|
|

April 20, 2001
This document describes the problems fixed in Catalyst 3900 switch main image Release 3.0(8) and in ATM firmware image Release 1.2(5). It also lists the known problems for these releases and contains information about the Catalyst 3900 and Catalyst 3920 Token Ring switches that was not included in the user guides. This document is available on the Cisco Connection Documentation CD-ROM or in print.
Sections in this document include the following:
This section lists problems that have been resolved in Release 3.0(8) of the Catalyst 3900 series main image and Release 1.2(5) of the ATM firmware image.
The following is a list of problems found in the Catalyst 3900 series main image that have been resolved in Release 3.0(8).
| Problem Identifier | Problem Description |
|---|---|
CSCdr24694 | When using long fiber cables, the Catalyst 3900 fiber Token Ring ports fail to connect. When this problem occurs, a "QMAC not responding" error message might display on the console. |
CSCds10660 | In a Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) environment, continuous pings to the IP address of a Catalyst 3900 will fail approximately every 10 minutes. These ping failures can last up to a minute and will automatically recover themselves. |
CSCds28966 | Problems with the CAM table might be experienced. Rapidly moving a station from a high-numbered port (for example, port 20) to a low-numbered port (for example, port 1) might cause the original port number to become locked as the CAM entry. This problem causes traffic to be incorrectly switched. |
CSCds54442 | Many receive frame errors are reported on ports that have redundant ring in/ring out (RI/RO) connections to a CAU. These errors might not have a noticeable impact on performance. |
CSCdt56434 | A defect exists that allows SNMP objects to be viewed and modified without authorization using an undocumented and hidden ILMI community string. Affected devices might be vulnerable to an unauthorized configuration if they are not protected against unauthorized use of the ILMI community string. |
The following is a list of problems found in the Catalyst 3900 ATM firmware image that have been resolved in the Release 1.2(5).
| Problem Identifier | Problem Description |
|---|---|
CSCdk48384 | When defining a traffic profile to use for mapping outgoing traffic for an ATM connection, setting the VCC Type parameter on the Traffic Profile Mapping panel to Any does not use the profile for any VCC type. Instead, the default traffic profile is used by VCCs when the VCC Type parameter is set to Any. However, setting the VCC Type to DataDirect will apply the traffic profile map to any VCC type. |
CSCdm01728 | In rare circumstances, the processing of Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) messages might cause a loss of service for the ATM module. This problem results connectivity loss across the ATM network. The local Token Ring network connectivity is not affected. |
CSCdm47776 | After extended periods of uninterrupted operation, a Catalyst 3900 switch might begin to truncate (and therefore corrupt) frames that it receives from the ATM network that are to be forwarded to the local network. |
CSCdm92419 | In large network configurations in which many TrCRFs are configured, assigning an ATM module to a TrCRF might result in the LEC associated with that TrCRF not connecting with LANE services. When this problem occurs, the Status field (located on the ATM LEC Setup panel) displays Going Up and never progresses to Up or Forwarding mode. Also, when this problem occurs, no traffic passes to the ATM network for that TrCRF. |
CSCdm92420 | Under light traffic loads, the forwarding of a packet out of an ATM module might be delayed by a Catalyst 3900 switch until another packet is sent out of the module. This problem results in sporadic traffic flow and slow throughput for transport protocols that have long timeouts. |
This section lists the currently known problems in Release 3.0(8).
Problem: Addresses across the stack are not distributed on TokenChannel ports (CSCdm32568)
Problem: Loss of power to a Catalyst Matrix causes STP to malfunction (CSCdm62365)
Problem: Powering off a Catalyst Matrix might cause the loss of VTP VLAN configuration information on secondary switches (CSCdm64562)
Problem: IP over ISL uses a ring number of zero if the ring number has not been manually configured (CSCdm67270)
Problem: The status of a disabled ISL port might display as up and inserted (CSCdp78073)
Problem: Cisco Discovery Protocol neighbors are not being discovered in Catalyst stacks (CSCdp88897)
This section contains information that was not included in the Catalyst 3900 or Catalyst 3920 User Guides. The headings in this section correspond with the applicable section titles in the documentation.
The option to configure the insert LED to blink on disabled ports has been added to the Switch Configuration panel. By configuring the insert LED to blink on ports that are disabled, you can visually identify which ports are currently disabled. When you configure the insert LEDs to blink on disabled ports, if the switch is part of a stack, the setting applies to all switches in the stack. If you enable and then disable this feature, the insert LEDs on the disabled ports will continue to blink until the switch is rebooted.
To configure the insert LED to blink on ports that are disabled, complete the following steps:
Step 2 Select the Blink Disabled Port LEDs option and press Enter.
Step 3 Select Yes if you want the insert LEDs to blink on disabled ports. Select No if you do not want the insert LEDs to blink on disabled ports. The default is No.
Step 4 Select Return to save your changes and to exit the Switch Configuration panel.
The Catalyst 3900 and 3920 Token Ring switches support source-route bridging (SRB), source-route transparent bridging (SRT), and source-route switching. You can enable either SRB or SRT for the logical connections between the TrCRF and the TrBRF. Source-route switching is used for frame forwarding within the TrCRF and is always enabled.
The list of MIBs documented in the "SNMP-Based Management" section of the user guide is not complete. In addition to the documented MIBs, the Catalyst 3900 also supports two additional standard MIBs and one additional private MIB.
The Catalyst 3900 supports the following additional standard MIBs:
The Catalyst 3900 also supports the following private MIB:
The description of the Token Ring Ring Station Group is incorrect. This section should read as follows:
If you plan to interconnect your Catalyst 3900 with a Catalyst 5000, your Catalyst 5000 should have Supervisor Card revision 2, or later, with NMP version 3.0(201), or later. Also, because VTP pruning is currently not supported by the Catalyst 3900, if you extend a TrBRF from a Catalyst 3900 to a Catalyst 5000 that is using VTP pruning, you must set the TrBRF to ineligible on the Catalyst 5000.
CiscoView shows the burned-in MAC address and the configured locally administered address in non-canonical format. The Switch Configuration panel allows you to choose whether the MAC addresses displayed on the console panels are in canonical or non-canonical format. The default is non-canonical.
The Hw Rev column on the Module Information panel has been updated to reflect the revision numbers of the module and the associated ASICs. For the base switch and the Token Ring fiber and copper expansion modules, the hardware revision is now displayed in the format x.y.z, where:
The two sentences at the end of the third paragraph in the "Configuring VLANs and VTP" section of the user guide are misleading.
The last sentence of the paragraph, "Likewise, a device may belong to multiple management domains if the VLANs defined for the device belong to different management domains" is not correct because a stack of Catalyst 3900 switches can only be part of one VTP management domain.
The second to last sentence of the paragraph, "Different devices may belong to the same management domain if the VLANs defined for the devices belong to the same management domain" is misleading because VTP would not be useful if multiple switches in the same domain were not supported. Therefore, multiple switches in the same domain is a supported function.
Changing the Local Mode field on the VTP Administrative Configuration panel from Client to Transparent or Server generates the following message when the number of defined VLANs is greater than the amount that can be stored in NVRAM:
Mode must be Client. There are too many VLANs to store on local device.
Performing the same procedure via an SNMP manager generates the following message:
WRONG_VALUE_ERROR.
An information panel, the VTP Configuration Information panel, has been added that displays how many local VLANs are currently defined and how many preferred VLANs are currently available.
To access the VTP Configuration panel, select Info on the VTP VLAN Configuration panel. The VLAN Configuration Information panel (Figure 1) is displayed.
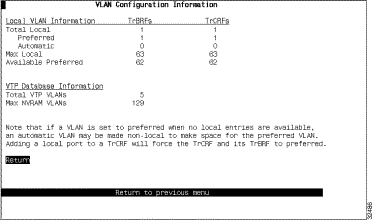
The following information is displayed on this panel:
The VLAN Parameter Configuration panel for a TrBRF has been changed to prevent you from configuring an MTU size larger than 4472 for a TrBRF that contains an ATM port. This change has been made because the Catalyst 3900 ATM module does not support MTUs greater than 4472.
With the Catalyst 3900 main image Release 3.0(3) or later, if you specify an MTU greater than 4472 for a TrBRF that contains an ATM port, the ATM port is removed from the TrBRF and the following message is displayed:
ATM Port removed from TrBRF since BRF MTU > 4K
port=25, crf=1003, brf=1005, vlanmtu=8144
 |
Note Upgrading the Catalyst 3900 main image to Release 3.0(3) or later on a switch on which an MTU greater that 4472 was configured for a TrBRF that contains an ATM port results in the same action. |
As stated in the "Adding or Changing TrCRF VLAN Parameters" section of the User Guide, to enable ring number learning, you must set the Local Mode (on the VTP Administrative Configuration panel) to Transparent (which is the default) and the ring number to auto (which is the default). If you have set the local mode to Client or Server, you cannot set the ring number to auto.
With Release 3.0(3) or later of the Catalyst 3900 main image, if you have previously set the Local Mode of the default TrCRF (1003) to Transparent and the ring number to auto, you can now change the Local Mode while ring number learning is in progress.
If the default TrCRF(1003) is the only TrCRF for which the ring number is set to auto, the ring number is automatically be set to the learned ring number or, if the ring number has not been learned, it is set to 0xCCC.
If you attempt to assign a port to a TrCRF to which remote ports have already been assigned, the following message is generated:
Error - TrCRF has remote ports assigned
If you attempt the same procedure via an SNMP manager, the following message is generated:
WRONG_VALUE_ERROR
An additional option, Management VLAN, has been added to the SNMP Configuration panel. This option enables you to select the VLAN that has the IP address you want to use for the following:
With Catalyst 3900 Token Ring software Release 3.0(6) and later, an additional TrCRF STP mode is available. When configuring the STP mode of a TrCRF via the Spanning Tree for a TrCRF panel, you can now select auto-fast mode in addition to auto, blocked, or forwarding mode.
When the STP mode of a TrCRF is auto (the default), a Token Ring port state change (coming up or going down) causes the TrCRF-to-TrBRF link to cycle through spanning tree states. Until the spanning tree state returns to forwarding, stations in the TrCRF lose connectivity with stations in other TrCRFs associated with the same TrBRF.
However, when the TrCRF STP mode is auto-fast, Token Ring port state changes do not impact the spanning tree state of the TrCRF-to-TrBRF link unless the port happens to be the first active port in the TrCRF.
When configuring a port to operate in adaptive cut-through, you can specify a threshold for errored frames. If this threshold is exceeded, the port transitions from cut-through to store-and-forward mode. Errored frames include frames with CRC errors, aborted frames, and frames that are considered too short.
The ATM LEC Setup panel has been modified to indicate that the Catalyst 3900 ATM module supports MTUs up to 4472.
In the User Guide, the possible values listed for the MTU field are 1500, 4472, 8144, and 17800. With this release of the Catalyst 3900 main image, the possible values for the MTU field on the ATM LEC Setup panel are 1500 and 4472.
The Port Configuration panel for an ISL port has been updated to reflect the operation mode of the port. This new field, labeled Operation Mode, read-only and the only possible value is FDX trunking.
You can now define filters based on the DSAP values 0x00 and 0xAA. If you include a DSAP of 0xAA in a protocol filter, all SNAP frames will be filtered regardless of any EtherType currently specified.
If you attempt to define a filter based on both an EtherType and the DSAP value 0xAA the following message is generated:
Warning - Ethertype filtering will be ignored while filtering with DSAP 0xAA.
For a list of additional SAP values on which you can base filters, refer to the "Service Access Points" section of the "Codes and IDs" appendix of the User Guide.
Additional changes to the Protocol Class Assignment panel include the following:
Because the required hardware has not become available in the marketplace to support passive monitoring of network traffic, the Catalyst 3900 no longer allows the configuration of passive SPAN.
As mentioned in the User Guide, you must place your SPAN port in a separate TrCRF (and TrBRF) that contains no other ports. If you plan to use SPAN, we recommend that you create a TrCRF and TrBRF upon initial configuration just for this purpose. It is also a good idea to leave a port on the switch assigned to this TrCRF for the purposes of future SPAN use.
The Filters & Port Security panel has been changed to make it easier for you to configure MAC address and protocol filters. As a result a new panel, the MAC Address Filters panel, has been added. The new options available on the Filters & Port Security panel are:
You can now find the following options that were displayed on the Filter & Port Security panel on the MAC Address Filters panel:
For more information about these options, refer to the "Limiting Scope and Access" section of the User Guide.
Two fields on the General Statistics panel for a port have been changed to clarify the information the counters are reflecting. The Frames Filtered - Addr and Frames Filtered DSAP fields in the left-hand column have been changed to the following:
Two fields on the Frame Forwarding Statistics panel for an ATM port have been changed to clarify the information the counters are reflecting. The Frames Filtered - Addr and Frames Filtered - DSAP fields in the left-hand column have been changed to the following:
The Invalid ISL VLAN error counter that was available on the ISL Port Error Statistics panel has been moved to the ISL Port General Statistics panel and renamed to Non-Local VLAN Frames Received.
The Non-Local VLAN Frames Received field displays the number of frames received that contained a source VLAN ID that was unknown (based on the current configuration of the switch).
Fields that identify the Spanning-Tree Protocol running at the TrBRF and TrCRF levels have been added to the Current Spanning Tree Information panel.
When viewing the Spanning-Tree parameters for a TrBRF, the protocol running per TrCRF displays in the Ptcl column. Possible values are IBM, IEEE, or blank.
When viewing the Spanning-Tree parameters for a TrCRF, the protocol running on that TrCRF displays in the Protocol field. Possible values for the Protocol field are Cisco and IEEE.
When changes are made to the Catalyst 3900 software, the new image is posted to CCO. You can then obtain a copy of the image and download it to your switch.
The following sections provide sources for obtaining documentation from Cisco Systems.
You can access the most current Cisco documentation on the World Wide Web at the following sites:
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available in a CD-ROM package, which ships with your product. The Documentation CD-ROM is updated monthly and may be more current than printed documentation. The CD-ROM package is available as a single unit or as an annual subscription.
Cisco documentation is available in the following ways:
If you are reading Cisco product documentation on the World Wide Web, you can submit technical comments electronically. Click Feedback in the toolbar and select Documentation. After you complete the form, click Submit to send it to Cisco.
You can e-mail your comments to bug-doc@cisco.com.
To submit your comments by mail, use the response card behind the front cover of your document, or write to the following address:
Attn Document Resource Connection
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-9883
We appreciate your comments.
Cisco provides Cisco.com as a starting point for all technical assistance. Customers and partners can obtain documentation, troubleshooting tips, and sample configurations from online tools. For Cisco.com registered users, additional troubleshooting tools are available from the TAC website.
Cisco.com is the foundation of a suite of interactive, networked services that provides immediate, open access to Cisco information and resources at anytime, from anywhere in the world. This highly integrated Internet application is a powerful, easy-to-use tool for doing business with Cisco.
Cisco.com provides a broad range of features and services to help customers and partners streamline business processes and improve productivity. Through Cisco.com, you can find information about Cisco and our networking solutions, services, and programs. In addition, you can resolve technical issues with online technical support, download and test software packages, and order Cisco learning materials and merchandise. Valuable online skill assessment, training, and certification programs are also available.
Customers and partners can self-register on Cisco.com to obtain additional personalized information and services. Registered users can order products, check on the status of an order, access technical support, and view benefits specific to their relationships with Cisco.
To access Cisco.com, go to the following website:
The Cisco TAC website is available to all customers who need technical assistance with a Cisco product or technology that is under warranty or covered by a maintenance contract.
If you have a priority level 3 (P3) or priority level 4 (P4) problem, contact TAC by going to the TAC website:
P3 and P4 level problems are defined as follows:
In each of the above cases, use the Cisco TAC website to quickly find answers to your questions.
To register for Cisco.com, go to the following website:
http://www.cisco.com/register/
If you cannot resolve your technical issue by using the TAC online resources, Cisco.com registered users can open a case online by using the TAC Case Open tool at the following website:
http://www.cisco.com/tac/caseopen
If you have a priority level 1(P1) or priority level 2 (P2) problem, contact TAC by telephone and immediately open a case. To obtain a directory of toll-free numbers for your country, go to the following website:
http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/687/Directory/DirTAC.shtml
P1 and P2 level problems are defined as follows:
This document is to be used in conjunction with the Catalyst 3900 Token Ring Switch User Guide and the Catalyst 3920 Token Ring Switch User Guide publications.
AccessPath, AtmDirector, Browse with Me, CCDA, CCDE, CCDP, CCIE, CCNA, CCNP, CCSI, CD-PAC, CiscoLink, the Cisco NetWorks logo, the Cisco Powered Network logo, Cisco Systems Networking Academy, the Cisco Systems Networking Academy logo, Fast Step, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, FrameShare, GigaStack, IGX, Internet Quotient, IP/VC, iQ Breakthrough, iQ Expertise, iQ FastTrack, the iQ Logo, iQ Net Readiness Scorecard, MGX, the Networkers logo, Packet, PIX, RateMUX, ScriptBuilder, ScriptShare, SlideCast, SMARTnet, TransPath, Unity, Voice LAN, Wavelength Router, and WebViewer are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn, Discover All That's Possible, and Empowering the Internet Generation, are service marks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; and Aironet, ASIST, BPX, Catalyst, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, the Cisco IOS logo, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Enterprise/Solver, EtherChannel, EtherSwitch, FastHub, FastSwitch, IOS, IP/TV, LightStream, MICA, Network Registrar, Post-Routing, Pre-Routing, Registrar, StrataView Plus, Stratm, SwitchProbe, TeleRouter, and VCO are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. or its affiliates in the U.S. and certain other countries.
All other brands, names, or trademarks mentioned in this document or Web site are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (0102R)
Copyright © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc.
All rights reserved.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Tue Apr 30 00:19:20 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.