|
|

This appendix describes how to mount a CD-ROM, from a local or remote system, so that you can install and configure CiscoWorks Blue Maps on a workstation. It describes how to export the CD-ROM from a remote workstation, and then mount it on the local workstation. This appendix contains these major sections:
You can install CiscoWorks Blue Maps from a CD-ROM drive attached to your system or from a drive connected to a remote system. You must first use SMIT to mount the local or remote device on the local AIX system.
| Caution Avoid exposing the CiscoWorks Blue Maps CD-ROM to direct sunlight because it could harm the contents. |
To install Maps on AIX from a CD-ROM, you can do one of the following:
This section describes how to mount the CD-ROM drive from the local workstation. If you have already performed this procedure, or if another device is already mounted on the mount point, this process will fail.
Step 1 Insert the Maps CD-ROM into the CD-ROM drive.
Step 2 Log in as the root user. (For instructions about how to become the root user, see "Becoming the Root User" in the "Preparing to Install CiscoWorks Blue Maps" chapter.)
Step 3 Enter the following smit command:
# smit
The main SMIT menu appears, as shown in Figure A-1.
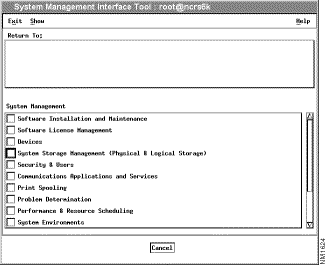
Step 4 From the System Management menu, click System Storage Management (Physical & Logical Storage).
Step 5 Select File Systems.
Step 6 Select Add/Change/Show/Delete File Systems.
Step 7 Select CDROM File Systems.
Step 8 Select Add a CDROM File System.
Step 9 Click the "DEVICE name" List button and select the device name (such as /dev/cd0) from the list that appears.
Step 10 In the Mount point field, enter the name of a mount point directory (such as /cdrom).
Step 11 Click OK and read the output.
Step 12 Click Done.
Step 13 Terminate SMIT by pressing F12 or by selecting Exit SMIT from the Exit menu.
Step 14 Use the mountfs command, as shown below, to mount the file system:
# smit mountfs
Step 15 Click the "FILE SYSTEM name" List button and select a device name (such as /dev/cd0) from the list that appears.
Step 16 In the "DIRECTORY field," enter the name of a mount point directory (such as /cdrom).
Step 17 Click the "TYPE of file system" List button and select cdrfs as the file system type.
Step 18 Set the "Mount as Read-Only System" field to yes.
Step 19 Click OK and read the output, and then click Done.
Step 20 Terminate SMIT by pressing F12 or by selecting Exit SMIT from the Exit menu.
This section describes how to mount a remote CD-ROM on your local workstation. Installation of CiscoWorks Blue Maps does not require any disk space on the remote system. The software is copied across the network to the local workstation.
To mount the CD-ROM on the local file system from a remote CD-ROM drive, first mount the CD-ROM on the remote system using the following procedure. If you have already performed this procedure, or if another device is already mounted on the mount point, this process will fail.
Step 1 Insert the Maps CD-ROM into the CD-ROM drive.
Step 2 Log in as the root user. (For instructions, see "Becoming the Root User" in the "Preparing to Install CiscoWorks Blue Maps" chapter.)
Step 3 To start SMIT, enter the smit command:
# smit
The main SMIT menu appears, as shown earlier in Figure A-1.
Step 4 On the System Management list, select System Storage Management (Physical & Logical Storage).
Step 5 Select File Systems.
Step 6 Select Add/Change/Show Delete File Systems.
Step 7 Select CDROM File Systems.
Step 8 Select Add a CDROM File System.
Step 9 Click the "DEVICE name" List button and select the device name (such as /dev/cd0) from the list that appears.
Step 10 In the "Mount point field," enter the name of a mount point directory (such as /cdrom).
Step 11 Click OK and read the output.
Step 12 Click Done.
Step 13 Terminate SMIT by pressing F12 or by selecting Exit SMIT from the Exit menu.
Step 14 Use the mountfs command, shown below, to mount the file system:
# smit mountfs
Step 15 Click the "FILE SYSTEM name" List button and select a device name (such as /dev/cd0) from the list that appears.
Step 16 In the "DIRECTORY field," enter the name of a mount point directory (such as /cdrom).
Step 17 Click the "TYPE of file system" LIST button and select cdrfs as the file system type.
Step 18 Set the "Mount as Read-Only System" field to yes.
Step 19 Click OK and read the output, and then click Done.
Step 20 Terminate SMIT by pressing F12 or by selecting Exit SMIT on the Exit menu.
Step 21 Enter the following command at the system prompt
# smit mknfsexp
Step 22 In the "PATHNAME of directory to export" field, enter the path name (such as /cdrom).
Step 23 Use the arrow keys to change the "Mode to Export Directory" field to read-only.
Step 24 Enter the appropriate information, if necessary, into any of the other fields.
Step 25 Click OK, read the output, then click Done.
Step 26 Terminate SMIT by pressing F12 or by selecting Exit SMIT from the Exit menu.
Perform the following steps on the local system to mount the remote file system.
Step 1 Enter the smit command, as shown below:
# smit mountfs
Step 2 In the "FILE SYSTEM name" field, enter the device name from the remote system (such as /cdrom).
Step 3 In the "DIRECTORY over which to mount" field, enter the name of the mount point directory (such as /cdrom).
Step 4 Click the "TYPE of file system" List button and select nfs as the file system type.
Step 5 In the "REMOTE NODE" field, enter the name of the remote host, such as host1.cisco.com.
Step 6 Set the "Mount as Read-Only System" field to yes.
Step 7 Click OK and read the output, and then click Done.
Step 8 Terminate SMIT by pressing F12 or by selecting Exit SMIT on the Exit menu.
The CD-ROM is ready for installation of software.
You can install CiscoWorks Blue Maps from a CD-ROM drive attached to your system or from a drive connected to a remote system. You must first mount the local or remote device on the local system.
| Caution Avoid exposing the CiscoWorks Blue Maps CD-ROM to direct sunlight because it could harm the contents. |
To install Maps on HP-UX or Solaris from a CD-ROM, you do the following:
This section describes how to export a CD-ROM file system from a remote system..
| Caution The instructions for mounting a remotely exported CD-ROM drive on a local system are for like systems. For example, the instructions are for exporting a CD-ROM file system from an HP-UX system and mounting it on another HP-UX system for installation, or for exporting from a Solaris system and mounting on Solaris, but not for cross-platform operation. If necessary, your system administrator can help you with cross-platform exporting and mounting |
To export a CD-ROM file system from an HP-UX or Solaris system, perform the following steps on the remote system:
Step 1 Insert the Maps CD-ROM in the CD-ROM drive.
Step 2 Log in as the root user. (For information about how to become the root user, see the section "Becoming the Root User" in the "Preparing to Install CiscoWorks Blue Maps" chapter.)
Step 3 If the /cdrom directory already exists, proceed to the next step. If the /cdrom directory does not exist, create it with the mkdir command:
# mkdir /cdrom
Step 4 If an exports file does not exist, create one using a text editor.
Step 5 Edit the export file to include this line:
/cdrom -ro
Step 6 If you just created a new exports file (/etc/dfs/dfstab or /etc/exports) in Step 4, you must now enable your workstation as a Network File System (NFS) server. To start the nfsd server, enter the commands shown below.
On Solaris
# /etc/init.d/nfs.server start
On HP-UX
# /sbin/init.d/nfs.server start
# /usr/sbin/rpc.mountd -n
Step 7 On Solaris only, add the following line to the etc/dfs/dfstab file:
share -F nfs -o -ro /cdrom/cdrom0
Step 8 Mount the CD-ROM.
On Solaris
The vold server automatically manages the CD-ROM device and performs the mounting. The CD-ROM may automatically mount onto the /cdrom/cdrom0 directory. If you are running File Manager, a separate File Manager window displays the contents of the CD-ROM disk. If the /cdrom/cdrom0 directory is empty because the CD was not mounted, or if File Manager did not open a window showing the contents of the CD-ROM disk, verify whether the vold server is running by entering the following sequence of commands:
# ps -ef | grep vold | grep -v grep
If the system does not display anything, restart the server:
# /usr/sbin/vold &
If the vold server is running but did not mount the CD, stop the vold server process and then restart it:
# kill -15 process_ID
# /usr/sbin/vold &
Where process_ID is the UNIX process ID of the vold server.
Then enter the mount command:
# /usr/sbin/mount -r /dev/sr0 /cdrom/cdrom0
On HP-UX
Use the following commands to mount the CD-ROM:
# /etc/mount -o ro -t cdfs /dev/device_filename /cdrom
Where:
-o ro mounts the CD-ROM in read-only mode.
-t indicates the type of file system: hsfs for the ISO 9660 standard, or cdfs for the High Sierra standard with Rock Ridge extensions.
device_filename is the name of the device you want to mount (for example /dev/dsk/c201d2s0) or a different device name reported by the /etc/ioscan program for the CD-ROM device.
Step 9 If the /etc/exports file existed previously (before Step 4), enter the following command to run exportfs:
# exportfs -va
If /etc/exports did not exist previously, reboot your system.
# reboot
You can continue to the next section, "Mounting a Remotely Exported CD-ROM File System on a Local System."
To mount a file system that is exported from a remote system, perform the following steps on the local HP-UX or Solaris system:
Step 1 Log in as the root user. (For information about how to become the root user, see the section "Becoming the Root User" in the "Preparing to Install CiscoWorks Blue Maps" chapter.)
Step 2 If a /cdrom directory does not already exist, create it by entering the mkdir command:
# mkdir /cdrom
Step 3 To mount a file system that is exported from a remote system, use the mount command, as shown below:
# mount remote_hostname:remote_filesystem local_mount_point
Where:
remote_hostname is the name of the remote workstation.
remote_filesystem is the name of the file system on the remote workstation.
local_mount_point is the name to be used on the local workstation.
For example, to mount the /cdrom file system from a remote host called faraway on a local directory named /cdrom, you would use the following command:
# mount faraway:/cdrom /cdrom
The remote CD-ROM is ready for installation of software on the local system.
To prepare the system for installation of software from a local CD-ROM drive, complete the following steps:
Step 1 Insert the Maps CD-ROM in the CD-ROM drive.
Step 2 Log in as the root user. (For information about how to become the root user, see the section "Becoming the Root User" in the "Preparing to Install CiscoWorks Blue Maps" chapter.)
Step 3 If the /cdrom directory already exists, proceed to the next step.
If a /cdrom directory does not exist, create it with the mkdir command:
# mkdir /cdrom
Step 4 Mount the CD-ROM.
On Solaris
The vold server automatically manages the CD-ROM device and performs the mounting. The CD-ROM may automatically mount onto the /cdrom/cdrom0 directory. If you are running File Manager, a separate File Manager window displays the contents of the CD-ROM disk. If the /cdrom/cdrom0 directory is empty because the CD was not mounted, or if File Manager did not open a window displaying the contents of the CD-ROM disk, verify that the vold server is running by entering the following sequence of commands:
# ps -ef | grep vold | grep -v grep
If the system does not display anything, restart the vold server using the following command:
# /usr/sbin/vold &
If the vold server is running but did not mount the CD-ROM, stop and restart the vold server process:
# kill -15 process_ID
# /usr/sbin/vold &
Where process_ID is the UNIX process ID of the vold server.
On HP-UX
# /etc/mount -o ro -t cdfs /dev/device_filename /cdrom
Where:
-o ro mounts the CD-ROM in read-only mode.
-t indicates the type of file system: hsfs for the ISO 9660 standard, and cdfs for the High Sierra standard with Rock Ridge extensions.
device_filename is the name of the device you want to mount (for example /dev/dsk/c201d2s0) or a different device name reported by the /etc/ioscan program for the CD-ROM device.
Unmount the CD by logging in as the root user and entering the following commands at the local or remote workstation on which the CD-ROM is mounted:
# cd /
# umount /cdrom
AIX unmounts the CD-ROM device from the /cdrom directory. Remove the CD-ROM from the drive.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Thu Aug 19 11:04:31 PDT 1999
Copyright 1989-1999©Cisco Systems Inc.