|
|

This appendix contains procedures for updating your system after it has been installed.
For systems at V5.1.4, enter "summ4" at the License Configuration screen to set the timeslot license to its maximum value. For more details consult the V5.1.4 Release Notes or the System Administrator's Guide. Both are available at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/tel_pswt/.
 |
Note If SPC-TONE is used in place of Tone Generator (DTG-2), confusing output in the License
Configuration screen may appear. This confusing output, if it appears, will be explaned
later but will have no operational efect on system performance. SPC-TONE, although selectable in V5.1.4 is not usable or supported in that version. SPC-TONE is fully supported in V5.2.0 and higher. To learn more about SPC-TONE, refer to the V5.2.0 Release Notes available at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/tel_pswt/. |
 |
Note In releases prior to Generic release V5.1.4, the License Configuration screen may display 4096 ports available instead of the true maximum value of 4088. See bug report CSCdr05012. |
You can manually increase the number of timeslot licenses on a CPU when you have any of the following conditions:
New CPUs are shipped from Cisco prelicensed for 1024 time slots. When you install the new CPU, the following message appears in the lower right corner of the admin console. This will be at the Administrator Main menu if your system is licensed for more than 1024 time slots:
Exceeding Time-Slot capacity By <X>
Where X = |(Number of Time-Slots Allocated) - (Number of Time-Slots Available)|
No log file message will appear. Only the message indicated above will appear.
 |
Note The System Configuration menu / License Configuration screen uses the terms Number of Time-Slots Allocated and Number of Time-Slots Available. These are defined below. |
The message on the screen appears because a license of 1024 time slots was entered into the NVRAM of the new CPU at the Cisco factory. Your system is detecting this and comparing the size of this license with the number of ports allocated in the system.
 |
Note 1024 has been the timeslot license applied to all CPUs shipped by Cisco after February 1999; before that time CPUs were licensed for 880 time slots. |
 |
Note The system will run and process calls even if the system is underlicensed. If your system
is not processing calls, then underlicensing is not the cause. Licensing restricts only the
process of adding new resources to the Card Maintenance screen. If you delete resources from the Card Maintenance screen while the system is underlicensed, then you will not be able to re-add or add new resources to this screen until you obtain the proper license from Cisco TAC. Furthermore, standard problem isolation scenarios would never require you to delete (remove) resources from the Card Maintenance screen. The risk to a system while it is underlicensed is virtually nonexistent. See the "License Update Procedure" section for the procedure for obtaining a new license number from Cisco TAC. |
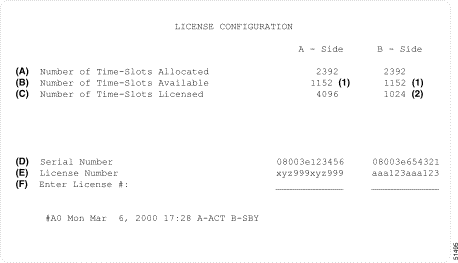
Your system is licensed for 3960 + 128 = 4088 timeslots (the maximum number of licensed time slots available) and you swapped out the B-side CPU. You will see the configuration displayed in the System Configuration Menu/License Configuration screen (Figure C-1). The number and letter callouts are defined below.
 |
Note Serial numbers and license numbers shown are fictitious and are used only for illustrative purposes. |
 |
Note The value 3960 displaying as 4096 is a known display error scheduled to be corrected in a later release. |
The following procedures assume that the system has both A and B side control hardware, making it a redundant system.
If you have a nonredundant system, then it is assumed that the control hardware, i.e., the NBC3 and Combined Controller are installed in the A-side; slots 1, 3, and 4, of the system. You should be able to intuitively modify the following procedures to meet your needs.
Follow these steps to apply the license(s):
Step 1 Make the state of the switch A-ACT/B-SBY.
 |
Note If you cannot make the system A-ACT/B-SBY, then go to Procedure #2. |
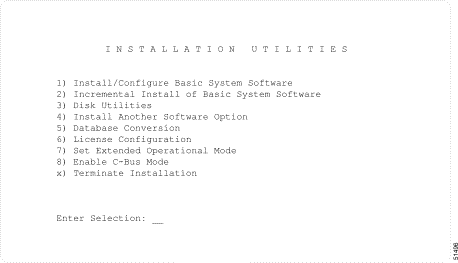
Step 2 Log in to the A-side and go to the System Configuration menu / License Configuration screen. Select this screen from the Installation Utilities screen (see Figure C-2).
Step 3 From this A-side login, enter the new license of one of the CPUs and press Enter.
Step 4 If you must also license the second CPU in this system, then from this A-side login, enter the new license of the second CPU and press Enter.
Step 5 See Figure C-5, Figure C-6, and Figure C-7 for how the Administrator Main Menu, License Configuration, and Card Maintenance screens will appear after the new license is correctly applied.
Follow these steps to apply the license(s):
Step 1 Make the state of the switch A-SBY/B-ACT.
Step 2 Log in to the B-side and go to the System Configuration menu / License Configuration screen.
Step 3 From this B-side log-in, enter the new license of one of the CPUs and press Enter.
Step 4 If you have to also license the second CPU in this system, then from this B-side log-in, enter the new license of the second CPU and press Enter.
Step 5 See Figure C-5, Figure C-6, and Figure C-7 showing the Administrator Main Menu, License Configuration, and Card Maintenance screens after the new license is correctly applied.
The only other way to install the new license number into the CPU is to boot from Generic floppy diskette #1, or any of the optional software diskettes: Ethernet and Telerouter (for V5.1(2) or lower) or the Optional Software diskette. This will bring you to the Installation Utilities screen (see Figure C-2).
Step 1 Insert Generic floppy diskette #1, or any of the optional software diskettes into the side of the system that has the CPU license update. Press the appropriate button on the AAC card to reset that side. The following output appears on the local console screen:
Copyright Motorola Inc. 1988 - 1997 All Rights Reserved
MVME147 Monitor/Debugger Release 2.44 - 8/7/97
CPU running at 33 MHz
FPC passed test
MMU passed test
COLD Start
Onboard RAM start = $00000000, stop = $00FFFFFF
147-Bug> Searching for ROM Boot
147-Bug>G FFA0002C
Effective address: FFA0002C
SDS Initializing...
Hard disk mounted successfully
Hard disk dismounted successfully
Reading boot file from disk device A:/boot/boot.sds
Loading file A:/boot/install.exe
Hard disk mounted successfully
Hard disk dismounted successfully
 |
Note Line (4)appears as "Install Optional Software Package" for Generic V5.1(3) and higher. |
Step 2 Type 6 and press Return to get to the License Configuration screen (see Figure C-3).

 |
Note Serial numbers and license numbers shown are fictitious and are used only for illustrative purposes. |
Step 3 Type the new license number.
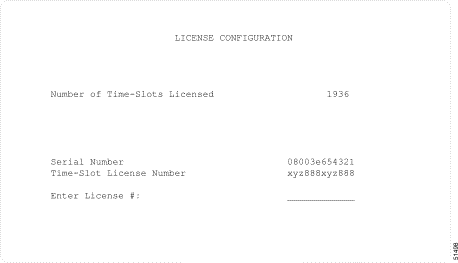
If you entered a license number for 3960 time slots (the email from Cisco TAC would say that this is a license number for 4088 time slots), then you would see the output shown in Figure C-4.
 |
Note Serial numbers and license numbers shown are fictitious and are used only for
illustrative purposes. There is a display bug in the Installation Utilities / License Configuration screen. When you enter a license number that equates to 2096, 2632, 3168, 3704, or 3960 time slots (the email from Cisco TAC would say that the license number for 3960 time slots is a license number for 4088 time slots), the "Number of Time-Slots Licensed" field always displays 1936. When you enter a license number that equates to 1024, or 1560 time slots, the "Number of Time-Slots Licensed" field displays correctly. |
Step 4 To return to the Installation Utilities screen after entering the license number, press Return. Type x to terminate the Installation Utilities screen, then press Return. The following prompt appears:
Terminate Installation Utility (Y/N) =N?
Step 5 Type Y and press Return.
Remove Installation Diskette NOW!
Suspending Installation Process...
Rebooting.....................
Reset System NOW!
 |
Note The message Reset System NOW! may not appear. If it does, press the appropriate button on the ACC card. |
Step 6 Remove the Installation Diskette. The following will display:
Copyright Motorola Inc. 1988 - 1997 All Rights Reserved
MVME147 Monitor/Debugger Release 2.44 - 8/7/97
CPU running at 33 MHz
FPC passed test
MMU passed test
COLD Start
Onboard RAM start = $00000000, stop = $00FFFFFF
147-Bug> Searching for ROM Boot
147-Bug>G FFA0002C
Effective address: FFA0002C
SDS Initializing...
Hard disk mounted successfully
Hard disk dismounted successfully
A: drive has no floppy or Unreadable/Unformatted Floppy
Trying C drive
Reading boot file from disk device C:/boot/boot.sds
Loading file C:/boot/globals.exe
Loading file C:/boot/syswd.exe
Loading file C:/boot/hostmgr.exe
Loading file C:/boot/redmgr.exe
Loading file C:/boot/netmgr.exe
Loading file C:/boot/permgr.exe
Loading file C:/boot/snmp.exe
SW version loaded - Ver.Rev FSR : 5.1 001
Hard disk mounted successfully
Hard disk dismounted successfully
Loading File < syscnfg.TBL > ...
Loading File < card.TBL > ...
Loading File < port.TBL > ...
Loading File < hostcnfg.TBL > ...
Loading File < resgroup.TBL > ...
Loading File < supvtmpl.TBL > ...
Loading File < iprule.TBL > ...
Loading File < oprule.TBL > ...
Loading File < isdnsupv.TBL > ...
Loading File < isdnmsg.TBL > ...
Loading File < routesum.TBL > ...
Loading File < routetbl.TBL > ...
Loading File < exroute.TBL > ...
Loading File < nfascnfg.TBL > ...
Loading File < promptlb.TBL > ...
Loading File < subrate.TBL > ...
Loading File < motomap.TBL > ...
Loading File < license.TBL > ...
Step 7 The login screen appears. Log in.
Applying Procedure #1, #2, or #3 will produce the results shown in Figure C-5, Figure C-6, or Figure C-7. The results shown are for licensing a CPU to 3960 time slots on a system with 2392 time slots allocated.

 |
Note "2392 Out Of 4096 Time-Slots Allocated" should display as "2392 Time-Slots Allocated Out Of 4088 Time-slots Available" (3960 + 128 for the active DTG-2 card = 4088). This is a known display error scheduled for correction in a later release. |

 |
Note Serial numbers and license numbers shown are fictitious and are used only for
illustrative purposes. (1) The correct number is 4088, the true maximum available for use. (2) The correct number is 3960 These are known display errors scheduled for correction in a later release. |

 |
Note Card layouts shown are fictitious and are used only for illustrative purposes. "2392 Out Of 4088 Time-Slots Allocated" should display as "2392 Time-Slots Allocated Out Of 4088 Time-slots Available" (3960 + 128 for the active DTG-2 card = 4088). |
To obtain a new license, send email to nh-tech_sup@cisco.com as follows:
Step 1 Obtain the system serial number from the label on the rear of the chassis of the VCO/4K.
Step 2 Obtain the system serial number from the License Configuration screen. Log in to the active side of the system (record exactly what you see).
 |
Note If you are replacing a CPU, first replace the CPU before recording this information. If you are not replacing a CPU, then simply record the information that you see. |
Number of Time-Slots Allocated, A-side:
Number of Time-Slots Allocated, B-side:
Number of Time-Slots Available, A-side:
Number of Time-Slots Available, B-side:
Number of Time-Slots Licensed, A-side:
Number of Time-Slots Licensed, B-side:
Serial Number, A-side:
Serial Number, B-side:
License Number, A-side:
License Number, B-side:
Step 3 Obtain the following information from your engineers:
How many time slots does the system need to be licensed for?
Number of time slots to increase to:
Increase the A-side (Y/N)?
Increase the B-side (Y/N)?
Reason for the time slot license:
Swapped out defective CPUs (Y/N)?
Upgraded from V4.x to V5.x (Y/N)?
Need to add more resources to the system (Y/N)?
Step 4 Obtain the following information from the Administrator Main Menu:
Table C-1 shows the number of time slots, within the licensed range of time slots or "licensed time slot pool," each VCO/4K resource uses.
| Hardware Name | Card Maintenance Screen Name | Licensed Time Slots Used |
|---|---|---|
DTG-2 | Tone Generator | 128 (1)(6) |
IPRC8 | 8 Port Prompt/Record | 008 |
IPRC64 | 64 Port Prompt/Record | 064 |
IPRC128 | 128 Port Prompt/Record | 128 |
SSC | Subrate Switch Card | varies/ |
D+I | Drop and Insert Card | 008 |
ICC | ICC-T1 | 024 |
ICC | ICC-E1 | 032 |
LTC-8 | 8-Line Test Card | 008 |
ICC | ICC-T1 PRI/NI2 | 024 |
ICC | ICC-T1 PRI/5ESS | 024 |
ICC | ICC-T1 PRI/4ESS | 024 |
ICC | ICC-T1 PRI/NTI | 024 |
ICC | ICC-T1 PRI/NTT | 024 |
ICC | ICC-E1 PRI/NET5 | 032 |
ICC | ICC-E1 PRI/QSIG | 032 |
ICC | ICC-E1 PRI/TS014 | 032 |
SPC | SPC-DTMF | none (3) |
SPC | SPC-CPA | none (3) |
SPC | SPC-MFR1 | none (3)(4) |
SPC | SPC-MFCR2 | 024 |
SPC | SPC-OUTP | 064 |
SPC | SPC-CONF | 032 |
- | virtual ports | none (3)(5) |
| Time Slot Increment Number | Time Slot Increment Increase | Number of Time Slots Licensed | Number of Time Slots Available(1) | Number of Time Slots Allocated(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | - | 1024 | 1152 | - |
1 | 536 | 1560 | 1688 | - |
2 | 536 | 2096(3) | 2224 | - |
3(6) | 536 | 2632 | 2760 | - |
4(6) | 536 | 3168 | 3296 | - |
5(6) | 536 | 3704 | 3832 | - |
6(6) | 256 | 3960(4) | 4088(5) | - |
If ECPT modules are not seen as loaded on EBS software installation or no blank line is seen for ecpt devices on EBS startup, then the ECPT drivers were not installed properly.
SS7 signaling links will not align even though EBS and cktint configured properly and started.
There are two instances described here:
When a system is upgraded to new software, a script, install_ebs.sh, installs EBS software. This script replaces previous AccessManager modules with new modules. During the loading of new modules, you must see ECPT drivers loaded, i.e., you must see the following lines:
CCTC module is now installed.
Installing TRMOD module ...
TRMOD module is now installed.
Installing ECPT module ...
ECPT module is now installed.
Installation of AccessMANAGER modules is now complete.
When executing ebs_start or start-ss7.sh scripts, EBS is started first and you must see a blank line for ECPT drivers loaded. See ecpt 1 in the following example:
start-ss7.sh
This script will assist you in bringing up your Integrated
SS7 system in a controlled fashion.
Would you like to start the EBS stack [y/n]?y
Starting Signaling Point 0
Starting ebs_start...
Signalling Point Manager - Version 3.5.3
Copyright (c) 1991-1995, EBS
All Rights Reserved
Loading /dev/ecp0 - device does not exist
Loading /dev/ecp1 - device does not exist
Loading /dev/ecp2 - device does not exist
Loading /dev/ecp3 - device does not exist
Loading /dev/ecp4 - device does not exist
Loading /dev/ecp5 - device does not exist
Loading /dev/ecp6 - device does not exist
Loading /dev/ecp7 - device does not exist
Loading /dev/ecpt0 - device does not exist
*****************************************
******* AccessALARM is in service *******
***** Console Output is DISABLED *****
*****************************************
Loading /dev/ecpt1
Loading /dev/ecpt2 - device does not exist
Loading /dev/ecpt3 - device does not exist
Loading /dev/ecpt4 - device does not exist
Loading /dev/ecpt5 - device does not exist
Loading /dev/ecpt6 - device does not exist
Loading /dev/ecpt7 - device does not exist
AccessMANAGER Ready
Starting upmd...
 |
Note In an 8-link SS7 system, you must see two blank lines for loaded drivers. Usually, ecpt0 and ecpt 1 represent 4-Link (SBUS ports) each. |
The following procedure describes how to reinstall ECPT drivers:
Step 1 Stop the SS7 stack completely and verify that no process is running. Type the following:
ebs_ps
Step 2 Type the following to change directories:
cd $EBSHOME/access/install
Step 3 Change user to SU (superuser).
Step 4 Type the following command to remove EBS drivers:
./rmEBSdrv
You will see all drivers and modules being removed one by one. Make sure everything is removed successfully. Focus on ECPT modules specifically.
For example:
# ./rmEBSdrv
You are about to remove the AccessMANAGER modules.
Do you wish to continue [y/n]? y
Unloading CCTC module ...
CCTC module is now unloaded.
Unloading ANTC module ...
ANTC module is now unloaded.
Unloading SCCP module ...
SCCP module is now unloaded.
Unloading SNM module ...
SNM module is now unloaded.
Unloading UPM module ...
UPM module is now unloaded.
Unloading TRMOD module ...
TRMOD module is now unloaded.
Unloading ECPT module ...
ECPT module is now unloaded.
Unloading SPM module ...
SPM module is now unloaded.
Removing CCTC module ...
CCTC module is now removed.
Removing ANTC module ...
ANTC module is now removed.
Removing SCCP module ...
SCCP module is now removed.
Removing SNM module ...
SNM module is now removed.
Removing UPM module ...
UPM module is now removed.
Removing ECPT module ...
ECPT module is now removed.
Removing SPM module ...
SPM module is now removed.
Removing TRMOD module ...
TRMOD module is now removed.
All AccessMANAGER modules are now removed.
#
Step 5 Type sync a couple of times for files to synchronize the file system.
Step 6 Reboot the Sparc with the reboot command while you are in SU (superuser) mode.
Step 7 When the system is ready, log in as cktint and confirm that no process is running.
Step 8 Type the following to change directories:
cd $EBSHOME/access/install
Step 9 Change user to SU (superuser).
Step 10 Type the following command to set up EBS drivers:
./setupEBSdrv
You will see all drivers and modules loading one by one. Make sure everything is loaded successfully without any error. Focus on ECPT.
# ./setupEBSdrv
You are about to install the AccessMANAGER modules.
Do you wish to continue [y/n]?
Installing SPM module ...
SPM module is now installed.
Installing UPM module ...
UPM module is now installed.
Installing SNM module ...
SNM module is now installed.
Installing SCCP module ...
SCCP module is now installed.
Installing ANTC module ...
ANTC module is now installed.
Installing CCTC module ...
CCTC module is now installed.
Installing TRMOD module ...
TRMOD module is now installed.
Installing ECPT module ...
ECPT module is now installed.
Installation of AccessMANAGER modules is now complete.
#
If you don't see the message "ECPT module is now installed" or you still find difficulty in loading of ecpt drivers on startup, follow Steps 1 to 5. Then, instead of rebooting in Step 6, type halt or shutdown.
Power down the SS7. (On a redundant platform, only the side that is being upgraded).
Step 11 After powering down, wait for 30 seconds and power up the side again.
Once the system is ready, follow Steps 7 to 10.
Use the following procedure to upgrade existing Sparc 5 CPU with 4-link SBUS to 8-link SBUS to support a total of eight SS7 signaling links:
Step 1 Verify that the current /export/home/EBSkeyfile.dat is licensed for the support of eight SS7 links. (Or that it is a new EBS license diskette included with an upgrade package.)
Step 2 If the system is redundant, manually make the A-side active (via the Fallback/Selector/AB switch-box and VCO AAC) to start with an upgrade of the B-side (standby) first.
Step 3 Rename the existing EBSkeyfile.dat to (for example) EBSkeyfile.dat.old. This saves the existing file for possible later use or recovery.
Step 4 Ensure that you are using the correct diskette for the B-side license file.
Verify that the host ID on the diskette label is for the B-side Sparc. License files are different for A and B side Sparc systems.
Step 5 Copy the EBS license file, EBSkeyfile.dat (support for 8-links) from the diskette to the B-side /export/home directory.
The procedure for copying the files from diskette is given in the appropriate VCO/4K Integrated SS7 System Supplement.
Step 6 Stop the SS7 on the B-side and change the directory to $EBSHOME/access/install.
Step 7 Change user to SU (superuser).
Step 8 Type the following command to remove EBS drivers:
./rmEBSdrv
Step 9 Once drivers are removed, type:
halt
Step 10 If you are using a separate SS7 VME shelf with your VCO/4K system, power off the B-side SS7.
Step 11 Add the additional 4-link SBUS next to the existing SBUS on the Sparc CPU card.
Remove the serial/parallel card and put the new 4-link SBUS card in its place.
Step 12 Remove the power cable from the fallback switch.
Since fallback/selector/AB switch-box was manually selected to make the A-side active, all the links should stay aligned.
Step 13 Remove one of the existing slave cards.
Step 14 Set the dip switches on each new slave card to match the dip-switch settings of the card you removed.
Step 15 Exchange the existing slave cards with the new slave cards.
Step 16 Power up the fallback switch.
Step 17 Ensure that the system boots properly after the B-side SS7 is powered up.
Step 18 Log in as cktint.
Step 19 Change user to SU (superuser):
cd $EBSHOME/access/install
Step 20 Install the new drivers with the command:
./setupEBSdrv
Step 21 Modify the mtpmml file to include ports 5,6,7, and 8 for the additional 4-links.
Step 22 Recompile to update the database.
Any change in mml files requires re-creating or modifying the database files. Refer to the Integrated SS7 Supplement for help on mtp mml file configuration and re-creating or modifying the database.
Step 23 Start the SS7 stack and verify that the operation is normal.
Step 24 Initiate a switchover (manually select the B-side to be active) and ensure that the links are aligned and call processing is resumed.
Step 25 Upgrade the A-side.
Repeat the same procedure used for B-side except that you do not need to add or modify hardware (cards etc.).
 |
Note For a nonredundant system, you need to power off the SS7 for hardware (SBUS) upgrade, therefore you can power off the fallback as well at the same time. The traffic/calls will drop because with a nonredundant system, powering off the SS7 will stop all traffic. This limitation for a nonredundant system must be clearly understood prior to the upgrade. The customer needs to provide a maintenance window for upgrade. |
All SS7 systems display a "#" prompt when you have logged in as root or have changed to superuser (su) with the root password. When you log in as cktint, the SS7 system displays a "%" prompt.
Occasionally (particularly during a new install or an upgrade) both the root and cktint logins have the "%" as prompt. As a result, users actually log in as root.
Thinking that they were logged in as cktint, users have deleted system files that have affected operations of the system.
It looks as if root has been defined or has been modified as for UNIX C-shell (csh) instead of standard shell (sh) /etc/passwd file.
Step 1 Change to superuser. Type su and enter abc123 as the password.
vi /etc/passwd
Step 2 The first line in the file might be like one below:
root:x:0:1:Super-User:/:/bin/csh
Step 3 If that is what you find, edit the file and correct it as follows:
root:x:0:1:Super-User:/:/sbin/sh
Step 4 Save the file.
The change will set the root prompt to "#."
Use this information to partition 1-GB (MSM-1000), 2-GB (MSM-2000), 4-GB (MSM-4000), and 9-GB (MSM-4000 Replacement) hard drives. Use this when reinstalling Solaris 2.6 and/or troubleshooting problems involving writing entries to SS7 log files.
During troubleshooting, this information can be verified by typing df -k and then pressing Return.
Partitioning information for 1-Gigabyte drives is in Table C-3.
| Slice | Partition (Mount) | Size (MB) |
|---|---|---|
0 | / | 28 |
1 | - | - |
2 | swap | 85 |
3 | /usr/openwin | 260 |
4 | /var | 55 |
5 | /opt | 65 |
6 | /usr | 260 |
7 | /export/home | 256 |
Partitioning information for 2-Gigabyte drives is in Table C-4.
| File System | Size (MB) | Mount |
|---|---|---|
/dev/dsk/cot3d0s0 | 24923 | / |
/dev/dsk/cot3d0s6 | 203415 | /usr |
.proc | 0 | /proc |
fd | 0 | /dev/fd |
/dev/dsk/cot3d0s4 | 480586 | /var |
/dev/dsk/cot3d0s7 | 871413 | /export/home |
/dev/dsk/cot3d0s5 | 166007 | /opt |
/dev/dsk/cot3d03 | 228707 | /usr/openwin |
swap | 107104 | /tmp |
Partitioning information for 4-Gigabyte drives is in Table C-5.
| File System | Size (MB) | Mount |
|---|---|---|
/dev/dsk/cot3d0s0 | 30859 | / |
/dev/dsk/cot3d0s3 | 480799 | /usr |
.proc | 0 | /proc |
fd | 0 | /dev/fd |
/dev/dsk/cot3d0s4 | 480799 | /var |
/dev/dsk/cot3d0s7 | 2430349 | /export/home |
/dev/dsk/cot3d0s5 | 480799 | /opt |
/dev/dsk/cot3d06 | 268897 | /usr/openwin |
swap | 107868 | /tmp |
Partitioning information for 9-Gigabyte drives is in Table C-6.
| File System | Size (MB) | Mount |
|---|---|---|
/dev/dsk/cot3d0s0 | 385007 | / |
/dev/dsk/cot3d0s6 | 481263 | /usr |
.proc | 0 | /proc |
fd | 0 | /dev/fd |
/dev/dsk/cot3d0s4 | 481263 | /var |
/dev/dsk/cot3d0s7 | 6494301 | /export/home |
/dev/dsk/cot3d0s5 | 481263 | /opt |
/dev/dsk/cot3d03 | 288751 | /usr/openwin |
swap | 77204 | /tmp |
The following are the dip switch settings for Master and Slave Cards used for SS7 signaling links in Fallback/Selector/AB switch Selector Shelf Cards.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Sat Sep 28 18:07:19 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.