|
|

The Cisco Broadband Access Center software enables you to provision services on broadband aggregators.
Provisioning occurs after you create administrative networks and network devices. See "Managing Devices" For information about creating administrative networks and network devices.
Table 7-1 Provisioning Broadband Aggregators Topics
| If you want to... | Go to the... |
|---|---|
Add service profiles and service features to a broadband aggregator |
|
Manage service profiles and service features, including selecting a method of downloading configuration information |
"Downloading Service Profiles and Service Features" section. |
From the Network tab, you can provision the Cisco IOS devices that act as broadband aggregators on your network. Before you begin to provision broadband aggregators, you should understand:
You can configure Cisco broadband aggregators with the roles defined in Table 7-2.
Table 7-2 Roles of Network Devices
The encapsulation method for a broadband aggregator depends upon its role in the network:
 |
Note With a PTA using a PPP encapsulation type, authentication occurs at the service provider using a local database or a AAA server. RBE users are not authenticated and, instead, are routed directly to the Internet. |
Figure 7-1 illustrates encapsulation for a LAC/LNS network.
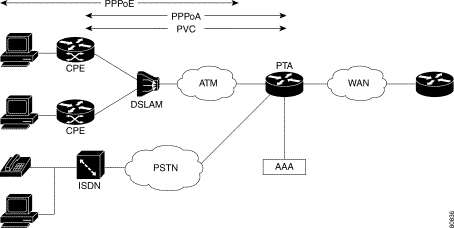
Figure 7-2 illustrates encapsulation for a PTA network.
Once you determine the role that a device plays on your network and what encapsulation method it supports, you identify the service profiles and service features with which to provision it. Table 7-3 defines what a service profile is and what a service feature is.
Table 7-3 Service Profile and Service Feature Definitions
BAC supports two types of templates:
 |
Note In the Web UI, BAC displays default values for many attributes that it derives from the configuration templates. |
Routers perform single or multiple roles in a broadband aggregation network, depending on the services with which you configure them. Organizing and managing services involves the following procedures.
2. Adding the Basic service feature to the service profile.
3. Optionally, adding additional service features to the service profile.
4. Repeating 1 through 3 for each role that a router performs.
A service profile describes the role and the encapsulation type of a broadband aggregator. A service feature is comparable to a Cisco IOS configlet, which consists only of the commands necessary to modify the router's current configuration to enable a particular service.
Selecting a service profile determines the service features that you can configure on a router. Table 7-4 summarizes the service features available with each service profile:
Table 7-4 Service Profiles and Associated Service Features
The service features that you download to a router become part of its running configuration. Table 7-5 provides an overview of all the service features.
 |
Note You can customize any BAC service feature using Template Manager. For more information, see "Customizing Broadband Access Center." |
Table 7-5 Service Features Overview
To add a service profile, follow these steps:
Step 2 Click the Network tab. The system displays the Administrative Network Management page in the main window.
Step 3 In the Object Selector, select the network where the device is located.
Step 4 In the subtask bar, click Device Management. The system displays the Device Management page in the main window.
Step 5 On the Device Management page, select the device to which you want to add a service profile.
Step 6 Click Add Service. The system displays the Service Profile Selection page.
Step 7 Select the service that you want to add; for example, select PTAPPPoEoA.
Step 8 Click Next. The system displays the Service Feature Selection page.
Step 9 Begin to add service features. At a minimum, you must add Basic service. For more information, see "Setting Up Basic Service" section.
The next sections of this chapter provided detailed procedures for adding each of the service features.
Set up Basic service to define the basic configuration of a router.
When you add Basic service, you define the fields listed in Table 7-6.
Table 7-6 Basic Service Fields
To create Basic service, complete the procedure described in "To Add a Service Profile" section and then follow these steps:
Step 2 In the Service Feature Data page, enter the Basic service information, as defined in Table 7-6.
Step 3 Optionally, click Download Method to select a method of download the running configuration. The system displays the Subscriber Provisioning - Device Configuration Download dialog box. For more information, see "Downloading Service Profiles and Service Features" section.
Step 4 If desired, click one of the following action buttons:
Step 5 Click Next to download the configuration. The system displays the Configuration Download Status box.
Step 6 Click Finish.
Set up RADIUS service to identify the AAA server that you want to use for authentication and authorization.
When you add RADIUS service, you define the fields listed in Table 7-7.
Table 7-7 RADIUS Service Fields
To create RADIUS service, follow these steps:
Step 2 If necessary, in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box, select RADIUS. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data page in the content area of the main window.
 |
Note You need to select RADIUS from the drop-down list, if you selected RADIUS along with one or more other service features on the Service Feature Selection page. |
Step 3 Click Add. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box.
Step 4 In the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, enter the RADIUS service information, as defined in Table 7-7.
Step 5 When you are done, click OK. The system redisplays the Service Feature Data page.
Step 6 Click Download Method to select a method of download the running configuration. The system displays the Subscriber Provisioning - Device Configuration Download dialog box. For more information see "Downloading Service Profiles and Service Features" section.
Step 7 Click Next to begin downloading the configuration. The system displays the Configuration Download Status box.
Step 8 Click Finish.
Set up RADIUS group service to enable round-robin use of multiple, local AAA servers.
When you add RADIUS Group service, you define the fields listed in Table 7-8.
Table 7-8 RADIUS Group Service Fields
 |
Note You must set up RADIUS service before you set up RADIUS Group service. |
To create RADIUS Group service, follow these steps:
Step 2 If necessary, in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box, select Radius Group. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data in the content area of the main window.
 |
Note If you selected RADIUS Group along with one or more other service features on the Service Feature Selection page, you need to select Radius Group in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box. |
Step 3 Click Add. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, which is superimposed over the main window.
Step 4 In the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, enter the RADIUS Group service information, as defined in Table 7-7.
Step 5 When you are done, click OK. The system redisplays the Service Feature Data page.
Step 6 Click Next to begin downloading the configuration. The system displays the Configuration Download Status box.
Step 7 Click Finish.
Set up IP Pool service to define the pool of local IP addresses available to the router.
When you add IP Pool service, you define the fields listed in Table 7-9.
To create IP Pool service, follow these steps:
Step 2 If necessary, in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box, select IP Pool. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data in the content area of the main window.
 |
Note If you selected IP Pool along with one or more other service features on the Service Feature Selection page, you need to select IP Pool in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box. |
Step 3 In the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, enter the IP Pool information, as defined in Table 7-9.
Step 4 Click Add. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, which is superimposed over the main window.
Step 5 Click Next to begin downloading the configuration. The system displays the Configuration Download Status box.
Step 6 Click Finish.
Set up DHCP service to define the IP address of the DHCP server you use for IP address assignment.
When you add DHCP service, you define the field listed in Table 7-10.
Table 7-10 DHCP Service FIelds
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
The IP address of the DHCP server that you want to use for dynamic address assignment. |
To create DHCP service, follow these steps:
Step 2 If necessary, in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box, select DHCP. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data in the content area of the main window.
 |
Note If you selected DHCP along with one or more other service features on the Service Feature Selection page, you need to select DHCP in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box. |
Step 3 Click Add. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, which is superimposed over the main window.
Step 4 In the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, enter the DHCP service information, as defined in Table 7-7.
Step 5 When you are done, click OK.
Step 6 Click Next to begin downloading the configuration. The system displays the Configuration Download Status box.
Step 7 Click Finish.
Set up Virtual Template service to provide generic configuration on an as-needed basis to a virtual interface on a router. Virtual Template service is available only in LACPPPoA and PTAPPPoA environments.
When you add Virtual Template service, you define the fields listed in Table 7-11.
Table 7-11 Virtual Template FIelds
To create Virtual Template service, follow these steps:
Step 2 If necessary, in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box, select Virtual Template. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data in the content area of the main window.
 |
Note If you selected Virtual Template, along with one or more other service features on the Service Feature Selection page, you need to select Virtual Template in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box. |
Step 3 Click Add. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, which is superimposed over the main window.
Step 4 In the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, enter the Virtual Template service information, as defined in Table 7-11.
Step 5 When you are done, click OK. The system redisplays the Service Feature Data window.
Step 6 Click Next to begin downloading the configuration. The system displays the Configuration Download Status box.
Set up PVC Range service to provision a range of PVCs on an ATM subinterface. You can group a number of PVCs on a multipoint ATM subinterface and simplify their configurations.
 |
Note In LACPPPoA and PTAPPPoA environments, this service is called PVCRangeoA. |
When you add PVC Range service for LAC and PTA service profiles, you define the fields listed in Table 7-12.
Table 7-12 LAC and PTA PVC Range Service Fields
 |
Note For more detailed information about configuring PVC ranges, see the Cisco IOS documentation which describes ATM PVC range and Routed Bridge Encapsulation subinterface grouping. |
When you add PVC Range service for an RBE service profile, you define the properties in listed in Table 7-13.
Table 7-13 RBE PVC Range Service Fields
To create PVC Range service, follow these steps:
Step 2 If necessary, in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box, select PVC Range. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data in the content area of the main window.
 |
Note If you selected PVC Range along with one or more other service features on the Service Feature Selection page, you need to select PVC Range in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box. |
Step 3 Click Add. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, which is superimposed over the main window.
Step 4 In the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, enter the PVC service data. If you are adding PVC range service to a LAC or PTA profile, see Table 7-12. If you are adding PVC range service to an RBE profile, see Table 7-13.
Step 5 When you are done, click OK. The system redisplays the Service Feature Data window.
Step 6 Click Next to begin downloading the configuration. The system displays the Configuration Download Status box.
Set up Single PVC service to provision single PVCs on ATM and RBE subinterface.
 |
Note In LACPPPoA and PTAPPPoA environments, this service is called SinglePVCoA. |
When you add Single PVC service for LAC and PTA service profiles, you define the fields listed in Table 7-14.
Table 7-14 LAC and PTA Single PVC Service Fields
When you add PVC Range service for an RBE service profile, you define the fields in listed in Table 7-15.
Table 7-15 RBE Single PVC Service Fields
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
The quality of service (QoS) type for this PVC range. The possible values are: |
|
The subscriber facing module on the broadband aggregator that this PVC range uses. |
|
To create Single PVC service, follow these steps:
Step 2 If necessary, in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box, select Single PVC. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data in the content area of the main window.
 |
Note If you selected Single PVC along with one or more other service features on the Service Feature Selection page, you need to select Single PVC in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box. |
Step 3 Click Add. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, which is superimposed over the main window.
Step 4 In the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, enter the PVC service information. To create Single PVC service for a LAC or PTA profile, see Table 7-14. To create PVC service for an RBE profile, see Table 7-15.
Step 5 When you are done, click OK. The system redisplays the Service Feature Data window.
Step 6 Click Next to begin downloading the configuration. The system displays the Configuration Download Status box.
Step 7 Click Finish. The system redisplays the Device Management page.
Set up L2TP service to specifies the LAC and LNS that use a specified the Layer 2 tunnel. The properties differ depending on which profile you select.
When you select one of the LAC profiles, you define the L2TP fields listed in Table 7-16.
Table 7-16 L2TP Service Fields for a LAC Profile
To create L2TP service to a LAC, make sure that you have selected one of the LAC service profiles. Then, follow these steps:
Step 2 If necessary, in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box, select L2TP. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data in the content area of the main window.
 |
Note If you selected L2TP along with one or more other service features on the Service Feature Selection page, you need to select L2TP in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box. |
Step 3 Click Add. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, which is superimposed over the main window
Step 4 In the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, enter the L2TP service information, as defined in Table 7-16.
Step 5 When you are done, click OK. The system redisplays the Service Feature Data window.
Step 6 Click Next to begin downloading the configuration. The system displays the Configuration Download Status box.
Step 7 Click Finish.
When you select the LNS service profile, you define the L2TP fields listed in Table 7-17.
Table 7-17 L2TP Service Fields for the LNS Profile
To create L2TP service to an LNS, make sure that you have selected one of the LNS service profiles. Then, follow these steps:
Step 2 If necessary, in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box, select L2TP. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data in the content area of the main window.
 |
Note If you selected L2TP along with one or more other service features on the Service Feature Selection page, you need to select L2TP in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box. |
Step 3 Click Add. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, which is superimposed over the main window.
Step 4 In the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, enter the L2TP service information, as described in Table 7-17.
Step 5 When you are done, click OK. The system redisplays the Service Feature Data window.
Step 6 Click Next to begin downloading the configuration. The system displays the Configuration Download Status box.
Step 7 Click Finish.
Set up Enable PPPoE service so that you can enable or disable PPPoE on an ethernet interface.
When you add EnablePPPoE service, you define the field listed in Table 7-18.
Table 7-18 Enable PPPoE Service Field
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
The subscriber-facing interface on the broadband aggregator that you want to enable. |
To create Enable PPPoE service, follow these steps:
Step 2 If necessary, in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box, select EnablePPPoE. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data in the content area of the main window.
 |
Note If you selected EnablePPPoE along with one or more other service features on the Service Feature Selection page, you need to select EnablePPPoE in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box. |
Step 3 Click Add. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, which is superimposed over the main window.
Step 4 In the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, do the following:
a. In the Subscriber-facing Interface Selector field, enter the value for the subscriber-facing module that this PVC uses; or, to browse for the interface, click Select. The system displays the Popup Selection window.
b. Select the interface, expanding the interface hierarchy as needed, and click Select. The system redisplays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box.
Step 5 When you are done, click OK. The system redisplays the Service Feature Data page.
Step 6 Click Next to begin downloading the configuration. The system displays the Configuration Download Status box.
Step 7 Click Finish. The system redisplays the Device Management page.
Set up VPDN service to enables virtual private dialup networking on a router.
When you create VPDN service, you define the fields listed in Table 7-19.
Table 7-19 VPDN Service Fields
To create VPDN service, follow these steps:
Step 2 If necessary, in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box, select VPDN. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data in the content area of the main window.
 |
Note If you selected VPDN along with one or more other service features on the Service Feature Selection page, you need to select VPDN in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box. |
Step 3 Click Add. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, which is superimposed over the main window.
Step 4 In the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, enter the VPDN service information, as defined in Table 7-19.
Step 5 When you are done, click OK. The system redisplays the Service Feature Data window.
Step 6 Click Next to begin downloading the configuration. The system displays the Configuration Download Status box.
Step 7 Click Finish.
Set up VLAN range service to provision multiple Ethernet virtual LAN subinterfaces.
 |
Note If you try download VLAN Range service to a device using HTTP, the Cisco IOS software generates an error message. Download VLAN Range service using Telnet, instead. |
When you add VLAN Range service, you define the fields listed in Table 7-20.
Table 7-20 VLAN Range Service Fields
 |
Note If you attempt to download a VLAN range using either Telnet, Cisco IOS reports an error. The other download methods operate properly. |
To create VLAN Range service, follow these steps:
Step 2 If necessary, in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box, select VLAN. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data in the content area of the main window.
 |
Note If you selected VLAN Range along with one or more other service features on the Service Feature Selection page, you need to select VLAN Range in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box. |
Step 3 Click Add. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, which is superimposed over the main window.
Step 4 In the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, enter the VLAN Range service information, as defined in Table 7-20.
Step 5 When you are done, click OK. The system redisplays the Service Feature Data window.
Step 6 Click Next to begin downloading the configuration. The system displays the Configuration Download Status box.
Set up Single VLAN service to enable provisioning a single Ethernet virtual LAN subinterface.
When you add Single VLAN service, you define the fields listed in Table 7-21.
Table 7-21 Single VLAN Service Fields
To create Single VLAN service, follow these steps:
Step 2 If necessary, in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box, select Single VLAN. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data in the content area of the main window.
 |
Note If you selected Single VLAN along with one or more other service features on the Service Feature Selection page, you need to select Single VLAN in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box. |
Step 3 Click Add. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, which is superimposed over the main window.
Step 4 In the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, enter the Single VLAN service information, as defined in Table 7-21.
Step 5 When you are done, click OK. The system redisplays the Service Feature Data window.
Step 6 Click Next to begin downloading the configuration. The system displays the Configuration Download Status box.
Step 7 Click Finish.
Set up Network Address Translation (NAT) service to enable NAT if you have implemented private IP address space.
When you add NAT service, you define the fields listed in Table 7-22.
Table 7-22 Network Address Translation Service Field
To create NAT service, follow these steps:
Step 2 In the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box, select NAT. The system displays the Service Feature Data Page.
 |
Note If you selected NAT along with one or more other service features on the Service Feature Selection page, you need to select NAT in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box. |
Step 3 Click Add. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, which is superimposed over the main window.
Step 4 In the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, enter the NAT service information, as defined in Table 7-22.
Step 5 When you are done, click OK. The system redisplays the Service Feature Data page.
Step 6 Click Next to begin downloading the configuration. The system displays the Configuration Download Status box.
Step 7 Click Finish.
BAC enables you to apply QoS policy maps to a router through Policy service. Policy maps define QoS actions and rules. You create them as network resources using the Network Services tab. For more information, see "Managing Network Services."
When you add Policy service, you define the fields listed in Table 7-23.
Table 7-23 Policy Service Fields
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
The name of the policy map that you want to apply to a router. |
|
To create Policy service, follow these steps:
Step 2 On the Service Feature Selection page, check Policy and click Next. The system displays the Service Feature Data page.
Step 3 If necessary, in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box, select Policy. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data page.
Step 4 Click Add. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature dialog box.
Step 5 In the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, enter the Policy service information, as defined in Table 7-23.
Step 6 When you are done, click OK. The system redisplays the Service Feature Data page.
Step 7 Click Next to begin downloading the configuration. The system displays the Configuration Download Status box.
You set up Route Map service to enable policy routing and redistribution of routing information.
When you add Route Map service, you define the fields listed in Table 7-23.
Table 7-24 Route Map Service Fields
To create Route Map service, follow these steps:
Step 2 On the Service Feature Selection page, check Route Map and click Next. The system displays the Service Feature Data page.
Step 3 If necessary, in the Select a Service Feature drop-down list box, select Route Map. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data page.
Step 4 Click Add. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Service Feature dialog box.
Step 5 In the Device Provisioning-Service Feature Data dialog box, enter the Route Map service information, as defined in Table 7-24.
Step 6 When you are done, click OK. The system redisplays the Service Feature Data page.
Step 7 Click Next to begin downloading the configuration. The system displays the Configuration Download Status box.
Step 8 Click Finish.
BAC enables you to select from among several methods of downloading configuration files to your network devices.
Select a download method from the options listed in Table 7-25.
Table 7-25 Configuration Download Methods
To choose a download method, follow these steps:
Step 2 Click Download Method. The system displays the Device Provisioning-Device Configuration Download dialog box.
Step 3 Select one of the methods for downloading.
Step 4 In the SSH Type drop-down list box, enable or disable security encryption by selecting one of the following:
Step 5 In the Destination drop-down list box, select one of the following:
Step 6 Click OK.
BAC enables you to download text files containing Cisco IOS configuration commands to generic devices. You cannot provision generic devices with services and BAC templates are unavailable for them. You might use a text file to download commands to a device in the following scenarios:
When you download configuration commands to a generic device, you set the fields listed in Table 7-26.
Table 7-26 Generic Device Configuration Fields
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Sets the method you use to download. For more information, see the "About Download Methods" section. |
|
Sets the console port number to use when downloading, if you select the console port method. This field is not displayed with the other download options. |
|
Determines whether this file is downloaded to the running configuration file only of the router, or downloaded to running configuration and then copied to the startup configuration file. |
To download configuration commands to a generic device, follow these steps:
Step 2 Log in to BAC and click the Network tab. The system displays the Administrative Network Management page in the content area of the main window.
Step 3 In the Object Selector, select the network where the device is located.
Step 4 In the subtask bar, click Device Management. The system displays the Device Management page in the main window.
Step 5 On the Device Management page, select the generic device to which you want to download configuration commands.
Step 6 Click Download Configuration. The system displays the Device Configuration Selection page in the main window. In the Device Field, it displays the path to the device.
Step 7 Click Browse to select the configuration file that you want to download.
Step 8 Click Next. The system displays the Device Configuration Download page in the main window.
Step 9 In the Device Configuration Download page, enter the download information as defined in Table 7-26.
Step 10 Click Next. The system displays the Device Configuration Status page in the main window.
Step 11 Click Finish.
To delete a service profile or a service feature from a router, follow these steps:
Step 2 In the Object Selector, select the network where the device is located.
Step 3 In the subtask bar, click Device Management. The system displays the Device Management page in the main window.
Step 4 On the Device Management page, select the device from which you want to delete a service feature.
Step 5 Click Delete Service. The system displays the Existing Role Selection page.
Step 6 Under Device Un-Provisioning - Existing Roles, click the icon for the role.
Step 7 Click Next. The system displays the Service Feature Selection page.
Step 8 Check the feature or features that you want to delete.
 |
Note To remove a service profile from a router, you must delete all service features you have assigned to the profile. Deleting the service features, removes the service profile from the router. |
Step 9 Click Next. The system displays the Service Feature Data page.
Step 10 From the Select A Service Feature drop-down list box, select the feature that you want to delete.
Step 11 Click Next.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Wed May 21 08:47:45 PDT 2003
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.