|
|

The GigaStack GBIC (model WS-X3500-XL) adds port density and high-performance connectivity to supporting switches. When installed in a supporting switch, the GigaStack GBIC supports Gigabit connections in a cascaded stack or point-to-point configuration. The GigaStack GBIC autonegotiates the duplex setting of each port to maximize the bandwidth for your configuration.
This section describes the GigaStack GBIC features:
Figure 1-1 shows the LED locations on the GigaStack GBIC, and Table 1-1 describes the LED colors and their meanings.

| Color | Meaning |
|---|---|
Off | No link. |
Green | Link present. This link occurs if there is connectivity with another network device and the GigaStack GBIC port. |
Amber | Power-on self-test (POST) failure or use of an incorrect cable. |
Flashing amber | Loop detection activated. |
Figure 1-2 shows the GBIC module slot LED on the front of a supporting switch, and Figure 1-3 shows the GBIC LED location when the GigaStack GBIC is installed in the 1000BASE-X module.
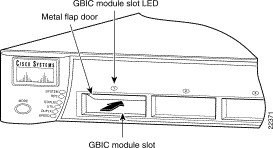
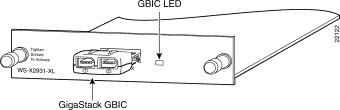
Table 1-2 describes the switch and 1000BASE-X module GBIC slot LED colors and port status.
| Color | Meaning |
|---|---|
Off | No link, or port was administratively shut down. |
Green | Link present. |
Flashing green | Activity. Port is transmitting or receiving data. |
Alternating green-amber | Link fault. Error frames can affect connectivity, and errors such as excessive collisions, cyclic redundancy check (CRC) errors, and alignment and jabber errors are monitored for a link-fault indication. |
Solid amber | Port is blocked by Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and is not forwarding data. Note After a port is reconfigured, the port LED can remain amber for up to 30 seconds as STP checks the switch for possible loops. |
Flashing amber | Port is blocked by STP and is sending or receiving packets. |
The GigaStack GBIC uses the following Cisco proprietary cables. See Figure 1-4 and Table 1-3 for more information.
The maximum distance for a GBIC-to-GBIC connection is 1 meter. The GigaStack GBIC requires Cisco proprietary signaling and cabling. For more information about cabling, see "Connectors and Cables."
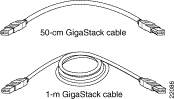
| Part Number | Cable Length |
CAB-GS-50CM | 50 cm |
CAB-GS-1M | 1 m |
The 50-cm cable comes with the GigaStack GBIC. You can order additional cables.
 |
Caution Do not use the GigaStack GBIC with standard IEEE 1394 equipment. You might damage the equipment or lose data. |
Refer to the online GigaStack Gigabit Interface Converter Switch Compatibility Matrix listed with the GBIC documentation on www.cisco.com for the most current list of products supporting the GBIC.
 |
Caution Installing the GBIC in or connecting it to an unauthorized device might cause damage to the GBIC, the other device, or both. |
Table 1-4 lists the switches and the module supporting the GigaStack GBIC.
| Switch Series or Module | Model Number | Description |
|---|---|---|
| WS-X2931-XL module for Catalyst 2900 series XL switches | WS-X2931-XL | 1 1000BASE-X port1 |
| Catalyst 2900 XL switches | Catalyst 2912MF XL | 12 100BASE-FX ports and 2 module slots |
Catalyst 2924M XL | 24 autosensing 10/100 Ethernet ports and 2 module slots | |
| Catalyst 2950 switches | Catalyst 2950G-12-EI | 12 autosensing 10/100 Ethernet ports and 2 GBIC module slots |
Catalyst 2950G-24-EI | 24 autosensing 10/100 Ethernet ports and 2 GBIC module slots | |
Catalyst 2950G-24-EI-DC | 24 autosensing 10/100 Ethernet ports and 2 GBIC module slots with DC-input power | |
Catalyst 2950G-48-EI | 48 autosensing 10/100 Ethernet ports and 2 GBIC module slots | |
| Catalyst 3500 XL switches | Catalyst 3508G XL | 8 GBIC module slots |
Catalyst 3512 XL | 12 autosensing 10/100 Ethernet ports and 2 GBIC module slots | |
Catalyst 3524 XL | 24 autosensing 10/100 Ethernet ports and 2 GBIC module slots | |
Catalyst 3524 PWR XL | 24 autosensing 10/100 inline-power Ethernet ports and 2 GBIC module slots | |
Catalyst 3548 XL | 48 autosensing 10/100 Ethernet ports and 2 GBIC module slots | |
| Catalyst 3550 switches | Catalyst 3550-12G | 2 autosensing 10/100/1000 Ethernet ports and 10 GBIC module slots |
Catalyst 3550-12T | 10 autosensing 10/100/1000 Ethernet ports and 2 GBIC module slots | |
Catalyst 3550-24-SMI | 24 autosensing 10/100 Ethernet ports and 2 GBIC module slots | |
Catalyst 3550-48-SMI | 48 autosensing 10/100 Ethernet ports and 2 GBIC module slots |
| 1The 1000BASE-X module provides one switched 1000-Mbps port in half-duplex, full-duplex, or autonegotiation mode for a GigaStack GBIC. The port supports the IEEE 802.3Z 1000BASE-X standard. |
To ensure support for redundant loop configurations when using the GigaStack GBIC in a cascaded stack configuration, make sure that every switch in the stack is running at least the minimum IOS Release listed in Table 1-5.
| Supported Switch | Minimum IOS Release |
|---|---|
Modular 2900 XL switches | 12.0(5)XU (April 2000) |
2950 switches | 12.1(6)EA2 (December 2000) |
3500 XL switches | 12.0(5)XU (April 2000) |
3550 multilayer switches | 12.1(4)EA1 (May 2001) |
 |
Note All switches in a series must run the same software version. For example, if the stack includes only Catalyst 2900 series XL and 3500 series XL switches, they must run Release 12.0(5)XU or later. If the stack includes a mixture of Catalyst 2900 series XL, 3500 series XL, 2950, and 3550 switches, all the 2900 XL and 3500 XL switches must run Release 12.0(5)XW or later, all the Catalyst 2950 switches must run Release 12.1(6)EA2 or later, and all the Catalyst 3550 switches must run Release 12.1(4)EA1 or later. |
For more information, see the "Cascaded Stack Connections with a Redundant Link" section. For switch software upgrade information, refer to the release notes for your switch.
This section contains examples that use the GigaStack GBIC as a Gigabit uplink to aggregate traffic in a switched and shared network.
Figure 1-5 shows the GigaStack GBIC cascaded in a half-duplex stack configuration.

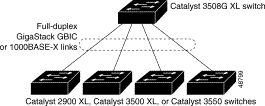
Figure 1-6 shows the 3500 XL switch aggregating traffic by using a GigaStack GBIC as a full-duplex, point-to-point uplink connection.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Fri Mar 29 14:57:25 PST 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.