|
|

CiscoWorks Blue Maps and CiscoWorks Blue SNA View provide a set of UNIX Motif and Web-based applications for diagnosing problems in, and managing, integrated networks based on Systems Network Architecture (SNA) and Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) environments.
This chapter introduces the functions and capabilities of CiscoWorks Blue Maps and SNA View. It contains the following main sections:
The world of SNA networking is divided into these three fundamental environments:
The world of SNA networks is illustrated in Figure 1-1.
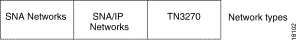
In these SNA networks, the mix of protocols run by the mainframe computer, the network, and the end user devices varies, as shown in Figure 1-2.
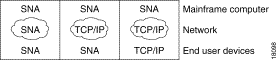
These various SNA networks run a variety of protocols to transport data between the mainframe computer and the network nodes over the network. The SNA network protocols are shown in Figure 1-3.
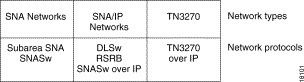
Network management programs, tools that you use to manage these SNA networks, also vary depending on the protocols used, as shown in Figure 1-4.
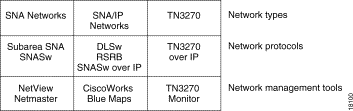
One tool lets you identify and isolate outages in all SNA networks. SNA View, as shown in Figure 1-5, lets you see network connectivity views for the three types of SNA networks.
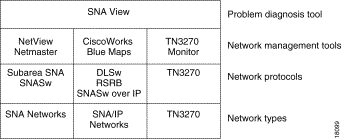
When managing and diagnosing SNA networks, the distinctions between diagnosis and management must be clear:
Cisco offers a set of SNA network management and problem diagnosis tools to help you perform these tasks.
When you use the CiscoWorks Blue SNA View application, you can start with a few bits of information about a network outage, perhaps the LU name or the MAC address, and view the entire path from a network terminal back through the network of routers or communication controllers to the SNA mainframe computer. When you use the CiscoWorks Blue Maps applications, you can manage the Cisco routers that control communication in networks that are enabled for RSRB, DLSw, or APPN.
There is a trend in network management to reduce the need for separate network resource managers by providing direct management of heterogeneous multi-vendor networks from a single, integrated network management system. In keeping with this strategy, CiscoWorks Blue Maps uses information from Virtual Telecommunications Access Method (VTAM) and the Multiple Virtual Storage system (MVS) to enable network administrators to monitor and manage SNA resources. To further simplify and enhance network management, use Maps to display your SNA resources on graphical network maps.
The Maps workstation program runs on a UNIX workstation to collect SNA network information provided by the Maps and SNA View mainframe program. It provides the SNA control and correlation needed to manage SNA devices from a UNIX platform, allowing the network administrator to see beyond the routers to the SNA physical unit (PU) and logical unit (LU) resources. Maps gets PU and LU resource information from VTAM at a mainframe computer and correlates that information with the Cisco routers that are associated with the PUs and LUs. By interacting with the mainframe, Maps adds vital PU and LU information to the graphical maps. Because Maps correlates PU and LU names with the routers in the network, you can more easily isolate problems to the IP network or to the SNA network. Resource information is dynamically updated to provide a snapshot of the network as it appears at any given time. This information allows the administrator to display a graphical map that depicts details from the PU back toward the VTAM host, providing information such as the PU and LU status and the PU and LU dependency relationships.
This section presents a brief overview of the functions provided by CiscoWorks Blue SNA View. SNA View is a web-based application. The SNA View web server runs in a UNIX workstation gathering information about routers and SNA LUs and PUs from the SNA View and Maps data base. When you link to the SNA View web page, you can display SNA session paths. The web page then displays a session connectivity view, as shown in Figure 1-6.
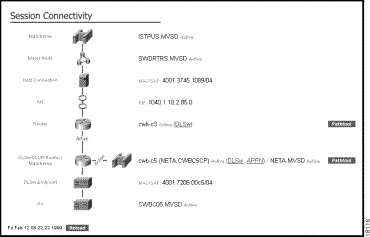
The CiscoWorks Blue SNA View product is a tool for problem diagnosis in all SNA networks.
CiscoWorks Blue SNA View offers web-based client and server applications. These applications start with as much information about a failing node as you can provide and then display the network devices between that node and the mainframe computer.
CiscoWorks Blue Maps is a set of applications that let you manage Cisco routers in an IBM SNA network. Each Maps application focuses on a particular protocol: DLSw, RSRB, or APPN. Maps displays graphical views of SNA networks connected with Cisco routers. These views are dynamically updated to provide snapshots of the network as it appears at any time.
Maps also lets you see beyond the routers to the SNA PUs and LUs that use the DLSw, RSRB, or APPN protocols. Maps mainframe component discovers the PUs and LUs from VTAM information at the mainframe, monitors those PUs and LUs, and reports their changing status to the Maps workstation applications to update the Maps database and the graphical maps.
The CiscoWorks Blue Maps product provides the following Motif and web-based applications that show, in a graphical or tabular format, the routers that make up your integrated SNA and TCP/IP network:
CiscoWorks Blue Maps applications provide the features described in the following sections:
CiscoWorks Blue Maps applications get network data from the MIBs to provide detailed logical maps of the SNA-related protocols. These maps are automatically drawn to depict specific protocols in the network. For example, the DLSw key devices map provides a view of the key DLSw routers with their peer routers and the rings and peer connections between them. Topology is drawn based on the DLSw protocol, and you can focus on different components of the DLSw network such as individual routers and links. Figure 1-7 is a sample DLSw key devices view. It shows you a small set of routers that you designate as "key devices" based on their networking attributes. This map also shows you the peer routers to those key routers, and it shows you the peer connections that connect the key routers to their peers.
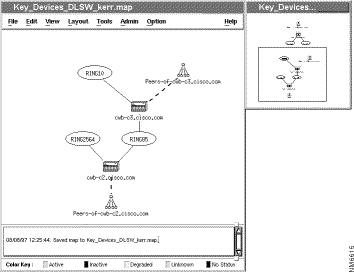
CiscoWorks Blue Maps provides the network administrator with the tools needed to manage growing integrated SNA and TCP/IP networks. This set of Maps applications (RSRB, DLSw, and APPN) can be integrated with popular Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) management platforms such as IBM NetView for AIX, HP OpenView, or SunNet Manager. From the graphical maps, you can display path information or go directly to a device view using CiscoView.
You can use the graphical maps to efficiently identify and diagnose problems related to the specific protocol under observation (RSRB, DLSw, and APPN). Having identified the problem area, you can easily access additional information by invoking other menus in the application. For instance, in a DLSw network, you can use a key routers view to display a selected set of routers and their peer connections. From this view, you can then display information about peer routers, peer connections, and DLSw circuits. You can also view new nodes as they are added, and view the changing status of the devices and links dynamically.
CiscoWorks Blue Maps offers both Motif-based and web-based network management applications.
CiscoWorks Blue Maps offers a set of network management applications that use the X Window System and Motif graphical interfaces to display graphical maps of the nodes and links in your network. Each application focuses on a particular protocol: DLSw, RSRB, or APPN.
CiscoWorks Blue Maps offers a set of web-based client/server applications that let you use web browsers to display information about RSRB, DLSw, and APPN networks. The network information is presented in a tabular format. The web server runs on your Maps workstation and collects information from the Cisco routers in the network. You can use a web browser from any workstation in the network to connect to the web server to view the network.
When you install the CiscoWorks Blue products, you always install all the code, whether you license maps, SNA View, or both. Maps and SNA View use many common functions:
This section lists the major changes for CiscoWorks Blue Maps and SNA View 2.0.
| Old Interface | New Interface |
|---|---|
runappn | cwb start appn |
rundlsw | cwb start dlsw |
runrsrb | cwb start rsrb |
cwbconfigure | cwb config |
runprocess process_name | cwb start process_name |
cwbinstall | setup.sh |
cwbhttpd_start.sh | autostarted by Process Manager |
cwbhttpd_stop.sh | autostopped by Process Manager |
dbutil | cwb verify |
dbutil -c | cwb clear db |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Wed Jun 30 06:36:03 PDT 1999
Copyright 1989-1999©Cisco Systems Inc.