|
|

This chapter contains the following information about cable Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification (DOCSIS) 1.0 service identifier (SID) to MPLS VPN integration:
Figure 4-1 shows the topology associated with a VPN-capable service provider's MPLS backbone. In this scenario, you should assume that the customer has outsourced all remote access operations to its service provider.
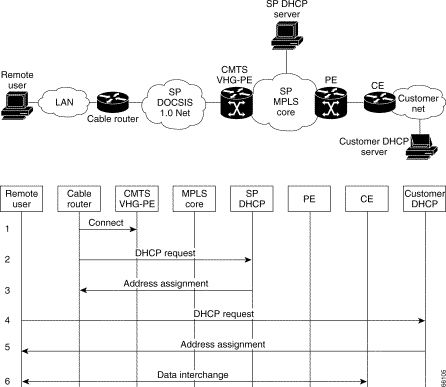
In DOCSIS 1.0, all traffic from a given cable router (or cable modem) carries the same service identifier (SID). On the Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS) virtual home gateway (VHG)/ provider edge router (PE), all traffic with the same SID value terminates on the same subinterface. At the CMTS VHG/PE, the subinterface is statically configured to map all traffic to a specific VPN Routing and Forwarding (VRF) instance. As a result, traffic from all customer premises equipment (CPE) behind a given cable router is mapped to the same VPN. There is no remote user authorization and authentication in this architecture. Address assignment is based on Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
For tips and reminders on using the command- line interface (CLI) for viewing the different debug outputs shown throughout this chapter, refer to "Initiating and Viewing Command Output" section.
This section describes the following debugging topics:
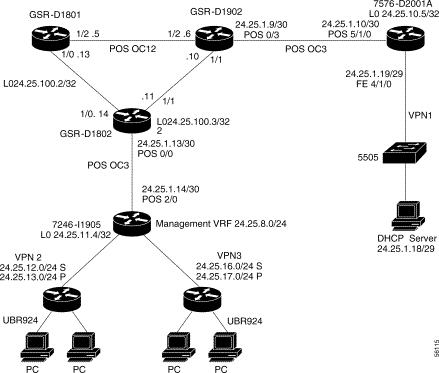
The information in this section uses the sample network in Figure 4-2.
 |
Note The troubleshooting steps in this section assume that a management and provisioning VRF has been configured and that the cable modem DHCP server is connected to the management VRF. In the example network in Figure 4-2 and configured as described in the "Troubleshooting Cisco uBR7200 VHG/PE Routers" section, a single Cisco Network Registrar (CNR) DHCP server provides IP addresses to both cable modems and hosts. |
Once MPLS is successfully configured, the cable modems and subscriber PCs should function as described in the following sections:
When properly configured, the cable modems (CMs) interact with the CMTS subinterfaces as follows:
When using secondary addresses on each ISP's subinterface, PC IP address acquisition should behave as follows:
Cable modem DHCP renewal requires that the CM have continued access to the Multiservice Operator's (MSO's) CNR server.
However, in certain failure situations (for example, partial network outages) the CM may not be able to receive a DHCP renewal. If this is the case, DOCSIS cable modems reinitalize and the complete initialization process begins again with only minor interruption of service.
As soon as a CMTS receives a DHCP response for a cable modem's request, it associates that cable modem with the corresponding subinterface. The DHCP process does not need to fully complete for this to occur. If the DHCP process does not fully complete, the cable modem rebroadcasts a DHCP request. The GIADDR field of the request is set to the IP address of the CMTS subinterface that provides the routing function for the cable modem's assigned IP address, not the IP address of the first logical cable subinterface.
For information on troubleshooting uBR cable modems, see the tech note at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/warp/customer/109/troubleshooting_cm_online.html
This tech note discusses the different states that cable modems (CMs) go through before coming online and establishing IP connectivity. The tech note highlights the most commonly used Cisco IOS troubleshooting commands to verify what state the CM is in and the reasons that can cause the modem to arrive at that state. This is illustrated by debug and show commands at both the Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS) and the CM. The tech note also discusses some of steps that can be taken to arrive at the correct status, online.
The troubleshooting steps in this section use the sample network in Figure 4-2. Routers 7246-I1904 and 7576-D2001A function as provider edge (PE) routers. The CNR DHCP server is connected to an interface in VPN1. The configurations of the PE routers are described below.
Current configuration:
!
version 12.1
service timestamps debug uptime
service timestamps log uptime
no service password-encryption
!
hostname 7246-I1905
!
no cable qos permission update
cable qos permission modems
cable time-server
ip subnet-zero
ip cef
no ip finger
no ip domain-lookup
!
!
ip vrf vpn1
rd 100:1
route-target export 100:1
route-target import 100:1
route-target import 1000:1000
!
ip vrf vpn2
rd 200:1
route-target export 1000:1000
route-target export 200:1
route-target import 200:1
route-target import 100:1
!
ip vrf vpn3
rd 300:1
route-target export 300:1
route-target export 1000:1000
route-target import 100:1
route-target import 300:1
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 24.25.11.4 255.255.255.255
!
!
interface POS2/0
ip address 24.25.1.14 255.255.255.252
ip route-cache flow
load-interval 30
tag-switching ip
clock source internal
!
interface Cable3/0
no ip address
ip route-cache flow
load-interval 30
no keepalive
cable downstream rate-limit token-bucket shaping
cable downstream annex B
cable downstream modulation 64qam
cable downstream interleave-depth 32
cable downstream frequency 583000000
cable upstream 0 frequency 37008000
cable upstream 0 power-level -10
no cable upstream 0 shutdown
cable upstream 1 shutdown
cable upstream 2 shutdown
cable upstream 3 shutdown
cable dhcp-giaddr policy
cable privacy mandatory
cable privacy kek life-time 3600
cable privacy tek life-time 3600
!
interface Cable3/0.1
description ****** Provisioning and Management *****
ip vrf forwarding vpn1
ip address 24.25.8.1 255.255.255.0
cable dhcp-giaddr policy
cable helper-address 24.25.1.18
!
interface Cable3/0.2
description *****VPN2 Cable Modem and Users Subnet****
ip vrf forwarding vpn2
ip address 24.25.12.1 255.255.255.0 secondary
ip address 24.25.13.1 255.255.255.0
cable dhcp-giaddr policy
cable helper-address 24.25.1.18
!
interface Cable3/0.3
description ***** VPN3 Cable Modem and Users Subnet ********
ip vrf forwarding vpn3
ip address 24.25.16.1 255.255.255.0 secondary
ip address 24.25.17.1 255.255.255.0
cable dhcp-giaddr policy
cable helper-address 24.25.1.18
!
router ospf 1
log-adjacency-changes
network 24.25.1.14 0.0.0.0 area 0
!
router bgp 200
no synchronization
bgp log-neighbor-changes
bgp scan-time 5
neighbor 24.25.10.4 remote-as 200
neighbor 24.25.10.4 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 24.25.10.5 remote-as 200
neighbor 24.25.10.5 update-source Loopback0
!
address-family ipv4 vrf vpn3
no auto-summary
no synchronization
network 24.25.16.0 mask 255.255.255.0
network 24.25.17.0 mask 255.255.255.0
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv4 vrf vpn2
no auto-summary
no synchronization
network 24.25.12.0 mask 255.255.255.0
network 24.25.13.0 mask 255.255.255.0
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv4 vrf vpn1
no auto-summary
no synchronization
network 24.25.8.0 mask 255.255.255.0
exit-address-family
!
address-family vpnv4
neighbor 24.25.10.5 activate
neighbor 24.25.10.5 send-community extended
bgp scan-time 15
bgp scan-time import 5
exit-address-family
!
ip classless
version 12.1
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log uptime
no service password-encryption
service compress-config
no service dhcp
!
hostname 7576-D2001A
!
no logging console
ip subnet-zero
no ip domain-lookup
!
!
!
ip vrf vpn1
rd 100:1
route-target export 100:1
route-target import 100:1
route-target import 1000:1000
!
ip vrf vpn2
rd 200:1
route-target export 1000:1000
route-target export 200:1
route-target import 200:1
route-target import 100:1
ip vrf vpn3
rd:300:1
route-target export 300:1
route-target export 1000:1000
route-target import 100:1
route-target import 300:1
ip cef
cns event-service server
!
!
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 24.25.10.5 255.255.255.255
!
interface FastEthernet4/1/0
description *** Provisioning and Management, CNR Server Attached***
ip vrf forwarding vpn1
ip address 24.25.1.17 255.255.255.248
no ip route-cache distributed
half-duplex
!
interface POS5/1/0
ip address 24.25.1.10 255.255.255.252
no ip route-cache distributed
tag-switching ip
crc 32
clock source internal
no cdp enable
!
router ospf 1
log-adjacency-changes
redistribute static metric 10 subnets
network 24.25.1.10 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 24.25.10.5 0.0.0.0 area 0
!
router bgp 200
no synchronization
bgp scan-time 5
neighbor 24.25.10.4 remote-as 200
neighbor 24.25.10.4 update-source Loopback0
no auto-summary
!
address-family ipv4 vrf vpn2
no auto-summary
no synchronization
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv4 vrf vpn1
redistribute connected route-map 1_to_world
no auto-summary
no synchronization
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv4 vrf forwarding
no auto-summary
no synchronization
exit-address-family
!
address-family vpnv4
neighbor 24.25.10.4 activate
neighbor 24.25.10.4 send-community extended
neighbor 24.25.11.4 activate
neighbor 24.25.11.4 send-community extended
no auto-summary
bgp scan-time 5
bgp scan-time import 5
exit-address-family
!
ip classless
no ip http server
!
access-list 40 permit 24.25.1.16 0.0.0.7
route-map 1_to_world permit 10
match ip address 40
!
!
end
In this configuration, the first cable subinterface is in a management VPN. Management VPN routes are exported to all other VPNs and the management VPN imports routes from all other VPNs. The CNR DHCP server provides IP addresses for all cable modems and hosts.
Ensure that the users' VPNs have routes to the DHCP server and that the management VRF on the PE that is connected to the DHCP server has a route to all cable modem and user subnets.
On router 7246-I1905:
7246-I1905# show ip route vrf vpn2
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set:
24.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 2 masks
B 24.25.8.0/24 is directly connected, 1d18h, Cable3/0.1
C 24.25.13.0/24 is directly connected, Cable3/0.2
C 24.25.12.0/24 is directly connected, Cable3/0.2
B 24.25.1.16/29 [200/0] via 24.25.10.5, 1d19h <<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<
On router 7576-D2001A:
7576-D2001A# show ip route vrf vpn1
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set:
24.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 11 subnets, 2 masks
B 24.25.3.0/24 [200/0] via 24.25.10.4, 1d19h
B 24.25.2.0/24 [200/0] via 24.25.10.4, 1d19h
B 24.25.4.0/24 [200/0] via 24.25.10.4, 00:00:58
B 24.25.7.0/24 [200/0] via 24.25.10.4, 1d19h
B 24.25.6.0/24 [200/0] via 24.25.10.4, 1d19h
B 24.25.8.0/24 [200/0] via 24.25.11.4, 1d18h
B 24.25.13.0/24 [200/0] via 24.25.11.4, 1d18h<<<<<<<<<<<<<
B 24.25.12.0/24 [200/0] via 24.25.11.4, 1d18h<<<<<<<<<<<<<
B 24.25.17.0/24 [200/0] via 24.25.11.4, 1d18h<<<<<<<<<<<<<
B 24.25.16.0/24 [200/0] via 24.25.11.4, 1d18h<<<<<<<<<<<<
C 24.25.1.16/29 is directly connected, FastEthernet4/1/0
B 24.25.16.0/24 [200/0] via 24.25.11.4, 1d18h
If the routing tables are not correct, check that the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) neighbor relationship is established between the two routers. Ensure that the route export and import rules are correct. If using import or export maps, ensure they are correct.
The debug ip bgp vpnv4 import command can be invoked and the neighbor relationship cleared.
 |
Caution Always send debug command output to the log file and not to the console. Clearing a BGP neighbor relationship may have detrimental effects on your network. Use with caution and preferably in a lab environment. |
*Mar 11 08:50:40.803: vpn: 300:1:24.25.6.0 (ver 18), imported as:
*Mar 11 08:50:40.803: vpn: 100:1:24.25.6.0 (ver 22)
*Mar 11 08:50:40.803: vpn: Start import processing for: 300:1:24.25.7.0
*Mar 11 08:50:40.803: vpn: Import check for vpn1; flags mtch
*Mar 11 08:50:40.803: vpn: Import for vpn1 permitted; import flags mtch
*Mar 11 08:50:40.803: BGP: Prefix 300:1:24.25.7.0/24 to be imported as 100:1:24.
25.7.0/24 -- Permitted
nexthop 24.25.10.4, origin i, localpref 100, metric 0, extended community RT:300
:1 RT:1000:1000
Once the respective routing tables are correct, use an extended ping command to confirm that there is connectivity between the VPN subinterfaces and the relative DHCP servers. In this example, connectivity between router 7246-I1905 VPN2's host subnet and the DHCP server is confirmed.
7246-I1905# ping vrf vpn2
Protocol [ip]:
Target IP address: 24.25.1.18
Repeat count [5]: 10
Datagram size [100]: 1500
Timeout in seconds [2]:
Extended commands [n]: y
Source address or interface: 24.25.12.1
Type of service [0]:
Set DF bit in IP header? [no]:
Validate reply data? [no]:
Data pattern [0xABCD]:
Loose, Strict, Record, Timestamp, Verbose[none]:
Sweep range of sizes [n]:
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 10, 1500-byte ICMP Echos to 24.25.1.18, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (10/10), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/3/4 ms
If the pings are not successful, check the CEF forwarding table for the remote route:
7246-I1905# show ip cef vrf vpn2 24.25.1.18 detail
24.25.1.16/29, version 1286, cached adjacency to POS2/0
0 packets, 0 bytes
Flow: AS 0, mask 29
tag information set
local tag: VPN-route-head
fast tag rewrite with PO2/0, point2point, tags imposed: {55 45}
via 24.25.10.5, 0 dependencies, recursive
next hop 24.25.1.13, POS2/0 via 24.25.10.5/32
valid cached adjacency
tag rewrite with PO2/0, point2point, tags imposed: {55 45}
7246-I1905#
Note the tags imposed field. The first tag is the tag used to reach the BGP next hop, in this case the loopback interface of router 7576-D2001A. The second tag is the tag advertised to this PE by the remote PE router.
Ensure that the first tag is the correct tag used to reach the BGP next hop. If the outgoing tag is incorrect, the BGP relationship between the two devices should not be established.
7246-I1905# show tag forwarding 24.25.10.5 255.255.255.255
Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes tag Outgoing Next Hop
tag tag or VC or Tunnel Id switched interface
63 55 24.25.10.5/32 0 PO2/0 point2point
7246-I1905#
Ensure that the BGP table matches the tag displayed by the CEF table. If they are different, record the information and then try clearing the route. Open a case with the Cisco TAC; for more information, see "Obtaining Technical Assistance" in the Preface.
7246-I1905# show ip bgp vpnv4 vrf vpn2 tags
Network Next Hop In tag/Out tag
Route Distinguisher: 200:1 (vpn2)
24.25.1.16/29 24.25.10.5 notag/45
On the remote PE router, ensure that the tag it advertises to the local PE matches what the local PE displays. The in tag is the one we are concerned about.
7576-D2001A# show ip bgp vpnv4 vrf vpn1 tags
Network Next Hop In tag/Out tag
Route Distinguisher: 100:1 (vpn1)
24.25.1.16/29 0.0.0.0 45/aggregate(vpn1)
If the tags are different, open a case with the Cisco TAC; for more information, see "Obtaining Technical Assistance" in the Preface.
If there is network connectivity between the cable subinterfaces and the DHCP server, the next step is to ensure that the DHCP requests are forwarded to the DHCP servers. In a typical setup, the command cable dhcp-giaddr policy is placed on the cable subinterface. This is followed by one or more cable helper addresses. If the keyword modem follows the cable helper command, the DHCP requests from modems are sent to the listed DHCP server. If the keyword host is used, the DHCP requests from the devices attached to the cable modem DHCP requests are forwarded to the listed DHCP server. If neither keyword is used, then all DHCP requests are forwarded to the listed server.
If the show cable modem command indicates the cable modem hangs in the init(d) state, this indicates that the cable modem is not getting an answer to its DHCP request.
The initial DHCP request from a modem has its GIADDR field set to the IP address of the first logical cable subinterface. After the initial reply is received from the DHCP server, the CMTS sets the GIADDR to the IP address of the cable subinterface that is to provide routing for the cable modem.
Use the commands debug ip dhcp server packet, debug ip udp, and debug ip packet detail access-list, where the access-list allows all packets to and from the DHCP server to be recorded. Ensure that debug command output is sent to the log only by executing the no logging console command.
The debug commands below show that the initial DHCP discover packet GIADDR field is set to the IP address of the first cable subinterface (24.25.8.1). After the router forwards the initial offer, the GIADDR field of subsequent packets is set to the IP address of the router interface that provides routing for the cable modem.
7246-I1905# show access-list 150
Extended IP access list 150
permit udp any host 24.25.1.18
permit udp host 24.25.1.18 any
7246-I1905# debug ip packet detail 150
IP packet debugging is on (detailed) for access list 150
7246-I1905# debug ip udp
UDP packet debugging is on
7246-I1905# debug ip dhcp server packet
00:06:09: BOOTP: opcode 1 on interface Cable3/0.1, 0 secs, 0 hops
00:06:09: DHCPD: setting giaddr to 24.25.8.1.
00:06:09: UDP: sent src=24.25.8.1(67), dst=24.25.1.18(67), length=604
00:06:09: datagramsize=576, IP 0: s=24.25.8.1 (local), d=24.25.1.18, totlen 604,
fragment 0, fo 0, cef process switched
00:06:09: UDP src=67, dst=67
00:06:09: datagramsize=576, IP 0: s=24.25.8.1 (local), d=24.25.1.18, totlen 604,
fragment 0, fo 0, cef process switched
00:06:09: UDP src=67, dst=67
00:06:09: DHCPD: BOOTREQUEST from 0100.3080.ea8e.53 forwarded to 24.25.1.18.
00:06:09: UDP: rcvd src=24.25.1.18(67), dst=24.25.8.1(67), length=308
00:06:09: DHCPD: forwarding BOOTREPLY to client 0030.80ea.8e53.
00:06:09: DHCPD: broadcasting BOOTREPLY to client 0030.80ea.8e53.
00:06:09: UDP: sent src=0.0.0.0(67), dst=255.255.255.255(68), length=328
00:06:09: UDP: rcvd src=0.0.0.0(68), dst=255.255.255.255(67), length=584
00:06:09: BOOTP: opcode 1 on interface Cable3/0.3, 0 secs, 0 hops
00:06:09: DHCPD: setting giaddr to 24.25.17.1.
00:06:09: UDP: sent src=24.25.17.1(67), dst=24.25.1.18(67), length=604
00:06:09: datagramsize=576, IP 2: s=24.25.17.1 (local), d=24.25.1.18, totlen 604
, fragment 0, fo 0, cef process switched
00:06:09: UDP src=67, dst=67
00:06:09: datagramsize=576, IP 2: s=24.25.17.1 (local), d=24.25.1.18, totlen 604
, fragment 0, fo 0, cef process switched
00:06:10: UDP src=67, dst=67
00:06:10: UDP: rcvd src=24.25.1.18(67), dst=24.25.17.1(67), length=308
00:06:10: DHCPD: forwarding BOOTREPLY to client 0030.80ea.8e53.
00:06:10: DHCPD: broadcasting BOOTREPLY to client 0030.80ea.8e53.
00:06:10: UDP: sent src=0.0.0.0(67), dst=255.255.255.255(68), length=328
Ensure that the DHCP request is forwarded to the correct server IP address and that an answer is forwarded to the cable modem. If no answer is received or the answer is received and forwarded but the cable modem still stays in the init(d) state, troubleshoot the CNR DHCP server.
Typically the CNR server is configured to use client class processing for cable modem DHCP requests. The client's MAC address is placed into a client class that has a scope selection tag defined. The selection tag matches those assigned to the desired scope. Since the initial DHCP request for all cable modems arrives with the GIADDR field set to the IP address of the first logical cable subinterface, secondary scopes must be used. A typical configuration is to have a scope whose IP address range includes the first logical cable subinterface configured as a primary scope. The actual IP addresses to be assigned to the cable modems are contained within scopes that are secondary to the first scope. The correct secondary scope is selected because it has scope selection tags that match the ones defined by the client class.
When the initial DHCP discover arrives, the primary scope is selected based on the GIADDR. The primary scope can be configured with only a single IP address and this IP address could be reserved to a bogus MAC address. The CNR server then uses client class processing to select the desired scope that is a secondary to this primary.
To eliminate the need to configure each and every MAC address into a client class, you can define a default client class. The MAC address contained within the client class would be the default. This MAC address matches all MAC addresses that are not defined in another client class. Attach a scope selection tag to this client class and to all scopes that can provide IP addresses to clients (both cable modem and end user hosts) whose MAC addresses are not listed in client classes.
The first step in troubleshooting CNR problems is to ensure that the DHCP request is getting to the CNR server and that the GIADDR field of the request is as expected.
$ cd /opt/nwreg2/usrbin
$ ./nrcmd -s
100 Ok
session:
cluster = localhost
default-format = user
user-name = admin
visibility = 5
nrcmd> server dhcp setDebug 10
100 Ok
nrcmd>
03/11/2001 13:39:57 name/dhcp/1 Activity Server 0 04619 Server received a DHCPDI
SCOVER packet 'R49173' from: CID: 01:00:30:80:ea:8e:53 via: Gateway 24.25.8.1,
1 in use.
03/11/2001 13:39:57 name/dhcp/1 Info Configuration 0 04630 The server could not
return option 'merit-dump', which a client requested.
03/11/2001 13:39:57 name/dhcp/1 Info Configuration 0 04630 The server could not
return option 'host-name', which a client requested.
03/11/2001 13:39:57 name/dhcp/1 Info Configuration 0 04630 The server could not
return option 'boot-file', which a client requested.
03/11/2001 13:39:57 name/dhcp/1 Info Configuration 0 04630 The server could not
return option 'log-servers', which a client requested.
03/11/2001 13:39:57 name/dhcp/1 Info Configuration 0 04630 The server could not
return option 'domain-name', which a client requested.
03/11/2001 13:39:57 name/dhcp/1 Info Configuration 0 04630 The server could not
return option 'domain-name-servers', which a client requested.
03/11/2001 13:39:57 name/dhcp/1 Info Configuration 0 04630 The server could not
return option 'mcns-security-server', which a client requested.
03/11/2001 13:39:57 name/dhcp/1 Activity Protocol 0 04993 24.25.17.101 Lease off
ered to CID: 01:00:30:80:ea:8e:53 packet 'R49173' until Sun, 11 Mar 2001 13:41
:57 -0500. 4 ms.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Sun Sep 29 17:40:09 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.