|
|

This chapter takes you through first-time startup. Use the information you entered on the Global and Interface Configuration Worksheets as you interact with the setup command facility's System Configuration Dialog. If you have not completed the worksheets, you should read the "Preparing for First-Time Startup" chapter before starting up.
This chapter includes sample worksheets that are filled in to show you how this information is used when the setup command facility runs through the System Configuration Dialog.
The first time you start up the system, the setup command facility operates automatically. An interactive dialog called the System Configuration Dialog appears on the system console screen. The dialog navigates you through the configuration process by prompting you for the information you have recorded on the configuration worksheets. Default and help information available within the dialog is described later in this section.
The setup command facility prompts you for configuration information for each installed interface. When you finish configuring one interface, the setup command facility prompts you for the next interface and continues until each interface is configured.
At first-time startup, you must complete the following tasks:
For many prompts in the facility's System Configuration Dialog, default answers appear in square brackets following the question. To accept a default value, press the Return key. If the system was previously configured, the defaults that appear are the currently configured values. If you are configuring the system for the first time, the defaults that appear are factory defaults. If no factory default exists, as in the case of passwords, nothing appears after the question mark.
At any time during use of the setup command facility, you may request help by typing a question mark (?) at a given prompt. If the prompt requires a yes or no answer, no further help is available. If the prompt offers a range of acceptable answers, the help facility gives you some guidance. For example, if the setup command facility prompts you to select the number of bits in a subnet mask for your previously entered Class A IP address, the help facility prompts you to choose a decimal number between 0 and 22.
Additionally, if you enter invalid information at a prompt, the help facility automatically asks you for the correct information. For example, if you answer "okay" instead of "yes" at a prompt, the help facility guides you with the following information:
%Please answer 'yes' or 'no'.
As another example, if you answer a prompt with a value of 0 and the required value must be a decimal between 1 and 65535, then the help facility automatically prompts you with the following message:
%A decimal number between 1 and 65535
Before powering up your system, check for correct AC power voltages.
 | Caution Check the voltage rating label at the back of the unit for correct voltage configuration. The factory configures the ASM-CS for either 110 VAC or 220 VAC operation, as requested when ordered. The 500-CS automatically configures the power supply for the applied input voltage and may be connected to any AC source from 100 to 240 VAC. Like the 500-CS, the Cisco 2500 has a variable power supply and may be connected to any AC source from 100 to 240 VAC. |
Now you can safely power up your system. To power up your ASM-CS or Cisco 2500, flip on the On/Off switch on the back panel. To power up your 500-CS, simply plug in the power cord.
When you first power up your console and server product, a script similar to the following appears on the screen. The first section of the script displays banner information, including the software version and the System Configuration Dialog. (A sample of the complete configuration script produced is included at the end of this chapter.)
Restricted Rights Legend
Use, duplication, or disclosure by the Government is
subject to restrictions as set forth in subparagraph
(c) of the Commercial Computer Software - Restricted
Rights clause at FAR sec. 52.227-19 and subparagraph
(c) (1) (ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer
Software clause at DFARS sec. 252.227-7013.
cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, California 95134
Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software
IOS (tm) 3000 Software (IGS-BFPX), Version 10.3
Copyright (c) 1986-1994 by cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Fri 02-Dec-94 17:40 by chansen
Image text-base: 0x03000060, data-base: 0x00001000
The next portion of the script lists installed hardware and software options. The system displays appropriate interfaces for these options during the configuration process.
% System running from device (System flash) being initialized.
Setting System flash access to read-only.
SNMP Research SNMP Agent Resident Module Version 12.2.0.0
Copyright 1989, 1990, 1991, 1992, 1993, 1994 SNMP Research, Inc.
cisco 2500 (68030) processor (revision A) with 1024K/1024K bytes of memory.
Processor board serial number 01244571
X.25 software, Version 2.0, NET2, BFE and GOSIP compliant.
Bridging software.
SuperLAT software (copyright 1990 by Meridian Technology Corp).
Authorized for Enterprise software set. (0x0)
1 Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 interface.
2 Serial network interfaces.
8 terminal lines.
32K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory.
4096K bytes of processor board System flash. (Read only mode)
Notice: NVRAM invalid, possibly due to write erase.
The System Configuration Dialog appears next, and prompts for configuration information. Press the Return key to accept the default settings, which appear in square brackets.
--- System Configuration Dialog ---
At any point you may enter a question mark '?' for help.
Refer to the 'Getting Started' Guide for additional help.
Use ctrl-c to abort configuration dialog at any prompt.
Default settings are in square brackets '[]'.
Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes]:
At this point, you can choose to exit the System Configuration Dialog by answering No at the prompt. To begin the initial configuration process, answer Yes. If you answer Yes, the System Configuration Dialog asks whether you want to view the current interface summary. Answer Yes to see the summary.
First, would you like to see the current interface summary? [yes]:
In the following example, the summary shows a server product at first-time startup. That is, nothing has been configured, and the summary reflects that fact.
Any interface listed with OK? value "NO" does not have a valid configuration
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Ethernet0 unassigned NO not set up down
Serial0 unassigned NO not set down down
Serial1 unassigned NO not set down down
The interface summary contains six columns. The Interface column lists the server product's installed interfaces.The IP-Address column lists the IP address for each interface or states that an IP address for an interface is currently unassigned. Because this example shows the summary at first-time startup (i.e., prior to configuration) no IP addresses have yet been assigned. The OK? column describes whether an interface has a valid configuration. Again, no configuration exists, so the OK? column contains NO for each interface. The Method column describes where an interface gets its configuration information—manually or from NVRAM. If you have not configured the interface with an IP address, the column shows "not set" for the interface. The Status column indicates whether an interface is up, down, or administratively down. Ethernet interfaces have a default status of up. Therefore, when you power up your server product, Ethernet interfaces are usually up. Serial interfaces are not up unless they receive the correct carrier detect signal on the line. The Protocol column lists the line protocol for an interface. A line protocol tells you whether the interface line missed the last three keepalives. If so, the column contains "down" for that interface.
Notice that the previous sample interface summary does not contain any information about the server product's asynchronous lines. At first-time startup, the interface summary does not list asynchronous lines because the lines have not yet been configured. Once you have configured the asynchronous lines, they will appear in the interface summary when you run the setup facility again. For example, the following setup interface summary shows 16 asynchronous lines that were previously configured:
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Ethernet0 unassigned YES not set administratively down down
Serial0 unassigned YES not set administratively down down
Serial1 unassigned YES not set administratively down down
Async1 171.69.228.10 YES not set down down
Async2 171.69.228.10 YES not set down down
Async3 171.69.228.10 YES not set down down
Async4 171.69.228.10 YES not set down down
Async5 171.69.228.10 YES not set down down
Async6 171.69.228.10 YES not set up up
Async7 171.69.228.10 YES not set up up
Async8 171.69.228.10 YES not set down down
Async9 171.69.228.10 YES not set down down
Async10 171.69.228.10 YES not set down down
Async11 171.69.228.10 YES not set down down
Async12 171.69.228.10 YES not set down down
Async13 171.69.228.10 YES not set down down
Async14 171.69.228.10 YES not set down down
Async15 171.69.228.10 YES not set down down
Async16 171.69.228.10 YES not set down down
After displaying the interface summary, the dialog begins to prompt you for global configuration parameters. You can press Ctrl-C to abort the process at any time. Ctrl-C returns you to the privileged EXEC prompt (cs#). You can then configure the server product from this mode. For information about configuring the server product, refer to the Access and Communication Servers Configuration Guide. For more information about configuring your Cisco 2500 as a router, refer to the Router Products Configuration Guide.
When a --More-- prompt appears during the dialog, press the space bar to continue.
The System Configuration Dialog prompts you for global parameters, then interface parameters. Enter the values you recorded on the two configuration worksheets. To accept default settings that appear in square brackets, press the Return key.
When you answer the last prompt for installed interfaces on your server product, the setup command facility presents the configuration command script that was created. It also asks you whether you want to use this configuration. If you answer Yes, the configuration is saved to nonvolatile memory. If you answer No, the configuration is not saved and the process begins again. There is no default for this prompt; you must answer either Yes or No.
Once you have answered Yes to this last question, your system is now ready for use. To modify the configuration you have just established, refer to the "Where to Go from Here" chapter.
Figure 3-1 and Figure 3-2 show a sample completed Global Configuration Worksheet for a first-time startup configuration. Figure 3-3, Figure 3-4, and Figure 3-5 show sample completed Interface Configuration Worksheets for the same first-time startup configuration. Following the worksheets is the actual screen output for the setup command facility at first-time startup and the user responses from the completed worksheets.
In the sample System Configuration Dialog, when it appears that no response was made, the user pressed the Return key to accept the default.
Turn off XNS to prevent network conflicts or Turn off Apollo to prevent network conflicts. These comments do not instruct you to turn off the configurations you set during the System Configuration Dialog. Instead, these comments inform you that the setup command facility is turning off all previous XNS or Apollo networks before adding the new ones you specified via the dialog. Removing previous configurations avoids potential network conflicts and ensures configuration of these networks according to your specifications during the dialog.
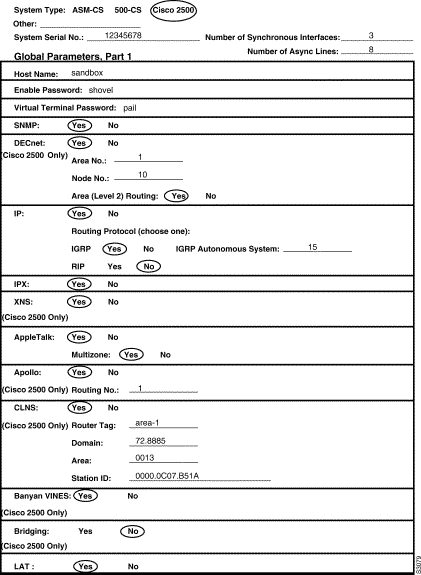

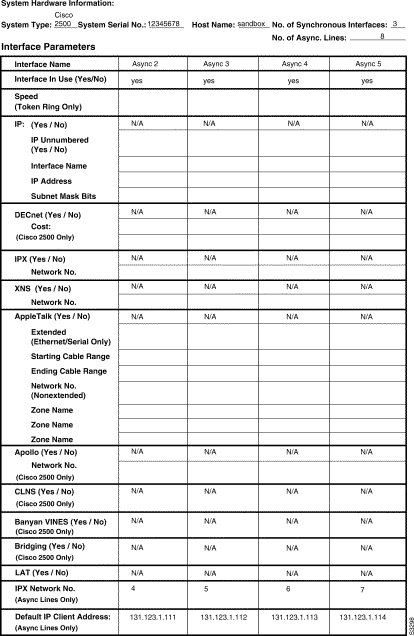
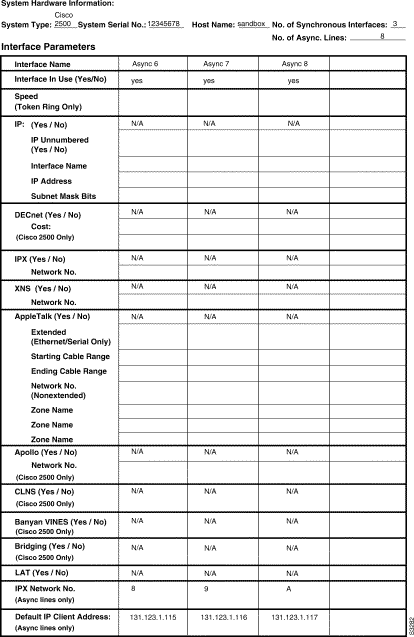
--- System Configuration Dialog ---
At any point you may enter a question mark '?' for help.
Refer to the 'Getting Started' Guide for additional help.
Use ctrl-c to abort configuration dialog at any prompt.
Default settings are in square brackets '[]'.
Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes]:
First, would you like to see the current interface summary? [yes]:
Any interface listed with OK? value "NO" does not have a valid configuration
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Ethernet0 unassigned NO not set up down
Serial0 unassigned NO not set down down
Serial1 unassigned NO not set down down
Configuring global parameters:
Enter host name [Router]: sandbox
Enter enable password: shovel
Enter virtual terminal password: pail
Configure SNMP Network Management? [no]:
Community string [public]:
Configure DECnet? [no]: yes
Your area number [1]:
Your node number [1]: 10
Area (level 2) routing? [no]: yes
Configure IP? [yes]:
Configure IGRP routing? [yes]:
Your IGRP autonomous system number [1]: 15
Configure IPX? [no]: yes
Configure XNS? [no]: yes
Configure AppleTalk? [no]: yes
Multizone networks? [no]: yes
Configure Apollo? [no]: yes
Apollo routing number [1]:
Configure CLNS? [no]: yes
CLNS router tag [area_1]:
CLNS domain [49]: 72.8885
CLNS area [0001]: 0013
CLNS station id [0000.0C07.B51A]:
Configure Vines? [no]: yes
Configure bridging? [no]:
Configure LAT? [no]: yes
Configure Async lines? [yes]:
Async line speed [9600]:
Configure for HW flow control? [yes]:
Configure for modems? [yes/no]: yes
Configure for default chat script? [yes]:
Configure for Dial-in IP SLIP/PPP access? [no]: yes
Configure for Dynamic IP addresses? [yes]: yes
Configure Default IP addresses? [no]: yes
Configure for TCP Header Compression? [yes]:
Configure for routing updates on async links? [no]:
Configure for Async IPX? [yes]:
Configure XRemote font servers? [no]: yes
Enter a font server IP address or press RETURN to exit: 131.108.1.111
Enter a font server IP address or press RETURN to exit: 131.108.1.112
Enter a font server IP address or press RETURN to exit: 131.108.1.113
Enter a font server IP address or press RETURN to exit: 131.108.1.114
Enter a font server IP address or press RETURN to exit:
Configure for Appletalk Remote Access? [yes]:
AppleTalk Network for ARA clients [1]: 5678
Zone name for ARA clients [*]: shamu
Configuring interface parameters:
Configuring interface Ethernet0:
Is this interface in use? [no]: yes
Configure IP on this interface? [no]: yes
IP address for this interface: 198.92.73.37
Number of bits in subnet field [0]:
Class C network is 198.92.73.0, 0 subnet bits; mask is 255.255.255.0
Configure DECnet on this interface? [no]: yes
DECnet cost [10]:
Configure IPX on this interface? [no]: yes
IPX network number [1]: 10
Configure XNS on this interface? [no]: yes
XNS network number [1]: 10
Configure AppleTalk on this interface? [no]: yes
Extended AppleTalk network? [no]: yes
AppleTalk starting cable range [0]:
Configure Apollo on this interface? [no]: yes
Apollo network number [1]: 10
Configure CLNS on this interface? [no]: yes
Configure Vines on this interface? [no]: yes
Configure LAT on this interface? [no]: yes
Configuring interface Serial0:
Is this interface in use? [no]: yes
Configure IP on this interface? [no]: yes
Configure IP unnumbered on this interface? [no]: yes
Interface name?: Ethernet0
Configure DECnet on this interface? [no]:
Configure IPX on this interface? [no]:
Configure XNS on this interface? [no]:
Configure AppleTalk on this interface? [no]:
Configure Apollo on this interface? [no]:
Configure CLNS on this interface? [no]:
Configure Vines on this interface? [no]:
Configure LAT on this interface? [no]:
Configuring interface Serial1:
Is this interface in use? [yes]: no
Configuring interface Async1:
IPX network number [3]:
Default client IP address for this interface [none]: 131.123.1.110
Configuring interface Async2:
IPX network number [4]:
Default client IP address for this interface [131.123.1.111]:
Configuring interface Async3:
IPX network number [5]:
Default client IP address for this interface [131.123.1.112]:
Configuring interface Async4:
IPX network number [6]:
Default client IP address for this interface [131.123.1.113]:
Configuring interface Async5:
IPX network number [7]:
Default client IP address for this interface [131.123.1.114]:
Configuring interface Async6:
IPX network number [8]:
Default client IP address for this interface [131.123.1.115]:
Configuring interface Async7:
IPX network number [9]:
Default client IP address for this interface [131.123.1.115]:
Configuring interface Async8:
IPX network number [A]:
Default client IP address for this interface [131.123.1.117]:
The following configuration command script was created:
hostname sandbox
enable password shovel
line vty 0 4
password pail
snmp-server community public
!
decnet routing 1.10
decnet node-type area
ip routing
ipx routing
xns routing
appletalk routing
apollo routing 1
clns routing
router iso-igrp area_1
net 72.8885.0013.0000.0C07.b51A.00
vines routing
no bridge 1
chat-script cisco-default ABORT ERROR "" "AT Z" OK "ATDT \T" TIMEOUT 30 \c CONNECT \c
!
line 1 8
speed 9600
flowcontrol hardware
modem inout
modem chat-script cisco-default
!
arap network 5678 sandbox
line 1 8
arap enable
autoselect
!
! Turn off IPX to prevent network conflicts.
interface Ethernet0
no ipx network
interface Serial0
no ipx network
interface Serial1
no ipx network
!
! Turn off XNS to prevent network conflicts.
interface Ethernet0
no xns network
interface Serial0
no xns network
interface Serial1
no xns network
!
! Turn off Apollo to prevent network conflicts.
interface Ethernet0
no apollo network
interface Serial0
no apollo network
interface Serial1
no apollo network
!
interface Ethernet0
ip address 198.92.73.37 255.255.255.0
decnet cost 10
ipx network 10
xns network 10
appletalk cable-range 0-0 0.0
appletalk discovery
Apollo network 10
vines metric
mop enabled
!
interface Serial0
no ip address
ip unnumbered
interface name Ethernet0
no vines metric
no mop enabled
!
interface Serial1
shutdown
no ip address
!
Interface Async1
ipx network 3
ip unnumbered Ethernet0
async default ip address 131.123.1.110
ip tcp header-compression passive
async mode interactive
async dynamic address
!
Interface Async2
ipx network 4
ip unnumbered Ethernet0
async default ip address 131.123.1.111
ip tcp header-compression passive
async mode interactive
async dynamic address
!
Interface Async3
ipx network 5
ip unnumbered Ethernet0
async default ip address 131.123.1.112
ip tcp header-compression passive
async mode interactive
async dynamic address
!
Interface Async4
ipx network 6
ip unnumbered Ethernet0
async default ip address 131.123.1.113
ip tcp header-compression passive
async mode interactive
async dynamic address
!
Interface Async5
ipx network 7
ip unnumbered Ethernet0
async default ip address 131.123.1.114
ip tcp header-compression passive
async mode interactive
async dynamic address
!
Interface Async6
ipx network 8
ip unnumbered Ethernet0
async default ip address 131.123.1.115
ip tcp header-compression passive
async mode interactive
async dynamic address
!
Interface Async7
ipx network 9
ip unnumbered Ethernet0
async default ip address 131.123.1.116
ip tcp header-compression passive
async mode interactive
async dynamic address
!
Interface Async8
ipx network A
ip unnumbered Ethernet0
async default ip address 131.123.1.117
ip tcp header-compression passive
async mode interactive
async dynamic address
!
router igrp 15
network 198.92.73.0
network 1.0.0.0
!
end
Use this configuration? [yes/no]:
Press RETURN to get started!
[OK]
Use the enabled mode 'configure' command to modify this configuration.
First-time startup is complete. Your server product is now ready to use. To modify the configuration you have just established during first-time startup, use the setup command facility described in the "Where to Go from Here" chapter. To perform more complex configurations, use the configure command described in the Access and Communication Servers Configuration Guide and the Access and Communication Servers Command Reference publication. To make telecommuting or terminal service connections, refer to the Cisco Access Connection Guide.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Mon Oct 21 11:30:49 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.