|
|

This chapter tells how to use the Cisco ICS System Manager initial configuration program (also referred to as ICSConfig) to complete the initial software configuration on the Cisco Integrated Communications System 7750 (Cisco ICS 7750), and how to complete the hardware installation. The chapter is organized as follows:
To configure the system for use, you run ICSConfig, a web-browser-based program that prompts you to enter IP address and other network information. The Cisco ICS 7750 uses this information to send data and voice information over the local network, over the WAN, and to the public switched telephone network (PSTN). When the initial configuration program is complete, you can use the System Manager software to configure and manage the system or to access additional applications such as Cisco CallManager or Cisco Unity Voice Mail.
 |
Caution To enable the initial configuration program to run correctly, the Cisco ICS 7750 must not be connected to the Ethernet network. Do not remove the sticker covering the Ethernet ports on the SSP card until you are directed to do so.You will connect the Ethernet 10/100 ports on the SSP to the Ethernet 10/100 ports on the external Catalyst 3524-PWR XL switches after you run the initial configuration program. |
 |
Note Tasks that can be completed using the ICSConfig application or the System Manager should be done using those applications, not the Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI). For more information about when to use ICSConfig or System Manager and when to use the CLI, see the section "Best Practices When Using the IOS CLI" in the Cisco ICS 7750 Administration and Troubleshooting Guide. |
Perform the following tasks before you launch the initial configuration program (ICSConfig):
Collect the information to complete Table 4-1 before you run the initial configuration program. The initial configuration program prompts you to enter this information during the setup process.
Make sure that the PC that you use to run the initial configuration program and System Manager meets the requirements listed in the "PC Requirements" section.
Before connecting your PC to the Cisco ICS 7750, your PC must have an IP address in the same IP subnet as the Cisco ICS 7750. Complete the following steps to change the IP address on your PC.
 |
Note You will need to return your PC to its original configuration after the Cisco ICS 7750 has been configured. We recommend that you write down your PC IP address settings before changing them. |
Step 2 Choose Properties.
Step 3 Click the Protocols tab (Windows NT), or right-click Local Area Connection and choose Properties (Windows 2000).
Step 4 Choose TCP/IP Protocol (Windows NT) or Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) (Windows 2000).
Step 5 Click Properties.
Step 6 Click the Specify an IP address radio button (Windows NT) or the Use the following IP address radio button (Windows 2000).
Step 7 In the IP Address field, enter a unique (unused) IP address, such as 10.0.0.250. (By default, system cards are assigned IP addresses in the range beginning with 10.0.0.1 and ending with 10.0.0.127.)
This IP address must meet the following requirements:
Step 8 In the Subnet Mask field, enter 255.255.255.0.
Step 9 Click OK.
Step 10 If a message appears which indicates that your PC must be rebooted to apply the changes, click Yes.
To use the web-browser-based configuration program (ICSConfig), configure your web browser as follows.
 |
Note To access the ICS System Manager, your browser must be configured as described. If you reconfigure your browser for a different application, you must configure the browser as described in "Netscape Communicator 4.7" or "Internet Explorer 5.01" before you can use the System Manager. Netscape Communicator version 4.7 and Internet Explorer version 5.01 are the only supported browsers. |
If you are using Netscape Communicator 4.7 on your PC, follow these steps to configure it to work with System Manager:
Step 2 Choose Edit > Preferences.
Step 3 In the Preferences window, click Advanced.
Step 4 Check the Enable Java, Enable JavaScript, and Enable Style Sheets check boxes.
Step 5 From the Advanced drop-down list, choose Cache.
Step 6 Under Document in Cache Is Compared to Document on Network, choose Every time.
Step 7 Click OK.
If you are using Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.01 on your PC, follow these steps to configure it to work with System Manager.
 |
Note During the installation of this browser, check the Install Minimal or Customize Your Browser check box. In the Component Options window in the Internet Explorer 5 section, check the Microsoft Virtual Machine check box to display applets written in Java. |
Step 2 Choose Tools > Internet Options.
Step 3 In the Internet Options window, click the Advanced tab.
a. Under Microsoft VM, check the Java logging enabled and JIT compiler for virtual machine enabled check boxes.
If you do not see this section, you need to reinstall the browser and follow the instructions in the note at the beginning of this section.
Step 4 In the Internet Options window, click the General tab.
a. In the Temporary Internet Files section, click Settings.
b. In the Settings window, choose Every visit to the page, and click OK.
Step 5 In the Internet Options window, click the Security tab.
a. Click the Trusted Sites icon, and click Sites.
Step 6 While still in the Security tab of the Internet Options window, click Custom Level.
If you do not see this section, you need to reinstall the browser and follow the instructions in the note at the beginning of this section.
Step 7 In the Trusted Sites window, click the Edit Permissions tab.
Step 8 In the Security Settings window, click OK.
Step 9 In the Internet Options window, click the Content tab.
a. In the Personal Information section, click AutoComplete.
b. In the Use AutoComplete For section, uncheck the User Names and Passwords on Forms check box.
Step 10 In the Internet Options window, click OK.
If Microsoft Terminal Services Client is not installed on your PC, complete the following steps:
Step 2 In the Location or Address field, enter the following URL:
Step 3 Follow the instructions to download and install Microsoft Terminal Services Client.
Peel back the sticker from one of the Ethernet 10/100 ports (labeled 1x and 2x) on the SSP card, and use a straight-through Ethernet cable (yellow) to connect the SSP 1x or 2x port to your PC Ethernet NIC.
Step 2 Enter the following command to verify communication with the SPE310:
If ping is successful (a connection is established), you will see output similar to the following:
The following messages mean that you have no connection:
If you are not able to make a connection with the SPE310, verify the following:
Repeat the steps in the "Verifying That Your PC Can Communicate with the Cisco ICS 7750" section. If ping is still unsuccessful, you do not have a connection with the Cisco ICS 7750. Contact your technical support representative for assistance.
To begin configuring the system, follow these steps:
Step 2 In the Location or Address field, enter the following URL:
You are prompted for a user ID and password.
Step 3 In the User ID field, enter administrator.
Step 4 In the Password field, enter changeme.
Step 5 Click OK.
The browser displays the software license agreement.
 |
Note If you are using a version of Internet Explorer later than version 5.01 or a version of Netscape Communicator later than version 4.7, you will receive a warning. Click Continue to run Cisco ICS 7700 System Manager to bypass this screen and view the license agreement. |
Step 6 Read and accept the license agreement that appears on your screen.
The User Consent to Availability Monitoring page appears, as described in the "User Consent to Availability Monitoring Page" section.
For Cisco to improve the hardware and software performance of the Cisco ICS 7750, the System Manager software can be configured to anonymously send e-mail information to Cisco about certain availability and reliability system events. The User Consent to Availability Monitoring page is shown in Figure 4-1.
This page describes availability monitoring, which you can enable or disable. After you read the feature description, select whether or not to accept the automatic monitoring, and click Continue>> to begin the initial configuration process. (If you do not enable availability monitoring now, you can enable it later by using the Event Manager component of System Manager.)
 |
Note After you click Continue>>, the configuration program begins a discovery process to determine which system cards are present in your Cisco ICS 7750. This might take several minutes. |
Use the configuration wizard to configure the default settings of your system. Enter the information you collected in Table 4-1 in the "Collecting Required Information for the Initial Configuration Program" section. The configuration wizard takes you through the following tasks:
The Network Configuration—System Cards page, shown in Figure 4-2, collects IP address information for the system cards installed in your Cisco ICS 7750. Table 4-2 describes the Network Configuration—System Cards page fields.
In addition to the fields listed in Table 4-2, the Network Configuration—System Cards page displays a list of all the system cards installed in your Cisco ICS 7750. This table is initially populated with the IP addresses discovered for the system cards. You can change the start and end ranges, but the table values must remain consistent. Each card IP address must be unique and must fall within the range between the start and end IP addresses.
The Network Configuration—IP Device Addresses page, shown in Figure 4-3, collects IP address and directory information for your IP phones. The page also collects IP address information for the other IP devices on your network. Table 4-3 describes the Network Configuration—IP Device Addresses page fields.
The Network Configuration—DNS and Gateway page, shown in Figure 4-4, collects DNS and default gateway information that you enter for your network. Table 4-4 describes the Network Configuration page fields.
The Security Setup for IOS-Based Cards page, shown in Figure 4-5, collects password information that you enter for access to IOS-based cards (the SSP, MRPs, and ASIs) and to the SAP card.
See the "Password Rules" section for password guidelines and descriptions.
Assign the enable and read-only passwords according to the following rules:
Fields on the Security Setup for IOS-based Cards page are described as follows:
Enter and reenter a new password to change the login password from the default password, which is changeme.
The login password is used to log in to any IOS-based card. You cannot use this password to change the configuration of an IOS-based card. It is used as the console and vty password for IOS-based cards.
Enter and reenter a new password to change the enable password from the default password, which is changeme.
The enable password is used to change the configuration of an IOS-based card or the SAP. This password cannot be the keyword level.
 |
Caution If you forget your passwords, you cannot recover them. We recommend that you write your passwords on the provided worksheet (see the "Collecting Required Information for the Initial Configuration Program" section) and then store this document in a safe place. |
The Security Setup for SNMP page, shown in Figure 4-6, collects the community strings that you enter and reenter. Community strings make possible SNMP access to system cards (MRPs, ASIs, SSP, and SPE310).
SNMP community strings can contain as many as 32 alphanumeric characters, excluding spaces and the ?, tab (\t), new line (\n), and return (\r) characters. SNMP community strings are case sensitive.
It is highly recommended that you change the default SNMP community strings even if you do not use SNMP. The Cisco ICS 7750 uses SNMP internally; therefore, leaving the SNMP community strings at their default values creates a security risk on the system.
You use the SPE310 administrator password for administrator-level access to the Windows 2000 operating system running on the SPE310. With administrator access, you can change operating system settings or you can upgrade or modify the operating system as needed. The user ID for the SPE310 administrator is set to Administrator. This user ID cannot be changed.
The Security Setup for SPE Cards page, shown in Figure 4-7, collects the new password that you enter to use for access to the SPE310 cards.
 |
Note Do not configure the Windows 2000 administrator password through the Windows 2000 user interface. Using ICSConfig to configure the administrator password ensures that all SPE310s have the same password, for easier management. |
Fields on the Security Setup for SPE Cards page are described as follows:
Enter a new password to change the SPE310 administrator password from the default password, which is changeme.
Reenter the password entered in the first field.
The Security Setup for ICS 7700 System page, shown in Figure 4-8, collects the new password that you enter for access to System Manager. This password is used to gain access to all areas of the ICS system manager software. By default, the user ID for the ICS Super Admin user ID is set to admin. This user ID cannot be changed.
Fields on the Security Setup for ICS 7700 System page are described as follows:
Enter a new password to change the ICS Super Admin password from the default of admin. Note that this password is case sensitive.
Reenter the password entered in the first field.
The ICS Event Manager Preferences page, shown in Figure 4-9, collects information that you enter if you choose to enable e-mail, paging, and forwarding related to system events. Table 4-5 describes the fields in the ICS Event Manager Preferences page.
 |
Note If you need to modify these settings later, use the Event Manager Preferences page in the System Manager. |
The Event Manager monitors system messages. The Event Manager can be configured to forward messages to other syslog servers, to send e-mail, or to page an administrator when it receives specified system messages.
If you consent to having System Manager automatically send event messages to Cisco Systems, then you must complete all the E-mail Setting fields.The Event Forwarding Setting and Page Setting fields are optional.
If you do not consent to monitoring availability, then all the fields are optional.
When you have configured all the settings, the Summary page, shown in Figure 4-10, is displayed.
The Summary page displays a list of all the configuration pages and the data entered in each field. All the page names listed on the Summary page are links to the configuration pages, where you can change any of the information that you entered.
To change any of your settings, click the associated hyperlinked page.
By clicking the Save As button, you can save a report of your configuration settings to a file on your local PC hard disk. This is useful for later reviewing of your configuration.
The Ready to Submit page, shown in Figure 4-11, provides instructions on what to do after you submit the changes to your Cisco ICS 7750. Submitting and processing these changes can take up to 20 minutes to complete.
 |
Caution Do not reboot your Cisco ICS 7750 or perform any configuration tasks during this process. |
When the changes are complete, the Setup Complete page appears, as shown in Figure 4-12. At this time, the connection to the server is lost (because of the IP address change), and you must readdress the client PC to continue.
After you run the initial configuration program, you must return your PC to its original IP address setting and connect it to your local network.
After your PC is rebooted, it is safe to connect the Cisco ICS 7750 to your network. (See the "Connecting to the LAN" section.)
This section describes how to install Cisco CallManager on SPE310 cards.
Cisco CallManager provides support for distributed call processing. You can distribute the call-processing load for your system across multiple Cisco CallManagers as a single cluster. A cluster is a set of Cisco CallManagers that share the same database.
In a Cisco CallManager distributed system, one server maintains the master, or publisher, database, and all others in the cluster maintain subscriber databases. Subscriber databases are backup copies of the master database. During normal operation, all Cisco CallManagers in the cluster read data from and write data to the publisher database. Periodically, the subscriber copies of the database are updated automatically from the publisher database.
Before you begin installing Cisco CallManager for a distributed call-processing system, you should plan your system configuration. At a minimum, you should determine how many Cisco CallManager servers the cluster will contain, which server will house the publisher database, and where backup tasks will be performed. Additional planning should include a strategy for distributing the devices (such as Cisco IP Phones or gateways) among the Cisco CallManagers in the cluster to achieve the type of distribution you want.
 |
Note For more information on planning a Cisco CallManager distribution system, refer
to the "Designing the IP Telephony Network" chapter in the
IP Telephony Solution Guide: http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/ip_tele/solution/4_desig n.htm |
When configuring a subscriber database server, ensure that the server you are installing can connect to the publishing database server during the installation. This connection facilitates copying the publisher database from the publisher server to the local drive on the subscriber server. The publisher database server for that cluster must be installed, connected to the network, and configured properly, and the subscriber server you are configuring must be able to connect to it.
 |
Caution If you are configuring a subscriber database server, the publishing database server for that cluster must be installed, connected to the network, and configured properly to work as a distributed system. If the publisher server cannot be authenticated during the installation for any reason, the installation will not continue. For more information on configuring the publishing database server, refer to the "Cisco CallManager Configuration" chapter in the Cisco CallManager Administration Guide. |
To install Cisco CallManager on the Cisco ICS 7750:
The CallManager installation program starts and displays the Cisco CallManager 3.1 and DC Directory dialog box.
 |
Note If the installation wizard does not start, start Windows Explorer, and browse to the CD-ROM drive. Double-click the file stistage.exe to start the installation program. |
Step 2 Enter the following Cisco CallManager product key:
Step 3 Click OK.
The Cisco CallManager Installation Wizard Welcome page appears.
Step 4 Click Next.
The CallManager Components page appears, as shown in Figure 4-13. This page lets you select which Cisco CallManager components you want to install. These are the components listed:
Step 5 Select the components you want to install by checking the associated check boxes. For more information about the components, see the Cisco CallManager Administration Guide.
Step 6 Click Next.
The Cisco CallManager Database Distribution page appears, as shown in Figure 4-14.
Step 7 Select whether this instance of Cisco CallManager will be the publisher of this cluster or will be a subscriber to a publisher running on another server. If you select subscriber, you must also enter the host name of the CallManager publisher to which you will subscribe. For more information about Cisco CallManager publishers and subscribers, see the section "Understanding Distributed Call Processing," or refer to the Cisco CallManager System Guide.
 |
Note If this is your only instance of Cisco CallManager, this instance must be the publisher. In addition, if you are installing multiple instances of Cisco CallManager, the first instance you install must be the publisher. |
Step 8 Click Next.
Step 9 Enter and confirm a password for the CallManager DC Directory Administrator account. All instances of CallManager in this cluster should use the same password for this account. Skip Step 10, and continue with Step 11.
Step 10 Enter the Windows 2000 Administrator password exactly as entered while running ICSConfig and the SQL user name and password of the Cisco CallManager publisher to which you will subscribe.
Step 11 Click Next.
The Ready to Install page appears.
Step 12 Click Next.
The installation program begins copying the Cisco CallManager software from the CD-ROM to the SPE310. This process takes approximately 30 minutes. When copying is finished, the Cisco IP Telephony Applications Backup Utility Setup loads, as shown in Figure 4-16. This application lets you configure the Cisco CallManager backup utility to perform backups of your Cisco CallManager data.
Step 13 Specify whether this instance of Cisco CallManager server will act as a backup target or as the backup server during the backup and restore operation.
Choose either Backup Server or Backup Target.
Step 14 Click OK.
If you chose Backup Server in the previous step, you must configure the backup utility. To configure the backup utility, follow the guidelines below:
If you chose Backup Target in Step13, the Cisco IP Telephony Applications Setup Complete dialog box appears, which indicates that you do not need to do any further configuration of the backup utility.
Step 15 Click OK.
The Administrator Account dialog box appears, as shown in Figure 4-17.
Step 16 This password is the same as the CCMAdmin user password and the Windows 2000 Administrator password. Enter and then reenter the Windows 2000 Administrator password for this SPE310. This password must be entered exactly as it was entered when you ran the initial configuration (ICSConfig) program in the "Configuring SPE310 Card Security" section. These fields cannot be left blank.
Step 17 Click OK.
The SQL Server SA Account dialog box appears, as shown in Figure 4-18.
Step 18 Enter a new password for the SQL server SA account. This is the SQLSvc account used by Microsoft SQL. Be sure that this password is the same as that for all other SQL servers in this CallManager cluster.
 |
Caution This password should not be left blank. Failure to enter a password could pose a security risk to your network. |
 |
Note Anytime you upgrade Cisco CallManager, the SQL server SA account password is reset. You must change this password after every upgrade. |
Step 19 Click OK.
The Cisco Product Activation dialog box appears.
Step 20 Click OK.
The Installation Complete dialog box appears.
Step 21 Remove the Cisco CallManager CD-ROM from the CD-ROM drive, and disconnect the CD-ROM drive.
Step 22 Click Yes.
This section provides information about the following types of connections to Catalyst switches:
 |
Note Use the supplied crossover Ethernet cables (yellow with a black stripe) to connect both 10/100 Ethernet ports on the SSP to the Catalyst switch 10/100 Ethernet ports. If you are using more than one Catalyst switch in your system, connect each SSP Ethernet port to a separate Catalyst switch to ensure redundancy between the Cisco ICS 7750 and the Catalyst switches. |
In the gigabit cascaded configuration, shown in Figure 4-19, the Catalyst 3524-PWR XL switches have 1000BaseX GBIC modules and GigaStack Gigabit Interface Converter (GBIC) modules installed.
Each switch is connected to the one above it and the one below it through the GigaStack GBIC module ports, by using the 50-cm cable supplied with the GigaStack GBIC module. Two crossover Ethernet cables (yellow with black stripe) are included in the hardware accessory kit for connecting the two SSP ports to two different switches in the switch stack for redundant connectivity. The GigaStack GBIC module ports are available for high-speed connections to network resources.
In a gigabit cascaded configuration, you can use any 10/100 ports that are not connected to the SSP for connecting local Cisco IP phones, printers, servers, and workstations. You can use this configuration to connect up to nine switches, supporting as many as 214 connections.
 |
Note Refer to the installation guide that came with your switch for instructions on making the necessary connections. |
In the star-wired 100-Mbps configuration, shown in Figure 4-20, the Catalyst switches are connected by using the 10/100 switch ports. You can use this configuration for switches that do not have1000BaseX or GigaStack GBIC modules installed. Two crossover Ethernet cables (yellow with black stripe) are included in the hardware accessory kit for connecting the two SSP ports to the switch stack. You must provide any additional crossover cables required to interconnect the 10/100 switch ports.
In this configuration, the Catalyst switch on the top functions as an aggregator and is star-wired to the SSP and the other switches in the stack, ensuring optimal performance. The four bottom switches are cascaded to provide a redundant path if the aggregator switch fails.
This type of configuration reduces the number of switch ports available for connecting to local Cisco IP Phones, printers, servers, and workstations. You can use this configuration to connect up to nine switches.
Any data network equipment—including desktop PCs, servers, and Cisco IP Phones—that you intend to use on the same LAN as the Cisco ICS 7750 should be connected to the system through the ports on the Catalyst switches.
The Catalyst 3524-PWR XL 10/100 ports can supply inline power to a Cisco IP Phone across the Ethernet cable that connects the Cisco IP Phone to the Catalyst switch.
 |
Caution Before connecting Cisco IP Phones to the Catalyst 3524-PWR XL switches, refer to the Catalyst 3500 Series XL Hardware Installation Guide and the documentation that came with the Cisco IP Phone. |
This section tells how to make a direct modem connection with an SAP and a remote dial-in connection (via the connected modem) with an MRP or ASI. A modem must be configured appropriately to establish these connections. For the SAP, you must manually configure the modem before attaching it to the system console port.
The following sections explain how to configure the modem:
 |
Note To connect and configure a modem for remote System Manager dial-up access, refer to the Cisco ICS 7750 Administration and Troubleshooting Guide. |
You have to provide the modem with an initialization string and other settings that tell it how to function with the system. The initialization string is a series of parameter settings that configure the modem to interact with the system. This section describes how to determine the correct initialization string for your modem.
Modem command sets vary widely. Although most modems use the Hayes command set (prefixing commands with AT), Hayes-compatible modems do not use identical AT command sets.
Refer to your modem manufacturer's documentation to learn how to examine the current and stored configuration of the modem you are using. Generally, you enter AT commands such as &v, i4, or *o to view, inspect, or observe the settings.
The following is an example of a modem initialization string for a U.S. Robotics Courier modem. This example is for a modem attached to the system console port on the SAP.
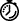 |
TimeSaver Initialization strings for other modems are listed in the "Configuring and Troubleshooting Modems" appendix in the Dial Services Command Reference publication. |
 |
Note Ensure that automatic baud rate detection is turned off so that the modem speed is not changed. |
A modem initialization string configures the following functions:
Other terms that vendors might use to refer to locking of the port speed are port-rate adjust, speed conversion, or buffered mode. Enabling error correction often puts the modem in the buffered mode (see the "Checking Other Modem Settings" section).
The following are other settings that might be necessary or desirable, depending on your modem:
This section describes how to initialize a modem for an SAP. You must initialize the modem and save its configuration externally before attaching it to the console port of the SAP.
 |
Note You cannot use the SAP to configure a modem. You must configure it externally. |
Follow these steps to initialize a U.S. Robotics Courier modem for an SAP:
Step 2 Configure the modem with an initialization string. The following example is a string for a U.S. Robotics Courier modem:
Step 3 Save the configuration settings on the modem.
 |
Note Some modems need to be strapped so that they start up with saved settings when they are powered on, rather than starting up using default settings. Make sure that your modem is strapped accordingly. |
Step 4 Test the modem on the SAP:
a. Connect the modem to the SAP console port.
b. Connect a telephone line to the modem.
c. Dial up the modem, and establish a remote connection with the SAP.
This section explains how to initialize a modem attached to your PC for a dial-up connection to an MRP or ASI.
 |
Note You must first create a direct Telnet or connection session to the modem before you can send an initialization string. You can use AT&F as a basic modem initialization string in most cases. |
Follow these steps to initialize a U.S. Robotics Courier modem on line 1 (decimal number 2000 + line number 1 = 2001):
Step 2 Establish a direct Telnet session to the modem:
Step 3 (Optional) Set the modem to its factory defaults:
Step 4 Configure the modem with an initialization string. The following example is a string for a U.S. Robotics Courier modem:
Step 5 Store the modem settings in NVRAM on the modem:
 |
Note Some modems need to be strapped so that they start up with saved settings when they are powered on, rather than starting up using default settings. Make sure that your modem is strapped accordingly. |
Step 6 Suspend and disconnect your Telnet session:
Test your modem connectivity to make sure that dial-up access is properly configured. The following is an example of a successful connection from a PC using a U.S. Robotics Courier modem to dial in to an MRP or ASI:
 |
Note The same configuration issues exist between the client data terminal equipment (DTE) and the client modem. Make sure that you have the correct EIA/TIA-232 cabling and the correct modem initialization string for your client modem. |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Sun Jan 19 13:27:08 PST 2003
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.