|
|

The Catalyst 3900 and the Catalyst 5000 Token Ring switching module are shipped with a default configuration that allows you to use the switch without modification in many small networks. One aspect of this default configuration is that the switch is configured as a single VLAN. However, for more complex networks, you can subdivide the Catalyst 3900 or Catalyst 5000 Token Ring switching module into multiple virtual rings (TrCRFs) that can be connected by one or more internal bridges (TrBRFs). Initially, all ports are assigned to the default ring (trcrf-default) and the default ring is associated with the default bridge (trbrf-default).
To assist you in understanding how to subdivide your switch, this section provides an example of configuring two additional VLANs for a Catalyst 3900.
In this scenario, yours is a small company that is growing. Last year, there were only 10 employees in the human resources and payroll departments. Now there are 34 employees. When there were only 10 employees, they could share a single server that contains a database of records. Now, however, each department needs a dedicated server.
Figure 7-1 illustrates the initial VLAN configuration of the Catalyst 3900. You want to add a new ring that includes ports 1 and 2 for the employees of the human resources department and another ring that includes ports 3 and 4 for the employees of the payroll department.
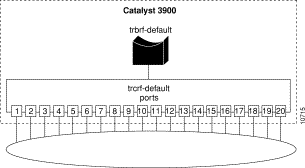
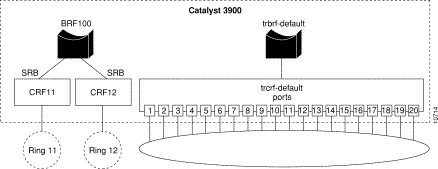
Only the default ring (or TrCRF) can be assigned to the default bridge (or TrBRF). You cannot assign new rings to the default bridge. Therefore, you must first define a new bridge, then you can define the rings and assign ports to them.
You have met with the IS department and have decided to create two new rings, with ring numbers 1 and 4, and connect them with a bridge, which will have the bridge number of 1. Because the network contains a large number of Cisco devices, you are using VTP to distribute information about the VLANs in the network. You have decided to assign the VLAN IDs as follows:
| Ring number | VLAN ID | VLAN Name |
|---|---|---|
11 | 11 | CRF11 |
12 | 12 | CRF14 |
The bridge will be assigned a VLAN ID of 100 and a VLAN name of BRF100.
Microsegmenting the ring involves creating multiple rings, which means you are creating multiple VLANs. You are going to put the users and their servers in separate TrCRFs and join them using a TrBRF.
You have physically separated the servers from the users. Next, you must attach the rings and the servers to separate ports on the Catalyst 3900 switches.
On both switches, do the following:
The ports will automatically sense the speed and mode of the connection.
Next, you must define the VLANs. You will need a new TrBRF and two TrCRFs; one for the Human Resources users and their server and one for the Payroll users and their server.
To define a bridge (TrBRF), complete the following steps:
Step 1 On the Catalyst 3900 Main Menu, select Configuration. The Configuration panel is displayed.
Step 2 On the Configuration panel, select VLAN and VTP Configuration. The VLAN and VTP Configuration panel is displayed.
Step 3 On the VLAN and VTP Configuration panel, select VTP VLAN Configuration. The VTP VLAN Configuration panel is displayed.
Step 4 On the VTP VLAN Configuration panel, select Add.
Step 5 At the prompt, enter a VLAN ID of 100 .
Step 6 At the prompt, select TrBRF. The VLAN Parameter Configuration for TrBRF panel is displayed.
Step 7 On the VLAN Parameter Configuration for TrBRF panel, specify:
See Figure 7-2.
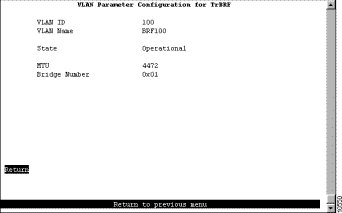
Step 8 Select Return to save your changes.
Figure 7-3 illustrates the VLAN configuration of the Catalyst 3900 after the additional bridge has been configured. Notice that no rings are assigned to it yet.
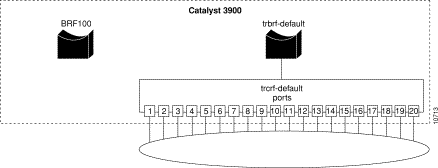
To define the ring (TrCRF) for the Human Resources users, complete the following steps:
Step 1 On the VTP VLAN Configuration panel, select Add.
Step 2 At the prompt, enter a VLAN ID of 11.
Step 3 At the prompt, select TrCRF. The VLAN Parameter Configuration for TrCRF panel is displayed.
Step 4 On the VLAN Parameter Configuration for TrCRF panel, specify:
See Figure 7-4.
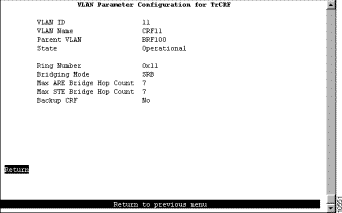
Step 5 Select Return to save your changes.
To define the ring (TrCRF) for the Payroll users, repeat Step 1 through Step 4 and use the following values:
Figure 7-5 illustrates the VLAN configuration of the Catalyst 3900 after the additional rings have been configured. Notice that the rings are configured and associated with the bridge, but no ports are assigned to the rings.
Next, you must assign the ports to the appropriate rings (TrCRFs). On the Catalyst 3900, do the following:
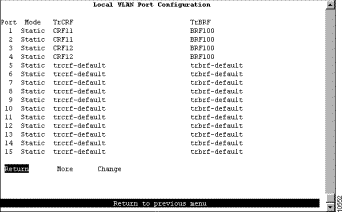
Step 1 On the VLAN and VTP Configuration panel, select Local VLAN Port Configuration. The Local VLAN Port Configuration panel is displayed.
Step 2 On the Local VLAN Port Configuration panel, select Change.
Step 3 At the prompt enter port number 1.
Step 4 Select CRF11 from the list of possible TrCRFs. To select the TrCRF, use your cursor movement keys to highlight the desired TrCRF, press the space bar to select it, and press Enter to implement the change. See Figure 7-6.
Step 5 Repeat Step 2 through Step 4 for port 2.
Step 6 Again, on the Local VLAN Port Configuration panel, select Change.
Step 7 At the prompt enter port number 3.
Step 8 Select CRF12 from the list of possible TrCRFs.
Step 9 Repeat Step 6 through Step 8 for port 4.
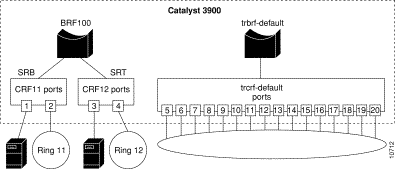
Step 10 Select Return to save the changes.
You now have a network with improved performance because the number of users per ring has been reduced and the servers have dedicated bandwidth. See Figure 7-7.
This section contains tips that may be useful in creating a configuration similar to the one in this scenario.
If you install an external bridge to create a backup path between rings 1 and 4, you introduce possible loops into your network. You can use the Spanning-Tree Protocols to prevent these loops. By default, no Spanning-Tree Protocol is run at the bridge (TrBRF) or the ring (TrCRF) level, therefore, you must configure the Spanning-Tree Protocol.
To configure the Spanning-Tree Protocol for the bridge (TrBRF), complete the following steps:
Step 1 On the Catalyst 3900 Main Menu, select Configuration.
Step 2 On the Configuration panel, select Spanning Tree and select BRF100. The Spanning Tree for TrBRF panel is displayed.
Step 3 On the Spanning Tree for TrBRF panel, set the STP Participation to Base on Bridging Mode. If the bridging mode is SRB, the IBM Spanning-Tree Protocol is used. If the bridging mode is SRT, the IEEE Spanning-Tree Protocol is used.
To configure the Spanning-Tree Protocol for the ring (TrCRF), complete the following steps:
Step 1 While still on the Spanning Tree for TrBRF panel, select TrCRF & Port Spanning Tree Parameters and select CRF11. This is the SRB ring.
Step 2 On the Spanning Tree for TrCRF panel, set the STP Participation to IEEE.
Step 3 Select Return.
Step 4 Repeat Steps 1 through Step 3 for CRF12.
Step 5 Select Return again.
To aid in network management and network identification, we recommend that:
To further improve performance, if you have 16 Mbps connections and the server's NIC supports FDX, you can configure the ports connected to the servers to operate in FDX mode. To configure FDX:
Step 1 Select Port Configuration on the Configuration panel.
Step 2 Specify the port to which the server is attached. In this scenario, that would be either port 2 or 4.
Step 3 On the Port Configuration panel, move to the Operation Mode and select a mode of FDX port.
Step 4 Select Return.
You can create a similar configuration using two Catalyst 5000 Series Token Ring switching modules. The Catalyst 5000 provides a command line interface rather than a menu-driven interface, so the steps are slightly different. This section provides an overview of the configuration steps to achieve a similar configuration using two Catalyst 5000 Token Ring modules.
To define the bridge (TrBRF), complete the following steps:
Step 1 At the Catalyst 5000 command prompt, enter enable.
Step 2 At the enable prompt, enter set vlan 100 name brf100 type trbrf bridge 1.
Step 3 To verify the configuration of the new VLAN, enter show vlan.
The output, as shown in Figure 7-8, indicates that brf100 has been added but that it does not have any TrCRFs assigned to it yet.
VLAN Name Status Mod/Ports, Vlans
---- -------------------------------- --------- ----------------------------
1 default active 1/1-2
2/1-48
100 brf100 active
1002 fddi-default active
1003 trcrf-default active 3/1-16
1004 fddinet-default active
1005 trbrf-default active 1003
To define the ring (TrCRF) for the Human Resource users, complete the following steps:
Step 1 At the enable prompt, enter set vlan 11 name crf11 type trcrf ring 11 parent 100 mode srb.
Step 2 To verify the configuration of the new VLAN, enter show vlan.
The output, as shown in Figure 7-9, indicates that crf11 has been added but that it does not have any ports assigned to it yet. It also shows that brf100 is the parent of the VLAN with the ID of 11.
VLAN Name Status Mod/Ports, Vlans
---- -------------------------------- --------- ----------------------------
1 default active 1/1-2
2/1-48
11 crf11 active
100 brf100 active 11
1002 fddi-default active
1003 trcrf-default active 3/1-16
1004 fddinet-default active
1005 trbrf-default active 1003
VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BrdgNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2
---- ----- ---------- ----- ------ ------ ------ ---- -------- ------ ------
1 enet 100001 1500 - - - - - 0 0
11 trcrf 100110 4472 100 0x11 - - srb 0 0
100 trbrf 100100 4472 - - 0x1 ibm - 0 0
1002 fddi 101002 1500 - 0x0 - - - 0 0
1003 trcrf 101003 4472 1005 0xccc - - srb 0 0
1004 fdnet 101004 1500 - - 0x0 ieee - 0 0
1005 trbrf 101005 4472 - - 0xf ibm - 0 0
To define the TrCRF for the Payroll users, do the following:
Step 1 At the enable prompt, enter set vlan 12 name crf12 type trcrf ring 12 parent 100 mode srb.
Step 2 To verify the configuration of the new VLAN, enter show vlan.
The output, as shown in Figure 7-10, indicates that crf12 has been added but that it does not have any ports assigned to it yet. It also shows that brf100 is the parent of the VLAN with the ID of 12.
VLAN Name Status Mod/Ports, Vlans
---- -------------------------------- --------- ----------------------------
1 default active 1/1-2
2/1-48
11 crf11 active
12 crf12 active
100 brf100 active 11, 12
1002 fddi-default active
1003 trcrf-default active 3/1-16
1004 fddinet-default active
1005 trbrf-default active 1003
VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BrdgNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2
---- ----- ---------- ----- ------ ------ ------ ---- -------- ------ ------
1 enet 100001 1500 - - - - - 0 0
11 trcrf 100110 4472 100 0x11 - - srb 0 0
12 trcrf 100120 4472 100 0x12 - - srb 0 0
100 trbrf 100100 4472 - - 0x1 ibm - 0 0
1002 fddi 101002 1500 - 0x0 - - - 0 0
1003 trcrf 101003 4472 1005 0xccc - - srb 0 0
1004 fdnet 101004 1500 - - 0x0 ieee - 0 0
1005 trbrf 101005 4472 - - 0xf ibm - 0 0
To assign the ports to the rings (TrCRFs), complete the following steps:
Step 1 At the enable prompt, enter set vlan 11 3/1-2.
Step 2 At the enable prompt, enter set vlan 12 3/3-4.
The output, shown in Figure 7-11, shows that ports 1 and 2 on module 3 are assigned to crf11 and that ports 3 and 4 on module 3 are assigned to crf12.
VLAN Name Status Mod/Ports, Vlans
---- -------------------------------- --------- ----------------------------
1 default active 1/1-2
2/1-48
11 crf11 active 3/1-2
12 crf12 active 3/3-4
100 brf100 active 11, 12
1002 fddi-default active
1003 trcrf-default active 3/5-16
1004 fddinet-default active
1005 trbrf-default active 1003
By default, the TrBRF runs the IBM Spanning-Tree Protocol. The Spanning-Tree Protocol run on the TrCRFs is determined by the specified bridging mode. TrCRFs with a bridge mode of SRB will run the IEEE Spanning-Tree Protocol and TrCRFs with a bridge mode of SRT will run the Cisco Spanning-Tree Protocol.
The Catalyst 5000 Token Ring switching module considers the combination of the IBM Spanning-Tree Protocol at the TrBRF and the bridge mode of SRT to be incompatible. As a result, if you had configured one of the TrCRFs (for example, CRF12) with a bridge mode of SRT, the Catalyst 500 Token Ring switching module would automatically block the logical port of the TrCRF that is configured for SRT. Use the show spantree command to view the state of the logical ports (see Figure 7-12.).
VLAN 100
Spanning tree enabled
Spanning tree type ibm
Designated Root 00-e0-1e-2f-6c-63
Designated Root Priority 32768
Designated Root Cost 0
Designated Root Port 1/0
Root Max Age 6 sec Hello Time 2 sec Forward Delay 4 sec
Bridge ID MAC ADDR 00-e0-1e-2f-6c-63
Bridge ID Priority 32768
Bridge Max Age 6 sec Hello Time 2 sec Forward Delay 4 sec
Port,Vlan Vlan Port-State Cost Priority Fast-Start Group-method
--------- ---- ------------- ----- -------- ---------- ------------
1/2 100 forwarding 19 32 disabled
11 100 forwarding 80 32 disabled
12 100 blocking 80 32 disabled
* = portstate set by user configuration
You can then use the set spantree portstate command to change the forwarding mode of the logical port.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Wed Oct 2 03:40:09 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.