|
|

The Cisco 12000 series Gigabit Switch Routers (GSR) is a new product class of routers that perform Internet routing and switching at gigabit speeds. The Cisco 12012 and Cisco 12008 meet the exponential growth in demand for Internet bandwidth and bring scalability and high-performance services to IP-based networks. Designed to meet current and future Internet traffic requirements, the Cisco 12000 series initially supports IP backbone links at OC-3/STM-1 (155 Mbps) and OC-12/STM-4 (622 Mbps)--facilities up to four times faster than those used today.
The Cisco 12000 series is built around a high-speed switching fabric that provides nonblocking bandwidth to support high-performance IP-based LANs and WANs. The switching fabric is scalable from 15 to 60 Gbps on the Cisco 12012 and from 10 to 40 Gbps on the Cisco 12008. Both the Cisco 120012 and Cisco 12008 support IP over SONET/SDH and ATM interfaces.
The Cisco 12012 has 12 user-configurable slots, and the Cisco 12008 has eight user-configurable slots. These slots contain line cards and Gigabit Route Processor (GRP). Network interfaces reside on line cards that provide connection between the router's switch fabric and the external networks.
For more information on the Cisco 12000 series, refer to the Cisco 12012 Gigabit Switch Router Installation and Configuration Guide and the Cisco 12008 Gigabit Switch Router Installation and Configuration Guide.
Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF)--An advanced Layer 3 switching technology for IP. CEF optimizes network performance and scalability for networks with large and dynamic traffic patterns, such as those associated with the Internet, Web-based applications, and interactive sessions.
Gigabit Route Processor (GRP)--Serves as the console for the Cisco 12000 series, handles environmental monitoring for the entire system, and provides the line cards with routing table updates.
Line cards--Provide connection between the router and the network and are available in a variety of network media types (based on your order). Line cards communicate with each other and with the GRP through the switch fabric.
Switch fabric--The circuitry that carries the user traffic between line cards or between the GRP and a line card.
Command descriptions use these conventions:
The Cisco 12000 series supports the following MIBs:
For descriptions of supported MIBs and how to use MIBs, see Cisco's MIB website on CCO at http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml.
The Cisco 12000 series supports the following RFCs:
The following configuration tasks are listed for the Cisco 12000 series because they are in addition to or different from configuration information listed in the Cisco IOS documentation set. All tasks are optional.
In addition to the above configuration tasks, also refer to the "Cisco Express Forwarding" feature module for information on how to configure CEF on the Cisco 12000 series.
For information on configuring IP and IP Routing, refer to the "Configuring IP" and "Configuring IP Routing Protocols" chapters in the Network Protocols Configuration Guide, Part 1.
For information on configuring the line cards and Gigabit Route Processor, refer to the following publications that accompanies the hardware:
Loading a Cisco IOS image on the GRP on a Cisco 12000 series router is the same as loading images on Cisco 7500 series routers. In addition to the Cisco IOS image that resides on the GRP, each line card on the Cisco 12000 series has a Cisco IOS image. When the router is reloaded, the specified Cisco IOS image is loaded onto the GRP, and that image is automatically dowloaded to all the line cards.
For information on how to load Cisco IOS images, refer to the "Loading Images and Configuration Files" chapter in the Configuration Fundamentals Configuration Guide. For additional information, refer to the "Observing System Startup and Performing a Basic Configuration" chapter in the Cisco 12012 Gigabit Switch Router Installation and Configuration Guide.
Normally, you want the same Cisco IOS image on the GRP and all line cards. However, if you want to upgrade a line card with a new version of microcode for testing or to fix a defect, you might need to load a Cisco IOS image that is different from the one on the line card. Additionally, you might need to load a new image on the line card to work around a problem that is affecting only one of the line cards.
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Step 1 Specify the type of line card, location of the Cisco IOS image, and the slot of the line card to download the image. If the slot number is omitted, the image is downloaded to all line cards. | microcode {oc12-atm | oc12-pos | oc3-pos-4} flash file_id slot-number |
| Step 2 Reload the image on the specified line card. | microcode reload slot-number |
| Step 3 Exit configuration mode. | exit |
| Step 4 Connect to the line card and verify that the new Cisco IOS image is on the line card by checking the version number in the display output. | execute-on slot slot-number show version
or attach slot-number show version exit |
The following sections provide some tools to troubleshoot problems on the Cisco 12000 series routers. For more information, refer to the troubleshooting and diagnostic chapters in the Cisco 12000 series installation and configuration guides.
For a listing of system error messages, refer to the "System Error Messages" feature module.
Also refer to the "Monitoring and Maintaining the Cisco 12000 Series" section, later in this document, for information on the show commands that might also be useful to troubleshoot problems.
To perform field diagnostic testing on a line card, perform the following tasks in privileged EXEC mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Step 1 Specify the line card that you want to perform diagnostic testing on.
Optionally, specify that previous test results are displayed, that only extended power-on self-tests (POST) be performed, that the maximum messages are displayed, or that the Cisco IOS software not be reloaded on the line card after successful completion of the tests. | diag slot-number [previous | post | verbose | wait] |
| Step 2 At the prompt, press Return to confirm that you want to perform field diagnostic testing on the specified line card, or type no to stop the testing. | Running Diags will halt ALL activity on the requested slot. [confirm] |
To stop field diagnostic testing on a line card, perform the following tasks in privileged EXEC mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Specify the line card that you want to stop perform diagnostic testing on. | diag slot-number halt
or no diag slot-number |
 Caution Use the exception linecard global configuration command only when directed by a technical support representative and only enable options that the technical support representative requests you to enable.
Caution Use the exception linecard global configuration command only when directed by a technical support representative and only enable options that the technical support representative requests you to enable.
To enable and configure the crash information options for a line card, perform the following task in global configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Specify the line card that you want crash information for when a line card resets. Optionally, specify the type and amount of memory to be stored. | exception linecard {all | slot number} [corefile filename | main-memory size [k | m] | queue-ram size [k | m] | rx-buffer size [k | m] | sqe-register-rx | sqe-register-tx | tx-buffer size [k | m]] |
The following sections describe some of the show commands you can use to obtain information about the Cisco 12000 series, describe how to set the LED message on the line cards, and describe the software components on the Cisco 12000 series and how to obtain information about these components.
To use the show commands on a line card, you can use the execute-on privileged EXEC command or you can connect to the Cisco IOS image running on the line card by using the attach privileged EXEC command.
Refer to the "Command Reference" section for detailed command syntax for the new or modified commands listed in this section.
Perform these tasks in privileged EXEC mode to display the information described:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Display information about the hardware. | show controllers |
| Display information stored in NVRAM when the router crashes. This command is only useful to technical support representatives. | show context |
| Display part number, revision number, and version number information for the line cards. | show diag |
| Display the current environmental specifications. | show environment |
| Display hardware information. | show gsr |
| Display the state of syslog error and event logging. | show logging |
| Display memory pool statistics including summary information about the activities of the system memory allocator and a block-by-block listing of memory use. | show memory |
| Display the microcode bundled into the system image. | show microcode |
| Display information about all active processes. | show processes |
| Display the configured protocols. | show protocols |
| Display stack usage of processes and interrupt routines, including the reason for the last system reboot. This command is only useful to your technical support representative. | show stacks |
| Display the status of TCP connections. | show tcp |
| Display a concise description of TCP connection endpoints. | show tcp brief [all] |
| Display general information about the router when reporting a problem. | show tech-support [page] [password] |
| Display configuration of the system hardware, the software version, the names and sources of configuration files, and the boot image. | show version |
You can specify the message that is displayed on the LED on the front panel of one or more line cards. You can also remove the user-specified message that is displayed on the LED on the front panel of one or more line cards and revert to the normal status message for the line card.
To set or clear the LED message, perform one of the following tasks in privileged EXEC mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Set the message displayed on the LED on the front panel of one or more line cards. | set card-message {all | slot number} [expire seconds] [blink seconds] message |
| Clear the user-specified message that is displayed on the LED on the front panel of one or more line cards and revert to the normal status message for the line card. | clear card-message {all | slot number} |
There are many software components bundled with the Cisco IOS image for the Cisco 12000 series. In most cases you do not need to know about these components; however, during troubleshooting, you might be asked for the specific version number of the various components. Table 1 describes these software components, including those that are bundled with the Cisco IOS image for the Cisco 12000 series and lists the command you would use to determine the version of the component.
| Software Component | Description | Version Information |
|---|---|---|
| MBus Agent Code | MBus agent code is bundled with the Cisco IOS image on the GRP card. When the router is powered on, the MBus agent powers on the GRP card. | show diag1 |
| GRP Cisco IOS Image | Cisco IOS image that runs on the GRP card. This is the main image for the Cisco 12000 series GSR. It contains images for all the line card types and various microcode bundles. | show version |
| GRP Boot Image | Cisco IOS image that runs on the GRP when it is booting from the network. This image is essentially the same as the Cisco IOS image, but it has large portions of the routing software removed because it only acts as an IP host to boot the router. It has all the same line card images and microcode bundles as the Cisco IOS image. | show version |
| Line Card Fabric Downloader | Code that the MBus downloads to the line card so the Cisco IOS image can be downloaded from the GRP over the switch fabric. This is a bootstrap loader that knows how to run the fabric only. There is only one version of the downloader, and it is bundled with the GRP Cisco IOS image. | show diag |
| Line Card Cisco IOS Image | Cisco IOS image that runs on the line card. This image is the main operational code for the line card, and the image senses the type of line card it is running on and adapts. It also supports all variants of the line card. The line card Cisco IOS image is bundled in the GRP Cisco IOS image. | execute-on slot slot-number show version
or attach slot-number show version| exit |
| SQE Microcode | Silicon queuing engine microcode on the line card that controls the data paths on the line card. A different microcode image might exist for each type of line card and different microcode images support different Cisco IOS features (for example, weighted fair queueing). There is a default microcode image that is used when no special features or requirements exist. The SQE microcode is bundled with the line card Cisco IOS image. | execute-on slot slot-number show controllers tofab bma microcode
execute-on slot slot-number show controllers frfab bma microcode or attach slot-number show controllers tofab bma microcode show controllers frfab bma microcode exit |
| ATM OC-12 SAR Microcode | Microcode from the vendor of the SAR-622 chip used on the ATM line card. The ATM SAR microcode is bundled with the line card Cisco IOS image. | execute-on slot slot-number show controllers atm
or attach slot-number show controllers atm exit |
| GRP Field Diagnostic Image | Image that runs on the GRP when field diagnostics are run with the diag command. | None |
| Line Card Field Diagnostic Image | Image that runs on the line card when field diagnostics are run with the diag command. | None |
| GRP ROM Monitor | The ROM monitor is responsible for booting the system from the local Flash devices. It is loaded into the Flash ROM on the GRP when the board is manufactured. | show version |
| Line Card ROM Monitor | The ROM monitor is responsible for booting the line card via the MBus. It is loaded into the Flash ROM on the line card when the board is manufactured. | execute-on slot slot-number show version
or attach slot-number show version exit |
| ROM Monitor Library Image | Image that allows the GRP ROM monitor to access the internal Flash bank and PCMCIA Flash cards. It is bundled with the GRP Cisco IOS image so it can be put on the Flash cards when they are formatted. The GRP ROM monitor gets the ROM monitor image from the Flash device before accessing it. | None |
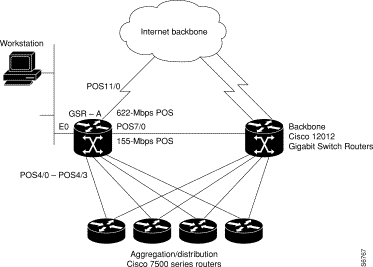
In a typical Internet service provider environment, the Cisco 12000 series routers reside within the core of the network and can support as many as 44 OC-3/STM-1 IP over SONET/SDH optical links to Cisco 7500 series routers or aggregation devices. Below is a typical configuration file for the Cisco 12012. Important configuration commands are bolded. In this example, a Cisco 12000 series router called GSR-A connects to the Internet backbone through interface POS11/0, connects to a second Cisco 12000 series router through interface POS7/0, and connects to Cisco 7500 series routers through interfaces POS4/0, POS4/1, POS4/2, and POS4/3. In addition, GSR-A also has a connection to a workstation through interface E0 for TFTP functions only (no routing is performed).
Current configuration:
!
! Last configuration change at 15:41:46 PDT Tue Sep 30 1997
! NVRAM config last updated at 15:29:07 PDT Tue Sep 30 1997
!
version 11.2
service timestamps debug datetime msec localtime
service timestamps log datetime msec localtime
service internal
service udp-small-servers
service tcp-small-servers
!
hostname GSR-A
!
boot host config.dat 223.255.255.254
boot system banana/bfr/gsr-p-mz.fib20 223.255.255.254
boot system flash slot1:gsr-p-mz
boot system flash slot1:gsr-p-mz.fib19
boot bootldr bootflash:gsr-boot-mz.fib20
enable password 7 1222227220E09
!
ip subnet-zero
no ip domain-lookup
ip host peaches 223.255.254.254
ip host oranges 223.255.254.253
! Enable CLNS routing on the router
clns routing
clock timezone PST -8
clock summer-time PDT recurring
clock calendar-valid
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 1.1.1.31 255.255.255.255
bandwidth 10000000
! Configure the Ethernet interface used for TFTP from the workstation
interface Ethernet0
ip address 16.4.237.10 255.255.0.0
ip broadcast-address 16.4.255.255
! Interfaces POS4/0 through POS4/3 are the OC3c connections
! to the Cisco 7500 series routers with scrambling
interface POS4/0
ip address 71.1.0.2 255.255.0.0
pos scramble-atm
crc 16
clock source internal
!
interface POS4/1
ip address 71.2.0.2 255.255.0.0
pos scramble-atm
crc 16
clock source internal
!
interface POS4/2
ip address 71.3.0.2 255.255.0.0
pos scramble-atm
crc 16
clock source internal
!
interface POS4/3
ip address 102.102.102.1 255.255.255.0
ip broadcast-address 102.102.102.255
pos scramble-atm
crc 16
clock source internal
! Interface POS7/0 is the OC12 connection
! to the second Cisco 12012 router
interface POS7/0
ip address 101.101.101.1 255.255.255.0
pos scramble-atm
crc 32
clock source internal
! Interface POS11/0 is the OC12 connection
! to the Internet
interface POS11/0
ip address 103.103.103.1 255.255.255.0
pos scramble-atm
crc 32
clock source internal
! Routing configured for the Ethernet interface (optional)
router eigrp 1009
passive-interface Ethernet0
network 107.0.0.0
network 108.0.0.0
!
router isis
redistribute connected metric 0 metric-type internal level-2
passive-interface Loopback0
net 47.0000.0031.0031.0000.0031.00
is-type level-2-only
! Routing configured for the Ethernet interface
router igrp 199
network 16.0.0.0
!
router bgp 10
no synchronization
redistribute connected
redistribute static
neighbor 1.1.1.3 remote-as 10
neighbor 1.1.1.3 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 1.1.1.13 remote-as 10
neighbor 1.1.1.13 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 1.1.1.20 remote-as 10
neighbor 1.1.1.20 update-source Loopback0
no auto-summary
!
ip classless
ip default-network 33.0.0.0
ip route 33.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 33.34.0.0
ip route 223.255.0.0 255.255.0.0 Ethernet0
ip route 223.255.253.0 255.255.255.0 16.4.0.1
ip route 223.255.254.0 255.255.255.0 16.4.0.1
logging buffered 2000000 debugging
no logging console
tftp-server flash slot0:rsp-tpgenv-m.CZ.vjp alias rsp-tpgenv-m.CZ.vjp
!
snmp-server community public RO
snmp-server community passthru RW
snmp-server location HighEnd,Bldg.B,San Jose,CA
snmp-server contact Curt Applebee (capplebee@company.com)
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
password secret1
login
line aux 0
exec-timeout 0 0
transport input all
line vty 0 4
exec-timeout 0 0
password secret2
login
!
ntp clock-period 17179665
ntp update-calendar
no scheduler max-task-time
end
This section documents new or modified commands. All other commands used with this feature are documented in the Cisco IOS Release 11.2 command references.
To access the Cisco IOS software image on a line card to monitor and maintain information on the line card, use the attach privileged EXEC command. To exit from the Cisco IOS software image on the line card and return to the Cisco IOS image on the GRP card, use the exit command.
attach slot-number| slot-number | Slot number of the line card you want to connect to. Slot numbers range from 0 to 11 for the Cisco 12012 and 0 to 7 for the Cisco 12008. If the slot number is omitted, you are prompted for the slot number. |
Access to the Cisco IOS software image running on the GRP card.
Privileged EXEC
This command was added in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 GS to support the Cisco 12000 series Gigabit Switch Routers.
Use the attach EXEC command to get specific information about a line card.
After you connect to the Cisco IOS image on the line card using the attach command, the prompt changes to "LC-Slotx#," where x is the slot number of the line card.
You can also use the execute-on slot privileged EXEC command to execute commands on one or all line cards.
The following example connects to the Cisco IOS image running on the line card in slot 9, gets a list of valid show commands, and returns the Cisco IOS image running on the GRP:
Router# attach 9
Entering Console for 4 Port Packet Over SONET OC-3c/STM-1 in Slot: 9
Type exit to end this session
Press RETURN to get started!
LC-Slot9# show ?
cef Cisco Express Forwarding
clock Display the system clock
context Show context information about recent crash(s)
history Display the session command history
hosts IP domain-name, lookup style, nameservers, and host table
ipc Interprocess communications commands
location Display the system location
sessions Information about Telnet connections
terminal Display terminal configuration parameters
users Display information about terminal lines
version System hardware and software status
LC-Slot9# exit
Disconnecting from slot 9.
Connection Duration: 00:01:04
Router#
execute-on slot
To set the mode of operation and thus control type of the ATM cell used for cell-rate decoupling on the SONET PLIM, use the atm sonet interface configuration command. To restore the default Synchronous Transport Signal level 12, concatenated (STS-12c) operation, use the no form of this command.
atm sonet [stm-4]| stm-4 | (Optional) Synchronous Digital Hierarchy/Synchronous Transport Signal level 4 (SDH/STM-4) operation (ITU-T specification). |
STS-12c
Interface configuration
This command was modified in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 GS to add the stm-4 keyword.
Use STM-4 in applications where SDH framing is required.
Use the default (STS-12c) in applications where the ATM switch requires "unassigned cells" for rate adaptation. An unassigned cell contains 32 zeros.
The following example sets the mode of operation to SONET STM-4 on ATM interface 3/0:
Router(config)# interface atm 3/0
Router(config-if)# atm sonet stm-4
Router(config-if)# end
Router#
To remove the user-specified message that is displayed on the LED on the front panel of one or more line cards and revert to the normal status message for the line card, use the clear card-message privileged EXEC command.
clear card-message {all | slot slot-number}| all | Clears the user-specified LED message on all line cards. |
| slot slot-number | Clears the user-specified LED message on a specific line card. Slot numbers range from 0 to 11 for the Cisco 12012 and 0 to 7 for the Cisco 12008. |
Privileged EXEC
This command was added in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 GS to support the Cisco 12000 series Gigabit Switch Routers.
To specify the message that is displayed on the LED on the front panel of one or more line cards, use the set card-message global configuration command.
The following example clears any user-specified message from all line cards.
Router# clear card-message all
Router#
To clear messages from the logging buffer, use the clear logging privileged EXEC command.
clear logging {all | slot slot-number} [counts | messages]| all | Clears the logging buffer for all slots. |
| slot slot-number | Clears the logging buffer for a specific slot. Slot numbers range from 0 to 11 for the Cisco 12012 and 0 to 7 for the Cisco 12008. |
| counts | (Optional) Clears the message counters only from the logging buffer. The messages are kept. |
| messages | (Optional) Clears the messages from logging buffer (that is, discard all messages in the log). |
If no options are specified, clear the counters and messages from the logging buffer for all line cards.
Privileged EXEC
This command was modified in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 GS to include the all, slot, counts, and messages keywords.
Use the show logging command to display logging information.
In the following example, the counters and messages are cleared from the logging buffer on all line cards. The show logging command shows the information before and after the log is cleared.
Router# show logging
Syslog logging: enabled (0 messages dropped, 0 flushes, 0 overruns)
Console logging: level debugging, 32 messages logged
Monitor logging: level debugging, 0 messages logged
Trap logging: level informational, 189 message lines logged
Buffer logging: level debugging, 32 messages logged
Log Buffer (1638 bytes):
2d17h: %SCHED-3-THRASHING: Process thrashing on watched managed timer (0x608610B0).
-Process= "User LED Message Process", ipl= 6, pid= 14
-Traceback= 600CF7F0 600CFB18 60128900 600BFF88 600BFF74
2d17h: %SCHED-3-STUCKMTMR: Sleep w/expired mgd timer 6085F090, time 0xE151558 (0 0:00:07 ago).
-Process= "User LED Message Process", ipl= 6, pid= 14
-Traceback= 600CF750 600CFB18 60128900 600BFF88 600BFF74
...
Router# clear logging
Clear logging buffer [confirm]
Router# show logging
Syslog logging: enabled (0 messages dropped, 0 flushes, 0 overruns)
Console logging: level debugging, 33 messages logged
Monitor logging: level debugging, 0 messages logged
Trap logging: level informational, 192 message lines logged
Buffer logging: level debugging, 33 messages logged
Log Buffer (1638 bytes):
Router#
logging buffered
logging linecard
show logging
To perform field diagnostics on a line card, on the Gigabit Route Processor (GRP), on the Switch Fabric Cards (SFC), and on the Clock Scheduler Card (CSC) in the Cisco 12000 series Gigabit Switch Routers, use the diag privileged EXEC command. To disable field diagnostics on a line card, use the no form of this command.
diag slot-number [halt | previous | post | verbose [wait] | wait]| slot-number | Slot number of the line card you want to test. Slot numbers range from 0 to 11 for the Cisco 12012 and 0 to 7 for the Cisco 12008. Slot numbers for the CSC are 16 and 17 and for the FSC are18, 19, and 20. |
| halt | (Optional) Stops the field diagnostic testing on the line card. |
| previous | (Optional) Displays previous test results (if any) for the line card. |
| post | (Optional) Initiates a EPROM-based extended power-on self-test (EPOST) only. The EPOST test suite is not as comprehensive as the field diagnostics, and a pass/fail message is the only message displayed on the console. |
| verbose [wait] | (Optional) Enables the maximum status messages to be displayed on the console. By default, only the minimum status messages are displayed on the console. If you specify the optional wait keyword, the Cisco IOS software is not be automatically reloaded on the line card after the test completes successfully. |
| wait | (Optional) Stops the automatic reloading of the Cisco IOS software on the line card after the successful completion of the field diagnostic testing. If you use this keyword, you must use the microcode reload slot global configuration command, or manually remove and insert the line card (to power it up) in the slot so that the GRP will recognize the line card and download the Cisco IOS software image to the line card. |
No field diagnostics tests are performed on the line card.
Privileged EXEC
This command was added in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 GS to support the Cisco 12000 series Gigabit Switch Routers.
Perofrm diagnostics on the CSC only if a redendant CSC is in the router.
Diagnostics will stop and ask you for confirmation before altering the router's configuration. For example, running diagnostics on a SFC or CSC will cause the fabric to go from full bandwidth to one quarter bandwidth. Bandwidth is not affected by GRP or line card diagnostics.
The field diagnostic software image is bundled with the Cisco IOS software and is downloaded automatically from the GRP to the target line card prior to testing.
 Caution Performing field diagnostics on a line card stops all activity on the line card. Before the diag EXEC command begins running diagnostics, you are prompted to confirm the request to perform field diagnostics on the line card.
Caution Performing field diagnostics on a line card stops all activity on the line card. Before the diag EXEC command begins running diagnostics, you are prompted to confirm the request to perform field diagnostics on the line card.
In normal mode, if a test fails, the title of the failed test is displayed on the console. However, not all tests that are preformed are displayed. To view all the tests that are performed, use the verbose keyword.
After all diagnostic tests are completed on the line card, a PASSED or TEST FAILURE message is displayed. If the line card sends a PASSED message, the Cisco IOS software image on the line card is automatically reloaded unless the wait keyword is specified. If the line card sends a TEST FAILURE message, the Cisco IOS software image on the line card is not automatically reloaded.
If you want to reload the line card after it fails diagnostic testing, use the microcode reload slot global configuration command.
If the line card fails the test, the line card is defective and should be replaced. In future releases this might not be the case because DRAM and SDRAM SIMM modules might be field replaceable units. For example, if the DRAM test failed you might only need to replace the DRAM on the line card.
For more information, refer to the Cisco 12000 series installation and configuration guides.
The following example shows the output when field diagnostics are performed on the line card in slot 3. After the line card passes all field diagnostic tests, the Cisco IOS software is automatically reloaded on the card. Before starting the diagnostic tests, you must confirm the request to perform these tests on the line card because all activity on the line card is halted. The total/indiv. timeout set to 600/220 sec. message indicates that 600 seconds are allowed to perform all field diagnostics tests, and that no single test should exceed 220 seconds to complete.
Router# diag 3
Running Diags will halt ALL activity on the requested slot. [confirm]
Router#
Launching a Field Diagnostic for slot 3
Running DIAG config check
RUNNING DIAG download to slot 3 (timeout set to 400 sec.)
sending cmd FDIAG-DO ALL to fdiag in slot 3
(total/indiv. timeout set to 600/220 sec.)
Field Diagnostic ****PASSED**** for slot 3
Field Diag eeprom values: run 159 fial mode 0 (PASS) slot 3
last test failed was 0, error code 0
sending SHUTDOWN FDIAG_QUIT to fdiag in slot 3
Board will reload
...
Router#
The following example shows the output when field diagnostics are performed on the line card in slot 3 in verbose mode.
Router# diag 3 verbose
Running Diags will halt ALL activity on the requested slot. [confirm]
Router#
Launching a Field Diagnostic for slot 3
Running DIAG config check
RUNNING DIAG download to slot 3 (timeout set to 400 sec.)
sending cmd FDIAG-DO ALL to fdiag in slot 3
(total/indiv. timeout set to 600/220 sec.)
FDIAG_STAT_IN_PROGRESS: test #1 R5K Internal Cache
FDIAG_STAT_PASS test_num 1
FDIAG_STAT_IN_PROGRESS: test #2 Sunblock Ordering
FDIAG_STAT_PASS test_num 2
FDIAG_STAT_IN_PROGRESS: test #3 Dram Datapins
FDIAG_STAT_PASS test_num 3
...
Field Diags: FDIAG_STAT_DONE
Field Diagnostic ****PASSED**** for slot 3
Field Diag eeprom values: run 159 fial mode 0 (PASS) slot 3
last test failed was 0, error code 0
sending SHUTDOWN FDIAG_QUIT to fdiag in slot 3
Board will reload
...
Router#
microcode reload
To enable storing of crash information for a line card and optionally specify the type and amount of information stored, use the exception linecard global configuration command. To disable the storing of crash information for the line card, use the no form of this command.
exception linecard {all | slot slot-number} [corefile filename | main-memory size [k | m] || all | Stores crash information for all line cards. |
| slot slot- number | Stores crash information for the line card in the specified slot. Slot numbers range from 0 to 11 for the Cisco 12012 and 0 to 7 for the Cisco 12008. |
| corefile filename | (Optional) Stores the crash information in the specified file in NVRAM. The default file name is hostname-core-slot-number (for example, c12012-core-8). |
| main-memory size | (Optional) Stores the crash information for the main memory on the line card and specify the size of the crash information. Size of the memory to store is 0 to 268435456. |
| queue-ram size | (Optional) Stores the crash information for the queue RAM memory on the line card and specify the size of the crash information. Size of the memory to store can be from 0 to 1048576. |
| rx-buffer size
tx-buffer size | (Optional) Stores the crash information for the receive and transmit buffer on the line card and specify the size of the crash information. Size of the memory to store can be from 0 to 67108864. |
| sqe-register-rx
sqe-register-tx | (Optional) Stores crash information for the receive or transmit silicon queueing engine registers on the line card. |
| k
m | (Optional) The k option multiplies the specified size by 1K (1024), and the m option multiplies the specified size by 1M (1024*1024). |
No crash information is stored for the line card.
If enabled with no options, the default is to store 256 MB of main memory.
Global configuration
This command was added in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 GS to support the Cisco 12000 series Gigabit Switch Routers.
Use the exception linecard global configuration command only when directed by a technical support representative and only enable options that the technical support representative requests you to enable. Technical support representatives need to be able to look at the crash information from the line card to troubleshoot serious problems on the line card. The crash information contains all the line card memory information including the main memory and transmit and receive buffer information.
 Caution Use caution when enabling the exception linecard global configuration command. Enabling all options could cause a large amount (150 to 250 MB) of crash information to be sent to the server
Caution Use caution when enabling the exception linecard global configuration command. Enabling all options could cause a large amount (150 to 250 MB) of crash information to be sent to the server
The following example enables the storing of crash information for line card 8. By default, 256 MB of main memory is stored.
Router(config)# exception linecard slot 8
Router(config)# end
Router#
To execute commands remotely on a line card, use the execute-on slot privileged EXEC command.
execute-on {slot slot-number | all} command| slot-number | Executes the command on the line card in the specified slot. Slot numbers range from 0 to 11 on the Cisco 12012 and 0 to 7 on the Cisco 12008. |
| all | Executes the command on all line cards. |
| command | Cisco IOS command to execute on the line card. |
Privileged EXEC
This command was added in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 GS to support the Cisco 12000 series Gigabit Switch Routers.
Use this command to execute a command on one or all line cards to monitor and maintain information on one or more line cards.
You can use the execute-on privileged EXEC command only from Cisco IOS software running on the GRP card.
You can also use the attach privileged EXEC command, but using the execute-on slot command saves you some steps. For example, first you must use the attach command to connect you to the Cisco IOS software running on the line card, next you must issue the command, and finally you must disconnect from the line card to return to the Cisco IOS software running on the GRP card. With the execute-on slot command, you can perform three steps with one command.
In addition, the execute-on all command allows you to perform the same command on all line cards.
The following example shows how to execute the show controllers command on the line card in slot 4:
Router# execute-on slot 4 show controllers
========= Line Card (Slot 4) =======
Interface POS0
Hardware is BFLC POS
lcpos_instance struct 6033A6E0
RX POS ASIC addr space 12000000
TX POS ASIC addr space 12000100
SUNI framer addr space 12000400
SUNI rsop intr status 00
CRC16 enabled, HDLC enc, int clock
no loop
Interface POS1
Hardware is BFLC POS
lcpos_instance struct 6033CEC0
RX POS ASIC addr space 12000000
TX POS ASIC addr space 12000100
SUNI framer addr space 12000600
SUNI rsop intr status 00
CRC32 enabled, HDLC enc, int clock
no loop
Interface POS2
Hardware is BFLC POS
lcpos_instance struct 6033F6A0
RX POS ASIC addr space 12000000
TX POS ASIC addr space 12000100
SUNI framer addr space 12000800
SUNI rsop intr status 00
CRC32 enabled, HDLC enc, int clock
no loop
Interface POS3
Hardware is BFLC POS
lcpos_instance struct 60341E80
RX POS ASIC addr space 12000000
TX POS ASIC addr space 12000100
SUNI framer addr space 12000A00
SUNI rsop intr status 00
CRC32 enabled, HDLC enc, ext clock
no loop
Router#
To log messages to an internal buffer on a line card, use the logging linecard global configuration command. To cancel the use of the internal buffer on the line cards, use the no form of this command.
logging linecard [size | message-level]| size | (Optional) Size of the buffer used for each line card. The range is 4096 to 65536 bytes. The default is 8 KB. |
| message-level | (Optional) Limits the logging of messages displayed on the console terminal to a specified level. The message level can be:
· alerts--Immediate action needed · critical--Critical conditions · debugging--Debugging messages · emergencies--System is unusable · errors--Error conditions · informational--Informational messages · notifications--Normal but significant conditions · warnings--Warning conditions |
The Cisco IOS software logs messages to the internal buffer on the GRP card.
Global configuration
This command was added in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 GS to support the Cisco 12000 series Gigabit Switch Routers.
Specifying a message level causes messages at that level and numerically lower levels to be stored in the internal buffer on the line cards. Table 2 lists the message levels and associated numerical level. For example, if you specify a message level of critical, all critical, alert, and emergency messages will be logged.
| Level Name | Level |
|---|---|
| emergencies | 0 |
| alerts | 1 |
| critical | 2 |
| errors | 3 |
| warnings | 4 |
| notifications | 5 |
| informational | 6 |
| debugging | 7 |
To display the messages that are logged in the buffer, use the EXEC command show logging slot. The first message displayed is the oldest message in the buffer.
Do not make the buffer size too large because the router could run out of memory for other tasks. You can use the show memory EXEC command to view the free processor memory on the router; however, this is the maximum available and should not be approached.
The following example enables logging to an internal buffer on the line cards using the default buffer size and logging warning, error, critical, alert, and emergency messages:
Router(config)# logging linecard warnings
Router(config)# end
Router#
To load a Cisco IOS software image on a line card from Flash memory or the GRP card on a Cisco 12000 series Gigabit Switch Router, use the microcode global configuration command. To load the microcode bundled with the GRP system image, use the no form of this command.
microcode interface {flash file-id [slot] | system [slot]}| interface | One of the following interface names: oc12-atm, oc12-pos, or oc3-pos-4. |
| flash | Loads the image from the Flash file system. |
| file-id | Specifies the device and filename of the image file to download. A colon (:) must separate the device and filename (for example, slot0:gsr-p-mz). Valid devices are as follows:
· bootflash--Internal Flash memory. · slot0--First PCMCIA slot. · slot1--Second PCMCIA slot. |
| slot | (Optional) Slot number of the line card that you want to copy the software image to. Slot numbers range from 0 to 11 for the Cisco 12012 and 0 to 7 for the Cisco 12008. If you do not specify a slot number, the Cisco IOS software image is downloaded on all line cards. |
| system | Loads the image from the software image on the GRP card. |
The default is to load the image from the GRP card.
Global configuration
This command was modified in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 GS to load the Cisco IOS software image onto a line card in the Cisco 12000 series Gigabit Switch Routers.
In addition to the Cisco IOS image that resides on the GRP card, each line card on a Cisco 12000 series has a Cisco IOS image. When the router is reloaded, the specified Cisco IOS image is loaded onto the GRP card, and that image is automatically dowloaded to all the line cards.
Normally, you want the same Cisco IOS image on the GRP card and all line cards. However, if you want to upgrade a line card with a new version of microcode for testing or to fix a defect, you might need to load a Cisco IOS image that is different from the one on the line card. Additionally, you might need to load a new image on the line card to work around a problem that is affecting only one of the line cards.
To load a Cisco IOS image on a line card, first use the copy tftp command to download the Cisco IOS image to a slot on one of the PCMCIA Flash memory cards. After you have downloaded the Cisco IOS image on the Flash memory card, use the microcode command to download the image to the line card followed by the microcode reload command to start the image. To verify that the correct image is running on the line card, use the execute-on slot slot show version command.
For information on how to load Cisco IOS images, refer to the "Loading Images and Configuration Files" chapter in the Configuration Fundamentals Configuration Guide. For additional information, refer to the "Observing System Startup and Performing a Basic Configuration" chapter in the Cisco 12000 series installation and configuration guides.
In the following example, the Cisco IOS software image in slot 0: is downloaded to the line card in slot 10. This is the software image that is used when the system is booted, when a line card is inserted or removed, or when the microcode reload global configuration command is issued.
To verify that the correct version is loaded, use the execute-on slot 10 show version command.
Router(config)# microcode oc3-POS-4 flash slot0:fip.v141-7 10
Router(config)# microcode reload 10
Router(config)# exit
Router#
To reload the Cisco IOS image on a line card on Cisco 12000 series routers after all microcode configuration commands have been entered, use the microcode reload global configuration command.
microcode reload [slot-number]| slot-number | (Optional) Slot number of the line card that you want to reload the Cisco IOS software image on. Slot numbers range from 0 to 11 for the Cisco 12012 and 0 to 7 for the Cisco 12008. If you do not specify a slot number, the Cisco IOS software image is reloaded on all line cards. |
Global configuration
This command was modified in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 GS to add the slot-number option.
In addition to the Cisco IOS image that resides on the GRP card, each line card on Cisco 12000 series routers has a Cisco IOS image. When the router is reloaded, the specified Cisco IOS image is loaded onto the GRP card, and that image is automatically dowloaded to all the line cards.
Normally, you want the same Cisco IOS image on the GRP card and all line cards. However, if you want to upgrade a line card with a new version of microcode for testing or to fix a defect, you might need to load a Cisco IOS image that is different from the one on the line card. Additionally, you might need to load a new image on the line card to work around a problem that is affecting only one of the line cards.
To load a Cisco IOS image on a line card, first use the copy tftp command to download the Cisco IOS image to a slot on one of the PCMCIA Flash memory cards. After you have downloaded the Cisco IOS image on the Flash memory card, use the microcode command to download the image to the line card followed by the microcode reload command to start the image. To verify that the correct image is running on the line card, use the execute-on slot slot show version command.
For information on how to load Cisco IOS images, refer to the "Loading Images and Configuration Files" chapter in the Configuration Fundamentals Configuration Guide. For additional information, refer to the "Observing System Startup and Performing a Basic Configuration" chapter in the Cisco 12000 series installation and configuration guides.
In the following example, the Cisco IOS software is reloaded on the line card in slot 10:
Router(config)# microcode reload 10
Router(config)# end
Router#
microcode (Cisco IOS image)
microcode query
To set the SONET overhead bytes in the frame header to meet a specific standards requirement or to ensure interoperability with another vendor's equipment, use the pos flag interface configuration command. To remove the setting of the SONET overhead bytes, use the no form of this command.
pos flag {c2 | j0 | s1s0} value| c2 value | Path signal identifier used to identify the payload content type. Use the following values to tell the SONET transmission equipment the payload type:
· For PPP (or HDLC when required), use 0xCF (this is the default). · For ATM, use 0x13. · For other equipment, use any non-zero value. The byte value can be 0 to 255. |
| j0 value | Section trace byte (formerly the C1 byte). For interoperability with SDH equipment in Japan, use the value 0x1. The byte value can be 0 to 255. |
| sls0 value | S1 and S0 bits (bits 5 and 6 of the H1 #1 payload pointer byte). Use the following values to tell the SONET transmission equipment the SS bit:
· For OC-3c, use 0 (this is the default). · For AU-4 container in SDH, use 2. The S1 and S0 bits can be 0 to 3. Values 1 and 3 are undefined. |
The default c2 value is 0xCF, and the default sls0 value is 0.
Interface configuration
This command was added in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 GS to support the Cisco 12000 series Gigabit Switch Routers.
The following example sets the path signal identifier used to identify the payload content type to ATM on the line card in slot 9:
Router(config)# interface pos 9/0
Router(config-if)# pos flag c2 0x13
Router(config-if)# end
Router#
To specify the framing used on the POS interface, use the pos framing interface configuration command. To return to the default SONET STS-3c framing mode, use the no form of this command.
pos framing {sdh | sonet}| sdh | Selects SDH STM-1 framing. This framing mode is typically used in Europe. |
| sonet | Selects SONET STS-3c framing. This is the default. |
SONET STS-3c framing
Interface configuration
This command was modified in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 GS to change the command syntax from pos framing-sdh to pos framing and add the sonet keyword.
In the following example, the interface is configured for SDH STM-1 framing:
Router(config)# interface pos 3/0
Router(config-if)# pos framing sdh
Router(config-if)# no shutdown
Router(config-if)# end
Router#
interface pos
To enable SONET payload scrambling on a POS interface, use the pos scramble-atm interface command. To disable scrambling, use the no form of this command.
pos scramble-atmThis command has no keywords or arguments.
Disabled.
Interface configuration
This command was added in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 GS to support the Cisco 12000 series Gigabit Switch Routers.
SONET payload scrambling applies a self-synchronous scrambler (x^43+1) to the Synchronous Payload Envelope (SPE) of the interface to ensure sufficient bit transition density.
Both ends of the connection must use the same scrambling algorithm.
When enabling POS scrambling on a VIP2 POSIP on the Cisco 7500 series that has a hardware revision of 1.5 or higher, you can specify CRC 16 only (that is, CRC 32 is currently not supported). To determine the hardware version of the POSIP, use the show diag command. The POS interface on the Cisco 12000 series has no restrictions.
To determine whether scrambling is enabled on the interface, use the show interface pos command or show startup-config command.
The following example enables scrambling on the interface:
Router(config)# interface pos 3/0
Router(config-if)# pos scramble-atm
Router(config-if)# no shutdown
Router(config-if)# end
Router#
interface pos
show interface pos
To specify the message that is displayed on the LED on the front panel of one or more line cards, use the set card-message privileged EXEC command. To remove the message, use the clear card-message global command.
set card-message {all | slot slot-number} [expire seconds] [blink seconds] message| all | Specifies that the LED message is set on all line cards. |
| slot slot-number | Specifies that the LED message is set on a specific line card. Slot numbers range from 0 to 11 for the Cisco 12012 and 0 to 7 for the Cisco 12008. |
| expire seconds | (Optional) Specifies how long the message is displayed on the front panel LED. The range is 0 to 31536000 seconds. When you select 0, the message remains on the LED until you clear it by using the clear card-message command. When the time expires, the user-specified message is removed, and the LED displays the status message based on the line card's last state. |
| blink seconds | (Optional) Specifies how often the message blinks (that is, goes on and off) in seconds. The range is 1 to 10 seconds. If blink is not specified, the message does not blink. |
| message | Specifies the text to display on the LED on the front panel of one or more line cards. The message can be up to eight alphanumeric characters (four characters per line). |
System LED message is displayed.
Privileged EXEC
This command was added in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 GS to support the Cisco 12000 series Gigabit Switch Routers.
The user-specified message is also displayed in the show diag command output.
To revert to the normal status message for the line card, use the clear card-message global configuration command.
The following example sets the message USER MSG to display on the LED on line card 3. This message blinks every two seconds.
Router# set card-message slot 3 blink 2 USER MSG
To display information stored in NVRAM when the router crashes, use the show context EXEC command.
show context summary| summary | Displays a summary of all the crashes recorded. |
| all | Displays all crashes for all the slots. When optionally used with the slot keyword, displays crash information for the specified slot. |
| slot slot-number [crash-index] | Displays information for a particular line card. Slot numbers range from 0 to 11 for the Cisco 12012 and 0 to 7 for the Cisco 12008. Index number allows you to look at previous crash contexts. Contexts from the last 24 line card crashes are saved on the GRP card. If the GRP reloads, the last 24 line card crash contexts are lost. For example, show context slot 3 2 shows the second most recent crash for line card in slot 3. Index numbers are displayed by the show context summary command |
| debug | (Optional) Displays crash information as hex record dump in addition to one of the options listed above. |
EXEC
This command was modified in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 GS to add the all, debug, slot, and summary keywords.
The display from the show context command includes the following information:
The following is sample output from the show context command following a system failure:
Router> show context
System was restarted by error - a Software forced crash, PC 0x60189354
GS Software (RSP-PV-M), Experimental Version 11.1(2033) [ganesh 111]
Compiled Mon 31-Mar-97 13:21 by ganesh
Image text-base: 0x60010900, data-base: 0x6073E000
Stack trace from system failure:
FP: 0x60AEA798, RA: 0x60189354
FP: 0x60AEA798, RA: 0x601853CC
FP: 0x60AEA7C0, RA: 0x6015E98C
FP: 0x60AEA7F8, RA: 0x6011AB3C
FP: 0x60AEA828, RA: 0x601706CC
FP: 0x60AEA878, RA: 0x60116340
FP: 0x60AEA890, RA: 0x6011632C
Fault History Buffer:
GS Software (RSP-PV-M), Experimental Version 11.1(2033) [ganesh 111]
Compiled Mon 31-Mar-97 13:21 by ganesh
Signal = 23, Code = 0x24, Uptime 00:04:19
$0 : 00000000, AT : 60930120, v0 : 00000032, v1 : 00000120
a0 : 60170110, a1 : 6097F22C, a2 : 00000000, a3 : 00000000
t0 : 60AE02A0, t1 : 8000FD80, t2 : 34008F00, t3 : FFFF00FF
t4 : 00000083, t5 : 3E840024, t6 : 00000000, t7 : 11010132
s0 : 00000006, s1 : 607A25F8, s2 : 00000001, s3 : 00000000
s4 : 00000000, s5 : 00000000, s6 : 00000000, s7 : 6097F755
t8 : 600FABBC, t9 : 00000000, k0 : 30408401, k1 : 30410000
gp : 608B9860, sp : 60AEA798, s8 : 00000000, ra : 601853CC
EPC : 60189354, SREG : 3400EF03, Cause : 00000024
Router>
The following is sample output from the show context summary command on a Cisco 12012 router. The show context summary command displays a summary of all the crashes recorded.
Router# show context summary
CRASH INFO SUMMARY
Slot 0 : 0 crashes
Slot 1 : 0 crashes
Slot 2 : 0 crashes
Slot 3 : 0 crashes
Slot 4 : 0 crashes
Slot 5 : 0 crashes
Slot 6 : 0 crashes
Slot 7 : 2 crashes
1 - crash at 18:06:41 UTC Tue Nov 5 1996
2 - crash at 12:14:55 UTC Mon Nov 4 1996
Slot 8 : 0 crashes
Slot 9 : 0 crashes
Slot 10: 0 crashes
Slot 11: 0 crashes
Router#
show processes
show stacks
To display information that is specific to the hardware, use the show controllers privileged EXEC command.
show controllers [atm number | clock | csar [register] | csc-fpga | dp83800 | fab-clk || atm number | (Optional) Displays the ATM controllers. Number is slot-number/ port-number (for example, 4/0). Slot numbers range from 0 to 11 for the Cisco 12012 and 0 to 7 for the Cisco 12008. |
| clock | (Optional) Displays the clock card configuration. |
| csar [register] | (Optional) Displays the Cisco Cell Segmentation and Reassembly (CSAR) information. CSAR is the name of the chip on the card that handles traffic between the GRP and the switch fabric interface ASICs. |
| csc-fpga | (Optional) Displays the clock and scheduler card register information in the field programmable gate array (FPGA). |
| dp83800 | (Optional) Displays the Ethernet information on the GRP card. |
| fab-clk | (Optional) Display the switch fabric clock register information. The switch fabric clock FPGA is a chip that monitors the incoming fabric clock generated by the switch fabric. This clock is needed by each card connecting to the switch fabric to properly communicate with it. There are two switch fabric clocks arriving at each card; only one can be used. The FPGA monitors both clocks and selects which one to use if only one of them is running. |
| fia [register] | (Optional) Displays the fabric interface ASIC information and optionally display the register information. |
| pos [number] [details] | (Optional) Displays the POS framer state and optionally displays all the details for the interface. Number is slot-number/ port-number (for example, 4/0). Slot numbers range from 0 to 11 for the Cisco 12012 and 0 to 7 for the Cisco 12008. |
| queues [slot-number] | (Optional) Displays the SDRAM buffer carve information and optionally displays the information for a specific line card. The SDRAM buffer carve information displayed is suggested carve information from the GRP card to the line card. Line cards might change the shown percentages based on SDRAM available. Slot numbers range from 0 to 11 for the Cisco 12012 and 0 to 7 for the Cisco 12008. |
| sca | (Optional) Displays the SCA register information. The SCA is an ASIC that arbitrates among the line cards requests to use the switch fabric. |
| xbar | (Optional) Displays the crossbar register information. The XBAR is an ASIC that switches the data as it passes through the switch fabric. |
Privileged EXEC
This command was added in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 GS to support the Cisco 12000 series Gigabit Switch Routers.
The following example is sample output from the show controllers pos command for a Cisco 12012.
Router# show controllers pos 7/0
POS7/0
SECTION
LOF = 2 LOS = 0 BIP(B1) = 5889
Active Alarms: None
LINE
AIS = 2 RDI = 2 FEBE = 146 BIP(B2) = 2106453
Active Alarms: None
PATH
AIS = 2 RDI = 4 FEBE = 63 BIP(B3) = 3216
LOP = 0 PSE = 8 NSE = 3 NEWPTR = 2
Active Alarms: None
APS
COAPS = 3 PSBF = 2
State: PSBF_state = False
Rx(K1/K2): F0/15 Tx(K1/K2): 00/00
S1S0 = 00, C2 = 64
PATH TRACE BUFFER : STABLE
Remote hostname : GSR-C
Remote interface: POS10/0
Remote IP addr : 10.201.101.2
Remote Rx(K1/K2): F0/15 Tx(K1/K2): 00/00
Router#
clear controllers
show controllers (line card image)
To display information that is specific to the hardware on a line card, use the attach privileged EXEC command to connect to the line card and then use the show controllers privileged EXEC command or the execute-on privileged EXEC command.
show controllers atm [[port-number] [all | sar | summary]]| atm [[port-number] [all | sar | summary]] | Displays the ATM controller information. Optionally displays ATM controllers for a specific line card and lists all details, lists SAR interactive command, or lists SAR status summary. |
| fia [register] | Displays the fabric interface ASIC information and optionally displays the register information. |
| {frfab | tofab} | Displays the from fabric (transmit) or to fabric (receive) information. |
| bma {microcode | ms-inst | register} | For the frfab or tofab keywords, displays silicon queueing engine (SQE) information for the microcode bundled in the line card and currently running version, the micro sequencer instructions, or the registers. The silicon queueing engine is the same as the BMA. |
| qelem start-queue [end-queue] | For the frfab or tofab keywords, displays the SDRAM buffer pool queue element summary information by specifying the start queue element number (0 to 65535) and optionally the end queue element number (0 to 65535). |
| qnum start-queue [end-queue] | For the frfab or tofab keywords, displays the SDRAM buffer pool queue detail information by specifying the start free queue number (0 to 127) and optionally the end free queue number (0 to 127). |
| queues | For the frfab or tofab keywords, displays the SDRAM buffer pool information. |
| statistics | For the frfab or tofab keywords, displays the BMA counters. |
| io | Displays input/output registers. |
| l3 | Displays Layer 3 ASIC information. |
| pos {framers | queues | registers | rxsram port-number queue-start-address [queue-length] | txsram port-number queue-start-address [queue-length]} | Displays the POS framer registers, queue information, ASIC registers, receive queue SRAM, or transmit queue SRAM information. When you display the transmit or receive queue information, you must specify a port (valid range is 0 to 3) and the queue SRAM logical starting address. You can also optionally specify the queue SRAM length. |
Privileged EXEC
This command was added in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 GS to support the Cisco 12000 series Gigabit Switch Routers.
Because you are executing this command on the line card, you must use the execute-on command to perform the show command, or you must connect to the card using the attach command. All examples in this section use the execute-on command
The following is partial sample output from the show controllers atm command.
Router# execute-on slot 4 show controllers atm 0
TX SAR (Beta 1.0.0) is Operational;
RX SAR (Beta 1.0.0) is Operational;
Interface Configuration Mode:
STS-12c
Active Maker Channels: total # 6
VCID ChnnlID Type OutputInfo InPkts InOAMs MacString
1 0888 UBR 0C010010 0 0 08882000AAAA030000000800
2 0988 VBR 04010020 0 0 09882000
3 8BC8 UBR 0C010030 0 0 8BC82000AAAA030000000800
4 0E08 UBR 0C010040 0 0 0E082000AAAA030000000800
10 1288 VBR 040100A0 0 0 12882000
11 8BE8 VBR 0C0100B0 0 0 8BE82000AAAA030000000800
SAR Total Counters:
total_tx_idle_cells 215267 total_tx_paks 0 total_tx_abort_paks 0
total_rx_paks 0 total_rx_drop_paks 0 total_rx_discard_cells 15
Switching Code Counters:
total_rx_crc_err_paks 0 total_rx_giant_paks 0
total_rx_abort_paks 0 total_rx_crc10_cells 0
total_rx_tmout_paks 0 total_rx_unknown_paks 0
total_rx_out_buf_paks 0 total_rx_unknown_vc_paks 0
BATMAN Asic Register Values:
hi_addr_reg 0x8000, lo_addr_reg 0x000C, boot_msk_addr 0x0780,
rmcell_msk_addr 0x0724, rmcnt__msk_addr 0x07C2, txbuf_msk_addr 0x070C,
...
CM622 SAR Boot Configuration:
txind_q_addr 0x14000 txcmd_q_addr 0x20000
...
SUNI-622 Framer Register Values:
Master Rst and Ident/Load Meters Reg (#0x0): 0x10
Master Configuration Reg (#0x1): 0x1F
Master Interrupt Status Reg (#0x2): 0x00
PISO Interrupt Reg (#0x3): 0x04
Master Auto Alarm Reg (#0x4): 0x03
Master Auto Alarm Reg (#0x5): 0x07
Parallel Output Port Reg (#0x6): 0x02
...
BERM Line BIP Threshold LSB Reg (#0x74): 0x00
BERM Line BIP Threshold MSB Reg (#0x75): 0x00
Router#
The following is partial sample output from the show controllers command.
Router# execute-on slot 6 show controllers
Interface POS0
Hardware is BFLC POS
lcpos_instance struct 60311B40
RX POS ASIC addr space 12000000
TX POS ASIC addr space 12000100
SUNI framer addr space 12000400
SUNI rsop intr status 00
CRC32 enabled, HDLC enc, int clock
no loop
Interface POS1
Hardware is BFLC POS
lcpos_instance struct 603142E0
RX POS ASIC addr space 12000000
TX POS ASIC addr space 12000100
SUNI framer addr space 12000600
SUNI rsop intr status 00
CRC32 enabled, HDLC enc, int clock
no loop
...
Router#
The following is partial sample output from the show controllers pos framers command.
Router# execute-on slot 6 show controllers pos framers
Framer 0, addr=0x12000400:
master reset C0
master config 1F rrate sts3c trate sts3c fixptr
master control 00
clock rcv cntrl D0
RACP control 84
RACP gfc control 0F
TACP control status 04 hcsadd
RACP intr enable 04
RSOP cntrl intr enable 00
RSOP intr status 00
TPOP path sig lbl (c2) 13
SPTB control 04 tnull
SPTB status 00
Framer 1, addr=0x12000600:
master reset C0
master config 1F rrate sts3c trate sts3c fixptr
master control 00
clock rcv cntrl D0
RACP control 84
RACP gfc control 0F
TACP control status 04 hcsadd
RACP intr enable 04
RSOP cntrl intr enable 00
RSOP intr status 00
TPOP path sig lbl (c2) 13
SPTB control 04 tnull
SPTB status 00
Framer 2, addr=0x12000800:
master reset C0
master config 1F rrate sts3c trate sts3c fixptr
master control 00
clock rcv cntrl D0
RACP control 84
RACP gfc control 0F
TACP control status 04 hcsadd
RACP intr enable 04
RSOP cntrl intr enable 00
RSOP intr status 00
TPOP path sig lbl (c2) 13
SPTB control 04 tnull
SPTB status 00
...
Router#
The following is partial sample output from the show controllers fia command.
Router# execute-on slot 7 show controllers fia
========= Line Card (Slot 7) =======
Fabric configuration: Full bandwidth redundant
Master Scheduler: Slot 17
From Fabric FIA Errors
-----------------------
redund fifo parity 0 redund overflow 0 cell drops 0
crc32 lkup parity 0 cell parity 0 crc32 0
0 1 2 3 4
-------- -------- -------- -------- --------
los 0 0 0 0 0
crc16 0 0 0 0 0
To Fabric FIA Errors
-----------------------
sca not pres 0 req error 0 uni fifo overflow 0
grant parity 0 multi req 0 uni fifo undrflow 0
cntrl parity 0 uni req 0 crc32 lkup parity 0
multi fifo 0 empty dst req 0 handshake error 0
clear controllers
show controllers (GRP image)
To display hardware information including DRAM and SRAM on the line cards, use the show diag privileged EXEC command.
show diag [slot-number] [details] [summary]| slot-number | (Optional) Slot number of the interface. |
| details | (Optional) Displays more details than the normal show diag output. |
| summary | (Optional) Displays a summary (one line per slot) of the chassis. |
Privileged EXEC
This command was modified in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 GS to include sample output from the Cisco 12000 series Gigabit Switch Routers.
Use this command to determine the type of hardware installed in your router.
The following is sample output from the show diag command:
Router# show diag 3
SLOT 3 (RP/LC 3 ): 4 Port Packet Over SONET OC-3c/STM-1 Multi Mode
MAIN: type 33, 00-0000-00 rev 70 dev 0
HW config: 0x01 SW key: 00-00-00
PCA: 73-2147-02 rev 94 ver 2
HW version 1.0 S/N 04499695
MBUS: MBUS Agent (1) 73-2146-05 rev 73 dev 0
HW version 1.1 S/N 04494882
Test hist: 0x00 RMA#: 00-00-00 RMA hist: 0x00
DIAG: Test count: 0x05000001 Test results: 0x00000000
MBUS Agent Software version 01.27 (RAM) using CAN Bus A
ROM Monitor version 00.0D
Fabric Downloader version used 00.0D (ROM version is 00.0D)
Board is analyzed
Board State is Line Card Enabled (IOS RUN )
Insertion time: 00:00:10 (00:04:51 ago)
DRAM size: 33554432 bytes
FrFab SDRAM size: 67108864 bytes
ToFab SDRAM size: 16777216 bytes
Router#
The following is sample output from the show diag summary command:
Router# show diag summary
SLOT 0 (RP/LC 0 ): Route Processor
SLOT 2 (RP/LC 2 ): 4 Port Packet Over SONET OC-3c/STM-1 Single Mode
SLOT 4 (RP/LC 4 ): 4 Port Packet Over SONET OC-3c/STM-1 Single Mode
SLOT 7 (RP/LC 7 ): 4 Port Packet Over SONET OC-3c/STM-1 Single Mode
SLOT 9 (RP/LC 9 ): 4 Port Packet Over SONET OC-3c/STM-1 Single Mode
SLOT 11 (RP/LC 11): 4 Port Packet Over SONET OC-3c/STM-1 Single Mode
SLOT 16 (CSC 0 ): Clock Scheduler Card
SLOT 17 (CSC 1 ): Clock Scheduler Card
SLOT 18 (SFC 0 ): Switch Fabric Card
SLOT 19 (SFC 1 ): Switch Fabric Card
SLOT 20 (SFC 2 ): Switch Fabric Card
SLOT 24 (PS A1 ): AC Power Supply
SLOT 26 (PS B1 ): AC Power Supply
SLOT 28 (TOP FAN ): Blower Module
SLOT 29 (BOT FAN ): Blower Module
Router#
The following is sample output from the show diag details command:
Router# show diag 4 details
SLOT 4 (RP/LC 4): 4 Port Packet Over SONET OC-3c/STM-1 Single Mode
MAIN: type 33, 800-2389-01 rev 71 dev 16777215
HW config: 0x00 SW key: FF-FF-FF
PCA: 73-2275-03 rev 75 ver 3
HW version 1.1 S/N 04529465
MBUS: MBUS Agent (1) 73-2146-06 rev 73 dev 0
HW version 1.1 S/N 04541395
Test hist: 0xFF RMA#: FF-FF-FF RMA hist: 0xFF
DIAG: Test count: 0x05000001 Test results: 0x00000000
EEPROM contents (hex):
00: 01 00 01 00 49 00 08 62 06 03 00 00 00 FF FF FF
10: 30 34 35 34 31 33 39 35 FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF
20: 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF
30: A5 FF A5 A5 A5 A5 FF A5 A5 A5 A5 A5 A5 A5 A5 A5
40: 00 21 01 01 00 49 00 08 E3 03 05 03 00 01 FF FF
50: 03 20 00 09 55 01 01 FF FF FF 00 FF FF FF FF FF
60: 30 34 35 32 39 34 36 35 FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF
70: FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF 05 00 00 01 00 00 00 00
MBUS Agent Software version 01.24 (RAM)
Fabric Downloader version 00.0D
Board is analyzed
Flags: 0x4
Board State is Line Card Enabled (IOS RUN)
Insertion time: 00:00:10 (00:04:51 ago)
DRAM size: 33554432 bytes
FrFab SDRAM size: 67108864 bytes
ToFab SDRAM size: 16777216 bytes
Router#
To display temperature, voltage, and blower information on the Cisco 12000 series Gigabit Switch Router, use the show environment privileged EXEC command.
show environment [alarms | all | fans | hardware | last | leds | power-supply | table | temperatures | voltages]| alarms | (Optional) Displays the alarm contact information. |
| all | (Optional) Displays a detailed listing of the power supplies, temperature readings, voltage readings, and blower speeds. |
| fans | (Optional) Displays blower and fan information. |
| hardware | (Optional) Displays hardware-specific information. |
| last | (Optional) Displays information on the last measurement made. |
| leds | (Optional) Displays the status of the MBus LEDs on the clock and scheduler cards and switch fabric cards. |
| power-supply | (Optional) Displays power supply voltage and current information. |
| table | (Optional) Displays the temperature, voltage, and blower thresholds. |
| temperature | (Optional) Displays temperature information. |
| voltages | (Optional) Displays voltage information. |
If no options are specified, the current environmental parameters are displayed.
Privileged EXEC
This command was modified in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 GS to include the alarms, fans, hardware, leds, power-supply, temperature, and voltages keywords and to provide sample output for the Cisco 12000 series Gigabit Switch Routers.
Once a minute a routine is run that gets environmental measurements from sensors and stores the output into a buffer. This buffer is displayed on the console when show environment is invoked.
If a measurement exceeds desired margins, but has not exceeded fatal margins, a warning message is printed to the system console. The system software queries the sensors for measurements once a minute, but warnings for a given test point are printed at most once every hour for sensor readings in the warning range and once every 5 minutes for sensor readings in the critical range. If a measurement is out of line within these time segments, an automatic warning message appears on the console. As noted, you can query the environmental status with the show environment command at any time to determine whether a measurement is at the warning or critical tolerance.
If a shutdown occurs because of detection of fatal environmental margins, the last measured value from each sensor is stored in internal nonvolatile memory.
For environmental specifications, refer to the hardware installation and configuration publication for your individual chassis.
If the Cisco 12000 series exceeds environmental conditions, a message similar to the one below is displayed on the console:
%GSR_ENV-2-WARNING: Slot 3 Hot Sensor Temperature exceeds 40 deg C;
Check cooling systems
The following examples are for the Cisco 12000 series Gigabit Switch Routers.
The following is sample output from the show environment command for a Cisco 12012. Slots 0 through 11 are the line cards, slots 16 and 17 are the clock and scheduler cards, slots 18 through 20 are the switch fabric cards, slots 24 through 27 are the power supplies, and slots 28 and 29 are the blowers. An "NA" in the table means that no values was returned. In some cases it is because the equipment is not supported for that environmental parameter (for example, the power supply and blowers in slots 24, 26, 28, and 29 do not have a 3V power supply so an NA is displayed).
Router# show environment
Slot # 3V 5V MBUS 5V Hot Sensor Inlet Sensor
(mv) (mv) (mv) (deg C) (deg C)
0 3300 4992 5040 42.0 37.0
2 3296 4976 5136 40.0 33.0
4 3280 4992 5120 38.5 31.5
7 3280 4984 5136 42.0 32.0
9 3292 4968 5160 39.5 31.5
11 3288 4992 5152 40.0 30.5
16 3308 NA 5056 42.5 38.0
17 3292 NA 5056 40.5 36.5
18 3304 NA 5176 36.5 35.0
19 3300 NA 5184 37.5 33.5
20 3304 NA 5168 36.5 34.0
24 NA 5536 5120 NA 31.5
26 NA 5544 5128 NA 31.5
28 NA NA 5128 NA NA
29 NA NA 5104 NA NA
Slot # 48V AMP_48
(Volt) (Amp)
24 46 12
26 46 19
Slot # Fan 0 Fan 1 Fan 2
(RPM) (RPM) (RPM)
28 2160 2190 2160
29 2130 2190 2070
Router#
Table 3 describes the fields shown in the output and lists the equipment that is supported by each environmental parameter. If an "NA" is listed in the field and the equipment is supported, it means that the reading could not be obtained. Try the command again.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Slot # | Slot number of the equipment. On the Cisco 12012, slots 0 through 11 are the line cards, slots 16 and 17 are the clock and scheduler cards, slots 18 through 20 are the switch fabric cards, slots 24 through 27 are the power supplies, and slots 28 and 29 are the blowers. |
| 3V (mv) | Measures the 3-volt power supply on the card. The 3-volt power supply is on the line cards, GRP card, clock and scheduler cards, and switch fabric cards. |
| 5V (mv) | Measures the 5-volt power supply on the card. The 5-volt power supply is on the line cards, GRP card, and power supplies. |
| MBUS 5V (mv) | Measures the 5-volt MBus on the card. The 5-volt MBus is on all equipment. |
| Hot Sensor (deg C) | Measures the temperature at the hot sensor on the card. The hot sensor is on the line cards, GRP card, clock and scheduler cards, switch fabric cards, and blowers. |
| Inlet Sensor (deg C) | Measures the current inlet temperature on the card. The inlet sensor is on the line cards, GRP card, clock and scheduler cards, switch fabric cards, and power supplies. |
| 48V (Volt) | Measures the DC power supplies. |
| AMP_48 (Amp) | Measures the AC power supplies. |
| Fan 0, Fan 1, Fan 2 | Measures the fan speed in rotations per minute. |
The following is sample output from the show environment all command for the Cisco 12008. Slots 0 through 7 are the line cards, slots 16 and 17 are the clock scheduler cards (the clock scheduler cards control the fans), slots 18 through 20 are the switch fabric cards, and slots 24 and 26 are the power supplies. The Cisco 12008 does not support slots 25, 27, 28, and 29. An "NA" in the table means that no values was returned. In some cases it is because the equipment is not supported for that environmental parameter (for example, the power supplies in slots 24 and 26 do not have a hot sensor, so an NA is displayed).
Router# show environment all
Slot # Hot Sensor Inlet Sensor
(deg C) (deg C)
2 31.0 22.0
5 33.5 26.5
16 25.5 21.5
18 22.0 21.0
19 22.5 21.0
24 NA 29.5
26 NA 24.5
Slot # 3V 5V MBUS 5V
(mv) (mv) (mv)
2 3292 5008 5136
5 3292 5000 5128
16 3272 NA 5128
18 3300 NA 5128
19 3316 NA 5128
Slot # 5V MBUS 5V 48V AMP_48
(mv) (mv) (Volt) (Amp)
24 0 5096 3 0
26 5544 5144 47 3
Slot # Fan Information
16 Voltage 16V Speed slow: Main Fans Ok Power Supply fans Ok
Alarm Indicators
No alarms
Slot # Card Specific Leds
16 Mbus OK SFCs Failed
18 Mbus OK
19 Mbus OK
24 Input Failed
26 Input Ok
The following is sample output from the show environment table command for a Cisco 12012. The show environment table command lists the warning, critical, and shutdown limits on your system and includes the GRP card and line cards (slots 0-15), clock and scheduler cards (slots 16-17), switch fabric cards (slots 18-20), and blowers.
Router# show environment table
Hot Sensor Temperature Limits (deg C):
Warning Critical Shutdown
GRP/GLC (Slots 0-15) 40 46 57
CSC (Slots 16-17) 46 51 65
SFC (Slots 18-20) 41 46 60
Inlet Sensor Temperature Limits (deg C):
Warning Critical Shutdown
GRP/GLC (Slots 0-15) 35 40 52
CSC (Slots 16-17) 40 45 59
SFC (Slots 18-20) 37 42 54
3V Ranges (mv):
Warning Critical Shutdown
Below Above Below Above Below Above
GRP/GLC (Slots 0-15) 3200 3400 3100 3500 3050 3550
CSC (Slots 16-17) 3200 3400 3100 3500 3050 3550
SFC (Slots 18-20) 3200 3400 3100 3500 3050 3550
5V Ranges (mv):
Warning Critical Shutdown
Below Above Below Above Below Above
GRP/GLC (Slots 0-15) 4850 5150 4750 5250 4680 5320
MBUS_5V Ranges (mv):
Warning Critical Shutdown
Below Above Below Above Below Above
GRP/GLC (Slots 0-15) 5000 5250 4900 5350 4750 5450
CSC (Slots 16-17) 4820 5150 4720 5250 4750 5450
SFC (Slots 17-20) 5000 5250 4900 5350 4750 5450
Blower Operational Range (RPM):
Top Blower:
Warning Critical
Below Below
Fan 0 1000 750
Fan 1 1000 750
Fan 2 1000 750
Bottom Blower:
Warning Critical
Below Below
Fan 0 1000 750
Fan 1 1000 750
Fan 2 1000 750
The following is sample output from the show environment leds command for a Cisco 12012. The show environment leds command lists the status of the MBus LEDs on the clock and scheduler cards and switch fabric cards.
Router# show environment leds
16 leds Mbus OK
18 leds Mbus OK
19 leds Mbus OK
20 leds Mbus OK
To display hardware information on the Cisco 12000 series Gigabit Switch Routers (GSR), use the show gsr EXEC command.
show gsr [chassis-info [details]]| chassis-info | (Optional) Displays backplane NVRAM information. |
| details | (Optional) In addition to the information displayed, this option includes hexadecimal output of the backplane NVRAM information. |
EXEC
This command was added in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 GS to support the Cisco 12000 series Gigabit Switch Routers.
Use this command to determine the type of hardware installed in your router.
The following is sample output from the show gsr command for a Cisco 12012. This command shows the type of card installed in the slot and the state of the card.
Router# show gsr
Slot 0 type = Route Processor
state = IOS Running MASTER
Slot 7 type = 1 Port Packet Over SONET OC-12c/STM-4c
state = Card Powered
Slot 16 type = Clock Scheduler Card
state = Card Powered PRIMARY CLOCK
The following is sample output from the show gsr chassis-info command for a Cisco 12012:
Router# show gsr chassis-info
Backplane NVRAM [version 0x20] Contents -
Chassis: type 12012 Fab Ver: 1
Chassis S/N: ZQ24CS3WT86MGVHL
PCA: 800-3015-1 rev: A0 dev: 257 HW ver: 1.0
Backplane S/N: A109EXPR75FUNYJK
MAC Addr: base 0000.EAB2.34FF block size: 1024
RMA Number: 0x5F-0x2D-0x44 code: 0x01 hist: 0x1A
To display the state of logging (syslog), use the show logging privileged EXEC command.
show logging [history | slot slot-number | summary]| history | (Optional) Displays information in the syslog history table only. |
| slot slot-number | (Optional) Displays information in the syslog history table for a specific line card. Slot numbers range from 0 to 11 for the Cisco 12012 and 0 to 7 for the Cisco 12008. |
| summary | (Optional) Displays counts of messages by type for each line card. |
Privileged EXEC
This command was modified in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 GS to add the slot and summary keywords.
This command displays the state of syslog error and event logging, including host addresses, and whether console logging is enabled. This command also displays Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) configuration parameters and protocol activity.
The following is sample output from the show logging command:
Router# show logging
Syslog logging: enabled
Console logging: disabled
Monitor logging: level debugging, 266 messages logged.
Trap logging: level informational, 266 messages logged.
Logging to 192.180.2.238
SNMP logging: disabled, retransmission after 30 seconds
0 messages logged
Router#
Table 4 describes significant fields shown in the display.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Syslog logging | When enabled, system logging messages are sent to a UNIX host that acts as a syslog server; that is, it captures and saves the messages. |
| Console logging | If enabled, states the level; otherwise, this field displays disabled. |
| Monitor logging | Minimum level of severity required for a log message to be sent to a monitor terminal (not the console). |
| Trap logging | Minimum level of severity required for a log message to be sent to a syslog server. |
| SNMP logging | Shows whether SNMP logging is enabled and the number of messages logged, and the retransmission interval. |
The following is sample output from the show logging history command:
Router# show logging history
Syslog History Table: 1 maximum table entry, saving level notifications or higher
0 messages ignored, 0 dropped, 15 table entries flushed,
SNMP notifications not enabled
entry number 16: SYS-5-CONFIG_I
Configured from console by console
timestamp: 1110
Router#
Table 5 describes the significant fields shown in the display.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| maximum table entry | Number of messages that can be stored in the history table. Set with the logging history size command. |
| saving level notifications or higher | Level of messages that are stored in the history table and sent to the SNMP server (if SNMP notification is enabled). Set with the logging history command. |
| messages ignored | Number of messages not stored in the history table because the severity level is greater than that specified with the logging history command. |
| dropped | Number of messages that could not be processed due to lack of system resources. Dropped messages do not appear in the history table and are not sent to the SNMP server. |
| table entries flushed | Number of messages that have been removed from the history table to make room for newer messages. |
| SNMP notifications | Whether syslog traps of the appropriate level are sent to the SNMP server. Syslog traps are either enabled or not enabled through the snmp-server enable command. |
| entry number | Number of the message entry in the history table. |
| SYS-5-CONFIG_I Configured from console by console | Cisco IOS syslog message consisting of the facility name (SYS) which indicates where the message came from, the severity level (5), the message name (CONFIG_I), and the message text. |
| timestamp | Time, based on the router's up time, that the message was generated. |
The following is sample output from the show logging summary command for the Cisco 12012. A number in the column indicates that the syslog contains that many messages for the line card. For example, line card in slot 9 has 1 error message, 4 warning messages, and 47 notification messages.
Router# show logging summary
+-----+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+
SLOT | EMERG | ALERT | CRIT | ERROR |WARNING| NOTICE| INFO | DEBUG |
+-----+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+
|* 0* | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| 1 | | | | | | | | |
| 2 | | | | 1 | 4 | 45 | | |
| 3 | | | | | | | | |
| 4 | | | | 5 | 4 | 54 | | |
| 5 | | | | | | | | |
| 6 | | | | | | | | |
| 7 | | | | 17 | 4 | 48 | | |
| 8 | | | | | | | | |
| 9 | | | | 1 | 4 | 47 | | |
| 10 | | | | | | | | |
| 11 | | | | 12 | 4 | 65 | | |
+-----+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+
Router#
Table 6 describes the logging level fields shown in the display.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| SLOT | Indicates the slot number of the line card. An asterisk next to the slot number indicates that this is the GRP card and error message counts are not displayed for the GRP card. For information on the GRP card, use the show logging command. |
| EMERG | Indicates the system is unusable. |
| ALERT | Indicates immediate action is needed. |
| CRIT | Indicates a critical condition. |
| ERROR | Indicates an error condition. |
| WARNING | Indicates a warning condition. |
| NOTIFICE | Indicates a normal but significant condition. |
| INFO | Indicates an informational message only. |
| DEBUG | Indicates a debugging message. |
clear logging
logging history size
logging linecard
This section documents the following new debug commands. All other debug commands used with this feature are documented in the Cisco IOS Release 11.2 Debug Command Reference.
To enable the display of MBus messages if a line card fails to come up properly, use the debug gsr mbus EXEC command. Use the no form of the command to disable debugging output.
[no] debug gsr mbusThis command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 GS.
Use the the debug gsr mbus command if the line card fails to come up (that is, does not reach the "Line Card Enabled" state when using the show gsr command). Reload the line card and review the output that provides a chronology of the boot process. If a lot of MBus errors are being generated, enable the debug gsr mbus command. Additional information can be obtained with the show mbus counters and show mbus can-error commands.
Figure 1 shows sample output from the debug gsr mbus command when microcode is reloaded on the line card in slot 4.
router# debug gsr mbus
Removed slot 4 for config
Enabling line card 242 on fabric
Added slot 4 for config
Enabling line card 252 on fabric
Launching fab down loader in slot 4
with Switch Cards 1F and
primary_clk CSC_1
Removed slot 4 for config
Enabling line card 242 on fabric
REQ_CONFIG_FIA from slot = 4
config send: code 3 primary 2 switch 1F csc_mode 2
CONFIG_FIA_OVER from slot 4
Added slot 4 for config
Enabling line card 252 on fabric
Table 7 describes the messages generated by this command in the sample output.
| Message | Description |
|---|---|
| Removed slot 4 for config Enabling line card 242 on fabric | Disabling slot 4 on the switching fabric. |
| Added slot 4 for config Enabling line card 252 on fabric | Enabling slot 4 on the switching fabric. |
| Launching fab down loader in slot 4 with Switch Cards 1F and primary_clk CSC_1 | Launching switching fabric downloader with switch cards 0x1F (all switch fabric cards) with CSC_1 as primary clock. |
| Removed slot 4 for config Enabling line card 242 on fabric | Disabling slot 4 on the switching fabric. |
| REQ_CONFIG_FIA from slot = 4 config send: code 3 primary 2 switch 1F csc_mode 2 CONFIG_FIA_OVER from slot 4 | Configuring the FIA in slot 4. |
| Added slot 4 for config Enabling line card 252 on fabric | Enabling slot 4 on the switching fabric. |
To enable warnings and errors from the Interprocess Communications (IPC) on the line card or Gigabit Route Processor (GRP), use the debug ipc errors EXEC command. Use the no form of the command to disable debugging output.
[no] debug ipc errorsThis command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 GS.
Use the debug ipc errors command if you observe IPC error messages or IPC timeout messages and the error counters are increasing when you use the show ipc statistics command.
 Caution On the GRP, if there are a lot of IPC timeout error messages or messages such as Unicast send timeout, verify other statistics with the show controller csar and show controller fia command to further diagnose the problem before enabling the debug ipc errors command.
Caution On the GRP, if there are a lot of IPC timeout error messages or messages such as Unicast send timeout, verify other statistics with the show controller csar and show controller fia command to further diagnose the problem before enabling the debug ipc errors command.
To use the debug ipc errors on a line card, use the if-con slot-number or exec slot slot-number command. It is safer to use the if-con command rather than the exec slot command to enable the debug ipc errors command on a line card. If there are IPC problems between the GRP and the line card, the exec slot command might fail or wait a long time for the line card to respond.
 Caution On the line card, before enabling the debug ipc errors command, use the show ip statistics command. If the error counters in the show ipc statistics command increase at a fast rate, enabling the debug ipc errors command might generate a lot of output. Too many log messages from the line card might cause the messages to get dropped over the MBus. In this case, it might be useful to use the show controller frfab queues command and check whether the number of elements in the non-IPC free queues or IPC queue is zero. If the number of elements in the non-IPC free queues or IPC queue is zero, it could indicate that the buffers are exhausted.
Caution On the line card, before enabling the debug ipc errors command, use the show ip statistics command. If the error counters in the show ipc statistics command increase at a fast rate, enabling the debug ipc errors command might generate a lot of output. Too many log messages from the line card might cause the messages to get dropped over the MBus. In this case, it might be useful to use the show controller frfab queues command and check whether the number of elements in the non-IPC free queues or IPC queue is zero. If the number of elements in the non-IPC free queues or IPC queue is zero, it could indicate that the buffers are exhausted.
Figure 2 shows sample output from the debug ipc errors command.
router# debug ipc errors
IPC: Failed opening master port
Table 8 lists the possible messages that could be generated by this command.
| Message | Description |
|---|---|
| IPC: Couldn't get cached message block | There was no message in the IPC message cache. |
| IPC: Open port error, port not there | Cannot find the IPC port while trying to initialize it. |
| IPC: Open port error, no more room on port | The maximum number of IPC ports have been opened. |
| IPC: Failed opening master port | While trying to locate an IPC port from the master IPC port, the software could not open the master port. |
| IPC: Could not find seat | Output seat of an IPC port is not present. |
| IPC: Open port unknown_transport port | Transport should be either reliable, unreliable, or unreliable with notification. |
| IPC: No memory for close port request | Cannot allocate an IPC message to send a close port request message. |
| IPC: Cannot open control port 0x0004000 IPC Master:Init (timeout) | Reason for the problem: timeout.
Port id: 0x0040000. You can verify the port ID with the show ipc ports command. Port name: IPC Master: Init. You can verify the port name with the show ipc ports command. |
| IPC: No memory for remove port request | Cannot allocate an IPC message to send a remove port request message. |
| IPC: Can't remove port 0x00009000 (timeout) | Cause of the problem: timeout.
Port id: 0x00009000. You can verify the port ID with the show ipc ports command. |
| Failed to allocate msg for RTTY response | Cannot allocate an IPC message to send a remote TTY response. |
| Err opening RTTY server port | Remote TTY client cannot open the RTTY server port. |
| Not attached to RTTY server port | Remote TTY client is not attached to server to handle response message. |
| Cannot get buffer for detach response msg | Remote TTY client cannot get IPC message to send detach response. |
| No server port to detach | Remote TTY client cannot handle detach message as it is not attached to RTTY server. |
| Cannot register RTTY client IPC port | Remote TTY client cannot register port with IPC. |
| Cannot write to NULL RTTY server port | RTTY server port no longer exists while RTTY client is sending data. |
| Cannot write to closed RTTY server port | RTTY server port is closed while RTTY client is sending data. |
| Cannot get buffer to write RTTYC data | Remote TTY client cannot allocate IPC message to send data to RTTY server. |
| Cannot output to Null RTTY server | Remote TTY server port is removed while RTTY client is sending output to it. |
| Err in output to closed RTTY server port | Remote TTY server port is closed while RTTY client is sending output to it. |
| Err in sending RPC msg to RTTY server | IPC RPC error while sending a message from RTTY client to RTTY server. |
| Malloc failed for RTTY server port | Memory problems while allocating server port information in RTTY client. |
| Failed to open RTTY server port | RTTY client cannot open IPC port to RTTY server. |
| Cannot allocate TTY | RTTY client cannot allocate TTY to communicate with RTTY server. |
| Failed to duplicate server name | RTTY client cannot copy server port name during initialization. |
| Cannot get buffer for output rsp msg | RTTY server cannot allocate IPC message for response message. |
| Cannot register port | RTTY server cannot register its IPC port. |
| Failed to alloc server port name | RTTY server cannot copy server port name during initialization. |
| Failed to create server port | RTTY server cannot create IPC port. |
| IPC: Invalid message received from GRP 7 | Line card error message for IPC message from GRP. The message type is 7. |
| IPC: Init failed due to null IPC globals | Line card initialization failed due to IPC globals failure. |
| Cannot create named IPC Master:Init port | GRP cannot create port.
Port name: IPC Master: Init. You can verify the port name with the show ipc ports command. |
| IPC: Invalid message received from master 0200 | Slave GRP initialization failure because of invalid message from master GRP. The message type is 0200. |
| Seat exists already (IPC Master:Init, 09000200) | GRP cannot initialize slot as the seat already exists.
Seat name: IPC Master: Init. You can verify the seat name with the show ipc nodes command. The seat id is 09000200. |
To enable the display of low-level mbus messages, use the debug mbus system EXEC command. Use the no form of the command to disable debugging output.
[no] debug mbus systemThis command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 GS.
The debug mbus system command is useful for low-level debug of the MBus system.
Enable the debug mbus system command if you are getting a lot of MBus errors. Additional information can be obtained with the show mbus counters and show mbus can-error commands.
Enabling the debug mbus system command typically displays the CAN message that generated the error condition. The debug mbus system is usually restricted to developers. MBus errors typically manifest as errors in the applications running over the MBus. You can enable debug for that particular application to get more information (for example, debug gsr mbus is one such application debug).
Figure 3 shows sample output from the debug mbus system command. In this example, the first packet of a new message was received from a selected slot/stream combination while there was already a message in progress. The previous message remains incomplete and is dropped. The MBus system software allows only one message to be sent from a particular slot/stream combination at any given instant.
router# debug mbus system
Reassembly error; incomplete message:
C8 02 80 01 11 08 01 00 01 00 00 00
|
|