|
|

This chapter provides detailed steps for installing the hardware and software components required for VCO/4K Ethernet communications. The installation process includes connecting the appropriate physical cables for host links, installing software, and configuring peripherals for network access.
Additional details pertaining to application-specific Ethernet communications are provided in "Host Communications."
The Ethernet host communication link terminates on the Storage/Control I/O Module, which is located at the back of the system. The Storage/Control I/O Module and the Ethernet host communication link are shown in Figure 2-1.

Table 2-1 lists the DB-15 connector pinouts, which are the same for the CPU-TM card and the Storage/Control I/O Module.
| Pin | Signal | Signal Name |
|---|---|---|
2 | C+ | Collision + (Input) |
3 | T+ | Transmit + (Output) |
5 | R+ | Receive + (Input) |
6 | GND | Ground |
9 | C- | Collision - (Input) |
10 | T- | Transmit - (Output) |
12 | R- | Receive - (Input) |
13 | +12VF | +12 Vdc Power |
Use an office Attachment Unit Interface (AUI) cable between the DB-15 connector and the network transceiver. The physical Ethernet network determines the transceiver type.
For users of system software version 5.1(3) and higher, install and configure Ethernet communications from the System Configuration menu by selecting the Ethernet/NFS/SNMP Configuration option. For information on using this configuration screen, refer to Chapter 4 of the Cisco VCO/4K System Administrator's Guide. When the Ethernet/NFS/SNMP configuration is complete, reboot the CPU from the Alarm Arbiter Card.
For users of system software version 5.1(2) or earlier, install and configure the Ethernet optional software by using the following steps. Repeat these procedures for installing software on the B-side.
Step 1 Insert the Ethernet software diskette and press Enter.
After the system loads the Ethernet files from the diskette, the Ethernet Installation Utilities menu is displayed. (See Figure 2-2.)
The cursor is located in the Enter Selection data entry field.

Step 2 Type 1 and press Enter to begin the Ethernet software installation process.
The following message is displayed:
Do You Wish To Back-Up The System Data Base? (Y/N) =N?_
Step 3 Press Enter (this defaults to N).
You will not be backing up the database at this time.
The Ethernet Configuration menu is displayed. (See Figure 2-3.)
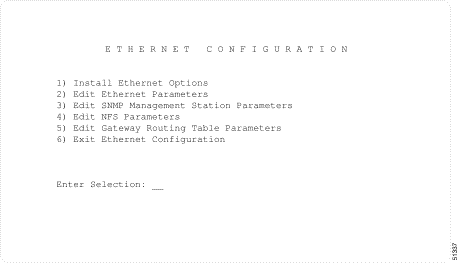
Type 1 and press Enter. The following message is displayed:
Copy A:/BOOT/ETHERMGR.EXE
1 file(s) copied
Ethernet Option Enabled
 |
Note If you do not need to edit Ethernet parameters (system Ethernet address and/or subnet
mask), SNMP management station parameters, NFS parameters, or gateway routing
parameters, type 6 and press Enter to exit the Ethernet installation. Otherwise, continue
with the next section. If you installed an updated CPU as part of this upgrade, you must edit Ethernet/NFS/SNMP parameters. |
Step 1 Type 2 (Edit Ethernet Parameters) and press Enter.
The following message is displayed:
System Internet Address = 107.3.254.98?
 |
Note The Ethernet and Internet address numbers that you see in the screen messages in this section are only examples. In your system these numbers are replaced by numbers that represent your system addresses. |
Step 2 Set the Internet address of this system and press Enter.
The following message is displayed:
Set System Internet Address To 107.3.254.98 (Y/N) =Y?
Step 3 If you change the address, you are prompted to confirm your new address. Type Y to confirm your selections.
The following confirmation message is displayed:
System Internet Address Configured
Step 4 Set the system subnet mask, or press Enter to accept the displayed value.
After you complete this step, you can connect a remote console to your system via Telnet.
Step 1 Type 3 and press Enter to set the SNMP management station Internet address.
The following message is displayed:
SNMP Management Internet Address = 0.0.0.0?
Step 2 Set the Internet address to the address of the system that you are using as the NMS (Network Management System), and press Enter. If you are not using SNMP and a NMS, then set this address to the address of your host.
The following message is displayed:
Set SNMP Management Internet Station Address To [internet address] (Y/N) =Y?
Step 3 Type Y to confirm your selections.
The following confirmation message is displayed:
SNMP Management Station Internet Address Configured
After you complete this step, the system reports SNMP trap messages to the NMS that you selected.
Step 1 Create a directory for log and trace files on your NFS server and set the appropriate access permissions.
Step 2 Make an entry in the /etc/exports file on your NFS server that indicates the path for the NFS mount point. This allows the file to be shared.
Step 3 Type 4 to set the Network File System (NFS) server parameters.
The following selections appear one at a time. Enter the information for your system. For more information concerning these selections, refer to Table 2-2.
Enable NFS Access (Y/N) =Y?
NFS Server Internet Address = 000.0.000.000?
NFS Server Name =xxx?
NFS Mount Directory Point #?
Target System Name =
Target System User Id =
Target System Group Id =
Target System Umask =
Update NFS Configuration With Above Data (Y/N) =Y?
| Parameter | Definition | Options | Recommended Value |
|---|---|---|---|
NFS Server Internet Address | Internet address assigned to the device (usually the host computer) on which the log and trace files are to be stored. | Valid internet address in standard dot notation | Value supplied by NFS administrator. |
NFS Server Name | Name assigned to the device (usually the host computer) on which the log and trace files are to be stored. | — | Value supplied by NFS administrator. |
NFS Mount Directory Point | Name of the mount directory device into which the log and trace files are to be stored. | Valid directory specification created for system log and trace files. | Value supplied by NFS administrator. |
Target System Name | Name assigned to the VCO by the system administrator. | This name can not include underscore characters. For configurations that include NFS, this name must also be included in the NFS server's /etc/hosts file. | Value supplied by VCO administrator. |
Target System User Id | UNIX user ID associated with the directory (log or trace files) of the NFS system. | Valid user ID in decimal notation. | Value supplied by NFS administrator. |
Target System Group Id | UNIX group ID associated with the directory (log or trace files) of the NFS system. | Valid group ID in decimal notation. | Value supplied by NFS administrator. |
Target System Umask | User mask associated with the NFS server. | Valid user mask in hex notation. This must match the permission on the NFS server. No other value is acceptable. | — |
Step 4 After you update the NFS configuration with the new data, the following message is displayed:
NFS Configuration Updated
You can now save the log files and database to a remote location.
Step 1 Type 5 to set Gateway Routing Table parameters.
The following selections appear. Enter the information for your system.
Route No. 1
Destination Subnet Address =0.0.0.0?Gateway System Internet Address =0.0.0.0? Route No. 2
Destination Subnet Address =0.0.0.0?Gateway System Internet Address =0.0.0.0? Route No. 3
Destination Subnet Address =0.0.0.0?Gateway System Internet Address =0.0.0.0? Route No. 4
Destination Subnet Address =0.0.0.0?Gateway System Internet Address =0.0.0.0?Update Gateway Routing Table Configuration With Above Data (Y/N) =Y?_Step 2 Type Y to update the gateway routing table configuration with the data changes.
If you type N at the final prompt, the following message is displayed, and the Ethernet Configuration screen is displayed:
Gateway Routing Table Configuration Aborted
 |
Note The Destination Subnet Address refers to the destination subnet address field in the Gateway Routing Configuration screen. The Gateway System Internet Address refers to the gateway IP address field in the Gateway Routing Configuration screen. |
Step 1 Type 6 (Exit Ethernet Configuration), and press Enter.
The Installation Utilities menu is displayed. (See Figure 2-2.)
Step 2 Remove the Ethernet diskette from drive A.
Step 3 To install additional optional software, type 4 (Install Another Software Option).
To configure a VCO/4K on a UNIX-host LAN, follow these steps:
Step 1 Define the station name and Ethernet address in the '/etc/ethers' file as follows:
uu:vv:ww:xx:yy:zz VCO_Name
The uu:vv:ww:xx:yy:zz value is the hex Ethernet address printed on the system CPU and the VCO_Name is a user-defined name for the system. Each CPU in a redundant system has a unique Ethernet address and should also have a unique name.
Step 2 Define the station name and Internet address in the '/etc/hosts/' file as follows:
www.xxx.yyy.zzz VCO_Name
The www.xxx.yyy.zzz value is the Internet address specific to the LAN on which the system resides and VCO_Name is the same as that specified in Step 1.
Because network file support enables Internet access to the system, network security is required to limit Internet hosts from connecting to the system.
From the Host Configuration screen, you can use the following NFS parameters to tailor Ethernet network security:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Sun Sep 29 01:13:40 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.