|
|

CiscoView Wireless (CV) is an SNMP-based device management software application with which you can configure and monitor information for Cisco Internetworking Products.
CiscoView Wireless runs in two distinct modes:
The stand-alone version of CiscoView Wireless is a Windows application. All components of CiscoView Wireless and its support software are on the same system and communicate directly with the managed devices.
CiscoWorks for Windows (CWW5.0) suite includes the stand-alone version of CiscoView Wireless.
For detailed information on CWW 5.0, refer to the Cisco Works Windows 5.0 documentation, or go to:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/cwfw/cw_5_0_1/index.htm
CiscoView Wireless runs as a client applet within a browser. The server component of the client server is called CD One. A CiscoView Wireless client can talk to a managed device by using the server. The client/server version is available for two different operating systems:
Because the CiscoView Wireless client runs within a browser, you can run the client on Solaris and Microsoft Windows operating platforms.
For documentation on CD One 3rd Edition and CiscoView Wireless client that runs on CD One, go to:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/cw2000/cw2000_d
 |
Note CiscoView Wireless Quick Reference Guide describes only the client/server version of CiscoView Wireless that runs on the Solaris operating system. |
The CiscoView Wireless CD contains the client/server version of CiscoView Wireless and these components:
The following software components are in the following locations:
Software components required but not included in the CiscoView Wireless CD are:
The CiscoView Wireless CD contains the CiscoView Wireless packages with support for point-to-multipoint wireless feature set. These packages will be updated as problems are solved and new features are added. You can download the updated packages from: ftp://ftp.cisco.com/cisco/netmgmt/ciscoview/5.0/packages
or
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-in/Software/CiscoView/cv5devices.cgi
In an operational system, a wireless link is established between a point-to-multipoint (P2MP) radio line card in a Cisco uBR7200 series universal broadband router at one end and a complementary P2MP radio line card in a Cisco 26xx or a 36xx series router at the other end. CiscoView Wireless supports the P2MP line card on the following three platforms:
The P2MP radio line card supports two views:
As a radio line card starts a wireless interface, you can see the physical appearance of the radio line card and its real-time status in the physical view. The wireless line card also starts one over-the-air downstream channel and multiple over-the-air upstream channels, which appear in the logical view as tangible connectors.
These connectors look and behave like physical connectors and provide access to the characteristics of downstream and upstream channels supported by the line card. You can switch between the physical and logical views by using menus associated with the line card.
For example, Figure 1 shows the physical view for a Cisco uBR7200 series router with two P2MP radio line cards in slots 2 and 3. Each line card has:

Figure 2 shows the logical view of the P2MP headend line card in the Cisco uBR7200 router and shows the downstream and upstream channels supported by the line card.

Table 2 shows the supported feature set for the wireless point-to-multipoint headend line card.
| Element | Feature | Description | Navigational path |
|---|---|---|---|
Radio Frequency (RF) | Revision Information | Assembly and board revision information | Physical view: Configure>RF Head>Main RF>Hardware details or Right click on the main connector. |
| Configuration | Antenna Diversity, CableLoss, and so on. | Physical view: Configure>Radio Channel |
| Config param state | Information about min/max frequency, RF oscillator, supply voltage, temp status, and so on | Physical view: Configure>RF Head>Main RF>Status Or Right-click on the main connector. |
| Statistics Histograms Timelines Snapshots Thresholds | Control, summary, and graph | Physical view: Monitor>Radio Signal Attributes> You can create specification, graph and summary by using the specification table option. |
| Diagnostics
| Self Test Loopback at various RF points | Physical view: Configure>Radio Channel |
Intermediate Frequency (IF) | Revision info | Assembly and board revision information | Physical view: Configure>IF board>Hardware details |
| Config params state | Tx/Rx Osc state and input/output frequency | Physical view: Configure>IF board>Status |
| Diagnostics | Loopback at various IF points | Physical view: Configure>Radio Channel |
Duplexer | Config information | Passband Min/Max frequency and insertion loss | Physical view: Configure> Duplexer>Main/Diversity |
Light emitting diode (LED) | Config and status | Transmitdata, receivedata, out-of-service, major-alarm, minor-alarm, carrier, interface enable | Available on the physical view |
Upstream | Configuration | Configuration for a single upstream channel | Physical view: Configure>RF Sub-Channels>Upstream Logical view: Click on the US port for a menu. Configure>Upstream Channel |
| Modulation profile | Describes modulation profile for an interval usage code for one or more upstream channels | Physical View: Configure>Modulation Profile To create a new modification profile menu, use the modulation profile table. Logical view: Click on the US port for a menu. Configure>Modulation profile |
| Signal Quality | Describes the quality of upstream channels in terms of codeword errors, SINR, and so on | Logical view: Click on the US port for a menu. Configure>Signal quality |
Downstream | Configuration | Configuration for a single downstream channel | Physical view: Configure>RFsub-Channels> Downstream or Logical view: Click on the DS port for a menu. Configure> Downstream Channel |
Media Access Control (MAC) | Configuration | Describes attributes of each media access control (MAC) interface | Logical view: Configure>HE MAC |
| Status | Status for a single MAC layer | Logical view: Monitor>HE MAC status |
Subscriber Units | Status Reset SU | Status information for each subscriber unit in the system | Logical view: Configure>Visible SUs Logical view: Click on the US port for a menu. Configure>Visible SUs |
Service | Profile | Describes attributes of a single class of service | Physical view: Configure>Qos>Qos details |
| Scheduler | Attributes for each upstream MAC scheduler (QOS) used to control subscriber registration Rate limiting attributes for each upstream/downstream scheduler supporting QOS | Logical view: Configure>Qos (Su-Registration)
Logical view: Configure>Qos (Bandwidth-control) |
| Queues | Describes the attributes of a single upstream bandwidth service queue | Logical view: Configure>HE services queue Logical view: Configure>Request Q>Details |
Table 3 shows the supported feature set for the wireless point-to-multipoint headend line card.
| Element | Feature | Description | Navigational Path |
|---|---|---|---|
RF | Revision information | Assembly and board revision information
| Physical view: Configure>RF Head>Main RF>Hardware details or Right click on the Main connector. |
| Configuration | NumRxAnt, Cable loss, TxMuteDuration, and so on | Physical view: Configure>Radio Channel
|
| Configuration parameter and state
| Information about min/max freq, RF Osc/supply/temp status, and so on | Physical view: Configure>RF Head>Main RF> Status OR Right click on the Main connector. |
| Statistics Histograms
Timelines
Snapshots
Thresholds | Control, summary, and data tables
| Physical view: Monitor> Radio Signal Attributes
Logical View: Click on the DS port for a menu. Monitor>Radio Signal Attributes |
| Diagnostics | Loopback at various RF points | Physical view: Configure>Radio Channel |
IF | Revision information
| Assembly and board revision information | Physical view: Configure>IF board>Hardware details |
| Configuration parameter and state | Tx/Rx Osc state, input/output frequency | Physical view: Configure>IF board> Status |
| Diagnostics | Loopback at various IF points | Physical view: Configure>Radio Channel |
Duplexer
| Configuration information | Passband min/max frequency and insertion loss | Physical view: Configure> Duplexer> Main/Diversity |
LED | Configuration and status | Tx:tranmitdata Rx:recievedata OS:outofservice MA:majoralarm, MI:minoralaram, CR:carrier EN:interfaceEnable indication | Available on the physical view. |
Upstream | Configuration | Configuration for a single upstream channel | Physical view: Configure>Upstream Channels Logical view: Click on the US port for a menu. Configure> Upstream |
| Service Queues | Describes the attributes of a single upstream bandwidth service queue | Logical view: Configure>Service queues |
Downstream | Configuration
| Configuration for a single downstream channel | Physical view: Configure>Downstream Channels Logical view: Right click on the DS port for a menu. Configure>Downstream |
| Signal quality | Describes physical sublayer (PHY) quality for a downstream channel | Logical view: Right click on the DS port for a menu. Configure>Signal Quality Monitor>Radio link metrics |
Media Access Control (MAC) | Configuration | Describes attributes of each MAC interface | Logical view: Configure>Mac Info |
| Status | Status for a single MAC layer | Logical view: Monitor>Mac Status>Status Objects Monitor>Mac Status>Status Counters |
With CiscoView Wireless, you can configure and monitor radio signal parameters in various ways. You can change the following signal attributes:
Common to both headends and subscriber units:
Specific to subscriber units only
CiscoView Wireless provides the following classes of features to configure and monitor radio signal parameters:
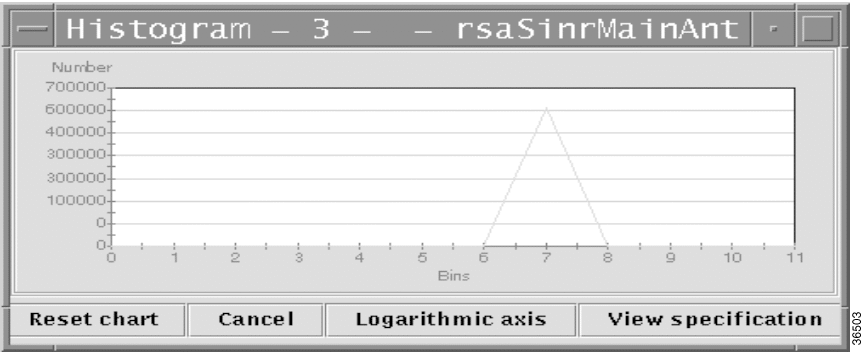
A Histogram represents:
With CiscoView Wireless, you can create histogram specifications on the managed device. Once the specification is created, the managed device captures the signal information. Then, you can set up the histogram to capture data for a long period of time for a single upstream or for one subscriber unit that is registered with the headend. CiscoView Wireless can then graph the collected data in a periodic manner.
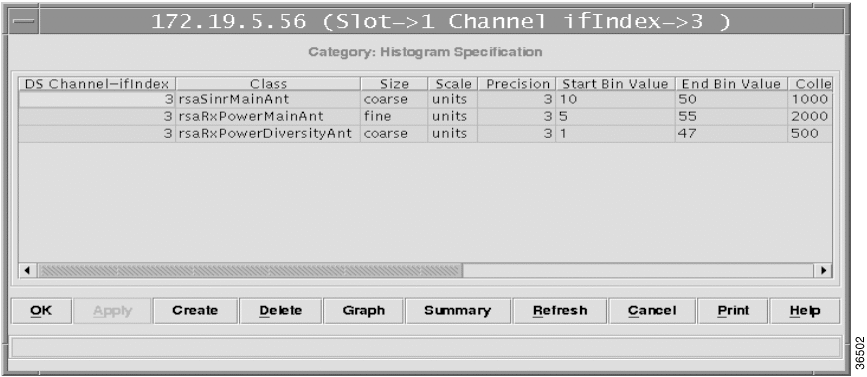
With CiscoView Wireless, you can retrieve the captured histogram data (from the managed device) at regular intervals and store them in a database at the server. You can retrieve and view the stored data at a later date
Step 2 Select the Persistent option in the histogram specification. The Histogram specification appears in the Histogram History. [Chassis>Histogram History>This device/All devices].
For each entry in the Histogram History Table, there is a data file in binary format on the server at the location <CD One install directory>/CSCOpx/www/classpath/devpkg_P2MP where the histogram values are updated as specified by update rate parameter.
Step 3 To stop the collection of histograms permanently, click Stop Collection.
Step 4 To convert the data in the binary file to ASCII format, select the histogram specification from the histogram history table, and click Bin to ASCII.
Step 5 To graph the saved data, select a specification from the Histogram History Table and click Graph.
With CiscoView Wireless, you can establish thresholds on radio signal parameters. A threshold is defined as a transition relative to a specified value. The different types of transitions are:
When a threshold is crossed, the managed device generates a trap. You can associate a threshold with a timeline, and when the threshold is crossed, the timeline is captured.
Timelines represent:
You can create timeline specifications on the managed device. Once the specification is created, the managed device captures the signal information. Once captured, the data must be cleared by another clear request before you can initiate another capture. You can capture the data under two conditions:
You can create timeline specifications on the managed device for the radio signal attributes and graph the data captured by a timeline specification.
Snapshots represent:
You can create snapshot specifications on the managed device. Once the specification is created, the managed device captures the signal information. Once the data is captured, it must be cleared by another clear request before you can initiate another capture. You can also graph the data captured by a snapshot specification.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Tue Mar 27 13:55:23 PST 2001
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2001 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.