|
|

CiscoWorks Blue Maps includes an interface that you can use to display network map information from a web browser such as the Netscape Navigator or Microsoft Internet Explorer. This interface provides, in tabular format, functions similar to those provided by the standard Motif interface. Access Maps information from any web browser on any workstation platform, such as a PC running Microsoft Windows, or a UNIX workstation.
The Maps and SNA View web pages are described in the following topics:
This topic describes how to access the CiscoWorks Blue Maps web interface with a web browser.
To use your web browser with the CiscoWorks Blue web page, configure your web browser as follows:
To access the CiscoWorks Blue Maps web server, use the following URL:
http://workstation[:port_number]
Where:
workstation is the IP address or host name of the workstation on which you installed CiscoWorks Blue Maps.
port_number is the CiscoWorks Blue web server port. The default is port 80. However, if port 80 is already in use, the CiscoWorks Blue web server uses backup port 8080. If the server is using port 80, you can omit this option. If the server is using another port, for example port 8080, you must specify it with this option. For example, if you installed Maps on a workstation with the address wwwblue.company.com, using port 8080, you would set your browser to the following URL:
http://wwwblue.company.com:8080
Start a a web browser from the Maps Tools menu. To start the Maps web browser, select Tools>Web Browser from the Maps application menu bar.
If you have problems, review the /opt/CSCOcb/etc/runweb script to ensure that the setting of environment variables, the name of the web browser, and the path to the web browser match the directory structure on your workstation. You can modify the
/opt/CSCOcb/etc/runweb file with any editor, such as vi:
vi /opt/CSCOcb/etc/runweb
When the web browser finds the CiscoWorks Blue URL, it displays the CiscoWorks Blue home page (Figure 2-1).
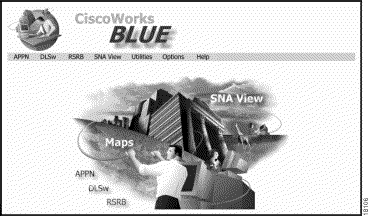
Use the links on the Maps home page to start one of the Maps or SNA View applications.
The menu bar provides links to the Maps applications:
This topic presents some conventions that apply to all Maps and SNA View web pages.
When you resize a dialog for a Maps or SNA View web page, the browser remembers the size for the next time you display that dialog. For example, if the Options dialog is too small, just drag it to a more convenient size. The browser remembers the setting the next time you display that dialog.
You can use the following buttons at the bottom of most Maps web pages. (Cookies must be enabled for these to work correctly.)
The hypertext links on Maps pages help you find your way through the network information. Configure your web browser to underscore hypertext links so you will more easily see them. Because many of the hypertext links are unique to the specific protocol-based applications, they are described in the remaining topics. The following two hypertext link types are common to all the applications:
All pages displayed by the web interface are static pages. They are not updated dynamically. To update the information on a web page, do one of the following:
When you click Reload, the web server collects its data from the database or from the network devices, depending on which web page you are displaying. For example, when you click Reload on the DLSw Peer Statistics page, the web server collects data from the network topology agent in the network.
This topic explains some conventions for entering values such as IP addresses, node names, and MAC and SAP addresses.
The SNA Resource Information page displays SNA resources (PUs and LUs) and sessions in the network using the SNA Resource Information page from a web browser. It contains the following topics:
The intent of SNA View is to show you a picture of a network session connectivity path from a PU or LU, back through the SNA or TCP/IP network to an SNA mainframe computer. It asks you to enter as much information as you know about an end user device, then searches a database to find all the sessions that match your criteria. From this list you can select a single session to display. SNA View then displays the path for that session.
Select SNA View from the CiscoWorks Blue home page to display one or more SNA sessions based on a set of search criteria. The SNA Resource Information page is displayed. Enter your search criteria on the SNA Resource Information page, then click go. Enter as much information as you can to identify an SNA resource. The more information you enter, the more focused the resulting list of sessions will be. You may even be able to identify a single session.
If your search does uniquely identify a session, you will then see the network path taken by that session from the end user device to the SNA mainframe computer.
If your search results in more than one session, you will see a listof those sessions in the SNA Filter Results Page. Scroll through the session list to find the one session you want. Click Session Path to see the network path taken by that session from the end user device to the SNA mainframe computer.
The Session Connectivity Display Page displays a picture of the network showing your selected session from the end user device to the SNA mainframe. Each device in the path has its own network icon. When there are IP devices in the network path, click Pathtool to see the hops between pairs of routers.
On the SNA Resource Information page (Figure 2-2), you provide as much information as you can to identify an SNA resource. For example, when a network user calls in with an outage, you can get such information as the MAC address, the LU name, or the PU name. For example, from a computer running Windows 95 the user can enter the winipcfg command to display the current IP address. The web server displays either a unique SNA resource, when you provide enough information, or a list of SNA resources with similar characteristics.
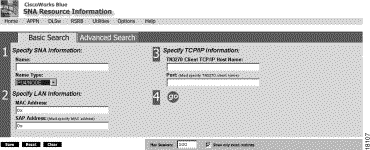
Use one of the following search methods:
The result of either search can be the single session that matches the criteria, or a list of sessions that match the criteria.
The Basic Search tab is intended for network operators to be able to display network information commonly provided by an end user.
Step 1 In the Specify SNA Information field, enter the following values:
If you enter nothing in this field, you must enter a value in one of the other fields on this tab in order to get a list of resources.
Step 2 In the Specify LAN Information field, identify an SNA resource by its MAC and SAP address.
If you enter nothing in this field, you must enter a value in one of the other fields on this tab in order to get a list of resources.
Step 3 In the Specify TCP/IP Information field, you identify one or more SNA resources by their TCP/IP attributes. For example, from a computer running Windows 95 the user can enter the winipcfg command to display the current IP address.
If you enter nothing in this field, you must enter a value in one of the other fields on this tab in order to get a list of resources.
Step 4 Optionally select Show only exact matches to display only those sessions that exactly match your criteria. If you deselect this field, you will see a list of sessions that match any of your criteria.
Step 6 Click go.
The SNA Filter Results Page is displayed.
Use the Advanced Search page to display a list of sessions based on their naming convention, PU or LU status, protocol, router dependency, or APPN attributes.
Step 1 In the Specify Basic Search Information field, enter the following values:
Use wildcard characters in the PU Name, LU Name, CP Name, and Client IP Name or Address fields.
Step 2 In the Specify PU Status field, specify one of the following values:
If you select all states or no states, state filtering is bypassed and PUs in any state are displayed.
Step 3 In the Specify Session Protocols field, select one of the following protocols:
Step 4 In the Specify Router Dependencies field, either enter the IP addresses or host names of one or more routers (separated by commas) on which the SNA resource depends. Use the Browse button to select a router from the displayed list of routers that match the protocols selected in Step 3 above. Use wildcard characters in Router Dependency field.
Use this option to see which sessions depend on a router and would be affected by a router problem.
Step 5 In the Specify APPN Criteria field, specify the following values:
Step 6 Optionally select Show only exact matches to display only sessions that exactly match your criteria.
Step 8 Click go.
The SNA Filter Results Page is displayed.
The SNA Filter Results page displays all the SNA sessions that matched the criteria that you entered in the Basic or Advanced search on the SNA Resource Information Page. The SNA Filter Results page displays information in the following areas:
The menu bar on the Filter Results page provides links to other applications:
The Summary table displays a summary of the state of all sessions selected by your search criteria.
The Summary table contains the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
PU/LU States | Inactive---Total number of sessions whose VTAM status is INACT. Active---Total number of sessions whose VTAM status is ACTIV. Connectable---Total number of sessions whose VTAM status is CONCT. Pending---Total number of sessions whose VTAM status is a PENDING status. Never active---Total number of sessions whose VTAM status is NEVAC. Other---Total number of sessions with some other status. Unknown---Displays the total number of sessions with no reported status. Pending Active---Total number of sessions whose status is pending active. Pending Inactive---Total number of sessions whose status is pending inactive. |
Total # of sessions | Number of sessions in this connection state that meet the criteria that you specified. |
The Sessions table displays details of all sessions selected by your search criteria. There can be one or two Sessions tables:
The Sessions tables might contain the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Session Path | Click Session Path to see a Session Connectivity view for the session, as described in "Session Connectivity Display Page." |
LU Name.Domain | LU name and domain name for each session that meets your criteria. |
PU Name.Domain | PU name and domain name for each session that meets your criteria. |
State | Shows the state of each session: Active---VTAM status is ACTIV. Inactive---VTAM status is INACT. Connectable---VTAM status is CONCT. Pending---VTAM status is one of the pending statuses. Never active--- VTAM status is NEVAC. Other---Session has some other status; often used for a session, such as a DLSw circuit, that could not be correlated to a PU. Unknown---No reported status. Pending Active --- Status is pending active. Pending Inactive --- Status is pending inactive. |
Client IP | IP address of the client PU. |
Client MAC/SAP1 | MAC and SAP addresses of the PU. |
Destination MAC/SAP2 | MAC and SAP addresses of the host network connection. |
XID | Exchange identification. |
CPNAME | CPNAME of the PU. |
DLUR Name | APPN control point name of the device that provides the DLUR services to the LU. |
DLUS Name | APPN control point name of the VTAM host. |
TN3270 | Name of the TN3270 server for this PU session (for TN3270 sessions only). |
The Session Connectivity Display page shows the path that a session takes from an end user device back to the SNA mainframe computer. The Session Connectivity view (Figure 2-3) is displayed when you do one of the following:
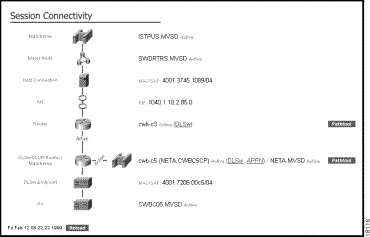
The Session Connectivity page shows you the paths of one SNA session:
Next to each device on the page, the following information is provided:
There are a variety of links on this page:
The menu bar on the Session Connectivity Display page provides links to other applications:
The Pathtool page displays the hops between two selected devices using the same techniques used by the CiscoWorks Path tool. It contains the Pathtool table, which displays information about each hop in the path.
Step 1 In the Session Connectivity Display Page, click Pathtool next to the node for which you want to see the session path.
Step 2 If the Select Routers window is displayed, because there are more than two routers in the Session Connectivity Display, select the two routers for which you want a path.
Step 3 Select whether to include intermediate routers.
Step 4 Click OK.
The Pathtool page displays the Pathtool table.
The Pathtool table contains the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Hop | Number of the hop, starting with the origin node. |
Device Name | Device name of the device at this hop. |
IP Address | IP address of the device at this hop. |
Interface (In) | Identifies the type of network interface into the device for this hop. |
Interface (Out) | Identifies the type of network interface out from the device for this hop. |
This topic describes how to display the APPN page from a web browser and how to view the nodes and transmission groups that make up the APPN network topology. It contains the following topics:
This topic describes how to use the APPN page. From the CiscoWorks Blue home page, click APPN. The APPN page is displayed (Figure 2-4).
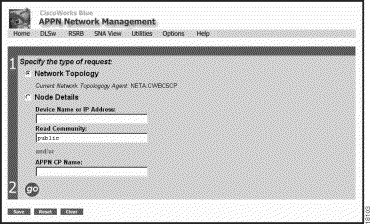
You can perform the following on the APPN page:
Click one of the buttons in the Request field to review the following information.
Click go to display the requested page.
The APPN web pages contain several kinds of hypertext links to help you navigate through the topology information. When you click a hypertext link, APPN displays more information about the item that you clicked. The APPN pages use the following hypertext links:
| When you click this... | APPN displays this... |
|---|---|
Link Name | Link Properties page |
NETID.CPNAME | APPN Node Details page |
Port Name | Port Properties page |
Node State | List of nodes in that state |
TG Number | TG Properties page |
Intermediate Session | Intermediate session page, including session route |
This topic explains how to display a summary of all nodes and TGs that have the same status. When you select Network Topology from the APPN page, the Network Topology page displays the summary information about the nodes and transmission groups (TGs). It lists the number of nodes in each node state and the number of TGs in each TG state. The Network Topology page contents are described in the following topics:
When you display the Network Topology page, the box in the upper-right corner displays the name of the topology agent. If no topology agent was found, the box displays the message "No topology agent."
The menu bar provides the following links:
The Node Summary table displays the number of nodes in each node state.
The Node Summary table has the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Node States | Status of each node. |
Number of Nodes | Total number of APPN nodes reported by the topology agent in each node state. |
Details | Click Details to display the Node table for the selected node state, as described in "Node Details Page." |
The TG Summary table displays the number of TGs in each TG state.
The TG Summary table has the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
TG States | Status of each transmission group. |
Number of TGs | Total number of APPN transmission groups (TGs) reported by the topology agent in each state. |
Details | Click Details to display the detailed table for the selected TG state, as described in "TG Properties Page." |
The Node List page includes a list of all nodes that have the same state. For each node state present in the network (unknown, degraded, active, and virtual routing nodes) there is a Node page that shows all the nodes in the specified state. There are up to four node pages, one for each possible node state:
When you display a Node List page, the box in the upper-right corner displays the name of the topology agent. Each Node List page contains a menu bar and a Node table.
The menu bar on each Node List page contains the following items:
The Node table lists all the nodes with the same state.
The Node table has the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Node Name | Name of the selected node. Click the node name to display the Node Details page, as described in the "Node Details Page." |
TG Number | TG number for each TG on the selected node. Click the TG number to display the TG Information page, as described in the "TG Properties Page." |
Destination Node | Name of the destination node that is connected to the selected node by this TG. Click the node name to display the Node Details page, as described in the "Node Details Page." |
CP-CP Sessions | Indicates whether there are CP-CP sessions on the selected connection. |
The TG List page contains a list of all TGs that have the same status. For each TG state present in the network there is a TG page that shows all the TGs in the specified state. There can be up to three TG pages, one for each possible state:
When you display a TG List page, the box in the upper-right corner displays the name of the topology agent.
The menu bar on each TG page contains the following items:
For each TG state present in the network, the summary page shows a table that displays the source node and destination node for each TG in a TG state. There are up to three TG tables, one for each possible TG state:
The TG table has the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Node Name | Name of the selected node. Click the node name to display the Node Details page, as described in the "Node Details Page." |
TG Number | TG number for each TG on the selected node. Click the TG number to display the TG Information page, as described in the "TG Properties Page." |
Destination Node | Name of the destination node that is connected to the selected node by this TG. Click the node name to display the Node Details page, as described in the "Node Details Page." |
CP-CP Sessions | Indicates whether there are CP-CP sessions on the selected connection. |
You can display detailed information about one specific node. When you select Topology Agent Details from the APPN page, or when you click a node or device name or IP address from any APPN web page, the APPN Node Details page displays information about the selected node in a series of tables described in the following topics:
The menu bar provides links to the following applications:
The General table identifies the selected APPN node.
The General table has the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
SNMP Device Name | Name of the device. |
CP Name | CP name in the format network_ID.CP_name. |
APPN Node State | Status of the node. |
Node Type | Type of the node. |
The IP Addresses table displays all the IP addresses and their subnet masks configured for the node.
The IP Addresses table has the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
IP Address | All IP addresses configured for the node. |
Net Mask | Subnet mask for each IP address. |
Interface Type | Interface type configured for each IP address. |
The Ports and Links table displays all the ports and links configured for the node.
The Ports and Links table has the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Link | Link name of each link configured on the node. Click the name to display the Port Properties page, as described in the "Link Properties Page." |
Port | Port name of each port configured on the node. Click the name to display the Port Properties page, as described in the "Port Properties Page." |
TG Number | TG name of each transmission group configured on the node. Click the number to display the TG Properties page, as described in the "TG Properties Page." |
Adjacent Node | Name of the adjacent node. Click the node name to display the Node Details page, as described in the "Node Details Page." |
The DLUS/DLUR table has the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
PU Name | Name of each PU served by the DLUR function at the selected node. Click PU Name to link to the SNA Resources Session Connectivity web page for this PU (requires SNA View license). |
PU State | Status of each PU. |
DLUS Node Name | Name of the DLUS node. Click the node name to display the Node Details page for that node. |
DLUR-DLUS State | Status of the DLUS/DLUR control session. |
The Directory table has the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
LU Name | Name of each LU supported by the selected node. |
Owning CP Name | Network name of the owning CP. Click the node name to display the Node Details page, as described in the "Node Details Page." |
Serving NN Name | Name of the network node that supports the LU. Click the node name to display the Node Details page, as described in the "Node Details Page." |
The Intermediate Sessions table has the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Primary LU | Name of the primary LU in each session. |
Secondary LU | Name of the secondary LU in the session. |
Mode Name | Name of the VTAM mode table used by the session. |
PCID CP Name | CP name of the node that assigned the Procedure Correlation Identifier (PCID) for the intermediate session. |
FQPCID | Unique identifier assigned by the PCID CP name. |
Details | Links to the Intermediate Sessions page, as described in the "Intermediate Sessions Page." |
The TG Properties page contains detailed information about one specific TG. When you select a TG, the TG Properties page displays the TG information as perceived by each node that owns this TG. This information is taken from the topology database and might not reflect actual TG properties if a network outage is preventing this information from being reported to the network topology agent. In this case, the TG connection is displayed in blue on the map to reflect unknown status.
When you display a TG Properties page, the box in the upper-right corner displays the names of the nodes at each end of the TG.
The TG Properties page contains a General table and a Details table.
The General table displays two columns of information. Each column describes the properties of the TG in the direction from the node in that column to the node in the other column ("N/A" means that the information for that field is unavailable.)
The General table has the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
CP Name | CP name of device owning the TG. |
TG Number | Number that identifies this TG and the two CP names. |
Status | Indicates whether this TG is available for inclusion in an APPN route. |
CP-CP Sessions | Indicates whether CP-CP sessions are supported in this TG. |
Virtual Node | Indicates whether the node that supports this TG is a virtual node. |
Quiescing | Indicates whether this TG is in the process of being shut down. |
The Details table displays two columns of information. Each column describes the properties of the TG in the direction from the node in that column to the node in the other column ("N/A" means that the information for that field is unavailable).
The Details table has the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Security Level | Security level of this link; values include Non-Secure, Public Switched Network, Underground Cable, Secure Conduit, Guarded Conduit, Encrypted, and Guarded Radiation. |
Propagation Delay | Relative length of time it takes a signal to travel the length of this link; values include minimum, negligible, terrestrial, packet, long, and maximum. |
Effective Capacity | Capacity of the TG, in kilobits per second. |
Cost/Connect Time | Relative cost per unit of time to use this TG, in the range 0 to 255, where 0 is low cost. |
Cost/Byte | Relative cost of transmitting a byte over this link, in the range 0 to 255, where 0 is low cost. |
Days Until Deletion | Number of days until this TG is deleted from the network topology agent's database. This value is meaningful only when this TG is not operational. |
User-defined 1 | User-defined route calculation constraint number 1, in the range 0 to 255. |
User-defined 2 | User-defined route calculation constraint number 2, in the range 0 to 255. |
User-defined 3 | User-defined route calculation constraint number 3, in the range 0 to 255. |
The Port Properties page displays information about a port that is configured on a node. To see port properties, select a port on a Node Details page. The Port Properties page displays information about that port.
The Port Properties page has the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Port Name | Name of the port as configured at the owning node. |
Status | State of this port; values include Inactive, Pending-Inactive, Active, or Pending-Active), according to the owning node. |
Owning CP Name | Network name of the owning node. |
Maximum BTU Size | Maximum basic transmission unit size that a link station on this port can receive, in the range 0 to 32767. |
Maximum I-Frame Size | Maximum number of I-frames that can be received by the XID sender before an acknowledgment is received. |
Port Type | Type of line used by the port (Leased, Switched, or Shared Access Facility). |
Link Station Role | Initial role for link stations activated through this port (Primary, Secondary, Negotiable, or Asynchronous Balance Mode). |
DLC Type | Data-link control type of the port (SDLC, Ethernet, Token Ring, or Other). Other includes RSRB, DLSw, and Frame Relay. |
Local Address (Shown only if DLC=token ring) | Local MAC address used by this port (if the DLC type is Token Ring). |
SAP (Shown only if DLC=token ring) | Service access point used by this port (if the DLC type is Token Ring). |
SIM/RIM Supported | Indicates whether Set Initialization Mode and Receive Initialization Mode are supported. |
The Link Properties page displays information about a link that is configured on a node. To see link properties, select a link on a node's focus view. The Link Properties page displays information about that link. The Link Properties page contains the General table and the Details table.
The General table lists each link station.
The General table contains the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Link Name | Name of the link as configured at the owning node. |
Status | State of this link station (Inactive, Pending-Inactive, Active, or Pending-Active), according to the owning node. |
Owning CP Name | Network name of the owning node. |
Destination CP Name | Network name of the destination node. |
Port Name | Name of the port under which this link station is defined. |
DLC Type | Data-link control type of the port (SDLC, Ethernet, Token Ring, or Other). Other includes RSRB, DLSw, and Frame Relay. |
CP-CP Support | Indicates whether CP-CP sessions are supported on this link. |
The Details table lists detailed information about each link.
The Details table contains the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
TG Number | Number of the TG associated with this link station. |
Max Send BTU Size | Numeric value between 0 and 32767, inclusive, indicating the desired number of bytes in a basic transmission unit that can be sent on this TG. |
Dynamic Link | Indicates whether a link definition for this link station was created dynamically as a result of an incoming link activation request. |
Limited Resource | Indicates whether this link station will be deactivated when all sessions using it have ended. |
The Intermediate Sessions page displays information about an intermediate session. To display an intermediate session, select Details from the Intermediate Sessions table of the Node Details page for a router. The Intermediate Sessions page is displayed. The Intermediate Sessions page contains a set of tables of APPN information about a node through which APPN sessions pass. There are three areas on the Intermediate Sessions page:
The General Table identifies the nodes and LUs of the intermediate session. The General table contains the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Intermediate Node Name | Name of the intermediate node; this is the node that was queried. |
Session PCID Originator Node Name | Node name for the originating node. |
PCID | Procedure correlation ID of the intermediate session, as assigned by the session PCID originator node. |
Primary LU Name | Name of the primary LU. |
Secondary LU Name | Name of the secondary LU. |
Mode Name | Name of the APPN mode. |
Class Of Service Name | Class of service name associated with the mode name. |
Transmission Priority | Transmission priority of the intermediate session. |
Session Up Time | Time this intermediate session has been active. |
The Details Table provides the detailed information about the intermediate session.
The Details table contains the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Adjacent CP Name | CP name for the adjacent network node for primary and secondary side of the session. |
Adjacent TG Number | TG number to the adjacent network node for primary and secondary side of the session. |
Max BTU Size | Maximum basic transmission unit that can be carried by Send and Receive values for primary and secondary side of the session. |
Pacing Type | Type of pacing used (fixed or adaptive) for Send and Receive values for primary and secondary side of the session. |
Residual Pacing Count | APPN residual pacing count for Send and Receive values for primary and secondary side of the session. |
Next Window Size | Window size, in bytes, of the next pacing window for the session for Send and Receive values for primary and secondary side of the session. |
The Session Route list displays the nodes and TGs in the path of the overall APPN session.
This topic describes how to display the DLSw page from a web browser and how to view the routers and rings that make up the DLSw network. It contains the following topics:
This topic describes how to use the DLSw page. To display the DLSw page (Figure 2-5), select DLSw from the CiscoWorks Blue home page.
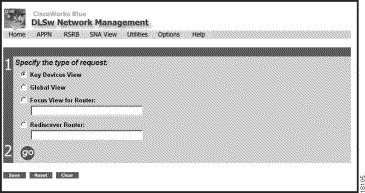
Click one of the buttons in the Request field and then click go.
The DLSw web pages contain several kinds of hypertext links to help you navigate through the network information.
The DLSw pages use the following hypertext links:
| When you click this... | DLSw displays |
|---|---|
Peer Statistics | Peer statistics for the selected router or peer connection. |
Router name or IP address | DLSw Focus view for that router. |
Details in a Router or Peer Connection State table | Routers or peer connections in that state. |
This topic tells you how to display a list of routers that are considered key devices in your network. When you select Key Devices View from the DLSw page, the Key Devices View page displays the key routers in the network.
The Key Devices View page contains the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Name | Host name of each router identified as a key device. Click a router name or IP address to display a focus view for that router. |
Inactive Connections | Number of peer connections with status Inactive. |
Degraded Connections | Number of peer connections with status Degraded. |
Unknown Connections | Number of peer connections with status Unknown. |
Active Connections | Number of peer connections with status Active. |
The DLSw Global View page displays a summary of all the DLSw routers and all DLSw connections in your network. When you select Global View from the DLSw page, the DLSw Global View page is displayed. The Global View page contains the following items:
The menu bar on the Global View page provides the following links:
The Router Summary table displays summary views of the DLSw routers.
The Router Summary area contains the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Router States | Lists the possible router states. |
Number of Routers | Shows the total number of routers in each state. |
Details | Click Details to display the list of routers in the selected state. See the "Router Pages" topic for more information. |
The Connection Summary table displays summary views of the DLSw peer connections.
The Connection Summary area contains the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
DLSw Peer States | Lists the possible DLSw peer-router states. |
Number of Connections | Shows the total number of peer connections in each state. |
Details | Click Details to display the list of connections in the selected state. See the "Connections Pages" topic for more information. |
Each DLSw Router page displays a list of all DLSw routers that have the same state. There is a DLSw Router page for each router state in the network: Inactive, Degraded, Unknown, and Active. Each router page contains a menu bar and a Router table. The Router table lists all routers in the same state. The possible router pages are as follows:
The menu bar on each Router page contains the following items:
There is a Router page for routers in each router state.
The fields in a router table apply to all router states. Click any router name or IP address to display DLSw peer information for that router. Each Routers table contains the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Local Router Name | Lists each local router by name or IP address. |
Peer Connection State | Shows the total number of routers in each router state. |
Peer Router | Shows the host name of the peer router. |
Peer Statistics | Provides a Peer Statistics link to the DLSw Peer Statistics page for the peer router. |
Each DLSw Connection page displays a list of all DLSw connections that have the same state. There is a DLSw Connection page for each connection state in the network: Inactive, Degraded, Unknown, and Active. Each Connection page contains a menu bar and a Connection table. The Connection table lists all connections in the same state. The possible Connection pages are as follows:
Each Connection page contains a menu bar and a connection table.
The menu bar on each Connection page contains the following items:
Each Connection page has a Connection table for its state. The possible tables are as follows:
The fields apply to all connection states. Click any router name or IP address to display the Focus View table for that router. Each Connections table contains the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Router #1 | For each peer connection, lists the name or IP address of router 1, and shows its state. |
Router #2 | Lists the name or IP address of router 2, and shows its state. |
Peer Statistics | Provides links to the DLSw Peer Statistics page for the peer routers. The arrow indicates the direction. The icon #1-->#2 shows statistics from router 1 to router 2. The icon #2-->#1 shows statistics from router 2 to router 1. |
The DLSw Focus View page displays detailed information about a specific DLSw router. Display the focus view for a router in one of the following ways:
The Focus View page for a router displays the information described in the following topics:
When you display the Focus View, the box in the upper-right corner displays the name of the router.
The menu bar on each Focus View page contains the following items:
The Connections table displays the focus router's peer connections in each connection state.
The Connections table contains the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Peer Connection State | State of the selected peer connection. |
Peer Router | Device name or IP address of the peer router for the selected peer connection. Click the address or name to display the focus view for that peer router. |
Peer Router State | State of the selected peer router. |
Click Peer Statistics to display the Peer Statistics page for the selected connection. | |
Attached Rings | List of rings attached to this peer router. |
The General table displays the focus router's peer connections in each connection state.
The General table contains the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Device Name | Host name of the focus router. |
Status | State of the focus router. |
IOS Version String | Cisco IOS release running on the focus router (SNMP collects this information on demand). |
The Details table displays DLSw protocol and connection information for the focus router, such as the maximum frame size. SNMP collects this information on demand.
The Details table contains the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
DLSw Version | Version of DLSw used by the router. |
Vendor ID | Vendor identification. |
Largest Frame Size | Largest frame supported by this router. |
Pacing Support | Level of pacing supported by this router. |
DLSw Up-Time | Length of time DLSw has been continuously active on this router. |
Active Peer Connections | Number of active peer connections to this router. |
Busy Connections Closed | Number of busy connection that have been closed on this router. |
Circuits Created | Number circuits that have been created with this router. |
Active Circuits | Number of currently active circuits. |
The IP Addresses table contains the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
IP Address | IP addresses configured at the focus router. |
Net Mask | Subnet mask for each IP address. |
Interface Type | Interface type configured for each IP address. |
The DLSw Peer Statistics page displays detailed information about one DLSw peer connection. To display the Peer Statistics page, click Peer Statistics in the Global View or Focus View page. The Peer Statistics page contains the information described in the following topics:
When you display the Peer Statistics page, the box in the upper-right corner identifies the peer connection.
The menu bar on each Peer Statistics page contains the following items:
The General table displays information about the selected peer connection.
The General table has the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
State | State of the transport connection. |
Local Address | Local transport address for this transport connection. |
Remote Address | Remote transport address of the transport connection. |
Transport | Transport domain of the transport connection. |
Flow Control Mode | Flow control mechanism in use on the transport connection; values are Undetermined, Pacing, and Other. |
Circuits Created | Number of times that circuits entered a circuit-established state (not counting transitions from circuit restart). |
Active Circuits | Number of currently active circuits on this transport connection. |
The Details table displays detailed information about the peer router.
The Details table has the following fields:
Data Packets In | Number of SSP messages of type DGRMFRAME, DATAFRAME, or INFOFRAME received on this transport connection. |
Data Packets Out | Number of SSP messages of type DGRMFRAME, DATAFRAME, or INFOFRAME transmitted on this connection. |
Data Octets In | Number of octets in SSP messages of type DGRMFRAME, DATAFRAME, or INFOFRAME received on this transport connection. |
Data Octets Out | Number of octets in SSP messages of type DGRMFRAME, DATAFRAME, or INFOFRAME transmitted on this connection. |
Control Packets In | Number of SSP messages received on this transport connection that were not of type DGRMFRAME, DATAFRAME, or INFOFRAME. |
Control Packets Out | Number of SSP messages transmitted on this transport connection that were not of type DGRMFRAME, DATAFRAME, or INFOFRAME. |
CanUReach Xxpl In | Number of CanUReach_ex messages received on the transport connection. |
CanUReach Expl Out | Number of CanUReach_ex messages sent on the transport connection. |
ICanReach expl In | Number of ICanReach_ex messages received on the transport connection. |
ICanReach Expl Out | Number of ICanReach_ex messages sent on the transport connection. |
NETBIOS NQ In | Number of NetBIOS_NQ_ex messages received in the transport connection. |
NETBIOS NR Out | Number of NETBIOS_NR_ex messages sent on this transport connection. |
NETBIOS NR In | Number of NetBIOS_NQ_ex messages received in the transport connection. |
NETBIOS NQ Out | Number of NetBIOS_NQ_ex messages sent on the transport connection. |
The DLSw Circuit Information page displays information about one DLSw circuit. From a focus view for a router, you can click Circuits on the menu bar to display information about all circuits on the focus router.
The Circuit Information page has the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
MAC address and SAP address of SNA resource 1. | |
PUNAME.DOMAIN of SNA resource 2. | |
MAC address and SAP address of SNA resource 2. | |
Status of the circuit. | |
Details | Click Details to display a detailed DLSw Circuit Information page for the selected circuit. |
The DLSw Circuit Details page displays information about one DLSw circuit. It contains the following tables:
The Circuit Information table displays summary information about a selected circuit.
The Circuit Information table contains the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Resource 1 | |
MAC 1 Address | MAC address of SNA resource 1. |
SAP 1 Address | SAP address of SNA resource 1. |
Resource 2 | PUNAME.DOMAIN of SNA resource 2. |
MAC 2 Address | MAC address of SNA resource 2. |
SAP 2 Address | SAP address of SNA resource 2. |
Status | Status of the circuit. |
The Circuit Details table displays detailed information about a selected circuit.
The Circuit details table contains the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Router Name | Host names of the local and remote routers. |
IP Address | IP addresses of the local and remote routers. |
Status | Status of the local and remote routers. |
Circuit Identifier | Circuit identifier assigned by this DLSw node to this circuit. The first four octets are the DLC port ID. The second four octets are the data-link correlator. |
DLC Type | DLC protocol in use between the DLSw node and the SNA resource. The possible values are QLLC, SDLC, LLC, NA, or Other. |
Interface Index | Entry index of the local interface through which the SNA resource can be reached. |
Route Information | For source-route bridging between the DLSw node and the SNA resource, the routing information field describing the path between the two devices. Otherwise, the value will be an octet string of zero length. |
Transport Domain | Transport domain of the transport connection. |
Max Messages Sendable | Number of paced SSP messages that this DLSw router is authorized to send on this circuit before it must stop and wait for an additional flow control indication from the partner DLSw router. |
Max Messages Receivable | Current number of paced SSP messages that this DLSw router has authorized the partner DLSw router to send on this circuit before the partner DLSw must stop and wait for an additional flow control indication from this DLSw router. |
Send Window Size | Current window size that this DLSw peer is using in its role as a data sender. This is the value by which the router can increase the number of messages it is authorized to send if it receives a flow control indication with the bits specifying "repeat window." |
Receive Window Size | Current window size that this DLSw router uses in its role as a data receiver. This is the number of additional paced SSP messages that this DLSw router can authorize its DLSw partner router to send if this DLSw router sends a flow control indication with the bits specifying "repeat window." |
Send Largest Window | Largest Send Largest Window value (with respect to this DLSw router) granted by the partner DLSw router during the current activation of this circuit. |
Receive Largest Window | Largest Receive Window Size value granted by this DLSw router during the current activation of this circuit. This is not the largest number of messages granted at any time, but the largest window size as represented by FCIND operator bits. |
Halve Window Sent | Number of Halve window operations this DLSw has sent on this circuit, in its role as a data receiver. |
Halve Window Received | Number of Halve window operations this DLSw router has received on this circuit, in its role as a data sender. |
Reset Window Sent | Number of Reset window operations this DLSw router has sent on this circuit in its role as a data receiver. |
Reset Window Received | Number of Reset window operations this DLSw router has received on this circuit in its role as a data sender. |
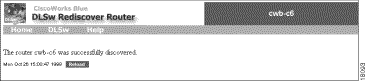
Step 1 Select Rediscover Router on the DLSw page.
Step 2 Enter the IP address or host name of the router as it appears in the database. (You can browse the DLSw Global View page to find the router and then select the Focus view for that router.)
Step 3 Click go.
When the router is discovered, the Rediscover Router page (Figure 2-6) is displayed.
This topic describes how to display the RSRB page from a web browser and how to view the routers, rings, and virtual rings that make up the RSRB network. It contains the following topics:
To display the RSRB page (Figure 2-7), select RSRB from the CiscoWorks Blue home page.
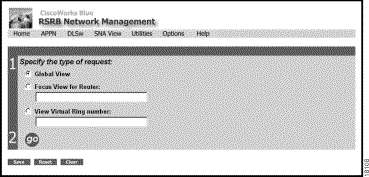
Click one of the buttons in the Request field and click go.
The RSRB web pages contain the following hypertext links to help you navigate through the network information:
| When you click this... | RSRB displays |
|---|---|
Details in Router state field | In Focus view, list of active routers in that state. In Virtual Ring view, list of active virtual rings in that state. |
Router name or IP address | RSRB Focus View page for that router. |
Virtual ring number | Virtual Ring view for that virtual ring. |
Select Global View on the RSRB page to display the RSRB Global View page, which contains the following areas:
The Summary area contains the Summary table, which displays the number of routers in each router state.
The Summary area contains the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Router States | Shows state for each router. |
Number of routers | Number of routers in each router state. |
Details | Click Details for a router state to see a list of routers in that state. |
The Unknown Routers area lists the name or address of each unknown router. If there are no unknown routers, the Unknown Routers area is not displayed. Click a router name or address to display the Focus View page for that router.
The Active Routers area lists the name or address of each active router. If there are no active routers, the Active Routers area is not displayed. Click a router name or address to display the Focus View page for that router.
The Virtual Rings area lists all virtual rings discovered in the network; for each virtual ring there is a list of routers on that virtual ring. If there are no virtual rings, the Virtual Rings area is not displayed. Click a virtual ring number to display the Virtual Ring page for that ring.
The Token Rings area lists all Token Rings discovered in the network; for each Token Ring there is a list of routers on that ring and a link to the Ring Information page. If there are no Token Rings, the Token Rings area is not displayed. Click a Token Ring number to display the Ring Properties page for that ring.
The Other Rings area lists all discovered rings that are neither virtual rings nor Token Rings; for each ring there is a list of routers on that ring. If there are no other rings, the Other Rings area is not displayed. Click a router name to display the Focus View page for that router.
Display the Focus View for an RSRB router in one of the following ways:
When you display the Focus View, the box in the upper-right corner displays the name of the focus router.
The menu bar on each Focus View page contains the following items:
The RSRB Focus View page displays information about a specific router.
The Focus View page contains the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Lists all the IP addresses, their subnet masks, and their interface types, configured on the router. | |
Virtual Rings | Lists all the virtual rings configured on the router; click the virtual ring number to display the Virtual Ring View page. |
Token Rings | Lists all the Token Rings configured on the router. |
Other Rings | Lists all the other rings configured on the router. |
The RSRB Virtual Ring View page, displayed when you select a virtual ring number on the Focus View or Global View page, describes the virtual rings in the RSRB network. Click the Ring Information link to display the Ring Statistics page for that ring.
When you display the Virtual Ring view, the box in the upper-right corner displays the number of the virtual ring.
The Virtual Ring View page contains the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Lists the total number of RSRB-enabled routers, of each connection state, that make up the selected virtual ring. Click the router name to display the Focus View page for that router. | |
Token Rings | Lists the Token Rings connected to the selected virtual ring. Click the Ring Information link to display the Ring Statistics page for that ring. |
Other Rings | Lists the other rings on the selected virtual ring. Click the Ring Information link to display the Ring Statistics page for that ring. |
The RSRB Peer Statistics page provides information and statistics for the selected peer. The Peer Statistics page contains the General table and the Details table.
The General table provides information for the selected peer.
The General table contains the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
State | Current status of the peer. |
Source Router | Name of the source router. |
Peer Router | Name of the peer router. |
Virtual Ring Number | Number of the virtual ring. |
The Details table provides information for the selected peer.
The Details table contains the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Encapsulation Type | RSRB encapsulation: Serial, LAN, Fast-Sequenced Transport (FST), or Frame Relay. |
Interface Index | Local interface index value of the RSRB remote peer. |
Packets Received | Number of packets received from remote peer. |
Packets Sent | Number of packets sent to remote peer. |
Bytes Received | Number of bytes received from the remote peer. |
Bytes Sent | Number of bytes sent to remote peer. |
Explorers Received | Number of explorer packets received from the remote peer. |
TCP Queue Length | Number of packets being held by the local router in the TCP output queue for the remote peer. |
Packets Dropped | Number of received packets discarded by the local router (packets are dropped because of problems with the configuration, queue overflow, and protocol errors). |
Local Acknowledgment | Indicates whether local acknowledgment is used for the sessions going to the remote peer. |
RSRB Version | Version of RSRB used between local and remote peers. |
The RSRB Ring Properties page provides information and statistics for the selected ring.
The Ring Properties page contains the following fields:
| Field | Description |
Source Router | Peer router for which you queried ring information. |
Ring Number | Number of the ring. |
Bridge Number | Configured number of the bridge that connects this entry's ring to the virtual ring. |
Ring Type | Ring type, which can be static, dynamic, SDLC, QLLC, or virtual. |
MAC Address | MAC address of either the local router's interface to the ring for local ring entries or the remote peer's interface to the ring for remote ring entries. |
Local Ring | Indicates whether the entry represents a local or remote ring: YES indicates a local ring; NO indicates a remote ring. |
Interface Index | Local interface into the ring for local ring entries. |
Packets Sent | Number of packets forwarded by the local router onto this ring. |
This topic describes how to use the Maps web-based utilities on the Utilities page. Select Utilities from the CiscoWorks Blue home page. The Utilities page (Figure 2-8) is displayed.
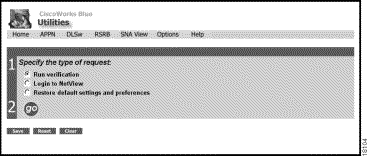
On this page, choose one of the following:
Select Run verification from the Utilities page to verify that you have installed CiscoWorks Blue correctly. The verification utility checks your configured protocols and tests the tables in the database. Review the displayed data, in the Verification Results Page, to verify that each table contains the correct number of entries.
You can access the NetView web page from a web browser. Use the following procedure.
Step 1 Select Utilities from the Maps home page.
Step 2 Select Options from the menu bar. The Options page is displayed (Figure 2-9).
Step 3 Complete the fields on the Options page, as described in "Using the Options Page."
Step 4 Select Login to NetView from the CiscoWorks Blue home page.
If you have not yet used the Options page to configure NetView for Maps, the web browser displays following message:
Please configure the NetView Web Interface using the Options dialog.
If you receive this message, configure the NetView options as described in "Using the Options Page."
This topic describes how to restore the settings and preferences in your browser after you make changes on a Maps or SNA View web page. Select Restore settings and preferences from the Utilities page. The web browser restores your settings to their default values.
The Verification page does the following tasks:
The first section provides a time and date stamp.
=======================================================================
CiscoWorks Blue Verification
Mon Mar 15 09:10:14 1999
cwb-aix11.cisco.com
Configuration File:/opt/CSCOcb/etc/cwbinit
=======================================================================
The next section describes the applied licenses.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
License Information
------------------------------------------------------------------------
CiscoWorks Blue SNA View: Licensed
CiscoWorks Blue Maps: Licensed
The next section tells you which processes you configured at installation, and whether they are ready for use.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Process Summary
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Name Configured Ready
------ ------------ -------
APPN Yes Yes
Base Yes Yes
DLSw Yes Yes
RSRB Yes Yes
SNA Yes Yes
TN3270 Yes Yes
The next section summarizes the devices in your database by protocol.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Database Summary
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Total number of devices: 13
APPN: 3
DLSw: 8
RSRB: 3
TN3270: 2
DLSw Key Devices: 6
Physical Units: 7
Logical Units: 7
The last section reports any changes you should make to your installation.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Action Summary
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Warnings:
1. No APPN Network Topology Agent was specified in the cwbinit file.
Please specify a Network Topology Agent by editing the cwbinit file
(/opt/CSCOcb/etc/cwbinit) and setting the following parameters:
nettopoagentdevname = [Agent IP address or name]
nettopordcommstr = [Agent read community string]
-OR-
nettopoagentcpname = [Agent control point name]
Use the Options page to setup SNA preferences and to configure links to the NetView and CiscoWorks 2000 web pages.
Step 1 Select Options from the menu bar. The Options page (Figure 2-9) is displayed.
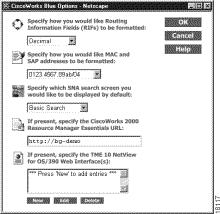
Step 2 In the field "Specify how you would like RIFs to be formatted," select one of the following choices:
0x0a30410200a241000000.
1040.2.10.2.1040.0.0.0
Step 3 In the field "Specify how you would like MAC and SAP addresses to be formatted," select one of the following choices:
Step 4 In the field "Specify which SNA Resource Information tab you would like displayed by default," select one of the following choices:
Step 5 Use the field "If present, specify the CiscoWorks 2000 Resource Manager Essentials URL" to contain a link to the CiscoWorks 2000 web interface. Enter the CiscoWorks 2000 URL in this field.
Step 6 Use the field "If present, specify the TME 10 NetView for OS/390 Web Interface(s)" to add, delete, or change a link to the NetView web interface.
Step 7 Click OK to accept the options and close the Options dialog.
To change a NetView interface, use the following procedure after clicking Edit on the Options page:
Step 1 In the "Please specify the NetView Identifier" dialog, enter or change the name you want to associate with the NetView web interface.
Step 2 Click OK.
Step 3 In the "Please specify the URL" window, enter or change the URL for the NetView web interface.
Step 4 Click OK to return to the Options page.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Wed Jun 30 06:23:40 PDT 1999
Copyright 1989-1999©Cisco Systems Inc.