|
|

The Digital Equipment Corporation (Digital) Local Area Transport (LAT) protocol is the one used most often to connect to Digital hosts. LAT is a Digital-proprietary protocol. Cisco provides LAT technology licensed from Digital. This chapter describes how to configure the LAT transmission protocol on communication servers. For a complete description of the commands in this chapter, see the Access and Communication Servers Command Reference publication. For information about making a LAT connection through a communication server, refer to the Cisco Access Connection Guide.
The LAT protocol allows a user to establish a LAT connection to a host at another site, then pass the keystrokes from one system to the other. A user can establish a LAT connection through the communication server to a LAT host simply by entering the host name. Cisco supports the LAT 5.2 specification.
Unlike the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), LAT was designed to be used on local-area networks (LANs) and it cannot be routed because it does not have a routing layer. However, a bridge or combined bridge and router, such as the Cisco router, can be used to carry LAT traffic across a wide-area network (WAN). Protocol translation can be used to carry LAT traffic over a WAN by first translating LAT to X.25 or Telnet, as shown in Figure 12-1.
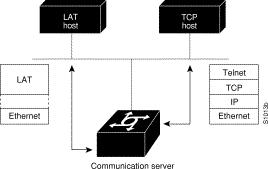
The LAT protocol is asymmetrical; it has master and slave functionality. First, the LAT master starts a LAT circuit by sending a circuit start message, and then a LAT slave responds with its own circuit start message. From 1 to 255 LAT sessions can then be multiplexed on this circuit.
In a typical setup, where the user's terminal is connected to a communication server, the communication server acts as the master, and the target VMS host acts as the slave.
For example, the following command results in the communication server CS1 acting as the master (or server) and the target VMS host, wheel, acting as the slave (or host).
CS1> lat wheel
A communication server can also act as a slave. This happens if the user connects from one communication server to another.
For example, the following command results in CS1 acting as the master (server) and CS2 acting as the slave (host).
CS1> lat cs2
In a LAT host-initiated connection, the VMS system always acts as the LAT slave. For example, a print job originating from a VMS system initiates or triggers the communication server to which the printer is connected to act as the LAT master. In short, the master-slave relationship also applies to host-initiated sessions from a LAT slave.
Resources such as modems, computers, and application software are viewed in a LAT network as services that, potentially, any user in the network can use. A LAT node can offer one or more such LAT services and more than one LAT node can offer the same LAT service.
A LAT node that offers one or more services, collectively called advertised services, broadcasts its services in the form of Ethernet multicast messages, called LAT service announcements. Conversely, a LAT node can listen for LAT service announcements on the network. These messages are cached in a dynamic table of known LAT services, collectively called learned services.
Your communication server supports both learned and advertised services and, therefore, it also supports incoming and outgoing LAT sessions. The services rating of its advertised nodes are determined dynamically but can also beset statically.
To establish outgoing connections to a LAT service, the communication server searches for the service in the learned services cache. If one or more nodes is offering the same service, the node with the highest rating is chosen. For example, a LAT connection to a service offered by a VAXcluster connects to the node in that cluster that has the smallest load and thus the highest service rating. This is how load-balancing works in relation to a group of nodes offering the same service.
An incoming LAT session connects from another LAT node to the service advertised by the local LAT node.
Because potentially any user on a LAT network can access any of the services on the network, a LAT server manager uses the concept of group codes to allow or restrict access to the services.
When both the communication server and the LAT host share a common group code, a connection can be established between the two. If the default group codes have not been changed on either the communication servers or the LAT hosts, a user on any communication server can connect to any learned service on the network.
However, if you define groups for communication servers and LAT hosts, you can partition these services into logical subnetworks. You can organize the groups so that users on one communication server view one set of services, and users on another communication server (or another line on the same server) view a different set. You might also design a plan that correlates group numbers with organizational groups, such as departments. The section "Define a Group List for Outgoing Connections" later in this chapter describes how to enter group code lists in your communication server configuration file.
A LAT host node's services cannot be accessed individually; access is granted, per node, on an
all-or-none basis.
A LAT session is a two-way logical connection between a LAT service and the communication server. All this is transparent to the user at a console connected to a LAT session; to the user it appears that connection has been made to the desired device or application program.
When a host print job connects to a communication server, this is called a host-initiated connection. The communication server maintains a queue of hosts requesting connection by sending periodic status messages to the requesting host.
You can establish host-initiated connections by specifying a port number or by defining a service on the communication server. These same services are used for connections from other communication servers.
The process of connecting to a VMS host is slightly different if you are connecting to a VMS host running VMS Version 5.4 or earlier than when connecting to a VMS host running VMS Version 5.5 or later software.
If a host-initiated connection is received that specifies a destination port number that corresponds to a virtual port on the communication server, a virtual EXEC process will be created for the user to log in with. This process can be used, in conjunction with the Digital set host/dte command on VMS, to connect to a Cisco communication server named ABLE from a VMS host node, as shown in the following example:
$lcp :==$latcp
$lcp create port lta300:
$lcp set port lta300:/service=able /node=able
$set host/dte lta300:
Turn on the VMS LAT hosts's outgoing connections and use the Digital set host/lat command, as shown in the following example:
$lcp :== $latcp
$lcp set node/connection =outgoing
$set host/lat able
When you configure a LAT printer, the LAT port name is the line number without the "tty." For example, if you configure terminal line 10 of your communication server, named ABLE, to be a LAT printer port, the OpenVMS command to associate an arbitrary LTA device to a LAT port name is as follows:
$lcp :== $lcp
$lcp create port lta300:
$lcp set port/node=ABLE/port=10 lta300:
The LAT port name is the line number without the "tty," regardless of whether the format of the tty line number is decimal or octal. Refer to the line configuration chapter in this manual for more information about configuring the communication server's line to the correct terminal characteristics (for example, baud rate, EXEC, flow control, and so forth).
Cisco's communication server software fully supports the LAT protocol suite, and provides the following features:
Cisco's LAT protocol is supplied with a default configuration and does not require additional configuration for you to use it. The software does provide commands for customizing the LAT software for your environment, if desired.
Perform the tasks in the following sections to enable LAT, to customize LAT for your particular network environment, and to monitor and maintain LAT connections:
See the examples at the end of this chapter for ideas on how to configure LAT in your network.
LAT is enabled by default on the communication server. If it has been disabled, you must reenable it. Perform the following tasks in interface configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Enable the LAT protocol. | lat enabled |
| Disable the LAT protocol. | no lat enabled |
You can give the communication server a node name that is different than the host name. Perform the following task in global configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Define a LAT node name. | lat node node-name |
You can define the list of services to which a user can connect. Do this by defining the group code lists used for connections from specific lines. Perform the following task in line configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Define the group list for an outgoing connection on a specified line. | lat out-group {groupname | number | range | all} |
You can limit the connection choices for an individual line by defining the group code lists for an outgoing connection. When a user initiates a connection with a LAT host, the user's line must share a common group number with the remote LAT host before a connection can be made.
You can specify a name for group lists to simplify the task of entering individual group codes. A name makes it easier to refer to a long list of group code numbers. Perform the following task in global configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Specify logical names for group lists. | lat group-list groupname {number | range | all} [enabled | disabled] |
To display the defined groups, use the show lat groups command.
You can specify a group code mask to use when advertising all services for a node. You can enter more than one group code by listing the numbers. You can also enter both a group code name and group codes. Perform the following task in global configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Specify logical names for group lists. | lat service-group {groupname | number | range | all} [enabled | disabled] |
Just as LAT services are offered by host computers, they also can be offered by communication servers. A communication server implements both the host and server portions of the LAT protocol. This allows connections from either hosts or communication servers. When a host connects to a communication server, this is called a host-initiated connection.
The tasks described in this section define support for host-initiated connections. This support includes refining the list of services that the communication server will support. An incoming session can be to either a port or a service. The port name is the terminal line number, as reported by the EXEC command show users all. Perform any of the following tasks in global configuration mode:
Use the show lat advertised EXEC command to display LAT services offered to other systems on the network.
A service must be specifically enabled, but not all of the attributes in the previous task table are necessary in a particular environment.
You can configure your communication server to support the service responder feature that is part of the LAT Version 5.2 specification.
Specifically, the DECserver90L+, which has less memory than other DECservers, does not maintain a cache of learned services. Instead, the DECserver90L+ solicits information about services as they are needed.
LAT Version 5.2 nodes can respond for themselves, but LAT Version 5.1 nodes, for example VMS Version 5.4 or earlier nodes, cannot. Instead, a LAT Version 5.2 node configured as a service responder can respond in proxy for those LAT Version 5.1 nodes.
Your communication server can be configured as a LAT service responder. Of course, if all your nodes are LAT Version 5.2 nodes, you do not need to enable the service responder features.
You can control service announcements and service solicitations by performing the tasks in the following sections:
You can configure the communication server to respond to solicit information requests addressed to LAT Version 5.1 nodes. This function allows nodes that do not cache service advertisements to interoperate with nodes that do not respond to solicit requests. Perform the following task in global configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Enable a proxy node to respond to solicit-information multicast messages. | lat service-responder |
Figure 12-2 shows how a communication server can act as a proxy for LAT servers.
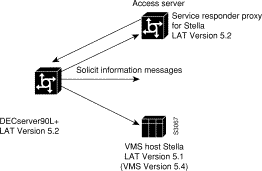
The DECserver90L+ broadcasts a solicit information request in search of service "stella's" address. The VMS host, stella, is unable to respond to the request because it is running LAT Version 5.1. The communication server is running LAT Version 5.2 with service responder enabled and informs the DECserver90L+ of stella's address.
You can disable periodic broadcasts of service announcements. If service announcements are enabled, the LAT node will periodically broadcast service advertisements. If service announcements are disabled, the LAT node will not send service announcements, so a remote node requiring connection to the local node has to use solicit information messages to look up node information. Perform the following task in global configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Disable periodic broadcasts of service advertisements. | no lat service-announcements |
Only disable service announcements if all of the nodes on the LAN support the service responder feature.
You can adjust the time between LAT service advertisements for services offered by the communication server. This is useful in large networks with many LAT services and limited bandwidth. Perform the following task in global configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Adjust the time between service announcements. | lat service-timer interval |
You can customize the environment for transmitting LAT messages. Cisco's implementation of LAT allows you to set the following features:
These features affect all LAT connection types. Perform the following tasks in global configuration mode, as necessary:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Set the message retransmit limit. | lat retransmit-limit number |
| Set the keepalive timer. | lat ka-timer seconds |
| Set the virtual-circuit timer. | lat vc-timer milliseconds |
You can optimize performance for your LAT environment by performing the tasks in the following sections:
You can set the number of sessions multiplexed over a single a LAT virtual circuit. The maximum, (and default) number of sessions is 255. Perform the following task in global configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Set the maximum number of sessions on a LAT virtual circuit. | lat vc-sessions number |
You can set the number of messages received by a host at one time. Increasing this number can enhance performance. Before LAT Version 5.2, LAT allowed only one outstanding message at one time on a virtual circuit. This restriction could limit the performance of communication servers processing a large number of messages because only one Ethernet packet of data could be in transit at a time. During virtual circuit startup, each side communicates to the other how many outstanding messages it is willing to accept. Perform the following task in global configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Allow a LAT host node to receive more than one message at a time. | lat host-buffers receive-buffers |
You can set the number of messages received by a server at one time. Increasing this number can enhance performance. Before LAT Version 5.2, LAT allowed only one outstanding message on a virtual circuit at a time. This restriction could limit the performance of communication servers processing a large number of messages because only one Ethernet packet of data could be in transit at a time. With LAT Version 5.2, nodes can indicate that they are willing to receive more than one message at a time. During virtual circuit startup, each side communicates to the other how many outstanding messages it is willing to accept. Perform the following task in global configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Allow a LAT server node to receive more than one message at a time. | lat server-buffers receive-buffers
|
Because LAT groups were not intended to implement security or access control, the communication server software supports access lists to provide these functions. An access list is a sequential collection of permit and deny conditions that serve to restrict access to or from LAT nodes on a specific terminal line. Each access list statement defines a permit or deny condition and a matching criterion for the node name.
When a LAT connection is attempted (either incoming or outgoing), the node name of the destination service (not the service name) is compared against the regular expression. If they match, the connection is permitted or denied as specified.
Perform the following tasks to define access lists and conditions:
You can configure a LAT line so that a remote LAT node can change the operating characteristics of the line. To enable remote LAT modification, perform the following task in line configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Enable remote LAT modification of line characteristics. | lat remote-modification
|
To monitor and maintain LAT activity, perform one or more of the following tasks in EXEC mode:
The following sections contain LAT configuration examples:
The following example establishes the LAT service ABLE for your communication server. Subsequently, your communication server will advertise ABLE (with default group code 0) on the LAN. Other LAT nodes can connect to your communication server using LAT service ABLE, provided the group codes on the LAT nodes and the group codes for ABLE intersect. By default, most LAT nodes, such as OpenVMS Version 5.5 hosts, have user group code set to 0, so you have default access to ABLE.
! Create LAT service with password protection and
! identification string using the following global configuration commands
lat service ABLE password secret
lat service ABLE ident Welcome to my machine
The following example establishes the LAT service ABLE from your communication server with selected group codes 1, 4 through 7, and 167. This limits inbound access to those LAT nodes that have group codes that intersect with those for LAT service ABLE.
! Establish a LAT group list
lat group-list HUBS 1 4-7 167
!
! Enable LAT group list for the service-group
lat service-group HUBS enabled
!
! Create LAT service with password protection and
! identification string
lat service ABLE password secret
lat service ABLE ident Welcome to my machine
The following example demonstrates how you can check which LAT services are on the same LAN as your communication server. Note that your communication server's own LAT service ABLE is also listed, with the "Interface" column listing the interface as "Local."
able> show lat services
Service Name Rating Interface Node (Address)
CAD 16 Ethernet0 WANDER
ABLE 16 Local
CERTIFY 33 Ethernet0 STELLA
The following example establishes a LAT session to remote LAT service HELLO using an interactive session:
able> lat HELLO
The following example illustrates how LAT services are logically partitioned by terminal line. At the example site, lines 1 through 7 go to the shop floor, lines 8 through 11 go to the Quality Assurance department, and lines 12 through 16 go to a common area.
! Define LAT groupnames
lat group-list DEFAULT 0
lat group-list FLOOR 3
lat group-list QA 4
line 1 7
lat out-group FLOOR enabled
lat out-group DEFAULT disabled
line 8 11
lat out-group QA enabled
lat out-group DEFAULT disabled
line 12 16
lat out-group DEFAULT QA FLOOR enabled
The following example illustrates how to configure a range of lines for rotary connections, then establishes the LAT service named Modems for rotary connection:
! Establish rotary groups
line 3 7
rotary 1
!
! Establish modem rotary service
!
lat service Modems rotary 1
lat service Modems enabled
See the section "Configure Rotary Groups" in the "Configuring Terminal Lines and Modem Support" chapter for more information about rotary groups.
The following example illustrates incoming permit conditions for all IP hosts and LAT nodes with specific characters in their names and a deny condition for X.25 connections to a printer. Outgoing connections, however, are less restricted.
! Permit all IP hosts, LAT nodes beginning with "VMS" and no X.25
! connections to the printer on line 5
!
access-list 1 permit 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255
lat access-list 1 permit ^VMS.*
x29 access-list 1 deny .*
!
line 5
access-class 1 in
!
! Meanwhile, permit outgoing connections to various places on all the
! other lines.
!
! Permit IP access within cisco
access-list 2 permit 131.108.0.0 0.0.255.255
!
! Permit LAT access to the Stella/blue complexes.
lat access-list 2 permit ^STELLA$
lat access-list 2 permit ^BLUE$
!
! Permit X25 connections to infonet hosts only.
x29 access-list 2 permit ^31370
!
line 0 99
access-class 2 out
The following example illustrates how to define access lists that permit all connections, thereby conforming to software behavior prior to Software Release 9.0. Keep in mind that the value supplied for the list argument in both variations of the access-class commands is used for all protocols supported by the communication server. If you are already using an IP access list, it will be necessary to define LAT (and possibly X.25) access lists permitting connections to everything, to emulate the behavior of earlier software versions.
access-list 1 permit 131.108.0.0 0.0.255.255
access-list 1 permit 150.136.0.0 0.0.255.255
!
line 1 40
access-class 1 out
! define LAT access list that permits all connections
lat access-list 1 permit .*
The following example defines a service that communicates with a specific line and defines a rotary with only that line specified. Establish rotary groups using line configuration commands and the rotary line configuration command.
hostname ciscots
! Service name for the communication server as a whole
lat service ciscopt enable
! Set up some lines with unique service names
line 1
rotary 1
lat service ciscopt1 rotary 1
lat service ciscopt1 enable
!
line 2
rotary 2
lat service ciscopt2 rotary 2
lat service ciscopt2 enable
|
|