|
|

The system internal processing uses a simple state machine representation to track the current condition of all resources in the system. Transitions between states occur as a result of externally generated events (incoming calls, for example), commands from the host, or inpulse/outpulse rule processing.
Two variables are maintained on a per-port basis to track the current state of a port:
MStates represent points within specific call processing routines. SStates monitor detailed activity within those states. Because of the structure of the state machine and the nature of call processing activity, several SStates can exist simultaneously during a single MState.
The current MState and SState for a port can be viewed using the system diagnostics Port Display screen (refer to the Cisco VCO/4K System Administrator's Guide). This screen is especially useful in the debugging process because it shows the actions being performed for a specific port, any inpulse/outpulse rule processing activity, and all links and voice paths (including conferences) associated with that port.
There are four MStates in conference port call processing. These states are shown in Figure 3-1 and explained in the text that follows. In addition to the MStates listed here, the system uses multiple SStates to track and indicate the status of a conference structure.
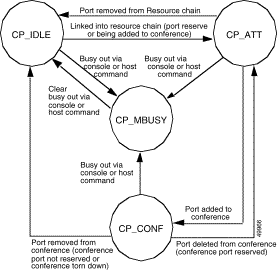
Definition: | CP_IDLE is an MState during which there is no activity on a conference port. |
Transition Event: | Conference port is linked into a chain (host command request to reserve, start, or add). |
New State: - or - | CP_ATT |
Event: | Port is put into maintenance busy using either the Card Maintenance function of System Administration (refer to the Cisco VCO/4K System Administrator's Guide) or a Change Port Status ($90) host command (refer to the Cisco VCO/4K Standard Programming Reference and the Cisco VCO/4K Extended Programming Reference). |
New State: | CP_MBUSY |
Definition: | CP_ATT is an MState during which a conference port is linked into a chain but is not being used. Either the conference port is reserved but has no associated line/trunk port or the conference port plus an associated line/trunk port are being placed into a conference. A reserved port remains in CP_ATT until the conference is torn down by a host command. The SStates that exist under this MState are discussed in the "Conference Port SSTATES" section. |
Transition Event: | Host command adds line/trunk port to conference and uses this conference resource port. |
New State: - or - | CP_CONF |
Event: | Conference port is removed from resource chain by a host command (tear down conference) or its card goes OOS. |
New State: - or - | CP_IDLE |
Event: | Port is put into maintenance busy using either the Card Maintenance function of System Administration (refer to the Cisco VCO/4K System Administrator's Guide) or a Change Port Status ($90) host command (refer to the Cisco VCO/4K Standard Programming Reference and the Cisco VCO/4K Extended Programming Reference). Any call in which this port is participating is torn down. |
New State: | CP_MBUSY |
Definition: | CP_CONF is an MState during which a conference port has an associated line/trunk port and is actively participating in a conference. The SStates that exist under this MState are discussed in the "Conference Port SSTATES" section. |
Transition Event: | Line/trunk port associated with conference port is deleted from conference by a host command or disconnect, or error, or the line/trunk port associated with the conference port is busied out. |
New State: - or - | CP_ATT (if conference port was reserved) CP_IDLE (if conference port was not reserved). |
Event: | Conference is torn down or card on which this conference port resides goes OOS. |
New State: - or - | CP_IDLE |
Event: | Port is put into maintenance busy using either the Card Maintenance function of System Administration (refer to the Cisco VCO/4K System Administrator's Guide) or a Change Port Status ($90) host command (refer to the Cisco VCO/4K Standard Programming Reference and the Cisco VCO/4K Extended Programming Reference). Any call in which this port is participating is torn down. |
New State: | CP_MBUSY |
Definition: | CP_MBUSY is an MState during which a conference port is in a maintenance busy condition and cannot be used for a call. |
Transition Event: | Port is unbusied using either the Card Maintenance function of System Administration (refer to the Cisco VCO/4K System Administrator's Guide) or a Change Port Status ($90) host command (refer to the Cisco VCO/4K Standard Programming Reference and the Cisco VCO/4K Extended Programming Reference). Any call in which this port is participating is torn down. |
New State: | CP_IDLE |
The MState CP_CONF describes all actions that take place during call processing for active conference ports. Several SStates exist under CP_CONF that represent specific actions being performed by call processing. These SStates can be seen using the system diagnostics Port Display screen. Refer to "Viewing Conferences via System Administration," of this document and the Cisco VCO/4K System Administrator's Guide. This screen is especially useful in the debugging process because it shows what actions are being performed for a specific port, any inpulse/outpulse rule processing activity, and all links and voice paths associated with that port.
Several SStates can exist simultaneously under a single MState. When more than one SState is present, the Diagnostics Port Display combines the names of the SStates. The character(s) that appear next to the SState name indicate the abbreviation that may be seen on the screen for each SState.
Call processing enters this SState when it attempts to perform any action involving a conference port. During this state, call processing is sending instructions to the port.
Call processing enters this SState when the conference port acknowledges the instructions sent by call processing.
Call processing enters this SState when the conference port has been reserved as specified by a host command. The port remains in this state until the conference is torn down by a host command.
Call processing enters this SState when the conference port is being used for a one-way voice path from a conference. One or more associated line/trunk ports are linked to this conference port. The conference port is also linked to a resource chain containing all conference ports involved in the conference. The port remains in this state as long as the one-way path is established.
Call processing enters this SState when the conference port is being used for a two-way voice path to/from a conference. One associated line/trunk port is linked to this conference port. The conference port is also linked to a resource chain containing all conference ports involved in the conference. The port remains in this state as long as the two-way path is established.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Fri Oct 4 08:46:03 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.