|
|

From the perspective of a network manager, network management takes place between two major types of systems: those in control, called managing systems, and those observed and controlled, called managed systems. The most common managing system is called a Network Management System (NMS). Managed systems can include hosts, servers, or network components such as routers or intelligent repeaters.
To promote interoperability, cooperating systems must adhere to a common framework and a common language, called a protocol. In the Internet Network Management Framework, that protocol is the Simple Network Management Protocol, commonly called SNMP.
The exchange of information between managed network devices and a robust NMS is essential for reliable performance of a managed network. Because some of these devices may have a limited ability to run management software, the software must minimize its performance impact on the managed device. The bulk of the computer processing burden, therefore, is assumed by the NMS. The NMS in turn runs the network management applications, such as CiscoWorks or CiscoView, that present management information to network managers and other users.
In a managed device, the specialized low-impact software modules, called agents, access information about the managed devices and make it available to the NMS. Managed devices maintain values for a number of variables and report those, as required, to the NMS. For example, an agent might report such data as the number of bytes and packets in and out of the device, or the number of broadcast messages that were sent and received. In the Internet Network Management Framework, each of these variables is referred to as a managed object. A managed object is a classification of anything that can be managed, anything that an agent can access and report back to the NMS. All managed objects are contained in the Management Information Base (MIB), a database of the managed objects.
An NMS can control a managed device by sending a message to the agent (of that managed device) requiring the device to change the value of one or more of its variables. The managed devices can respond to commands such as Sets or Gets. Sets are used by the NMS to control the device. Gets are used by the NMS to monitor the device.
The Cisco MIB User Quick Reference lists the MIB variables that are proprietary to Cisco devices. However, many other internet-standard MIBS are supported by Cisco agents. These standard MIBs are defined in documents called Requests for Comments (RFCs). (For information on the RFC MIBs supported by Cisco, refer to the section "Cisco-Supported MIBs" later in this guide.) Therefore, in order to find specific MIB information, examine the Cisco proprietary MIB structure and the standard RFC MIBs supported by Cisco.
If your NMS is unable to get requested information from a managed device, such as a Cisco router, the MIB that allows that specific data collection might be missing. Typically, if an NMS cannot retrieve a particular MIB variable, either the NMS does not recognize the MIB variable or the agent does not support the MIB variable. If the NMS does not recognize a specified MIB variable, the MIB might need to be loaded into the NMS, usually by means of a MIB compiler. As an NMS administrator, you might need to load the Cisco MIB or the supported RFC MIB into the NMS in order to execute a specified data collection. If the agent does not support a specified MIB variable, you need to find out what version of IOS or system software you are running. Different MIBs are supported in different software releases.
Use this guide to determine whether your version of software actually supports the specified MIB variable. (See the section "MIBs Supported by Cisco Software Releases" at the end of this guide.) Or, you might want to use this guide to see what variables are available for a given software release. As you reference this guide, read the descriptions of the variables to learn what they are and what they do. Check the Access or Max-Access type to learn what operations, such as reading Gets or writing Sets, can be performed on a particular MIB variable. Check the Syntax type to determine the data type for the MIB variable. Some variables provide textual information (for example, syntax of DisplayString), while others provide numeric information (for example, syntax of Integers or Counters). Once you identify a needed MIB variable, you can easily load the file into the NMS. To learn how to access a Cisco MIB file, refer to the section "Accessing Cisco MIB Files." Cisco Systems also supports many MIB variables developed by other vendors. To learn about other-vendor supported MIBs, refer to the section "Accessing Other-Vendor MIB Variables Supported by Cisco."
This guide describes the Cisco Systems private, or local, Management Information Base (MIB) for Internetwork Operating System (IOS) Release 10.3. The Cisco MIB is provided with all Cisco software releases and with CiscoWorks router management software. The MIB file contains variables that can be set or read to provide information on network devices and interfaces.
The Cisco MIB is a set of variables that are private extensions to the Internet standard MIB II and many other internet standard MIBs. MIB II is documented in RFC 1213, Management Information Base for Network Management of TCP/IP-based Internets: MIB-II.
The Cisco MIB is described by a number of MIB files, which can be obtained by FTP from the Cisco server. The listing of Cisco MIB variables in those files is identical to the listing in this guide.
You can obtain the files that describe the Cisco MIB by using the ftp ftp.cisco.com command. Log in with the username anonymous and enter your e-mail name when prompted for the password. Use the cd pub/mibs command to go to the directory that contains the MIB files, and then issue the get README command to display the readme file containing a list of available files. IOS Release 10.2 MIB files are in the subdirectory mib.dir102, which has its own README file. You can then use the get filename command to retrieve the desired MIB file (for example, after using cd mib.dir102, use CISCO-PING-MIB-mib.my to retrieve the Cisco ping MIB).
You can obtain the files that describe other-vendor MIB variables supported by Cisco by using the ftp ftp.venera.isi.edu command. Log in with the username anonymous and enter your e-mail name when prompted for the password. Use the cd mib command to go to the directory that contains the MIB files, and then issue the get README command to display the readme file containing a list of available files. You can then use the get filename command to retrieve the desired MIB file (for example, use get novell-nlsp-mib.my to retrieve the Novell NLSP MIB).
The Cisco MIB variables are accessible via the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), which is an application-layer protocol designed to facilitate the exchange of management information between network devices. The SNMP system consists of three parts: SNMP manager, SNMP agent, and MIB.
Instead of defining a large set of commands, SNMP places all operations in a get-request, get-next-request, get-bulk-request, and set-request format. For example, an SNMP manager can get a value from an SNMP agent or store a value into that SNMP agent. The SNMP manager can be part of a network management system (NMS), and the SNMP agent can reside on a networking device such as a router. You can compile the Cisco MIB with your network management software. If SNMP is configured on a router, the SNMP agent can respond to MIB-related queries being sent by the NMS.
An example of an NMS is the CiscoWorks network management software. CiscoWorks uses the Cisco MIB variables to set device variables and to poll devices on the internetwork for specific information. The results of a poll can be graphed and analyzed in order to troubleshoot internetwork problems, increase network performance, verify the configuration of devices, monitor traffic loads, and more.
As shown in Figure 1, the SNMP agent gathers data from the MIB, which is the repository for information about device parameters and network data. The agent also can send traps, or notification of certain events, to the manager. The Cisco trap file, mib.traps, which documents the format of the Cisco traps, is available on the Cisco host ftp.cisco.com.

The SNMP manager uses information in the MIB to perform the operations described in Table 1.
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
Retrieve a value from a specific variable. | |
Retrieve the value following the named variable. Often used to retrieve variables from within a table1. | |
The reply to a get-request, get-next-request, get-bulk-request, and set-request sent by an NMS. | |
get-bulk-request | Similar to get-next-request, but fill the get-response with up to max-repetition number of get-next interactions. |
Store a value in a specific variable. | |
trap | An unsolicited message sent by an SNMP agent to an SNMP manager indicating that some event has occurred. |
| 1With this operation, an SNMP manager does not need to know the exact variable name. A sequential search is performed to find the needed variable from within the MIB. |
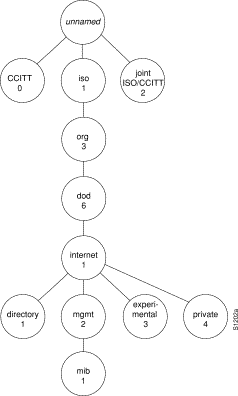
The MIB structure is logically represented by a tree hierarchy. (See Figure 2.) The root of the tree is unnamed and splits into three main branches: Consultative Committee for International Telegraph and Telephone (CCITT), International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and joint ISO/CCITT.
These branches and those that fall below each category have short text strings and integers to identify them. Text strings describe object names, while integers allow computer software to create compact, encoded representations of the names. For example, the Cisco MIB variable authAddr is an object name and is denoted by number 5, which is listed at the end of its object identifier number 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.2.1.5.
The object identifier in the Internet MIB hierarchy is the sequence of numeric labels on the nodes along a path from the root to the object. The Internet standard MIB is represented by the object identifier 1.3.6.1.2.1. It also can be expressed as iso.org.dod.internet.mgmt.mib. (See Figure 2.)
 Internet MIB Hierarchy
Internet MIB Hierarchy
The private Cisco MIB is represented by the object identifier 1.3.6.1.4.1.9, or iso.org.dod.internet.private.enterprise.cisco. The Cisco MIB includes the following subtrees: local (2), temporary (3), and, ciscoMgmt (9).
The local subtree contains MIB objects defined prior to Internetwork Operating System (IOS) Release 10.2. MIB objects defined prior to Software Release 10.2 implemented the SNMPv1 Structure of Management Information (SMI). Beginning with IOS 10.2, however, Cisco MIBs are defined using the SNMPv2 SMI. MIBs defined using SNMPv2 are being placed in the ciscoMgmt tree. (See Figure 3.) MIBs currently defined in the local subtree are being deprecated by Cisco as an ongoing process, and being replaced with new objects defined in the ciscoMgmt subtree. For example, the TCP group that was in the local group has been deprecated and replaced with a new TCP group in the ciscoMgmt tree.

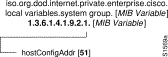
In Figure 3, the local variables group is identified by 2; its subgroup, called lsystem, is identified by 1; and the first variable is romId with a value of 1. Therefore, the variable romId has a value of 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.2.1.1.0. The appended 0 indicates that 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.2.1.1.0 is the one and only instance of romId.
In this guide, each group of Cisco MIB variables is accompanied by an illustration that indicates the specific object identifier for each variable.
For example, in Figure 4 the object identifier 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.2.1 at the top of the illustration indicates the labeled nodes. The last value is the number of the Cisco MIB variable. For example, the MIB variable hostConfigAddr is indicated by the number 51. The object identifier for hostConfigAddr is iso.org.dod.internet.private.enterprise.cisco.local variables.system group.hostConfigAddr or 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.2.1.51.
 Object Identifier Example for a Cisco MIB Variable
Object Identifier Example for a Cisco MIB Variable
When network management protocols use names of MIB variables in messages, each name has a suffix appended. For simple variables, the suffix 0 refers to the instance of the variable with that name. A MIB also can contain tables of related variables.
Following is an excerpt of the information on the IP Routing table (known as lipRoutingTable) from the associated mib file:
lipRoutingTable OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX SEQUENCE OF LIpRouteEntry
ACCESS not-accessible
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"A list of IP routing entries."
::= { lip 2 }
lipRouteEntry OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX LIpRouteEntry
ACCESS not-accessible
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"A collection of additional objects in the
cisco IP routing implementation."
INDEX { ipRouteDest }
::= { lipRoutingTable 1 }
LIpRouteEntry ::=
SEQUENCE {
locRtMask
IpAddress,
locRtCount
INTEGER,
}
The local IP Routing table, lipRoutingTable, is described in Table 7. The lipRoutingTable contains two variables: locRtMask and locRtCount. The index for this table is the destination address of the IP route, or ipRouteDest. If there are n number of routes available to a device, there will be n rows in the IP Routing table.
In Table 2, for the route with the destination IP address of 131.104.111.1, the IP Routing table network mask is 255.255.255.0. The number of parallel routes within the routing table is 3.
| ipRouteDest | locRtMask | locRtCount |
|---|---|---|
131.104.111.1 | 255.255.255.0 | 3 |
133.45.244.245 | 255.255.255.0 | 1 |
In this guide, when variables belong to a table, they are listed in the section describing the table. The following tag is used to indicate the end of a table:
End of Table
All variables before this tag are part of the table.
The local variables section pertains to all Cisco devices and contains the following groups.
This section is equivalent to the experimental space defined by the Structure of Management Information (SMI). These variables are subject to change for each Cisco Systems software release.
Temporary variables consists of the following groups, which are presented in alphabetical order. (See Figure 3.)
The ciscoMgmt subtree consists of the following variables:
The MIB variables of other vendors, including Novell, that are supported by Cisco are identified in the section "Accessing Other-Vendor MIB Variables Supported by Cisco" later in this document. The Novell subtree consists of the following variables:
This section presents the syntax and access type categories used to describe each variable. For details on syntax, refer to RFC 1155, and to RCF 1442 for SNMPv2.
The syntax describes the format of the information, or value, that is returned upon monitoring or setting information in a device with a MIB variable.
The syntax can be any one of the following categories:
The access type, which applies to SNMPv1, describes whether a MIB variable can be used under one of the following circumstances:
This variable, which applies to SNMPv2, can represent one of the following four states: read-create, read-write, read-only, and not-accessible.
The International Organization for Standards (ISO) Network Management Forum defined five areas of network management: fault, configuration, security, performance, and accounting. Cisco MIB variables can be mapped to each of these areas (as described in this section) and used to manage your internetwork.
Although a variable might have a primary use for one aspect of network management, variables often overlap multiple areas. For example, locIPhow and locIPwho, discussed next under "Configuration Management," can also be used for fault management if a system is not loading properly.
Cisco supports several MIBs, which are described in the following Requests for Comments (RFCs). Also listed are RFCs describing the Internet standards that Cisco Systems follows with regard to its MIB format and the SNMP protocol.
To obtain copies of RFCs, use the ftp nic.ddn.mil command. Log in as anonymous and enter your e-mail name when prompted for the password. Enter the cd rfc command to change to the correct directory. Use the get rfc-index.txt command to retrieve a list of all available RFCs. To obtain a copy of any specific RFC, enter get rfcnnnn.txt, where nnnn is the RFC number.
For detailed information on configuration and troubleshooting commands, refer to the following Cisco publications:
Users of the CiscoWorks router management software can refer to the CiscoWorks User Guide for information on CiscoWorks router management software features and its use of MIB variables for the purposes of graphing and analyzing network performance, ensuring configuration consistency, troubleshooting, and more.
Following are suggested reading materials:
The figures in this section provide a visual overview of the Cisco MIB variables along with the object identifier numbers for each MIB variable. The MIB variables are arranged alphabetically within each figure (in the same order in which they appear in the sections of this guide).
 Local Variables: Flash File Table and Flash Group
Local Variables: Flash File Table and Flash Group
 FSIP Group Variables
FSIP Group Variables
 Local Variables: Interface Group Table
Local Variables: Interface Group Table

 Local Variables: Interface Group—VINES
Local Variables: Interface Group—VINES
 Local Variables: Interface Group—XNS
Local Variables: Interface Group—XNS
 Local Variables: Internet Protocol (IP) Group
Local Variables: Internet Protocol (IP) Group
 Local Variables: IP Accounting Table
Local Variables: IP Accounting Table
 Local Variables: IP Checkpoint Accounting Table
Local Variables: IP Checkpoint Accounting Table
 Local Variables: System Group—Buffers
Local Variables: System Group—Buffers
 Local Variables: Terminal Services Group
Local Variables: Terminal Services Group


 Temporary Variables: AppleTalk and Chassis
Temporary Variables: AppleTalk and Chassis
 Temporary Variables: DECnet
Temporary Variables: DECnet
 Temporary Variables: DECnet Tables
Temporary Variables: DECnet Tables
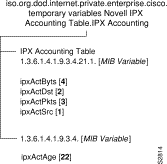 Temporary Variables: IPX Accounting Table I
Temporary Variables: IPX Accounting Table I
 Temporary Variables: IPX Checkpoint Accounting Table
Temporary Variables: IPX Checkpoint Accounting Table


 Novell MIB Variables: IPX Tables
Novell MIB Variables: IPX Tables
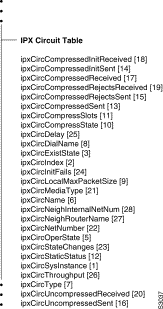 Novell MIB: IPX Circuit Table
Novell MIB: IPX Circuit Table
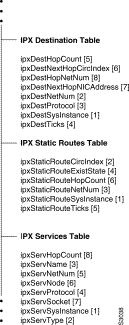


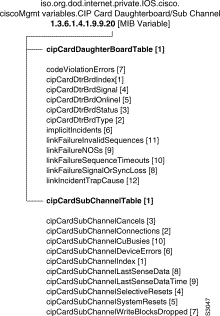
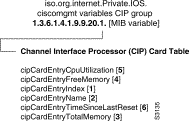 ciscoMgmt: CIP Card Table
ciscoMgmt: CIP Card Table





 ciscoMgmt Cisco Repeater (ciscoRptr) MIB
ciscoMgmt Cisco Repeater (ciscoRptr) MIB




This section describes the MIB variables within the Cisco product line. Certain groups of variables might or might not be present, depending upon the software options and configuration in the managed device.
The Flash memory card is an add-in card of Flash EPROM (erasable programmable read-only memory) storage onto which system software images can be stored, booted, and rewritten.
The local Flash File table, lflashFileDirTable, contains information on a per file basis and includes the following three variables: flashDirName, flashDirSize, and flashDirStatus. The index to this table is flashEntries, or the number of Flash files. If the device has n number of Flash files, the table will contain n number of rows.
For example, in Table 3, the flash1 file has a directory size of 50 octets, and its status is valid, represented by the integer 1.
| flashEntries | flashDirName | flashDirSize | flashDirStatus |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | flash1 | 50 | 1 |
2 | flash2 | 100 | 1 |
3 | flash3 | 200 | 2 |
Provides the name associated with a Flash directory entry.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the size (in octets) of a Flash directory entry.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the status of the Flash directory entry.
Syntax: Integer (1 = valid, 2 = deleted)
Access: Read-only
End of Table
Provides the type of card connected to the Flash card installed in the router. For example, the type of card connected to the Flash card could be either CSC-MS or CSC-MC+.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the type of Flash controller (either CCTL or CCTL2) installed in the router.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of directory entries, or files, that exist in the Flash memory directory.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Sets a request to erase Flash memory, freeing up all available memory space. All of the Flash memory is erased out. Individual files cannot be erased from Flash memory.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Write-only
Indicates the status of current or last erasing of Flash memory.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the value of sysUpTime the last time the Flash memory was erased.
Syntax: Timeticks
Access: Read-only
Provides the amount of available Flash memory in octets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
flashSize
Provides the amount of total Flash memory in octets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
flashStatus
Indicates the status of the availability of Flash memory.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Requests to write the Flash memory to a Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server. The value (display string) is the name of the Flash file being sent, or written, to the server. The instance ID is the IP address of the TFTP host.
This copy of the system image can serve as a backup copy and can also be used to verify that the copy in the Flash memory is the same as the original file.
The Flash memory card can be used as a TFTP file server for other routers on the network. This feature allows you to boot a remote router with an image that resides in the Flash server memory.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Write-only
Indicates the status of the current or last flash to net transfer.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the value of sysUpTime the last time a file was copied from the Flash memory in the router to the TFTP host.
Syntax: Timeticks
Access: Read-only
Provides the status of the VPP DIP jumper on the Flash memory card. Files can be written to the Flash memory card only if the VPP DIP jumper is turned on.
Syntax: Integer (1 = VPP enabled/Flash write enabled, 2 = VPP disabled/Flash write disabled)
Access: Read-only
Copies a software image from Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server to the Flash memory on the router. The value (display string) is the name of the file being sent, or written, to the Flash memory. The instance ID is the IP address of the TFTP host.
The TFTP image copied to the Flash memory must be at least System Software Release 9.0 or later. If earlier system software is copied into the Flash memory, the host processor card will not recognize the CSC-MC+ card upon the next reboot.
If free Flash memory space is unavailable, or if the Flash memory has never been written to, the erase routine is required before new files can be copied.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Write-only
Indicates the status of the current or next-to-last flash transfer.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the value of sysUpTime the last time a file was copied from a Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server to the Flash memory on the router.
Syntax: Timeticks
Access: Read-only
The local FSIP Card table, lfsipTable, contains information about FSIP cards used by the Cisco 7000 and includes the following six variables that provide information about the processor: locIfFSIPtype, locIfFSIPrts, locIfFSIPcts, locIfFSIPdtr, locIfFSIPdcd, and locIfFSIPdsr. The index to this table is locIfSIPIndex, which indicates the interface index of the card corresponding to its IfIndex.
| locIfFSIPIndex | locIfFSIPtype | locIfFSIPrts | locIfFSIPcts | and so on |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | DCE | 1 | 2 |
|
2 | DTE | 1 | 3 |
|
and so on |
|
|
|
|
Indicates whether the CTS (clear to send) signal is up or down.
Syntax: Integer (1 = not available, 1 = up, 2 = down)
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the DCD (data carrier detect) signal is up or down.
Syntax: Integer (1 = not available, 2 = up, 3 = down)
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the DSR (data set ready) signal is up or down.
Syntax: Integer (1 = not available, 2 = up, 3 = down)
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the DTR (data terminal ready) signal is up or down.
Syntax: Integer (1 = not available, 2 = up, 3 = down)
Access: Read-only
Indicates the index interface port of the corresponding ifIndex. (RFC 1213)
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the RTS (request to send) signal is up or down.
Syntax: Integer (1 = not available, 2 = up, 3 = down)
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the FSIP line uses DCE (data communications equipment) or DTE (data terminal equipment).
Syntax: Integer (1 = not available, 2 = DTE, 3 = DCE)
Access: Read-only
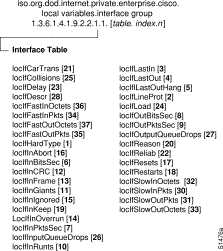
The following variables apply to interfaces attached to Cisco devices. These variables can be used to monitor the performance of the network in terms of the number of packets dropped, time allocations for input and output packets, and so on. These variables also can be used for fault management. For example, variable values indicate which interfaces are dropping packets or have had to be restarted several times.
The Interface table, lifTable, contains all of the variables in the Interface group. The index to the table is ifIndex, which indicates the number of the interface. If the device has n number of interfaces, the Interface table will contain n rows.
In the Interface table shown in Table 5, the first column indicates the number of interfaces on the device. Each of the variables in the interface table occupies one column; for example, locIfHardType is shown in a column, followed by locIfLineProt in the next column, and so on.
| Interface Numer | locIfHardType | locIfLineProt | and so on |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Ethernet | 1 |
|
2 | TokenRing | 0 |
|
3 | FDDI | 1 |
|
and so on |
|
|
|
This section contains basic interface variables that apply to all interfaces and are not protocol-specific.
Provides the number of times the serial interface received the Carrier Detect (CD) signal. If the carrier detect line is changing state often, it might indicate modem or line problems.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output collisions detected on this interface.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the media-dependent delay in transferring a packet to another interface on the media. The delay is indicated in microseconds. Used by Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP).
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides a description of the interface (such as Ethernet, serial, and so on) that corresponds to the user-configurable interface description commands
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-write
Provides the octet count for inbound traffic routed with fast and autonomous switching.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the packet count for inbound traffic routed with fast and autonomous switching.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the octet count for outbound traffic routed with fast and autonomous switching.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the packet count for outbound traffic routed with fast and autonomous switching.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the type of interface (such as Ethernet, serial, FDDI, and so on).
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input packets that were aborted. Aborted input packets usually indicate a clocking problem between the serial interface and the data-link equipment.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides a weighted 5-minute exponentially decaying average of interface input bits per second.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input packets that had cyclic redundancy checksum (CRC) errors. The CRC generated by the originating station or far-end device does not match the checksum calculated from the data received. On a serial link, CRCs usually indicate noise, gain hits, or other transmission problems on the data link.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input packets that were received incorrectly with framing errors. On a serial line, this is usually the result of noise or other transmission problems.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input packets that were discarded because they exceeded the maximum packet size allowed by the physical media.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input packets that were ignored by this interface because the interface hardware ran low on internal buffers. Broadcast storms and bursts of noise can cause the ignored count to be increased.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether keepalives are enabled on this interface.
Syntax: Integer (1 = enabled, 2 = disabled)
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of times the serial receiver hardware was unable to send data to a hardware buffer because the input rate exceeded the ability of the receiver to handle the data.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides a weighted 5-minute exponentially decaying average of input packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of packets dropped because the input queue was full.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input packets that were discarded because they were smaller than the minimum packet size allowed by the physical media.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the elapsed time in milliseconds since the last line protocol input packet was successfully received by an interface. Useful for knowing when a dead interface failed.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the elapsed time in milliseconds since the last line protocol output packet was successfully transmitted by an interface. Useful for knowing when a dead interface failed.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the elapsed time in milliseconds since the last line protocol output packet could not be successfully transmitted.
OR
Provides the elapsed time (in milliseconds) since the interface was last reset because of a transmission that took too long.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the interface is up or down.
Syntax: Integer (1 = up, 2 = down)
Access: Read-only
Provides the loading factor of the interface. The load on the interface is calculated as an exponential average over 5 minutes and expressed as a fraction of 255 (255/255 is completely saturated). Used by Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP).
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides a weighted 5-minute exponentially decaying average of interface output bits per second for the specific protocol.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides a weighted 5-minute exponentially decaying average of interface output packets per second for the specific protocol.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of packets dropped because the output queue
was full.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the reason for the most recent status change of the interface.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the level of reliability for the interface. The reliability of the interface is calculated as an exponential average over 5 minutes and expressed as a fraction of 255 (255/255 is 100 percent). Used by Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP).
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of times the interface was reset internally. An interface can be reset if packets queued for transmission were not sent within several seconds. On a serial line, this can be caused by a malfunctioning modem that is not supplying the transmit clock signal or by a cable problem. If the system notices that the carrier detect line of a serial interface is up, but the line protocol is down, it periodically resets the interface in an effort to restart it. Interface resets also can occur when an interface is looped back or shut down.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of times the interface needed to be completely restarted because of errors.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the octet count for inbound traffic routed with process switching.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the packet count for inbound traffic routed with process switching.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the packet count for outbound traffic routed with process switching.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the octet count for outbound traffic routed with process switching.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
End of Table
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP). ARP provides dynamic addressing between 32-bit IP addresses and Ethernet addresses. For detailed information on ARP, refer to the Router Products Configuration and Reference publication.
Provides the ARP input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the ARP input packet count. It indicates the number of ARP Reply packets received by this router on this interface from other hosts.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the ARP output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the ARP output packet count. It indicates the number of ARP Request packets sent by this router on this interface to other hosts on the network.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running AppleTalk:
Provides the AppleTalk protocol input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the AppleTalk protocol input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the AppleTalk protocol output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the AppleTalk protocol output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running Apollo:
Provides the Apollo protocol input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the Apollo protocol input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the Apollo protocol output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the Apollo protocol output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running bridging protocols:
Provides the bridged protocol input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the bridged protocol input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the bridged protocol output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the bridged protocol output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the Source-Route Bridging (SRB) protocol input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the SRB protocol input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the SRB protocol output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the SRB protocol output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running Connectionless Network Service (CLNS):
Provides the CLNS protocol input byte count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the CLNS protocol input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the CLNS protocol output byte count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the CLNS protocol output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running DECnet:
Provides the DECnet protocol input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the DECnet protocol input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the DECnet protocol output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the DECnet protocol output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running HP Probe, an address resolution protocol developed by Hewlett-Packard:
Provides the HP Probe protocol input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the HP Probe protocol input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the HP Probe protocol output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the HP Probe protocol output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running the Internet Protocol (IP):
Provides the IP input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the IP input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the IP output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the IP output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the LAN Network Manager protocol input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the LAN Network Manager protocol input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the LAN Network Manager protocol output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the LAN Network Manager protocol output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running the Maintenance Operation Protocol (MOP):
Provides the MOP input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the MOP input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the MOP output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the MOP output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running Novell:
Provides the Novell protocol input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the Novell protocol input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the Novell protocol output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the Novell protocol output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group record the number of input and output packets and octets for interfaces running protocols other than those listed in the Interface group:
Provides the input octet count for protocols other than those listed in the Interface group.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the input packet count for protocols other than those listed in the Interface group.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the output octet count for protocols other than those listed in the Interface group.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the output packet count for protocols other than those listed in the Interface group.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces using the Serial Tunnel (STUN) protocol. STUN allows devices that use Synchronous Data Link Control (SDLC) or High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC) to be connected through one or more Cisco routers across different network topologies.
Provides the STUN protocol input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the STUN protocol input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the STUN protocol output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the STUN protocol output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running the Spanning Tree protocol. Used in bridging, spanning trees provide root and designated bridges to notify all other bridges in the network when an address change has occurred, thereby eliminating loops.
Provides the spanning-tree input octet packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the spanning-tree input protocol packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the spanning-tree output octet packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the spanning-tree output protocol packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running the Banyan Virtual Integrated Network Service (VINES) protocol. This proprietary protocol is derived from the Xerox Network Systems (XNS) protocol. The VINES variables provide the number of input and output packets and octets on a per interface basis.
Provides the VINES protocol input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running Xerox Network Systems (XNS).
Provides the XNS protocol input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the XNS input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the XNS protocol output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the XNS protocol output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The Internet Protocol (IP) group provides variables pertaining to the IP, such as the determination of how an interface obtained its IP address, who supplied the address, and Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) messages about IP packet processing.
The Cisco IP Address table, lipAddrTable, contains the following six variable entries, or rows: locIPHelper, locIPHow, locIPRedirects, locIPSecurity, locIPUnreach, and locIPWho. The index to this table is the IP address of the device, or ipAdEntAddr. If a device has n number of IP addresses, there will be n rows in the table.
For simplification, Table 6 shows only the locIpHow and locIPWho variables. The locIPHow variable value shows that the device at 131.108.201.245 obtained its address through nonvolatile memory. The locIPWho variable value indicates the device was assigned its current address by the device at 131.101.200.248.
| IP Address | locIPHow | locIPWho | and so on |
|---|---|---|---|
131.108.201.245 | nonvolatile | 131.101.200.248 |
|
142.111.202.244 | nonvolatile | 131.56.70.249 |
|
and so on |
|
|
|
Provides the IP address for broadcast forwarding support. Provides the destination broadcast or IP address that the router should use when forwarding User Datagram Protocol (UDP) broadcast datagrams, including BootP, received on the interface.
Syntax: IpAddress
Access: Read-only
Describes how this interface obtained its IP address. Typically, the address is determined by nonvolatile memory.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) redirects will be sent. A router sends an ICMP Redirect message to the originator of any datagram that it is forced to resend through the same interface on which it was received. It does so because the originating host presumably could have sent that datagram to the ultimate destination without involving the router at all. ICMP Redirect messages are sent only if the router is configured with the ip redirects command.
Syntax: Integer (1 = sent, 2 = not sent)
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether IP security is enabled on the interface. For details on IP security levels, see RFC 1108, U.S. Department of Defense Security Options for the Internet Protocol.
Syntax: Integer (0 = false, 1 = true)
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) packets indicating unreachable addresses will be sent for a specific route.
If this variable is set, and the router receives a datagram that it cannot deliver to its ultimate datagram (because it knows of no route to the destination address), it replies to the originator of that datagram with an ICMP Host Unreachable message.
Syntax: Integer (0 = false, 1 = true)
Access: Read-only
Provides the IP address of the device from which this interface received its IP address. If the interface does not use an IP address from another device, a value of 0.0.0.0 displays.
Syntax: IpAddress
Access: Read-only
End of Table
The local IP routing table, lipRoutingTable, contains two variables: locRtCount and locRtMask. The index for this table is the destination address of the IP route, or ipRouteDest. If there are n number of routes available to a device, there will be n rows in the IP routing table.
In Table 7, for the route with the destination IP address of 131.104.111.1, the routing table network mask is 255.255.255.0. The number of parallel routes within the routing table is 3, and the route was used in a forwarding operation two times.
| ipRouteDest | locRtMask | locRtCount |
|---|---|---|
131.104.111.1 | 255.255.255.0 | 3 |
133.45.244.245 | 255.255.255.0 | 1 |
Provides the number of parallel routes within the IP Routing table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the IP Routing table network mask. For example, 255.255.255.0.
Syntax: IpAddress
Access: Read-only
End of Table
Provides the total number of bytes of lost IP packets as a result of accounting failure.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of IP packets that were lost due to memory limitations and accounting failure.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the threshold of IP accounting records in use before IP traffic will be discarded.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Cisco routers maintain two accounting databases: an active database and a checkpoint database. The router takes a snapshot of the running, or active database, and copies it into the checkpoint database. For detailed information on active and checkpoint databases, refer to the Router Products Configuration and Reference and Router Products Command Reference publications.
This group provides access to the active database that is created and maintained if IP accounting is enabled on a router. The active database contains information about the number of bytes and packets switched through a system on a source and destination IP address basis. Only transit IP traffic is measured and only on an outbound basis; traffic generated by the router or terminating in the router is not included in the accounting statistics. Internetwork statistics obtained through these variables can be analyzed to improve network performance.
The local IP accounting table, lipAccountingTable, includes four related variables: actByts, actDst, actPkts, and actSrc. The index for this table is actSrc and actDst. For example, in the first row in Table 8, the source host address is 131.24.35.248, and the destination host address is 138.32.28.245. Fifty IP packets and 400 bytes of data have been sent between the source and destination address.
| actByts | actDst | actPkts | actSrc |
|---|---|---|---|
400 | 138.32.28.245 | 50 | 131.24.35.248 |
1259 | 128.52.33.101 | 110 | 128.52.33.96 |
Provides the total number of bytes in IP packets from the source to destination host.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the IP destination address for the host traffic matrix.
Syntax: Ip Address
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of IP packets sent from the source to destination host.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the IP address for the host traffic matrix.
Syntax: IpAddress
Access: Read-only
Specifies the access list number violated by packets from this source to this destination. A zero value indicates that no access list was violated.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
End of Table
Provides the age of the accounting data in the current data matrix of the active database.
Syntax: Timeticks
Access: Read-only
The Cisco router maintains two accounting databases: an active database and a checkpoint database. For detailed information on active and checkpoint databases, refer to the Router Products Configuration and Reference publication.
The running, or active database, is copied into the checkpoint database. If the checkpoint database already has data obtained previously from the active database, the router appends the latest copy of the active database to the existing data in the checkpoint database. The checkpoint database stores data retrieved from the active database until actCheckPoint is set or you delete the contents of this database by using the clear ip accounting [checkpoint] command.
A network management system (NMS) can use checkpoint MIB variables to analyze stable data in the checkpoint database.
The local IP Checkpoint Accounting table, lipCkAccountingTable, includes four related variables: ckactByts, ckactDst, ckactPkts, and ckactSrc. The index for this table is ckacSrc and ckactDst. For example, in Table 9, the source host address is 131.24.35.248. The destination host address is 138.32.28.245. Fifty IP packets and 400 bytes of data have been sent between the source and destination address.
| ckactByts | ckactDst | ckactPkts | ckacSrc |
|---|---|---|---|
400 | 138.32.28.245 | 50 | 131.24.35.248 |
480 | 124.45.222.246 | 60 | 123.34.216.244 |
Provides the total number of bytes in IP packets from source to destination in the checkpoint matrix.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the IP destination address of the host receiving the IP packets. The address is listed in the checkpoint traffic matrix.
Syntax: IpAddress
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of IP packets sent from the source to the destination address in the checkpoint matrix.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the IP source address of the host sending the IP packets. The address is listed in the checkpoint traffic matrix.
Syntax: IP address
Access: Read-only
Provides the access list number violated by packets from source to destination in the checkpoint matrix.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
End of Table
Activates a checkpoint database. This variable must be read and then set to the same value that was read. The value read and then set will be incremented after a successful set request.
For detailed information on active and checkpoint databases, refer to the Router Products Command Reference and Router Products Configuration and Reference publications.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Provides information on how long ago the data was first stored in the checkpoint matrix.
Syntax: Timeticks
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of packets dropped due to access control failure.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The IPX Accounting table allows a related set of IPX accounting variables to be applied across several devices or interfaces.
Provides the total bytes of lost IPX packets.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the lost IPX packets due to memory limitations.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the threshold of IPX accounting records in use before IPX traffic will be unaccounted.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
The local IPX accounting table (see Table 10), lipxAccountingTable, provides access to the Cisco IPX accounting support. The Local IPX Accounting Table (see Table 11) includes the following variables: ipxActSrc, ipxActDst, ipxActPkts, and ipxActByts.
| ipxActByts | ipxActDst | ipxActPkts | ipxActSrc |
|---|---|---|---|
10,000 | 1.000.0230.0110 | 40 | BADDAD.0110.0220.0333 |
Provides the total number of bytes in IPX packets from source to destination.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the IPX Destination address for host traffic matrix.
Syntax: Octet String
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of IPX packets sent from source to destination.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the IPX source address for host traffic matrix.
Syntax: Octet String
Access: Read-only
End of Table
Provides the age of the data in the current IPX data matrix.
Syntax: TimeTicks
Access: Read-only
The Local IPX Checkpoint Accounting table, ipxCkAccountingTable, includes four related variables: ipxckActByts, ipxckActDst, ipxckActPkts, and ipxckActSrc. The index for this table is ckActSrc and ckActDst.
| ipxckActByts | ipxckActDst | ipxckActPkts | ipxckActSrc |
|---|---|---|---|
10,000 | 1.000.0230.0110 | 40 | BADDAD.0110.0220.0333 |
Provides the IPX destination address for host in checkpoint traffic matrix.
Syntax: Octet String
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of IPX packets sent from source to destination in checkpoint matrix.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the IPX source address for host in checkpoint traffic matrix.
Syntax: Octet String
Access: Read-only
End of Table
Provides the age of data in the IPX checkpoint matrix.
Syntax: TimeTicks
Access: Read-only
Provides a checkpoint to the IPX accounting database. This MIB variable must be read and then set with the same value for the checkpoint to succeed. The value read and then set will be incremented after a successful set request
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
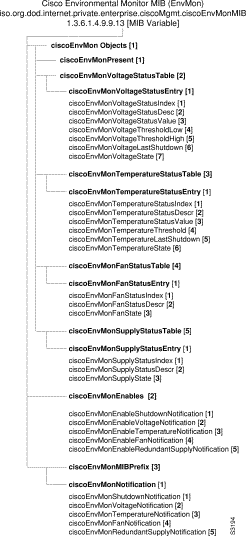
This section describes the group of MIB variables managed by Cisco Systems.
The MIB module in this section describes the management of VINES routing information in Cisco devices.
Specifies the VINES network number of this router.
Syntax: VinesNetworkNumber
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES host (subnetwork) number of this router.
Syntax: VinesHostNumber
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the next VINES client host (subnetwork) number to be assigned by this router.
Syntax: VinesHostNumber
Max-Access: Read-only
The Cisco VINES Neighbor Table contains the objects listed in this section.
Specifies the number of neighbors in the neighbor table, cvForwNeighborTable.
Syntax: Gauge32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of paths in the neighbor table, cvForwNeighborTable.
Syntax: Gauge32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the version number of the neighbor table, cvForwNeighborTable, which is incremented each time a route or path is added or deleted.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies a table of information about neighbors of this router.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF CvForwNeighborEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the network part of the neighbor's VINES internet address.
Syntax: VinesNetworkNumber
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the host part of the neighbor's VINES internet address.
Syntax: VinesHostNumber
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the neighbor's physical address on the network interface as indicated by this entry's ifIndex and interpreted according to ifType at ifIndex in ifTable.
Syntax: PhysAddress
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the source of this entry.
Syntax: Integer 1 = unrecognized, 2 = self, 3= rtpRedirect, 4 = rtpUpdate, 5 = manualRoute, 6 = igrp, 7 = test, 8 = manualNeighbor
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the version of RTP through which the entry was learned.
Syntax: Integer32 (0-255)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the way in which this path will be used to forward a message.
Syntax: Integer 1 = next, 2 = roundRobin, 3 = backup
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the age of the entry, in seconds. The value -1 indicates not applicable for RTP Version 0 neighbors on WAN interfaces when the interface is configured for delta-only updates.
Syntax: Integer32 (-1-65535)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the expected one-way delay to send a message to this neighbor
Syntax: VinesMetric
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of times the path has been used to forward a message for all cvForwNeighborSource values except "manualRoute." For a "manualRoute," the cvForwNeighborUses variable specifies the number of static routes that use this neighbor as its first hop.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
End of Table
The VINES Route table contains the objects specified in this section.
Specifies the number of routers (servers) in the route table, cvForwRouteTable.
Syntax: Gauge32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of routes in the route table, cvForwRouteTable.
Syntax: Gauge32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the version number of the route table, cvForwRouteTable, incremented each time a route or server (router) is added or deleted.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of seconds until the next routing update.
Syntax: Gauge32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies a table of information about routes from this router to other VINES networks.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF CvForwRouteEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the remote network's VINES network number.
Syntax: VinesNetworkNumber
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the network part of the VINES internetwork address of the neighbor that is the next hop to the remote network. Because the neighbor is a router by definition, its host number is 1.
Syntax: VinesNetworkNumber
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the source of this entry.
Syntax: Integer 1 = unrecognized, 2 = self, 3 = rtpRedirect, 4 = rtpUpdate, 5 = manualRoute, 6 = igrp, 7 = test
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the version of RTP through which the entry was learned.
Syntax: Integer32 (0-255)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies whether this route is the one to use next to get to the remote network.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies whether this route will be used to forward a broadcast from a serverless network.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies whether this route is temporarily being suppressed as normal operation before eventually advertising it.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies whether this route is eligible for load sharing because its metric is equal to the best metric for the same neighbor.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the age of the entry, in seconds. The value -1 indicates not applicable for RTP Version 0 neighbors on WAN interfaces when the interface is configured for delta-only updates.
Syntax: Integer32 (-1-65535)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the expected one-way delay, in milliseconds to send a message on this route.
Syntax: VinesMetric
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of times the route has been used to forward a message.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
The global total counters used by the Cisco VINES MIB contains objects listed in this section.
Specifies the total count of number of VINES input packets.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total count of number of VINES output packets.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total count of VINES input packets for this host.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total count of number of VINES packets forwarded.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total count of number of VINES input broadcast packets.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total count of number of VINES output broadcast packets.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cvTotalBroadcastForwardPackets
Specifies the total count of number of VINES broadcast packets forwarded.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total count of number of VINES broadcast packets not forwarded to all interfaces because the LAN ONLY bit was set.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total count of number of VINES broadcast packets not forwarded to all interfaces because the OVER 4800 BPS bit was set.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total count of number of VINES broadcast packets not forwarded to all interfaces because the NO CHARGES only bit was set.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total count of VINES input packets with header errors.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total count of VINES input packets with checksum errors.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total count of VINES input packets that have exceeded the maximum hop count.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total count of VINES packets dropped due to no route.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total count of VINES packets dropped due to output encapsulation failed.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total count of unknown VINES input packets.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total count of VINES ICP packets received.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total count of VINES ICP packets generated.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total count of VINES ICP Metric Notification packets generated.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total count of VINES MAC level Echo packets received.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total count of VINES MAC level Echo packets generated.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total count of VINES Echo packets received.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total count of VINES Echo packets generated.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total count of proxy packets sent.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total count of responses to proxy packets.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
The Interface Configuration Table (cvInterface) contains the objects listed in this section.
Specifies the VINES protocol metric value.
Syntax: VinesMetric
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol default encapsulation
Syntax: Integer 1 = arpa, 2 = tokenRing, 3 = snap
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol outgoing access list number.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol propagation control.
Syntax: Integer 1 = never, 2 = always, 3 = dynamic
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol arp replies enabled.
Syntax: Integer 1 = never, 2 = always, 3 = dynamic
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies that VINES protocol serverless support is enabled.
Syntax: Integer 1 = never, 2 = dynamic, 3 = always, 4 = alwaysBroadcast
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol redirect interval in milliseconds.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies that the VINES protocol split horizon is disabled.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies whether the VINES protocol line is up or down.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies whether the VINES protocol fast switching is supported.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies whether the VINES protocol fast switching was requested.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol filter on received routing information source address.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol filter on received routing information content.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol filter on transmitted routing information content.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
End of Table
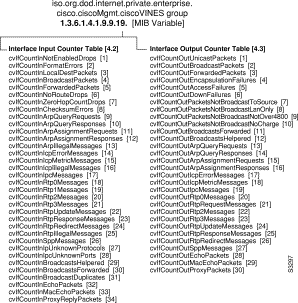
The Interface Input Counter Table (cvIfCountInTable) contains the objects listed in this section.
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input packets that were discarded because the interface was not configured.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input packets with format errors.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input packets destined for this router.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol input broadcast count.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input packets forwarded to another interface.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input packets that were dropped because there was no route to the destination.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input packets that were dropped due to a zero hop count.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input packets with checksum errors.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input ARP Query Request messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input ARP Query Response messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cvIfCountInArpAssignmentRequests
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input ARP Assignment Request messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cvIfCountInArpAssignmentResponses
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input ARP Assignment Response messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input illegal ARP messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input ICP error messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input ICP metric messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input illegal ICP messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input IPC messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input RTP type 0 messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input RTP Request messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input RTP type 2 messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input RTP type 3 messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input RTP Update messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cvIfCountInRtpResponseMessages
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input RTP Response messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cvIfCountInRtpRedirectMessages
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input RTP Redirect messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input illegal RTP messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input SPP messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input packets of unknown VINES protocols.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input packets of unknown VINES IPC ports.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input packets helpered to another server.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cvIfCountInBroadcastsForwarded
Specifies the VINES protocol input broadcast forwarded to other interface(s).
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cvIfCountInBroadcastDuplicates
Specifies the VINES protocol input duplicate broadcast count.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input IPC echo messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input MAC layer echo frames.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of responses to proxy packets.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
End of Table
The VINES interface output counter table (cvIfCountOutTable) contains the objects in this section.
Specifies the VINES protocol unicast packets generated.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol broadcast packets generated.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of forwarded packets.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cvIfCountOutEncapsulationFailures
Specifies the VINES protocol output encapsulation failures.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol output access list failures.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol output interface down count.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cvIfCountOutPacketsNotBroadcastToSource
Specifies the VINES protocol output broadcast not sent because interface leads back to the source.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cvIfCountOutPacketsNotBroadcastLanOnly
Specifies the VINES protocol output broadcast not sent due to Lan Only class.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cvIfCountOutPacketsNotBroadcastNotOver4 800
Specifies the VINES protocol output broadcast not sent due to High Speed class.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cvIfCountOutPacketsNotBroadcastNoCharg e
Specifies the VINES protocol output broadcast not sent due to No Charges class.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cvIfCountOutBroadcastsForwarded
Specifies the VINES protocol output broadcast forwarded from another interface.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cvIfCountOutBroadcastsHelpered
Specifies the VINES protocol output broadcast helpered to a VINES server.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of output ARP Query Request messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of output ARP Query Response messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cvIfCountOutArpAssignmentRequests
Specifies the VINES protocol count of output ARP Assignment Request messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cvIfCountOutArpAssignmentResponses
Specifies the VINES protocol count of input ARP Assignment Response messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of output IPC Error messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of output IPC metric messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of output ICP messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of output RTP type 0 messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cvIfCountOutRtpRequestMessages
Specifies the VINES protocol count of output RTP Request messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of output RTP type 2 messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of output RTP type 3 messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of output RTP Update messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cvIfCountOutRtpResponseMessages
Specifies the VINES protocol count of output RTP Response messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cvIfCountOutRtpRedirectMessages
Specifies the VINES protocol count of output RTP Redirect messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of output SPP messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of output IPC echo messages.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of output IPCMAC layer echo frames.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the VINES protocol count of proxy packets sent.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
The MIB module in this section describes the management of the Cisco Discovery Protocol in Cisco devices.
The (conceptual) table containing the status of CDP on the device's interfaces.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF CdpInterfaceEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies an entry (conceptual row) in the cdpInterfaceTable containing the status of CDP on an interface.
Syntax: CdpInterfaceEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the ifIndex value of the local interface. For 802.3 Repeaters on which the repeater ports do not have ifIndex values assigned, this value is a unique value for the port, and greater than any ifIndex value supported by the repeater; in this case, the specific port is indicated by corresponding values of cdpInterfaceGroup and cdpInterfacePort, where these values correspond to the group number and port number values of RFC 1516.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Provides an indication of whether the Cisco Discovery Protocol is currently running on this interface.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the interval at which CDP messages are to be generated on this interface. The default value is 60 seconds.
Syntax: Integer (10-300). Units are in seconds.
Max-Access: Read-write
This object is only relevant to interfaces that are repeater ports on 802.3 repeaters. In this situation, it indicates the RFC1516 group number of the repeater port which corresponds to this interface.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
This object is only relevant to interfaces that are repeater ports on 802.3 repeaters. In this situation, it indicates the RFC1516 port number of the repeater port that corresponds to this interface.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
End of Table
Specifies the (conceptual) table containing the cached information obtained by means of receiving CDP messages.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF CdpCacheEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies an entry (conceptual row) in the cdpCacheTable containing the information received by means of CDP on one interface from one device.
Syntax: CdpCacheEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Normally specifies the ifIndex value of the local interface. For 802.3 Repeaters for which the repeater ports do not have ifIndex values assigned, this value is a unique value for the port, and greater than any ifIndex value supported by the repeater; the specific port number, in this case, is given by the corresponding value of cdpInterfacePort.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies a unique value for each device from which CDP messages are being received.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Provides an indication of the type of address contained in the corresponding instance of cdpCacheAddress.
Syntax: CiscoNetworkProtocol
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the (first) network-layer address of the device's SNMP-agent as reported in the most recent CDP message. For example, if the the corresponding instance of cacheAddressType had the value ip(1), then this object would be an IP-address.
Syntax: CiscoNetworkAddress
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the Version string as reported in the most recent CDP message. The zero-length string indicates no Version field (TLV) was reported in the most recent CDP message.
Syntax: DisplayString
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the Device-ID string as reported in the most recent CDP message. The zero-length string indicates no Device-ID field (TLV) was reported in the most recent CDP message.
Syntax: DisplayString
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the Port-ID string as reported in the most recent CDP message. This will typically be the value of the ifName object (for example, Ethernet0). The zero-length string indicates no Port-ID field (TLV) was reported in the most recent CDP message.
Syntax: DisplayString
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the device's hardware platform as reported in the most recent CDP message. The zero-length string indicates that no Platform field (TLV) was reported in the most recent CDP message.
Syntax: DisplayString
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the device's functional capabilities as reported in the most recent CDP message. For latest set of specific values, see the latest version of the CDP specification. The zero-length string indicates no Capabilities field (TLV) was reported in the most recent CDP message.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE (0-4))
Max-Access: Read-only
Describes the status of the ISDN Interfaces on Cisco devices.The ISDN hardware interface Basic Rate Interface (BRI) or Primary Rate Interface (PRI) will be represeted by the D channel. This will have an ifType value of basicISDN(20) or primaryISDN(21). For related information, refer to RFC 1213.
Each B channel will also be represented in an an entry in the ifTable. The B channels will have an ifType value of other(1). This model will be used while defining objects and tables for management.
The ISDN MIB will allow sub-layers. For example, the data transfer over a B channel may take place with PPP encapsulation. While the ISDN MIB will describe the B channel, a media specific MIB for PPP can be used on a layered basis. This will be as per RFC 1573. The isdn call information will be stored in the neighbor table
Specifies the list of neighbors from which the router will accept calls or to which it will place them.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF DemandNbrEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies a single Neighbor. This entry is effectively permanent, and contains information describing the neighbor, his permissions, his last call attempt, and his cumulative effects.
Syntax: DemandNbrEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the ifIndex value of the physical interface the neighbor will be called on. On an ISDN interface, this is the ifIndex value of the D channel.
Syntax: Integer32 (1—2147483647)
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies an arbitrary sequence number associated with the neighbor.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the ifIndex value of virtual interface associated with the neighbor.This interface maintains a queue of messages holding for the neighbor awaiting call completion, and all statistics.
Syntax: Integer32 (1..2147483647)
Max-Access: Read-create
Specifies the ASCII name of the neighbor.
Syntax: DisplayString
Max-Access: Read-create
Specifies the Call Address at which the neighbor should be called.Consider this address as the set of characters following 'ATDT 'or the 'phone number' included in a D channel call request.
Syntax: DisplayString
Max-Access: Read-create
Specifies the applicable permissions.
Syntax: Integer 1 = iCanCallHim, 2 = heCanCallMe, 3 = weCanCallEachOther
Max-Access: Read-create
Maximum call duration in seconds. Zero means 'unlimited'.
Syntax: Integer32 (1..2147483647)
Max-Access: Read-create
Specifies the duration of last call in seconds.
Syntax: Integer32 (1—2147483647)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the ASCII reason that the last call terminated.
Syntax: DisplayString
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the encoded reason for the last call tear down.
Syntax: OCTET STRING
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of completed calls to neighbor since system reset.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of call attempts that have failed.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of calls accepted from the neighbor.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of calls from neighbor that we have refused.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the sysUpTime of last call attempt.
Syntax: TimeStamp
Max-Access: Read-only
Enables a new vendor to manage the device using SNMP...
Syntax: RowStatus
Max-Access: Read-create
End of Table
This section lists the trap associated with the ciscoISDN MIB group.
demandNbrCallInformation
This trap/inform is sent to the manager whenever a successful call clears, or a failed call attempt is determined to have ultimately failed. In the event that call retry is active, then this is after all retry attempts have failed. However, only one such trap is sent in between successful callattempts; subsequent call attempts result in no trap.
The QLLC MIB includes a managed entity or LS (link station). The managed entity includes objects needed to configure and monitor the logical connections.
This table contains objects that can be changed for each qllc entry. Changing one of these parameters will take effect in the operating LS immediately. Each qllc connection will have an entry in this table.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF QllcLSAdminEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the interface index value for the qllc connection.
Syntax: IfIndexType
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the virtual circuit number for the logical channel identifier or PVC number depending on the type of circuit on this interface.
Syntax: IfIndexType
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the circuit type on this interface.
Syntax: Integer 1 = switchedVC, 2 = permanentVC
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the role that the QLLC link station shall assume.
Syntax: Integer 1 = primary, 2 = secondary, 3 = peerToPeer
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the X.25 address associated with the qllc connection.
Syntax: X121Address
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the modulus for QLLC link station. It determines the size of the rotating ACK window and can take values of 8 and 128.
Syntax: Integer 1 = modulo8, 2 = modulo128
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the largest QLLC packet allowed to go out on the QLLC/X.25 side.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies an entry for each qllc connection.
Specifies the interface index value for the qllc connection.
Syntax: IfIndexType
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the virtual circuit number for the logical channel identifier on this interface.
Syntax: IfIndexType
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the circuit type on this interface.
Syntax: Integer 1 = switchedVC, 2 = permanentVC
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the role of the QLLC link station.
Syntax: Integer 1 = primary, 2 = secondary, 3 = peerToPeer
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the remote X.25 address associated with the qllc connection.
Syntax: X121Address
Max-Access: Read-only
The modulus for QLLC link station. It determines the size of the rotating ACK window and can take values of 8 and 128.
Syntax: Integer 1 = modulo8, 2 = modulo128
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the state of a particular QLLC connection. Inop, closed, opening, closing, recovery, and opened are states defined in the IBM document SC30-3409-1, The X.25 1984/1988 DTE/DCE and DTE/DTE Interface Architecture Reference.
Syntax: Integer 1 = lsStateInop, 2 = lsStateClosed, 3 = lsStateOpening, 4 = lsStateClosing, 5 = lsStateRecovery, 6 = lsStateOpened
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the largest QLLC packet allowed to go out on the QLLC/X.25 side.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
The qllcLSStatsTable defines link station statistics kept for each qllc connection.
Specifies the link station statistics.
Syntax: QllcLSStatsEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the interface index value for the qllc connection.
Syntax: IfIndexType
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the virtual circuit number for the logical channel identifier on this interface.
Syntax: IfIndexType
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of XIDs received from the LS on this VC.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of XIDs sent to the LS on this VC.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of TEST packets received from the LS on this VC.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of TEST packets sent to the LS from this VC.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of times the connection quenched off for this connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of times the connection quenched on for this connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total number of information packets received on this interface.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total number of information packets sent on this interface.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total number of bytes in the information packets received on this connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total number of bytes in the information packets sent on this connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of QSMs received on this connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of QSMs sent on this connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of DISCs received on this connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of DISCs sent on this connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of DMs received on this connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of DMs sent on this connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of FRMRs received on this connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of FRMRs sent on this connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of packets dropped due to buffer allocation or other internal problems.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of HDLC protocol errors detected.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
This group specifies a collection of objects providing configuration capability.
Specifies the interface index value for the qllc connection.
Syntax: IfIndexType
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the virtual circuit number for the logical channel identifier or PVC number depending on the type of circuit on this interface.
Syntax: IfIndexType
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the role that the QLLC link station shall assume.
Syntax: Integer 1 = primary, 2 = secondary, 3 = peerToPeer
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the circuit type on this interface.
Syntax: Integer 1 = switchedVC, 2 = permanentVC
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the X.25 address associated with the qllc connection.
Syntax: X121Address
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the modulus for QLLC link station. It determines the size of the rotating ACK window and can take values of 8 and 128.
Syntax: Integer 1 = modulo8, 2 = modulo128
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the largest QLLC packet allowed to go out on the QLLC/X.25 side.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-write
This group specifies a collection of objects providing operational control capability.
Specifies the interface index value for the qllc connection.
Syntax: IfIndexType
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the virtual circuit number for the logical channel identifier on this interface.
Syntax: IfIndexType
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the circuit type on this interface.
Syntax: Integer 1 = switchedVC, 2 = permanentVC
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the role of the QLLC link station.
Syntax: Integer 1 = primary, 2 = secondary, 3 = peerToPeer
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the remote X.25 address associated with the qllc connection.
Syntax: X121Address
Max-Access: Read-only
The modulus for QLLC link station. It determines the size of the rotating ACK window and can take values of 8 and 128.
Syntax: Integer 1 = modulo8, 2 = modulo128
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the state of a particular QLLC connection. Inop, closed, opening, closing, recovery, and opened are states defined in the IBM document SC30-3409-1, The X.25 1984/1988 DTE/DCE and DTE/DTE Interface Architecture Reference.
Syntax: Integer 1 = lsStateInop, 2 = lsStateClosed, 3 = lsStateOpening, 4 = lsStateClosing, 5 = lsStateRecovery, 6 = lsStateOpened
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the largest QLLC packet allowed to go out on the QLLC/X.25 side.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
This group specifies a collection of objects providing statistics.
Specifies the link station statistics.
Syntax: QllcLSStatsEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the interface index value for the qllc connection.
Syntax: IfIndexType
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the virtual circuit number for the logical channel identifier on this interface.
Syntax: IfIndexType
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of XIDs received from the LS on this VC.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of XIDs sent to the LS on this VC.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of TEST packets received from the LS on this VC.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of TEST packets sent to the LS from this VC.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of times the connection quenched off for this connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of times the connection quenched on for this connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total number of information packets received on this interface.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total number of information packets sent on this interface.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total number of bytes in the information packets received on this connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total number of bytes in the information packets sent on this connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of QSMs received on this connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of QSMs sent on this connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of DISCs received on this connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of DISCs sent on this connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of DMs received on this connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of DMs sent on this connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of FRMRs received on this connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of FRMRs sent on this connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of packets dropped due to buffer allocation or other internal problems.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of HDLC protocol errors detected.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
The Qualified Logical Link Control (QLLC) conversion provides data link layer support for SNA communication. The CONV(ersion) MIB includes a managed entity (link station). The managed entity includes objects to configure and monitor the logical connections. Managed objects fall in one of the following categories:
The permissions allowed on these objects are as follows:
This is the MIB module for objects used to manage QLLC-to-SDLC and QLLC-to-LLC2 conversion.
This table contains objects that can be changed for each qllc entry. Changing one of these parameters will take effect in the operating LS immediately. Each qllc connection will have an entry in this table.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF ConvQllcAdminEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies configured parameter values for a specific qllc connection.
Syntax: ConvQllcAdminEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the virtual address assigned to the qllc connection. It is in the form of 802.3, 802.5 MAC address.
Syntax: MacAddress
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the conversion that is being used. The conversion is from QLLC to one of unknown-conversion is not one of sdlc (QLLC to SDLC), llc (QLLC to LLC), or localAck (QLLC to local acknowledgment.)
Syntax: Integer 1 = unknown, 2 = sdlc, 3 = llc, 4 = localAck
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the SDLC address associated with the qllc connection.
Syntax: Integer (0-255)
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the X.25 connection partner of the other DLC (SDLC or LLC2). It is in the form of 802.3, 802.5 MAC address.
Syntax: MacAddress
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies that the Virtual ring number QLLC end-stations are on. It is used for LLC<->QLLC only.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the Bridge number QLLC end-stations are on. It is used for LLC<->QLLC only.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the ring number LLC end-stations are on. It is used for LLC
<->QLLC only.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the largest QLLC packet allowed to go out on the SDLC side.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the largest QLLC packet allowed to go out on the LLC2 side.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the LS destination sap address.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the LS source sap address.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the qllc XID that is being used for the particular connection.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE ( 0 | 4 ))
Max-Access: Read-write
This table contains objects for each qllc connection.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF ConvQllcOperEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the operational values for a specific qllc connection.
Syntax: ConvQllcOperEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the virtual address assigned to the qllc connection. It is in the form of 802.3, 802.5 MAC address.
Syntax: MacAddress
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the conversion that is being used. The conversion is from QLLC to one of unknown; conversion is not one of the following sdlc-QLLC to SDLC llc-QLLC to LLC localAck-QLLC to local acknowledgment
Syntax: Integer 1 = unknown, 2 = sdlc, 3 = llc, 4 = localAck
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the SDLC address associated with the qllc connection.
Syntax: Integer (0-255)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the X.25 connection partner of the other DLC (SDLC or LLC2). It is in the form of 802.3, 802.5 MAC address.
Syntax: MacAddress
Max-Access: Read-only
The Virtual ring number QLLC end-stations are on. It is used for LLC
<-> QLLC only.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
The Bridge number QLLC end-stations are on. It is used for LLC
<->QLLC only.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the ring number LLC end-stations are on. It is used for LLC
<->QLLC only.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the largest QLLC packet allowed to go out on the SDLC side.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the largest QLLC packet allowed to go out on the LLC2 side.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the LS destination sap address.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the LS source sap address.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the qllc XID that is being used for the particular connection.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE ( 0 | 4 ))
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the LNX state. Cisco uses similar states for both LNX and SNX.
Syntax: Integer 1 = lnxDisconnect, 2 = lnxDwQllc, 3 = lnxAwQllcPri, 4 = lnxAwNetQllcSec, 5 = lnxNetContactPending, 6 = lnxDwNet, 7 = lnxAwNet, 8 = lnxAwQllcSec, 9 = lnxAwConnect
Max-Access: Read-only
This object and convQllcOperLsLciVcIndex defines the corresponding row in the qllcLSOperTable in the cisco-qllc01-mib. The corresponding row is that for which this object and convQllcOperLsLciVcIndex match qllcLSOperIfIndex and qllcLSOperLciVcIndex in table qllcLSOperTable in cisco-qllc01-mib respectively.
Syntax: IfIndexType
Max-Access: Read-only
This object and convQllcOperLsLciVcIndex defines the corresponding row in the qllcLSOperTable in the cisco-qllc01-mib. The corresponding row is that for which this object and convQllcOperLsLciVcIndex match qllcLSOperIfIndex and qllcLSOperLciVcIndex in table qllcLSOperTable in cisco-qllc01-mib respectively.
Syntax: IfIndexType
Max-Access: Read-only
This is the MIB module for objects used to manage the Cisco Snapshot Routing MIB.
ciscoSnapshotForceActive
Forces the snapshot state to active for all entries of the ciscoSnapshotActivityTable whose ciscoSnapshotIfIndex value is specified as parameter. The interface must have been previously configured for snapshot routing, and be a client interface. Retrieval of this object will return the value of the of the interface that was last forced into the active state, or 0 if no interfaces have been forced into the active state since the router was reset.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-write
The ciscoSnapshotInterfaceTable defines a list of pre-interface Snapshot Routing entries.
ciscoSnapshotInterfaceEntry
Specifies a pre-interface Snapshot Routing entry. A management station acting to create an entry should create the associated instance of the row status object. The management station should also modify, either in the same or in successive PDUs, the values for the other objects if the defaults are not appropriate. Once the appropriate instance of all the configuration objects have been created, either by an explicit SNMP set request or by default, the row status should be set to active to initiate the request.
Syntax: CiscoSnapshotInterfaceEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
ciscoSnapshotIfIndex
Specifies the interface to which this entry pertains.
Syntax: InterfaceIndex
Max-Access: Not-accessible
ciscoSnapshotClient
When set to true, this router is the client snapshot router on the interface. When false, this router is the server snapshot router on the interface.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-create
ciscoSnapshotDialer
Indicates whether snapshot routing on this interface uses Dial-on-Demand routing.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-create
ciscoSnapshotActiveInterval
Specifies the amount of time in minutes during which routes may be exchanged between the client and server routers.
Syntax: Integer32 (5-1000)
Max-Access: Read-create
ciscoSnapshotQuietInterval
Specifies the amount of time in minutes during which routes are retained and frozen between active periods. An instance of this object may only be present if the value of the associated ciscoSnapshotClient object is true.
Syntax: Integer32 (8-100000)
Max-Access: Read-create
ciscoSnapshotRetryInterval
Specifies the amount of time in minutes to wait and retry a route exchange in the event that an active period elapses with no routes being exchanged. For example, if an interface is down (or a DDR phone number is busy, or a DDR interface is unavailable) during the active interval, instead of waiting for the amount of time specified by ciscoSnapshotQuietTime to elapse before an attempt is made to exchange routing updates again, the attempt is made after the amount of time specified by this object has elapsed. This value is calculated automatically based on the ciscoSnapshotActiveInterval. An instance of this object may only be present if the value of the associated ciscoSnapshotClient object is true.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoSnapshotIfUpAction
Specifies the action that takes place when the interface associated with this entry transitions to the "up" state while snapshot routing on the interface is in quiet mode.
A value of goActive will cause the immediate transition to the active state.
A value of noAction will cause no such transition. Instead, the transition to the active state will occur normally when the current quiet period has expired.
Going active immediately incurs extra routing protocol overhead, but allows a fresh set of routing updates be exchanged each time the line is brought up. This is useful in a Dial-on-Demand routing environment.
An instance of this object may only be present if the value of the associated ciscoSnapshotClient object is true.
Syntax: Integer 1 = goActive, 2 = noAction
Max-Access: Read-create
ciscoSnapshotRowStatus
Specifies the status of this table entry. Once the entry status is set to active, the snapshot routing process will be enabled for this interface.
Syntax: RowStatus
Max-Access: Read-create
Specifies a list of snapshot routing activity entries.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF CiscoSnapshotActivityEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
ciscoSnapshotActivityEntry
Specifies a snapshot routing activity entry. Entries in this table are added for active row entries in the ciscoSnapshotInterfaceTable. If a row entry in the ciscoSnapshotInterfaceTable is set to notInService, or deleted, associated entries in this table will be deleted.
Syntax: CiscoSnapshotActivityEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
ciscoSnapshotActivityIndex
Specifies an index value that uniquely identifies a Snapshot Activity Entry on a given interface.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Not-accessible
ciscoSnapshotActivityState
Specifies the current state of snapshot routing for this entry. active means that routing information may be exchanged. quiet, only present on a client snapshot interface, means that routes are frozen, and that no routing information may be exchanged until the active state is reentered. serverPostActive, only present on a server snapshot interface, means that the active period has expired, but routing information will still be accepted from (but not sent to) the associated client router. transitionToQuiet, and transitionToActive, only present on a client, are temporary states entered after the active state, wherein any down to up transition of the interface will cause a move to the quiet or active state, respectively. limbo is a temporary state for activity blocks that are in the process of being created or destroyed.
Syntax: Integer 1 = active, 2 = quiet, 3 = serverPostActive, 4 = transitionToQuiet, 5 = transitionToActive, 6 = limbo
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoSnapshotActivityTimer
Specifies the time in minutes remaining in the current state.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoSnapshotExchangeTimer
Specifies the time in minutes during the last active state, in which protocol exchanges occurred. The minimum time required to allow updates to be exchanged for a "successful update cycle" is the greater of 3 minutes, or 1/2 the active time. If the ciscoSnapshotExchangeTimer is less than this, the quiet state will use the retry interval to determine when next to go active.
An instance of this object will only be present when the associated value of ciscoSnapshotClient is true for this interface.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoSnapshotDialerMap
Specifies the index of the dialer map entry associated with this snapshot activity record. A value of 0 indicates that no dialer map is associated with this entry. An instance of this object will only be present when the associated value of ciscoSnapshotClient is true.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoSnapshotSourceProtocol
Specifies the protocol of the host that initiated the snapshot routing activity associated with this record. An instance of this object will only be present when the associated value of ciscoSnapshotClient is false.
Syntax: CiscoNetworkProtocol
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoSnapshotSourceAddress
Specifies the address of the host that initiated the snapshot routing activity associated with this record.An instance of this object will only be present when the associated value of ciscoSnapshotClient is false.
Syntax: CiscoNetworkAddress
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoSnapshotProtocolsExchanged
Specifies an array of bits that indicates whether or not routing information has been exchanged for all protocols. The most significant bit of the first octet represents the protocol associated with CiscoNetworkProtocol value of 0; the least significant bit of the first octet represents the protocol associated with CiscoNetworkProtocol value of 7; the most significant bit of the second octet represents the protocol associated with the CiscoNetworkProtocol value of 8; and so forth.
Routing information for a given protocol has been exchanged if the associated bit is set.An instance of this object will only be present when the associated value of ciscoSnapshotClient is true.
Syntax: OCTET STRING
Max-Access: Read-only
The CIP Group specifies the MIB module for objects used to manage the cisco channel interface processor card.
The cipCardTable contains a list of values for the CIP card that can be obtained on a per cip-card basis and include the following variables: cipCardEntryIndex, cipCardEntryName, cipCardEntryTotalMemory, cipCardEntryFreeMemory, cipCardEntryCpuUtilization, and cipCardEntryTimeSinceLastReset. This table extends CardTable in the cisco.mib.
Syntax: Sequence of CipCardEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the configured name for the CIP.
Syntax: DisplayString
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies total memory on the card in kilobytes.
Syntax: UInteger32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total free memory on the card, that is the amount of memory in kilobytes not in use.
Syntax: UInteger32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the average percentage of time, over the last minute, that this processor was not idle.
Syntax: Integer (0-100)
Max-Access: Read-only
cipCardEntryTimeSinceLastReset
Specifies the number of seconds the CIP has been running.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
End of Table
This table contains a list of objects pertaining to the daughter board on the CIP card.
Specifies which daughter board is being referenced for a particular CIP card.
Syntax: UInteger32
Max-Access: Read-only
Indicates the channel path interface type.
Syntax: Integer
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies that the microcode for the daughter board has been successfully loaded and is executing.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-only
For ESCON, specifies that the LED has been seen, and synchronization has been established. ESCON is the fiber-optic connection from the IBM mainframe to the peripheral. This is layer 1 of the channel. Older technology (still in use) is called BUS and TAB and consists of two bulky copper cables. For Parallel Channel Adapter (PCA), specifies that the operational out has been sensed.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-only
For ESCON, specifies that a path has been established with at least one channel. For PCA, specifies that the PCA is online to the channel. It will respond to at least one device address.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-only
Counts the number of times the ESCON Processor recovers from an internal error.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of recognized code-violation errors. A trap is issued when this number exceeds the bit error rate threshold for ESCON. The bit error rate threshold is set at 15 error burst within a 5-minute period. An error burst is the time period of 1.5 seconds + or - 0.05 seconds during which one or more code violations errors occur.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of link failures recognized as a result of a loss of signal or loss of synchronization that persisted longer than the link interval duration. The link interval duration is 1 second with a tolerance of +1.5 seconds and -0 seconds.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of link failures recognized as a result of the not-operational sequence (NOS).
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of link failures recognized as a result of a connection recovery timeout or response timeout occurring while in transmit OLS state.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of link failures recognized as a result of an invalid sequence for Link-Level-Facility State. Either a UD or UDR sequence was recognized while in wait-for-offline-sequence state.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Indicates the condition which caused the last SNMP trap.
Syntax: Integer
1 = reason other than what is defined in conditions 2-7.
2 = indicates that the daughter board status has changed.
3 = indicates that a condition, that might cause the recognition
of a link incident in the attached node, has occurred.
4 = indicates that the code violation error rate exceeded the
threshold. 5 = indicates a loss of signal or loss of
synchronization that persisted longer than the link interval
duration.
6 = indicates the recognition of not-operational sequence,
usually due to the operator taking the channel offline.
7 = indicates a connection recovery timeout or response timeout
occurring while in transmit OLS state.
8 = indicates a UD or UDR sequence was recognized while in
wait-for-offline-sequence state.
Max-Access: Read-only
This table contains a list of objects pertaining to subchannel connections referenced by the CIP card or its daughter board.
Indicates which subchannel is being referenced for a particular daughter board on a CIP card.
Syntax: UInteger32
Max-Access: Read-only
Indicates the number of times a device was connected to the subchannel. For some devices, this correlates with the number of start subchannels.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of halt subchannels.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cipCardSubChannelSelectiveResets
Specifies the number of selective resets.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of system resets.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of device level errors.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cipCardSubChannelWriteBlocksDropped
Specifies the number of times a block was received by the channel and a router buffer was not available so the block was discarded.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cipCardSubChannelLastSenseData
Specifies the last sense data sent to the channel by this device.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE (2))
Access: Read-only
cipCardSubChannelLastSenseDataTime
Specifies the time when the last sense data was sent to the channel by this device.
Syntax: TimeStamp
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of control unit busies sent to the channel when this device was requested.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
End of Table
This table contains status and other information not covered in the following tables for the Common Link Access to Workstation (CLAW) protocol.
Syntax: Sequence of CipCardClawEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies which CLAW link is being referenced for a particular subchannel on a daughter board on a CIP card.
Syntax: UInteger32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the CLAW connection status.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-only
Contains configuration information for the Common Link Access to Workstation (CLAW) protocol.
Syntax: Sequence of CipCardClawConfigEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies a list of CLAW configuration values.
Syntax: CipCardClawConfigEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the Hex path identifier for the switch port containing the fiber from the channel on the host to which this task connects. This is a concatenation of the switch port number, the channel logical address, and the control unit logical address. For a directly connected channel, the switch port number is usually 01.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE (2))
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies Device address for the device the host will use to communicate with this task.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE(2))
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the IP address of the host application for this task.
Syntax: IpAddress
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the CLAW host name for this CLAW device.
Syntax: DisplayString
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the CLAW router name for this CLAW device.
Syntax: DisplayString
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the CLAW host application name for this CLAW connection.
Syntax: DisplayString
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the CLAW router application name for this CLAW connection.
Syntax: DisplayString
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies a list of objects pertaining to data transfer statistics per CLAW Logical Link.
Syntax: Sequence of CipCardClawDataXferStatsEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies a list of daughter board statistics.
Syntax: CipCardClawDataXferStatsEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
cipCardClawDataXferStatsBlocksRead
Specifies the number of read data transfer channel command words (CCWs) from the channel perspective.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cipCardClawDataXferStatsBlocksWritten
Specifies the number of successful write data transfer CCWs from the channel perspective.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cipCardClawDataXferStatsBytesRead
Specifies the number of bytes successfully read from the channel perspective.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of bytes successfully written from the channel perspective.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cipCardClawDataXferStatsHCBytesRead
Specifies the number of bytes successfully read from the channel perspective. The HC (High Capacity) objects are the 64-bit equivalent of their 32-bit counterparts modeled after RFC 1573.
Syntax: Counter64
Max-Access: Read-only
cipCardClawDataXferStatsHCBytesWritten
Specifies the number of bytes successfully written from the channel perspective. The HC (High Capacity) objects are the 64-bit equivalent of their 32-bit counterparts modeled after RFC 1573.
Syntax: Counter64
Max-Access: Read-only
cipCardClawDataXferStatsReadBlocksDrop ped
Specifies the number of bytes written.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cipCardClawDataXferStatsWriteBlocksDrop ped
Specifies the number of read blocks dropped.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
cipCardClawDataXferStatsBufferGetRetryC ount
Specifies the number of times a buffer was requested and none was available.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
The variables described in this section provide the necessary information for the definition and management of ciscoTCP objects. The ciscoTCP variables succeed the TCP variables found in the Local Variables subtree.
The ciscoTcpConnTable augments the tcpConnTable defined in RFC 1213. The ciscoTcpConnTable contains TCP connection-specific information.
Specifies the number of bytes input on this TCP connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of bytes output on this TCP connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of packets input on this TCP connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of packets output on this TCP connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the amount of time this TCP connection has been established.
Syntax: TimeTicks
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies a "smoothed" round-trip time, in milliseconds, for this TCP connection.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
End of Table
This group specifies a collection of objects providing TCP connection monitoring.
ciscoTcpConnInBytes
Specifies the number of bytes input on this TCP connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoTcpConnOutBytes
Specifies the number of bytes output on this TCP connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoTcpConnInPkts
Specifies the number of packets input on this TCP connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoTcpConnOutPkts
Specifies the number of packets output on this TCP connection.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoTcpConnElapsed
Specifies the Amount of time in milliseconds that this TCP connection has been established.
Syntax: TimeTicks
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoTcpConnSRTT
Specifies a "smoothed" round-trip time in milliseconds for this TCP connection.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
The variables described in this section provide the necessary information for the definition and management of DSPU objects.
Specifies whether the RSRB feature is enabled for the DSPU node.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies local virtual ring number used by DSPU node. LocalVirtualRing is zero if RSRB is not enabled.
Syntax: Integer (0-4096)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the bridge number connecting the DSPU LocalVirtualRing with the RSRB TargetVirtualRing. Currently, the only valid bridge number supported is 1. The bridge number must be 1 if RSRB is enabled. The bridge number is zero if RSRB is not enabled.
Syntax: Integer (0-15)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the target virtual ring number used for RSRB. TargetVirtualRing is zero if RSRB not enabled.
Syntax: Integer (0-4096)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the virtual MAC address of the DSPU node. VirtualMacAddress is zero if RSRB is not enabled
Syntax: MacAddress
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies if the Default-PU feature is enabled for the DSPU node. The default value is disabled (2).
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the send/receive window size to be used across the link between the default-PU and a remote PU.
Syntax: Integer (1-127)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the maximum size of an I-frame that can be transmitted/received across the link between the default-PU and a remote PU.
Syntax: Integer (64-18432)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the value of the activation pacing window. The pacing window is used by the DSPU node to limit the number of activation RUs sent for a given SAP before waiting for responses from the remote.
Syntax: Integer (1-65535)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the last change to DSPU configuration parameters. LastConfigChgTime reflects any change in DSPU configuration.
Syntax: TimeStamp
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies a table listing defined pool classes for the DSPU node. A pool class is defined at the DSPU node as a pool of upstream LUs that can be shared among downstream PUs.
Each entry in the table represents a separate pool class definition.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF DspuPoolClassEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Each entry represents a defined pool class.
Syntax: DspuPoolClassEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the index of pool class entry defined in the dpsuPoolClassTable.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the name identifier of the pool class.
Syntax: DisplayString (SIZE(0-10))
Max-Access: Read-only
dspuPoolClassInactivityTimeout
Specifies the value (in minutes) of the inactivity timeout that will be applied to active LU sessions assigned from the pool class. The inactivity timeout feature for pooled LUs is disabled if the Inactivity Timeout value is zero.
Syntax: Integer (0-255)
Max-Access: Read-only
dspuPoolClassOperUpStreamLuDefs
Specifies the number of upstream LUs defined in the pool class.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
dspuPoolClassOperDnStreamLuDefs
Specifies the number of downstream LUs defined in the pool class.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
End of Table
Table listing all LUs defined in a specified pool class.
The entries in the table provide information such that the downstream LUs in the pool can be correlated with the upstream LUs to which they might be assigned and vice versa.
If all upstream LUs have been assigned, downstream LUs might be waiting for assignment.
If there are no downstream LUs waiting for assignment, upstream LUs might be unassigned.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF DspuPooledLuEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Each entry represents an LU that is defined as a member of the specified pool class.
Syntax: DspuPooledLuEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the index (dspuPuOperIndex) of the peer PU that owns the peer LU. The PeerPuIndex is zero if the peer LU has not been assigned.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
dspuPooledLuPeerLuLocalAddress
Specifies the NAU address (dspuLuOperLuLocalAddress) of the peer LU. The PeerLuLocalAddress is zero if peer LU has not been assigned.
Syntax: Integer (0-254)
Max-Access: Read-only
End of Table
Table listing all defined upstream/downstream PUs that are owned by the DSPU node.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF DspuPuAdminEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Each entry represents a defined upstream/downstream PU.
Syntax: DspuPuAdminEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the index of a PU in the dspuPuAdminTable.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the name of the upstream/downstream PU.
Syntax: DisplayString (SIZE(0-8))
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies PU type as either upstream or downstream.
Syntax: Integer 1 = upstreamPu, 2 = dnstreamPu
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the MAC address of the remote PU.
Syntax: MacAddress
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the SAP address of the remote PU.
Syntax: Integer (1-254)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the SAP address of the local PU. The default value of the local SAP address is 8.
Syntax: Integer (1-254)
Max-Access: Read-only
For upstream PUs, specifies the XID that will be sent to the remote PU. For downstream PUs, specifies the XID that must be received from the remote PU.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the type of XID format used during activation of the link between this dspuNode and the remote PU.
Syntax: Integer 1 = formatUnknown, 2 = format0, 3 = format3
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the send/receive window size to be used across the link between this dspuNode and the remote PU.
Syntax: Integer (1-127)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the maximum size of an I-frame that can be transmitted/received across the link between this dspuNode and the remote PU.
Syntax: Integer (64-18432)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of times that the DSPU node will attempt to activate the link between the dspuNode and the remote PU.
Syntax: Integer (0-255)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the value (in seconds) for the delay between link activation attempts between the dspuNode and the remote PU.
Syntax: Integer (1-600)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies whether the dspuNode should attempt link activation with the remote PU.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the DLC type used by the dspuNode for link activation with the remote PU.
Syntax: Integer 1 = undefined, 2 = sdlc, 5 = Ethernet, 6 = tokenRing, 8 = rsrb, 9 = Framerelay, 10 = FDDI
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the DLC unit used by the dspuNode for link activation with the remote PU.
Syntax: Integer (0-255)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the DLC port used by the dspuNode for link activation with the remote PU.
Syntax: Integer (0-255)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies whether the PU serves as a focal point for alert notification forwarding. Only an upstream PU can be defined as a focal point. Downstream PUs can never be defined as a focal point. The DSPU node can define only one upstream PU as a focal point PU.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the status of a row entry in the dspuPuAdminTable.
Syntax: RowStatus
Max-Access: Read-only
End of Table
Table listing all active upstream/downstream PUs that are owned by the DSPU node (including default PUs).
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF DspuPuOperEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Each entry represents an active upstream/downstream PU.
Syntax: DspuPuOperEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the index of a PU entry in the dspuPUOperTable.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the name of the PU.
Syntax: DisplayString (SIZE(0-8))
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the PU type as either upstream or downstream.
Syntax: Integer 1 = upstreamPu, 2 = dnstreamPu
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the MAC address of the remote PU.
Syntax: MacAddress
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the SAP address of the remote PU.
Syntax: Integer (0-254)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the SAP address of the local PU used by the dspuNode.
Syntax: Integer (1-254)
Max-Access: Read-only
For upstream PUs, specifies the XID that was sent to the remote PU. For downstream PUs, specifies the XID that was received from the remote PU.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the type of XID format used during activation of the link between this dspuNode and the remote PU.
Syntax: Integer 1 = formatUnknown, 2 = format0, 3 = format3
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the send/receive window size used across the link between this dspuNode and the remote PU.
Syntax: Integer (1-127)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the maximum size of an I-frame that can be transmitted/received across the link between this dspuNode and the remote PU.
Syntax: Integer (64-18432)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of times that the DSPU node will attempt to activate the link between the dspuNode and the remote PU.
Syntax: Integer (0-255)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the value (in seconds) for the delay between link activation attempts between the dspuNode and the remote PU.
Syntax: Integer (1-600)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies whether the dspuNode should attempt link activation with the remote PU.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the DLC type used by the dspuNode for link activation with the remote PU.
Syntax: Integer 1 = undefined, 2 = sdlc, 5 = Ethernet, 6 = tokenRing, 8 = rsrb, 9 = Framerelay, 10 = FDDI
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the DLC unit used by the dspuNode for link activation with the remote PU.
Syntax: Integer (0-255)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the DLC port used by the dspuNode for link activation with the remote PU.
Syntax: Integer (0-255)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies if the PU serves as a focal point for alert notification forwarding. Only an upstream PU can be defined as a focal point. Downstream PUs can never be defined as a focal point. The DSPU node may define only one upstream PU as a focal point PU.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the operational state of the PU as either active or inactive.
Syntax: Integer 1 = active, 2 = inactive
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the current FSM state of the PU. The defined FSM state values are defined as follows:
Syntax: Integer 1 = linkReset, 2 = linkPendConnOut, 3 = linkPendConnIn, 4 = linkPendXid, 5 = linkXidNeg, 6 = linkConnOut, 7 = linkConnIn, 8 = linkConnected, 9 = puPendAct, 10 = puActive 11 = puBusy, 12 = puPendInact, 13 = linkPendDisc, 14 = linkPendClose
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the timestamp of PU activation (when ACTPU +rsp received).
Syntax: TimeStamp
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the TimeStamp of the last PU state change between active and inactive
Syntax: TimeStamp
Max-Access: Read-only
End of Table
Table listing the statistics recorded for each PU.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF DspuPuStatsEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Each entry represents an active upstream/downstream PU and has a corresponding entry in the dspuOperPuTable.
Syntax: DspuPuStatsEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the number of bytes sent by this PU.
Syntax: Counter32
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of bytes received by this PU.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of frames sent by this PU.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of frames received by this PU.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of negative responses sent by this PU.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of negative responses received by this PU.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of active LUs on this PU (LU becomes active when ACTLU +rsp received).
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of inactive LUs on this PU (LU is inactive until ACTLU rq or ACLTU +rsp received).
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of LUs on this PU which are active-in-session (LU is active-in-session when BIND rq received).
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of activation failures for this PU.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
dspuPuStatsLastActivationFailureReason
Specifies the reason for last activation failure of this PU
Syntax: Integer 1 = noError (no PU activation failure has been detected), 2 = otherError (undefined error detected during PU activation), 3 = internalError (internal resources error detected during PU activation), 4 = configuration error (PU could not be activated), 5 = puNegativeResponse (Negative ACTPU response received from remote PU), 6 = puAlreadyActive (PU is already active)
Max-Access: Read-only
End of Table
Table listing all LUs owned by the PU.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF DspuLuAdminEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Each entry represents a defined LU owned by the PU.
Syntax: DspuLuAdminEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the NAU address of the local LU.
Syntax: Integer (1-254)
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies whether the LU is pooled or dedicated.
Syntax: Integer 1 = pooled, 2 = dedicated
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the pool class to which the LU is defined as a member. The dspuLuAdminPoolClassName is valid for pooled LUs only.
Syntax: DisplayString (SIZE(0-10))
Max-Access: Read-only
For downstream LUs, the PeerPuIndex identifies the upstream PU that owns the upstream LU to which this downstream LU is assigned.
For upstream LUs, the PeerPuIndex identifies the downstream PU that owns the downstream LU to which this upstream LU is assigned.
The PeerPuIndex is valid for dedicated LUs only; otherwise, the PeerPuIndex is zero.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
For downstream LUs, the PeerLuLocalAddress identifies the NAU address of the upstream LU to which this downstream LU is assigned. For upstream LUs, the PeerLuLocalAddress identifies the NAU address of the downstream LU to which this upstream LU is assigned. The dspuLuAdminPeerLuLocalAddress is valid for dedicated LUs only; otherwise, the PeerLuLocalAddress is zero.
Syntax: Integer (1-254)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the status of a row entry in the dspuLuAdminTable.
Syntax: RowStatus
Max-Access: Read-only
End of Table
Table listing all LUs owned by the PU.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF DspuLuOperEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Each entry represents a defined LU owned by the PU.
Syntax: DspuLuOperEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the NAU address of the local LU.
Syntax: Integer (1-254)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies whether the LU is pooled or dedicated.
Syntax: Integer 1 = pooled, 2 = dedicated
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the pool class of which the LU is a member. The dspuLuOperPoolClassName is valid for pooled LUs only.
Syntax: DisplayString (SIZE(0-10))
Max-Access: Read-only
For downstream LUs, the PeerPuIndex identifies the upstream PU that owns the upstream LU to which this downstream LU is assigned.
For upstream LUs, the PeerPuIndex identifies the downstream PU that owns the downstream LU to which this upstream LU is assigned.
If the PeerPuIndex is zero, the LU is a pooled LU and has not been assigned a peer LU from the pool.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
For downstream LUs, the PeerLuLocalAddress identifies the NAU address of the upstream LU to which this downstream LU is assigned.
For upstream LUs, the PeerLuLocalAddress identifies the NAU address of the downstream LU to which this upstream LU is assigned. If the PeerLuLocalAddress is zero, the LU is a pooled LU and has not been assigned a peer LU from the pool.
Syntax: Integer (1-254)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the operational state of the LU as either active or inactive.
Syntax: Integer 1 = active, 2 = inactive
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the current FSM state of the LU as follows:
Syntax: Integer 1 = reset, 2 = dnLuStarted, 3 = upLuActive, 4 = dnLuPendAct, 5 = dnLuActUnav, 6 = upLuPendAvail, 7 = bothAvail, 8 = dnLuPendInact, 9 = upLuPendInact, 10 = luInactivityTimeout, 11 = dnInactivityPendInact
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the operational state of the LU session as either bound or unbound.
Syntax: Integer1 = bound, 2 = unbound
Max-Access: Read-only
End of Table
Table listing the SAPs that are enabled for the DSPU node.
Syntax: SEQUENCE of DspuSapEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Each entry represents an enabled SAP for the DSPU node.
Syntax: DspuSapEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the SAP address of the local SAP.
Syntax: Integer (1-254)
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the local SAP type as either an upstreamSap or a downstreamSap.
Syntax: Integer 1 = upstreamSap, 2 = dnstreamSap
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the DLC type of the adapter that owns the local SAP.
Syntax: Integer 1 = undefined, 2 = sdlc, 5 = Ethernet, 6 = tokenring, 8 = rsrb, 9 = Framerelay, 10 = FDDI
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the DLC unit of the adapter that owns the local SAP.
Syntax: Integer (0-255)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the DLC port of the adapter that owns the local SAP.
Syntax: Integer (0-255)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the operational state of the local SAP as follows:
Syntax: Integer 1 = sapClosed, 2 = sapOpening, 3 = sapOpened, 4 = sapClosed
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the status of a row entry in the dspuSapTable.
Syntax: RowStatus
Max-Access: Read-only
End of Table
The variables described in this section apply to the Cisco Flash MIB definitions.
ciscoFlashDevicesSupported
Specifies the number of Flash devices supported by the system. If the system does not support any Flash devices, this MIB will not be loaded on that system. The value of this object will therefore be at least 1.
Syntax: Integer32 (1-32)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the Table of Flash device properties for each initialized Flash device. Each Flash device installed in a system is detected, sized, and initialized when the system image boots up. For removable Flash devices, the device properties will be dynamically deleted and recreated as the device is removed and inserted. In this case, the newly inserted device may not be the same as the one that was removed earlier.
The ciscoFlashDeviceInitTime object is available for a management station to determine the time at which a device was initialized, and thereby detect the change of a removable device. A removable device that has not been installed will also have an entry in this table. This is to let a management station know about a removable device that has been removed.
Since a removed device obviously cannot be sized and initialized, the table entry for such a device will have ciscoFlashDeviceSize, ciscoFlashDeviceMinPartitionSize, ciscoFlashDeviceMaxPartitions, ciscoFlashDevicePartitions, and ciscoFlashDeviceChipCount equal to zero. ciscoFlashDeviceRemovable will be true to indicate it is removable.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF CiscoFlashDeviceEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies an entry in the table of flash device properties for each initialized flash device. Each entry can be randomly accessed by using ciscoFlashDeviceIndex as an index into the table. Note that removable devices will have an entry in the table even when they have been removed. However, a non-removable device that has not been installed will not have an entry in the table.
Syntax: CiscoFlashDeviceEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the Flash device sequence number to index within the table of initialized flash devices. The lowest value should be 1. The highest should be less than or equal to the value of the ciscoFlashDevicesSupported object.
Syntax: Integer32 (1-32)
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the total size in bytes of the Flash device. For a removable device, the size will be zero if the device has been removed.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoFlashDeviceMinPartitionSize
Specifies that this object will give the minimum partition size supported for this device. For systems that execute code directly out of Flash, the minimum partition size needs to be the bank size. (Bank size is equal to the size of a chip multiplied by the width of the device. In most cases, the device width is 4 bytes, and so the bank size would be four times the size of a chip). This has to be so because all programming commands affect the operation of an entire chip (in the case of Cisco chips, an entire bank is affected because all operations are done on the entire width of the device) even though the actual command may be localized to a small portion of each chip. So when executing code out of Flash, one needs to be able to write and erase some portion of Flash without affecting the code execution.
For systems that execute code out of DRAM or ROM, it is possible to partition Flash with a finer granularity (for example, at erase sector boundaries) if the system code supports such granularity.
This object will let a management entity know the minimum partition size as defined by the system. If the system does not support partitioning, the value in bytes will be equal to the device size in ciscoFlashDeviceSize. The maximum number of partitions that can be configured will be equal to the minumum number of ciscoFlashDeviceMaxPartitions and the quotient that is derivd when ciscoFlashDeviceSize is divided by ciscoFlashDeviceMinPartitionSize.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the maximum number of partitions supported by the system for this Flash device. The default is 1, which actually means that partitioning is not supported. Note that this value will be defined by system limitations, not by the flash device itself (for example, the system may impose a limit of 2 partitions even though the device may be large enough to be partitioned into 4 based on the smallest partition unit supported). On systems that execute code out of Flash, partitioning is a way of creating multiple file systems in the Flash device so that writing into or erasing of one file system can be done while executing code residing in another file system. For systems executing code out of DRAM, partitioning gives a way of sub-dividing a large Flash device for easier management of files.
Syntax: Integer32 (1-8)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the Flash device partitions that are actually present. The number of partitions cannot exceed the minimum number of ciscoFlashDeviceMaxPartitions and the quotient that is derived when ciscoFlashDeviceSize is divided by ciscoFlashDeviceMinPartitionSize.
The number of partitions will be equal to at least 1 when the partition spans the entire device (actually no partitioning). A partition in turn will contain one or more minimum partition units where a minimum partition unit is defined by ciscoFlashDeviceMinPartitionSize.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total number of chips within the Flash device. The purpose of this object is to provide a management station with information on how much chip information to expect. In addition, this object can help double check the chip index against an upper limit when randomly retrieving chip information for a partition.
Syntax: Integer32 (1-64)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the name of the Flash device . This name is used to refer to the device within the system. Flash operations get directed to a device based on this name. The system has a concept of a default device. This device would be the primary or most used in case of multiple devices. The system directs an operation to the default device whenever a device name is not specified. The device name is therefore mandatory except when the operation is being done on the default device, or, the system supports only a single Flash device. The device name will always be available for a removable device, even when the device has been removed.
Syntax: DisplayString (SIZE (0-16) )
Max-Access: Read-only
Description of a Flash device. The description is meant to explain what the Flash device and its purpose is. Current values are:
The ciscoFlashDeviceDescr, ciscoFlashDeviceController (if applicable), and ciscoFlashDeviceCard objects are expected to collectively give all information about a Flash device.
The device description will always be available for a removable device, even when the device has been removed.
Syntax: DisplayString (SIZE (0-64))
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the flash device controller (in other words, the card that actually controls Flash read/write/erase. This object is relevant for AGS+ systems where Flash may be controlled by the MC+, STR or the Environmental Monitor cards—cards that may not actually contain the Flash chips.
For systems that have removable PCMCIA flash cards that are controlled by a PCMCIA controller chip, this object may contain a description of that controller chip.
Where irrelevant (in other words, when flash is a direct memory mapped device accessed directly by the main processor), this object will have an empty (NULL) string.
Syntax: DisplayString (SIZE (0-64))
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies an instance of a card entry in the cardTable. The card entry will give details about the card on which the Flash device is actually located. For most systems, this is usually the main processor board. On AGS+ systems, Flash is located on a separate multibus card such as the MC. This object will therefore be used to essentially index into cardTable to retrieve details about the card such as cardDescr, cardSlotNumber, and so forth.
Syntax: InstancePointer
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoFlashDeviceProgrammingJumper
Specifies the state of a jumper (if present and can be determined) that controls the programming voltage called Vpp to the Flash device. Vpp is required for programming (erasing and writing) Flash. For certain older technology chips, it is also required for identifying the chips (which in turn is required to identify which programming algorithms to use; different chips require different algorithms and commands).
The purpose of the jumper, on systems where it is available, is to write protect a Flash device. On most of the newer remote access routers, this jumper is unavailable since users are not expected to visit remote sites just to install and remove the jumpers when upgrading software in the Flash device. The unknown(3) value will be returned for such systems and can be interpreted to mean that a programming jumper is not present or not required on those systems.
On systems where the programming jumper state can be read back by means of a hardware register, the installed(1) or notInstalled(2) value will be returned.
This object is expected to be used in conjunction with the ciscoFlashPartitionStatus object whenever that object has the readOnly(1) value. In such a case, this object will indicate whether the programming jumper is a possible reason for the readOnly state.
Syntax: Integer 1 = installed, 2 = notInstalled, 3 = unknown
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the system time at which the device was initialized. For fixed devices, this will be the system time at boot up. For removable devices, it will be the time at which the device was inserted, which may be boot up time, or a later time (if device was inserted later). If a device (fixed or removable) was repartitioned, it will be the time of repartitioning.
The purpose of this object is to help a management station determine if a removable device has been changed. The application should retrieve this object prior to any operation and compare with the previously retrieved value. Note that this time will not be real time but a running time maintained by the system. This running time starts from zero when the system boots up. For a removable device that has been removed, this value will be zero.
Syntax: TimeStamp
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies whether the Flash device is removable. Generally, only PCMCIA Flash cards will be treated as removable. Socketed Flash chips and Flash SIMM modules will not be treated as removable. Simply put, only those Flash devices that can be inserted or removed without opening the hardware casing will be considered removable. Further, removable Flash devices are expected to have the necessary hardware support including 1) on-line removal and insertion and 2) interrupt generation on removal or insertion.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-only
End of Table
Specifies the table of Flash device chip properties for each initialized Flash device. This table is intended primarily to support error diagnosis.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF CiscoFlashChipEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies an entry in the table of chip information for each flash device initialized in the system. An entry is indexed by two objects: 1) the device index and 2) the chip index within that device.
Syntax: CiscoFlashChipEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the chip sequence number within selected flash device. Used to index within chip info table. Value starts from 1 and should not be greater than ciscoFlashDeviceChipCount for that device.
When retrieving chip information for chips within a partition, the sequence number should lie between ciscoFlashPartitionStartChip & ciscoFlashPartitionEndChip (both inclusive).
Syntax: Integer32 (1-64)
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the manufacturer and device code for a chip. The lower byte will contain the device code.The upper byte will contain the manufacturer code. If a chip code is unknown because it could not be queried out of the chip, the value of this object will be 00:00.
Syntax: FlashChipCode
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the flash chip name corresponding to the chip code. The name will contain the manufacturer and the chip type. It will be of the form Intel 27F008SA.
In the case where a chip code is unknown, this object will be an empty (NULL) string. In the case where the chip code is known but the chip is not supported by the system, this object will be an empty (NULL) string.
A management station is therefore expected to use the chip code and the chip description in conjunction to provide additional information whenever the ciscoFlashPartitionStatus object has the readOnly(1) value.
Syntax: DisplayString (SIZE (0-32))
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies a cumulative count (since last system boot up or initialization) of the number of write retries that were done in the chip. If no writes have been done to Flash, the count will be zero. Typically, a maximum of 25 retries are done on a single location before flagging a write error. A management station is expected to get this object for each chip in a partition after a write failure in that partition. To keep a track of retries for a given write operation, the management station would have to retrieve the values for the concerned chips before and after any write operation.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies a cumulative count (since last system boot up or initialization) of the number of erase retries that were done in the chip. Typically, a maximum of 2000 retries are done in a single erase zone (which may be a full chip or a portion, depending on the chip technology) before flagging an erase error.
A management station is expected to get this object for each chip in a partition after an erase failure in that partition. To keep a track of retries for a given erase operation, the management station would have to retrieve the values for the concerned chips before and after any erase operation.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the maximum number of write retries done at any single location before declaring a write failure.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the maximum number of erase retries done within an erase sector before declaring an erase failure.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
End of Table
A flash partition is a logical sub-division of a flash device and may or may not be equal to the entire device itself. When there is no explicit partitioning done, a single partition is assumed to exist, spanning the entire device.
Partitioning has the following restrictions:
Specifies the Table of flash device partition properties for each initialized flash partition. Whenever there is no explicit partitioning done, a single partition spanning the entire device will be assumed to exist. There will therefore always be atleast one partition on a device.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF CiscoFlashPartitionEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies an entry in the table of flash partition properties for each initialized flash partition. Each entry will be indexed by a device number and a partition number within the device.
Syntax: CiscoFlashPartitionEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the flash partition sequence number used to index within table of initialized flash partitions.
Syntax: Integer32 (1-8)
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the chip sequence number of first chip in partition. Used as an index into the chip table.
Syntax: Integer32 (1—64)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the chip sequence number of last chip in partition. Used as an index into the chip table.
Syntax: Integer32 (1—64)
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies in bytes the flash partition size. It should be an integral multiple of ciscoFlashDeviceMinPartitionSize. If there is a single partition, this size will be equal to ciscoFlashDeviceSize.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies in bytes the free space within a Flash partition.
Certain file systems may also have a partition or device header overhead to be considered when computing the free space. Free space will be computed as total partition size less size of all existing files (valid/invalid/deleted files and including file header of each file), less size of any partition header, less size of header of next file to be copied in. In short, this object will give the size of the largest file that can be copied in. The management entity will not be expected to know or use any overheads such as file and partition header lengths, since such overheads may vary from file system to file system.
Deleted files in Flash do not free up space. A partition has to be erased in order to reclaim the space occupied by files. (The irspFileSystem file system provides an alternate method, through the squeeze command, of reclaiming free space occupied by deleted files. Support for this file system may however not be available on all systems).
Syntax: Gauge32
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoFlashPartitionFileCount
Specifies the count of all files in a flash partition. Both good and bad (deleted or invalid checksum) files will be included in this count.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoFlashPartitionChecksumAlgorithm
Specifies the checksum algorithm identifier for checksum method used by the file system. Normally, this would be fixed for a particular file system. When a file system writes a file to Flash, it checksums the data written. The checksum then serves as a way to validate the data read back whenever the file is opened for reading.
Since there is no way, when using TFTP, to guarantee that a network download has been error free (since UDP checksums may not have been enabled), this object together with the ciscoFlashFileChecksum object provides a method for any management station to regenerate the checksum of the original file on the server and compare checksums to ensure that the file download to Flash was error free.
simpleChecksum represents a simple 1s complement addition of short word values. Other algorithm values will be added as necessary.
Syntax: Integer, 1=simpleChecksum
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies that flash partition status can be one of the following:
Syntax: Integer 1 = ReadOnly, 2 = runFromFlash, 3 = readWrite
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoFlashPartitionUpgradeMethod
Specifies the flash partition upgrade method, In other words, specifies the method by which new files can be downloaded into the partition.
FLH stands for Flash Load Helper, a feature provided on run-from-Flash systems for upgrading Flash. This feature uses the bootstrap code in ROMs to help in automatic download.
This object should be retrieved if the partition status is runFromFlash(2). If the partition status is readOnly(1), the upgrade method would depend on the reason for the readOnly status. For example, it may simply be a matter of installing the programming jumper, or it may require execution of a version of software that supports the Flash chips.
| Partition Status | Meaning |
|---|---|
unknown | The current system image does not know how Flash can be programmed. A possible method would be to reload the ROM image and perform the upgrade manually. |
rxbootFLH | The Flash Load Helper is available to download files to Flash. A copy-to-flash command can be used and this system image will automatically reload the Rxboot image in ROM and direct it to carry out the download request. |
direct | Will be done directly by this image. |
Syntax: Integer 1 = unknown, 2 = rxbootFLH, 3 = direct
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the flash partition name used to refer to a partition by the system. This can be any alpha-numeric character string of the form AAAAAAAAnn, where A represents an optional alpha character and n a numeric character.
Any numeric characters must always form the trailing part of the string. The system will strip off the alpha characters and use the numeric portion to map to a partition index.
Flash operations get directed to a device partition based on this name. The system has a concept of a default partition. This would be the first partition in the device. The system directs an operation to the default partition whenever a partition name is not specified. The partition name is therefore mandatory except when the operation is being done on the default partition, or the device has just one partition (is not partitioned).
Syntax: DisplayString (SIZE (0-16))
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoFlashPartitionNeedErasure
This object indicates whether a partition requires erasure before any write operations can be done in it.
A management station should therefore retrieve this object prior to attempting any write operation. A partition requires erasure after it becomes full free space left is less than or equal to the (filesystem file header size).
A partition also requires erasure if the system does not find the existance of any file system when it boots up.
The partition may be erased explicitly through the erase(5) command, or by using the copyToFlashWithErase(1) command. If a copyToFlashWithoutErase(2) command is issued when this object has the TRUE value, the command will fail.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoFlashPartitionFileNameLength
Maximum file name length supported by the file system. Max file name length will depend on the file system implemented. Today, all file systems support a max length of 48 bytes. But the irsp file system may support a larger length. A management entity must use this object when prompting a user for, or deriving the Flash file name length.
Syntax: Integer32 (1-256)
Max-Access: Read-only
End of Table
Specifies the table of information for files in a Flash partition.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF CiscoFlashFileEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies an entry in the table of Flash file properties for each initialized Flash partition. Each entry represents a file and gives details about the file. An entry is indexed using the device number, partition number within the device, and file number within the partition.
Syntax: CiscoFlashFileEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the Flash file sequence number used to index within a Flash partition directory table.
Syntax: Integer32 (1-32)
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the size of the file in bytes. Note that this size does not include the size of the filesystem file header. File size will always be non-zero.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies a File checksum stored in the file header. This checksum is computed and stored when the file is written into Flash. It serves to validate the data written into Flash. Whereas the system will generate and store the checksum internally in hexadecimal form, this object will provide the checksum in a string form. The checksum will be available for all valid and invalid-checksum files.
Syntax: ChecksumString
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the status of a file. A file could be explicitly deleted if the file system supports such a user command facility. Alternately, an existing good file would be automatically deleted if another good file with the same name were copied in. Note that deleted files continue to occupy prime Flash real estate.
A file is marked as having an invalid checksum if any checksum mismatch was detected while writing or reading the file. Incomplete files (files truncated either because of lack of free space, or a network download failure) are also written with a bad checksum and marked as invalid.
Syntax: Integer, 1 = deleted, 2 = invalidChecksum, 3 = valid
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the Flash file name as specified by the user copying in the file. The name should not include the colon (:) character as it is a special separator character used to delineate the device name, partition name, and the file name.
Syntax: DisplayString (SIZE (1-255))
Max-Access: Read-only
End of Table
Flash operations are used for copying to or from flash partitioning, and miscellaneous functions such as erasing, file verification.
Specifies a table of Flash copy operation entries. Each entry represents a Flash copy operation (to or from Flash) that has been initiated.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF CiscoFlashCopyEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies a Flash copy operation entry. Each entry consists of a command, a source, and optional parameters such as protocol to be used, a destination, a server address, and so forth.
A management station wishing to create an entry should first generate a pseudo-random serial number to be used as the index to this sparse table. The station should then create the associated instance of the row status object. It must also, either in the same or in successive PDUs, create the associated instance of the command and parameter objects. It should also modify the default values for any of the parameter objects if the defaults are not appropriate.
Once the appropriate instances of all the command objects have been created, either by an explicit SNMP set request or by default, the row status should be set to active to initiate the operation. Note that this entire procedure may be initiated by means of a single set request which specifies a row status of createAndGo as well as specifies valid values for the non-defaulted parameter objects.
Once an operation has been activated, it cannot be stopped. Once the operation completes, the management station should retrieve the value of the status object (and time if desired), and delete the entry. In order to prevent old entries from clogging the table, entries will be aged out, but an entry will never be deleted within 5 minutes of completing.
Syntax: CiscoFlashCopyEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies a unique entry in the table. A management station wishing to initiate a copy operation should use a pseudo-random value for this object when creating or modifying an instance of a ciscoFlashCopyEntry.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the copy command to be executed. Mandatory. Note that it is possible for a system to support multiple file systems (different file systems on different Flash devices, or different file systems on different partitions within a device). Each such file system may support only a subset of these commands. If a command is unsupported, the invalidOperation(3) error will be reported in the operation status.
| Command | Remarks |
|---|---|
copyToFlashWithErase | Copy a file to flash; erase flash before copy. Use the TFTP or rcp protocol |
copyToFlashWithoutErase | Copy a file to flash; do not erase. Note that this command will fail if the PartitionNeedErasure object specifies that the partition being copied to needs erasure. Use the TFTP or rcp protocol. |
copyFromFlash | Copy a file from flash using the TFTP, rcp or lex protocol. Note that the lex protocol can only be used to copy to a lex device. |
copyFromFlhLog | Copy contents of FLH log to server using TFTP protocol. Command table parameters include copyToFlashWithErase, CopyProtocol, CopyServerAddress, CopySourceName, CopyDestinationName (optional), CopyRemoteUserName (optional), CopyNotifyOnCompletion (optional), copyToFlashWithoutErase, CopyProtocol, CopyServerAddress, CopySourceName, CopyDestinationName (optional), CopyRemoteUserName (optional), CopyNotifyOnCompletion (optional), copyFromFlash, CopyProtocol, CopySourceName, CopyDestinationName (optional), CopyRemoteUserName (optional), CopyNotifyOnCompletion (optional), copyFromFlhLog, CopyProtocol, CopyServerAddress, CopyDestinationName, CopyNotifyOnCompletion (optional) |
Syntax: Integer 1 = copyToFlashWithErase,
copy {tftp|rcp} flash
2 = copyToFlashWithoutErase,
copy {tftp|rcp} flash
3 = copyFromFlash,
copy flash {tftp|rcp|lex}
4 = copyFromFlhLog
copy flhlog tftp
Max-Access: Read-create
Specifies the protocol to be used for any copy. Optional. Will default to tftp if not specified. Since feature support depends on a software release, version number within the release, platform, and maybe the image type (subset type), a management station would be expected to somehow determine the protocol support for a command.
Syntax: Integer 1 = tftp, 2 = rcp , 3 = lex
Max-Access: Read-create
Specifies the server address to be used for any copy. Optional. Will default to 'FFFFFFFF'H (or 255.255.255.255).
Syntax: IpAddress
Max-Access: Read-create
Specifies the source file name, either in Flash or on a server, depending on the type of copy command. Mandatory. For a copy from Flash, File name must be of the form
[device>:][<partition>:]<file>
where <device> is a value obtained from FlashDeviceName, <partition> is obtained from FlashPartitionName and <file> is the name of a file in Flash.
A management station could derive its own partition name as per the description for the ciscoFlashPartitionName object. If <device> is not specified, the default Flash device will be assumed.
If <partition> is not specified, the default partition will be assumed. If a device is not partitioned into 2 or more partitions, this value may be left out.
For a copy to Flash, the file name will be as per the file naming conventions and path to the file on the server.
Syntax: DisplayString (SIZE (1-255))
Max-Access: Read-create
Specifies the destination file name. For a copy to Flash,the file name must be of the form
{device>:][<partition>:]<file>
where <device> is a value obtained from FlashDeviceName, <partition> is obtained from FlashPartitionName and <file> is any character string that does not have embedded colon characters. A management station could derive its own partition name as per the description for the ciscoFlashPartitionName object.
If <device> is not specified, the default Flash device will be assumed. If <partition> is not specified, the default partition will be assumed. If a device is not partitioned into 2 or more partitions, this value may be left out. If <file> is not specified, it will default to <file> specified in ciscoFlashCopySourceName.
For a copy from Flash by means of tftp or rcp, the file name will be as per the file naming conventions and destination sub-directory on the server. If not specified, <file> from the source file name will be used.
For a copy from Flash by means of lex, this string will consist of numeric characters specifying the interface on the lex box that will receive the source flash image.
Syntax: DisplayString (SIZE (0-255))
Access: Read-create
Specifies the remote user name for copy by means of the rcp protocol. Optional. This object will be ignored for protocols other than rcp. If specified, it will override the remote user-name configured through the rcmd remote-username <username> configuration command. The remote user-name is sent as the server user-name in an rcp command request sent by the system to a remote rcp server.
Syntax: DisplayString (SIZE (1-255))
Max-Access: Read-create
Specifies the status of the specified copy operation, as defined in the following table.
| Status Message | Meaning |
|---|---|
copyInProgress | specified operation is active |
copyOperationSuccess | specified operation is supported and completed successfully |
copyInvalidOperation | command invalid or command-protocol-device combination unsupported |
copyInvalidProtool | invalid protocol specified |
copyInvalidSourceName | invalid source file name specified For the copy from flash to lex operation, this error code will be returned when the source file is not a valid lex image. |
copyInvalidDestName | invalid target name (file or partition or device name) specified For the copy from flash to lex operation, this error code will be returned when no lex devices are connected to the router or when an invalid lex interface number has been specified in the destination string.
|
copyInvalidServerAddress | invalid server address specified |
copyDeviceBusy | specified device is in use and locked by another process |
copyDeviceOpenError | invalid device name |
copyDeviceError | device read, write or erase error |
copyDeviceNotProgrammable | device is read-only but a write or erase operation was specified |
copyDeviceFull | device is filled to capacity |
copyFileOpenError | invalid file name; file not found in partition |
copyFileTransferError | file transfer was unsuccessfull; network failure |
copyFileChecksumError | file checksum in Flash failed |
copyNoMemory | system running low on memory |
copyUnknownFailure | failure unknown |
Syntax: Integer 1 = copyInProgress, 2 = copyOperationSuccess, 3 = copyInvalidOperation, 4 = copyInvalidProtocol, 5 = copyInvalidSourceName, 6 = copyInvalidDestName,7 = copyInvalidServerAddress, 8 = copyDeviceBusy, 9 = copyDeviceOpenError, 10 = copyDeviceError, 11 = copyDeviceNotProgrammable, 12 = copyDeviceFull, 13 = copyFileOpenError, 14 = copyFileTransferError, 15 = copyFileChecksumError, 16 = copyNoMemory, 17 = copyUnknownFailure
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoFlashCopyNotifyOnCompletion
Specifies whether or not a notification should be generated on the completion of the copy operation. If specified, ciscoFlashCopyCompletionTrap will be generated. It is the responsibility of the management entity to ensure that the SNMP administrative model is configured in such a way as to allow the notification to be delivered.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-create
Specifies the time taken for the copy operation. This object will be like a stopwatch, starting when the operation starts, stopping when the operation completes. If a management entity keeps a database of completion times for various operations, it can then use the stopwatch capability to display percentage completion time.
Syntax: TimeTicks
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the status of this table entry.
Syntax: RowStatus
Max-Access: Read-create
End of Table
Specifies atable of Flash partitioning operation entries. Each entry represents a Flash partitioning operation that has been initiated.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF CiscoFlashPartitioningEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies a Flash partitioning operation entry. Each entry consists of the command, the target device, the partition count, and optionally the partition sizes.
A management station wishing to create an entry should first generate a pseudo-random serial number to be used as the index to this sparse table. The station should then create the associated instance of the row status object. It must also, either in the same or in successive PDUs, create the associated instance of the command and parameter objects. It should also modify the default values for any of the parameter objects if the defaults are not appropriate.
Once the appropriate instances of all the command objects have been created, either by an explicit SNMP set request or by default, the row status should be set to active to initiate the operation. Note that this entire procedure may be initiated via a single set request which specifies a row status of createAndGo as well as specifies valid values for the non-defaulted parameter objects.
Once an operation has been activated, it cannot be stopped. Once the operation completes, the management station should retrieve the value of the status object (and time if desired), and delete the entry. In order to prevent old entries from clogging the table, entries will be aged out, but an entry will never be deleted within 5 minutes of completing.
Syntax: CiscoFlashPartitioningEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
ciscoFlashPartitioningSerialNumber
Specifies the object which identifies a unique entry in the partitioning operations table. A management station wishing to initiate a partitioning operation should use a pseudo-random value for this object when creating or modifying an instance of a ciscoFlashPartitioningEntry.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the partitioning command to be executed. Mandatory. If the command is unsupported, the partitioningInvalidOperation error will be reported in the operation status.
Syntax: Integer 1 = partition
Max-Access: Read-create
| Command | Remarks | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
partition | Partition a Flash device. All the prerequisites for partitioning must be met for this command to succeed. | PartitioningDestinationName, PartitioningPartitionCount, PartitioningPartitionSizes (optional), PartitioningNotifyOnCompletion (optional) |
ciscoFlashPartitioningDestinationName
Specifies the destination device name. This name will be the value obtained from FlashDeviceName. If the name is not specified, the default Flash device will be assumed.
Syntax: DisplayString (SIZE (0-255))
Max-Access: Read-create
ciscoFlashPartitioningPartitionCount
Specifies the number of partitions to be created. Its value cannot exceed the value of ciscoFlashDeviceMaxPartitions.
To undo partitioning (revert to a single partition), this object must have the value 1.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-create
ciscoFlashPartitioningPartitionSizes
Specifies the size of each partition to be created. The size of each partition will be in units of ciscoFlashDeviceMinPartitionSize. The value of this object will be in the form:
<part1>:<part2>...:<partn>
If partition sizes are not specified, the system will calculate default sizes based on the partition count, the minimum partition size, and the device size. Partition size need not be specified when undoing partitioning (partition count is 1). If partition sizes are specified, the number of sizes specified must exactly match the partition count. If not, the partitioning command will be rejected with the invalidPartitionSizes error.
Syntax: DisplayString
Max-Access: Read-create
Specifies the status of the specified partitioning operation.
| Operation | Meaning |
|---|---|
partitioningInProgress | The specified operation is active |
partitioningOperationSuccess | The specified operation has completed successfully |
partitioningInvalidOperation | command invalid or command-protocol-device combination unsupported |
partitioningInvalidDestName | invalid target name (file or partition or device name) specified |
partitioningInvalidPartitionCount | invalid partition count specified for the partitioning command |
partitioningInvalidPartitionSizes | invalid partition size, or invalid count of partition sizes |
partitioningDeviceBusy | The specified device is in use and locked by another process |
partitioningDeviceOpenError | invalid device name |
partitioningDeviceEror | device read, write or erase error |
partitioningNoMemoy | system running low on memory |
partitioningUnknownFailure | failure unknown |
Syntax: Integer 1 = partitioningInProgress, 2 = partitioningOperationSuccess, 3 = partitioningInvalidOperation, 4 = partitioningInvalidDestName, 5 = partitioningInvalidPartitionCount, 6 = partitioningInvalidPartitionSizes, 7 = partitioningDeviceBusy, 8 = partitioningDeviceOpenError , 9 = partitioningDeviceError,10 = partitioningNoMemory, 11 = partitioningUnknownFailure
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoFlashPartitioningNotifyOnCompletion
Specifies whether or not a notification should be generated on the completion of the partitioning operation. If specified, ciscoFlashPartitioningCompletionTrap will be generated. It is the responsibility of the management entity to ensure that the SNMP administrative model is configured in such a way as to allow the notification to be delivered.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-create
Specifies the time taken for the operation. This object will be like a stopwatch, starting when the operation starts, stopping when the operation completes. If a management entity keeps a database of completion times for various operations, it can then use the stopwatch capability to display percentage completion time.
Syntax: TimeTicks
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoFlashPartitioningEntryStatus
Specifies the status of this table entry.
Syntax: RowStatus
Max-Access: Read-create
End of Table
Specifies a table of miscellaneous Flash operation entries. Each entry represents a Flash operation that has been initiated.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF CiscoFlashMiscOpEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies a Flash operation entry. Each entry consists of a command, a target, and any optional parameters.
A management station wishing to create an entry should first generate a pseudo-random serial number to be used as the index to this sparse table. The station should then create the associated instance of the row status object. It must also, either in the same or in successive PDUs, create the associated instance of the command and parameter objects. It should also modify the default values for any of the parameter objects if the defaults are not appropriate.
Once the appropriate instances of all the command objects have been created, either by an explicit SNMP set request or by default, the row status should be set to active to initiate the operation. Note that this entire procedure may be initiated via a single set request which specifies a row status of createAndGo as well as specifies valid values for the non-defaulted parameter objects.
Once an operation has been activated, it cannot be stopped.
Once the operation completes, the management station should retrieve the value of the status object (and time if desired), and delete the entry. In order to prevent old entries from clogging the table, entries will be aged out, but an entry will never be deleted within 5 minutes of completing.
Syntax: CiscoFlashMiscOpEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies a unique entry in the table. A management station wishing to initiate a flash operation should use a pseudo-random value for this object when creating or modifying an instance of a ciscoFlashMiscOpEntry.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the command to be executed. Mandatory. Note that it is possible for a system to support multiple file systems (different file systems on different Flash devices, or different file systems on different partitions within a device). Each such file system may support only a subset of these commands. If a command is unsupported, the miscOpInvalidOperation(3) error will be reported in the operation status.
| Command | Remarks |
|---|---|
erase | Erase flash |
verify | Verify flash file checksum |
delete | Delete a file. |
undelete | Revive a deleted file. Note that there are limits on the number of times a file can be deleted and undeleted. When this limit is exceeded, the system will return the appropriate error. |
squeeze | Recover space occupied by deleted files. This command preserves the good files, erases out the file system, then restores the preserved good files. |
|
|
Syntax: Integer 1 = erase, 2 = verify, 3 = delete, 4 = undelete, 5 = squeeze
Max-Access: Read-create
| Command | Parameters |
|---|---|
erase | MiscOpDestinationName, MiscOpNotifyOnCompletion (optional) |
verify | MiscOpDestinationName, MiscOpNotifyOnCompletion (optional) |
delete | MiscOpDestinationName, MiscOpNotifyOnCompletion (optional) |
undelete | MiscOpDestinationName, MiscOpNotifyOnCompletion (optional) |
squeeze | MiscOpDestinationName, MiscOpNotifyOnCompletion (optional) |
ciscoFlashMiscOpDestinationName
Syntax: DisplayString (SIZE (0-255))
Max-Access: Read-create
Specifies the destination file, or partition name. The file name must be of the following form:
[device>:][<partition>:]<file>
where <device> is a value obtained from FlashDeviceName, <partition> is obtained from FlashPartitionName and <file> is the name of a file in Flash. While leading and/or trailing whitespaces are acceptable, no whitespaces are allowed within the path itself.
A management station could derive its own partition name as per the description for the ciscoFlashPartitionName object. If <device> is not specified, the default Flash device will be assumed.
If <partition> is not specified, the default partition will be assumed. If a device is not partitioned into 2 or more partitions, this value may be left out.
For an operation on a partition, such as the erase command, this object would specify the partition name in the form:
[device>:][<partition>:]
Specifies the status of the given operation.
Syntax: Integer
1 = miscOpInProgress, 2 = miscOpOperationSuccess, 3 = miscOpInvalidOperation, 4 = miscOpInvalidDestName, 5 = miscOpDeviceBusy, 6 = miscOpDeviceOpenError, 7 = miscOpDeviceError, 8 = miscOpDeviceNotProgrammable, 9 = miscOpFileOpenError, 10 = miscOpFileDeleteFailure, 11 = miscOpFileUndeleteFailure, 12 = miscOpFileChecksumError, 13 = miscOpNoMemory, 14 = miscOpUnknownFailure
Max-Access: Read-only
| Operation | Meaning |
|---|---|
miscOpInProgress | specified operation is active |
miscOpOperationSuccess | specified operation has completed successfully |
miscOpInvalidOperation | command invalid or command-protocol-device combination unsupported |
miscOpInvalidDestName | invalid target name (file or partition or device name) specified |
miscOpDeviceBusy | specified device is in use and locked by another process |
miscOpDeviceOpenError | invalid device name |
miscOpDeviceError | device read, write or erase error |
miscOpDeviceNotProgrammable | device is read-only but a write or erase operation was specified |
miscOpFileOpenError | invalid file name; file not found in partition |
miscOpFileDeleteFailure | file could not be deleted; delete count exceeded |
miscOpFileUndeleteFailure | file could not be undeleted; undelete count exceeded |
miscOpFileChecksumError | file has a bad checksum |
miscOpNoMemory | system running low on memory |
miscOpUnknownFailure | failure unknown |
ciscoFlashMiscOpNotifyOnCompletion
Specifies whether a notification should be generated on the completion of an operation. If specified, ciscoFlashMiscOpCompletionTrap will be generated. It is the responsibility of the management entity to ensure that the SNMP administrative model is configured in such a way as to allow the notification to be delivered.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-create
Specifies the time taken for the operation. This object will be like a stopwatch, starting when the operation starts, stopping when the operation completes. If a management entity keeps a database of completion times for various operations, it can then use the stopwatch capability to display percentage completion time.
Syntax: TimeTicks
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the status of this table entry.
Syntax: RowStatus
Max-Access: Read-create
End of Table
The following notifications are supported with the ciscoFlash MIB:
A ciscoFlashCopyCompletionTrap is sent at the completion of a flash copy operation if such a trap was requested when the operation was initiated.
ciscoFlashPartitioningCompletionTrap
A ciscoFlashPartitioningCompletionTrap is sent at the completion of a partitioning operation if such a trap was requested when the operation was initiated.
ciscoFlashMiscOpCompletionTrap
A ciscoFlashMiscOpCompletionTrap is sent at the completion of a miscellaneous flash operation (enumerated in ciscoFlashMiscOpCommand) if such a trap was requested when the operation was initiated.
A ciscoFlashDeviceChangeTrap is sent whenever a removable Flash device is inserted or removed.
The variables described in this section apply to the Cisco Ping MIB definitions.
Provides a table of ping request entries. The ping group consists of a single table, the ciscoPingTable, and includes the ciscoPing entries described in this subsection.
Syntax: Sequence of CiscoPingEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
The address of the device to be pinged. An instance of this object cannot be created until the associated instance of ciscoPingProtocol is created. Once an instance of this object is created, its value cannot be changed.
Syntax: CiscoNetworkAddress
Max-Access: Read-Write
Provides a ping request entry. A management station choosing to create an entry should first generate a pseudo-random serial number to be used as the index to this sparse table. The station should then create the associated instance of the row status and row owner objects. It must also, either in the same or in successive protocol data units (PDUs), create the associated instance of the protocol and address objects. It should also modify the default values for the other configuration objects if the defaults are not appropriate.
Once the appropriate instance of all the configuration objects has been created, either by an explicit SNMP set request or by default, the row status should be set to active to initiate the request. Note that this entire procedure can be initiated by means of a single set request which specifies a row status of createAndGo as well as specifies values for the non-defaulted configuration objects.
Once the ping sequence has been activated, it cannot be stopped; it will run until the configured number of packets have been sent.
Once the sequence completes, the management station should retrieve the values of the status objects of interest, and should then delete the entry. In order to prevent old entries from clogging the table, entries will be aged out, but an entry will never be deleted within 5 minutes of completing.
Syntax: CiscoPingEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the protocol stack over which the ping packet is being sent. For IOS Release 10.2, Cisco supports the SNMP ping over IP, IPX, AppleTalk, CLNS, DECnet, and VINES.
Syntax: Cisco Network Protocol
Max-Access: Read-Create
Specifies a unique entry in the ciscoPingTable. A management station choosing to initiate a ping operation should use a pseudo-random value for this object when creating or modifying an instance of a ciscoPingEntry. The RowStatus semantics of the ciscoPingEntryStatus object will prevent access conflicts.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the number of ping packets to send to the target in this sequence.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-create
Specifies the size of ping packets to send to the target in this sequence. The lower and upper boundaries of this object are protocol-dependent. An instance of this object cannot be modified unless the associated instance of ciscoPingProtocol has been created (so as to allow protocol-specific range checking on the new value).
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-create
Specifies the amount of time to wait for a response to a transmitted packet before declaring the packet dropped.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-create
Specifies the minimum amount of time to wait before sending the next packet in a sequence after receiving a response or declaring a timeout for a previous packet. The actual delay may be greater due to internal task scheduling.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-create
Specifies whether a ciscoPingCompletion trap should be issued on completion of the sequence of pings. If such a trap is sought, it is the responsibility of the management entity to ensure that the SNMP administrative model is configured in such a way as to allow the trap to be delivered.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-create
Specifies the number of ping packets that have been sent to the target in this sequence.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of ping packets that have been received from the target in this sequence.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the minimum round trip time of all the packets sent in this sequence. This object will not be created until the first ping response in a sequence is received.
Syntax: Integer
Max-Access: Read-only
The average round trip time of all the packets sent in this sequence. This object will not be created until the first ping response in a sequence is received.
Syntax: Integer
Max-Access: Read-only
The maximum round trip time of all the packets sent in this sequence. This object will not be created until the first ping response in a sequence is received.
Syntax: Integer
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies a setting of true when all the packets in this sequence have been answered or have timed out.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the entity that configured this device.
Syntax: OwnerString
Max-Access: Read-create
Specifies the status of this table entry. Once the entry status is set to active, the associate entry cannot be modified until the sequence is completed (in other words, ciscoPingCompleted is true).
Syntax: RowStatus
Max-Access: Read-create
The Cisco Repeater Group specifies proprietary MIB extensions to RFC 1516. These extensions support the standard-repeater (hub), including the Cisco 2516, features such as link-test, auto-polarity, source-address control, and the MDI/MDI-X switch status.
Specifies the port's MDI/MDI-X switching status. The crossover(2) status indicates the port is configured to be in MDI-X mode (crossover function is enabled to allow for connection to a chained hub). The normal(1) status indicates the port is configured to be standard MDI as defined by the 10BaseT Standard. The notSwitchable(3) status indicates the port is not switchable between MDI and MDI-X mode.
Syntax: Integer 1 = normal, 2 = crossover, 3 = notSwitchable
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies whether or not Link Integrity Test Function is enabled for the port as specified by the 10BaseT Standard. When the link test function is enabled, the absence of the Link Test pulses and receive data on the port will cause the port to go into a Link Fail state. In this state, the data transmission, data reception and collision detection functions are disabled until valid data or 4 consecutive Link Test pulses appear on RXD+/- pair of the port. With the Link Integrity Test Function disabled, the data driver, receiver and collision detection remain enabled irrespective of the presence or absence of data or Link Test pulses on the port.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-write
Specifies the status of the Link Test function for the port. Set to false indicates valid data or 4 consecutive Link Test pulses have been detected on the port. Set to true indicates the failure of the Link Test function for the port. In the Link Test Fail state, data transmission, data reception and collision detection functions are disabled until valid data or 4 consecutive Link Test pulses appear on the RXD+/- pair of the port.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoRptrPortAutoPolarityEnabled
Specifies whether or not the Automatic Receiver Polarity Reversal is enabled for the port. This feature provides the ability to invert the polarity of the signals appearing at the RXD+/- pair of the port prior to re-transmission if the polarity of the received signal is reversed (such as in the case of wiring error).
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-write
ciscoRptrPortAutoPolarityCorrected
Specifies the status of the Automatic Receiver Polarity Reversal for the port. Set to true indicates the polarity of the port has been detected as reversed and is corrected. Set to false indicates the polarity for the port as having correct polarity.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies whether or not the Source Address Control feature is enabled for the port. This feature provides the ability to control which device's specific MAC address is allowed access to the network. If the management entity specified an address via ciscoRptrPortAllowedSrcAddr, only the device with the configured MAC address is allowed access to the network. If the management entity does not specified an address, the allowed source address is learned from the last source address if valid; otherwise, the allowed source address is learned from the MAC address of the first valid packet detected on the port. When another MAC address other than the allowed source address is detected on the port, the port is partitioned.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-write
For write access, this object specifies the allowed source address that is to be configured for source address control feature for the port. For read access, if no allowed source address was specifically specified by the manager, the agent shall return the learned address to control. Otherwise, the specified allowed source address is returned if configured by management entity.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE(0 | 6))
Max-Access: Read-write
ciscoRptrPortAllowedSrcAddrStatus
Specifies the status of ciscoRptrPortAllowedSrcAddr for the port. allowedSrcAddrConfig(1) status indicates that the allowed source address was explicitly configured by management entity. The allowedSrcAddrLearn(2) status indicates that the allowed source address was learned for the port. The allowedSrcAddrUndefined(3) status indicates that currently there is no restriction on the source address for the port.
Syntax: Integer 1 = allowedSrcAddrConfig, 2 = allowedSrcAddrLearn, 3 = allowedSrcAddrUndefined
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoRptrPortLastIllegalSrcAddr
Specifies the last illegal source address which caused this port to be partitioned. If the port is never partitioned due to Source Address Control, the agent shall return a string of length zero.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE(0 | 6))
Max-Access: Read-only
The variables described in this section are system-wide and apply to all Cisco Systems products.
The following variables pertain to basic information such as system software description and version number, host and domain names, and number of bytes of free memory in the managed device:
Provides the IP address of the device causing the last SNMP authorization failure. The device did not use a configured community string or tried a SET with a read-only community string.
Syntax: IP address
Access: Read-only
Provides the IP address of the host that supplied the software currently running on the managed device.
Syntax: IP address
Access: Read-only
Provides the domain portion of the domain name of the host.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of bytes of free memory available in the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Represents the name of the host in printable ASCII characters.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Contains a printable octet string that contains the system bootstrap description and version identification.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Contains a printable octet string that contains the reason why the system was last restarted.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
The following variables are used to monitor the amount and type of buffer space available within a managed device. Buffers are blocks of memory used to hold network packets. There are five types of buffers based on size: small, middle, big, large, and huge. There are several pools of different-sized buffers. These pools grow and shrink based upon demand. Some buffers are temporary and are created and destroyed as warranted. Others are permanently allocated.
Contains the total number of allocation requests that have failed due to lack of any free buffers.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Counts the number of failures caused by insufficient memory to create a new buffer.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Buffer elements are blocks of memory used in internal operating system queues.
Contains the number of new buffer elements created for the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of buffer elements that are not currently allocated and are available for use in the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of successful attempts to allocate a buffer element when needed.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the maximum number of buffer elements the managed device can have.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of allocation attempts that failed because there were no buffer elements available.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Small buffer sizes are configurable.
Contains the number of small buffers created in the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of small buffers that are currently available to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of successful attempts to allocate a small buffer when needed.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the maximum number of small buffers that can be allocated to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of allocation attempts that failed because there were no small buffers available.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the size (in bytes) of small buffers.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of small buffers allocated to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the small buffers that have been destroyed in the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Middle buffer sizes are configurable.
Contains the number of middle buffers created in the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of middle buffers that are currently available to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of successful attempts to allocate a middle buffer when needed.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the maximum number of middle buffers that can be allocated to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of allocation attempts that failed because there were no middle buffers available.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the size (in bytes) of middle buffers.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of middle buffers allocated to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the middle buffers that have been destroyed in the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Big buffer sizes are configurable.
Contains the number of big buffers created in the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of big buffers that are currently available to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of successful attempts to allocate a big buffer when needed.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the maximum number of big buffers that can be allocated to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of allocation attempts that failed because there were no big buffers available.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the size (in bytes) of big buffers.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of big buffers allocated to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the big buffers that have been destroyed in the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Large buffer sizes are configurable.
Contains the number of large buffers created in the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of large buffers that are currently available to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of successful attempts to allocate a large buffer when needed.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the maximum number of large buffers that can be allocated to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of allocation attempts that failed because there were no large buffers available.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the size (in bytes) of large buffers.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of large buffers allocated to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the large buffers that have been destroyed in the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Huge buffer sizes are configurable.
Contains the number of huge buffers created in the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of huge buffers that are currently available to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of successful attempts to allocate a huge buffer when needed.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the maximum number of huge buffers that can be allocated to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of allocation attempts that failed because there were no huge buffers available.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the size (in bytes) of huge buffers.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of huge buffers allocated to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the huge buffers that have been destroyed in the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
The following variables provide statistics on the CPU utilization of a device:
Provides a cumulative average of the CPU usage percentage over a 1-minute period. This variable, called by the scheduler every 5 seconds, computes the busy time in the last 5-second period, and the 5-minute, exponentially decayed busy time. The following equation shows the average sampling time:
average = ((average-interval) * exp (-t/C)) + interval
where t is 5 seconds and C is 1 minute, exp(-5/60) == .920 ~= 942/1024
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides a cumulative average of the CPU usage percentage over a 5-minute period. This variable, called by the scheduler every 5 seconds, computes the busy time in the last 5-second period, and the 5-minute, exponentially decayed busy time. The following equation shows the average sampling time:
average = ((average-interval) * exp (-t/C)) + interval
where t is 5 seconds and C is five minutes, exp(-5/60*5)) == .983 ~= 1007/1024
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the percentage of CPU usage over the first 5-second period in the scheduler. The scheduler determines which process or task takes priority over another and triggers them accordingly.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the Cisco name and address for reference purposes. This MIB variable applies only to router products that were purchased from Cisco.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
The environmental monitor card is provided only with the Cisco AGS+ router. This card checks input air temperature and air flow through the system card cage and card cage backplane power supplies. It also provides nonvolatile and system bus memory for the system. The Cisco 7000 and Cisco 7010 have built-in environmental monitoring functionality, and so does not use the card. The Cisco 7000 and Cisco 7010 routers provide environmental monitoring, reporting, and if necessary, system shutdown.
The following MIB module describes the status of the Environmental Monitor on those devices which support one:
Specifies the type of environmental monitor located in the chassis. An oldAgs environmental monitor card is identical to an ags environmental card except that it is not capable of supplying data, and hence no instance of the remaining objects in this MIB will be returned in response to an SNMP query. Note that only a firmware upgrade is required to convert an oldAgs into an ags card.
Syntax: Integer, 1 = oldAgs, 2 = ags, 3 = c7000
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the table of voltage status maintained by the environmental monitor.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF CiscoEnvMonVoltageStatusEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
An entry in the voltage status table, representing the status of the associated testpoint maintained by the environmental monitor.
Syntax: CiscoEnvMonVoltageStatusEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies a unique index for the testpoint being instrumented. This index is for SNMP purposes only and has no intrinsic meaning.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Provides a textual description of the testpoint being instrumented. This description is a short textual label, suitable as a human-sensible identification for the rest of the information in the entry.
Syntax: DisplayString
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the current measurement in millivolts of the testpoint being instrumented.
Syntax: CiscoSignedGauge
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoEnvMonVoltageThresholdLow
Specifies the lowest value in millivolts that the associated instance of the object ciscoEnvMonVoltageStatusValue can obtain before an emergency shutdown of the managed device is initiated.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoEnvMonVoltageThresholdHigh
The highest value in millivolts that the associated instance of the object ciscoEnvMonVoltageStatusValue can obtain before an emergency shutdown of the managed device is initiated.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoEnvMonVoltageLastShutdown
The value in millivolts of the associated instance of the object ciscoEnvMonVoltageStatusValue at the time an emergency shutdown of the managed device was last initiated. This value is stored in nonvolatile RAM and hence is able to survive the shutdown.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the current state of the testpoint being instrumented.
Syntax: CiscoEnvMonState
Max-Access: Read-only
End of Table
Specifies the table of ambient temperature status maintained by the environmental monitor.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF CiscoEnvMonTemperatureStatusEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
ciscoEnvMonTemperatureStatusEntry
An entry in the ambient temperature status table, representing the status of the associated testpoint maintained by the environmental monitor.
Syntax: CiscoEnvMonTemperatureStatusEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
ciscoEnvMonTemperatureStatusIndex
Specifies the unique index for the testpoint being instrumented. This index is for SNMP purposes only and has no intrinsic meaning.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Not-accessible
ciscoEnvMonTemperatureStatusDescr
Specifies the textual description of the testpoint being instrumented. This description is a short textual label, suitable as a human-sensible identification for the rest of the information in the entry.
Syntax: DisplayString
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoEnvMonTemperatureStatusValue
Specifies the current measurement in degrees Celsius of the testpoint being instrumented.
Syntax: Gauge32
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoEnvMonTemperatureThreshold
Specifies the highest value in degrees Celsius that the associated instance of the object ciscoEnvMonTemperatureStatusValue can obtain before an emergency shutdown of the managed device is initiated.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
ciscoEnvMonTemperatureLastShutdown
Specifies the value in degrees Celsius of the associated instance of the object ciscoEnvMonTemperatureStatusValue at the time an emergency shutdown of the managed device was last initiated. This value is stored in nonvolatile RAM and hence is able to survive the shutdown.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the current state of the testpoint being instrumented.
Syntax: CiscoEnvMonState
Max-Access: Read-only
End of Table
Provides the fan status maintained by the environmental monitor.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF CiscoEnvMonFanStatusEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies an entry in the fan status table, representing the status of the associated fan maintained by the environmental monitor.
Syntax: CiscoEnvMonFanStatusEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies a unique index for the fan being instrumented. This index is for SNMP purposes only and has no intrinsic meaning.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Provides a textual description of the fan being instrumented. This description is a short textual label, suitable as a human-sensible identification for the rest of the information in the entry.
Syntax: DisplayString
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the current state of the fan being instrumented.
Syntax: CiscoEnvMonState
Max-Access: Read-only
End of Table
Specifies the table of power supply status maintained by the environmental monitor card.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF CiscoEnvMonSupplyStatusEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies an entry in the power supply status table, representing the status of the associated power supply maintained by the environmental monitor card.
Syntax: CiscoEnvMonSupplyStatusEntry
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Specifies a unique index for the power supply being instrumented. This index is for SNMP purposes only and has no intrinsic meaning.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Not-accessible
Provides a textual description of the power supply being instrumented. This description is a short textual label, suitable as a human-sensible identification for the rest of the information in the entry.
Syntax: DisplayString
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the current state of the power supply being instrumented.
Syntax: CiscoEnvMonState
Max-Access: Read-only
The following object identifiers are used to define SNMPv2 notifications that are backward compatible with SNMPv1 notifications, along with their associated notification enables:
ciscoEnvMonShutdownNotification
A ciscoEnvMonShutdownnotification is sent if the environmental monitor detects a testpoint reaching a critical state and is about to initiate a shutdown. This notification contains no objects so that it can be encoded and sent in the shortest amount of time possible. Even so, management applications should not rely on receiving such a notification because it might not be sent before the shutdown completes.
ciscoEnvMonEnableShutdownNotification
This variable indicates whether the system produces the ciscoEnvMonShutdownNotification.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-write
ciscoEnvMonEnableVoltageNotification
Specifies whether the system produces the ciscoEnvMonVoltageNotification. A false value will prevent voltage notifications from being generated by this system
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-write
ciscoEnvMonVoltageNotification
A ciscoEnvMonVoltageNotification is sent if the voltage measured at a given testpoint is outside the normal range for the testpoint. (In other words, is at the warning, critical, or shutdown stage.) Because such a notification is usually generated before the shutdown state is reached, it can convey more data and has a better chance of being sent than does the ciscoEnvMonShutdownNotification. The ciscoEnvMonVoltage includes the following variable bindings (varBinds): ciscoEnvMonVoltageStatusDescr, ciscoEnvMonVoltageStatusValue, and ciscoEnvMonVoltageState. (The varBinds comprise the data of an SNMP v.1 protocol data unit (PDU). Each varBind associates a particular variable with its current value—with the exception of get and get-next requests, for which the value is ignored).
ciscoEnvMonTemperatureNotification
A ciscoEnvMonTemperatureNotification is sent if the temperature measured at a given testpoint is outside the normal range for the testpoint (in other words, the testpoint is at the warning, critical, or shutdown stage). Because such a notification is usually generated before the shutdown state is reached, it can convey more data and has a better chance of being sent than does the ciscoEnvMonShutdownNotification. The ciscoEnvMonTemperatureNotification includes the following varBinds: ciscoEnvMonTemperatureStatusDescr, ciscoEnvMonTemperatureStatusValue, and ciscoEnvMonTemperatureState
ciscoEnvMonEnableTemperatureNotification
Specifies whether the system produces the ciscoEnvMonTemperatureNotification. A false value will prevent temperature notifications from being generated by this system.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-write
A ciscoEnvMonFanNotification is sent if any fan in the fan arrays fails. Because such a trap is usually generated before the shutdown state is reached, it can convey more data and has a better chance of being sent than does the ciscoEnvMonShutdownNotification. The ciscoEnvMonFanNotification includes the following varBinds: ciscoEnvMonFanStatusDescr, and ciscoEnvMonFanState
ciscoEnvMonEnableFanNotification
Specifies whether the system produces the ciscoEnvMonFanNotification. A false value will prevent fan notifications from being generated by this system.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-write
ciscoEnvMonRedundantSupplyNotification
A ciscoEnvMonRedundantSupplyNotification is sent if the redundant power supply (where extant) fails. Because such a notification is usually generated before the shutdown state is reached, it can convey more data and has a better chance of being sent than does the ciscoEnvMonShutdownNotification. The ciscoEnvMonRedundantSupplyNotification has the following varBinds included: ciscoEnvMonSupplyStatusDescr, and ciscoEnvMonSupplyState.
ciscoEnvMonEnableRedundantSupplyNotific ation
Specifies whether the system produces the ciscoEnvMonRedundantSupplyNotification. A false value will prevent redundant supply notifications from being generated by this system.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-write
The variables in this section , from the Environmental Monitor Card group in IOS Release 10.2, have been deprecated and replaced with the former Environmental Monitor group, also found in the ciscoMgmt tree.
The environmental card is provided only with the Cisco AGS+ router. This card checks input air temperature and air flow through the system card cage and card cage bckplane power supplies. It also provides nonvolatile and system bus memory for the system. The Cisco 7000 has built-in environmental monitoring functionality, and so does not use the card. The Cisco 7000 router provides environmental monitoring , reporting, and if necessary, system shutdown.
All MIB variables in this group apply to the Cisco AGS+. A subset of those variables apply to the Cisco 7000. the following variables are used to poll and display power supply voltage and air temperature (in Celsius) in an AGS+ to help prevent system problems.
Provides the date of the calibration of the environmental monitor card. (AGS+ only).
For example:
calibrated on 2-14-93.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the firmware level of the environmental monitor card. (AGS+ only).
For example:
Environmental controller firmware version 2.0
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether there is an environmental monitor card in a router.
Syntax: Integer (0 = no, 1 = yes, but unavailable to SNMP; 2 = yes and available to SNMP for AGS+ routers; 3 = yes and available to SNMP for Cisco 7000 routers)
Access: Read-only
Provides the serial number of the environmental monitor card. (AGS+ only)
Following is an example of a serial number:
00220846
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the technician ID for the environmental monitor card. (AGS+ only)
Following is an example of a technician ID:
rma
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Test point 1 is the temperature of air entering the router. (AGS+ and Cisco 7000)
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the temperature of air entering the AGS+ and the Cisco 7000 router when the last shutdown occurred. If the input air temperature exceeds 109ºF (43ºC) in an AGS+, an error is detected, and the CSC-ENVM card shuts down the power supply.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides warning and fatal threshold values of the internal intake air for the AGS+ router and Cisco 7000.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the current temperature of air entering the router. (AGS+ and Cisco 7000)
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the air temperature entering the router is at warning level. (AGS+ and Cisco 7000)
Syntax: Integer (1 = warning, 2 = no warning)
Access: Read-only
Provides the temperature of air leaving the router. (AGS+ and
Cisco 7000)
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the temperature of air leaving the router when the last shutdown occurred. (AGS+ and Cisco 7000)
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the fatal threshold value for the exhaust air flow of the router. (AGS+ and Cisco 7000)
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the temperature of the exhaust air flow of the router. (AGS+ and Cisco 7000)
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the temperature of air flow leaving the router is at a warning level. (AGS+ and Cisco 7000)
Syntax: Integer (1 = warning, 2 = no warning)
Access: Read-only
Test point 3 is the +5-volt (V) line on the router.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the value of the +5V line when the last shutdown occurred. (AGS+ and Cisco 7000)
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the warning and fatal thresholds for the +5V line to the power supply on the AGS+ router. The warning threshold is ± 5 percent above or below +5V. The fatal threshold at which the router shuts down is ± 10 percent above or below +5V. (AGS+ only)
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the current value for the +5V line to the power supply on the router. The value is expressed in millivolts. (AGS+ and Cisco 7000)
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the +5V line to the power supply is at warning level. The warning threshold is ±5 percent above or below +5V. (AGS+ and Cisco 7000)
Syntax: Integer (1 = warning, 2 = no warning)
Access: Read-only
Test point 4 is the +12V line to the power supply of the router.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the value of the +12V line when the last shutdown occurred.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the warning and fatal thresholds for the +12V line to the power supply on the AGS+ router. The warning threshold is ± 10 percent above or below +12V. The fatal threshold at which the router shuts down is ± 15 percent above or below +12V. (AGS+ only)
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the current value (in millivolts) of the +12V line to the power supply of the router.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the +12V line to the power supply is at warning level. The warning threshold is ± 10 percent above or below +12V.
Syntax: Integer (1 = warning, 2 = no warning)
Access: Read-only
Test point 5 is the -12V line to the power supply of the router.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the value of the -12V line when the last shutdown occurred.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the warning and fatal thresholds for the -12V line to the power supply on the router. The warning threshold is ± 10 percent above or below -12V. The fatal threshold at which the router shuts down is ± 15 percent above or below -12V. (AGS+ only)
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the current value (in millivolts) of the -12V line to the power supply of the router.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the -12V line to the power supply on the router is at the warning level. The warning threshold is ± 10 percent above or below -12V. (AGS+ only)
Syntax: Integer (1 = warning, 2 = no warning)
Access: Read-only
Test point 6 is the -5V line to the power supply of the AGS+ router and +24V line to the power supply of the Cisco 7000 router.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the value of the -5V line to the power supply of the AGS+ router and +24V line to the power supply of the Cisco 7000 router when the last shutdown occurred.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the warning and fatal thresholds for the -12V line to the power supply on the AGS+ router. The warning threshold is ± 5 percent above or below -5V. The fatal threshold at which the router shuts down is ± 10 percent above or below -5V. (AGS+ only)
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the current value (in millivolts) of the -5V line to the power supply of the AGS+ router and +24V line to the power supply of the Cisco 7000 router.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
For the Cisco 7000, this variable indicates whether the +P24V line to the power supply is at the warning level.
Syntax: Integer (1 = warning, 2 = no warning)
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the -5V line to the power supply of the AGS+ router or +24V line to the power supply of the Cisco 7000 router is at the warning level. The warning threshold is ± 10 percent above or below -5V (AGS+ router) or +24V (Cisco 7000 router).
Syntax: Integer (1 = warning, 2 = no warning)
Access: Read-only
Provides the type of environmental card (for example, CSC-ENVM).
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
The following variables are used to monitor and set host configuration file information:
Provides the address of the host that provided the host configuration file for the managed device. The host configuration file contains commands that apply to one network server in particular.
Syntax: IpAddress
Access: Read-only
Provides the name of the last host configuration file used by the device.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the protocol that supplied the host configuration file.
Syntax: Integer (1 = IP, 2 = MOP, 3 = not applicable)
Access: Read-only
Allows the network management system (NMS) to load a new host configuration file via Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) onto the managed device and indicate the name of this configuration file. The instance ID is the IP address of the TFTP host. The display string indicates the name of the configuration file.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Write-only
The following variables are used to monitor and remotely set network configuration file information for the device:
Provides the address of the host that supplied the network configuration file for the managed device. The network configuration file contains commands that apply to all network servers and terminal services on a network.
Syntax: IpAddress
Access: Read-only
Provides the name of the network configuration file that resides on the managed device.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the protocol that supplied the network configuration file.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Loads a new network configuration file via Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) onto the managed device and indicates the name of this configuration file. The instance ID is the IP address of the TFTP host. The display string indicates the name of the configuration file.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Write-only
The following variables are used to monitor and set system-wide parameters:
Performs a clearing of the entire Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) cache and Internet Protocol (IP) route cache. The ARP provides dynamic mapping between IP addresses and Ethernet addresses. The ARP Cache table, which keeps a record of these mappings, can be cleared for maintenance purposes.
The IP route cache controls the use of a high-speed switching cache for IP routing. The route cache is enabled by default and allows outgoing packets to be load balanced on a per-destination basis. The sysClearARP variable helps clear the IP route cache for maintenance purposes.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Write-only
Clears an interface that is given IfIndex as a value. To clear an interface, take the ifIndex for the interface (for example, a value of 4) and set the sysClearInt variable to the ifIndex value of 4.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Write-only
Provides the address of the host that supplied the system boot image for the managed device. New versions of software can be downloaded over the network with boot image files. The new file takes effect the next time the managed device is reloaded.
Syntax: IpAddress
Access: Read-only
Provides the name of the system boot image file. New versions of software can be downloaded over the network with boot image files. The new file takes effect the next time the managed device is reloaded.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the protocol type that supplied the system boot image.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Writes the current (running) router configuration into nonvolatile memory where it can be stored and retained even if the router is reloaded. Write configuration memory if 1. Erase configuration memory if 0.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Write-only
Sends a copy of the current configuration via Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) to a remote host. When it is stored on the host, the configuration file can be edited and retrieved by other network entities.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Write-only
Following are variables that can be applied to terminal services. This group of variables contains terminal service information on a per-line basis, such as line status, line type, line speed, type of flow control, and type of modem.
Provides the number of physical lines on the device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
tsClrTtyLine
Specifies the tty line to clear. Read returns the last line cleared. A value of -1 indicates that no lines have been cleared.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
The local terminal services line table, ltsLineTable, contains all of the variables described in this section. The index to this table is the number of the terminal services line. If there are n number of terminal lines associated with the device, there will be n rows in the table.
| Line Number | tsLineActive | tsLineAutobaud | and so on |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Contains all of the variables described in this section. | ||
2 |
|
|
|
and so on |
|
|
|
Indicates whether this line is active.
Syntax: Integer (1 = active, 2 = not active)
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the line is set to autobaud detection so that it can adapt to the rate at which data is being sent to it.
Syntax: Integer (1 = autobaud, 2 = not autobaud)
Access: Read-only
Indicates what is used to represent the escape (Esc) character. The escape character allows a user to break out of active sessions.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Indicates the type of flow control the line is using. The flow can be controlled from software or hardware. Input indicates that the flow control is coming from the device to the terminal service. Output indicates flow control is provided by the terminal service.
The possible integer values follow:
1 = unknown
2 = none
3 = software-input
4 = software-output
5 = software-both
6 = hardware-input
7 = hardware-output
8 = hardware-both
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Describes the physical location of the line. The integer values 1-3 represent commands that can be defined by the user.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Describes the type of modem control the line is using.
The possible integer values follow:
1 = unknown
2 = none
3 = call-in
4 = call-out
5 = cts-required
6 = ri-is-cd
7 = modem inout
Descriptions of the integer values follow:
Call-in indicates dial-in modems that use the status of Data Terminal Ready (DTR) to determine whether to answer an incoming call.
Call-out indicates modems that raise data terminal ready (DTR) to see
if Clear To Send (CTS) becomes high as an indication that the host has noticed its signal.
Cts-required indicates the form of modem control that requires CTS to be high throughout the use of the line.
ri-is-cd is used for lines with high-speed modems. The modem answers the call if DTR is high, uses its Carrier Detect (CD) signal to reflect the carrier presence, and has its CD signal wired to the ring input of the terminal service.
modem inout is used to configure a line for both incoming and outgoing calls. The command enables a line to be used for both incoming and outgoing calls on dial-in/dial-out modems.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of garbage characters received while the line is inactive.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the number of current sessions on the line.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of the rotary group to which the line belongs. If the first line in a rotary group is busy, a connection can be made to the next free line.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the length (in lines) of the screen of the terminal attached to the line.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the width (in characters) of the screen of the terminal attached to the line.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the interval (in seconds) for closing the connection when there is no input or output traffic during a session.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the input speed at which the line is running.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the output speed at which the line is running.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Describes the terminal type of the line.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Specifies the interval (in seconds) for closing the connection when there is no input or output traffic on the line.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Describes the terminal line type.
The possible integer values follow:
1 = unknown
2 = console
3 = terminal
4 = line-printer
5 = virtual-terminal
6 = auxiliary
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the Terminal Access Controller Access System (TACACS) username and indicates whether TACACS is enabled on this line. TACACS servers provide security for accessing terminals remotely.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Indicates the number of times a connection has been made to or from this line.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
End of Table
The Terminal Services Line Session table, ltsLineSessionTable, contains six variables: tslineSesAddr, tslineSesCur, tslineSesDir, tslineSesIdle, tslineSesName, and tslineSesType.
For simplification, Table 21 shows values for three of the variables contained in the Terminal Services Line Session table. The index to the table is the session number and line number. Line 1 in the first session illustrates a Telnet connection. The session was started by the terminal. The remote host for this session is located at the IP address of 131.38.141.244.
| Session no. Line no. | tslineSesAddr | tslineSesDir | tslineSesType |
|---|---|---|---|
1, 1 | 131.38.141.244 | 3 | 5 |
2, 4 | 138.121.128.243 | 2 | 3 |
Provides the address of the remote host for this session.
Syntax: Network address
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether this session is currently active.
Syntax: Integer (1 = active, 2 = not active)
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether this session was started by another device (incoming) or by the terminal (outgoing).
The possible integer values follow:
1 = unknown
2 = incoming
3 = outgoing
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the amount of time (in seconds) that this session has been idle.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the name of the remote host for this session.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Describes the type of session that is currently active.
The possible integer values follow:
1 = unknown
2 = X.3 Packet Assembler/Disassembler (PAD)
3 = stream (enables a raw TCP [Transmission Control Protocol] stream with no Telnet-control sequences)
4 = rlogin (for making remote connection to a host—part of TCP/IP)
5 = telnet (for making remote connection to a host—UNIX protocol)
6 = Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
7 = local-area transport (LAT)
8 = Maintenance Operation Protocol (MOP)
9 = Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP)
10 = XRemote (provides support for X Windows over a serial line)
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
End of Table
The following variables pertain to the parameters of terminal services messages:
Sets the length of time (in milliseconds) allocated to reissue a message. The minimum nonzero setting is 10000.0. A setting of 0 will not repeat the message.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Sets the interval (in milliseconds) that occurs between reissues of the same message. The minimum (nonzero) setting for this interval is
10,000 milliseconds. If set to 0, the intervals will become more frequent as the message duration gets close to expiring. For example, 2 hours, 1 hour, 30 minutes, 5 minutes, and 1 minute.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Determines what action to take after the message has been sent.
The possible integer values follow:
1 = nothing
2 = reload
3 = message done
4 = abort
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Sets the text of the message. Up to 256 characters can be included in the message.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-write
Determines whether to use the message text as a temporary banner.
Syntax: Integer (1 = no, 2 = yes, in addition to the regular banner)
Access: Read-write
Selects the TTY line to which you want the message sent. Setting this variable to -1 will send the message to all TTY lines.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
The following variables, from the TCP group in IOS Release 10.2, have been deprecated and replaced with the ciscoTCP group, found in the ciscoMgmt tree.
These variables can be applied to Cisco products running the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). These variables provide statistics on the number of input and output bytes and packets for TCP connections.
The TCP connection table, ltcpConnTable, contains five variables: loctcpConnElapsed, loctcpConnInBytes, loctcpConnInPkts, loctcpConnOutBytes, and loctcpConnOutPkts.
The index to this table includes the local host address and port number and the remote host address and port number for each TCP connection that is active for the device. These values are represented by tcpConnLocalAddress, tcpConnLocalPort, tcpConnRemAddress, and tcpConRemPort.
For n number of TCP connections, there are n rows in the table. The value n can change at any time if another TCP connection opens or if an existing TCP connection closes.
In Table 22, TCP A represents the first TCP connection in the table.
The TCP A connection shows 100 input bytes, 100 output bytes, 85 input packets, and 85 output packets for the connection. The connection has been established for 60 seconds, or 6000 timeticks.
| ltcpConnTable | Elapsed | InBytes | InPkts | OutBytes | OutPkts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
TCP A | 6000 | 100 | 85 | 100 | 85 |
TCP B | 4500 | 200 | 90 | 130 | 100 |
TCP C | 9000 | 300 | 100 | 250 | 95 |
Provides the length of time that the TCP connection has been established.
Syntax: Timeticks
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input bytes for the TCP connection.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input packets for the TCP connection.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output bytes for the TCP connection.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output packets for the TCP connection.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
End of Table
This section is equivalent to the experimental space defined by the Structure of Management Information (SMI). It contains variables that are useful to have, but are beyond the ability of Cisco to control and maintain. Support for these variables can change with each Cisco Systems software release.
The temporary variables section includes the following groups of variables:
The variables in this group have been deprecated and replaced with the ciscoVINES (cv) group, found in the ciscoMgmt tree:
Variables in this group can be used with all Cisco products running the AppleTalk protocol. These variables provide such information as total number of input and output packets, number of packets with errors,
and number of packets with Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) requests and replies.
Indicates the total number of input ARP probe packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk ARP reply packets output.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of input AppleTalk ARP request packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk ATP packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk input broadcast packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk output broadcast packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk input packets with checksum errors.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of illegal-sized AppleTalk Datagram Delivery Protocol (DDP) packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of long DDP packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of short DDP packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk echo packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of illegal AppleTalk echo packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk packets forwarded.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk input packets that have exceeded the maximum hop count.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk input packets with multicast addresses.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of input AppleTalk packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk input packets for this host.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk Name Binding Protocol (NBP) packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of NBP packets sent.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk packets dropped due to access control.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk packets lost due to no memory.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk packets that were dropped because they could not be encapsulated.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of number of AppleTalk packets dropped because the router did not know where to forward them.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk input packets received while AppleTalk routing was not enabled.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk output packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk Routing Table Maintenance Protocol (RTMP) packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of RTMP packets sent.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of unknown AppleTalk input packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk Zone Information Protocol (ZIP) packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of ZIP packets sent.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Variables in this group apply to the Cisco chassis and provide information about the hardware within the chassis such as the system software version of the read-only memory (ROM) and the type of chassis (Cisco 2000, Cisco 3000, and so on).
The Chassis Card table, cardTableEntry, contains information on a per-chassis basis and includes the following variables: cardDescr, cardHwVersion, cardIndex, cardSerial, cardSlotNumber, cardSwVersion, and cardType. The index to this table is cardIndex. If the device has n number of cards, the table will contain n number of rows.
Provides the unique ID number for the chassis. This number contains the value of the CPU serial number or ID number (if available); otherwise, it will be empty. This number also can be set with snmp-server chassis-id. An example of a value for a CPU serial number is 00160917.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-write
Specifies whether this chassis is a variant partner of a product.
Syntax: Integer (1 = cisco, 2 = synoptics, 3 = chipcom, 4 = cabletron,
5 = dec, 6 = ncr, 7 = usrobotics)
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of slots in this chassis, or -1 if no slots exist or the number of slots cannot be determined.
Syntax: Integer
Access: read-only
Indicates the type of chassis for the product. For example, c4000 indicates a Cisco 4000 router.
The following are integer values for this variable:
1 = Unknown
2 = Multibus (for example, CGS or ASM)
3 = AGS+
4 = IGS
5 = Cisco 2000
6 = Cisco 3000
7 = Cisco 4000
8 = Cisco 7000
9 = Communication server 500
10 = Cisco 7010
11 = Cisco 2500
12 = Cisco 4500
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the chassis hardware revision level, or an empty string if the information is unavailable. Examples of the types of chassis versions are D or AO.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Indicates the value of the configuration register.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the value of the configuration register at next reload.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the nonvolatile configuration memory in bytes.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of bytes of nonvolatile configuration memory in use.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the bytes of RAM available to the CPU of the device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the ROM system software version, or an empty string if unavailable. Following is an example of the type of information provided by the romVersion variable:
System Bootstrap, Version 4.5(3), SOFTWARE [fc1]
Copyright (c) 1986-1992 by cisco Systems
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the software version of the system software in ROM, or an empty string if the information is unavailable. Following is an example of the type of information provided by the romSysVersion variable:
GS Software (GS3), Version 10.2(3127) [jdoe 106]
Copyright (c) 1986-1993 by cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Thu 08-Apr-93 09:55
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
The Chassis Interface Card Table, cardTable, contains the cardTableEntry variable. The Cisco Card table, cardTableEntry, contains seven entries, or rows: cardDescr, cardHwVersion, cardIndex, cardSerial, cardSwVersion, cardSlotNumber, and cardType. The index to this table is cardIndex. If there are n number of cards associated with the device, there will be n rows in the table.
For example, in Table 23, there are 4 rows.
| cardType | cardDescr | cardHwVersion | cardSerial | and so on |
|---|---|---|---|---|
70 | MCI interface | 1.1 | 0 |
|
70 | MCI interface | 1.1 | 0 |
|
5 | 25 MHz 68040 |
| 0 |
|
24 | Environmental Monitor | 4 | 00196849 |
|
and so on |
|
|
|
|
Provides a description of the card used by the router. Examples of the descriptions are MEC Ethernet for an MEC board, 25MHz 68040 for the CSC/4, and CTR Token Ring for a CTR board.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the hardware revision level of this card, or an empty string if unavailable.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides index into card table (not physical chassis slot number).
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the serial number of this card, or zero if unavailable.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the chassis slot number. A value of -1 is provided if it is not applicable or cannot be determined.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the version of the firmware or microcode installed on this card, or an empty string if unavailable. For example, 1.8 indicates MCI microcode 1.8, and 3.0 MADGE 1.01/4.02, TI 000000 indicates
CSC-R16M.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides information that identifies the functional type of card.
The possible integer values follow:
1 = unknown
2 = csc1
3 = csc2
4 = csc3
5 = csc4
6 = rp
20 = csc-m
21 = csc-mt
22 = csc-mc
23 = csc-mcplus
24 = csc-envm
40 = csc-16
41 = csc-p
50 = csc-a
51 = csc-e1
52 = csc-e2
53 = csc-y
54 = csc-s
55 = csc-t
56 = sci4s
57 = sci2s2t
58 = sci4t
59 = mci1t
60 = mci2t
61 = mci1s
62 = mci1s1t
63 = mci2s
64 = mci1e
65 = mci1e1t
66 = mci1e2t
67 = mci1e1s
68 = mci1e1s1t
69 = mci1e2s
70 = mci2e
71 = mci2e1t
72 = mci2e2t
73 = mci2e1s
74 = mci2e1s1t
75 = mci2e2s
80 = csc-r
81 = csc-r16
82 = csc-r16m
83 = csc-1r
84 = csc-2r
100 = csc-cctl1
101 = csc-cctl2
110 = csc-mec2
111 = csc-mec4
112 = csc-mec6
113 = csc-fci
114 = csc-fcit
115 = csc-hsci
116 = csc-ctr
150 = sp
151 = eip
152 = fip
153 = hip
154 = sip
155 = trip
156 = fsip
157 = aip
158 = mip
159 = ssp
200 = npm-4000-fddi-sas
201 = npm-4000-fddi-das
202 = npm-4000-1e
203 = npm-4000-1r
204 = npm-4000-2s
206 = npm-4000-2e
210 = npm-4000-4b
211 = npm-4000-8b
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of slots in this chassis. A value of -1 is provided if the number is not applicable or cannot be determined.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Chassis cardTableIfIndex Table
The cardTableIfIndex Table, introduced in IOS Release 10.3, provides logical mapping between a device interface and a card's presence in the chassis. The variables in this table support only the Cisco 4000, Cisco 4500, Cisco7000, and Cisco 7010. By implementing the new MIB table in supported configurations, you can discover statistics about the card. The cardTableIfIndex table can provide significant solutions for CiscoWorks and CiscoView users.
Matches RFC1213 ifTable IfIndex.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the Chassis slot number, or -1 if neither is applicable nor determinable.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the Chassis port number, unique per port on a given card if available.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
This section describes the Cisco MIB variables pertaining to monitoring and managing a device running the DECnet protocol. These variables gather information, such as hop count, host name, total packets received and sent, and number of packets with header errors.
Provides the total number of received bad hello messages.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of bad Level 1 routing packets that have been received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of addresses that are too large.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of received data packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of DECnet packets received with header errors.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of DECnet packets forwarded.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of hello messages received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of output hello messages.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of Level 1 routing packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of Level 1 routing packets sent.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of Level 2 routing packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of Level 2 routing packets sent.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of packets dropped due to access control failure.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of packets that were dropped because they could not be encapsulated.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of transactions denied due to lack of memory.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of packets that were dropped because the router did not know where to forward them.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of packets that were received while not routing DECnet.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of unknown control packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of received packets not in the long DECnet format. This number should always be zero.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of missing routing vectors. Occurs when a packet is received for which there is no entry in the Routing table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of hello messages received from another area by a Level 1 router.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of Level 1 routing packets received from another area.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of Level 2 routing packets received from another area.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of total DECnet packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of packets received that exceeded the maximum hop count set for this device and have been discarded.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
The DECnet Area Routing table, dnAreaTable, includes seven variables: dnAAge, dnACost, dnAHop, dnAIfIndex, dnANextHop, dnAPrio, and dnArea. The index for this table is the DECnet area, or dnArea. If there are n number of areas for the device, there will be n rows in the table.
For example, in Table 24, the DECnet area is 44; the cost is 3; and the maximum number of hops allowed is 2. The interface used to get to area 44 is number 1; the address for the next hop is 46.5; the Routing table was updated 30 seconds ago; and the next hop area is prioritized
as 1.
| dn Area | dnACost | dnAHop |
dnA IfIndex | dnA Next Hop | dnAAge |
dnA Prio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
44 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 46.5 | 30 | 1 |
24 | 60 | 4 | 2 | 24.7 | 12 | 2 |
6 | 17 | 2 | 3 | 6.4 | 60 | 3 |
Provides the age (in seconds) of an area route. When a route is used or has been verified as functional, its age is reset to 0. If a route is not used, its age will gradually grow. Eventually, routes with large ages are cleared out.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the cost of the router area. The cost value can be an integer from 1 through 63. The cost signifies routing preference. The lower the cost, the better the path.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the maximum number of hops for a route to a distant area that the router will accept.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the instance ID of the interface providing the next hop address to the area. A zero denotes self. The DECnet table is indexed by dnArea. For example, dnAIfIndex.5 is the ifIndex for the next hop to DECnet area 5; dnAifIndex 7 is the ifIndex for the next hop to DECnet area 7; and so on.
If dnAIfIndex.5 is set to the value of 4, to get to the next hop for DECnet area 5, the router sends the packet via the interface that has an ifIndex of 4.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the DECnet address for the next hop.
Syntax: Octet string
Access: Read-only
Provides the priority of the next hop router for an area route.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the DECnet area for the device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
End of Table
The DECnet host table, dnHostTable, contains seven variables: dnHAge, dnHCost, dnHHop, dnHIfIndex, dnHNextHop, dnHost, and dnHPrio.
In Table 25, the first DECnet host address in the table is 44.5. Its cost is 3; the number of hops to the host is 4; and the interface number 1 provides the next hop to address 55.6. The route was updated 30 seconds ago, and the priority for the next hop is set to 4.
| dnHost |
dnH Cost |
dnH Hop | dnHIfIndex | dnH Next Hop |
dnH Age |
dnH Prio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
44.5 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 55.6 | 30 | 4 |
54.6 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 33.2 | 20 | 3 |
23.2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 25.1 | 60 | 2 |
Provides the age (in seconds) of the route to the host.When a route is used or has been verified as functional, its age is reset to 0. If a route is not used, the age of the route will gradually grow. Eventually, routes with large ages are cleared out.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the cost of the path to this device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of hops to this device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the index of the interface to the next hop address to the node.
0 denotes self.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the DECnet address of the next hop destination.
Syntax: Octet string
Access: Read-only
Provides the DECnet node address.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the priority of the next hop router for the node.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
End of Table
For example, in Table 26, interface 1 has a cost of 20; interface 2 has a cost of 31; and so on.
| Interface Number | dnIfCost |
|---|---|
1 | 20 |
2 | 31 |
3 | 12 |
Indicates the cost of this interface.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
End of Table
The variables in this group can be used with all Cisco products running the Novell protocol. These variables provide such information as total number of input and output packets, number of packets with errors, and number of packets with service access point (SAP) requests and replies.
Indicates the total number of Novell input broadcast packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell output broadcast packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell input packets with checksum errors.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell input packets with header errors.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell packets forwarded.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell input packets that exceeded the maximum hop count.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell input multicast packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell input packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell input packets for this host.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell packets dropped due to output encapsulation failure.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell packets dropped because the router did not know where to forward them.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell output packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell service access point (SAP) request packets sent.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell SAP reply packets sent.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell SAP request packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell SAP response packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of unknown Novell input packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
The variables in this section, from the VINES group in IOS 10.2, have been deprecated and replaced with the ciscoVINES (cv) group, found in the ciscoMgmt tree.
The variables in this group can be used with all Cisco products running the Banyan Virtual Integrated Network Service (VINES) protocol. This protocol is derived from the Xerox Network Systems (XNS) protocol. These variables provide information such as total number of input and output packets, number of packets with errors, and number of packets with Internet Control Protocol(ICP) requests and replies.
Indicates the total number of VINES broadcast packets forwarded.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES input broadcast packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES output broadcast packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES input packets with checksum errors.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the next VINES subnetwork number that this router will assign to a client.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES echo packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES echo packets generated.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES packets dropped because they could not be encapsulated.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES input packets with header errors.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES packets forwarded.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES input packets that have exceeded the maximum hop count.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES Internet Control Protocol (ICP) packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES ICP packets generated.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES input packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES input packets for this host.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES MAC level echo packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES Media Access Control (MAC) level echo packets generated.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES ICP metric notification packets generated.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the VINES network number of this router.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES broadcast packets not forwarded to all interfaces because the no charges only bit in the packet was set to on.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES packets dropped because the router did not know where to forward them.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES broadcast packets not forwarded to all interfaces because the over 4800 bps bit in the packet was set to on.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES broadcast packets not forwarded to all interfaces because the lan only bit in the packet was set to on.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES output packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES packets that were sent to an actual Banyan server as a proxy for a client.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of received VINES packets that were responses to proxy packets sent by the router.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Indicates the VINES subnet number of this router.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of unknown VINES input packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
The Banyan VINES Interface table, vinesIfTableEntry, contains all the variables described in the Banyan VINES group. The index to the table is ifIndex. ifIndex indicates the number of the interface. If the device has n number of interfaces, the VINES Interface table will contain n rows.
In Table 27, the first column indicates the number of interfaces on the devices. Each of the variables in the VINES Interface table occupies one column; for example, vinesIfMetric is shown in a column, followed by vinesIfEnctype in the next column, and so on.
| Interface Number | vinesIfMetric | vinesIfEnctype | and so on |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | 3 | 1 |
|
2 | 5 | 3 |
|
and so on |
|
|
|
Provides the outgoing access list number for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
vinesIfArpEnabled
Indicates how the router responds to the VINES protocol ARP.
Syntax: Integer (0 = never respond to ARP packets, 1 = always respond to ARP packets, 2 = respond to ARP packets only if servers are not present on the network)
Access: Read-only
Indicates the type of data link encapsulation that will be used on broadcasts sent by the router.
Syntax: Integer (1 = ARPA, 3 = SNAP, 5 = HDLC, 12 = X.25, 13 = X.25, 25 = VINES TR, 27 = Frame Relay, 28 = SMDS, 30 = PPP)
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether fast switching is supported for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Integer (0 = fast switching not requested or not supported,
1 = fast switching requested and supported)
Access: Read-only
Provides the access list number for filtering the content of received VINES routing information.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the access list number for filtering on the source of received VINES routing information.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the VINES protocol line is up or down.
Syntax: Integer (0 = down, 1 = up)
Access: Read-only
Provides the metric value for the VINES protocol. Banyan servers use delay metrics to compute timeouts when communicating with other hosts. The metric value is either manually assigned to the interface by using the vines metric command or is automatically assigned by the system. This number is returned in the format defined in the VINES Protocol Definition.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the access list number for filtering the content of transmitted VINES routing information.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the VINES protocol "propagate" is enabled.
Syntax: Integer (0 = never enabled, 1 = always enabled, 2 = enabled only if there are no local servers on any interface)
Access: Read-only
Provides the redirect interval for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether fast switching is supported for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input ARP query request messages for the VINES protocol. The four types of ARP messages following apply to vinesIfRxArp0-vinesIfRxArp3:
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input ARP query response messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input ARP assignment request messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input ARP assignment response messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input illegal ARP messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the input duplicate broadcast count for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol number of input packets forwarded to another interface.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol number of input packets helpered to another server. Helpered packets are broadcasts received from a serverless network that should be thrown away according to the fields in the VINES IP header. Instead of being thrown away, they are resent on another interface, so that they will be received by a VINES server.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the input broadcast count for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input packets with checksum errors for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input IPC echo messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input packets with format errors for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol number of input packets forwarded to another interface.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input interprocess communications (ICP) error messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input illegal ICP messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input ICP metric messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input IPC messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol number of input packets destined for this router.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input MAC layer echo frames for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol number of input packets that were dropped because there was no route to the destination.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol number of input packets that were discarded because the interface was not configured.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol number of responses to proxy packets.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of illegal input Routing Table Protocol (RTP) type 0 messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input RTP type 1 (request for information) messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of illegal input RTP type 2 messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of illegal input RTP type 3 messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input RTP type 4 update messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input RTP type 5 response messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input RTP type 6 redirect messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of all other illegal input RTP messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input messages from unknown VINES protocols.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input messages from unknown VINES IPC ports.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input SPP messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides VINES protocol number of input packets dropped due to a zero hop count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the VINES protocol serverless support is enabled.
Syntax: Integer (0 = never enabled, 1 = enabled only if servers are not present on the network, 2 = always enabled, 3 = always enabled to flood broadcasts)
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether VINES protocol serverless broadcasting support is enabled.
Syntax: Counter (0 = not enabled, 1 = enabled)
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the VINES protocol split horizon is enabled.
Syntax: Integer (0 = enabled, 1 = disabled)
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output ARP query request messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output ARP query response messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output ARP assignment request messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input ARP assignment response messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides broadcast packets that were generated by the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol output broadcast forwarded from another interface.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol output broadcast helpered to a Banyan server.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output IPC echo messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of packets to be output that failed on access list for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of VINES packets that could not be output because the interface was down.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides VINES packets to be output that could not be encapsulated.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of forwarded packets for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output IPC error messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output IPC metric messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output ICP messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output IPC MAC-layer echo frames for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol output broadcast not sent due to high- speed class. This occurs if a received packet is marked to be sent only on network interfaces with a speed of 4800 bps or greater. The counter is incremented on interfaces with a speed of less than 4800 whenever this type of packet should have been transmitted.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol output broadcast not sent due to LanOnly class. This occurs if a received packet is marked to be sent only if the network interface type is LanOnly. The counter is incremented on interfaces other than type LanOnly whenever this type of packet should have been transmitted.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides VINES protocol output broadcast not sent due to No Charges class. This occurs if a received packet is marked to be sent only if the sender's transmission is free of charge. The counter is incremented on interfaces carrying per-packet charges whenever this type of packet should have been transmitted.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol output broadcast packets that were not sent due to the interface leading back to the source.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of proxy packets sent by the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of illegal output RTP type 0 messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output RTP type 1 (request messages) for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of illegal output RTP type 2 messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of illegal output RTP type 3 messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output RTP type 4 (update messages) for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output RTP type 5 (response messages) for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output RTP type 6 (redirect messages) for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output SPP messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the unicast packets that were generated for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
This group is present in all router-based products running the Xerox Network Systems (XNS) protocol. These variables provide such information as the number of packets forwarded, total number of input packets, and total number of packets transmitted with errors.
Indicates the total number of XNS input broadcast packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS output broadcast packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS input packets with checksum errors.
Syntax: Integer
Syntax: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS echo reply packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS echo reply packets sent.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS echo request packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS echo request packets sent.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS error input packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS error output packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS packets forwarded.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS input packets with header errors.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS broadcast packets forwarded.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS input packets that exceeded the maximum hop count.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS input packets received with multicast addresses.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of input XNS packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS input packets for this host.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of XNS packets dropped because they could not be encapsulated.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS packets that were discarded because the router did not know where to forward them.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS input packets received while XNS routing was not enabled.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS output packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of unknown XNS input packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
This section documents the MIB variables of other vendors that are supported by Cisco.
The Novell subtree contains the Novell MIB (IPX) group, the Novell Link State Protocol (NLSP), and the Routing Information Protocol/Service Advertisement Protocol (RIPSAP) group.
This group contains general information about all instances of IPX on one system. The IPX variables are located in the other Enterprises group.
This table contains one entry for each instance of IPX running on the system. It contains the management information that should be made available by all implementations of the IPX protocol.
Specifies the unique identifier of the instance of IPX to which this row corresponds. This value can be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read
Specifies the validity of this entry in the IPX system table. Setting this field to off indicates that this entry can be deleted from the system table at the IPX implementation's discretion.
Syntax: Integer 1 = off, 2 = on
Access: Read-write
Specifies the network number portion of the IPX address of this system.
Syntax: NetNumber
Access: Read-write
Specifies the node number portion of the IPX address of this system.
Syntax: Octet String (size = 6)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the readable name for this system.
Syntax: Octet string (size (0-48))
Access: Read-write
Specifies the total number of IPX packets received, including those received in error.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of IPX packets discarded due to errors in their headers, including any IPX packet with a size less than the minimum of 30 bytes.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of IPX packets discarded because the destination socket was not open.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of IPX packets received but discarded due to reasons other than those accounted for by ipxBasicSysInHdrErrors, ipxBasicSysInUnknownSockets, ipxAdvSysInDiscards, and ipxAdvSysInCompressDiscards.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of IPX packets received with incorrect checksums.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the total number of IPX packets delivered locally, including packets from local applications.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of times no route to a destination was found.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of IPX packets supplied locally for transmission, not including any packets counted in ipxAdvForwPackets.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
ipxBasicSysOutMalformedRequests
Specifies the number of IPX packets supplied locally that contained errors in their structure.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of outgoing IPX packets discarded due to reasons other than those accounted for in ipxBasicSysOutMalformedRequests, ipxAdvSysOutFiltered, and ipxAdvSysOutCompressDiscards.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the total number of IPX packets transmitted.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the configured maximum number of IPX sockets that can be open at one time.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of IPX socket open calls that failed.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
This table contains one entry for each instance of IPX running on the system. It contains the advanced management information that might not be available from all implementations of the IPX protocol.
Specifies the unique identifier of the instance of IPX to which this row corresponds. This value can be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the maximum number of paths with equal routing metric value that this instance of the IPX can split between when forwarding packets.
Syntax: Integer (1-32)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the maximum number of hops a packet may take.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the number of IPX packets discarded due to exceeding the maximum hop count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: read-only
Specifies the number of incoming IPX packets discarded due to filtering.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of incoming IPX packets discarded due to decompression errors.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of NETBIOS packets received.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of IPX packets forwarded.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of outgoing IPX packets discarded due to filtering.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of outgoing IPX packets discarded due to compression errors.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of circuits known to this instance of IPX.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of currently reachable destinations known to this instance of IPX.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of services known to this instance of IPX.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
This group contains information about all circuits used by IPX on the system.
The Circuit Table contains management information for each circuit known to this system.
Specifies the unique identifier of the instance of IPX to which this entry corresponds. This value can be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer'
Access: Read-write
Specifies the identifier of this circuit, unique within the instance of IPX. This value can be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the validity of this circuit entry. A circuit with this value set to off can be deleted from the table at the IPX implementation's discretion.
Syntax: Integer 1 = off, 2 = on
Access: Read-write
Specifies the value of ifIndex for the interface used by this circuit. This value can be written only when creating a new entry in the table
Syntax: Integer 1 = down, 2 = up, 3 = sleeping
Access: Read-write
Specifies the readable name for the circuit.
Syntax: Octet string (size (0-48)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the type of the circuit.
Syntax: Integer 1 = other, 2 = broadcast, 3 = ptToPt, 4 = wanRIP, 5 = unnumberedRIP, 6 = dynamic, 7 = wanWS
Access: Read-write
Specifies the symbolic name used to reference the dialing information used to create this circuit. This value can be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Octet string (size (0-48))
Access: Read-write
Specifies the maximum size (including header), in bytes, that the system supports locally on this circuit.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the compression state on this circuit. This value can be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer 1 = off, 2 = on
Access: Read-write
Specifies the number of compression slots available on this circuit. This value can be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies whether the information about static routes and services reached via this circuit matches that saved in permanent storage (current).
Syntax: Integer 1 = unknown, 2 = current, 3 = changed, 4 = read, 5 = reading
Access: Read-write
Specifies the number of compressed packets sent.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of compression initialization packets sent.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The number of compressed packet rejected packets sent.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The number of packets sent without being compressed even though compression was turned on for this circuit.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The number of compressed packets received.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The number of compression initialization packets received.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
ipxCircCompressedRejectsReceived
The number of compressed packet rejected packets received.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The number of packets received without having been compressed even though compression was turned on for this circuit.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the media type used on this circuit
Syntax: Octet string (size = 2)
Access: Read-only
Specifies the IPX network number of this circuit.
Syntax: NetNumber
Access: Read-only
The number of times the circuit has changed state.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of times that initialization of this circuit has failed.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the period of time, in milliseconds, that it takes to transmit 1 byte of data, excluding protocol headers, to a destination on the other end of the circuit, if the circuit is free of other traffic.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the amount of data, in bits per second, that can flow through the circuit if there is no other traffic.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the name of the neighboring router on a WAN circuit.
Syntax: Octet string (size = 0-48)
Access: Read-only
Specifies the internal network number of the neighboring router on a WAN circuit.
Syntax: NetNumber
Access: Read-only
This group provides a representation of the forwarding database used by all instances of IPX on the system. This group contains generic routing information that must be provided by any IPX routing protocol.
The Destination table contains information about all known destinations. The routing information shown in this table represents the path currently being used to reach the destination.
Specifies the unique identifier of the instance of IPX to which this row corresponds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the IPX network number of the destination.
Syntax: NetNumber
Access: Read-only
Specifies the routing protocol from which knowledge of this destination was obtained.
Syntax: Integer 1 = other, 2 = local, 3 = rip, 4 = nlsp, 5 = static
Access: Read-only
Specifies the delay in ticks to reach this destination.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of hops necessary to reach the destination.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the unique identifier of the circuit used to reach the next hop.
Syntax: PhysAddress
Access: Read-only
Specifies the NIC address of the next hop.
Syntax: PhysAddress
Access: Read-only
Specifies the IPX network number of the next hop.
Syntax: NetNumbr
Access: Read-only
This table contains the information about all the static routes defined. There may be more than one static route to any given destination. Only the route currently being used will also be present in the Destination Table defined earlier.
Specifies the unique identifier of the instance of IPX to which this row corresponds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the unique identifier of the circuit used to reach the first hop in the static route.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the IPX network number of the route's destination.
Syntax: NetNumber
Access: Read-write
Specifies the validity of this static route. Entries with the value set to off can be deleted from the table at the implementation's discretion.
Syntax: Integer 1 = off, 2 = on
Access: Read-write
Specifies the delay, in ticks, to reach the route's destination.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the number of hops necessary to reach the destination.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
This group contains management information about all known services.
This table contains the services information indexed by service name and type.
Specifies the unique identifier of the instance of IPX to which this entry corresponds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the service type
Syntax: Octet string (size = 2)
Access: Read-only
Specifies the service name.
Syntax: Octet string (size = 1-48)
Access: Read-only
Specifies the protocol from which knowledge of this service was obtained.
Syntax: Integer 1 = other, 2 = local, 4 = nlsp, 5 = static, 6 = sap
Access: Read-only
Specifies the IPX network number portion of the IPX address of the service.
Syntax: NetNumber
Access: Read-only
Specifies the node portion of the IPX address of the service.
Syntax: Octet string (Size = 6)
Access: Read-only
Specifies the socket portion of the IPX address of the service.
Syntax: Octet string (Size = 2)
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of hops to the service.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
This table contains the services information indexed by address, name, and type.
Specifies the unique identifier of the instance of IPX to which this entry corresponds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the IPX network number portion of the IPX address of the service.
Syntax: NetNumber
Access: Read-only
Specifies the socket portion of the IPX address of the service.
Syntax: Octet string (Size = 2)
Access: Read-only
Specifies the name of the service
Syntax: Octet string (Size = 1-48)
Access: Read-only
Specifies the type of service
Syntax: Octet string (Size = 2)
Access: Read-only
Specifies the protocol from which knowledge of this service was obtained.
Syntax: Integer 1 = other, 2 = local, 4 = nlsp, 5 = static, 6 = sap
Access: Read-only
Identifies the number of hops to the service.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
This table contains information for all services reached via a static route.
Specifies the unique identifier of the instance of IPX to which this entry corresponds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the circuit used to reach this service.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the name of the service.
Syntax: Octet string (Size = 1-48)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the type of service.
Syntax: Octet string (Size = 2)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the validity of this static service. Entries with the value set to off may be deleted from the table at the implementation's discretion.
Syntax: Integer 1 = off, 2 = on
Access: Read-write
Specifies the IPX network number portion of the IPX address of the service.
Syntax: NetNumber
Access: Read-write
Specifies the node portion of the IPX address of the service.
Syntax: Octet string (Size = 6)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the socket portion of the IPX address of the service.
Syntax: Octet String (Size = 2)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the number of hops to the service.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
The Novell Link State Protocol (NLSP) MIB defines the management information for the NLSP protocol running in an IPX environment. It provides information in addition to that contained in the IPX MIB itself. All tables in this MIB are linked to an instance of IPX by way of the system instance identifier as defined in the IPX MIB.
This group contains global information about each instance of NLSP running on one system.
This table contains an entry for each instance of NLSP running on the system.
The nlspSysTable describes the NLSP system table.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF NLSPSysEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Specifies that each entry corresponds to one instance of NLSP running on the system.
Syntax: NLSPSysEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the unique identifier of the instance of NLSP to which this corresponds. This value links the instance of NLSP to an instance of IPX running on the system. (The value of nlspSysInstance should be the same as a value of ipxSysInstance.) This value can be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Indicates the operational state of this instance of NLSP.
Syntax: Integer 1 = off, 2 = nlspLevel1Router
Access: Read-write
Identifies the system ID for this instance of NLSP.
Syntax: SystemID
Access: Read-write
Specifies the minimum interval, in seconds, between transmission of LSPs on a nonbroadcast circuit.
Syntax: Integer (1-30)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the minimum interval, in seconds, between transmission of LSPs on a broadcast circuit.
Syntax: Integer (1-30)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the minimum interval, in seconds, between the generation of the same LSP.
Syntax: Integer (1-30)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the maximum interval, in seconds, between the generation of the same LSP.
Syntax: Integer (1-50000)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the value, in seconds, placed in the lifetime field of LSPs generated by this instance of NLSP.
Syntax: Integer (1-50000)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the interval, in seconds, at which NLSP Hellos will be sent on a broadcast circuit, if this system is not the designated router.
Syntax: Integer (1-100)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the interval, in seconds, at which NLSP Hellos will be sent on a nonbroadcast circuit.
Syntax: Integer (1-100)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the interval, in seconds, at which the designated router sends NLSP Hellos on a broadcast circuit.
Syntax: Integer (1-100)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the holding time multiplier used to specify the holding time for NLSP neighbor entries as a function of the NLSP Hello interval.
Syntax: Integer (2-20)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the interval, in seconds, between generation of Complete Sequence Number Packets by a designated router on a broadcast circuit.
Syntax: Integer (1-600)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the minimum interval, in seconds, between transmission of Partial Sequence Number Packets
Syntax: Integer (1-60)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the number of seconds to delay in the waiting state before entering the on state.
Syntax: Integer (1-300)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the maximum size of Level 1 LSPs originated by this instance of NLSP.
Syntax: Integer (512-4096)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the version number of this instance of NLSP.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of corrupt LSPs detected.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the NLSP Level 1 database is overloaded.
Syntax: Integer 1 = no, 2 = yes
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of times the NLSP Level 1 LSP database has become overloaded.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of times the router attempted to exceed NLSP's maximum sequence number.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of times a sequence number skip has occurred.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of LSPs transmitted by this system.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of LSPs received by this system.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of times a zero-aged copy of the router's own LSP has been received from some other node.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of times that a received NLSP packet was rejected because its version number was invalid.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of times that an incorrectly formatted NLSP packet was received.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether this instance of NLSP knows of an NLSP Level 2 router that currently can reach other areas using the default metric.
Syntax: Integer 1 = no, 2 = yes
Access: Read-only
Specifies the system ID of the nearest NLSP Level 2 router that currently can reach other areas using the default metric. The value is undefined if the value of nlspSysNearestL2DefaultExists is no.
Syntax: SystemID
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of times this instance of the NLSP has been unable to obtain needed resources (memory and so forth).
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The System Area Address table contains the area addresses configured for NLSP.
Specifies the unique identifier of the instance of NLSP and IPX (via ipxSysInstance) to which this row corresponds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the network address portion of the area address.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE(4))
Access: Read-write
Specifies the mask portion of the area address.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE(4))
Access: Read-write
The Actual Area Address table contains the area addresses actually used by NLSP.
Specifies the unique identifier of the instance of NLSP and IPX (via ipxSysInstance) to which this row corresponds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the network address portion of the area address.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE(4))
Access: Read-write
Specifies the mask portion of the area address.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE(4))
Access: Read-write
This group contains the NLSP information for each circuit known to this system.
Specifies the unique identifier of the instance of NLSP and IPX (via ipxSysInstance) to which this entry corresponds. This value can be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the identifier of this circuit, unique within the instance of NLSP. This value can be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Indicates whether NLSP information can be sent/received over this circuit.
Syntax: Integer 1 = off, 2 = on
Access: Read-write
Specifies the maximum pace, in packets per second, at which NLSP packets can be sent on this circuit.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the interval, in seconds, between NLSP Hello packets sent on this circuit.
Syntax: Integer (1-100)
Access: Read-write
Identifies the NLSP default cost of this circuit for Level 1 traffic.
Syntax: Integer (1-63)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the priority for becoming the NLSP LAN Level 1 Designated Router on a broadcast circuit.
Syntax: Integer (1-127)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the NLSP ID for this circuit.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE(7))
Access: Read-only
Specifies the system ID of the NLSP LAN Level 1 Designated Router on this circuit.
Syntax: SystemID
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of times the NLSP LAN Level 1 Designated Router has changed on this circuit.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of times an NLSP neighbor state change has occurred on this circuit.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of times that an NLSP neighbor has been rejected on this circuit.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of NLSP packets sent on this circuit.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of NLSP packets received on this circuit.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the actual maximum packet size (including header), in bytes, used on this circuit.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of PSNPs sent on this circuit.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of PSNPs received on this circuit.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
This group contains NLSP forwarding information in addition to that contained in the IPX forwarding group.
The Destination table contains additional NLSP forwarding information about all destinations learned about via NLSP.
The Destination table contains information about all known destinations learned about via NLSP.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF NLSPDestEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Specifies that each entry corresponds to one destination.
Syntax: NLSPDestEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the unique identifier of the instance of NLSP and IPX (via ipxSysInstance) to which this row corresponds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the IPX network number of the destination.
Syntax: NetNumber
Access: Read-only
Specifies the destination NLSP ID (6-octet system ID plus 1-octet pseudo-node ID).
Syntax: NLSPID
Access: Read-only
Specifies the estimated delay, in milliseconds, to reach the destination.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the estimated throughput, in bits per second, to the destination.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the NLSP ID (6-octet system ID plus 1-octet pseudo-node ID) of the next hop.
Syntax: NLSPID
Access: Read-only
Specifies the total path default cost to reach this destination.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
This group contains management information for each neighboring NLSP router known to the system.
Specifies the unique identifier of the instance of NLSP and IPX (via ipxSysInstance) to which this row corresponds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the identifier of the parent circuit of this neighbor within this instance of the NLSP and IPX.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the identifier for this NLSP neighbor entry, unique within the parent circuit.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the state of the connection to the neighboring NLSP router.
Syntax: Integer 1 = initializing, 2 = up, 3 = failed, 4 = down
Access: Read-only
Specifies the NIC Address of the neighboring NLSP router.
Syntax: PhysAddress
Access: Read-only
Specifies the type of the neighboring NLSP router.
Syntax: Integer = unknown, 2 = nlspLevel1 Router
Access: Read-only
Specifies the neighboring NLSP router's system ID.
Syntax: SystemID
Access: Read-only
Specifies the readable name for the neighboring NLSP router.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE(0-48))
Access: Read-only
Specifies the usage of the connection to the neighboring NLSP router.
Syntax: Integer 1 = undefined, 2 = level 1
Access: Read-only
Specifies the initial holding time, in seconds, for this NLSP neighbor entry as specified in the NLSP Hello packet.
Syntax: Integer (1-65535)
Access: Read-only
Specifies the remaining time to live, in seconds, for this NLSP neighbor entry.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the priority of the neighboring NLSP router for becoming the LAN Level 1 Designated router if the value of nlspNeighSysType is nlspLevel1Router.
Syntax: Integer (1-127)
Access: Read-only
The translation group contains tables providing mappings between network numbers, NLSP system IDs, and router names.
Maps NLSP system IDs to router names and IPX network numbers.
Maps NLSP system IDs to router names and IPX network numbers.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF NLSPIDMapEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Specifies that each entry maps one NLSP system ID to its corresponding router name and IPX network number.
Syntax: NLSPIDMapEntry
Access: Not-accessible
The unique identifier of the instance of NLSP and IPX (via ipxSysInstance) to which this row corresponds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
The NLSP ID (6-octet system ID plus the pseudo-node ID).
Syntax: NLSPID
Access: Read-only
The readable name corresponding to this NLSP ID.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE(0-48))
Access: Read-only
The IPX network number corresponding to this NLSP ID.
Syntax: NetNumber
Access: Read-only
Maps IPX network numbers to router names and NLSP IDs.
Maps IPX network numbers to router names and NLSP IDs.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF NLSPNetMapEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Each entry maps one IPX network number to its corresponding router name and NLSP ID.
Syntax: NLSPNetMapEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the unique identifier of the instance of NLSP and IPX (via ipxSysInstance) to which this row corresponds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the IPX network number.
Syntax: NetNumber
Access: Read-only
Specifies the router name corresponding to the IPX network number.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE(0-48))
Access: Read-only
Specifies the NLSP ID corresponding to the IPX network number.
Syntax: NLSPID
Access: Read-only
Maps router names to their corresponding IPX network number and NLSP ID.
Maps router names to the corresponding IPX network number and NLSP ID.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF NLSPNameMapEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Specifies that each entry maps one router name to its corresponding IPX network number and NLSP ID.
Syntax: NLSPNameMapEntry
Access: Not-accessible
The unique identifier of the instance of NLSP and IPX (via ipxSysInstance) to which this row corresponds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the readable name for this system.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE(0-48))
Access: Read-only
Specifies the IPX network number corresponding to the router name.
Syntax: NetNumber
Access: Read-only
Specifies the NLSP ID corresponding to the router name. This value is undefined if the value of nlspSysState is off.
Syntax: NLSPID
Access: Read-only
The Graph group provides a representation of the network topology. The group is optional.
Contains an entry for each node in the graph.
Contains an entry for each node in the graph.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF NLSPNodeEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Each entry corresponds to one graph node.
Syntax: NLSPNodeEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the unique identifier of the instance of NLSP and IPX (via ipxSysInstance) to which this row corresponds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the NLSP ID for this node.
Syntax: NLSPID
Access: Read-only
Specifies the IPX network number of this node.
Syntax: NetNumber
Access: Read-only
Specifies the type of system the node represents.
Syntax: Integer 1 = unknown, 2 = nlspLevel1Router, 3 = nlspLevel2Router, 4 = router, 5 = network
Access: Read-only
Specifies the estimated delay, in milliseconds, to reach the destination represented by this node.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the estimated throughput, in bits per second, to the destination represented by this node.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the maximum packet size, in bytes, that can be sent to the destination represented by this node.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the cost to reach this node. The cost value can be a whole number from 0-1023. Lower bandwidth links usually have higher cost; whereas, faster links usually have lower cost. The cost of a single link is 0-63; the cost of a path is 0-1023.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether this node is overloaded.
Syntax: Integer 1 = no, 2 = yes
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the destination represented by this node is reachable.
Syntax: Integer 1 = no, 2 = yes
Access: Read-only
Contains the entries for all of the links in the graph.
Specifies the unique identifier of the instance of NLSP and IPX (via ipxSysInstance) to which this row corresponds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the NLSP ID (6-byte system ID plus 1-octet pseudo-node ID) of the node to which this link belongs.
Syntax: NLSPID
Access: Read-only
Specifies the unique value identifying the link within the node.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the NLSP ID (6-byte system ID plus 1-octet pseudo-node ID) of the neighboring node.
Syntax: NLSPID
Access: Read-only
Specifies the cost to use this link to reach this node from the neighboring node.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the maximum size, in bytes, of a packet that can be sent over this link.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the link's maximum throughput, in bits per second.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the delay, in milliseconds, on this link.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the media type of this link.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE(2))
Access: Read-only
Specifies the cost to use this link to reach the neighbor from this node.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Allows the path(s) that a packet can take to reach a destination to be reconstructed. The entries in this table represent those links that are one hop closer to the source and would be used for the minimum cost path(s) to reach the destination.
Specifies the path table.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF NLSPPathEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Each row in this table represents a link to a node that is one hop closer to the source and would be used for the minimum cost path(s) to reach the destination.
Syntax: NLSPPathEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the unique identifier of the instance of NLSP and IPX (via ipxSysInstance) to which this row corresponds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the NLSP ID (6-octet system ID plus 1-octet pseudo-node ID) of this destination.
Syntax: NLSPID
Access: Read-only
Specifies the unique value identifying this link within the destination node.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
This table contains information about all of the XRoutes provided by a node in the graph.
Contains the information about the XRoutes associated with a node in the graph.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF NLSPGraphXRouteEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Each entry in the table contains the information for one XRoute associated with the node.
Syntax: NLSPGraphXRouteEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the unique identifier of the instance of NLSP and IPX (via ipxSysInstance) to which this entry corresponds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the NLSP ID of the node.
Syntax: NLSPID
Access: Read-only
Specifies the IPX network number of the XRoute destination.
Syntax: NetNumber
Access: Read-only
Specifies the cost to reach the XRoute's destination.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of hops necessary to reach the XRoute's destination.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
This table contains information about all of the services provided by a node in the graph.
This table contains the information about the services associated with a node in the graph.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF NLSPGraphServEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Each entry in the table contains the information for one service associated with the node.
Syntax: NLSPGraphServEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the unique identifier of the instance of NLSP and IPX (via ipxSysInstance) to which this entry corresponds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the NLSP ID of the node.
Syntax: NLSPID
Access: Read-only
Specifies the service name.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE(1-48))
Access: Read-only
Specifies the service type's hexadecimal value.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE(2))
Access: Read-only
Specifies the service type.
Syntax: Integer 1 = unknown
Access: Read-only
The IPX network number portion of the IPX address of the service.
Syntax: NetNumber
Access: Read-only
Specifies the node portion of the IPX address of the service.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE(6))
Access: Read-only
Specifies the socket portion of the IPX address of the service.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE(2))
Access: Read-only
The LSP group provides a representation of NLSP's LSP database. This group is optional.
The LSP header table contains summary information about each LSP in the database, as well as an OCTET STRING containing the entire LSP header.
Specifies the LSP header table.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF NLSPLSPEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Each entry corresponds to one LSP's header.
Syntax: NLSPLSPEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the unique identifier for the instance of NLSP and IPX (via ipxSysInstance) to which this entry corresponds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the value that uniquely identifies this LSP.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE(8))
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of seconds prior to the expiration of the LSP.
Syntax: Integer (0-65535)
Access: Read-only
Specifies the sequence number of the LSP.
Syntax: Integer (0-255)
Access: Read-only
Specifies the checksum value of the LSP.
Syntax: Integer (0-65535)
Access: Read-only
Specifies the type of the router that sent the LSP.
Syntax: Integer 1 = unknown, 2 = nlspLevel1Router
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the sending router's LSP database is overloaded.
Syntax: Integer 1 = no, 2 = yes
Access: Read-only
Specifies the complete LSP header.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE(27))
Access: Read-only
The LSP options table is used to obtain each option contained in an LSP.
Specifies the LSP Options table.
Syntax: SEQUENCE OF NLSPLSPOptEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Each entry corresponds to one option from an LSP.
Syntax: NLSPLSPOptEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the unique identifier of the instance of NLSP and IPX (via ipxSysInstance) to which this entry corresponds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the value that uniquely identifies the LSP.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE(8))
Access: Read-only
Specifies the value that uniquely identifies this option within the LSP.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the code that identifies the type of the option.
Syntax: Integer (0-255)
Access: Read-only
Indicates the length of the option's value field.
Syntax: Integer (0-255)
Access: Read-only
Specifies the option's value field.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE(0-255))
Access: Read-only
This MIB defines the management information for the RIP and SAP protocols running in an IPX environment. It provides information in addition to that contained in the IPX MIB itself. All tables in this MIB are linked to an instance of IPX via the system instance identifier as defined in the IPX MIB.
This group contains global information about each instance of RIP/SAP running on one system.
This table contains an entry for each instance of RIP running on the system.
Specifies the RIP system table.
Syntax: Sequence of RIPSysEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Specifies that each entry corresponds to one instance of RIP running on the system.
Syntax: RIPSysEntry
Access: Not-accessible
The unique identifier of the instance of RIP to which this row corresponds. This value links the instance of RIP to an instance of IPX running on the system (in other words, the value of ripSysInstance should be the same as a value of ipxSysInstance). This value can be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Indicates the operational state of this instance of RIP.
Syntax: Integer 1 = off, 2 = on
Access: Read-write
Specifies the number of times that an incorrectly formatted RIP packet was received.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
This table contains an entry for each instance of SAP running on the system.
Identifies the SAP system table.
Syntax: Sequence of SAPSysEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Specifies that each entry corresponds to one instance of SAP running on the system.
Syntax: SAPSysEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Specifies the unique identifier of the instance of SAP to which this row corresponds. This value links the instance of SAP to an instance of IPX running on the system (in other words, the value of SApSysInstance should be the same as a value of ipxSysInstance). This value can be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Indicates the operational state of this instance of SAP.
Syntax: Integer 1 = off, 2 = on
Access: Read-write
Specifies the number of times that an incorrectly formatted SAP packet was received.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
This group contains RIP and SAP management information for each circuit known to this system.
The RIP Circuit table contains an entry for the RIP information for each circuit known to the system.
Specifies the unique identifier of the instance of RIP and IPX (by means of ipxSysInstance) to which this entry corresponds. This value can be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the identifier of this circuit, unique within the instance of RIP. This value corresponds to the circuit identifier found in ipxCircIndex. This value can be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Indicates whether RIP information may be sent/received over this circuit.
Syntax: Integer 1 = off, 2 = on, 3 = auto-on, 5 = auto-off
Access: Read-write
Specifies the maximum pace, in packets per second, at which RIP packets may be sent on this circuit.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the RIP periodic update interval, in seconds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the holding multiplier for information received in RIP periodic updates.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the RIP packet size used on this circuit.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the number of RIP packets sent on this circuit.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of RIP packets received on this circuit.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The SAP Circuit table contains an entry for the SAP information for each circuit known to the system.
Identifies the SAP Circuit table.
Syntax: Sequence of SAPCircEntry
Access: not-accessible
Specifies that each entry corresponds to one circuit known to the system.
Syntax: SAPCircEntry
Access: Not-accessible
The unique identifier of the instance of SAP and IPX (by means of ipxSysInstance) to which this entry corresponds. This value may be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the identifier of this circuit, unique within the instance of SAP. This value corresponds to the circuit identifier found in ipxCircIndex. This value may be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Indicates whether SAP information can be sent/received over this circuit.
Syntax: Integer 1 = off, 2 = on, 3 = auto-on, 4 = auto-off
Access: Read-write
Specifies the maximum pace, in packets per second, at which SAP packets can be sent on this circuit.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the SAP periodic update interval, in seconds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the holding multiplier for information received in SAP periodic updates.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the SAP packet size used on this circuit.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Indicates whether to respond to SAP to get the nearest server requests received on this circuit.
Syntax: Integer 1 = no, 2 = yes
Access: Read-write
Indicates the number of SAP packets sent on this circuit.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of SAP packets received on this circuit.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
SNMP traps are set up on specific devices to obtain useful information such as the change in a device configuration or the absence of proper user authentication with a request. When the SNMP agent on the device detects a change, it immediately sends an SNMP trap to the NMS system.
Network managers must be wary of depending on traps for vital information. Because traps are sent as datagrams with no acknowledgement they can be lost in the network due to, for example, congestion or errors.
Cisco products, including the routers, access servers and communication servers, and protocol translators, support the SNMP traps specified in RFC 1213, Management Information Base for Network Management of TCP/IP-based Internets: MIB-II. The warmStart trap in MIB II is not supported by Cisco.
Following are the standard SNMP traps supported by Cisco:
This trap is sent to the NMS system if the SNMP agent detects that proper user authentication was not provided with a request. User authentication enhances the security of the devices by ensuring that only privileged users with valid community strings are allowed to access the system.
The SNMP agent sends a coldStart trap when its device has reinitialized itself.
An egpNeighborLoss trap indicates that an EGP (Exterior Gateway Protocol) neighbor is down. Neighboring routers are two routers that have interfaces to a common network and exchange routing information. An exterior router uses EGP to advertise its knowledge of routes to networks within its autonomous system. It sends these advertisements to the core routers, which then readvertise their collected routing information to the exterior router. A neighbor or peer router is any router with which the router communicates using EGP.
A linkDown trap is sent by the SNMP agent to the NMS system if a link in a configuration of a device has been shutdown. For example, the link could be a serial line connecting two devices or an Ethernet link between two networks.
A linkUp trap indicates the recognition of an SNMP agent that a link in a configuration of a device has become active.
Following are the Cisco private SNMP traps that are implemented in Cisco products including the router, access server and communication server, and protocol translator.
This trap signifies that the specified circuit has come up.
This trap signifies that the specified circuit has gone down.
A ciscoPingCompleted trap is sent at the completion of a sequence of pings if such a trap was requested when the sequence was initiated.
This trap is sent after a reload command is issued.
The tty trap indicates that a TCP connection, which existed previously for a tty session, has been terminated.
The following variables in RFC 1285 are supported in Software Release 9.0 and later:
snmpFddiSMTNumber
snmpFddiSMTIndex
snmpFddiSMTStationId
snmpFddiSMTOpVersionId
snmpFddiSMTHiVersionId
snmpFddiSMTLoVersionId
snmpFddiSMTCFState
snmpFddiMACNumber
snmpFddiMACSMTIndex
snmpFddiMACIndex
snmpFddiMACTReq
snmpFddiMACTNegj
snmpFddiMACTMax
snmpFddiMACTvxValue
snmpFddiMACMin
snmpFddiMACFrameCts
snmpFddiMACErrorCts
snmpFddiMACLostCts
snmpFddiMACChipSet
This section lists the Cisco private MIB variables that have been introduced after Software Release 8.0.
The following list describes the MIB variables introduced with Software Release 8.2:
writeMem
writeNet
busyPer
avgBusy1
avgBusy5
idleCount
idleWired
locIfCarTrans
locIfReliab
locIfDelay
locIfLoad
locIfCollisions
tsLineNoise
dnAreaTable
dnACost
dnAHop
dnAifIndex
dnANextHop
dnAAge
dnAPrio
vinesInput
vinesOutput
vinesLocaldest
vinesForwarded
vinesBcastin
vinesBcastout
vinesBcastfwd
vinesNotlan
vinesNotgt4800
vinesNocharges
vinesFormaterror
vinesCksumerr
vinesHopcout
vinesNoroute
vinesEncapsfailed
vinesUnknown
vinesIcpIn
vinesIcpOut
vinesMetricOut
vinesMacEchoIn
vinesMacEchoOut
vinesEchoIn
vinesEchoOut
The following list describes the MIB variables introduced with Software Release 8.3:
bufferHgsize
bufferHgTotal
bufferHgFree
bufferHgMax
bufferHgHit
bufferHgMiss
bufferHgTrim
bufferHgCreate
locIfInputQueueDrops
locIfOutputQueueDrops
ipNoaccess
actCheckPoint
tsMsgTtyLine
tsMsgIntervaltim
tsMsgDuration
tsMsgTest
tsMsgTmpBanner
tsMsgSend
dnIfTable
dnIfCost
The following list provides the MIB variables introduced with Software Release 9.0:
netConfigProto
hostConfigProto
sysConfigAddr
sysConfigName
sysConfigProto
sysClearARP
sysClearInt
envPresent
envTestPt1Descr
envTestPt1Measure
envTestPt2Descr
envTestPt2Measure
envTestPt3Descr
envTestPt3Measure
envTestPt4Descr
envTestPt4Measure
envTestPt5Descr
envTestPt5Measure
envTestPt6Descr
envTestPt6Measure
locIfDescr
locIfPakmon
The following list provides the MIB variables introduced with Software Release 9.1:
envTestPt4MarginPercent
envTestPt5MarginPercent
envTestPt6MarginPercent
envTestPt1last
envTestPt2last
envTestPt3last
envTestPt4last
envTestPt5last
envTestPt6last
envTestPt1MarginVal
envTestPt2MarginVal
envTestPt3MarginVal
envTestPt4MarginVal
envTestPt5MarginVal
envTestPt6MarginVal
envTestPt1warn
envTestPt2warn
envTestPt3warn
envTestPt4warn
envTestPt5warn
envTestPt6warn
envFirmVersion
envTechnicianID
envType
envBurnDate
envSerialNumber
locIfSlowInPkts
locIfSlowOutPkts
locIfSlowInOctets
locIfSlowOutOctets
locIfFastInPkts
locIfFastOutPkts
locIfFastInOctets
locIfFastOutOctets
locIfotherInPkts
locIfotherOutPkts
locIfotherInOctets
locIfotherOutOctets
locIfipInPkts
locIfipOutPkts
locIfipInOctets
locIfipOutOctets
locIfdecnetInPkts
locIfdecnetOutPkts
locIfdecnetInOctets
locIfdecnetOutOctets
locIfxnsInPkts
locIfxnsOutPkts
locIfxnsInOctets
locIfxnsOutOctets
locIfclnsInPkts
locIfclnsOutPkts
locIfclnsInOctets
locIfclnsOutOctets
locIfappletalkInPkts
locIfappletalkOutPkts
locIfappletalkInOctets
locIfappletalkOutOctets
locIfnovellInPkts
locIfnovellOutPkts
locIfnovellInOctets
locIfnovellOutOctets
locIfapolloInPkts
locIfapolloOutPkts
locIfapolloInOctets
locIfapolloOutOctets
locIfvinesInPkts
locIfvinesOutPkts
locIfvinesInOctets
locIfvinesOutOctets
locIfbridgedInPkts
locIfbridgedOutPkts
locIfbridgedInOctets
locIfbridgedOutOctets
locIfsrbInPkts
locIfsrbOutPkts
locIfsrbInOctets
locIfsrbOutOctets
locIfchaosInPkts
locIfchaosOutPkts
locIfchaosInOctets
locIfchaosOutOctets
locIfpupInPkts
locIfpupOutPkts
locIfpupInOctets
locIfpupOutOctets
locIfmopInPkts
locIfmopOutPkts
locIfmopInOctets
locIfmopOutOctets
locIflanmanInPkts
locIflanmanOutPkts
locIflanmanInOctets
locIflanmanOutOctets
locIfstunInPkts
locIfstunOutPkts
locIfstunInOctets
locIfstunOutOctets
locIfspanInPkts
locIfspanOutPkts
locIfspanInOctets
locIfspanOutOctets
locIfarpInPkts
locIfarpOutPkts
locIfarpInOctets
locIfarpOutOctets
locIfprobeInPkts
locIfprobeOutPkts
locIfprobeInOctets
locIfprobeOutOctets
flashSize
flashFree
flashcontoller
flashcard
flashVPP
flashErase
flashEraseTime
flashEraseStatus
flashToNet
flashToNetTime
flashToNetStatus
netToFlash
netToFlashTime
netToFlashStatus
flashStatus
flashEntries
flashDirName
flashDirSize
flashDirStatus
The following list identifies the MIB variables introduced with Software Release 9.21:
locIfDribbleInputs
vinesProxy
vinesProxyReply
vinesNet
vinesSubNet
vinesClient
vinesIfMetric
vinesIfEnctype
vinesIfAccesslist
vinesIfInputNetworkFilter
vinesIfInputRouterFilter
vinesIfOutputNetworkFilter
vinesIfPropagate
vinesIfArpEnabled
vinesIfServerless
vinesIfServerlessBcast
vinesIfRedirectInterval
vinesIfSplitDisabled
vinesIfLineup
vinesIfFastokay
vinesIfRouteCache
vinesIfIn
vinesIfOut
vinesIfInBytes
vinesIfOutBytes
vinesIfRxNotEnabled
vinesIfRxFormatError
vinesIfRxLocalDest
vinesIfRxBcastin
vinesIfRxForwarded
vinesIfRxNoRoute
vinesIfRxZeroHopCount
vinesIfRxChecksumError
vinesIfRxArp0
vinesIfRxArp1
vinesIfRxArp2
vinesIfRxArp3
vinesIfRxArpIllegal
vinesIfRxIcpError
vinesIfRxIcpMetric
vinesIfRxIcpIllegal
vinesIfRxIpc
vinesIfRxRtp0
vinesIfRxRtp1
vinesIfRxRtp2
vinesIfRxRtp3
vinesIfRxRtp4
vinesIfRxRtp5
vinesIfRxRtp6
vinesIfRxRtpIllegal
vinesIfRxSpp
vinesIfRxBcastHelpered
vinesIfRxBcastForwarded
vinesIfRxBcastDuplicate
vinesIfRxEcho
vinesIfRxMacEcho
vinesIfRxProxyReply
vinesIfTxUnicast
vinesIfTxBcast
vinesIfTxForwarded
vinesIfTxFailedEncaps
vinesIfTxFailedAccess
vinesIfTxFailedDown
vinesIfTxNotBcastToSource
vinesIfTxNotBcastNotlan
vinesIfTxNotBcastNotgt4800
vinesIfTxNotBcastPpcharge
vinesIfTxBcastForwarded
vinesIfTxBcastHelpered
vinesIfTxArp0
vinesIfTxArp1
vinesIfTxArp2
vinesIfTxArp3
vinesIfTxIcpError
vinesIfTxIcpMetric
vinesIfTxIpc
vinesIfTxRtp0
vinesIfTxRtp1
vinesIfTxRtp2
vinesIfTxRtp3
vinesIfTxRtp4
vinesIfTxRtp5
vinesIfTxRtp6
vinesIfTxSpp
vinesIfTxEcho
vinesIfTxMacEcho
vinesIfTxProxy
chassisType
chassisVersion
chassisId
romVersion
romSysVersion
processorRam
nvRAMSize
nvRAMUsed
configRegister
configRegNext
cardTable
cardTableEntry
cardIndex
cardType
cardDescr
cardSerial
cardHwVersion
cardSwVersion
cardSlotNumber
chassisSlots
The following list identifies the MIB variables introduced with IOS Release 10.0:
ipxThresh
ipxactLostPkts
ipxactLostByts
ipxactSrc
ipxactDst
ipxactPkts
ipxactByts
ipxactAge
ipxckactSrc
ipxckactDst
ipxckactPkts
ipckactByts
ipxckactAge
ipxactCheckPoint
vinesIfInputNetworkFilter
vinesIfInputRouterFilter
vinesIfOutputNetworkFilter
cardIfIndex
cardIfSlotNumber
cardIfPortNumber
The following list identifies the MIB variables introduced with IOS Release 10.2:
cipCardClawEntry
cipCardClawIndex
cipCardClawConnected
cipCardClawConfigTable
cipCardClawConfigEntry
cipCardClawConfigPath
cipCardClawConfigDevice
cipCardClawConfigIpAddr
cipCardClawConfigHostName
cipCardClawConfigRouterName
cipCardClawConfigHostAppl
cipCardClawConfigRouterAppl
cipCardClawDataXferStatsTable
cipCardClawDataXferStatsEntry
cipCardClawDataXferStatsBlocksRead
cipCardClawDataXferStatsBlocksWritten
cipCardClawDataXferStatsBytesRead
cipCardClawDataXferStatsBytesWritten
cipCardClawDataXferStatsHCBytesRead
cipCardClawDataXferStatsHCBytesWritten
cipCardClawDataXferStatsReadBlocksDropped
cipCardClawDataXferStatsWriteBlocksDropped
cipCardClawDataXferStatsBufferGetRetryCount
cipCardDtrBrdIndex
cipCardDtrBrdType
cipCardDtrBrdStatus
cipCardDtrBrdSignal
cipCardDtrBrdOnline
implicitIncidents
codeViolationErrors
linkFailureSignalOrSyncLoss
linkFailureNOSs
linkFailureSequenceTimeouts
linkFailureInvalidSequences
linkIncidentTrapCause
cipCardsubChannelIndex
cipCardsubChannelConnections
cipCardsubChannelCancels
cipCardsubChannelSelectiveResets
cipCardsubChannelSystemResets
cipCardsubChannelDeviceErrors
cipCardsubChannelWriteBlocksDropped
cipCardsubChannelLastSenseData
cipCardSubchannelLastSenseDataTime
cipCardSubChannelCuBusies
cipCardEntryIndex
cipCardEntryName
cipCardEntryTotalMemory
cipCardEntryFreeMemory
cipCardEntryCpuUtilization
cipCardEntryTimeSinceLastReset
ciscoFlash
ciscoPingAddress
ciscoPingTable
ciscoPingEntry
ciscoPingProtocol
ciscoPingSerialNumber
ciscoPingPacketCount
ciscoPingPacketSize
ciscoPingPacketTimeout
ciscoPingDelay
ciscoPingTrapOnCompletion
ciscoPingSentPackets
ciscoPingReceivedPackets
ciscoPingMinRtt
ciscoPingAvgRtt
ciscoPingMaxRtt
ciscoPingCompleted
ciscoPingEntryOwner
ciscoPingEntryStatus
ipxBasicSysInstance
ipxBasicSysExistState
ipxBasicSysNetNumber
ipxBasicSysNode
ipxBasicSysName
ipxBasicSysInReceives
ipxBasicSysInHdrErrors
ipxBasicSysInUnknownSockets
ipxBasicSysInDiscards
ipxBasicSysInBadChecksums
ipxBasicSysInDelivers
ipxBasicSysNoRoutes
ipxBasicSysOutRequests
ipxBasicSysOutMalformedRequests
ipxBasicSysOutDiscards
ipxBasicSysOutPackets
ipxBasicSysConfigSockets
ipxBasicSysOpenSocketFails
ipxAdvSysInstance
ipxAdvSysMaxPathSplits
ipxAdvSysMaxHops
ipxAdvSysInTooManyHops
ipxAdvSysInFiltered
ipxAdvSysInCompressDiscards
ipxAdvSysNETBIOSPackets
ipxAdvSysForwPackets
ipxAdvSysOutFiltered
ipxAdvSysOutCompressDiscards
ipxAdvSysCircCount
ipxAdvSysDestCount
ipxAdvSysServCount
ipxCircSysInstance
ipxCircIndex
ipxCircExistState
ipxCircOperState
ipxCircName
ipxCircType
ipxCircDialName
ipxCircLocalMaxPacketSize
ipxCircCompressState
ipxCircCompressSlots
ipxCircStaticStatus
ipxCircCompressedSent
ipxCircCompressedInitSent
ipxCircCompressedRejectsSent
ipxCircUncompressedSent
ipxCircCompressedReceived
ipxCircCompressedInitReceived
ipxCircCompressedRejectsReceived
ipxCircUncompressedReceived
ipxCircMediaType
ipxCircNetNumber
ipxCircStateChanges
ipxCircInitFails
ipxCircDelay
ipxCircThroughput
ipxCircNeighRouterName
ipxCircNeighInternalNetNum
ipxDestSysInstance
ipxDestNetNum
ipxDestProtocol
ipxDestTicks
ipxDestHopCount
ipxDestNextHopCircIndex
ipxDestNextHopNICAddress
ipxDestNextHopNetNum
ipxStaticRouteSysInstance
ipxStaticRouteCircIndex
ipxStaticRouteNetNum
ipxStaticRouteExistState
ipxStaticRouteTicks
ipxStaticRouteHopCount
ipxServSysInstance
ipxServType
ipxServName
ipxServProtocol
ipxServNetNum
ipxServNode
ipxServSocket
ipxServHopCount
ipxDestServSysInstance
ipxDestServNetNum
ipxDestServSocket
ipxDestServName
ipxDestServType
ipxDestServProtocol
ipxDestServHopCount
ipxStaticServSysInstance
ipxStaticServCircIndex
ipxStaticServName
ipxStaticServType
ipxStaticServExistState
ipxStaticServNetNum
ipxStaticServNode
ipxStaticServSocket
ipxStaticServHopCount
ripSysInstance
ripSysState
ripSysIncorrectPackets
sapSysInstance
sapSysState
sapSysIncorrectPackets
ripCircSysInstance
ripCircIndex
ripCircState
ripCircPace
ripCircUpdate
ripCircAgeMultiplier
ripCircPacketSize
ripCircOutPackets
ripCircInPackets
sapCircSysInstance
sapCircIndex
sapCircState
sapCircPace
sapCircUpdate
sapCircAgeMultiplier
sapCircPacketSize
sapCircGetNearestServerReply
sapCircOutPackets
sapCircInPackets
cardIfIndex
cardIfSlotNumber
cardIfPortNumber
The loctcp table has been replaced by the ciscoloctcp table.
The IOS Release 10.1 ping object was replaced by the IOS 10.2 ciscoPing table.
The loctcp table has been replaced by the ciscoloctcp table.
Internetwork Operating System (IOS) Release 10.3(2)
The following list identifies the MIB variables introduced with IOS Release 10.3(2):
ciscoRptrPortMDIStatus
ciscoRptrPortLinkTestEnabled
ciscoRptrPortLinkTestFailed
ciscoRptrPortAutoPolarityEnabled
ciscoRptrPortAutoPolarityCorrected
ciscoRptrPortSrcAddrCtrl
ciscoRptrPortAllowedSrcAddr
ciscoRptrPortAllowedSrcAddrStatus
ciscoRptrPortLastIllegalSrcAddr
The following list identifies the MIB variables introduced with IOS Release 10.3:
cardIfIndex
cardIfSlotNumber
cardIfPortNumber
ciscoEnvMonVoltageStatusIndex
ciscoEnvMonVoltageStatusDesc
ciscoEnvMonVoltageStatusValue
ciscoEnvMonVoltageThresholdLow
ciscoEnvMonVoltageThresholdHigh
ciscoEnvMonVoltageLastShutdown
ciscoEnvMonVoltageState
ciscoEnvMonTemperatureStatusEntry
ciscoEnvMonTemperatureStatusIndex
ciscoEnvMonTemperatureStatusDescr
ciscoEnvMonTemperatureStatusValue
ciscoEnvMonTemperatureThreshold
ciscoEnvMonTemperatureLastShutdown
ciscoEnvMonTemperatureState
ciscoEnvMonFanStatusIndex
ciscoEnvMonFanStatusDescr
ciscoEnvMonFanState
ciscoEnvMonSupplyStatusDescr
ciscoEnvMonSupplyState
ciscoEnvMonShutdownTrap
ciscoEnvMonEnableShutdownTrap
ciscoEnvMonVoltageTrap
ciscoEnvMonTemperatureTrap
ciscoEnvMonEnableTemperatureTrap
ciscoEnvMonRedundantSupplyTrap
ciscoEnvMonEnableRedundantSupplyTrap
dspuNodeRsrb
dspuNodeRsrbLocalVirtualRing
dspuNodeRsrbBridgeNumber
dspuNodeRsrbTargetVirtualRing
dspuNodeRsrbVirtualMacAddress
dspuNodeDefaultPu
dspuNodeDefaultPuWindowSize
dspuNodeDefaultPuMaxIframe
dspuNodeActivationWindow
dspuNodeLastConfigChgTime
dspuPoolClassEntry
dspuPoolClassIndex
dspuPoolClassName
dspuPoolClassInactivityTimeout
dspuPoolClassOperUpStreamLuDefs
dspuPoolClassOperDnStreamLuDefs
dspuPooledLuPeerLuLocalAddress
dspuPuAdminName
dspuPuAdminType
dspuPuAdminRemoteMacAddress
dspuPuAdminRemoteSapAddress
dspuPuAdminLocalSapAddress
dspuPuAdminXid
dspuPuAdminXidFmt
dspuPuAdminWindowSize
dspuPuAdminMaxIframe
dspuPuAdminLinkRetryCount
dspuPuAdminLinkRetryTimeout
dspuPuAdminStartPu
dspuPuAdminDlcType
dspuPuAdminDlcUnit
dspuPuAdminDlcPort
dspuPuAdminFocalPoint
dspuPuAdminRowStatus
dspuPuOperName
dspuPuOperType
dspuPuOperRemoteMacAddress
dspuPuOperRemoteSapAddress
dspuPuOperLocalSapAddress
dspuPuOperXid
dspuPuOperXidFmt
dspuPuOperWindowSize
dspuPuOperMaxIframe
dspuPuOperLinkRetryCount
dspuPuOperLinkRetryTimeout
dspuPuOperStartPu
dspuPuOperDlcType
dspuPuOperDlcUnit
dspuPuOperDlcPort
dspuPuOperFocalPoint
dspuPuOperState
dspuPuOperFsmState
dspuPuOperStartTime
dspuPuOperLastStateChgTime
dspuPuStatsSentBytes
dspuPuStatsRcvdBytes
dspuPuStatsSentFrames
dspuPuStatsRcvdFrames
dspuPuStatsSentNegativeRsps
dspuPuStatsRcvdNegativeRsps
dspuPuStatsActiveLus
dspuPuStatsInactiveLus
dspuPuStatsBindLus
dspuPuStatsActivationFailures
dspuPuStatsLastActivationFailureReason
dspuLuAdminLuLocalAddress
dspuLuAdminType
dspuLuAdminPoolClassName
dspuLuAdminPeerPuIndex
dspuLuAdminPeerLuLocalAddress
dspuLuAdminRowStatus
dspuLuOperEntry
dspuLuOperLuLocalAddress
dspuLuOperType
dspuLuOperPoolClassName
dspuLuOperPeerPuIndex
dspuLuOperPeerLuLocalAddress
dspuLuOperState
dspuLuOperFsmState
dspuLuOperSessionState
dspuSapAddress
dspuSapType
dspuSapDlcType
dspuSapDlcUnit
dspuSapDlcPort
dspuSapOperState
dspuSapRowStatus
cdpInterfaceEnable
cdpInterfaceMessageInterval
cdpInterfaceGroup
cdpInterfacePort
cdpCacheEntry
cdpCacheIfIndex
cdpCacheDeviceIndex
cdpCacheAddressType
cdpCacheAddress
cdpCacheVersion
cdpCacheDeviceId
cdpCacheDevicePort
cdpCachePlatform
cdpCacheCapabilities
qllcLSAdminLciVcIndex
qllcLSAdminCircuitType
qllcLSAdminRole
qllcLSAdminX25Add
qllcLSAdminModulo
qllcLSAdminLgX25
qllcLSOperCircuitType
qllcLSOperRole
qllcLSOperX25Add
qllcLSOperModulo
qllcLSOperState
qllcLSOperLgX25
qllcLSStatsLciVcIndex
qllcLSStatsXidIn
qllcLSStatsXidOut
qllcLSStatsTestIn
qllcLSStatsTestOut
qllcLSStatsQuenchOff
qllcLSStatsQuenchOn
qllcLSStatsInPaks
qllcLSStatsOutPaks
qllcLSStatsInBytes
qllcLSStatsOutBytes
qllcLSStatsNumRcvQsms
qllcLSStatsNumSndQsms
qllcLSStatsNumRcvDiscs
qllcLSStatsNumSndDiscs
qllcLSStatsNumRcvDms
qllcLSStatsNumSndDms
qllcLSStatsNumRcvFrmrs
qllcLSStatsNumSndFrmrs
qllcLSStatsNumDrops
qllcLSStatsNumErrs
cvBasicNetwork
cvBasicHost
cvBasicNextClient
cvForwNeighborNeighborCount
cvForwNeighborPathCount
cvForwNeighborVersion
cvForwNeighborTable
cvForwNeighborNetwork
cvForwNeighborHost
cvForwNeighborPhysAddress
cvForwNeighborSource
cvForwNeighborRtpVersion
cvForwNeighborUsageType
cvForwNeighborAge
cvForwNeighborMetric
cvForwNeighborUses
cvForwRouteRouterCount
cvForwRouteRouteCount
cvForwRouteVersion
cvForwRouteUpdateCountdown
cvForwRouteTable
cvForwRouteNetworkNumber
cvForwRouteNeighborNetwork
cvForwRouteSource
cvForwRouteRtpVersion
cvForwRouteUseNext
cvForwRouteForwardBroadcast
cvForwRouteSuppress
cvForwRouteLoadShareEligible
cvForwRouteAge
cvForwRouteMetric
cvForwRouteUses
cvTotalInputPackets
cvTotalOutputPackets
cvTotalLocalDestPackets
cvTotalForwardedPackets
cvTotalBroadcastInPackets
cvTotalBroadcastOutPackets
cvTotalBroadcastForwardPackets
cvTotalLanOnlyPackets
cvTotalNotOver4800Packets
cvTotalNoChargesPackets
cvTotalFormatErrors
cvTotalChecksumErrors
cvTotalHopCountsExceeded
cvTotalNoRouteDrops
cvTotalEncapsFailedDrops
cvTotalUnknownPackets
cvTotalIcpInPackets
cvTotalIcpOutPackets
cvTotalMetricOutPackets
cvTotalMacEchoInPackets
cvTotalMacEchoOutPackets
cvTotalEchoInPackets
cvTotalEchoOutPackets
cvTotalProxyOutPackets
cvTotalProxyReplyOutPackets
cvIfConfigMetric
cvIfConfigEncapsulation
cvIfConfigAccesslist
cvIfConfigPropagate
cvIfConfigArpEnabled
cvIfConfigServerless
cvIfConfigRedirectInterval
cvIfConfigSplitDisabled
cvIfConfigLineup
cvIfConfigFastokay
cvIfConfigRouteCache
cvIfConfigInputRouterFilter
cvIfConfigInputNetworkFilter
cvIfConfigOutputNetworkFilter
cvIfCountInNotEnabledDrops
cvIfCountInFormatErrors
cvIfCountInLocalDestPackets
cvIfCountInBroadcastPackets
cvIfCountInForwardedPackets
cvIfCountInNoRouteDrops
cvIfCountInZeroHopCountDrops
cvIfCountInChecksumErrors
cvIfCountInArpQueryRequests
cvIfCountInArpQueryResponses
cvIfCountInArpAssignmentRequests
cvIfCountInArpAssignmentResponses
cvIfCountInArpIllegalMessages
cvIfCountInIcpErrorMessages
cvIfCountInIcpMetricMessages
cvIfCountInIcpIllegalMessages
cvIfCountInIpcMessages
cvIfCountInRtp0Messages
cvIfCountInRtp1Messages
cvIfCountInRtp2Messages
cvIfCountInRtp3Messages
cvIfCountInRtpUpdateMessages
cvIfCountInRtpResponseMessages
cvIfCountInRtpRedirectMessages
cvIfCountInRtpIllegalMessages
cvIfCountInSppMessages
cvIfCountInIpUnknownProtocols
cvIfCountInIpcUnknownPorts
cvIfCountInBroadcastsHelpered
cvIfCountInBroadcastsForwarded
cvIfCountInBroadcastDuplicates
cvIfCountInEchoPackets
cvIfCountInMacEchoPackets
cvIfCountInProxyReplyPackets
cvIfCountOutUnicastPackets
cvIfCountOutBroadcastPackets
cvIfCountOutForwardedPackets
cvIfCountOutEncapsulationFailures
cvIfCountOutAccessFailures
cvIfCountOutDownFailures
cvIfCountOutPacketsNotBroadcastToSource
cvIfCountOutPacketsNotBroadcastLanOnly
cvIfCountOutPacketsNotBroadcastNotOver4800
cvIfCountOutPacketsNotBroadcastNoCharge
cvIfCountOutBroadcastsForwarded
cvIfCountOutBroadcastsHelpered
cvIfCountOutArpQueryRequests
cvIfCountOutArpQueryResponses
cvIfCountOutArpAssignmentRequests
cvIfCountOutArpAssignmentResponses
cvIfCountOutIcpErrorMessages
cvIfCountOutIcpMetricMessages
cvIfCountOutIpcMessages
cvIfCountOutRtp0Messages
cvIfCountOutRtpRequestMessages
cvIfCountOutRtp2Messages
cvIfCountOutRtp3Messages
cvIfCountOutRtpUpdateMessages
cvIfCountOutRtpResponseMessages
cvIfCountOutRtpRedirectMessages
cvIfCountOutSppMessages
cvIfCountOutEchoPackets
cvIfCountOutMacEchoPackets
cvIfCountOutProxyPackets
nlspSysInstance
nlspSysState
nlspSysID
nlspSysMinNonBcastLSPTransInt
nlspSysMinBcastLSPTransInt
nlspSysMinLSPGenInt
nlspSysMaxLSPGenInt
nlspSysMaxLSPAge
nlspSysBcastHelloInt
nlspSysNonBcastHelloInt
nlspSysDRBcastHelloInt
nlspSysHoldTimeMultiplier
nlspSysCompSNPInt
nlspSysPartSNPInt
nlspSysWaitTime
nlspSysOrigL1LSPBufSize
nlspSysVersion
nlspSysCorrLSPs
nlspSysL1Overloaded
nlspSysL1DbaseOloads
nlspSysMaxSeqNums
nlspSysSeqNumSkips
nlspSysTransmittedLSPs
nlspSysReceivedLSPs
nlspSysOwnLSPPurges
nlspSysVersionErrors
nlspSysIncorrectPackets
nlspSysNearestL2DefaultExists
nlspSysNearestL2DefaultRouter
nlspSysResourceFailures
nlspSysAreaSysInstance
nlspSysAreaNet
nlspSysAreaMask
nlspActAreaSysInstance
nlspActAreaNet
nlspActAreaMask
nlspCircSysInstance
nlspCircIndex
nlspCircState
nlspCircPace
nlspCircHelloTimer
nlspCircL1DefaultCost
nlspCircL1DesRouterPriority
nlspCircL1CircID
nlspCircL1DesRouter
nlspCircLANL1DesRouterChanges
nlspCircNeighChanges
nlspCircRejNeighbors
nlspCircOutPackets
nlspCircInPackets
nlspCircActualMaxPacketSize
nlspCircPSNPsSent
nlspCircPSNPsReceived
nlspDestSysInstance
nlspDestNetNum
nlspDestID
nlspDestEstDelay
nlspDestEstThroughput
nlspDestNextHopID
nlspDestCost
nlspNeighSysInstance
nlspNeighCircIndex
nlspNeighIndex
nlspNeighState
nlspNeighNICAddress
nlspNeighSysType
nlspNeighSysID
nlspNeighName
nlspNeighUsage
nlspNeighHoldTimer
nlspNeighRemainingTime
nlspNeighPriority
nlspIDMapEntry
nlspIDMapSysInstance
nlspIDMapID
nlspIDMapServerName
nlspIDMapNetNum
nlspNetMapSysInstance
nlspNetMapNetNum
nlspNetMapServerName
nlspNetMapID
nlspNameMapSysInstance
nlspNameMapServerName
nlspNameMapNetNum
nlspNameMapID
InlspNodeSysInstance
nlspNodeID
nlspNodeNetNum
nlspNodeType
nlspNodeEstDelay
nlspNodeEstThroughput
nlspNodeMaxPacketSize
nlspNodeCost
nlspNodeOverload
nlspNodeReachable
nlspLinkSysInstance
nlspLinkNLSPID
nlspLinkIndex
nlspLinkNeighNLSPID
nlspLinkFromNeighCost
nlspLinkMaxPacketSize
nlspLinkThroughput
nlspLinkDelay
nlspLinkMediaType
nlspLinkToNeighCost
nlspPathSysInstance
nlspPathDestNLSPID
nlspPathLinkIndex
nlspGraphXRouteSysInstance
nlspGraphXRouteNLSPID
nlspGraphXRouteNetNum
nlspGraphXRouteCost
nlspGraphXRouteHopCount
nlspGraphServSysInstance
nlspGraphServNLSPID
nlspGraphServName
nlspGraphServTypeValue
nlspGraphServType
nlspGraphServNetNum
nlspGraphServNode
nlspGraphServSocket
nlspLSPSysInstance
nlspLSPID
nlspLSPLifetime
nlspLSPSeqNum
nlspLSPChecksum
nlspLSPRouterType
nlspLSPOverload
nlspLSPHeader
nlspLSPOptSysInstance
nlspLSPOptLSPID
nlspLSPOptIndex
nlspLSPOptCode
nlspLSPOptLength
nlspLSPOptValue
The Environmental Monitor Card objects have been replaced by the IOS Release 10.3 by the Cisco Environmental Monitor MIB.
The Flash group objects found in Local Variables have been superceded by the ciscoFlash MIB found in ciscoMgmt.
The loctcp table has been replaced by the ciscoloctcp table.
The following list identifies the MIB variables introduced with IOS Release 10.3(3):
chassisPartner
ciscoRptrPortMDIStatus
ciscoRptrPortLinkTestEnabled
ciscoRptrPortLinkTestFailed
ciscoRptrPortAutoPolarityEnabled
ciscoRptrPortAutoPolarityCorrected
ciscoRptrPortSrcAddrCtrl
ciscoRptrPortAllowedSrcAddr
ciscoRptrPortAllowedSrcAddrStatus
ciscoRptrPortLastIllegalSrcAddr
demandNbrEntry
demandNbrPhysIf
demandNbrId
demandNbrLogIf
demandNbrName
demandNbrAddress
demandNbrPermission
demandNbrMaxDuration
demandNbrLastDuration
demandNbrClearReason
demandNbrClearCode
demandNbrSuccessCalls
demandNbrFailCalls
demandNbrAcceptCalls
demandNbrRefuseCalls
demandNbrLastAttemptTime
demandNbrStatus
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Mon Oct 21 11:31:09 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.