Examples
Multicast Routing Monitor
This feature module describes the Multicast Routing Monitor feature. It includes the following sections:
Feature Overview
The Multicast Routing Monitor (MRM) feature is a management diagnostic tool that provides network fault detection and isolation in a large multicast routing infrastructure. It is designed to notify a network administrator of multicast routing problems in near real time.
MRM has three components that play different roles: the Manager, the Test Sender, and the Test Receiver.
- If you want to test a multicast environment using test packets, perhaps before an upcoming multicast event, you need three components to perform the roles (Manager, Test Sender, and Test Receiver).
- If you want to monitor existing IP multicast traffic rather than test packets (the multicast event is already under way), you do not need a Test Sender. You need only two components to act as Manager and Test Receiver.
You create a test based on various test parameters, name the test, and start the test. The test runs in the background and the command prompt returns.
If the Test Receiver detects an error (such as packet loss or duplicate packets), it sends an error report to the router configured as the Manager. The Manager immediately displays the error report. Also, by issuing a certain show command, you can see the error reports, if any. You then troubleshoot your multicast environment as normal, perhaps using the mtrace command from the source to the Test Receiver. If the show command displays no error reports, the Test Receiver is receiving test packets without loss or duplicates from the Test Sender.
Benefits
Find Fault in Multicast Routing in Near Real Time
If a problem exists in the multicast routing environment, you will find out about it right away.
Can Verify a Multicast Environment Prior to an Event
You need not wait for real multicast traffic to fail in order to find out that a problem exists. You can test the multicast routing environment before a planned event.
Easy Diagnostics
The error information is easy for the user to understand.
Scalable
This diagnostic tool works well for many users.
Restrictions
You must make sure the underlying multicast forwarding network being tested has no access lists or boundaries that deny the MRM data and control traffic. Specifically, consider the following:
- MRM test data are User Datagram Protocol (UDP) and Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) packets addressed to the configured multicast group address.
- MRM control traffic between the Test Sender, Test Receiver, and Manager is addressed to the 224.0.1.111 multicast group, which all three components join.
Related Documents
- Cisco IOS Release 12.0 Network Protocols Configuration Guide, Part 1, "Configuring IP Multicast Routing" chapter
- Cisco IOS Release 12.0 Network Protocols Command Reference, Part 1, "IP Multicast Routing Commands" chapter
Supported Platforms
- Cisco 1600 series
- Cisco 2500 series
- Cisco 2600 series
- Cisco 3600 series
- Cisco 4000 series (Cisco 4000, 4000-M, 4500, 4500-M, 4700, 4700-M)
- Cisco 7200 series
- Cisco 7500 series
- Cisco 8540
- Cisco 12000 series
- RSM 5000
Supported Standards, MIBs, and RFCs
MIBs
No new or modified MIBs are supported by this feature.
For descriptions of supported MIBs and how to use MIBs, see the Cisco MIB web site on CCO at http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml.
RFCs
None
Standards
Internet-Draft of Multicast Routing Monitor (MRM), IETF, March 1999
Configuration and Testing Tasks
Perform the following tasks to configure and use the Multicast Routing Monitor feature:
Configuring a Test Sender and Test Receiver
You must configure a Test Receiver on a router or host:
| Step
|
Command
|
Purpose
|
| 1.
|
Router(config)# interface type number
|
Specifies an interface.
|
| 2.
|
Router(config-if)# ip mrm test-receiver
|
Configures the interface to be a Test Receiver.
|
| 3.
|
Router(config)# ip mrm accept-manager {access-list-name | access-list-number}
|
Optionally, specifies that the Test Receiver can accept status report requests only from Managers specified by the access list.
|
To use MRM on test packets instead of actual IP multicast traffic, you must also use the following commands to configure a Test Sender on a different router or host from where you configured the Test Receiver:
| Step
|
Command
|
Purpose
|
| 1.
|
Router(config)# interface type number
|
Specifies an interface.
|
| 2.
|
Router(config-if)# ip mrm test-sender
|
Configures the interface to be a Test Sender.
|
| 3.
|
Router(config)# ip mrm accept-manager {access-list-name | access-list-number}
|
Optionally, specifies that the Test Sender can accept status report requests only from Managers specified by the access list.
|
Monitoring Multiple Groups
If you have more than one multicast group to monitor, you could configure an interface that is a Test Sender for one group and a Test Receiver for another group.
Figure 1 illustrates an environment where the router on the left is the Test Sender for Group A and the Test Receiver for Group B.
Figure 1 Test Sender and Test Receiver for Different Groups on One Router
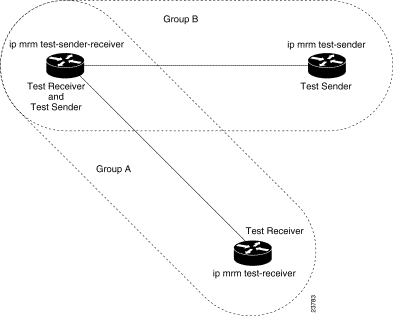
In this case, you would configure the Test Sender in Group B and the Test Receiver in Group A separately, as already discussed. You would also configure the following commands on the router or host that belongs to both Group A and Group B (in the upper left of Figure 1).
| Step
|
Command
|
Purpose
|
| 1.
|
Router(config)# interface type number
|
Specifies an interface.
|
| 2.
|
Router(config-if)# ip mrm test-sender-receiver
|
Configures the interface to be a Test Sender for one group and a Test Receiver for another group.
|
| 3.
|
Router(config)# ip mrm accept-manager {access-list-name | access-list-number}[test-sender | test-receiver]
|
Optionally, specifies that the Test Sender or Test Receiver can accept status report requests only from Managers specified by the access list. By default, the command applies to both the Sender and Receiver. Because this device is both, you might need to specify that the restriction applies to only the Sender or only the Receiver.
|
Configuring a Manager
You must configure a router as a Manager in order for MRM to function; a host cannot be a Manager. Perform the following steps:
| Step
|
Command
|
Purpose
|
| 1.
|
Router(config)# ip mrm manager test-name
|
Identifies a test by name, and places the router in manager configuration mode. The name is used to start, stop, and monitor a test.
|
| 2.
|
Router(config-mrm-manager)# manager type number group ip-address
|
Specifies which interface on the router is the Manager, and specifies the multicast group address the Test Receiver will listen to.
|
| 3.
|
Router(config-mrm-manager)# beacon [interval seconds][holdtime seconds] [ttl hops]
|
Changes the frequency, duration, or scope of beacon messages that the Manager sends to the Test Sender and Test Receiver.
|
| 4.
|
Router(config-mrm-manager)# udp-port [test-packet port-number] [status-report port-number]
|
Changes UDP port numbers to which the Test Sender sends test packets or the Test Receiver sends status reports.
|
| 5.
|
Router(config-mrm-manager)# senders {access-list-number | access-list-name}[packet-delay milliseconds][rtp | udp] [target-only | all-multicasts | all-test-senders]
|
Configures Test Sender parameters.
|
| 6.
|
Router(config-mrm-manager)# receivers {access-list-name | access-list-number} [sender-list {access-list-name | access-list-number} [packet-delay]] [window seconds] [report-delay seconds] [loss percentage] [no-join] [monitor | poll]
|
- Establishes Test Receivers for Multicast Routing Monitor.
- Specifies which Test Senders the Test Receivers will listen to.
- Specifies which sources the Test Receivers monitor.
- Specifies the packet delay.
- Changes Test Receiver parameters.
|
Verifying a Manager
Use the show ip mrm manager command to display the Manager configuration.
Conducting an MRM Test
Use the following command to start and subsequently stop your MRM test.
| Command
|
Purpose
|
Router# mrm test-name {start | stop}
|
Starts or stops the MRM test.
|
When the test begins, the Manager sends a unicast control packet to the Test Sender and Test Receiver, and then the Manager starts sending beacons. The Test Sender and Test Receiver send acknowledgments to the Manager and begin sending or receiving test packets. If an error occurs, the Test Receiver sends an error report to the Manager, which immediately displays the report.
You cannot change the Manager parameters while the test is in progress.
Monitoring and Maintaining the Multicast Routing Monitor
| Command
|
Purpose
|
Router# clear ip mrm status-report [ip-address]
|
Clears the status report cache buffer.
|
Router# show ip mrm interface [interface-unit]
|
Displays Test Sender and Test Receiver information.
|
Router# show ip mrm manager [test-name]
|
Displays MRM test information.
|
Router# show ip mrm status-report [ip-address]
|
Displays the status reports (errors) in the circular cache buffer.
|
Configuration Examples
Figure 2 illustrates a Test Sender, a Test Receiver, and a Manager in a Multicast Routing Monitor environment. The partial configurations for the three devices follow the figure.
Figure 2 Multicast
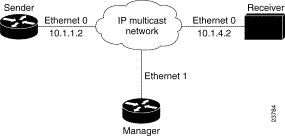 Routing Monitor Example
Routing Monitor Example
Test Sender
Test Receiver
Manager
manager Ethernet 1 group 239.1.1.1
senders 1
receivers 2 sender-list 1
access-list 1 permit 10.1.1.2
access-list 2 permit 10.1.4.2
Command Reference
This section documents new commands. All other commands used with this feature are documented in the Cisco IOS Release 12.0 command reference publications.
In Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T or later, you can search and filter the output for show and more commands. This functionality is useful when you need to sort through large amounts of output, or if you want to exclude output that you do not need to see.
To use this functionality, enter a show or more command followed by the "pipe" character (|), one of the keywords begin, include, or exclude, and an expression that you want to search or filter on:
command | {begin | include | exclude} regular-expression
Following is an example of the show atm vc command in which you want the command output to begin with the first line where the expression "PeakRate" appears:
show atm vc | begin PeakRate
For more information on the search and filter functionality, refer to the Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T feature module entitled CLI String Search.
beacon
To change the frequency, duration, or scope of beacon messages that the Manager sends to Test Senders and Test Receivers during a Multicast Routing Monitor test, use the beacon manager configuration command. To restore the default value, use the no form of the command.
- beacon [interval seconds] [holdtime seconds] [ttl hops]
no beacon [interval seconds] [holdtime seconds] [ttl hops]
Syntax Description
interval seconds
|
(Optional) Frequency of beacon messages in seconds. The default value is 60 seconds, meaning one beacon message every 60 seconds.
|
holdtime seconds
|
(Optional) Length of the test period in seconds. The Test Sender and Test Receiver are respectively sending and receiving test data constantly during the hold time. The default value is 1 day (86400 seconds).
|
ttl hops
|
(Optional) Time-to-live (TTL) of the beacon messages. The default value is 32 hops.
|
Defaults
interval seconds is 60
holdtime seconds is 86400 (1 day)
ttl hops is 32
Command Modes
Manager configuration
Command History
| Release
|
Modification
|
12.0(5)S
|
This command was introduced.
|
Usage Guidelines
The beacon message functions like a keepalive message. The Manager multicasts beacon messages to the Test Sender and Test Receiver. Beacon messages include the sender requests and receiver requests to start the test, thus providing redundancy in case the Test Sender or Test Receiver goes down.
You can increase the default interval to reduce beacon traffic.
You can decrease the holdtime to shorten the test time.
You can change the default number of ttl hops if your network were large and the beacon needed more than 32 hops to get from the Manager to the Test Sender or Test Receiver.
Examples
The following example customizes the Manager to send beacon messages every 30 minutes (1800 seconds), for a test period of 12 hours (43200 seconds), with a TTL of 40 hops:
beacon interval 1800 holdtime 43200 ttl 40
Related Commands
| Command
|
Description
|
manager
|
Specifies that an interface is the Manager for Multicast Routing Monitor.
|
clear ip mrm status-report
To clear the status report cache buffer, use the clear ip mrm status-report EXEC command.
- clear ip mrm status-report [ip-address]
Syntax Description
ip-address
|
(Optional) Address of the Test Receiver. Clears only those status reports received from the Test Receiver having this IP address. If no address is specified, all status reports are cleared from the cache buffer.
|
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
| Release
|
Modification
|
12.0(5)S
|
This command was introduced.
|
Usage Guidelines
You typically need not clear this circular cache buffer.
Examples
The following example clears status reports from the Test Receiver at 175.2.3.4:
clear ip mrm status-report 175.2.3.4
Related Commands
| Command
|
Description
|
show ip mrm status-report
|
Displays Multicast Routing Monitor status reports in the circular cache buffer.
|
ip mrm
To configure an interface to operate as a Test Sender or Test Receiver, or both, for Multicast Routing Monitor, use the ip mrm interface configuration command. To remove the interface as a Test Sender or Test Receiver, use the no form of the command.
- ip mrm {test-sender | test-receiver | test-sender-receiver}
no ip mrm {test-sender | test-receiver | test-sender-receiver}
Syntax Description
test-sender
|
Configures the interface to be a Test Sender.
|
test-receiver
|
Configures the interface to be a Test Receiver.
|
test-sender-receiver
|
Configures the interface to be both a Test Sender and Test Receiver (for different groups).
|
Defaults
The interface is neither a Test Sender nor a Test Receiver.
Command Modes
Interface configuration
Command History
| Release
|
Modification
|
12.0(5)S
|
This command was introduced.
|
Usage Guidelines
The Test Sender and Test Receiver can be either a router or a host.
If a router (or host) belongs to more than one test group, it can be a Test Sender for one group and a Test Receiver for the other group. It cannot be the Test Sender and Test Receiver for the same group.
Examples
The following example configures Ethernet interface 0 to be a Test Sender:
interface ethernet 0
ip mrm test-sender
Related Commands
| Command
|
Description
|
receivers
|
Configures Test Receiver parameters.
|
senders
|
Configures Test Sender parameters.
|
ip mrm accept-manager
To configure a Test Sender or Test Receiver to accept requests only from Managers that pass an access list, use the ip mrm accept-manager global configuration command. To remove the restriction, use the no form of the command.
- ip mrm accept-manager {access-list-name | access-list-number} [test-sender | test-receiver]
no ip mrm accept-manager {access-list-name | access-list-number}
Syntax Description
access-list-name
|
Named IP access list applied to the Managers.
|
access-list-number
|
Numbered IP access list applied to the Managers.
|
test-sender
|
(Optional) The access list applies only to the Test Sender.
|
test-receiver
|
(Optional) The access list applies only to the Test Receiver.
|
Defaults
If neither test-sender nor test-receiver is configured, the access list applies to both.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
| Release
|
Modification
|
12.0(5)S
|
This command was introduced.
|
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to control which Managers a Test Sender or Test Receiver must respond to.
Examples
The following example configures the Test Sender to respond only to Managers that pass the access list named supervisor:
ip access-list standard supervisor
remark Permit only the Manager from Central Office
permit 172.18.2.4
ip mrm accept-manager supervisor test-sender
Related Commands
| Command
|
Description
|
ip mrm
|
Configures an interface to operate as a Test Sender or Test Receiver, or both.
|
ip mrm manager
To identify a Multicast Routing Monitor (MRM) test and enter the mode in which you specify the test parameters, use the ip mrm manager global configuration command. To remove the test, use the no form of the command.
- ip mrm manager test-name
no ip mrm manager test-name
Syntax Description
test-name
|
Name of the group of MRM test parameters that follow.
|
Defaults
There is no MRM test.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
| Release
|
Modification
|
12.0(5)S
|
This command was introduced.
|
Usage Guidelines
The test-name identifies a test so that you can start, stop, or monitor the test.
After you enter this command, the router is in manager configuration mode and you must set the test parameters.
Examples
The following example identifies an MRM test named test1 and causes the system to enter manager configuration mode:
ip mrm manager test1
manager ethernet 0 group 239.1.1.1
Related Commands
| Command
|
Description
|
mrm
|
Starts and stops the MRM test specified by name.
|
show ip mrm manager
|
Displays MRM test information.
|
manager
To specify that an interface is the Manager for Multicast Routing Monitor, and to specify the multicast group address the Test Receiver will listen to, use the manager manager configuration command. To remove the Manager or group address, use the no form of the command.
- manager type number group ip-address
no manager type number group ip-address
Syntax Description
type number
|
Interface type and number of the Manager. The IP address associated with this interface is the source address of the Manager.
|
group ip-address
|
IP multicast group address that the Test Receiver will listen to.
|
Defaults
There is no MRM Manager.
Command Modes
Manager configuration
Command History
| Release
|
Modification
|
12.0(5)S
|
This command was introduced.
|
Usage Guidelines
This command identifies the interface that acts as the Manager, and therefore is required in order to run Multicast Routing Monitor.
Examples
The following example configures Ethernet interface 0 as the Manager. It also configures the Test Receiver to listen to multicast group 239.1.1.1.
manager ethernet 0 group 239.1.1.1
Related Commands
| Command
|
Description
|
beacon
|
Changes the frequency, duration, or scope of beacon messages that the Manager sends to Test Senders and Test Receivers during a Multicast Routing Monitor test.
|
ip mrm accept-manager
|
Configures a Test Sender or Test Receiver to accept requests only from Managers that pass an access list.
|
show ip mrm manager
|
Displays test information for Multicast Routing Monitor.
|
mrm
To start or stop a Multicast Routing Monitor (MRM) test, use the mrmtest EXEC command.
- mrm test-name {start | stop}
Syntax Description
test-name
|
Name of the MRM test, as defined by the ip mrm manager command.
|
start
|
Starts the MRM test specified by test-name.
|
stop
|
Stops the MRM test specified by test-name.
|
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
| Release
|
Modification
|
12.0(5)S
|
This command was introduced.
|
Usage Guidelines
You must use this command to run an MRM test. When the test runs, the Test Sender sends UDP or UDP/RTP packets (depending on the senders command) to the Test Receiver.
Examples
The following example starts the MRM test named test1:
Related Commands
receivers
To configure the following, use the receivers manager configuration command:
- Establish Test Receivers for Multicast Routing Monitor
- Specify which Test Senders the Test Receivers will listen to
- Specify which sources the Test Receivers monitor
- Specify the packet delay
- Change Test Receiver parameters
To restore the default values, use the no form of the command.
- receivers {access-list-name | access-list-number} [sender-list {access-list-name |
access-list-number} [packet-delay]] [window seconds] [report-delay seconds]
[loss percentage] [no-join] [monitor | poll]
no receivers {access-list-name | access-list-number} [sender-list {access-list-name |
access-list-number} [packet-delay]] [window seconds] [report-delay seconds]
[loss percentage] [no-join] [monitor | poll]
Syntax Description
access-list name | access-list number
|
IP named or numbered access list that establishes who the Test Receivers are. Only these Test Receivers are subject to the other keywords and arguments specified in this command.
|
sender-list access-list name | access-list number
|
(Optional) Specifies the sources that the Test Receiver should monitor. If the access list matches any access list specified in the senders command, the associated packet-delay milliseconds of that senders command is used in this command. Otherwise, packet-delay is required in this receivers command.
|
packet-delay
|
(Optional) Specifies the delay between test packets (in milliseconds). If the sender-list access list matches any access list specified in the senders command, the associated packet-delay milliseconds of that senders command is used in this command. Otherwise, packet-delay is required in this receivers command.
|
window seconds
|
(Optional) Duration (in seconds) of a test period. This is a sliding window of time in which packet count is collected, so that the loss percentage can be calculated. Default is 5 seconds.
|
report-delay seconds
|
(Optional) Delay (in seconds) between staggered status reports from multiple Test Receivers to the Manager. The delay prevents multiple receivers from sending status reports to the Manager at the same time for the same failure. Receiver 1 sends status, seconds later Receiver 2 sends status, seconds later Receiver 3 sends status, and so on. This value is relevant only if there are multiple Test Receivers. The default is 1 second.
|
loss percentage
|
(Optional) Threshold percentage of packet loss required before a status report is triggered. The default is 0%, which means that a status report is sent for any packet loss. (This value is not applied to packet duplication; a fault report is sent for any duplicated packets.) Loss percentage calculation is explained in the "Usage Guidelines" section of this command.
|
no-join
|
(Optional) Specifies that the Test Receiver does not join the monitored group. The default is that the Test Receiver joins the monitored group.
|
monitor | poll
|
(Optional) Specifies whether the Test Receiver monitors the test group or polls for receiver statistics. Monitor means the Test Receiver reports only if the test criteria are met. Poll means the Test Receiver sends status reports regularly, whether test criteria are met or not. The default is monitor.
|
Defaults
window seconds is 5 seconds
report-delay seconds is 1 second
loss percentage is 0 percent
monitor
Command Modes
Manager configuration
Command History
| Release
|
Modification
|
12.0(5)S
|
This command was introduced.
|
Usage Guidelines
This command is required for Multicast Routing Monitor to work; the keyword receivers and the first access list must be specified. The rest of the command is optional.
Loss percentage is calculated based on the packet-delay value of the senders command, which defaults to 200 milliseconds, or 5 packets per second. If the window keyword defaults to 5 seconds, then the Test Receiver expects 5 packets per second for 5 seconds = 25 packets. If the Test Receiver receives only 15 packets, then 25 - 15 = 10 lost packets. Lost packets divided by packets expected equals loss percentage. 10/25 equals a loss percentage of 40 percent.
Examples
In the following example, test2 has the proxy-sender address 10.1.1.10, and the corresponding receiver command has an explicit packet delay configured to match the default packet delay of the sender:
manager e4/0/1 group 239.1.1.1
receivers 2 sender-list 1
manager e4/0/1 group 239.1.1.1
receivers 2 sender-list 3 200
udp-port test-packet 16386 status-report 65533
access-list 1 permit 10.1.1.2
access-list 2 permit 10.1.4.2
access-list 3 permit 10.1.1.10
Related Commands
| Command
|
Description
|
senders
|
Configures Test Sender parameters used in Multicast Routing Monitor.
|
senders
To configure Test Sender parameters used in Multicast Routing Monitor, use the senders manager configuration command. To restore the default values, use the no form of the command.
- senders {access-list-name | access-list number} [packet-delay milliseconds] [rtp | udp]
[target-only | all-multicasts | all-test-senders] [proxy_src]
no senders {access-list-name | access-list number} [packet-delay milliseconds] [rtp | udp]
[target-only | all-multicasts | all-test-senders] [proxy_src]
Syntax Description
access-list name | access-list number
|
IP named or numbered access list that defines which Test Senders are involved in the test and which Test Senders these parameters apply to.
|
packet-delay milliseconds
|
(Optional) Specifies the delay between test packets (in milliseconds). The default is 200 milliseconds, which results in 5 packets per second.
|
rtp | udp
|
(Optional) Encapsulation of test packets, either RTP-encapsulated or UDP-encapsulated. The default is RTP-encapsulated.
|
target-only
|
(Optional) Specifies that test packets are sent out on the targeted interface only (that is, the interface with the IP address that is specified in the Test Sender request target field). By default, test packets are sent as described in all-multicasts.
|
all-multicasts
|
(Optional) Specifies that the test packets are sent out on all interfaces that are enabled with IP multicast. This is the default way that test packets are sent.
|
all-test-senders
|
(Optional) Specifies that test packets are sent out on all interfaces that have test-sender mode enabled. By default, test packets are sent as described in all-multicasts.
|
proxy_src
|
(Optional) Source IP address for which the Test Sender will proxy test packets. Use this if you want to test, for a specific source, whether the multicast distribution tree is working.
|
Defaults
packet-delay milliseconds is 200 milliseconds (that is, 5 packets per second)
rtp
all-multicasts
Command Mode
Manager configuration
Command History
| Release
|
Modification
|
12.0(5)S
|
This command was introduced.
|
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to specify which Test Senders are involved in the test and are affected by these parameters.
Examples
In the following example, test2 has the proxy-sender address 10.1.1.10, and the corresponding receivers command has an explicit packet delay configured to match the default packet delay of the sender:
manager e4/0/1 group 239.1.1.1
receivers 2 sender-list 1
manager e4/0/1 group 239.1.1.1
receivers 2 sender-list 3 200
udp-port test-packet 16386 status-report 65533
access-list 1 permit 10.1.1.2
access-list 2 permit 10.1.4.2
access-list 3 permit 10.1.1.10
Related Commands
| Command
|
Description
|
receivers
|
- Establishes Test Receivers for Multicast Routing Monitor.
- Specifies which Test Senders the Test Receivers will listen to.
- Specifies which sources the Test Receivers monitor.
- Specifies the packet delay.
- Changes Test Receiver parameters.
|
show ip mrm interface
To display Test Sender or Test Receiver information about Multicast Routing Monitor (MRM), use the show ip mrm interface EXEC command.
- show ip mrm interface [interface-unit]
Syntax Description
interface-unit
|
(Optional) Interface about which to display Test Sender or Test Receiver information. If no interface is specified, information about all Test Senders and Test Receivers is displayed.
|
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
| Release
|
Modification
|
12.0(5)S
|
This command was introduced.
|
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to see which interfaces are participating in MRM in which roles, and whether the interfaces are up or down.
Examples
The following example is sample output for the show ip mrm interface command:
Router#
show ip mrm interface
Interface Address Mode Status
Ethernet0 1.1.1.1 Test-Sender Up
Ethernet1 2.2.2.2 Test-Receiver Up
Table 1 describes the fields in the display.
Table 1 show ip mrm interface Field Descriptions
| Field
|
Description
|
Interface
|
List of interfaces on this router that serve as a Test Sender or Test Receiver.
|
Address
|
IP address of the interface.
|
Mode
|
Role that the interface plays in Multicast Routing Monitor, either Test Sender or Test Receiver.
|
Status
|
Status of the interface.
|
Related Commands
| Command
|
Description
|
ip mrm
|
Configures an interface to operate as a Test Sender or Test Receiver.
|
show ip mrm manager
To display test information for Multicast Routing Monitor (MRM), use the show ip mrm manager EXEC command.
- show ip mrm manager [test-name]
Syntax Description
test-name
|
(Optional) Name of the MRM test (as specified in the ip mrm manager command) for which to display information. If no name is specified, information about all Managers is displayed.
|
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
| Release
|
Modification
|
12.0(5)S
|
This command was introduced.
|
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to see information about the Manager.
Examples
The following example is sample output for the show ip mrm manager command executed at two different times:
Router#
show ip mrm manager test
Manager:test/1.1.1.1 is running, expire:1d00h
Beacon interval/holdtime/ttl:60/86400/32
Group:239.1.2.3, UDP port test-packet/status-report:16384/65535
Router#
show ip mrm manager test
Manager:test/1.1.1.1 is not running
Beacon interval/holdtime/ttl:60/86400/32
Group:239.1.2.3, UDP port test-packet/status-report:16384/65535
Table 2 describes the fields in the display.
Table 2 show ip mrm manager Field Descriptions
| Field
|
Description
|
Manager
|
Status of the test named "test" run by the Manager at 1.1.1.1.
|
Beacon interval/holdtime/ttl
|
Beacon parameters configured by the beacon command.
|
Group
|
IP multicast group that the Test Receiver will listen to, as configured by the manager command.
|
UDP port test-packet / status report
|
UDP port number to which test packets sent are by a Test Sender / status reports are sent by a Test Receiver, as configured by the udp-port command.
|
Test senders
|
IP address of Test Senders.
|
Test receivers
|
IP address of Test Receivers.
|
Related Commands
| Command
|
Description
|
ip mrm manager
|
Identifies a Multicast Routing Monitor test.
|
manager
|
Specifies that an interface is the Manager for Multicast Routing Monitor, and specifies the multicast group address the Test Receiver will listen to.
|
show ip mrm status-report
To display Multicast Routing Monitor (MRM) status reports of errors in the circular cache buffer, use the show ip mrm status-report EXEC command.
- show ip mrm status-report [ip-address]
Syntax Description
ip-address
|
(Optional) Displays information received from this IP address only. If no address is specified, all status reports in the cache buffer are displayed.
|
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
| Release
|
Modification
|
12.0(5)S
|
This command was introduced.
|
Usage Guidelines
Use this command during your MRM test period to see if any errors are reported. The Manager immediately displays error reports and sends error reports, if any, to the circular cache buffer. The buffer holds up to 1024 lines, with one line for each error report.
No errors reported indicates that the Test Receiver is receiving test packets without loss or duplicates from the Test Sender.
Examples
The following example is sample output for the show ip mrm status-report command:
Router#
show ip mrm status-report
IP MRM status report cache:
Timestamp Manager Test Receiver Pkt Loss/Dup (%) Ehsr
*Apr 20 07:36:08 1.1.1.1 3.3.3.3 5 (20%) 0
*Apr 20 07:36:09 1.1.1.1 3.3.3.3 10 (40%) 0
*Apr 20 07:36:10 1.1.1.1 3.3.3.3 15 (60%) 0
Table 3 describes the fields in the display.
Table 3 show ip mrm status-report Field Descriptions
| Field
|
Description
|
Timestamp
|
Time when status report arrived in cache. Month and date, hours:minutes:seconds.
|
Manager
|
IP address of the Manager.
|
Test Receiver
|
IP address of the Test Receiver.
|
Pkt Loss/Dup
|
Number of packets lost or duplicated.
|
%
|
Percentage of packets lost or duplicated. Loss percentage is calculated based on the packet-delay value of the senders command, which defaults to 200 milliseconds, or 5 packets per second. If the window keyword defaults to 5 seconds, then the Test Receiver expects 5 packets per second for 5 seconds = 25 packets. If the Test Receiver receives only 15 packets, then 25 - 15 = 10 lost packets. Lost packets divided by packets expected equals loss percentage. 10/25 equals a loss percentage of 40%.
A negative percentage indicates duplicate packets were received.
If the packet loss reaches 100%, the Test Receiver will back off and not send periodic reports until the packet loss decreases to less than 100%.
|
Ehsr
|
Extended highest sequence number received from Real Time Transport Protocol (RTP).
|
Related Commands
udp-port
To change UDP port numbers to which test packets sent are by a Test Sender or status reports are sent by a Test Receiver, use the udp-port manager configuration command. To remove the port numbers, use the no form of the command.
- udp-port [test-packet port-number] [status-report port-number]
no udp-port [test-packet port-number] [status-report port-number]
Syntax Description
test-packet port-number
|
(Optional) UDP port number to which test packets are sent by a Test Sender. The port number must be even if the packets are RTP-encapsulated. The default port number is 16384.
|
status-report port-number
|
(Optional) UDP port number to which status reports are sent by a Test Receiver. The port number must be odd if the packets are RTCP-encapsulated. The default port number is 65535.
|
Defaults
test-packet port-number is 16384, the minimum value of an audio port.
status-report port-number is 65535, the maximum value of a video port.
Command Modes
Manager configuration
Command History
| Release
|
Modification
|
12.0(5)S
|
This command was introduced.
|
Usage Guidelines
Change the default values if you want to listen to a different port.
Examples
The following example changes the UDP port number to which test packets are targeted to 20000:
udp-port test-packet 20000
Related Commands
| Command
|
Description
|
ip mrm
|
Configures an interface to operate as a Test Sender or Test Receiver.
|
Debug Commands
This section documents the new debug command related to the Multicast Routing Monitor feature.
debug ip mrm
To display Multicast Routing Monitor (MRM) control packet activity, use the debug ip mrm privileged EXEC command. Use the no form of the command to disable debugging output.
- [no] debug ip mrm
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Defaults
Debugging for MRM is not enabled.
Command History
| Release
|
Modification
|
12.0(5)S
|
This command was introduced.
|
Examples
The following example is sample output for the debug ip mrm command on the different devices:
On Manager
*Feb 28 16:25:44.009: MRM: Send Beacon for group 239.1.1.1, holdtime 86100 seconds
*Feb 28 16:26:01.095: MRM: Receive Status Report from 10.1.4.2 on Ethernet0
*Feb 28 16:26:01.099: MRM: Send Status Report Ack to 10.1.4.2 for group 239.1.1.1
*Feb 28 16:26:01.103: IP MRM status report -- Test:test2 Receiver:10.1.4.2
*Feb 28 16:26:01.107: Sender:10.1.1.10 Pkt Loss:4(16%) Ehsr:1380
The last two lines of output on the Manager are not part of the debug output; they appeared because an error report was received.
On Test-Sender
MRM: Receive Test-Sender Request/Local trigger from 1.1.1.1 on Ethernet0
MRM: Send TS request Ack to 1.1.1.1 for group 239.1.2.3
MRM: Send test packet src:2.2.2.2 dst:239.1.2.3 manager:1.1.1.1
On Test-Receiver
MRM: Receive Test-Receiver Request/Monitor from 1.1.1.1 on Ethernet0
MRM: Send TR request Ack to 1.1.1.1 for group 239.1.2.3
MRM: Receive Beacon from 1.1.1.1 on Ethernet0
MRM: Send Status Report to 1.1.1.1 for group 239.1.2.3
MRM: Receive Status Report Ack from 1.1.1.1 on Ethernet0




Posted: Thu Jan 16 21:00:15 PST 2003
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.


 Routing Monitor Example
Routing Monitor Example
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()