|
|

This guide describes the Cisco Systems private, or local, Management Information Base (MIB) for Internetwork Operating System (IOS) Release 10.2. The Cisco MIB is provided with all Cisco software releases and with CiscoWorks router management software. The MIB file contains variables that can be set or read to provide information on network devices and interfaces.
The Cisco MIB is a set of variables that are private extensions to the Internet standard MIB II. The MIB II is documented in RFC 1213, Management Information Base for Network Management of TCP/IP-based Internets: MIB-II.
The Cisco MIB is described by a number of MIB files, which can be obtained by FTP from the Cisco server. The listing of Cisco MIB variables in those files is identical to the listing in this guide, except that unlike the MIB files, the Cisco MIB variables are presented alphabetically in this guide for quick reference.
You can obtain the files which describe the Cisco MIB by using the ftp ftp.cisco.com command. Log in with the username anonymous and enter your e-mail name when prompted for the password. Use the cd pub/mibs command to go to the directory that contains the MIB files, and then issue the get README command to display the readme file containing a list of available files. You can then use the get filename command to retrieve the desired MIB file (for example, use get cisco-ping-mib.my to retrieve the Cisco Ping MIB).
The Cisco MIB variables are accessible via the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), which is an application-layer protocol designed to facilitate the exchange of management information between network devices. The SNMP system consists of three parts: SNMP manager, SNMP agent, and MIB.
Instead of defining a large set of commands, SNMP places all operations in a get-request, get-next-request, get-bulk-request, and set-request format. For example, an SNMP manager can get a value from an SNMP agent or store a value into that SNMP agent. The SNMP manager can be part of a network management system (NMS), and the SNMP agent can reside on a networking device such as a router. You can compile the Cisco MIB with your network management software. If SNMP is configured on a router, the SNMP agent can respond to MIB-related queries being sent by the NMS.
An example of an NMS is the CiscoWorks network management software. CiscoWorks uses the Cisco MIB variables to set device variables and to poll devices on the internetwork for specific information. The results of a poll can be graphed and analyzed in order to troubleshoot internetwork problems, increase network performance, verify the configuration of devices, monitor traffic loads, and more.
As shown in Figure 1, the SNMP agent gathers data from the MIB, which is the repository for information about device parameters and network data. The agent also can send traps, or notification of certain events, to the manager. The Cisco trap file, mib.traps, which documents the format of the Cisco traps, is available on the Cisco host ftp.cisco.com.
The SNMP manager uses information in the MIB to perform the operations described in Table 1.
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
Retrieve a value from a specific variable. | |
Retrieve a value from a variable within a table1. | |
The reply to a get-request, get-next-request, and set-request sent by an NMS. | |
get-bulk-request | The agent's response to the get-bulk operator isn't unlike the concatenation of the agent's responses from up to max-repetition number of get-next interactions. |
Store a value in a specific variable. | |
trap | An unsolicited message sent by an SNMP agent to an SNMP manager indicating that some event has occurred. |
| 1With this operation, an SNMP manager does not need to know the exact variable name. A sequential search is performed to find the needed variable from within a table. |
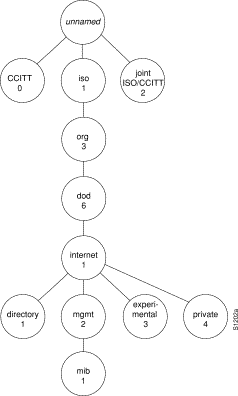
The MIB structure is logically represented by a tree hierarchy.
(See Figure 2.) The root of the tree is unnamed and splits into three main branches: Consultative Committee for International Telegraph and Telephone (CCITT), International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and joint ISO/CCITT.
These branches and those that fall below each category have short text strings and integers to identify them. Text strings describe object names, while integers allow computer software to create compact, encoded representations of the names. For example, the Cisco MIB variable authAddr is an object name and is denoted by number 5, which is listed at the end of its object identifier number 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.2.1.5.
The object identifier in the Internet MIB hierarchy is the sequence of numeric labels on the nodes along a path from the root to the object. The Internet standard MIB is represented by the object identifier 1.3.6.1.2.1. It also can be expressed as iso.org.dod.internet.mgmt.mib. (See
Figure 2.)
The private Cisco MIB is represented by the object identifier 1.3.6.1.4.1.9, or iso.org.dod.internet.private.enterprise.cisco. The Cisco MIB includes the following subtrees: local (2), temporary (3), otherEnterprises (6), and ciscoMgmt(9).
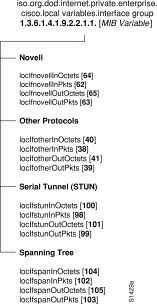
The local subtree contains MIB objects defined prior to Software Release 10.2. MIB objects defined prior to Software Release 10.2 implemented the SNMPv1 Structure of Management Information (SMI). Beginning with IOS 10.2, however, Cisco MIBs are defined using the SNMPv2 SMI. MIBs defined using SNMPv2 are being placed in the ciscoMgmt tree. (See Figure 3.) MIBs currently defined in the local subtree are being deprecated by Cisco as an ongoing process, and being replaced with new objects defined in the ciscoMgmt subtree. For example, the TCP group that was in the local group has been deprecated and replaced with a new TCP group in the ciscoMgmt tree. The Ping group is one of the new objects in the ciscoMgmt tree. The otherEnterprises subtree contains MIBS defined by other entities that Cisco has incorporated into its MIB structure. The new IPX and RIPSAP groups are examples of MIBs in the otherEnterprises tree.
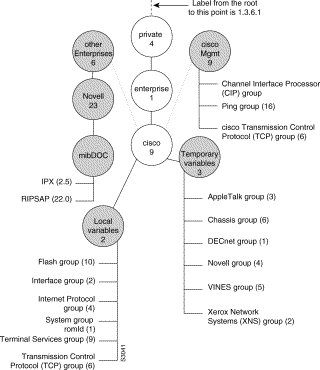
In Figure 3, the local variables group is identified by 2; its subgroup, called lsystem, is identified by 1; and the first variable is romId with a value of 1. Therefore, the variable romId has a value of 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.2.1.1.0. The appended 0 indicates that 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.2.1.1.0 is the one and only instance of romId.
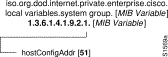
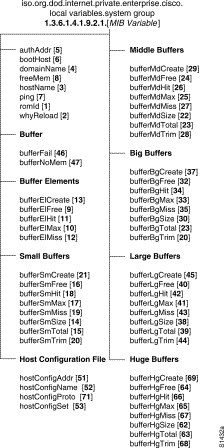
In this guide, each group of Cisco MIB variables is accompanied by an illustration that indicates the specific object identifier for each variable.
For example, in Figure 4 the object identifier 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.2.1 at the top of the illustration indicates the labeled nodes. The last value is the number of the Cisco MIB variable. For example, the MIB variable hostConfigAddr is indicated by the number 51. The object identifier for hostConfigAddr is iso.org.dod.internet.private.enterprise.cisco.local variables.system group.hostConfigAddr or 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.2.1.51.
When network management protocols use names of MIB variables in messages, each name has a suffix appended. For simple variables, the suffix 0 refers to the instance of the variable with that name. A MIB also can contain tables of related variables.
Following is an excerpt of the information on the IP Routing table (known as lipRoutingTable) from the associated mib file:
lipRoutingTable OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX SEQUENCE OF LIpRouteEntry
ACCESS not-accessible
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"A list of IP routing entries."
::= { lip 2 }
lipRouteEntry OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX LIpRouteEntry
ACCESS not-accessible
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"A collection of additional objects in the
cisco IP routing implementation."
INDEX { ipRouteDest }
::= { lipRoutingTable 1 }
LIpRouteEntry ::=
SEQUENCE {
locRtMask
IpAddress,
locRtCount
INTEGER,
}
The local IP Routing table, lipRoutingTable, is described in Table 7. The lipRoutingTable contains two variables: locRtMask and locRtCount. The index for this table is the destination address of the IP route, or ipRouteDest. If there are n number of routes available to a device, there will be n rows in the IP Routing table.
In Table 2, for the route with the destination IP address of 131.104.111.1, the IP Routing table network mask is 255.255.255.0. The number of parallel routes within the routing table is 3.
| ipRouteDest | locRtMask | locRtCount |
|---|---|---|
131.104.111.1 | 255.255.255.0 | 3 |
133.45.244.245 | 255.255.255.0 | 1 |
In this guide, when variables belong to a table, they are listed in the section describing the table. The following tag is used to indicate the end of a table:
End of Table
All variables before this tag are part of the table.
The local variables section pertains to all Cisco devices and contains the following groups.
This section is equivalent to the experimental space defined by the Structure of Management Information (SMI). These variables are subject to change for each Cisco Systems software release.
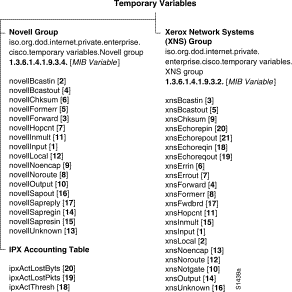
Temporary variables consists of the following groups, which are presented in alphabetical order. (See Figure 3.)
The ciscoMgmt subtree consists of the following variables:
The otherEnterprises subtree consists of the following variables:
This section presents the syntax and access type categories used to describe each variable. For details on syntax, refer to RFC 1155, and to RCF 1442 for SNMPv2.
The syntax describes the format of the information, or value, that is returned upon monitoring or setting information in a device with a MIB variable.
The syntax can be any one of the following categories:
The access type, which applies to SNMPv1, describes whether a MIB variable can be used under one of the following circumstances:
This variable, which applies to SNMPv2, can represent one of the following four states: read-create, read-write, read-only, and not-accessible.
The International Organization for Standards (ISO) Network Management Forum defined five areas of network management: fault, configuration, security, performance, and accounting. Cisco MIB variables can be mapped to each of these areas (as described in this section) and used to manage your internetwork.
Cisco supports several MIBs, which are described in the following Requests for Comments (RFCs). Also listed are RFCs describing the Internet standards that Cisco Systems follows with regard to its MIB format and the SNMP protocol.
To obtain copies of RFCs, use the ftp nic.ddn.mil command. Log in as anonymous and enter your e-mail name when prompted for the password. Enter the cd rfc command to change to the correct directory. Use the get rfc-index.txt command to retrieve a list of all available RFCs. To obtain a copy of any specific RFC, enter get rfcnnnn.txt, where nnnn is the RFC number.
For detailed information on configuration and troubleshooting commands, refer to the following Cisco publications:
Users of the CiscoWorks router management software can refer to the CiscoWorks User Guide for information on CiscoWorks router management software features and its use of MIB variables for the purposes of graphing and analyzing network performance, ensuring configuration consistency, troubleshooting, and more.
Following are suggested reading materials:
The figures in this section provide a visual overview of the Cisco MIB variables along with the object identifier numbers for each MIB variable. The MIB variables are arranged alphabetically within each figure (in the same order in which they appear in the sections of this guide).






















This section describes the MIB variables within the Cisco product line. Certain groups of variables may or may not be present, depending upon the software options and configuration in the managed device.
The Flash memory card is an add-in card of Flash EPROM (erasable programmable read-only memory) storage onto which system software images can be stored, booted, and rewritten.
The local Flash File table, lflashFileDirTable, contains information on a per file basis and includes the following three variables: flashDirName, flashDirSize, and flashDirStatus. The index to this table is flashEntries, or the number of Flash files. If the device has n number of Flash files, the table will contain n number of rows.
For example, in Table 3, the flash1 file has a directory size of 50 octets, and its status is valid, represented by the integer 1.
| flashEntries | flashDirName | flashDirSize | flashDirStatus |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | flash1 | 50 | 1 |
2 | flash2 | 100 | 1 |
3 | flash3 | 200 | 2 |
Provides the name associated with a Flash directory entry.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the size (in octets) of a Flash directory entry.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the status of the Flash directory entry.
Syntax: Integer (1 = valid, 2 = deleted)
Access: Read-only
End of Table
Provides the type of card connected to the Flash card installed in the router. For example, the type of card connected to the Flash card could be either CSC-MS or CSC-MC+.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the type of Flash controller (either CCTL or CCTL2) installed in the router.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of directory entries, or files, that exist in the Flash memory directory.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
This variable sets a request to erase Flash memory, freeing up all available memory space. All of the Flash memory is erased out. Individual files cannot be erased from Flash memory.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Write-only
Indicates the status of current or last erasing of Flash memory.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the value of sysUpTime the last time the Flash memory was erased.
Syntax: Timeticks
Access: Read-only
Provides the amount of available Flash memory in octets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
flashSize
Provides the amount of total Flash memory in octets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
flashStatus
Indicates the status of the availability of Flash memory.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Requests to write the Flash memory to a Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server. The value (display string) is the name of the Flash file being sent, or written, to the server. The instance ID is the IP address of the TFTP host.
This copy of the system image can serve as a backup copy and can also be used to verify that the copy in the Flash memory is the same as the original file.
The Flash memory card can be used as a TFTP file server for other routers on the network. This feature allows you to boot a remote router with an image that resides in the Flash server memory.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Write-only
Indicates the status of the current or last flash to net transfer.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the value of sysUpTime the last time a file was copied from the Flash memory in the router to the TFTP host.
Syntax: Timeticks
Access: Read-only
Provides the status of the VPP DIP jumper on the Flash memory card. Files can be written to the Flash memory card only if the VPP DIP jumper is turned on.
Syntax: Integer (1 = VPP enabled/Flash write enabled, 2 = VPP disabled/Flash write disabled)
Access: Read-only
Copies a software image from Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server to the Flash memory on the router. The value (display string) is the name of the file being sent, or written, to the Flash memory. The instance ID is the IP address of the TFTP host.
The TFTP image copied to the Flash memory must be at least System Software Release 9.0 or later. If earlier system software is copied into the Flash memory, the host processor card will not recognize the CSC-MC+ card upon the next reboot.
If free Flash memory space is unavailable, or if the Flash memory has never been written to, the erase routine is required before new files can be copied.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Write-only
Indicates the status of the current or next-to-last flash transfer.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the value of sysUpTime the last time a file was copied from a Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server to the Flash memory on the router.
Syntax: Timeticks
Access: Read-only
The local FSIP Card table, lfsipTable, contains information about FSIP cards used by the Cisco 7000 and includes the following six variables that provide information about the processor: locIfFSIPtype, locIfFSIPrts, locIfFSIPcts, locIfFSIPdtr, locIfFSIPdcd, and locIfFSIPdsr. The index to this table is locIfSIPIndex, which indicates the interface index of the card corresponding to its IfIndex.
| locIfFSIPIndex | locIfFSIPtype | locIfFSIPrts | locIfFSIPcts | and so on |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | DCE | 1 | 2 |
|
2 | DTE | 1 | 3 |
|
and so on |
|
|
|
|
locIfFSIPcts
Indicates whether the CTS (clear to send) signal is up or down.
Syntax: Integer (1 = not available, 1 = up, 2 = down)
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the DCD (data carrier detect) signal is up or down.
Syntax: Integer (1 = not available, 2 = up, 3 = down)
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the DSR (data set ready) signal is up or down.
Syntax: Integer (1 = not available, 2 = up, 3 = down)
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the DTR (data terminal ready) signal is up or down.
Syntax: Integer (1 = not available, 2 = up, 3 = down)
Access: Read-only
Indicates the index interface port of the corresponding ifIndex. (RFC 1213)
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the RTS (request to send) signal is up or down.
Syntax: Integer (1 = not available, 2 = up, 3 = down)
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the FSIP line uses DCE (data communications equipment) or DTE (data terminal equipment).
Syntax: Integer (1 = not available, 2 = DTE, 3 = DCE)
Access: Read-only
The following variables apply to interfaces attached to Cisco devices. These variables can be used to monitor the performance of the network in terms of the number of packets dropped, time allocations for input and output packets, and so on. These variables also can be used for fault management. For example, variable values indicate which interfaces are dropping packets or have had to be restarted several times.
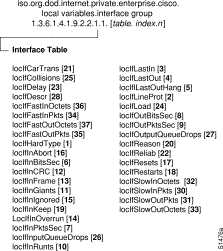
The Interface table, lifTable, contains all of the variables in the Interface group. The index to the table is ifIndex, which indicates the number of the interface. If the device has n number of interfaces, the Interface table will contain n rows.
In the Interface table shown in Table 5, the first column indicates the number of interfaces on the device. Each of the variables in the interface table occupies one column; for example, locIfHardType is shown in a column, followed by locIfLineProt in the next column, and so on.
| Interface Numer | locIfHardType | locIfLineProt | and so on |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Ethernet | 1 |
|
2 | TokenRing | 0 |
|
3 | FDDI | 1 |
|
and so on |
|
|
|
This section contains basic interface variables that apply to all interfaces and are not protocol-specific.
Provides the number of times the serial interface received the Carrier Detect (CD) signal. If the carrier detect line is changing state often, it might indicate modem or line problems.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output collisions detected on this interface.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the media-dependent delay in transferring a packet to another interface on the media. The delay is indicated in microseconds. Used by Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP).
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides a description of the interface (such as Ethernet, serial, and so on) that corresponds to the user-configurable interface description commands
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-write
Provides the octet count for inbound traffic routed with fast and autonomous switching.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
locIfFastInPkts
Provides the packet count for inbound traffic routed with fast and autonomous switching.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the octet count for outbound traffic routed with fast and autonomous switching.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the packet count for outbound traffic routed with fast and autonomous switching.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the type of interface (such as Ethernet, serial, FDDI, and so on).
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input packets that were aborted. Aborted input packets usually indicate a clocking problem between the serial interface and the data-link equipment.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides a 5-minute exponentially delayed average of CPU input bits per second.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input packets that had cyclic redundancy checksum (CRC) errors. The CRC generated by the originating station or far-end device does not match the checksum calculated from the data received. On a serial link, CRCs usually indicate noise, gain hits, or other transmission problems on the data link.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input packets that were received incorrectly with framing errors. On a serial line, this is usually the result of noise or other transmission problems.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input packets that were discarded because they exceeded the maximum packet size allowed by the physical media.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input packets that were ignored by this interface because the interface hardware ran low on internal buffers. Broadcast storms and bursts of noise can cause the ignored count to be increased.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether keepalives are enabled on this interface.
Syntax: Integer (1 = enabled, 2 = disabled)
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of times the serial receiver hardware was unable to send data to a hardware buffer because the input rate exceeded the ability of the receiver to handle the data.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides a weighted average of input bits and packets transmitted per second in the last 5 minutes.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of packets dropped because the input queue was full.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input packets that were discarded because they were smaller than the minimum packet size allowed by the physical media.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the elapsed time in milliseconds since the last line protocol input packet was successfully received by an interface. Useful for knowing when a dead interface failed.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the elapsed time in milliseconds since the last line protocol output packet was successfully transmitted by an interface. Useful for knowing when a dead interface failed.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the elapsed time in milliseconds since the last line protocol output packet could not be successfully transmitted.
OR
Provides the elapsed time (in milliseconds) since the interface was last reset because of a transmission that took too long.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the interface is up or down.
Syntax: Integer (1 = up, 2 = down)
Access: Read-only
Provides the loading factor of the interface. The load on the interface is calculated as an exponential average over 5 minutes and expressed as a fraction of 255 (255/255 is completely saturated). Used by Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP).
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides a 5-minute weighted average of output bits per second for the specific protocol.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides a 5-minute weighted average of output packets per second for the specific protocol.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of packets dropped because the output queue
was full.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the reason for the most recent status change of the interface.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the level of reliability for the interface. The reliability of the interface is calculated as an exponential average over 5 minutes and expressed as a fraction of 255 (255/255 is 100 percent). Used by Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP).
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of times the interface was reset internally. An interface can be reset if packets queued for transmission were not sent within several seconds. On a serial line, this can be caused by a malfunctioning modem that is not supplying the transmit clock signal or by a cable problem. If the system notices that the carrier detect line of a serial interface is up, but the line protocol is down, it periodically resets the interface in an effort to restart it. Interface resets also can occur when an interface is looped back or shut down.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of times the interface needed to be completely restarted because of errors.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the octet count for inbound traffic routed with process switching.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the packet count for inbound traffic routed with process switching.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the packet count for outbound traffic routed with process switching.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the octet count for outbound traffic routed with process switching.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
End of Table
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP). ARP provides dynamic addressing between 32-bit IP addresses and Ethernet addresses. For detailed information on ARP, refer to the Router Products Configuration and Reference publication.
Provides the ARP input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the ARP input packet count. It indicates the number of ARP Reply packets received by this router on this interface from other hosts.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the ARP output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the ARP output packet count. It indicates the number of ARP Request packets sent by this router on this interface to other hosts on the network.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running AppleTalk:
Provides the AppleTalk protocol input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the AppleTalk protocol input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the AppleTalk protocol output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the AppleTalk protocol output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running Apollo:
Provides the Apollo protocol input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the Apollo protocol input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the Apollo protocol output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the Apollo protocol output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running bridging protocols:
Provides the bridged protocol input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the bridged protocol input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the bridged protocol output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the bridged protocol output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the Source-Route Bridging (SRB) protocol input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the SRB protocol input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the SRB protocol output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the SRB protocol output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running Connectionless Network Service (CLNS):
Provides the CLNS protocol input byte count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the CLNS protocol input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the CLNS protocol output byte count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the CLNS protocol output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running DECnet:
Provides the DECnet protocol input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the DECnet protocol input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the DECnet protocol output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the DECnet protocol output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running HP Probe, an address resolution protocol developed by Hewlett-Packard:
Provides the HP Probe protocol input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the HP Probe protocol input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the HP Probe protocol output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the HP Probe protocol output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running the Internet Protocol (IP):
Provides the IP input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the IP input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the IP output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the IP output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the LAN Network Manager protocol input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the LAN Network Manager protocol input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the LAN Network Manager protocol output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the LAN Network Manager protocol output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running the Maintenance Operation Protocol (MOP):
Provides the MOP input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the MOP input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the MOP output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the MOP output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running Novell:
Provides the Novell protocol input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the Novell protocol input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the Novell protocol output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the Novell protocol output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group record the number of input and output packets and octets for interfaces running protocols other than those listed in the Interface group:
Provides the input octet count for protocols other than those listed in the Interface group.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the input packet count for protocols other than those listed in the Interface group.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the output octet count for protocols other than those listed in the Interface group.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the output packet count for protocols other than those listed in the Interface group.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces using the Serial Tunnel (STUN) protocol. STUN allows devices that use Synchronous Data Link Control (SDLC) or High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC) to be connected through one or more Cisco routers across different network topologies.
Provides the STUN protocol input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the STUN protocol input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the STUN protocol output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the STUN protocol output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running the Spanning Tree protocol. Used in bridging, spanning trees provide root and designated bridges to notify all other bridges in the network when an address change has occurred, thereby eliminating loops.
Provides the spanning-tree input octet packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the spanning-tree input protocol packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the spanning-tree output octet packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the spanning-tree output protocol packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running the Banyan Virtual Integrated Network Service (VINES) protocol. This proprietary protocol is derived from the Xerox Network Systems (XNS) protocol. The VINES variables provide the number of input and output packets and octets on a per interface basis.
Provides the VINES protocol input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The following variables in the Interface group apply to interfaces running Xerox Network Systems (XNS).
Provides the XNS protocol input octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the XNS input packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the XNS protocol output octet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the XNS protocol output packet count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The Internet Protocol (IP) group provides variables pertaining to the IP, such as the determination of how an interface obtained its IP address, who supplied the address, and Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) messages about IP packet processing.
The Cisco IP Address table, lipAddrTable, contains the following six variable entries, or rows: locIPHelper, locIPHow, locIPRedirects, locIPSecurity, locIPUnreach, and locIPWho. The index to this table is the IP address of the device, or ipAdEntAddr. If a device has n number of IP addresses, there will be n rows in the table.
For simplification, Table 6 shows only the locIpHow and locIPWho variables. The locIPHow variable value shows that the device at 131.108.201.245 obtained its address through nonvolatile memory. The locIPWho variable value indicates the device was assigned its current address by the device at 131.101.200.248.
| IP Address | locIPHow | locIPWho | and so on |
|---|---|---|---|
131.108.201.245 | nonvolatile | 131.101.200.248 |
|
142.111.202.244 | nonvolatile | 131.56.70.249 |
|
and so on |
|
|
|
Provides the IP address for broadcast forwarding support. Provides the destination broadcast or IP address that the router should use when forwarding User Datagram Protocol (UDP) broadcast datagrams, including BootP, received on the interface.
Syntax: IpAddress
Access: Read-only
Describes how this interface obtained its IP address. Typically, the address is determined by nonvolatile memory.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) redirects will be sent. A router sends an ICMP Redirect message to the originator of any datagram that it is forced to resend through the same interface on which it was received. It does so because the originating host presumably could have sent that datagram to the ultimate destination without involving the router at all. ICMP Redirect messages are sent only if the router is configured with the ip redirects command.
Syntax: Integer (1 = sent, 2 = not sent)
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether IP security is enabled on the interface. For details on IP security levels, see RFC 1108, U.S. Department of Defense Security Options for the Internet Protocol.
Syntax: Integer (0 = false, 1 = true)
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) packets indicating unreachable addresses will be sent for a specific route.
If this variable is set, and the router receives a datagram that it cannot deliver to its ultimate datagram (because it knows of no route to the destination address), it replies to the originator of that datagram with an ICMP Host Unreachable message.
Syntax: Integer (0 = false, 1 = true)
Access: Read-only
Provides the IP address of the device from which this interface received its IP address. If the interface does not use an IP address from another device, a value of 0.0.0.0 displays.
Syntax: IpAddress
Access: Read-only
End of Table
The local IP routing table, lipRoutingTable, contains two variables: locRtCount and locRtMask. The index for this table is the destination address of the IP route, or ipRouteDest. If there are n number of routes available to a device, there will be n rows in the IP routing table.
In Table 7, for the route with the destination IP address of 131.104.111.1, the routing table network mask is 255.255.255.0. The number of parallel routes within the routing table is 3, and the route was used in a forwarding operation two times.
| ipRouteDest | locRtMask | locRtCount |
|---|---|---|
131.104.111.1 | 255.255.255.0 | 3 |
133.45.244.245 | 255.255.255.0 | 1 |
Provides the number of parallel routes within the IP Routing table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
locRtMask
Provides the IP Routing table network mask. For example, 255.255.255.0.
Syntax: IpAddress
Access: Read-only
End of Table
Provides the total number of bytes of lost IP packets as a result of accounting failure.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of IP packets that were lost due to memory limitations and accounting failure.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the threshold of IP accounting records in use before IP traffic will be discarded.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Cisco routers maintain two accounting databases: an active database and a checkpoint database. The router takes a snapshot of the running, or active database, and copies it into the checkpoint database. For detailed information on active and checkpoint databases, refer to the Router Products Configuration and Reference and Router Products Command Reference publications.
This group provides access to the active database that is created and maintained if IP accounting is enabled on a router. The active database contains information about the number of bytes and packets switched through a system on a source and destination IP address basis. Only transit IP traffic is measured and only on an outbound basis; traffic generated by the router or terminating in the router is not included in the accounting statistics. Internetwork statistics obtained through these variables can be analyzed to improve network performance.
The local IP accounting table, lipAccountingTable, includes four related variables: actByts, actDst, actPkts, and actSrc. The index for this table is actSrc and actDst. For example, in the first row in Table 8, the source host address is 131.24.35.248, and the destination host address is 138.32.28.245. Fifty IP packets and 400 bytes of data have been sent between the source and destination address.
| actByts | actDst | actPkts | actSrc |
|---|---|---|---|
400 | 138.32.28.245 | 50 | 131.24.35.248 |
1259 | 128.52.33.101 | 110 | 128.52.33.96 |
Provides the total number of bytes in IP packets from the source to destination host.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the IP destination address for the host traffic matrix.
Syntax: Ip Address
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of IP packets sent from the source to destination host.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the IP address for the host traffic matrix.
Syntax: IpAddress
Access: Read-only
Specifies the access list number violated by packets from this source to this destination. A zero value indicates that no access list was violated.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
End of Table
Provides the age of the accounting data in the current data matrix of the active database.
Syntax: Timeticks
Access: Read-only
The Cisco router maintains two accounting databases: an active database and a checkpoint database. For detailed information on active and checkpoint databases, refer to the Router Products Configuration and Reference publication.
The running, or active database, is copied into the checkpoint database. If the checkpoint database already has data obtained previously from the active database, the router appends the latest copy of the active database to the existing data in the checkpoint database. The checkpoint database stores data retrieved from the active database until actCheckPoint is set or you delete the contents of this database by using the clear ip accounting [checkpoint] command.
A network management system (NMS) can use checkpoint MIB variables to analyze stable data in the checkpoint database.
The local IP Checkpoint Accounting table, lipCkAccountingTable, includes four related variables: ckactByts, ckactDst, ckactPkts, and ckactSrc. The index for this table is ckacSrc and ckactDst. For example, in Table 9, the source host address is 131.24.35.248. The destination host address is 138.32.28.245. Fifty IP packets and 400 bytes of data have been sent between the source and destination address.
| ckactByts | ckactDst | ckactPkts | ckacSrc |
|---|---|---|---|
400 | 138.32.28.245 | 50 | 131.24.35.248 |
480 | 124.45.222.246 | 60 | 123.34.216.244 |
Provides the total number of bytes in IP packets from source to destination in the checkpoint matrix.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the IP destination address of the host receiving the IP packets. The address is listed in the checkpoint traffic matrix.
Syntax: IpAddress
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of IP packets sent from the source to the destination address in the checkpoint matrix.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the IP source address of the host sending the IP packets. The address is listed in the checkpoint traffic matrix.
Syntax: IP address
Access: Read-only
Provides the access list number violated by packets from source to destination in the checkpoint matrix.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
End of Table
Activates a checkpoint database. This variable must be read and then set to the same value that was read. The value read and then set will be incremented after a successful set request.
For detailed information on active and checkpoint databases, refer to the Router Products Command Reference and Router Products Configuration and Reference publications.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Provides information on how long ago the data was first stored in the checkpoint matrix.
Syntax: Timeticks
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of packets dropped due to access control failure.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
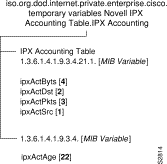
The IPX Accounting table allows a related set of IPX accounting variables to be applied across several devices or interfaces.
Provides the total bytes of lost IPX packets.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-Only
Provides the lost IPX packets due to memory limitations.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-Only
Provides the threshold of IPX accounting records in use before IPX traffic will be unaccounted.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-Only
The local IPX accounting table (see Table 10), lipxAccountingTable, provides access to the Cisco IPX accounting support. The Local IPX Accounting Table (see Table 11) includes the following variables: ipxActSrc, ipxActDst, ipxActPkts, and ipxActByts.
| ipxActByts | ipxActDst | ipxActPkts | ipxActSrc |
|---|---|---|---|
10,000 | 1.000.0230.0110 | 40 | BADDAD.0110.0220.0333 |
Provides the total number of bytes in IPX packets from source to destination.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-Only
Provides the IPX Destination address for host traffic matrix.
Syntax: Octet String
Access: Read-Only
Provides the number of IPX packets sent from source to destination.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-Only
Provides the IPX source address for host traffic matrix.
Syntax: Octet String
Access: Read-Only
End of Table
Provides the age of the data in the current IPX data matrix.
Syntax: TimeTicks
Access: Read-Only
The Local IPX Checkpoint Accounting table, ipxCkAccountingTable, includes four related variables: ipxckActByts, ipxckActDst, ipxckActPkts, and ipxckActSrc. The index for this table is ckActSrc and ckActDst.
| ipxckActByts | ipxckActDst | ipxckActPkts | ipxckActSrc |
|---|---|---|---|
10,000 | 1.000.0230.0110 | 40 | BADDAD.0110.0220.0333 |
Provides the IPX destination address for host in checkpoint traffic matrix.
Syntax: Octet String
Access: Read-Only
Provides the number of IPX packets sent from source to destination in checkpoint matrix.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-Only
Provides the IPX source address for host in checkpoint traffic matrix.
Syntax: Octet String
Access: Read-Only
End of Table
Provides the age of data in the IPX checkpoint matrix.
Syntax: TimeTicks
Access: Read-Only
ipxckActCheckPoint
Provides a checkpoint to the IPX accounting database. This MIB variable must be read and then set with the same value for the checkpoint to succeed. The value read and then set will be incremented after a successful set request
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-Write
The otherEnterprises subtree contains the Novell MIB (IPX) group and the RIPSAP group.
This group contains general information about all instances of IPX on one system. The IPX variables are located in the other Enterprises group.
This table contains one entry for each instance of IPX running on the system. It contains the management information that should be made available by all implementations of the IPX protocol.
Provides basic information for the IPX System table.
Syntax: Sequence of IPXBasicSysEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Specifies that each entry corresponds to one instance of IPX running on the system.
Syntax: IPXBasicSysEntry
Access: not-accessible
The unique identifier of the instance of IPX to which this row corresponds. This value may be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read
The validity of this entry in the IPX system table. Setting this field to off indicates that this entry may be deleted from the system table at the IPX implementation's discretion.
Syntax: Integer 1 = off, 2 = on
Access: Read-write
The network number portion of the IPX address of this system.
Syntax: NetNumber
Access: Read-write
The node number portion of the IPX address of this system.
Syntax: Octet String (size = 6)
Access: Read-write
The readable name for this system.
Syntax: Octet string (size (0..48))
Access: Read-write
The total number of IPX packets received, including those received in error.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The number of IPX packets discarded due to errors in their headers, including any IPX packet with a size less than the minimum of 30 bytes.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The number of IPX packets discarded because the destination socket was not open.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The number of IPX packets received but discarded due to reasons other than those accounted for by ipxBasicSysInHdrErrors, ipxBasicSysInUnknownSockets, ipxAdvSysInDiscards, and ipxAdvSysInCompressDiscards.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The number of IPX packets received with incorrect checksums.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The total number of IPX packets delivered locally, including packets from local applications.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The number of times no route to a destination was found.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The number of IPX packets supplied locally for transmission, not including any packets counted in ipxAdvForwPackets.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
ipxBasicSysOutMalformedRequests
The number of IPX packets supplied locally that contained errors in their structure.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The number of outgoing IPX packets discarded due to reasons other than those accounted for in ipxBasicSysOutMalformedRequests, ipxAdvSysOutFiltered, and ipxAdvSysOutCompressDiscards.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The total number of IPX packets transmitted.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The configured maximum number of IPX sockets that may be open at one time.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
The number of IPX socket open calls which failed.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
This table contains one entry for each instance of IPX running on the system. It contains the advanced management information that may not be available from all implementations of the IPX protocol.
Specifies the IPX System table - advanced information.
Syntax: Sequence of IPXAdvSysEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Each entry corresponds to one instance of IPX running on the system.
Syntax: IPXAdvSysEntry
Access: not-accessible
The unique identifier of the instance of IPX to which this row corresponds. This value may be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
The maximum number of paths with equal routing metric value which this instance of the IPX may split between when forwarding packets.
Syntax: Integer (1..32)
Access: Read-write
The maximum number of hops a packet may take.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
The number of IPX packets discarded due to exceeding the maximum hop count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: read-only
The number of incoming IPX packets discarded due to filtering.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The number of incoming IPX packets discarded due to decompression errors.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The number of NETBIOS packets received.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The number of IPX packets forwarded.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The number of outgoing IPX packets discarded due to filtering.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The number of outgoing IPX packets discarded due to compression errors.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The number of circuits known to this instance of IPX.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
The number of currently reachable destinations known to this instance of IPX.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
The number of services known to this instance of IPX.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
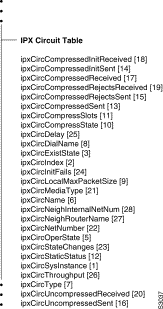
This group contains information about all circuits used by IPX on the system.
The Circuit Table contains management information for each circuit known to this system.
Specifies the Circuit table.
Syntax: Sequence of IPXCircEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Each entry corresponds to one circuit known to the system.
Syntax: IPXCircEntry
Access: Not-accessible
The unique identifier of the instance of IPX to which this entry corresponds. This value may be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
The identifier of this circuit, unique within the instance of IPX. This value may be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
The validity of this circuit entry. A circuit with this value set to off may be deleted from the table at the IPX implementation's discretion.
Syntax: Integer 1 = off, 2 = on
Access: Read-write
The value of ifIndex for the interface used by this circuit. This value may be written only when creating a new entry in the table
Syntax: Integer 1 = down, 2 = up, 3 = sleeping
Access: Read-write
Specifies the readable name for the circuit.
Syntax: Octet string (size (0..48)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the type of the circuit.
Syntax: Integer 1 = other, 2 = broadcast, 3 = ptToPt, 4 = wanRIP, 5 = unnumberedRIP, 6 = dynamic, 7 = wanWS
Access: Read-write
The symbolic name used to reference the dialing information used to create this circuit. This value may be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Octet string (size (0..48))
Access: Read-write
Specifies the maximum size (including header), in bytes, that the system supports locally on this circuit.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
The compression state on this circuit. This value may be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer 1 = off, 2 = on
Access: Read-write
The number of compression slots available on this circuit. This value may be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Indicates whether the information about static routes and services reached via this circuit matches that saved in permanent storage (current). Setting the value to write when it had the value changed will write the currently in use information to permanent storage, if supported. Setting the value to read when it had the value changed will replace any routes and services currently defined for the circuit with those read from permanent storage, if supported.
Syntax: Integer 1 = unknown, 2 = current, 3 = changed, 4 = read, 5 = reading, 6 = write, 7 = writing
Access: Read-write
Specifies the number of compressed packets sent.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of compression initialization packets sent.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The number of compressed packet rejected packets sent.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The number of packets sent without being compressed even though compression was turned on for this circuit.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The number of compressed packets received.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The number of compression initialization packets received.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
ipxCircCompressedRejectsReceived
The number of compressed packet rejected packets received.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The number of packets received without having been compressed even though compression was turned on for this circuit.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the media type used on this circuit
Syntax: Octet string (size = 2)
Access: Read-only
Specifies the IPX network number of this circuit.
Syntax: NetNumber
Access: Read-only
The number of times the circuit has changed state.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of times that initialization of this circuit has failed.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The period of time, in milliseconds, that it takes to transmit one byte of data, excluding protocol headers, to a destination on the other end of the circuit, if the circuit is free of other traffic.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
The amount of data, in bits per second, that may flow through the circuit if there is no other traffic.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
The name of the neighboring router on a WAN circuit.
Syntax: Octet string (size = 0..48)
Access: Read-only
The internal network number of the neighboring router on a WAN circuit.
Syntax: NetNumber
Access: Read-only
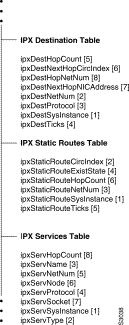
This group provides a representation of the forwarding database used by all instances of IPX on the system. This group contains generic routing information that must be provided by any IPX routing protocol.
The Destination table contains information about all known destinations. The routing information shown in this table represents the path currently being used to reach the destination.
The Destination table contains information about all known destinations.
Syntax: Sequence of IPXDestEntry
Access: Not accessible
Each entry corresponds to one destination
Syntax: IPXDestEntry
Access: Not accessible
The unique identifier of the instance of IPX to which this row corresponds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
The IPX network number of the destination.
Syntax: NetNumber
Access: Read-only
The routing protocol from which knowledge of this destination was obtained.
Syntax: Integer 1 = other, 2 = local, 3 = rip, 4 = nlsp, 5 = static
Access: Read-only
Specifies the delay in ticks to reach this destination.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of hops necessary to reach the destination.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the unique identifier of the circuit used to reach the next hop.
Syntax: PhysAddress
Access: Read-only
Specifies the NIC address of the next hop.
Syntax: PhysAddress
Access: Read-only
Specifies the IPX network number of the next hop.
Syntax: NetNumbr
Access: Read-only
This table contains the information about all the static routes defined. There may be more than one static route to any given destination. Only the route currently being used will also be present in the Destination Table defined earlier.
The Static Routes table contains information about all destinations reached via statically configured routes.
Syntax: Sequence of IPXStaticRouteEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Specifies that each entry corresponds to one static route.
Syntax: IPXStaticRouteEntry
Access: Not-accessible
The unique identifier of the instance of IPX to which this row corresponds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the unique identifier of the circuit used to reach the first hop in the static route.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the IPX network number of the route's destination.
Syntax: NetNumber
Access: Read-write
Specifies the validity of this static route. Entries with the value set to off may be deleted from the table at the implementation's discretion.
Syntax: Integer 1 = off, 2 = on
Access: Read-write
Specifies the delay, in ticks, to reach the route's destination.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the number of hops necessary to reach the destination.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
This group contains management information about all known services.
This table contains the services information indexed by service name and type.
Specifies the table of services, indexed by name and type.
Syntax: Sequence of IPXServEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Specifies that each entry corresponds to one service.
Syntax: IPXServEntry
Access: Not-accessible
The unique identifier of the instance of IPX to which this entry corresponds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the service type
Syntax: Octet string (size=2)
Access: read-only
Specifies the service name.
Syntax: Octet string (size=1..48)
Access: read-only
Specifies the protocol from which knowledge of this service was obtained.
Syntax: Integer 1=other, 2=local, 4=nlsp, 5=static, 6=sap
Access: Read-only
Specifies the IPX network number portion of the IPX address of the service.
Syntax: NetNumber
Access: Read-only
Specifies the node portion of the IPX address of the service.
Syntax: Octet string (Size=6)
Access: Read-only
Specifies the socket portion of the IPX address of the service.
Syntax: Octet string (Size=2)
Access: read-only
Specifies the number of hops to the service.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
This table contains the services information indexed by address, name, and type.
Specifies the table of services, indexed by address, name, and type.
Syntax: IPXDestServEntry
Access: not-accessible
Confirms that each entry corresponds to one service.
Syntax: IPXDestServEntry
Access: not-accessible
Specifies the unique identifier of the instance of IPX to which this entry corresponds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the IPX network number portion of the IPX address of the service.
Syntax: NetNumber
Access: Read-only
Specifies the socket portion of the IPX address of the service.
Syntax: Octet string (Size=2)
Access: Read-only
Specifies the name of the service
Syntax: Octet string (Size=1..48)
Access: Read-only
Specifies the type of service
Syntax: Octet string (Size=2)
Access: Read-only
The protocol from which knowledge of this service was obtained.
Syntax: Integer 1=other, 2=local, 4=nlsp, 5=static, 6=sap)
Access: Read-only
Identifies the number of hops to the service.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
This table contains information for all services reached via a static route.
The Static Services table contains information about all services reached via statically configured routes.
Syntax: Sequence of IPXStaticServEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Specifies that each entry corresponds to one service.
Syntax: IPXStaticServEntry
Access: Not-accessible
The unique identifier of the instance of IPX to which this entry corresponds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the circuit used to reach this service.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the name of the service.
Syntax: Octet string (Size=1..48)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the type of service.
Syntax: Octet string (Size=2)
Access: Read-write
The validity of this static service. Entries with the value set to off may be deleted from the table at the implementation's discretion.
Syntax: Integer 1=off, 2=on
Access: Read-write
The IPX network number portion of the IPX address of the service.
Syntax: NetNumber
Access: Read-write
Specifies the node portion of the IPX address of the service.
Syntax: Octet string (Size=6)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the socket portion of the IPX address of the service.
Syntax: Octet String (Size=2)
Access: Read-write
Specifies the number of hops to the service.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
This MIB defines the management information for the RIP and SAP protocols running in an IPX environment. It provides information in addition to that contained in the IPX MIB itself. All tables in this MIB are linked to an instance of IPX via the system instance identifier as defined in the IPX MIB.
This group contains global information about each instance of RIP/SAP running on one system.
This table contains an entry for each instance of RIP running on the system.
Specifies the RIP system table.
Syntax: Sequence of RIPSysEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Specifies that each entry corresponds to one instance of RIP running on the system.
Syntax: RIPSysEntry
Access: Not-accessible
The unique identifier of the instance of RIP to which this row corresponds. This value links the instance of RIP to an instance of IPX running on the system (in other words, the value of ripSysInstance should be the same as a value of ipxSysInstance). This value may be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: read-write
Indicates the operational state of this instance of RIP.
Syntax: Integer 1=off, 2=on
Access: Read-write
Specifies the number of times that an incorrectly formatted RIP packet was received.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
This table contains an entry for each instance of SAP running on the system.
Identifies the SAP system table.
Syntax: Sequence of SAPSysEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Specifies that each entry corresponds to one instance of SAP running on the system.
Syntax: SAPSysEntry
Access: Not-accessible
The unique identifier of the instance of SAP to which this row corresponds. This value links the instance of SAP to an instance of IPX running on the system (in other words, the value of SApSysInstance should be the same as a value of ipxSysInstance). This value may be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Indicates the operational state of this instance of SAP.
Syntax: Integer 1=off, 2=on
Access: Read-write
Specifies the number of times that an incorrectly formatted SAP packet was received.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
This group contains RIP and SAP management information for each circuit known to this system.
The RIP Circuit table contains an entry for the RIP information for each circuit known to the system.
Specifies the RIP Circuit table.
Syntax: Sequence of RIPCircEntry
Access: Not-accessible
Specifies that each entry corresponds to one circuit known to the system.
Syntax: RIPCircEntry
Access: Not-accessible
The unique identifier of the instance of RIP and IPX (by means of ipxSysInstance) to which this entry corresponds. This value may be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the identifier of this circuit, unique within the instance of RIP. This value corresponds to the circuit identifier found in ipxCircIndex. This value may be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Indicates whether RIP information may be sent/received over this circuit.
Syntax: Integer 1=off, 2=on, 3=auto-on, 5=auto-off
Access: Read-write
Specifies the maximum pace, in packets per second, at which RIP packets may be sent on this circuit.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the RIP periodic update interval, in seconds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the holding multiplier for information received in RIP periodic updates.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the RIP packet size used on this circuit.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the number of RIP packets sent on this circuit.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of RIP packets received on this circuit.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
The SAP Circuit table contains an entry for the SAP information for each circuit known to the system.
Identifies the SAP Circuit table.
Syntax: Sequence of SAPCircEntry
Access: not-accessible
Specifies that each entry corresponds to one circuit known to the system.
Syntax: SAPCircEntry
Access: Not-accessible
The unique identifier of the instance of SAP and IPX (by means of ipxSysInstance) to which this entry corresponds. This value may be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the identifier of this circuit, unique within the instance of SAP. This value corresponds to the circuit identifier found in ipxCircIndex. This value may be written only when creating a new entry in the table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Indicates whether SAP information may be sent/received over this circuit.
Syntax: Integer 1=off, 2=on, 3=auto-on, 4=auto-off
Access: Read-write
Specifies the maximum pace, in packets per second, at which SAP packets may be sent on this circuit.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the SAP periodic update interval, in seconds.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the holding multiplier for information received in SAP periodic updates.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Specifies the SAP packet size used on this circuit.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Indicates whether to respond to SAP to get the nearest server requests received on this circuit.
Syntax: Integer 1=no, 2=yes
Access: Read-write
Indicates the number of SAP packets sent on this circuit.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of SAP packets received on this circuit.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
This section describes the group of MIB variables managed by Cisco Systems.
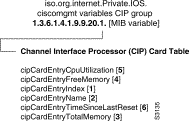
The CIP Group specifies the MIB module for objects used to manage the cisco channel interface processor card.
The cipCardTable contains a list of values for the CIP card which can be obtained on a per cip-card basis and include the following variables: cipCardEntryIndex, cipCardEntryName, cipCardEntryTotalMemory, cipCardEntryFreeMemory, cipCardEntryCpuUtilization, and cipCardEntryTimeSinceLastReset. This table extends CardTable in the cisco.mib.
Syntax: Sequence of CipCardEntry
Max-Access: not-accessible
cipCardEntryIndex
Specifies the index into cardTable (not physical chassis slot number, matches cisco chassis MIB cardindex)
Syntax: UInteger32
Max-Access: not-accessible
Specifies the configured name for the CIP.
Syntax: DisplayString
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies total memory on the card in kilobytes.
Syntax: UInteger32
Max-Access: Read-only
Specifies the total free memory on the card, that is the amount of memory in kilobytes not in use.
Syntax: UInteger32
Max-Access: read-only
The average percentage of time, over the last minute, that this processor was not idle.
Syntax: Integer (0..100)
Max-Access: read-only
cipCardEntryTimeSinceLastReset
Specifies the number of seconds the CIP has been running.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: read-only
End of Table
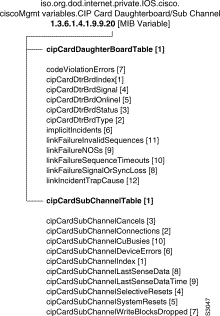
This table contains a list of objects pertaining to the daughter board on the CIP card.
Specifies which daughter board is being referenced for a particular CIP card.
Syntax: UInteger32
Max-Access: read-only
Indicates the channel path interface type.
Syntax: Integer
Max-Access: read-only
Specifies that the microcode for the daughter board has been successfully loaded and is executing.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: read-only
For ESCON, specifies that the LED has been seen and synchronization has been established. ESCON is the fiber optic connection from the IBM mainframe to the peripheral.This is layer 1 of the channel. Older technology (still in use) is called BUS and TAB and consists of 2 bulky copper cables. For Parallel Channel Adapter (PCA), specifies that the operational out has been sensed.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: read-only
For ESCON, specifies that a path has been established with at least one channel. For PCA, specifies that the PCA is online to the channel. It will respond to at least one device address.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: read-only
Counts the number of times the ESCON Processor recovers from an internal error.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: read-only
Specifies the number of recognized code-violation errors. A trap is issued when this number exceeds the bit error rate threshold for ESCON. The bit error rate threshold is set at 15 error burst within a 5 minute period. An error burst is the time period of 1.5 seconds plus or minus 0.05 seconds during which one or more code violations errors occur.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: read-only
Specifies the number of link failures recognized as a result of a loss of signal or loss of synchronization that persisted longer than the link interval duration. The link interval duration is one second with a tolerance of +1.5 seconds and -0 seconds.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: read-only
Specifies the number of link failures recognized as a result of the not-operational sequence (NOS).
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: read-only
Specifies the number of link failures recognized as a result of a connection recovery timeout or response timeout occurring while in transmit OLS state.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: read-only
Specifies the number of link failures recognized as a result of an invalid sequence for Link-Level-Facility State. Either a UD or UDR sequence was recognized while in wait-for-offline-sequence state.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: read-only
Indicates the condition which caused the last SNMP trap.
Syntax: Integer
1=reason other than what is defined in conditions 2-7.
2=indicates that the daughter board status has changed.
3=indicates that a condition, which may cause the recognition of a link incident in the attached node, has occurred.
4=indicates that the code violation error rate exceeded the threshold. 5=indicates a loss of signal or loss of synchronization that persisted longer than the link interval duration.
6=indicates the recognition of not-operational sequence, usually due to the operator taking the channel offline.
7=indicates a connection recovery timeout or response timeout occurring while in transmit OLS state.
8=indicates a UD or UDR sequence was recognized while in wait-for-offline-sequence state.
Max-Access: read-only
Indicates which subchannel is being referenced for a particular daughter board on a CIP card.
Syntax: UInteger32
Max-Access: read-only
Indicates the number of times a device was connected to the subchannel. For some devices, this correlates with the number of start subchannels.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: read-only
Specifies the number of halt subchannels.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: read-only
cipCardSubChannelSelectiveResets
Specifies the number of selective resets.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: read-only
Specifies the number of system resets.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: read-only
Specifies the number of device level errors.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: read-only
cipCardSubChannelWriteBlocksDropped
Specifies the number of times a block was received by the channel and a router buffer was not available so the block was discarded.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: read-only
cipCardSubChannelLastSenseData
Specifies the last sense data sent to the channel by this device.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE (2))
Access: read-only
cipCardSubChannelLastSenseDataTime
Specifies the time when the last sense data was sent to the channel by this device.
Syntax: TimeStamp
Max-Access: read-only
Specifies the number of control unit busies sent to the channel when this device was requested.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: read-only
This table contains status and other information not covered in the following tables for the Common Link Access to Workstation (CLAW) protocol.
Syntax: Sequence of CipCardClawEntry
Max-Access: not-accessible
Specifies which CLAW link is being referenced for a particular subchannel on a daughter board on a CIP card.
Syntax: UInteger32
Max-Access: read-only
Specifies the CLAW connection status.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: read-only
Contains configuration information for the Common Link Access to Workstation (CLAW) protocol.
Syntax: Sequence of CipCardClawConfigEntry
Max-Access: not-accessible
Specifies a list of CLAW configuration values.
Syntax: CipCardClawConfigEntry
Max-Access: not-accessible
Specifies the Hex path identifier for the switch port containing the fiber from the channel on the host to which this task connects. This is a concatenation of the switch port number, the channel logical address, and the control unit logical address. For a directly connected channel, the switch port number is usually 01.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE (2))
Max-Access: read-write
Specifies Device address for the device the host will use to communicate with this task.
Syntax: OCTET STRING (SIZE(2))
Max-Access: read-write
Specifies the IP address of the host application for this task.
Syntax: IpAddress
Max-Access: read-write
Specifies the CLAW host name for this CLAW device.
Syntax: DisplayString
Max-Access: read-write
Specifies the CLAW router name for this CLAW device.
Syntax: DisplayString
Max-Access: read-write
Specifies the CLAW host application name for this CLAW connection.
Syntax: DisplayString
Max-Access: read-write
Specifies the CLAW router application name for this CLAW connection.
Syntax: DisplayString
Max-Access: read-write
This table specifies a list of objects pertaining to data transfer statistics per CLAW Logical Link.
Syntax: Sequence of CipCardClawDataXferStatsEntry
Max-Access: not-accessible
Specifies a list of daughter board statistics.
Syntax: CipCardClawDataXferStatsEntry
Max-Access: not-accessible
cipCardClawDataXferStatsBlocksRead
Specifies the number of read data transfer channel command words (CCWs) from the channel perspective.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: read-only
cipCardClawDataXferStatsBlocksWritten
Specifies the number of successful write data transfer CCWs from the channel perspective.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: read-only
cipCardClawDataXferStatsBytesRead
Specifies the number of bytes successfully read from the channel perspective.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: read-only
Specifies the number of bytes successfully written from the channel perspective.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: read-only
cipCardClawDataXferStatsHCBytesRead
Specifies the number of bytes successfully read from the channel perspective. The HC (High Capacity) objects are the 64-bit equivalent of their 32-bit counterparts modeled after RFC 1573.
Syntax: Counter64
Max-Access: read-only
cipCardClawDataXferStatsHCBytesWritten
Specifies the number of bytes successfully written from the channel perspective. The HC (High Capacity) objects are the 64-bit equivalent of their 32-bit counterparts modeled after RFC 1573.
Syntax: Counter64
Max-Access: read-only
cipCardClawDataXferStatsReadBlocksDropped
Specifies the number of bytes written.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: read-only
cipCardClawDataXferStatsWriteBlocksDropped
Specifies the number of read blocks dropped.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: read-only
cipCardClawDataXferStatsBufferGetRetryCount
Specifies the number of times a buffer was requested and none was available.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: read-only
The variables described in this section apply to the Cisco Ping MIB Definitions.
Provides a table of ping request entries. The Ping group consists of a single table, the ciscoPingTable, and includes the ciscoPing entries described in this subsection.
Syntax: Sequence of CiscoPingEntry
Access: current
The address of the device to be pinged. An instance of this object cannot be created until the associated instance of ciscoPingProtocol is created. Once an instance of this object is created, its value cannot be changed.
Syntax: CiscoNetworkAddress
Access: Read-Write
Provides a ping request entry. A management station choosing to create an entry should first generate a pseudo-random serial number to be used as the index to this sparse table. The station should then create the associated instance of the row status and row owner objects. It must also, either in the same or in successive PDUs, create the associated instance of the protocol and address objects. It should also modify the default values for the other configuration objects if the defaults are not appropriate.
Once the appropriate instance of all the configuration objects has been created, either by an explicit SNMP set request or by default, the row status should be set to active to initiate the request. Note that this entire procedure may be initiated by means of a single set request which specifies a row status of createAndGo as well as specifies values for the non-defaulted configuration objects.
Once the ping sequence has been activated, it cannot be stopped; it will run until the configured number of packets have been sent.
Once the sequence completes, the management station should retrieve the values of the status objects of interest, and should then delete the entry. In order to prevent old entries from clogging the table, entries will be aged out, but an entry will never be deleted within 5 minutes of completing.
Syntax: CiscoPingEntry
Access: not-accessible
Specifies the protocol stack over which the ping packet is being sent. For IOS 10.2, Cisco supports the SNMP ping over IP, IPX, AppleTalk, CLNS, DECnet, and Vines.
Syntax: Cisco Network Protocol
Max-Access: Read-Create
Specifies a unique entry in the ciscoPingTable. A management station choosing to initiate a ping operation should use a pseudo-random value for this object when creating or modifying an instance of a ciscoPingEntry. The RowStatus semantics of the ciscoPingEntryStatus object will prevent access conflicts.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: not-accessible
Specifies the number of ping packets to send to the target in this sequence.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-create
Specifies the size of ping packets to send to the target in this sequence. The lower and upper boundaries of this object are protocol-dependent. An instance of this object cannot be modified unless the associated instance of ciscoPingProtocol has been created (so as to allow protocol-specific range checking on the new value).
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-create
Specifies the amount of time to wait for a response to a transmitted packet before declaring the packet dropped.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-create
Specifies the minimum amount of time to wait before sending the next packet in a sequence after receiving a response or declaring a timeout for a previous packet. The actual delay may be greater due to internal task scheduling.
Syntax: Integer32
Max-Access: Read-create
Specifies whether a ciscoPingCompletion trap should be issued on completion of the sequence of pings. If such a trap is sought, it is the responsibility of the management entity to ensure that the SNMP administrative model is configured in such a way as to allow the trap to be delivered.
Syntax: TruthValue
Max-Access: Read-create
The number of ping packets that have been sent to the target in this sequence.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
The number of ping packets that have been received from the target in this sequence.
Syntax: Counter32
Max-Access: Read-only
The minimum round trip time of all the packets that have been sent in this sequence. This object will not be created until the first ping response in a sequence is received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
The average round trip time of all the packets that have been sent in this sequence. This object will not be created until the first ping response in a sequence is received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
The maximum round trip time of all the packets that have been sent in this sequence. This object will not be created until the first ping response in a sequence is received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies a setting of true when all the packets in this sequence have been answered or have timed out.
Syntax: TruthValue
Access: Read-only
Specifies the entity that configured this device.
Syntax: OwnerString
Access: Read-create
Specifies the status of this table entry. Once the entry status is set to active, the associate entry cannot be modified until the sequence is completed (in other words, ciscoPingCompleted is true).
Syntax: RowStatus
Access: Read-create
The variables described in this section are system-wide and apply to all Cisco Systems products.
The following variables pertain to basic information such as system software description and version number, host and domain names, and number of bytes of free memory in the managed device:
Provides the IP address of the device causing the last SNMP authorization failure. The device did not use a configured community string or tried a SET with a read-only community string.
Syntax: IP address
Access: Read-only
Provides the IP address of the host that supplied the software currently running on the managed device.
Syntax: IP address
Access: Read-only
Provides the domain portion of the domain name of the host.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of bytes of free memory available in the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Represents the name of the host in printable ASCII characters.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Contains a printable octet string that contains the system bootstrap description and version identification.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Contains a printable octet string that contains the reason why the system was last restarted.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
The following variables are used to monitor the amount and type of buffer space available within a managed device. Buffers are blocks of memory used to hold network packets. There are five types of buffers based on size: small, middle, big, large, and huge. There are several pools of different-sized buffers. These pools grow and shrink based upon demand. Some buffers are temporary and are created and destroyed as warranted. Others are permanently allocated.
Contains the total number of allocation requests that have failed due to lack of any free buffers.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Counts the number of failures caused by insufficient memory to create a new buffer.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Buffer elements are blocks of memory used in internal operating system queues.
Contains the number of new buffer elements created for the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of buffer elements that are not currently allocated and are available for use in the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of successful attempts to allocate a buffer element when needed.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the maximum number of buffer elements the managed device can have.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of allocation attempts that failed because there were no buffer elements available.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Small buffer sizes are configurable.
Contains the number of small buffers created in the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of small buffers that are currently available to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of successful attempts to allocate a small buffer when needed.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the maximum number of small buffers that can be allocated to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of allocation attempts that failed because there were no small buffers available.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the size (in bytes) of small buffers.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of small buffers allocated to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the small buffers that have been destroyed in the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Middle buffer sizes are configurable.
Contains the number of middle buffers created in the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of middle buffers that are currently available to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of successful attempts to allocate a middle buffer when needed.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the maximum number of middle buffers that can be allocated to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of allocation attempts that failed because there were no middle buffers available.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the size (in bytes) of middle buffers.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of middle buffers allocated to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the middle buffers that have been destroyed in the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Big buffer sizes are configurable.
Contains the number of big buffers created in the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of big buffers that are currently available to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of successful attempts to allocate a big buffer when needed.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the maximum number of big buffers that can be allocated to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of allocation attempts that failed because there were no big buffers available.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the size (in bytes) of big buffers.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of big buffers allocated to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the big buffers that have been destroyed in the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Large buffer sizes are configurable.
Contains the number of large buffers created in the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of large buffers that are currently available to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of successful attempts to allocate a large buffer when needed.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the maximum number of large buffers that can be allocated to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of allocation attempts that failed because there were no large buffers available.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the size (in bytes) of large buffers.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of large buffers allocated to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the large buffers that have been destroyed in the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Huge buffer sizes are configurable.
Contains the number of huge buffers created in the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of huge buffers that are currently available to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of successful attempts to allocate a huge buffer when needed.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the maximum number of huge buffers that can be allocated to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the number of allocation attempts that failed because there were no huge buffers available.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the size (in bytes) of huge buffers.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of huge buffers allocated to the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Contains the huge buffers that have been destroyed in the managed device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
The following variables provide statistics on the CPU utilization of a device:
Provides a cumulative average of the CPU usage percentage over a 1-minute period. This variable, called by the scheduler every 5 seconds, computes the busy time in the last 5-second period, and the 5-minute, exponentially decayed busy time. The following equation shows the average sampling time:
average = ((average - interval) * exp (-t/C)) + interval
where t is five seconds and C is 1 minute, exp(-5/60) == .920 ~= 942/1024
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides a cumulative average of the CPU usage percentage over a 5-minute period. This variable, called by the scheduler every 5 seconds, computes the busy time in the last 5-second period, and the 5-minute, exponentially decayed busy time. The following equation shows the average sampling time:
average = ((average - interval) * exp (-t/C)) + interval
where t is five seconds and C is five minutes, exp(-5/60*5)) == .983 ~= 1007/1024
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the percentage of CPU usage over the first 5-second period in the scheduler. The scheduler determines which process or task takes priority over another and triggers them accordingly.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the Cisco name and address for reference purposes. This MIB variable applies only to router products that were purchased from Cisco.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
The environmental monitor card is provided only with the Cisco AGS+ router. This card checks input air temperature and air flow through the system card cage and card cage backplane power supplies. It also provides nonvolatile and system bus memory for the system. The Cisco 7000 has built-in environmental monitoring functionality, and so does not use the card. The Cisco 7000 router provides environmental monitoring, reporting, and if necessary, system shutdown.
All MIB variables in this group apply to the Cisco AGS+. A subset of those variables apply to the Cisco 7000. The following variables are used to poll and display power supply voltage and air temperature (in Celsius) in an AGS+ to help prevent system problems.
Provides the date of the calibration of the environmental monitor card. (AGS+ only)
For example:
calibrated on 2-14-93.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the firmware level of the environmental monitor card. (AGS+ only)
For example:
Environmental controller firmware version 2.0
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether there is an environmental monitor card in a router.
Syntax: Integer (0 = no, 1 = yes, but unavailable to SNMP; 2 = yes and available to SNMP for AGS+ routers; 3 = yes and available to SNMP for Cisco 7000 routers)
Access: Read-only
Provides the serial number of the environmental monitor card. (AGS+ only)
Following is an example of a serial number:
00220846
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the technician ID for the environmental monitor card. (AGS+ only)
Following is an example of a technician ID:
rma
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Test point 1 is the temperature of air entering the router. (AGS+ and Cisco 7000)
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the temperature of air entering the AGS+ and the Cisco 7000 router when the last shutdown occurred. If the input air temperature exceeds 109\xb0 F (43\xb0 C) in an AGS+, an error is detected, and the CSC-ENVM card shuts down the power supply.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides warning and fatal threshold values of the internal intake air for the AGS+ router and Cisco 7000.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the current temperature of air entering the router. (AGS+ and Cisco 7000)
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the air temperature entering the router is at warning level. (AGS+ and Cisco 7000)
Syntax: Integer (1 = warning, 2 = no warning)
Access: Read-only
Provides the temperature of air leaving the router. (AGS+ and
Cisco 7000)
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the temperature of air leaving the router when the last shutdown occurred. (AGS+ and Cisco 7000)
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the fatal threshold value for the exhaust air flow of the router. (AGS+ and Cisco 7000)
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the temperature of the exhaust air flow of the router. (AGS+ and Cisco 7000)
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the temperature of air flow leaving the router is at a warning level. (AGS+ and Cisco 7000)
Syntax: Integer (1 = warning, 2 = no warning)
Access: Read-only
Test point 3 is the +5-volt (V) line on the router.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the value of the +5V line when the last shutdown occurred. (AGS+ and Cisco 7000)
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the warning and fatal thresholds for the +5V line to the power supply on the AGS+ router. The warning threshold is ± 5 percent above or below +5V. The fatal threshold at which the router shuts down is ± 10 percent above or below +5V. (AGS+ only)
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the current value for the +5V line to the power supply on the router. The value is expressed in millivolts. (AGS+ and Cisco 7000)
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the +5V line to the power supply is at warning level. The warning threshold is ±5 percent above or below +5V. (AGS+ and Cisco 7000)
Syntax: Integer (1 = warning, 2 = no warning)
Access: Read-only
Test point 4 is the +12V line to the power supply of the router.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the value of the +12V line when the last shutdown occurred.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the warning and fatal thresholds for the +12V line to the power supply on the AGS+ router. The warning threshold is ± 10 percent above or below +12V. The fatal threshold at which the router shuts down is ± 15 percent above or below +12V. (AGS+ only)
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the current value (in millivolts) of the +12V line to the power supply of the router.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the +12V line to the power supply is at warning level. The warning threshold is ± 10 percent above or below +12V.
Syntax: Integer (1 = warning, 2 = no warning)
Access: Read-only
Test point 5 is the -12V line to the power supply of the router.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the value of the -12V line when the last shutdown occurred.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the warning and fatal thresholds for the -12V line to the power supply on the router. The warning threshold is ± 10 percent above or below -12V. The fatal threshold at which the router shuts down is ± 15 percent above or below -12V. (AGS+ only)
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the current value (in millivolts) of the -12V line to the power supply of the router.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the -12V line to the power supply on the router is at the warning level. The warning threshold is ± 10 percent above or below -12V. (AGS+ only)
Syntax: Integer (1 = warning, 2 = no warning)
Access: Read-only
Test point 6 is the -5V line to the power supply of the AGS+ router and +24V line to the power supply of the Cisco 7000 router.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the value of the -5V line to the power supply of the AGS+ router and +24V line to the power supply of the Cisco 7000 router when the last shutdown occurred.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the warning and fatal thresholds for the -12V line to the power supply on the AGS+ router. The warning threshold is ± 5 percent above or below -5V. The fatal threshold at which the router shuts down is ± 10 percent above or below -5V. (AGS+ only)
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the current value (in millivolts) of the -5V line to the power supply of the AGS+ router and +24V line to the power supply of the Cisco 7000 router.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
For the Cisco 7000, this variable indicates whether the +P24V line to the power supply is at the warning level.
Syntax: Integer (1 = warning, 2 = no warning)
Access: Read-only
envTestPt6warn
Indicates whether the -5V line to the power supply of the AGS+ router or +24V line to the power supply of the Cisco 7000 router is at the warning level. The warning threshold is ± 10 percent above or below -5V (AGS+ router) or +24V (Cisco 7000 router).
Syntax: Integer (1 = warning, 2 = no warning)
Access: Read-only
Provides the type of environmental card (for example, CSC-ENVM).
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
The following variables are used to monitor and set host configuration file information:
Provides the address of the host that provided the host configuration file for the managed device. The host configuration file contains commands that apply to one network server in particular.
Syntax: IpAddress
Access: Read-only
Provides the name of the last host configuration file used by the device.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the protocol that supplied the host configuration file.
Syntax: Integer (1 = IP, 2 = MOP, 3 = not applicable)
Access: Read-only
Allows the network management system (NMS) to load a new host configuration file via Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) onto the managed device and indicate the name of this configuration file. The instance ID is the IP address of the TFTP host. The display string indicates the name of the configuration file.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Write-only
The following variables are used to monitor and remotely set network configuration file information for the device:
Provides the address of the host that supplied the network configuration file for the managed device. The network configuration file contains commands that apply to all network servers and terminal services on a network.
Syntax: IpAddress
Access: Read-only
Provides the name of the network configuration file that resides on the managed device.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the protocol that supplied the network configuration file.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Loads a new network configuration file via Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) onto the managed device and indicates the name of this configuration file. The instance ID is the IP address of the TFTP host. The display string indicates the name of the configuration file.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Write-only
The following variables are used to monitor and set system-wide parameters:
Performs a clearing of the entire Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) cache and Internet Protocol (IP) route cache. The ARP provides dynamic mapping between IP addresses and Ethernet addresses. The ARP Cache table, which keeps a record of these mappings, can be cleared for maintenance purposes.
The IP route cache controls the use of a high-speed switching cache for IP routing. The route cache is enabled by default and allows outgoing packets to be load balanced on a per-destination basis. The sysClearARP variable helps clear the IP route cache for maintenance purposes.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Write-only
Clears an interface that is given IfIndex as a value. To clear an interface, take the ifIndex for the interface (for example, a value of 4) and set the sysClearInt variable to the ifIndex value of 4.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Write-only
Provides the address of the host that supplied the system boot image for the managed device. New versions of software can be downloaded over the network with boot image files. The new file takes effect the next time the managed device is reloaded.
Syntax: IpAddress
Access: Read-only
Provides the name of the system boot image file. New versions of software can be downloaded over the network with boot image files. The new file takes effect the next time the managed device is reloaded.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the protocol type that supplied the system boot image.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Writes the current (running) router configuration into nonvolatile memory where it can be stored and retained even if the router is reloaded. Write configuration memory if 1. Erase configuration memory if 0.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Write-only
Sends a copy of the current configuration via Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) to a remote host. When it is stored on the host, the configuration file can be edited and retrieved by other network entities.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Write-only
Following are variables that can be applied to terminal services. This group of variables contains terminal service information on a per-line basis, such as line status, line type, line speed, type of flow control, and type of modem.
Provides the number of physical lines on the device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
The local terminal services line table, ltsLineTable, contains all of the variables described in this section. The index to this table is the number of the terminal services line. If there are n number of terminal lines associated with the device, there will be n rows in the table.
| Line Number | tsLineActive | tsLineAutobaud | and so on |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Contains all of the variables described in this section. | ||
2 |
|
|
|
and so on |
|
|
|
Indicates whether this line is active.
Syntax: Integer (1 = active, 2 = not active)
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the line is set to autobaud detection so that it can adapt to the rate at which data is being sent to it.
Syntax: Integer (1 = autobaud, 2 = not autobaud)
Access: Read-only
Indicates what is used to represent the escape (Esc) character. The escape character allows a user to break out of active sessions.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Indicates the type of flow control the line is using. The flow can be controlled from software or hardware. Input indicates that the flow control is coming from the device to the terminal service. Output indicates flow control is provided by the terminal service.
The possible integer values follow:
1 = unknown
2 = none
3 = software-input
4 = software-output
5 = software-both
6 = hardware-input
7 = hardware-output
8 = hardware-both
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Describes the physical location of the line. The integer values 1-3 represent commands that can be defined by the user.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Describes the type of modem control the line is using.
The possible integer values follow:
1 = unknown
2 = none
3 = call-in
4 = call-out
5 = cts-required
6 = ri-is-cd
7 = modem inout
Descriptions of the integer values follow:
Call-in indicates dial-in modems that use the status of Data Terminal Ready (DTR) to determine whether to answer an incoming call.
Call-out indicates modems that raise data terminal ready (DTR) to see
if Clear To Send (CTS) becomes high as an indication that the host has noticed its signal.
Cts-required indicates the form of modem control that requires CTS to be high throughout the use of the line.
ri-is-cd is used for lines with high-speed modems. The modem answers the call if DTR is high, uses its Carrier Detect (CD) signal to reflect the carrier presence, and has its CD signal wired to the ring input of the terminal service.
modem inout is used to configure a line for both incoming and outgoing calls. The command enables a line to be used for both incoming and outgoing calls on dial-in/dial-out modems.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of garbage characters received while the line is inactive.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the number of current sessions on the line.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the number of the rotary group to which the line belongs. If the first line in a rotary group is busy, a connection can be made to the next free line.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the length (in lines) of the screen of the terminal attached to the line.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the width (in characters) of the screen of the terminal attached to the line.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Specifies the interval (in seconds) for closing the connection when there is no input or output traffic during a session.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the input speed at which the line is running.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the output speed at which the line is running.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Describes the terminal type of the line.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Specifies the interval (in seconds) for closing the connection when there is no input or output traffic on the line.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Describes the terminal line type.
The possible integer values follow:
1 = unknown
2 = console
3 = terminal
4 = line-printer
5 = virtual-terminal
6 = auxiliary
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the Terminal Access Controller Access System (TACACS) username and indicates whether TACACS is enabled on this line. TACACS servers provide security for accessing terminals remotely.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Indicates the number of times a connection has been made to or from this line.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
End of Table
The Terminal Services Line Session table, ltsLineSessionTable, contains six variables: tslineSesAddr, tslineSesCur, tslineSesDir, tslineSesIdle, tslineSesName, and tslineSesType.
For simplification, Table 13 shows values for three of the variables contained in the Terminal Services Line Session table. The index to the table is the session number and line number. Line 1 in the first session illustrates a Telnet connection. The session was started by the terminal. The remote host for this session is located at the IP address of 131.38.141.244.
| Session no. Line no. | tslineSesAddr | tslineSesDir | tslineSesType |
|---|---|---|---|
1, 1 | 131.38.141.244 | 3 | 5 |
2, 4 | 138.121.128.243 | 2 | 3 |
Provides the address of the remote host for this session.
Syntax: Network address
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether this session is currently active.
Syntax: Integer (1 = active, 2 = not active)
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether this session was started by another device (incoming) or by the terminal (outgoing).
The possible integer values follow:
1 = unknown
2 = incoming
3 = outgoing
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the amount of time (in seconds) that this session has been idle.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the name of the remote host for this session.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Describes the type of session that is currently active.
The possible integer values follow:
1 = unknown
2 = X.3 Packet Assembler/Disassembler (PAD)
3 = stream (enables a raw TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) stream with no Telnet-control sequences)
4 = rlogin (for making remote connection to a host—part of TCP/IP)
5 = telnet (for making remote connection to a host—UNIX protocol)
6 = Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
7 = local-area transport (LAT)
8 = Maintenance Operation Protocol (MOP)
9 = Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP)
10 = XRemote (provides support for X Windows over a serial line)
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
End of Table
The following variables pertain to the parameters of terminal services messages:
Sets the length of time (in milliseconds) allocated to reissue a message. The minimum nonzero setting is 10000.0. A setting of 0 will not repeat the message.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Sets the interval (in milliseconds) that occurs between reissues of the same message. The minimum (nonzero) setting for this interval is
10,000 milliseconds. If set to 0, the intervals will become more frequent as the message duration gets close to expiring. For example, 2 hours, 1 hour, 30 minutes, 5 minutes, and 1 minute.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Determines what action to take after the message has been sent.
The possible integer values follow:
1 = nothing
2 = reload
3 = message done
4 = abort
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
Sets the text of the message. Up to 256 characters can be included in the message.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-write
Determines whether to use the message text as a temporary banner.
Syntax: Integer (1 = no, 2 = yes, in addition to the regular banner)
Access: Read-write
Selects the TTY line to which you want the message sent. Setting this variable to -1 will send the message to all TTY lines.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-write
These variables can be applied to Cisco products running the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). These variables provide statistics on the number of input and output bytes and packets for TCP connections.
The TCP connection table, ltcpConnTable, contains five variables: loctcpConnElapsed, loctcpConnInBytes, loctcpConnInPkts, loctcpConnOutBytes, and loctcpConnOutPkts.
The index to this table includes the local host address and port number and the remote host address and port number for each TCP connection that is active for the device. These values are represented by tcpConnLocalAddress, tcpConnLocalPort, tcpConnRemAddress, and tcpConRemPort.
For n number of TCP connections, there are n rows in the table. The value n can change at any time if another TCP connection opens or if an existing TCP connection closes.
In Table 14, TCP A represents the first TCP connection in the table.
The TCP A connection shows 100 input bytes, 100 output bytes, 85 input packets, and 85 output packets for the connection. The connection has been established for 60 seconds, or 6000 timeticks.
| ltcpConnTable | Elapsed | InBytes | InPkts | OutBytes | OutPkts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
TCP A | 6000 | 100 | 85 | 100 | 85 |
TCP B | 4500 | 200 | 90 | 130 | 100 |
TCP C | 9000 | 300 | 100 | 250 | 95 |
Provides the length of time that the TCP connection has been established.
Syntax: Timeticks
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input bytes for the TCP connection.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input packets for the TCP connection.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output bytes for the TCP connection.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output packets for the TCP connection.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
End of Table
This section is equivalent to the experimental space defined by the Structure of Management Information (SMI). It contains variables that are useful to have, but are beyond the ability of Cisco to control and maintain. Support for these variables can change with each Cisco Systems software release.
The temporary variables section includes the following groups of variables:
Variables in this group can be used with all Cisco products running the AppleTalk protocol. These variables provide such information as total number of input and output packets, number of packets with errors,
and number of packets with Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) requests and replies.
Indicates the total number of input ARP probe packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk ARP reply packets output.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of input AppleTalk ARP request packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk ATP packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk input broadcast packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk output broadcast packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk input packets with checksum errors.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of illegal-sized AppleTalk Datagram Delivery Protocol (DDP) packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of long DDP packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of short DDP packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk echo packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of illegal AppleTalk echo packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk packets forwarded.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk input packets that have exceeded the maximum hop count.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk input packets with multicast addresses.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of input AppleTalk packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk input packets for this host.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk Name Binding Protocol (NBP) packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of NBP packets sent.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk packets dropped due to access control.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk packets lost due to no memory.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk packets that were dropped because they could not be encapsulated.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of number of AppleTalk packets dropped because the router did not know where to forward them.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk input packets received while AppleTalk routing was not enabled.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk output packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk Routing Table Maintenance Protocol (RTMP) packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of RTMP packets sent.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of unknown AppleTalk input packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of AppleTalk Zone Information Protocol (ZIP) packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of ZIP packets sent.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Variables in this group apply to the Cisco chassis and provide information about the hardware within the chassis such as the system software version of the read-only memory (ROM) and the type of chassis (Cisco 2000, Cisco 3000, and so on).
The Chassis Card table, cardTableEntry, contains information on a per-chassis basis and includes the following variables: cardDescr, cardHwVersion, cardIndex, cardSerial, cardSlotNumber, cardSwVersion, and cardType. The index to this table is cardIndex. If the device has n number of cards, the table will contain n number of rows.
Provides the unique ID number for the chassis. This number contains the value of the CPU serial number or ID number (if available); otherwise, it will be empty. This number also can be set with snmp-server chassis-id. An example of a value for a CPU serial number is 00160917.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-write
chassisSlots
Provides the number of slots in this chassis, or -1 if no slots exist or the number of slots cannot be determined.
Syntax: Integer
Access: read-only
Indicates the type of chassis for the product. For example, c4000 indicates a Cisco 4000 router.
The following are integer values for this variable:
1 = Unknown
2 = Multibus (for example, CGS or ASM)
3 = AGS+
4 = IGS
5 = Cisco 2000
6 = Cisco 3000
7 = Cisco 4000
8 = Cisco 7000
9 = Communication server 500
10 = Cisco 7010
11 = Cisco 2500
12 = Cisco 4500
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the chassis hardware revision level, or an empty string if the information is unavailable. Examples of the types of chassis versions are D or AO.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Indicates the value of the configuration register.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the value of the configuration register at next reload.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the nonvolatile configuration memory in bytes.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of bytes of nonvolatile configuration memory in use.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the bytes of RAM available to the CPU of the device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
romVersion
Provides the ROM system software version, or an empty string if unavailable. Following is an example of the type of information provided by the romVersion variable:
System Bootstrap, Version 4.5(3), SOFTWARE [fc1]
Copyright (c) 1986-1992 by cisco Systems
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the software version of the system software in ROM, or an empty string if the information is unavailable. Following is an example of the type of information provided by the romSysVersion variable:
GS Software (GS3), Version 10.2(3127) [jdoe 106]
Copyright (c) 1986-1993 by cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Thu 08-Apr-93 09:55
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
The Chassis Interface Card Table, cardTable, contains the cardTableEntry variable. The Cisco Card table, cardTableEntry, contains seven entries, or rows: cardDescr, cardHwVersion, cardIndex, cardSerial, cardSwVersion, cardSlotNumber, and cardType. The index to this table is cardIndex. If there are n number of cards associated with the device, there will be n rows in the table.
For example, in Table 15, there are 4 rows.
| cardType | cardDescr | cardHwVersion | cardSerial | and so on |
|---|---|---|---|---|
70 | MCI interface | 1.1 | 0 |
|
70 | MCI interface | 1.1 | 0 |
|
5 | 25 MHz 68040 |
| 0 |
|
24 | Environmental Monitor | 4 | 00196849 |
|
and so on |
|
|
|
|
Provides a description of the card used by the router. Examples of the descriptions are MEC Ethernet for an MEC board, 25MHz 68040 for the CSC/4, and CTR Token Ring for a CTR board.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides the hardware revision level of this card, or an empty string if unavailable.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
cardIndex
Index into card table (not physical chassis slot number).
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the serial number of this card, or zero if unavailable.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the chassis slot number. A value of -1 is provided if it is not applicable or cannot be determined.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the version of the firmware or microcode installed on this card, or an empty string if unavailable. For example, 1.8 indicates MCI microcode 1.8, and 3.0 MADGE 1.01/4.02, TI 000000 indicates
CSC-R16M.
Syntax: Display string
Access: Read-only
Provides information that identifies the functional type of card.
The possible integer values follow:
1 = unknown
2 = csc1
3 = csc2
4 = csc3
5 = csc4
6 = rp
20 = csc-m
21 = csc-mt
22 = csc-mc
23 = csc-mcplus
24 = csc-envm
40 = csc-16
41 = csc-p
50 = csc-a
51 = csc-e1
52 = csc-e2
53 = csc-y
54 = csc-s
55 = csc-t
56 = sci4s
57 = sci2s2t
58 = sci4t
59 = mci1t
60 = mci2t
61 = mci1s
62 = mci1s1t
63 = mci2s
64 = mci1e
65 = mci1e1t
66 = mci1e2t
67 = mci1e1s
68 = mci1e1s1t
69 = mci1e2s
70 = mci2e
71 = mci2e1t
72 = mci2e2t
73 = mci2e1s
74 = mci2e1s1t
75 = mci2e2s
80 = csc-r
81 = csc-r16
82 = csc-r16m
83 = csc-1r
84 = csc-2r
100 = csc-cctl1
101 = csc-cctl2
110 = csc-mec2
111 = csc-mec4
112 = csc-mec6
113 = csc-fci
114 = csc-fcit
115 = csc-hsci
116 = csc-ctr
150 = sp
151 = eip
152 = fip
153 = hip
154 = sip
155 = trip
156 = fsip
157 = aip
158 = mip
159 = ssp
200 = npm-4000-fddi-sas
201 = npm-4000-fddi-das
202 = npm-4000-1e
203 = npm-4000-1r
204 = npm-4000-2s
206 = npm-4000-2e
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of slots in this chassis. A value of -1 is provided if the number is not applicable or cannot be determined.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
This section describes the Cisco MIB variables pertaining to monitoring and managing a device running the DECnet protocol. These variables gather information, such as hop count, host name, total packets received and sent, and number of packets with header errors.
Provides the total number of received bad hello messages.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of bad Level 1 routing packets that have been received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of addresses that are too large.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of received data packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of DECnet packets received with header errors.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of DECnet packets forwarded.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of hello messages received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of output hello messages.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of Level 1 routing packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of Level 1 routing packets sent.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of Level 2 routing packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of Level 2 routing packets sent.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of packets dropped due to access control failure.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of packets that were dropped because they could not be encapsulated.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of transactions denied due to lack of memory.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of packets that were dropped because the router did not know where to forward them.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of packets that were received while not routing DECnet.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of unknown control packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of received packets not in the long DECnet format. This number should always be zero.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of missing routing vectors. Occurs when a packet is received for which there is no entry in the Routing table.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of hello messages received from another area by a Level 1 router.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of Level 1 routing packets received from another area.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of Level 2 routing packets received from another area.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of total DECnet packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of packets received that exceeded the maximum hop count set for this device and have been discarded.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
The DECnet Area Routing table, dnAreaTable, includes seven variables: dnAAge, dnACost, dnAHop, dnAIfIndex, dnANextHop, dnAPrio, and dnArea. The index for this table is the DECnet area, or dnArea. If there are n number of areas for the device, there will be n rows in the table.
For example, in Table 16, the DECnet area is 44; the cost is 3; and the maximum number of hops allowed is 2. The interface used to get to area 44 is number 1; the address for the next hop is 46.5; the Routing table was updated 30 seconds ago; and the next hop area is prioritized as 1.
| dn Area | dnACost | dnAHop |
dnA IfIndex | dnA Next Hop | dnAAge |
dnA Prio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
44 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 46.5 | 30 | 1 |
24 | 60 | 4 | 2 | 24.7 | 12 | 2 |
6 | 17 | 2 | 3 | 6.4 | 60 | 3 |
Provides the age (in seconds) of an area route. When a route is used or has been verified as functional, its age is reset to 0. If a route is not used, its age will gradually grow. Eventually, routes with large ages are cleared out.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the cost of the router area. The cost value can be an integer from 1 through 63. The cost signifies routing preference. The lower the cost, the better the path.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the maximum number of hops for a route to a distant area that the router will accept.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the instance ID of the interface providing the next hop address to the area. A zero denotes self. The DECnet table is indexed by dnArea. For example, dnAIfIndex.5 is the ifIndex for the next hop to DECnet area 5; dnAifIndex 7 is the ifIndex for the next hop to DECnet area 7; and so on.
If dnAIfIndex.5 is set to the value of 4, to get to the next hop for DECnet area 5, the router sends the packet via the interface that has an ifIndex of 4.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the DECnet address for the next hop.
Syntax: Octet string
Access: Read-only
Provides the priority of the next hop router for an area route.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the DECnet area for the device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
End of Table
The DECnet host table, dnHostTable, contains seven variables: dnHAge, dnHCost, dnHHop, dnHIfIndex, dnHNextHop, dnHost, and dnHPrio.
In Table 17, the first DECnet host address in the table is 44.5. Its cost is 3; the number of hops to the host is 4; and the interface number 1 provides the next hop to address 55.6. The route was updated 30 seconds ago, and the priority for the next hop is set to 4.
| dnHost |
dnH Cost |
dnH Hop | dnHIfIndex | dnH Next Hop |
dnH Age |
dnH Prio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
44.5 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 55.6 | 30 | 4 |
54.6 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 33.2 | 20 | 3 |
23.2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 25.1 | 60 | 2 |
Provides the age (in seconds) of the route to the host.When a route is used or has been verified as functional, its age is reset to 0. If a route is not used, the age of the route will gradually grow. Eventually, routes with large ages are cleared out.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the cost of the path to this device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of hops to this device.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the index of the interface to the next hop address to the node. 0 denotes self.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the DECnet address of the next hop destination.
Syntax: Octet string
Access: Read-only
Provides the DECnet node address.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the priority of the next hop router for the node.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
End of Table
For example, in Table 18, interface 1 has a cost of 20; interface 2 has a cost of 31; and so on.
| Interface Number | dnIfCost |
|---|---|
1 | 20 |
2 | 31 |
3 | 12 |
Indicates the cost of this interface.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
End of Table
The variables in this group can be used with all Cisco products running the Novell protocol. These variables provide such information as total number of input and output packets, number of packets with errors, and number of packets with service access point (SAP) requests and replies.
Indicates the total number of Novell input broadcast packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell output broadcast packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell input packets with checksum errors.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell input packets with header errors.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell packets forwarded.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell input packets that exceeded the maximum hop count.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell input multicast packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell input packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell input packets for this host.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell packets dropped due to output encapsulation failure.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell packets dropped because the router did not know where to forward them.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell output packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell service access point (SAP) request packets sent.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell SAP reply packets sent.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell SAP request packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of Novell SAP response packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of unknown Novell input packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
The variables in this group can be used with all Cisco products running the Banyan Virtual Integrated Network Service (VINES) protocol. This protocol is derived from the Xerox Network Systems (XNS) protocol. These variables provide information such as total number of input and output packets, number of packets with errors, and number of packets with Internet Control Protocol(ICP) requests and replies.
Indicates the total number of VINES broadcast packets forwarded.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES input broadcast packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES output broadcast packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES input packets with checksum errors.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the next VINES subnetwork number that this router will assign to a client.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES echo packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES echo packets generated.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES packets dropped because they could not be encapsulated.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES input packets with header errors.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES packets forwarded.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES input packets that have exceeded the maximum hop count.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES Internet Control Protocol (ICP) packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES ICP packets generated.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES input packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES input packets for this host.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES MAC level echo packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES Media Access Control (MAC) level echo packets generated.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES ICP metric notification packets generated.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the VINES network number of this router.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES broadcast packets not forwarded to all interfaces because the no charges only bit in the packet was set to on.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES packets dropped because the router did not know where to forward them.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES broadcast packets not forwarded to all interfaces because the over 4800 bps bit in the packet was set to on.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES broadcast packets not forwarded to all interfaces because the lan only bit in the packet was set to on.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES output packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of VINES packets that were sent to an actual Banyan server as a proxy for a client.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of received VINES packets that were responses to proxy packets sent by the router.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Indicates the VINES subnet number of this router.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of unknown VINES input packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
The Banyan VINES Interface table, vinesIfTableEntry, contains all the variables described in the Banyan VINES group. The index to the table is ifIndex. ifIndex indicates the number of the interface. If the device has n number of interfaces, the VINES Interface table will contain n rows.
In Table 19, the first column indicates the number of interfaces on the devices. Each of the variables in the VINES Interface table occupies one column; for example, vinesIfMetric is shown in a column, followed by vinesIfEnctype in the next column, and so on.
| Interface Number | vinesIfMetric | vinesIfEnctype | and so on |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | 3 | 1 |
|
2 | 5 | 3 |
|
and so on |
|
|
|
Provides the outgoing access list number for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
vinesIfArpEnabled
Indicates how the router responds to the VINES protocol ARP.
Syntax: Integer (0 = never respond to ARP packets, 1 = always respond to ARP packets, 2 = respond to ARP packets only if servers are not present on the network)
Access: Read-only
Indicates the type of data link encapsulation that will be used on broadcasts sent by the router.
Syntax: Integer (1 = ARPA, 3 = SNAP, 5 = HDLC, 12 = X.25, 13 = X.25, 25 = VINES TR, 27 = Frame Relay, 28 = SMDS, 30 = PPP)
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether fast switching is supported for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Integer (0 = fast switching not requested or not supported,
1 = fast switching requested and supported)
Access: Read-only
Provides the access list number for filtering the content of received VINES routing information.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the access list number for filtering on the source of received VINES routing information.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the VINES protocol line is up or down.
Syntax: Integer (0 = down, 1 = up)
Access: Read-only
Provides the metric value for the VINES protocol. Banyan servers use delay metrics to compute timeouts when communicating with other hosts. The metric value is either manually assigned to the interface by using the vines metric command or is automatically assigned by the system. This number is returned in the format defined in the VINES Protocol Definition.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the access list number for filtering the content of transmitted VINES routing information.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the VINES protocol "propagate" is enabled.
Syntax: Integer (0 = never enabled, 1 = always enabled, 2 = enabled only if there are no local servers on any interface)
Access: Read-only
Provides the redirect interval for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether fast switching is supported for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input ARP query request messages for the VINES protocol. The four types of ARP messages following apply to vinesIfRxArp0-vinesIfRxArp3:
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input ARP query response messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input ARP assignment request messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input ARP assignment response messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input illegal ARP messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the input duplicate broadcast count for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol number of input packets forwarded to another interface.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol number of input packets helpered to another server. Helpered packets are broadcasts received from a serverless network that should be thrown away according to the fields in the VINES IP header. Instead of being thrown away, they are resent on another interface, so that they will be received by a VINES server.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the input broadcast count for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input packets with checksum errors for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input IPC echo messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input packets with format errors for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol number of input packets forwarded to another interface.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input interprocess communications (ICP) error messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input illegal ICP messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input ICP metric messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input IPC messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol number of input packets destined for this router.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input MAC layer echo frames for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol number of input packets that were dropped because there was no route to the destination.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol number of input packets that were discarded because the interface was not configured.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol number of responses to proxy packets.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of illegal input Routing Table Protocol (RTP) type 0 messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input RTP type 1 (request for information) messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of illegal input RTP type 2 messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of illegal input RTP type 3 messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input RTP type 4 update messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input RTP type 5 response messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input RTP type 6 redirect messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of all other illegal input RTP messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input messages from unknown VINES protocols.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input messages from unknown VINES IPC ports.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input SPP messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides VINES protocol number of input packets dropped due to a zero hop count.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the VINES protocol serverless support is enabled.
Syntax: Integer (0 = never enabled, 1 = enabled only if servers are not present on the network, 2 = always enabled, 3 = always enabled to flood broadcasts)
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether VINES protocol serverless broadcasting support is enabled.
Syntax: Counter (0 = not enabled, 1 = enabled)
Access: Read-only
Indicates whether the VINES protocol split horizon is enabled.
Syntax: Integer (0 = enabled, 1 = disabled)
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output ARP query request messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output ARP query response messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output ARP assignment request messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of input ARP assignment response messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides broadcast packets that were generated by the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol output broadcast forwarded from another interface.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol output broadcast helpered to a Banyan server.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output IPC echo messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of packets to be output that failed on access list for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of VINES packets that could not be output because the interface was down.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides VINES packets to be output that could not be encapsulated.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of forwarded packets for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output IPC error messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output IPC metric messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output ICP messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output IPC MAC-layer echo frames for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol output broadcast not sent due to high- speed class. This occurs if a received packet is marked to be sent only on network interfaces with a speed of 4800 bps or greater. The counter is incremented on interfaces with a speed of less than 4800 whenever this type of packet should have been transmitted.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol output broadcast not sent due to LanOnly class. This occurs if a received packet is marked to be sent only if the network interface type is LanOnly. The counter is incremented on interfaces other than type LanOnly whenever this type of packet should have been transmitted.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides VINES protocol output broadcast not sent due to No Charges class. This occurs if a received packet is marked to be sent only if the sender's transmission is free of charge. The counter is incremented on interfaces carrying per-packet charges whenever this type of packet should have been transmitted.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the VINES protocol output broadcast packets that were not sent due to the interface leading back to the source.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of proxy packets sent by the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of illegal output RTP type 0 messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output RTP type 1 (request messages) for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of illegal output RTP type 2 messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of illegal output RTP type 3 messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output RTP type 4 (update messages) for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output RTP type 5 (response messages) for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output RTP type 6 (redirect messages) for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the number of output SPP messages for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
Provides the unicast packets that were generated for the VINES protocol.
Syntax: Counter
Access: Read-only
This group is present in all router-based products running the Xerox Network Systems (XNS) protocol. These variables provide such information as the number of packets forwarded, total number of input packets, and total number of packets transmitted with errors.
Indicates the total number of XNS input broadcast packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS output broadcast packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS input packets with checksum errors.
Syntax: Integer
Syntax: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS echo reply packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS echo reply packets sent.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS echo request packets received.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS echo request packets sent.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS error input packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS error output packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS packets forwarded.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS input packets with header errors.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS broadcast packets forwarded.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS input packets that exceeded the maximum hop count.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS input packets received with multicast addresses.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of input XNS packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS input packets for this host.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Provides the total number of XNS packets dropped because they could not be encapsulated.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS packets that were discarded because the router did not know where to forward them.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS input packets received while XNS routing was not enabled.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of XNS output packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
Indicates the total number of unknown XNS input packets.
Syntax: Integer
Access: Read-only
SNMP traps are set up on specific devices to obtain useful information such as the change in a device configuration or the absence of proper user authentication with a request. When the SNMP agent on the device detects a change, it immediately sends an SNMP trap to the NMS system.
Cisco products, including the routers, access servers and communication servers, and protocol translators, support the SNMP traps specified in RFC 1213, Management Information Base for Network Management of TCP/IP-based Internets: MIB-II. The warmStart trap in MIB II is not supported by Cisco.
Following are the standard SNMP traps supported by Cisco:
This trap is sent to the NMS system if the SNMP agent detects that proper user authentication was not provided with a request. User authentication enhances the security of the devices by ensuring that only privileged users with valid community strings are allowed to access the system.
The SNMP agent sends a coldStart trap when its device has reinitialized itself.
An egpNeighborLoss trap indicates that an EGP (Exterior Gateway Protocol) neighbor is down. Neighboring routers are two routers that have interfaces to a common network and exchange routing information. An exterior router uses EGP to advertise its knowledge of routes to networks within its autonomous system. It sends these advertisements to the core routers, which then readvertise their collected routing information to the exterior router. A neighbor or peer router is any router with which the router communicates using EGP.
A linkDown trap is sent by the SNMP agent to the NMS system if a link in a configuration of a device has been shutdown. For example, the link could be a serial line connecting two devices or an Ethernet link between two networks.
A linkUp trap indicates the recognition of an SNMP agent that a link in a configuration of a device has become active.
Following are the Cisco private SNMP traps that are implemented in Cisco products including the router, access server and communication server, and protocol translator.
ipxTrapCircuitUp
This trap signifies that the specified circuit has come up.
ipxTrapCircuitDown
This trap signifies that the specified circuit has gone down.
A ciscoPingCompleted trap is sent at the completion of a sequence of pings if such a trap was requested when the sequence was initiated.
This trap is sent after a reload command is issued.
The tty trap indicates that a TCP connection, which existed previously for a tty session, has been terminated.
The following variables in RFC 1285 are supported in Software Release 9.0 and later:
snmpFddiSMTNumber
snmpFddiSMTIndex
snmpFddiSMTStationId
snmpFddiSMTOpVersionId
snmpFddiSMTHiVersionId
snmpFddiSMTLoVersionId
snmpFddiSMTCFState
snmpFddiMACNumber
snmpFddiMACSMTIndex
snmpFddiMACIndex
snmpFddiMACTReq
snmpFddiMACTNegj
snmpFddiMACTMax
snmpFddiMACTvxValue
snmpFddiMACMin
snmpFddiMACFrameCts
snmpFddiMACErrorCts
snmpFddiMACLostCts
snmpFddiMACChipSet
This section lists the Cisco private MIB variables that have been introduced after Software Release 8.0.
The following list describes the MIB variables introduced with Software Release 8.2:
writeMem
writeNet
busyPer
avgBusy1
avgBusy5
idleCount
idleWired
locIfCarTrans
locIfReliab
locIfDelay
locIfLoad
locIfCollisions
tsLineNoise
dnAreaTable
dnACost
dnAHop
dnAifIndex
dnANextHop
dnAAge
dnAPrio
vinesInput
vinesOutput
vinesLocaldest
vinesForwarded
vinesBcastin
vinesBcastout
vinesBcastfwd
vinesNotlan
vinesNotgt4800
vinesNocharges
vinesFormaterror
vinesCksumerr
vinesHopcout
vinesNoroute
vinesEncapsfailed
vinesUnknown
vinesIcpIn
vinesIcpOut
vinesMetricOut
vinesMacEchoIn
vinesMacEchoOut
vinesEchoIn
vinesEchoOut
The following list describes the MIB variables introduced with Software Release 8.3:
bufferHgsize
bufferHgTotal
bufferHgFree
bufferHgMax
bufferHgHit
bufferHgMiss
bufferHgTrim
bufferHgCreate
locIfInputQueueDrops
locIfOutputQueueDrops
ipNoaccess
actCheckPoint
tsMsgTtyLine
tsMsgIntervaltim
tsMsgDuration
tsMsgTest
tsMsgTmpBanner
tsMsgSend
dnIfTable
dnIfCost
The following list provides the MIB variables introduced with Software Release 9.0:
netConfigProto
hostConfigProto
sysConfigAddr
sysConfigName
sysConfigProto
sysClearARP
sysClearInt
envPresent
envTestPt1Descr
envTestPt1Measure
envTestPt2Descr
envTestPt2Measure
envTestPt3Descr
envTestPt3Measure
envTestPt4Descr
envTestPt4Measure
envTestPt5Descr
envTestPt5Measure
envTestPt6Descr
envTestPt6Measure
locIfDescr
locIfPakmon
The following list provides the MIB variables introduced with Software Release 9.1:
envTestPt4MarginPercent
envTestPt5MarginPercent
envTestPt6MarginPercent
envTestPt1last
envTestPt2last
envTestPt3last
envTestPt4last
envTestPt5last
envTestPt6last
envTestPt1MarginVal
envTestPt2MarginVal
envTestPt3MarginVal
envTestPt4MarginVal
envTestPt5MarginVal
envTestPt6MarginVal
envTestPt1warn
envTestPt2warn
envTestPt3warn
envTestPt4warn
envTestPt5warn
envTestPt6warn
envFirmVersion
envTechnicianID
envType
envBurnDate
envSerialNumber
locIfSlowInPkts
locIfSlowOutPkts
locIfSlowInOctets
locIfSlowOutOctets
locIfFastInPkts
locIfFastOutPkts
locIfFastInOctets
locIfFastOutOctets
locIfotherInPkts
locIfotherOutPkts
locIfotherInOctets
locIfotherOutOctets
locIfipInPkts
locIfipOutPkts
locIfipInOctets
locIfipOutOctets
locIfdecnetInPkts
locIfdecnetOutPkts
locIfdecnetInOctets
locIfdecnetOutOctets
locIfxnsInPkts
locIfxnsOutPkts
locIfxnsInOctets
locIfxnsOutOctets
locIfclnsInPkts
locIfclnsOutPkts
locIfclnsInOctets
locIfclnsOutOctets
locIfappletalkInPkts
locIfappletalkOutPkts
locIfappletalkInOctets
locIfappletalkOutOctets
locIfnovellInPkts
locIfnovellOutPkts
locIfnovellInOctets
locIfnovellOutOctets
locIfapolloInPkts
locIfapolloOutPkts
locIfapolloInOctets
locIfapolloOutOctets
locIfvinesInPkts
locIfvinesOutPkts
locIfvinesInOctets
locIfvinesOutOctets
locIfbridgedInPkts
locIfbridgedOutPkts
locIfbridgedInOctets
locIfbridgedOutOctets
locIfsrbInPkts
locIfsrbOutPkts
locIfsrbInOctets
locIfsrbOutOctets
locIfchaosInPkts
locIfchaosOutPkts
locIfchaosInOctets
locIfchaosOutOctets
locIfpupInPkts
locIfpupOutPkts
locIfpupInOctets
locIfpupOutOctets
locIfmopInPkts
locIfmopOutPkts
locIfmopInOctets
locIfmopOutOctets
locIflanmanInPkts
locIflanmanOutPkts
locIflanmanInOctets
locIflanmanOutOctets
locIfstunInPkts
locIfstunOutPkts
locIfstunInOctets
locIfstunOutOctets
locIfspanInPkts
locIfspanOutPkts
locIfspanInOctets
locIfspanOutOctets
locIfarpInPkts
locIfarpOutPkts
locIfarpInOctets
locIfarpOutOctets
locIfprobeInPkts
locIfprobeOutPkts
locIfprobeInOctets
locIfprobeOutOctets
flashSize
flashFree
flashcontoller
flashcard
flashVPP
flashErase
flashEraseTime
flashEraseStatus
flashToNet
flashToNetTime
flashToNetStatus
netToFlash
netToFlashTime
netToFlashStatus
flashStatus
flashEntries
flashDirName
flashDirSize
flashDirStatus
The following list provides the MIB variables introduced with Software Release 9.21:
locIfDribbleInputs
vinesProxy
vinesProxyReply
vinesNet
vinesSubNet
vinesClient
vinesIfMetric
vinesIfEnctype
vinesIfAccesslist
vinesIfInputNetworkFilter
vinesIfInputRouterFilter
vinesIfOutputNetworkFilter
vinesIfPropagate
vinesIfArpEnabled
vinesIfServerless
vinesIfServerlessBcast
vinesIfRedirectInterval
vinesIfSplitDisabled
vinesIfLineup
vinesIfFastokay
vinesIfRouteCache
vinesIfIn
vinesIfOut
vinesIfInBytes
vinesIfOutBytes
vinesIfRxNotEnabled
vinesIfRxFormatError
vinesIfRxLocalDest
vinesIfRxBcastin
vinesIfRxForwarded
vinesIfRxNoRoute
vinesIfRxZeroHopCount
vinesIfRxChecksumError
vinesIfRxArp0
vinesIfRxArp1
vinesIfRxArp2
vinesIfRxArp3
vinesIfRxArpIllegal
vinesIfRxIcpError
vinesIfRxIcpMetric
vinesIfRxIcpIllegal
vinesIfRxIpc
vinesIfRxRtp0
vinesIfRxRtp1
vinesIfRxRtp2
vinesIfRxRtp3
vinesIfRxRtp4
vinesIfRxRtp5
vinesIfRxRtp6
vinesIfRxRtpIllegal
vinesIfRxSpp
vinesIfRxBcastHelpered
vinesIfRxBcastForwarded
vinesIfRxBcastDuplicate
vinesIfRxEcho
vinesIfRxMacEcho
vinesIfRxProxyReply
vinesIfTxUnicast
vinesIfTxBcast
vinesIfTxForwarded
vinesIfTxFailedEncaps
vinesIfTxFailedAccess
vinesIfTxFailedDown
vinesIfTxNotBcastToSource
vinesIfTxNotBcastNotlan
vinesIfTxNotBcastNotgt4800
vinesIfTxNotBcastPpcharge
vinesIfTxBcastForwarded
vinesIfTxBcastHelpered
vinesIfTxArp0
vinesIfTxArp1
vinesIfTxArp2
vinesIfTxArp3
vinesIfTxIcpError
vinesIfTxIcpMetric
vinesIfTxIpc
vinesIfTxRtp0
vinesIfTxRtp1
vinesIfTxRtp2
vinesIfTxRtp3
vinesIfTxRtp4
vinesIfTxRtp5
vinesIfTxRtp6
vinesIfTxSpp
vinesIfTxEcho
vinesIfTxMacEcho
vinesIfTxProxy
chassisType
chassisVersion
chassisId
romVersion
romSysVersion
processorRam
nvRAMSize
nvRAMUsed
configRegister
configRegNext
cardTable
cardTableEntry
cardIndex
cardType
cardDescr
cardSerial
cardHwVersion
cardSwVersion
cardSlotNumber
chassisSlots
The following list provides the MIB variables introduced with IOS Release 10.0:
ipxThresh
ipxactLostPkts
ipxactLostByts
ipxactSrc
ipxactDst
ipxactPkts
ipxactByts
ipxactAge
ipxckactSrc
ipxckactDst
ipxckactPkts
ipckactByts
ipxckactAge
ipxactCheckPoint
vinesIfInputNetworkFilter
vinesIfInputRouterFilter
vinesIfOutputNetworkFilter
The following list provides the MIB variables introduced with IOS Release 10.2:
cipCardClawEntry
cipCardClawIndex
cipCardClawConnected
cipCardClawConfigTable
cipCardClawConfigEntry
cipCardClawConfigPath
cipCardClawConfigDevice
cipCardClawConfigIpAddr
cipCardClawConfigHostName
cipCardClawConfigRouterName
cipCardClawConfigHostAppl
cipCardClawConfigRouterAppl
cipCardClawDataXferStatsTable
cipCardClawDataXferStatsEntry
cipCardClawDataXferStatsBlocksRead
cipCardClawDataXferStatsBlocksWritten
cipCardClawDataXferStatsBytesRead
cipCardClawDataXferStatsBytesWritten
cipCardClawDataXferStatsHCBytesRead
cipCardClawDataXferStatsHCBytesWritten
cipCardClawDataXferStatsReadBlocksDropped
cipCardClawDataXferStatsWriteBlocksDropped
cipCardClawDataXferStatsBufferGetRetryCount
cipCardDtrBrdIndex
cipCardDtrBrdType
cipCardDtrBrdStatus
cipCardDtrBrdSignal
cipCardDtrBrdOnline
implicitIncidents
codeViolationErrors
linkFailureSignalOrSyncLoss
linkFailureNOSs
linkFailureSequenceTimeouts
linkFailureInvalidSequences
linkIncidentTrapCause
cipCardsubChannelIndex
cipCardsubChannelConnections
cipCardsubChannelCancels
cipCardsubChannelSelectiveResets
cipCardsubChannelSystemResets
cipCardsubChannelDeviceErrors
cipCardsubChannelWriteBlocksDropped
cipCardsubChannelLastSenseData
cipCardSubchannelLastSenseDataTime
cipCardSubChannelCuBusies
cipCardEntryIndex
cipCardEntryName
cipCardEntryTotalMemory
cipCardEntryFreeMemory
cipCardEntryCpuUtilization
cipCardEntryTimeSinceLastReset
ciscoPingAddress
ciscoPingTable
ciscoPingEntry
ciscoPingProtocol
ciscoPingSerialNumber
ciscoPingPacketCount
ciscoPingPacketSize
ciscoPingPacketTimeout
ciscoPingDelay
ciscoPingTrapOnCompletion
ciscoPingSentPackets
ciscoPingReceivedPackets
ciscoPingMinRtt
ciscoPingAvgRtt
ciscoPingMaxRtt
ciscoPingCompleted
ciscoPingEntryOwner
ciscoPingEntryStatus
ipxBasicSysInstance
ipxBasicSysExistState
ipxBasicSysNetNumber
ipxBasicSysNode
ipxBasicSysName
ipxBasicSysInReceives
ipxBasicSysInHdrErrors
ipxBasicSysInUnknownSockets
ipxBasicSysInDiscards
ipxBasicSysInBadChecksums
ipxBasicSysInDelivers
ipxBasicSysNoRoutes
ipxBasicSysOutRequests
ipxBasicSysOutMalformedRequests
ipxBasicSysOutDiscards
ipxBasicSysOutPackets
ipxBasicSysConfigSockets
ipxBasicSysOpenSocketFails
ipxAdvSysInstance
ipxAdvSysMaxPathSplits
ipxAdvSysMaxHops
ipxAdvSysInTooManyHops
ipxAdvSysInFiltered
ipxAdvSysInCompressDiscards
ipxAdvSysNETBIOSPackets
ipxAdvSysForwPackets
ipxAdvSysOutFiltered
ipxAdvSysOutCompressDiscards
ipxAdvSysCircCount
ipxAdvSysDestCount
ipxAdvSysServCount
ipxCircSysInstance
ipxCircIndex
ipxCircExistState
ipxCircOperState
ipxCircName
ipxCircType
ipxCircDialName
ipxCircLocalMaxPacketSize
ipxCircCompressState
ipxCircCompressSlots
ipxCircStaticStatus
ipxCircCompressedSent
ipxCircCompressedInitSent
ipxCircCompressedRejectsSent
ipxCircUncompressedSent
ipxCircCompressedReceived
ipxCircCompressedInitReceived
ipxCircCompressedRejectsReceived
ipxCircUncompressedReceived
ipxCircMediaType
ipxCircNetNumber
ipxCircStateChanges
ipxCircInitFails
ipxCircDelay
ipxCircThroughput
ipxCircNeighRouterName
ipxCircNeighInternalNetNum
ipxDestSysInstance
ipxDestNetNum
ipxDestProtocol
ipxDestTicks
ipxDestHopCount
ipxDestNextHopCircIndex
ipxDestNextHopNICAddress
ipxDestNextHopNetNum
ipxStaticRouteSysInstance
ipxStaticRouteCircIndex
ipxStaticRouteNetNum
ipxStaticRouteExistState
ipxStaticRouteTicks
ipxStaticRouteHopCount
ipxServSysInstance
ipxServType
ipxServName
ipxServProtocol
ipxServNetNum
ipxServNode
ipxServSocket
ipxServHopCount
ipxDestServSysInstance
ipxDestServNetNum
ipxDestServSocket
ipxDestServName
ipxDestServType
ipxDestServProtocol
ipxDestServHopCount
ipxStaticServSysInstance
ipxStaticServCircIndex
ipxStaticServName
ipxStaticServType
ipxStaticServExistState
ipxStaticServNetNum
ipxStaticServNode
ipxStaticServSocket
ipxStaticServHopCount
ripSysInstance
ripSysState
ripSysIncorrectPackets
sapSysInstance
sapSysState
sapSysIncorrectPackets
ripCircSysInstance
ripCircIndex
ripCircState
ripCircPace
ripCircUpdate
ripCircAgeMultiplier
ripCircPacketSize
ripCircOutPackets
ripCircInPackets
sapCircSysInstance
sapCircIndex
sapCircState
sapCircPace
sapCircUpdate
sapCircAgeMultiplier
sapCircPacketSize
sapCircGetNearestServerReply
sapCircOutPackets
sapCircInPackets
The loctcp table has been replaced by the ciscoloctcp table.
The IOS 10.1 Ping object was replaced by the IOS 10.2 ciscoPing table.
The loctcp table has been replaced by the ciscoloctcp table.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Wed May 9 14:56:07 PDT 2001
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2001 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.