |
| 6 | (0) | 12 |
7 |
| 7 | (0) | 13 |
8 |
| 8 | (0) | 14 |
9 |
| 9 | (0) | 15 |
10 |
| 10 | (0) | 16 |
11 |
| 11 | (0) | 17 |
12 |
| 0 | (1) | 24 |
13 |
| 1 | (1) | 25 |
14 |
| 2 | (1) | 26 |
15 |
| 3 | (1) | 27 |
16 |
| 4 | (1) | 28 |
17 |
| 5 | (1) | 29 |
18 |
| 6 | (1) | 30 |
19 |
| 7 | (1) | 31 |
20 |
| 8 | (1) | 32 |
21 |
| 9 | (1) | 33 |
22 |
| 10 | (1) | 34 |
23 |
| 11 | (1) | 35 |
24 | out of order | 0 | (2) |
|
25 | out of order | 1 | (2) |
|
26 | out of order | 2 | (2) |
|
27 | out of order | 3 | (2) |
|
28 | out of order | 4 | (2) |
|
29 | out of order | 5 | (2) |
|
30 | out of order | 6 | (2) |
|
31 | out of order | 7 | (2) |
|
32 | out of order | 8 | (2) |
|
33 | out of order | 9 | (2) |
|
34 | out of order | 10 | (2) |
|
35 | out of order | 11 | (2) |
|
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Thu Jan 25 13:50:55 PST 2001
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2001 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.