|
|

Before using this chapter, be sure that you have planned your site's security policy, as described in "Introduction," and configured the PIX Firewall, as described in "Configuring the PIX Firewall." Acronyms in the text are defined in "Acronyms and Abbreviations."
This chapter provides network diagrams and the configuration instructions to create them. Further information about the commands in the configurations can be found in "Command Reference."
If you are starting a configuration, you may want to use the forms provided in "Configuration Forms," to help you plan a configuration.
This chapter includes the following sections:
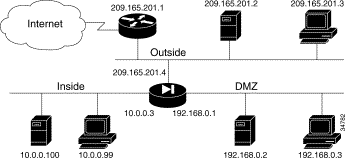
When you first add a PIX Firewall to an existing network, it is easiest to implement its use if you do not have to renumber all the inside and outside IP addresses. The configuration in Figure 5-1 illustrates this scenario. Syslog is enabled to facilitate troubleshooting. All inside hosts can start connections. All external hosts are blocked from initiating connections or sessions on inside hosts. If you use Inter-NIC registered IP addresses, only use those addresses that you own.
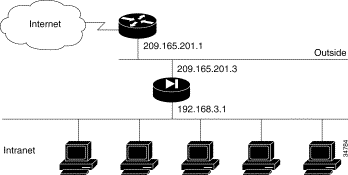
Table 5-1 lists the configuration.
| Configuration | Description |
|---|---|
nameif ethernet0 outside security0
nameif ethernet1 inside security100
interface ethernet0 auto
interface ethernet1 auto
| PIX Firewall provides nameif and interface command statements for the interfaces in the default configuration. |
ip address outside 209.165.201.3
255.255.255.224
ip address inside 172.31.2.100 255.255.255.0
| Identify the IP addresses for both interfaces. |
hostname pixfirewall
| Specifies the host name for the PIX Firewall. This name appears in the command line prompt. |
arp timeout 14400
| Sets the ARP timeout to 14,400 seconds (four hours). Entries are kept in the ARP table for four hours before they are flushed. Four hours is the standard default value for ARP timeouts. |
no failover
| Disables failover access. |
names
| Enables use of text strings instead of IP addresses. This makes your configuration files more readable. |
pager lines 24
| Enables paging so that if when 24 lines of information display, PIX Firewall pauses the listing and prompts you to continue. |
logging buffered debugging
| Enables syslog messages, which provide diagnostic information and status for the PIX Firewall. PIX Firewall makes it easy to view syslog messages with the show logging command. |
nat (inside) 0 172.31.2.0 255.255.255.0
| Lets inside IP addresses be recognized on the outside network and lets inside users start outbound connections. |
rip inside default
no rip inside passive
no rip outside default
no rip outside passive
| Sets RIP listening attributes. The first command causes the PIX Firewall to broadcast a default route on the inside interface. Broadcasting a default route sends network traffic to the PIX Firewall if your internal network is running RIP. The next command disables passive RIP listening on the inside. The next command disables broadcasting a default route on the outside. This is desirable when the network is attached to the Internet, but not when on an intranet. The last command disables passive RIP listening on the outside. |
route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 209.165.201.1 1
| Sets the outside default route to the router attached to the Internet. |
timeout xlate 3:00:00 conn 1:00:00
half-closed 0:10:00 udp 0:02:00
timeout rpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00
timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute
| Default values for the maximum duration that PIX Firewall resources can remain idle until being freed. Additional users cannot make connections until a connection resource is freed either by a user dropping a connection or by an xlate and conn timer time out. |
no snmp-server location
no snmp-server contact
snmp-server community public
| Specifies that SNMP information may be accessed by internal hosts that know the community string, but PIX Firewall does not send trap information to any host. |
mtu outside 1500
mtu inside 1500
| Sets the maximum transmission unit value for Ethernet access. |
In Figure 5-2, the PIX Firewall has two interfaces. In this configuration, there is no user authentication, no authorization, and no syslog or SNMP logging of troubleshooting messages. All inside users can start outbound connections and all connections from the outside are dropped. A configuration such as this is a good example of the basic commands used to create a secured network.
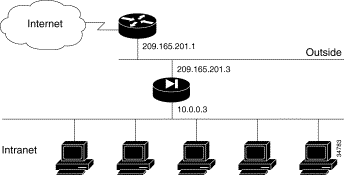
Table 5-2 lists the configuration.
| Configuration | Description |
|---|---|
nameif ethernet0 outside security0
nameif ethernet1 inside security100
interface ethernet0 auto
interface ethernet1 auto
| PIX Firewall provides nameif and interface command statements for the interfaces in the default configuration. |
ip address outside 209.165.201.3 255.255.255.224
ip address inside 10.0.0.3 255.0.0.0
| Identify the IP addresses for both interfaces. |
arp timeout 14400
| Set the ARP timeout to 14,400 seconds (four hours). Entries are kept in the ARP table for four hours before they are flushed. |
nat (inside) 1 0 0
| Permit all inside users to start outbound connections using the translated IP addresses from the global pool. |
global (outside) 1 209.165.201.10-209.165.201.30
global (outside) 1 209.165.201.8
| Create a pool of global addresses that translated addresses use when they exit the firewall from the protected networks to the unprotected networks. The global command statement is associated with a nat command statement by the NAT ID, which in this example is 1. Because there are limited IP addresses in the pool, a PAT (Port Address Translation) global is added to handle overflow. |
no rip inside default
no rip inside passive
no rip outside default
no rip outside passive
| PIX Firewall does use RIP information for its forwarding decisions, but these commands can be useful for broadcasting a default route—if your network uses the RIP protocol. However, most do not. In most cases, you can ignore these command statements. |
route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 209.165.201.1 1
| Sets the outside default route to the router attached to the Internet. |
timeout xlate 3:00:00 conn 1:00:00
half-closed 0:10:00 udp 0:02:00
timeout rpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00
timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute
| Sets default values for the maximum duration that PIX Firewall resources can remain idle until being freed. Additional users cannot make connections until a connection resource is freed either by a user dropping a connection or by an xlate and conn timer time out. |
access-list acl_grp permit icmp any any
access-group acl_grp in interface inside
access-group acl_grp in interface outside
| Allows inbound and outbound pings. |
no snmp-server location
no snmp-server contact
snmp-server community public
| Specifies that SNMP information may be accessed by internal hosts that know the community string, but PIX Firewall does not send trap information to any host. |
telnet 10.0.0.100 255.255.255.255
telnet timeout 15
| Specifies that host 10.0.0.100 is permitted to access the PIX Firewall console via Telnet and that 15 minutes are allowed before the idle timer runs out and the session is logged off. |
mtu outside 1500
mtu inside 1500
| Sets the maximum transmission unit value for Ethernet access. |
The configuration in Figure 5-3 provides an overview of how the various commands are used to create a configuration.
This configuration shows the use of PAT (Port Address Translation), denying Java applets, using the AAA commands, creating a mail server, permitting NFS, initializing SNMP, and setting console access with Telnet.
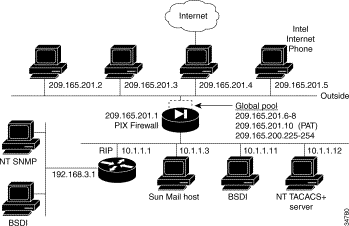
Table 5-3 lists the configuration.
| Configuration | Description |
|---|---|
nameif ethernet0 outside security0
nameif ethernet1 inside security100
interface ethernet0 auto
interface ethernet1 auto
| PIX Firewall provides nameif and interface command statements for the interfaces in the default configuration. |
ip address inside 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip address outside 209.165.201.1 255.255.255.224
| Identify the IP addresses for both interfaces. |
logging on
logging host 10.1.1.11
logging trap 7
logging facility 20
no logging console
| The logging host command statement specifies which host runs a syslog server. This command also causes the PIX Firewall to start sending syslog messages to that host. The logging trap command statement sets syslog to send all possible messages to the syslog host. The no logging console command statement disables displaying messages to the console. |
arp timeout 600
| Set an ARP timeout to 600 seconds (10 minutes). Use this arp timeout command statement when you set up a network and change inside and outside host addresses often. |
nat (inside) 1 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
nat (inside) 2 192.168.3.0 255.255.255.0
| Permit all inside users to start outbound connections using the translated IP addresses from the global pool. |
global (outside) 1 209.165.201.6-209.165.201.8
netmask 255.255.255.224
global (outside) 1 209.165.201.10 netmask
255.255.255.224
global (outside) 2 209.165.200.225-209.165.200.254
netmask 255.255.255.224
| Create pools of global addresses to let the nat command statements use the address pools for translating internal IP addresses to external addresses. Each pool is designated by the number from the nat command statement, in this case, 1 and 2. |
access-list acl_in permit icmp any any
access-list acl_out permit icmp any any
| Allow inbound and outbound pings. Access list group "acl_in" is bound to the inside interface and group "acl_out" is bound to the outside interface. |
access-list acl_in deny tcp host 192.168.3.3 any eq
1720
access-list acl_in deny tcp any any eq 80
access-list acl_in permit host 192.168.3.3 any eq 80
access-list acl_in permit host 10.1.1.11 any eq 80
| Create outbound access lists to determine which hosts can access services. The first access-list command statement denies host 192.168.3.3 from accessing H.323 (port 1720) services such as MS NetMeeting or InternetPhone. The next command statement denies all hosts from accessing the Web (port 80). The next command statement permits host 192.168.3.3 to use the Web. The last access-list command statement permits host 10.1.1.11 access to the Web (at port 80). |
access-group acl_in interface inside
| Specify that the access-list group regulates the activities of inside hosts starting outbound connections. |
filter java http 192.168.3.3 255.255.255.255 0 0
| Keep host 192.168.3.3 from downloading Java applets. |
no rip outside passive
no rip outside default
rip inside passive
rip inside default
| The first command disables RIP listening on the outside interface. The second command disables broadcasting a default route on the outside. The third command enables RIP listening on the inside and the last command causes PIX Firewall to broadcast a default route on the inside interface. |
route outside 0 0 209.165.201.4 1
| Set the default route on the outside network to be 209.165.201.4. This is the IP address of the gateway host connecting to the Internet. |
aaa-server TACACS+ (inside) host 10.1.1.12 1q2w3e
aaa authentication include any inside 192.168.3.0
255.255.255.0 0 0 TACACS+
aaa authorization include any inside 192.168.3.0
255.255.255.0 0 0
| The aaa-server command specifies the IP address of the TACACS+ authentication server. The aaa authentication command statement specifies that users on network 192.168.3.0 starting FTP, HTTP, and Web connections from the inside interface be prompted for their usernames and passwords before being permitted to access these servers on other interfaces. The aaa authorization command statement lets the users on 192.168.3.0 access FTP, HTTP, or Telnet, and any TCP connections to anywhere as authorized by the AAA server. Even though it appears that the aaa commands let the PIX Firewall set security policy, the authentication server actually does the work to decide which users are authenticated and what services they can access when authentication is permitted. |
static (inside, outside) 209.165.201.16 192.168.3.16
netmask 255.255.255.240
access-list acl_out permit tcp any host
209.165.201.16 eq h323
| The static command statement creates a net static command statement, which is a static command statement for a set of IP addresses, in this case for IP addresses 209.165.201.17 through 209.165.201.30. The access-list command statement lets users on the Internet send InternetPhone (port h323) requests to users on 192.168.3.x while addressing them as 209.165.201.x. |
static (inside, outside) 209.165.201.11 10.1.1.11
access-list acl_out permit tcp any host
209.165.201.11 eq 80
| The static command statement with the access-list command statement establishes an externally visible IP address for Web access (port 80 in the access-list command statement). |
access-list acl_out permit udp host 209.165.201.2
host 209.165.201.11 eq rpc
| Refine the accessibility of the static command by permitting Sun RPC over the UDP portmapper on port 111 with the rpc literal. Refer to the UNIX /etc/rpc file and the UNIX rpc(3N) command page for more information. Once you create an access-list command statement for RPC, you can use the following command from outside host 209.165.201.2 to track down the activity of a PCNFSD on RPC 150001: Another use of RPC is with the following command to see the exports of 209.165.201.11 if you want to allow NFS mounting from outside in: Many protocols based on RPC, as well as NFS, are insecure and should be used with caution. Review your security policies carefully before permitting access to RPC. |
access-list acl_out permit udp host 209.165.201.2
host 209.165.201.11 eq 2049
| |
static (inside, outside) 209.165.201.12 10.1.1.3 | Identify access to the 10.1.1.3 mail server through global address 209.165.201.12. The access-list command statement any outside host access to the static via SMTP (port 25). By default, PIX Firewall restricts all access to mail servers to RFC 821 section 4.5.1 commands of DATA, HELO, MAIL, NOOP, QUIT, RCPT, and RSET. This occurs via the Mail Guard service which is set with the following default configuration command: fixup protocol smtp 25 Another aspect of providing access to a mail server is setting being sure that you have a DNS MX record for the static's global address, which outside users access when sending mail to your site. |
access-list acl_out permit tcp any host
209.165.201.12 eq 113
access-group acl_out in interface outside
| Create access to port 113, the IDENT protocol. If the mail server has to talk to many mail servers on the outside which connect back with the now obsolete and highly criticized IDENT protocol, use this access-list command statement to speed up mail transmission. The access-group command statement binds the access-list command statements to the outside interface. |
snmp-server host 192.168.3.2
snmp-server location building 42
snmp-server contact polly hedra
snmp-server community ohwhatakeyisthee
| These commands specify that host 192.168.3.2 can receive SNMP events, which the PIX Firewall sends via syslog. The location and contact commands identify where the host is and who administers it. The community command describes the password in use at the SNMP server for verifying network access with the server. |
telnet 10.1.1.11 255.255.255.255
telnet 192.168.3.0 255.255.255.0
| These commands permit host access to the PIX Firewall console. The first telnet command permits a single host, 10.1.1.11 to access the PIX Firewall console with Telnet. The 255 value in the last octet of the netmask means that only the specified host can access the console. The second telnet command permits PIX Firewall console access from all hosts on the 192.168.3.0 network. The 0 value in the last octet of the netmask permits all hosts in that network access. However, Telnet only permits 16 hosts simultaneous access to the PIX Firewall console over Telnet. |
In Figure 5-4, the PIX Firewall has three interfaces. No address translation is performed between the interfaces.
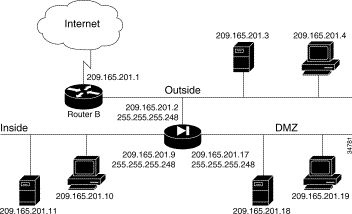
The network has the following IP addresses and network masks:
Table 5-4 lists the configuration.
| Configuration | Description |
|---|---|
nameif ethernet0 outside security0
nameif ethernet1 inside security100
nameif ethernet2 dmz security50
interface ethernet0 auto
interface ethernet1 auto
interface ethernet2 auto
| PIX Firewall provides nameif and interface command statements for the interfaces in the default configuration. |
ip address outside 209.165.201.2 255.255.255.248
ip address inside 209.165.201.9 255.255.255.248
ip address dmz 209.165.201.17 255.255.255.248
| Identify the IP addresses for each of the three interfaces. |
hostname pixfirewall
| Specifies the host name for the PIX Firewall. This name appears in the command line prompt. |
arp timeout 14400
| Sets the ARP timeout to 14,400 seconds (four hours). Entries are kept in the ARP table for four hours before they are flushed. Four hours is the standard default value for ARP timeouts. |
no failover
| Disables failover access. |
names
| Lets you use text strings instead of IP addresses, which makes your configuration easier to read. |
pager lines 24
| Enables paging so that if when 24 lines of information display, PIX Firewall pauses the listing and prompts you to continue. |
logging buffered debugging
| Enable syslog messages, which provide diagnostic information and status for the PIX Firewall. You can view the messages with the show logging command and clear the message buffer with the clear logging command. |
rip inside passive
no rip outside passive
no rip inside default
no rip outside default
| Sets RIP listening attributes. The first two command statements enable RIP listening on the inside, but disable it on the outside. The no rip interface default commands causes PIX Firewall to not broadcast a default route on either interface. |
route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 209.165.201.1 1
| Sets the outside default route to the gateway attached to the Internet. |
timeout xlate 3:00:00 conn 1:00:00
half-closed 0:10:00 udp 0:02:00
timeout rpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00
timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute
| Default values for the maximum duration that PIX Firewall resources can remain idle until being freed. |
no snmp-server location
no snmp-server contact
snmp-server community public
| Specifies that SNMP information may be accessed by internal hosts that know the community string, but PIX Firewall does not send trap information to any host. |
mtu outside 1500
mtu inside 1500
mtu dmz 1500
| Sets the maximum transmission unit value for Ethernet access. |
nat (inside) 0 209.165.201.8 255.255.255.248
| Disables NAT (Network Address Translation). |
static (dmz,outside) 209.165.201.19 209.165.201.19
netmask 255.255.255.248
access-list acl_out permit tcp any host
209.165.201.19
access-group acl_out in interface outside
| Maps access to the 209.165.201.19 host on the dmz interface. The access-list command lets any outside user access the host on any port. |
In Figure 5-5, the PIX Firewall has three interfaces and these attributes:
The network has the following IP addresses and network masks:
Table 5-5 lists the configuration.
| Configuration | Description |
|---|---|
nameif ethernet0 outside security0
nameif ethernet1 inside security100
nameif ethernet2 dmz security50
interface ethernet0 auto
interface ethernet1 auto
interface ethernet2 auto
| PIX Firewall provides nameif and interface command statements for the interfaces in the default configuration. |
ip address outside 209.165.201.4 255.255.255.224
ip address inside 10.0.0.3 255.0.0.0
ip address dmz 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0
| Identify the IP addresses for each of the three interfaces. |
hostname pixfirewall
| Specify the host name for the PIX Firewall. This name appears in the command line prompt. |
arp timeout 14400
| Set the ARP timeout to 14,400 seconds (four hours). Entries are kept in the ARP table for four hours before they are flushed. Four hours is the standard default value for ARP timeouts. |
no failover
| Disable failover access. |
names
| Lets you use text strings instead of IP addresses, which makes your configuration easier to read. |
pager lines 24
| Enable paging so that if after 24 lines of information display, PIX Firewall pauses the listing and prompts you to continue. |
logging buffered debugging
| Enable syslog messages, which provide diagnostic information and status for the PIX Firewall. You can view the messages with the show logging command and clear the message buffer with the clear logging command. |
no rip inside passive
no rip outside passive
no rip inside default
no rip outside default
| Disable RIP attributes. |
route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 209.165.201.1 1
| Set the outside default route to the router attached to the Internet. |
access-list ping_acl permit icmp any any
access-group ping_acl in interface inside
access-group ping_acl in interface dmz
access-list acl_out permit icmp any any
| Allow inbound and outbound pings. The "ping_acl" access-list command statement group is bound to the inside interface. The "acl_out" group is bound to the outside interface. This distinction accommodates the access-list command statement later in the configuration that applies permissions to a static command statement mapping. When troubleshooting is complete, remove the ICMP access-list statements. |
timeout xlate 3:00:00 conn 1:00:00
half-closed 0:10:00 udp 0:02:00
timeout rpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00
timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute
| Default values for the maximum duration that PIX Firewall resources can remain idle until being freed. |
no snmp-server location
no snmp-server contact
snmp-server community public
| Specify that SNMP information may be accessed by internal hosts that know the community string, but PIX Firewall does not send trap information to any host. |
mtu outside 1500
mtu inside 1500
mtu dmz 1500
| Set the maximum transmission unit value for Ethernet access. |
telnet 10.0.0.100 255.255.255.255
telnet timeout 15
| Give Telnet access to PIX Firewall console to inside host. Use the timeout feature to set the maximum time a Telnet session can be idle before PIX Firewall closes the connection to 15 minutes. The default is 5 minutes. |
global (outside) 1 209.165.201.10-209.165.201.30
global (outside) 1 209.165.201.5
global (dmz) 1 192.168.0.10-192.168.0.20
| Create a pool of global addresses for the outside and DMZ interfaces. Because there are limited outside IP addresses, add a PAT global to handle overflow. The global (dmz) command gives inside users access to the web server on the DMZ interface. |
nat (inside) 1 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
nat (dmz) 1 192.168.0.0 255.255.255.0
| Let inside users start connections on the DMZ and outside interfaces, and let DMZ users start connections on the outside interface. |
name 192.168.0.2 webserver
| Give the IP address of the web server a label. |
static (dmz,outside) 209.165.201.6 webserver
access-list acl_out permit tcp any host
209.165.201.6 eq 80
access-group acl_out in interface outside
| Let any user on the outside interface access the web server on the DMZ interface. The access-list command statement is bound to the outside interface by the access-group command statement. |
In Figure 5-6, the PIX Firewall has four interfaces. In this configuration, there is no user authentication and no authorization. NAT (Network Address Translation) is in effect to translate addresses. In this example, users on all interfaces have access to all the servers and hosts on the inside, dmz1, and dmz2 interfaces can start connections.
This section includes the following topics:
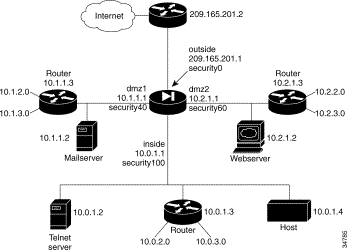
Configuring PIX Firewall for four interfaces requires more attention to detail than other configurations.
This section includes the following topics:
The most important guidelines to remember are as follows:
The sections that follow provide more information on these guidelines.
To let users on each higher security level interface access servers on each lower security level interface, follow these steps:
Step 1 Letting higher security level interface users access a lower security level interface has two components: you use the nat command to specify from where users start connections, and you use the global command to specify to where access is permitted. You associate the nat and global commands together with the NAT ID, which in this example configuration is 1. The nat command lets users start connections from the specified interface to all lower security interfaces, the global command permits access to translated connections from any higher security level interface.
To let users from the inside interface start connections, use the following command:
nat (inside) 1 0 0
Step 2 To let users on the dmz2 interface start connections, use the following command:
nat (dmz2) 1 0 0
Step 3 To let users on the dmz1 interface start connections, use the following command:
nat (dmz1) 1 0 0
Step 4 To permit access to the dmz2 interface for translated connections, use the following command:
global (dmz2) 1 10.2.1.10-10.2.1.254
Step 5 To permit access to the dmz1 interface for translated connections, use the following command:
global (dmz1) 1 10.1.1.10-10.1.1.254
Step 6 To permit access to the outside interface for translated connections, use the following command:
global (outside) 1 209.165.201.10-209.165.201.30
To let users on a lower security level interface access a server on a higher security level interface, use the static and access-list commands. The first IP address in the static command is the address users on the lower security level interface use when they want to access the server on the higher security level interface. The second IP address is the actual address of the server.
When you enter the static command statement in your configuration, always specify the security level of the interfaces as (higher,lower) and the IP addresses as lower and higher; for example:
static (inside,dmz1) 10.1.1.7 10.0.1.2
When users on the dmz1 interface access the Telnet server, they use IP address 10.1.1.7.
To let users on each lower security level interface access servers on each higher security level interface, follow these steps:
Step 1 To let users on the outside interface access the mail server on the dmz1 interface, use the following command:
static (dmz1,outside) 209.165.201.5 10.1.1.2 netmask 255.255.255.255
access-list acl_out permit tcp any host 209.165.201.5 eq smtp
access-group acl_out in interface outside
The access-group command binds the "acl_out" access-list command statement group to the outside interface. The access-group command also applies to the other "acl_out" group access-list command statements that follow.
Step 2 To let users on the outside interface access the web server on the dmz2 interface, use the following command:
static (dmz2,outside) 209.165.201.6 10.2.1.2 netmask 255.255.255.255
access-list acl_out permit tcp any host 209.165.201.6 eq www
Step 3 To let users on the outside interface access the Telnet server on the inside interface, use the following command:
static (inside,outside) 209.165.201.7 10.0.1.2 netmask 255.255.255.255
access-list acl_out permit tcp any host 209.165.201.7 eq telnet
Step 4 To let users on the dmz1 interface access the web server on the dmz interface, use the following command:
static (dmz2,dmz1) 10.1.1.6 10.2.1.2 netmask 255.255.255.255
access-list acl_dmz1 permit tcp any host 10.1.1.6 eq www
access-group acl_dmz1 in interface dmz1
The access-group command binds the "acl_dmz1" access-list command statement group to the outside interface. The access-group command also applies to the other "acl_dmz1t" group access-list command statements that follow.
Step 5 To let users on the dmz1 interface access the Telnet server on the inside interface, use the following command:
static (inside,dmz1) 10.1.1.7 10.0.1.2
access-list acl_dmz1 permit tcp any host 10.1.1.7 eq telnet
Step 6 To let users on the dmz2 interface access the Telnet server on the inside interface, use the following command:
static (inside,dmz2) 10.2.1.7 10.0.1.2
access-list acl_dmz2 permit tcp any host 10.2.1.7 eq telnet
access-group acl_dmz2 in interface dmz2
All configuration command statements are explained in greater detail in Table 5-6.
Once you sketch out your network and map these steps to your IP addresses and servers, the four-interface configuration can become a simpler task.
The addresses used in this configuration are as follows:
In addition, static route command statements are required to permit access to the networks that connect to the routers. A static route command statement directs traffic meant for a network to the router on the interface. The format for a static route command is shown in the following example:
route inside 10.0.2.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.1.3 1
This command statement instructs the PIX Firewall that when a packet needs to be sent to an address in the 10.0.2.0 network, send it to the router on the inside interface at 10.0.1.3.
Because there are routers on the inside, dmz2, and dmz1 interfaces with two networks connecting to each, six static route command statements are required—two for each interface.
Table 5-6 lists a four-interface configuration.
| Configuration | Description |
|---|---|
nameif ethernet0 outside security0
nameif ethernet1 inside security100
nameif ethernet2 dmz1 security40
nameif ethernet3 dmz2 security60
interface ethernet0 auto
interface ethernet1 auto
interface ethernet2 auto
interface ethernet3 auto
| PIX Firewall provides nameif and interface command statements for the interfaces in the default configuration. |
ip address outside 209.165.201.1 255.255.255.224
ip address dmz1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip address dmz2 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip address inside 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.0
| Identify the IP address for each interface. |
hostname pixfirewall
| Specify the host name for the PIX Firewall. This name appears in the command line prompt. |
arp timeout 14400
| Set the ARP timeout to 14,400 seconds (four hours). This command statement is provided in the default configuration. |
no failover
| Disable failover access. |
names
| Lets you use text strings instead of IP addresses, which makes your configuration easier to read. |
pager lines 24
| Enable paging so that if after 24 lines of information display, PIX Firewall pauses the listing and prompts you to continue. |
logging buffered debugging
| Enable syslog messages, which provide diagnostic information and status for the PIX Firewall. You can view the messages with the show logging command and clear the message buffer with the clear logging command. |
no rip inside passive
no rip outside passive
no rip inside default
no rip outside default
| Disable RIP attributes. |
route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 209.165.201.2 1
| Set the outside default route to the router attached to the Internet. |
access-list acl_in permit icmp any any
access-group acl_in in interface inside
access-list acl_out permit icmp any any
access-list acl_dmz1 permit icmp any any
access-list acl_dmz2 permit icmp any any
| Allow inbound and outbound pings. When you are done ping testing, remove these lines. Permitting anyone to ping through the PIX Firewall adds extra overhead to the PIX Firewall and permits attackers to probe network vulnerabilities. The access-group commands for the "acl_out," "acl_dmz1," and "acl_dmz2" access-list command statement groups appear later in the configuration. |
timeout xlate 3:00:00 conn 1:00:00
half-closed 0:10:00 udp 0:02:00
timeout rpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00
timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute
| Default values for the maximum duration that PIX Firewall resources can remain idle until being freed. |
no snmp-server location
no snmp-server contact
snmp-server community public
| Specify that SNMP information may be accessed by internal hosts that know the community string, but PIX Firewall does not send trap information to any host. |
mtu outside 1500
mtu inside 1500
mtu dmz1 1500
mtu dmz2 1500
| Set the maximum transmission unit value for Ethernet access. You need to add the MTU command statements for the dmz1 and dmz2 interfaces. |
telnet 10.0.1.4 255.255.255.255
telnet timeout 15
| Give Telnet access to PIX Firewall console to inside host. Use the timeout feature to let Telnet console sessions stay idle up to 15 minutes before PIX Firewall closes the connection. The default is 5 minutes. |
nat (inside) 1 0 0
| Let inside users start connections on all lower security level interfaces: dmz1, dmz2, and the outside. |
nat (dmz2) 1 0 0
| Let dmz2 users start connections on all lower security level interfaces: dmz1 and the outside. |
nat (dmz1) 1 0 0
| Let dmz1 users start connections on all lower security level interfaces, which in this case, is the outside. |
global (dmz2) 1 10.2.1.10-10.2.1.30 netmask
255.255.255.0
| Give access to the dmz2 interface for users on the inside interface. This global command statement lets inside users access the dmz2 web server and provides access to the 10.2.2.0 and 10.2.3.0 networks. |
global (dmz1) 1 10.1.1.10-10.1.1.254 netmask
255.255.255.0
| Give access to the dmz1 interface for users on the inside and dmz2 interfaces. This global command statement lets inside and dmz2 users access the dmz1 mail server and provides access to the 10.1.2.0 and 10.1.3.0 networks. |
global (outside) 1 209.165.201.10-209.165.201.254
netmask 255.255.255.224
global (outside) 1 209.165.201.8 netmask
255.255.255.224
| Create a pool of global addresses for the outside interface to permit users on all other interfaces to access the Internet. Because there are potentially more than 244 users on the 3 other interfaces, add a PAT global to handle overflow. |
static (dmz1,outside) 209.165.201.5 10.1.1.2
access-list acl_out permit tcp any host
209.165.201.5 eq smtp
access-group acl_out in interface outside
| Let outside users access the 10.1.1.2 mail server on the dmz1 interface. The outside users access the mail server via global address 209.165.201.5 on the outside interface. The access-list command statement lets users access the mail server on port 25 (smtp). The access-group command binds the "acl_out" access-list command statement group to the outside interface. The access-group command also applies to the other "acl_out" group access-list command statements that follow. |
static (dmz2,outside) 209.165.201.6 10.2.1.2
access-list acl_out permit tcp any host
209.165.201.6 eq www
| Let outside users access the 10.2.1.2 web server on the dmz2 interface. The outside users access the web server via global address 209.165.201.6 on the outside interface. The access-list command statement lets users access the web server on port 80 (www). |
static (inside,outside) 209.165.201.7 10.0.1.2
access-list acl_out permit tcp any host
209.165.201.7 eq telnet
| Let outside users access the 10.0.1.2 Telnet server on the inside interface. The outside users access the Telnet server via global address 209.165.201.7 on the outside interface. The access-list command statement lets users access the Telnet server on port 23 (telnet). |
static (dmz2,dmz1) 10.1.1.6 10.2.1.2
access-list acl_dmz1 permit tcp any host 10.1.1.6 eq
www
access-group acl_dmz1 in interface dmz1
| Let dmz1 users access the 10.2.1.2 web server on the dmz2 interface. The dmz1 users access the web server via global address 10.1.1.6 on the dmz1 interface. The access-list command statement lets users access the web server on the WWW port (80). The access-group command binds the "acl_dmz1" access-list command statement group to the dmz1 interface. The access-group command also applies to the other "acl_dmz1" group access-list command statements that follow. |
static (inside,dmz1) 10.1.1.7 10.0.1.2
access-list acl_dmz1 permit tcp any host 10.1.1.7 eq
telnet
| Let dmz1 users access the 10.0.1.2 Telnet server on the inside interface. The dmz1 users access the Telnet server via global address 10.1.1.7 on the dmz1 interface. The access-list command statement lets users access the Telnet server on port 23 (telnet). |
static (inside,dmz2) 10.2.1.7 10.0.1.2
access-list acl_dmz2 permit tcp any host 10.2.1.7 eq
telnet
access-group acl_dmz2 in interface dmz2
| Let dmz2 users access the 10.0.1.2 Telnet server on the inside interface. The dmz2 users access the Telnet server via global address 10.2.1.7 on the dmz2 interface. The access-list command statement lets users access the Telnet server on port 23 (telnet). The access-group command binds the "acl_dmz2" access-list command statement group to the dmz2 interface. |
route dmz1 10.1.2.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.1.3 1
route dmz1 10.1.3.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.1.3 1
| Provide static routes so that packets destined for the 10.1.2.0 and 10.1.3.0 networks are sent to the 10.1.1.3 router on the dmz1 interface. |
route dmz2 10.2.2.0 255.255.255.0 10.2.1.3 1
route dmz2 10.2.3.0 255.255.255.0 10.2.1.3 1
| Provide static routes so that packets destined for the 10.2.2.0 and 10.2.3.0 networks are sent to the 10.2.1.3 router on the dmz2 interface. |
route inside 10.0.2.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.1.3 1
route inside 10.0.3.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.1.3 1
| Provide static routes so that packets destined for the 10.0.2.0 and 10.0.3.0 networks are sent to the 10.0.1.3 router on the inside interface. |
In Figure 5-7, the PIX Firewall has six interfaces. In this configuration, there is no user authentication and no authorization. NAT (Network Address Translation) is in effect to translate addresses. In this example, users on all interfaces have access to all the servers and hosts on the inside, dmz1, dmz2, dmz3, and dmz4 interfaces can start connections.
This section includes the following topics:
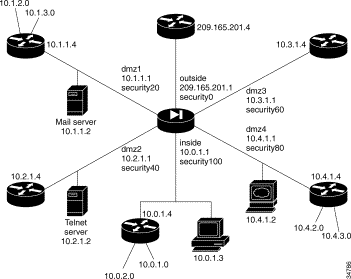
Configuring PIX Firewall for six interfaces is similar to the four interface example except that you have two more interfaces.
This section includes the following topics:
The most important guidelines to remember follow:
The sections that follow provide more information on these guidelines.
To let users on each higher security level interface access servers on each lower security level interface, follow these steps:
Step 1 Letting higher security level interface users access a lower security level interface has two components: you use the nat command to specify from where users start connections, and you use the global command to specify to where access is permitted. You associate the nat and global commands together with the NAT ID, which in this example configuration is 1. The nat command lets users start connections from the specified interface to all lower security interfaces, the global command permits access to translated connections from any higher security level interface.
nat (inside) 1 0 0
nat (dmz1) 1 0 0
nat (dmz2) 1 0 0
nat (dmz3) 1 0 0
nat (dmz4) 1 0 0
Step 2 Create global pools for the connections to start on each lower level interface:
global (outside) 1 209.165.201.10-209.165.201.30 netmask 255.255.255.224
global (dmz1) 1 10.1.1.10-10.1.1.254 netmask 255.255.255.0
global (dmz2) 1 10.2.1.10-10.2.1.254 netmask 255.255.255.0
global (dmz3) 1 10.3.1.10-10.3.1.254 netmask 255.255.255.0
To let users on a lower security level interface access a server on a higher security level interface, use the static and access-list command statements. The first IP address in the static command is the address users on the lower security level interface use when they want to access the server on the higher security level interface. The second IP address is the actual address of the server.
When you enter the static command statement in your configuration, always specify the security level of the interfaces as (higher,lower) and the IP addresses as lower and higher; for example:
static (inside,dmz1) 10.1.1.7 10.0.1.2
When users on the dmz1 interface access the Telnet server, they use IP address 10.1.1.7.
To let users on each lower security level interface access servers on each higher security level interface, follow these steps:
Step 1 To let users on the outside interface access the mail server on the dmz1 interface, use the following command:
static (dmz1,outside) 209.165.201.5 10.1.1.2 netmask 255.255.255.255
access-list acl_out permit tcp any host 209.165.201.5 eq smtp
access-group acl_out in interface outside
Step 2 To let users on the outside interface access the Telnet server on the dmz2 interface, use the following command:
static (dmz2,outside) 209.165.201.7 10.2.1.2 netmask 255.255.255.255
access-list acl_out permit tcp any host 209.165.201.7 eq telnet
Step 3 To let users on the dmz1 interface access the Telnet server on the dmz2 interface, use the following command:
static (dmz2,dmz1) 10.1.1.7 10.2.1.2
access-list acl_dmz1 permit tcp any host 10.1.1.7 eq telnet
access-group acl_dmz1 in interface dmz1
All configuration command statements are explained in greater detail in Table 5-7.
Once you sketch out your network and map these steps to your IP addresses and servers, the six-interface configuration becomes a simpler task.
The addresses used in this configuration are as follows:
In addition, static route command statements are required to permit access to the networks that connect to the routers. A static route command statement directs traffic meant for a network to the router on the interface. The format for a static route is shown in the following example:
route inside 10.0.2.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.1.4 1
This command statement instructs the PIX Firewall that when a packet needs to be sent to an address in the 10.0.2.0 network, send it to the router on the inside interface at 10.0.0.4.
Because there are routers on the inside, dmz1, and dmz4 interfaces with two networks connecting to each, six static route command statements are required—two for each interface.
Table 5-7 lists a six-interface configuration.
| Configuration | Description |
|---|---|
nameif ethernet0 outside security0
nameif ethernet1 inside security100
nameif ethernet2 dmz1 security20
nameif ethernet3 dmz2 security40
nameif ethernet4 dmz3 security60
nameif ethernet5 dmz4 security80
| PIX Firewall provides nameif command statements for all interfaces. In this case, the default perimeter names were changed to dmz1 through dmz4.
|
interface ethernet0 auto
interface ethernet1 auto
interface ethernet2 auto
interface ethernet3 auto
interface ethernet4 auto
interface ethernet5 auto
| PIX Firewall provides interface command statements for all six interfaces in the default configuration |
ip address outside 209.165.201.1 255.255.255.224
ip address dmz1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip address dmz2 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip address dmz3 10.3.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip address dmz4 10.4.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip address inside 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.0
| Identify the IP address for each interface. |
hostname pixfirewall
| Specify the host name for the PIX Firewall. This name appears in the command line prompt. |
arp timeout 14400
| Set the ARP timeout to 14,400 seconds (four hours). This command statement is provided in the default configuration. |
no failover
| Disable failover access. |
names
| Lets you use text strings instead of IP addresses, which makes your configuration easier to read. |
pager lines 24
| Enable paging so that if after 24 lines of information displays, PIX Firewall pauses the listing and prompts you to continue. |
logging buffered debugging
| Enable syslog messages, which provide diagnostic information and status for the PIX Firewall. You can view the messages with the show logging command and clear the message buffer with the clear logging command. |
no rip inside passive
no rip inside default
no rip outside passive
no rip outside default
no rip dmz1 passive
no rip dmz1 default
no rip dmz2 passive
no rip dmz2 default
no rip dmz3 passive
no rip dmz3 default
no rip dmz4 passive
no rip dmz4 default
| Disable RIP attributes. Add command statements for the perimeter interfaces. |
route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 209.165.201.4 1
| Set the outside default route to the router attached to the Internet. |
route dmz1 10.1.2.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.1.4 1
route dmz1 10.1.3.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.1.4 1
| Provide static routes so that packets destined for the 10.1.2.0 and 10.1.3.0 networks are sent to the 10.1.1.4 router on the dmz1 interface. |
route dmz4 10.4.2.0 255.255.255.0 10.4.1.4 1
route dmz4 10.4.3.0 255.255.255.0 10.4.1.4 1
| Provide static routes so that packets destined for the 10.4.2.0 and 10.4.3.0 networks are sent to the 10.4.1.4 router on the dmz4 interface. |
route inside 10.0.2.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.1.4 1
route inside 10.0.3.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.1.4 1
| Provide static routes so that packets destined for the 10.1.2.0 and 10.0.3.0 networks are sent to the 10.0.1.4 router on the inside interface. |
access-list acl_ping permit icmp any any
access-list acl_out permit icmp any any
access-list acl_dmz1 permit icmp any any
access-group acl_ping in interface inside
access-group acl_ping in interface dmz2
access-group acl_ping in interface dmz3
access-group acl_ping in interface dmz4
| Allow inbound and outbound pings. When you are done ping testing, remove these command statements to prevent extra overhead and vulnerability from probing. The access-group command statements for the "acl_out" and "acl_dmz1" command groups appear later in the configuration. |
timeout xlate 3:00:00 conn 1:00:00
half-closed 0:10:00 udp 0:02:00
timeout rpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00
timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute
| Default values for the maximum duration that PIX Firewall resources can remain idle until being freed. |
no snmp-server location
no snmp-server contact
snmp-server community public
| Specify that SNMP information may be accessed by internal hosts that know the community string, but PIX Firewall does not send trap information to any host. |
mtu outside 1500
mtu inside 1500
mtu dmz1 1500
mtu dmz2 1500
mtu dmz3 1500
mtu dmz4 1500
| Set the maximum transmission unit value for Ethernet access. You need to add the MTU command statements for the perimeter interfaces. |
telnet 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.255
telnet timeout 15
| Give Telnet access to PIX Firewall console to users on the Telnet server on dmz2 host. PIX Firewall checks the interface IP address to ensure it is an internal interface. This lets users outside the network Telnet to the server and then access the PIX Firewall console from the server. This is one method that can be used to troubleshoot or administer a PIX Firewall from a remote location. Use the timeout command feature to let Telnet console sessions stay idle up to 15 minutes before PIX Firewall closes the connection. The default is 5 minutes. |
nat (inside) 1 0 0
| Let inside users start connections on all lower security level interfaces: dmz1, dmz2, dmz3, dmz4, and the outside. |
nat (dmz1) 1 0 0
| Let dmz1 users start connections on the lower security level interface: the outside. |
nat (dmz2) 1 0 0
| Let dmz2 users start connections on all lower security level interfaces: dmz1 and the outside. |
nat (dmz3) 1 0 0
| Let dmz3 users start connections on all lower security level interfaces: dmz1, dmz2, and the outside. |
nat (dmz4) 1 0 0
| Let dmz4 users start connections on all lower security level interfaces: dmz1, dmz2, dmz3, and the outside. |
global (outside) 1 209.165.201.10-209.165.201.30
netmask 255.255.255.224
global (outside) 1 209.165.201.8 netmask
255.255.255.224
| Create a pool of global addresses for the outside interface to permit users on all other interfaces to access the Internet. Because there are a limited number of addresses in the global pool, add a PAT global to handle overflow. |
global (dmz1) 1 10.1.1.10-10.1.1.254 netmask
255.255.255.0
| Give access to the dmz1 interface for users on the dmz2, dmz3, dmz4, and the inside interfaces. This global command statement lets users on access these interfaces access the dmz1 mail server and provides access to the 10.1.2.0 and 10.1.3.0 networks. |
global (dmz2) 1 10.2.1.10-10.2.1.254 netmask
255.255.255.0
| Give access to the dmz2 interface for users on the inside interface. This global command statement lets inside users on the dmz3, dmz4, and inside access to the Telnet server of dmz2. |
global (dmz3) 1 10.3.1.10-10.3.1.254
| Give access to the dmz3 interface for users on the inside and dmz4 interfaces. |
global (dmz4) 1 10.4.1.10-10.4.1.254 netmask
255.255.255.0
| Give access to the dmz4 interface for users on the inside interface which also permits access to the 10.4.2.0 and 10.4.3.0 networks connected to the 10.4.1.4 router. |
static (dmz1,outside) 209.165.201.6 10.1.1.2 netmask
255.255.255.255
access-list acl_out permit tcp any host
209.165.201.6 eq smtp
| Give outside users access to the mailserver on the dmz1 interface. |
static (dmz2,outside) 209.165.201.7 10.2.1.2 netmask
255.255.255.255
access-list acl_out permit tcp any host
209.165.201.7 eq telnet
access-group acl_out in interface outside
| Give outside users access to the Telnet server on the dmz2 interface. |
static (dmz2,dmz1) 10.1.1.6 10.2.1.2 netmask
255.255.255.255
access-list acl_dmz1 permit tcp any host 10.1.1.6 eq
telnet
access-group acl_dmz1 in interface dmz1
| Give dmz1 users access to the Telnet server on the dmz2 interface. |
Figure 5-8 lists the network diagram for a failover configuration.
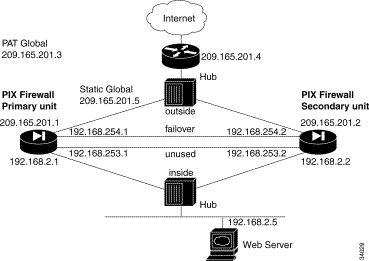
Follow these steps to configure the PIX Firewall units for use with failover:
Step 1 Set up the PIX Firewall without failover information.
Step 2 Add the failover ip address command for all interfaces including the one for the dedicated failover interface and any unused interfaces.
If there are any interfaces that have not been configured in the non-failover setup, configure them at this time with an IP address and a failover IP address. Also connect any unused interfaces to each other (a cross-over cable works great) so that the failover check-up messages can be sent and received properly. PIX Firewall requires that unused interfaces be connected to the Standby unit as well.
Step 3 If you want to configure Stateful Failover, add the failover link command and specify the interface the Stateful Failover will be using. For Stateful Failover, you must have a dedicated 100baseTx Stateful Failover interface in addition to all other interfaces.
Step 4 Use the write memory command on the Primary unit to save the new configuration.
Step 5 Plug the failover cable into the Primary unit and then power up the Secondary unit.
 |
Note If the Secondary unit has been previously configured, before you connect it to the failover cable to the Primary unit, boot it up, and enter the write erase command to remove any configuration. This will ensure a smooth synchronization. |
Step 6 Enter the write standby command from the Active unit to synchronize the current configuration to the Flash memory on the Standby unit.
In the example configuration in "Failover Configuration," the Ethernet2 interface (labeled "failover") is used as the dedicated interface for Stateful Failover. The Ethernet3 interface is a previously unconfigured interface and is currently not connected to any active network. There is a cross-over Ethernet cable connecting the unused interface so that the failover check up messages can be sent and received.
 |
Note PIX Firewall requires that unused interfaces be connected to the Standby unit and that each unused interface must be assigned an IP address. Even if an interface is administratively shut down, the PIX Firewall will try to send the failover check up messages to all internal interfaces. |
Table 5-8 lists the failover configuration.
| Configuration | Description |
|---|---|
nameif ethernet0 outside security0
nameif ethernet1 inside security100
nameif ethernet2 failover security10
nameif ethernet3 unused security20
| These statements identify the four interfaces. The "failover" interface is connected to the other PIX Firewall unit for use by Stateful Failover to convey messages between the units. |
enable password xxx encrypted
passwd xxx encrypted
hostname pixfirewall
fixup protocol ftp 21
fixup protocol http 80
fixup protocol smtp 25
fixup protocol h323 1720
fixup protocol rsh 514
fixup protocol sqlnet 1521
names
pager lines 20
| These default configuration command statements are for the following:
|
no logging timestamp
no logging standby
logging console errors
no logging monitor
no logging buffered
no logging trap
logging facility 20
logging queue 512
| The logging console errors command statement enables syslog message display at the console so that error, critical, and alert syslog messages are displayed. The logging facility 20 and logging queue 512 set the default values for the syslog message facility and message queue size. |
interface ethernet0 auto
interface ethernet1 auto
interface ethernet2 100full
interface ethernet3 auto
| The interface command statements set the outside and inside Ethernet interfaces for auto sensing. The first perimeter interface is set for 100baseTx, full-duplex, and the second perimeter interface is also set to auto sense. |
mtu outside 1500
mtu inside 1500
mtu failover 1500
mtu unused 1500
| The mtu command statements set the maximum transmission unit value to 1500 bytes, the default Ethernet setting. |
ip address outside 209.165.201.1 | The ip address command statements establish the IP addresses for each PIX Firewall interface. The outside interface is a NIC-registered address, whereas all other interfaces use the 192.168.n.n RFC 1918 Class C address. |
failover
failover ip address outside 209.165.201.2
failover ip address inside 192.168.2.2
failover ip address failover 192.168.254.2
failover ip address unused 192.168.253.2
failover link failover
| The failover command statements enable failover and specify the IP addresses of each interface on the Standby unit. If you are using Stateful Failover, the failover link command specifies the name of the Stateful Failover interface, in this case, the "failover" interface. |
arp timeout 14400
| Specify that ARP refresh its table every 4 hours. |
global (outside) 1 209.165.201.3 netmask
255.255.255.224
nat (inside) 1 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0 0
| Specify a PAT global for translating connections from the inside interface to the outside interface. Let all hosts on the inside start connections to the outside interface. |
static (inside,outside) 209.165.201.5 | Identify a global static address on the outside interface for a web server on the inside interface. The access-list command statements permit any host on the outside to access the inside web server on port 80, and to permit Pings on all interfaces. |
no rip outside passive
no rip outside default
no rip inside passive
no rip inside default
no rip failover passive
no rip failover default
| These rip command statements disable RIP listening on all interfaces. |
route outside 0 0 209.165.201.4 1
| Identify the outside router as the default router for the PIX Firewall. |
timeout xlate 3:00:00 conn 1:00:00 half-closed
0:10:00 udp 0:02:00
timeout rpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00
timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute
| The timeout commands specify the maximum durations that PIX Firewall resources can remain idle until being freed. These values are the default intervals. |
aaa-server TACACS+ protocol tacacs+
aaa-server RADIUS protocol radius
no snmp-server location
no snmp-server contact
snmp-server community public
no snmp-server enable traps
telnet timeout 5
terminal width 80
| These command statements are part of the default configuration that perform the following purposes:
|
In this example, two PIX Firewall units are used to create a Virtual Private Network (VPN) between the networks on each firewall unit's inside interface. This network is part of an intranet and therefore uses RFC 1918 addressing throughout.
In this example, the VPN is created without the use of IKE or a CA. Pre-shared keys are used.
The interfaces are as follows:
This section includes the following topics:
Follow these steps to program the PIX Firewall 1 unit for IPSec:
Step 1 Create a crypto map command statement.
Step 2 Create the access-list entries to select traffic for this policy.
 |
Note For manual keying, only one access-list permit command statement is permitted in the configuration. |
Step 3 Create the transform set for the crypto command statement entry.
Step 4 Define cryptographic state informations. These include SPI, and the necessary keys for manual keying and policy negotiation for ISAKMP.
Step 5 Repeat Steps 1-4 for each group of policies.
Step 6 Associate the crypto map command statement with an interface.
Table 5-9 lists the configuration for PIX Firewall 1.
| Configuration | Description |
nameif ethernet0 outside security0
nameif ethernet1 inside security100
interface ethernet0 auto
interface ethernet1 auto
| PIX Firewall provides nameif and interface command statements for the interfaces in the default configuration. |
ip address outside 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip address inside 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
| Identify the IP addresses for both interfaces. |
enable password 8Ry2YjIyt7RRXU24 encrypted
passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted
hostname pixfirewall
| Default values for the privileged mode password and host name. |
fixup protocol ftp 21
fixup protocol http 80
fixup protocol smtp 25
fixup protocol h323 1720
fixup protocol rsh 514
fixup protocol sqlnet 1521
| Default values that assign a port value for each service that the PIX Firewall provides special handling for. |
no failover
failover ip address outside 0.0.0.0
failover ip address inside 0.0.0.0
| Default settings to disable failover. |
names
pager lines 24
| Default settings that lets you use text strings instead of IP addresses, which makes your configuration easier to read, and sets the screen output so 24 lines display at a time before you are prompted to continue. |
no logging timestamp
logging console debugging
logging monitor errors
logging buffered errors
no logging trap
logging facility 20
| Enable syslog output to the console to receive debugging messages. |
mtu outside 1500
mtu inside 1500
| Default Ethernet MTU settings. |
arp timeout 14400
| Default value for the ARP timeout set to 14,400 seconds (four hours). Entries are kept in the ARP table for four hours before they are flushed. |
nat (inside) 1 0 0
| Permit all inside users to start outbound connections using the translated IP addresses from the global pool. |
global (outside) 1 192.168.1.100-192.168.1.150
| Create a pool of global addresses that translated addresses use when they exit the firewall from the protected networks to the unprotected networks. The global command statement is associated with a nat command statement by the nat_ID, which in this example is 1. |
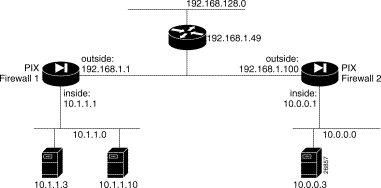
static (inside,outside) 192.168.128.3 10.1.1.3
netmask 255.255.255.255 0 0
| Create an inbound access address on the outside of the intranet on the 192.168.128.0 network so that the 10.1.1.3 server on PIX Firewall 1 is accessible from that network. |
no rip outside passive
no rip outside default
no rip inside passive
no rip inside default
| Default settings to disable RIP listening and broadcasting. |
route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.49 1
| Establish a default route on the outside interface so that packets are routed to the router on the outside interface. |
timeout xlate 3:00:00 conn 1:00:00 half-closed
0:10:00 udp 0:02:00
timeout rpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00
timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute
| Default timeout settings. |
no snmp-server location
no snmp-server contact
snmp-server community public
no snmp-server enable traps
| Default settings that disable SNMP access. |
sysopt connection tcpmss 1380
| |
sysopt connection permit-ipsec
| Enable IPSec traffic to bypass the check of conduit or access-group command statements. If you disable this option, you need to add a conduit command statement to your configuration to allow the required set of IPSec traffic. |
crypto map mymap 10 ipsec-manual
| Create a crypto map called "mymap" and specify with the ipsec-manual option that IKE will not be used to establish the IPSec security association. |
crypto ipsec transform-set myset ah-md5-hmac
esp-des
crypto map mymap 10 set transform-set myset
| Establish the transform set as myset, enable MD5 AH, and enable ESP with 56-bit DES encryption. Then associate the transform set with the crypto map entry. |
access-list 10 permit ip host 192.168.128.3
host 209.165.200.225
| Permit IP traffic and permit IP access from some external host on another network. |
crypto map mymap 10 match address 10
| Associate the map entry with the access list. |
crypto map mymap 10 set peer 192.168.1.100
| Establish PIX Firewall 2 as the peer. When IKE is not used, as in this example, only one peer is specified. |
crypto map mymap 10 set session-key inbound ah
400 123456789A123456789A123456789A12
| Establish the inbound AH session key. The SPI (security parameter index) is set to 400 and the string of characters after the SPI is the session key specified in hexadecimal. |
crypto map mymap 10 set session-key outbound ah
300 123456789A123456789A123456789A12
| Establish the outbound AH session key. The SPI is set to 300 and the string of characters after the SPI is the session key specified in hexadecimal. |
crypto map mymap 10 set session-key inbound esp
400 cipher abcd1234abcd1234
| Establish the inbound ESP session key. The SPI is set to 400. The cipher option indicates that the key string that follows the option is to be used with the ESP encryption transform. |
crypto map mymap 10 set session-key outbound
esp 300 cipher abcd1234abcd1234
| Establish the outbound ESP session key. The SPI is set to 300 and the cipher and authenticator keys are set to the same values as the inbound command statement. |
telnet timeout 5
terminal width 80
| Default values for the duration in minutes that a Telnet console session can be idle before being logged off, and for the number of characters wide that display during the console session. |
crypto map mymap interface outside
| Apply the crypto map set to the interface through which IPSec traffic will flow. |
Follow these steps to program the PIX Firewall 2 unit for IPSec:
Step 1 Create a crypto map command statement.
Step 2 Create the access-list entries to select traffic for this policy.
 |
Note For manual keying, only one access-list permit command statement is permitted in the configuration. |
Step 3 Create the transform set for the crypto command statement entry.
Step 4 Define cryptographic state informations. These include SPI, and the necessary keys for manual keying and policy negotiation for ISAKMP.
Step 5 Repeat steps 1-4 for each group of policies.
Step 6 Associate the crypto map command statement with an interface.
Table 5-10 lists the configuration for PIX Firewall 2.
| Configuration | Description |
nameif ethernet0 outside security0
nameif ethernet1 inside security100
interface ethernet0 auto
interface ethernet1 auto
| PIX Firewall provides nameif and interface command statements for the interfaces in the default configuration. |
ip address outside 209.165.201.3
255.255.255.224
ip address inside 10.0.0.3 255.255.255.0
| Identify the IP addresses for both interfaces. |
enable password 8Ry2YjIyt7RRXU24 encrypted
passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted
hostname pixfirewall
| Default values for the privileged mode password and host name. |
fixup protocol ftp 21
fixup protocol http 80
fixup protocol smtp 25
fixup protocol h323 1720
fixup protocol rsh 514
fixup protocol sqlnet 1521
| Default values that assign a port value for each service that the PIX Firewall provides special handling for. |
no failover
failover ip address outside 0.0.0.0
failover ip address inside 0.0.0.0
| Default settings to disable failover. |
names
pager lines 24
| Default settings that lets you use text strings instead of IP addresses, which makes your configuration easier to read, and sets the screen output so 24 lines display at a time before you are prompted to continue. |
no logging timestamp
logging console debugging
logging monitor errors
logging buffered errors
no logging trap
logging facility 20
| Enable syslog output to the console to receive debugging messages. |
mtu outside 1500
mtu inside 1500
| Default Ethernet MTU settings. |
arp timeout 14400
| Default value for the ARP timeout set to 14,400 seconds (four hours). Entries are kept in the ARP table for four hours before they are flushed. |
nat (inside) 1 0 0
| Permit all inside users to start outbound connections using the translated IP addresses from the global pool. |
static (inside,outside) 209.165.200.225
10.0.0.3 netmask 255.255.255.255 0 0
| Create a static mapping between the inside host and an external address beyond the outside router. |
access-list 10 permit ip host 209.165.200.225
host 192.168.128.3
| Permit access to the static mapping from the 192.168.128.0 network outside the router. |
route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.49 1
route inside 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.0.3 1
| Create the default route to the outside router, and a static route to send packets on the inside interface. |
timeout xlate 3:00:00 conn 1:00:00 half-closed
0:10:00 udp 0:02:00
timeout rpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00
timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute
| Default timeout settings. |
no snmp-server location
no snmp-server contact
snmp-server community public
no snmp-server enable traps
| Default settings that disable SNMP access. |
no rip outside passive
no rip outside default
no rip inside passive
no rip inside default
| Default settings to disable RIP listening and broadcasting. |
crypto map mymap 10 ipsec-manual
| Create a crypto map called "mymap" and specify with the ipsec-manual option that IKE will not be used to establish the IPSec security association. |
crypto ipsec transform-set myset ah-md5-hmac
esp-des
crypto map mymap 10 set transform-set myset
| Establish the transform set as myset, enable MD5 AH, and enable ESP with 56-bit DES encryption. Then associate the transform set with the crypto map entry. The transform set is used in the IPSec security association negotiation to protect the data flows specified by that crypto map entry's access list. Because IKE is not used to establish security associations, a single transform set must be used. The transform set is not negotiated. |
sysopt connection tcpmss 1380
| Set the TCP maximum segment size to 1380 bytes. This is recommended for data over the encrypted VPN channel. This value is set by default but does not display in the default configuration. |
crypto map mymap 10 match address 10
| Associate the map entry with the access list. |
crypto map mymap 10 set peer 192.168.1.1
| Establish PIX Firewall 1 as the peer. When IKE is not used, as in this example, only one peer is specified. |
crypto map mymap 10 set session-key inbound ah
300 123456789A123456789A123456789A12
| Establish the inbound AH session key. The SPI (security parameter index) is set to 300 and the string of characters after the SPI is the session key specified in hexadecimal. The SPI for PIX Firewall 2 is opposite of the values specified for PIX Firewall 1 (PIX Firewall 1 has an inbound SPI of 400 and an outbound SPI of 300). |
crypto map mymap 10 set session-key outbound ah
400 123456789A123456789A123456789A12
| Establish the outbound AH session key. The SPI is set to 400 and the string of characters after the SPI is the session key specified in hexadecimal. |
crypto map mymap 10 set session-key inbound esp
300 cipher abcd1234abcd1234
| Establish the inbound ESP session key. The SPI is set to 300. The cipher option indicates that the key string that follows the option is to be used with the ESP encryption transform. |
crypto map mymap 10 set session-key outbound
esp 400 cipher abcd1234abcd1234
| Establish the outbound ESP session key. The SPI is set to 400 and the cipher and authenticator keys are set to the same values as the inbound command statement. |
telnet timeout 5
terminal width 80
| Default values for the duration in minutes that a Telnet console session can be idle before being logged off, and for the number of characters wide that display during the console session. |
This section includes the following topics:
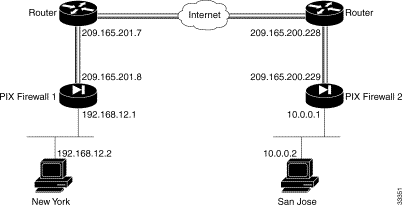
This example uses the network diagram shown in Figure 5-10:
Follow these steps to configure PIX Firewall 1:
Step 1 Define a host name:
hostname NewYork
Step 2 Define the domain name:
domain-name example.com
Step 3 Create a net static:
static (inside,outside) 192.168.12.0 192.168.12.0 netmask 255.255.255.0
Step 4 Configure an ISAKMP policy:
isakmp enable outside
isakmp policy 9 authentication pre-share
isakmp policy 9 encr 3des
Step 5 Configure pre-shared key and associate with the peer:
crypto isakmp key cisco1234 address 209.165.200.229
Step 6 Configure the supported IPSec transforms:
crypto ipsec transform-set strong esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
Step 7 Create an access list:
access-list 90 permit ip 192.168.12.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
Step 8 Define a crypto map:
crypto map toSanJose 20 ipsec-isakmp
crypto map toSanJose 20 match address 90
crypto map toSanJose 20 set transform-set strong
crypto map toSanJose 20 set peer 209.165.200.229
Step 9 Apply the crypto map to the outside interface:
crypto map toSanJose interface outside
Step 10 Specify that IPSec traffic be implicitly trusted (permitted):
sysopt connection permit-ipsec
Table 5-11 lists the configuration for PIX Firewall 1.
| Configuration | Description |
nameif ethernet0 outside security0
nameif ethernet1 inside security100
interface ethernet0 auto
interface ethernet1 auto
| PIX Firewall provides nameif and interface command statements for the interfaces in the default configuration. |
enable password 8Ry2YjIyt7RRXU24 encrypted
passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted
| Default values for the privileged mode password and the Telnet password. |
hostname NewYork
| Define a host name for the PIX Firewall. |
domain-name example.com
| Set the domain name. |
fixup protocol ftp 21
fixup protocol http 80
fixup protocol smtp 25
fixup protocol h323 1720
fixup protocol rsh 514
fixup protocol sqlnet 1521
| Default fixup protocol values that define port usage. |
names
pager lines 24
no logging on
| Default values that let you use names instead of an IP addresses, display 24 lines of text before you are prompted to continue, and disable syslog output. |
mtu outside 1500
mtu inside 1500
| Set the maximum transmission unit values for the Ethernet interfaces. |
ip address outside 209.165.201.8 255.255.255.224
ip address inside 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
| The IP addresses for each PIX Firewall interface. |
no failover
failover ip address outside 0.0.0.0
failover ip address inside 0.0.0.0
| Default values to disable failover. |
arp timeout 14400
| Default value specifying that the ARP cache be reinitialized every four hours. |
nat (inside) 0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0 0
| Disable NAT for the inside interface. |
nat 0 access-list 90
access-list 90 permit ip 192.168.12.0
255.255.255.0 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
| The nat 0 access-list command statement lets you to exempt traffic that is matched by the access-list command statement from the NAT services. Adaptive Security remains in effect with the nat 0 access-list command. The access-list command statement permits IP traffic on all hosts on the inside network to be accessed by the hosts on PIX Firewall 2. |
no rip outside passive
no rip outside default
rip inside passive
no rip inside default
| Default values to disable RIP listening or broadcasting. However, the inside interface does listen for RIP broadcasts. |
route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 209.165.201.7 1
| Specify the router on the outside interface for default routes. |
timeout xlate 3:00:00 conn 1:00:00 half-closed
0:10:00 udp 0:02:00
timeout rpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00
timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute
| Default timer values. |
aaa-server TACACS+ protocol tacacs+
aaa-server RADIUS protocol radius
| Default values that permit access to the TACACS+ or RADIUS protocols; however, AAA is not used in this configuration. |
no snmp-server location
no snmp-server contact
snmp-server community public
no snmp-server enable traps
| Default values to disable SNMP access. |
crypto ipsec transform-set strong esp-3des
esp-sha-hmac
crypto map toSanJose 20 ipsec-isakmp
crypto map toSanJose 20 match address 90
crypto map toSanJose 20 set peer 209.165.200.229
crypto map toSanJose 20 set transform-set strong
crypto map toSanJose interface outside
| Define the crypto map transforms, specify ISAKMP access, match the map to the access list (both use ID 90 to be associated), set the tunnel peer to be the outside interface IP address of PIX Firewall 2 (209.165.200.229), and apply the crypto map to the outside interface. |
isakmp enable outside
isakmp key cisco1234 address 209.165.200.229
netmask 255.255.255.255
isakmp policy 9 authentication pre-share
isakmp policy 9 encryption 3des
| Configure the ISAKMP policy. |
sysopt connection permit-ipsec
| Specify that IPSec traffic be implicitly trusted (permitted). |
telnet timeout 5
terminal width 80
| Default values for how long a Telnet console session can be idle and that a console session should display up to 80 characters wide on the console computer. |
Follow these steps to configure PIX Firewall 2:
Step 1 Define a host name:
hostname SanJose
Step 2 Define the domain name:
domain-name example.com
Step 3 Create a net static:
static (inside,outside) 10.0.0.0 10.0.0.0 netmask 255.0.0.0
Step 4 Configure the ISAKMP policy:
isakmp enable outside
isakmp policy 8 authentication pre-share
isakmp policy 8 encryption 3des
Step 5 Configure a pre-shared key and associate it with the peer:
crypto isakmp key cisco1234 address 209.165.201.8
Step 6 Configure IPSec supported transforms:
crypto ipsec transform-set strong esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
Step 7 Create an access list:
access-list 80 permit ip 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 192.168.12.0 255.255.255.0
Step 8 Define a crypto map:
crypto map newyork 10 ipsec-isakmp
crypto map newyork 10 match address 80
crypto map newyork 10 set transform-set strong
crypto map newyork 10 set peer 209.165.201.8
Step 9 Apply the crypto map to an interface:
crypto map newyork interface outside
Step 10 Specify that IPSec traffic be implicitly trusted (permitted):
sysopt connection permit-ipsec
Table 5-12 lists the configuration for PIX Firewall 2.
| Configuration | Description |
nameif ethernet0 outside security0
nameif ethernet1 inside security100
nameif ethernet2 dmz security50
nameif ethernet3 perimeter security40
| PIX Firewall provides nameif command statements for interfaces in the default configuration. In addition, the default configuration provides default names for the perimeter interfaces, but in this case, the configuration requires different names and security levels for the perimeter interfaces. |
enable password 8Ry2YjIyt7RRXU24 encrypted
passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted
| Default values for the privileged mode password and the Telnet password. |
hostname SanJose
| Define a host name for the PIX Firewall. |
domain-name example.com
| Set the domain name. |
fixup protocol ftp 21
fixup protocol http 80
fixup protocol smtp 25
fixup protocol h323 1720
fixup protocol rsh 514
fixup protocol sqlnet 1521
| Default fixup protocol values that define port usage. |
names
pager lines 24
no logging on
| Default values that let you use names instead of an IP addresses, display 24 lines of text before you are prompted to continue, and disable syslog output. |
interface ethernet0 auto
interface ethernet1 auto
interface ethernet2 auto
interface ethernet3 auto
| Default interface definitions indicating that each Ethernet interface has automatic sensing capabilities to determine line speed and duplex. |
mtu outside 1500
mtu inside 1500
mtu dmz 1500
mtu perimeter 1500
| Set the maximum transmission unit values for the Ethernet interfaces. |
ip address outside 209.165.200.229
255.255.255.224
ip address inside 10.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
ip address dmz 192.168.101.1 255.255.255.0
ip address perimeter 192.168.102.1 255.255.255.0
| The IP addresses for each PIX Firewall interface. |
no failover
failover ip address outside 0.0.0.0
failover ip address inside 0.0.0.0
failover ip address dmz 0.0.0.0
failover ip address perimeter 0.0.0.0
| Default values to disable failover. |
arp timeout 14400
| Default value specifying that the ARP cache be reinitialized every four hours. |
nat 0 access-list 80
access-list 80 permit ip 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
192.168.12.0 255.255.255.0
| The nat 0 access-list command statement lets you to exempt traffic that is matched by the access-list command statement from the NAT services. Adaptive Security remains in effect with the nat 0 access-list command. The access-list command statement permits IP traffic on all hosts on the inside network to be accessed by the hosts on PIX Firewall 1. |
no rip outside passive
no rip outside default
no rip inside passive
no rip inside default
no rip dmz passive
no rip dmz default
no rip perimeter passive
no rip perimeter default
| Default values to disable RIP listening or broadcasting. |
route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 209.165.200.228 1
| Specify the router on the outside interface for default routes. |
timeout xlate 3:00:00 conn 1:00:00 half-closed
0:10:00 udp 0:02:00
timeout rpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00
timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute
| Default timer values. |
aaa-server TACACS+ protocol tacacs+
aaa-server RADIUS protocol radius
| Default values that permit access to the TACACS+ or RADIUS protocols; however, AAA is not used in this configuration. |
no snmp-server location
no snmp-server contact
snmp-server community public
no snmp-server enable traps
| Default values to disable SNMP access. |
crypto ipsec transform-set strong esp-3des
esp-sha-hmac
crypto map newyork 10 ipsec-isakmp
crypto map newyork 10 match address 80
crypto map newyork 10 set peer 209.165.201.8
crypto map newyork 10 set transform-set strong
crypto map newyork interface outside
| Define the crypto map transforms, specify ISAKMP access, match the map to the access list (both use ID 80 to be associated), set the tunnel peer to be the outside interface IP address of PIX Firewall 1 (209.165.201.8), and apply the crypto map to the outside interface. |
isakmp enable outside
isakmp key cisco1234 address 209.165.201.8
netmask 255.255.255.255
isakmp policy 8 authentication pre-share
isakmp policy 8 encryption 3des
| Configure the ISAKMP policy. |
sysopt connection permit-ipsec
| Specify that IPSec traffic be implicitly trusted (permitted). |
telnet timeout 5
terminal width 80
| Default values for how long a Telnet console session can be idle and that a console session should display up to 80 characters wide on the console computer. |
This section includes the following topics:
This example uses the network diagram shown in Figure 5-11:
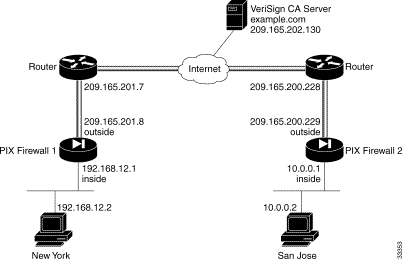
Follow these steps to configure PIX Firewall 1:
Step 1 Define a host name:
hostname NewYork
Step 2 Define the domain name:
domain-name example.com
Step 3 Create a net static:
static (inside,outside) 192.168.12.0 192.168.12.0
Step 4 Configure an ISAKMP policy:
isakmp enable outside
isakmp policy 8 auth rsa-signature
Step 5 Define VeriSign-related enrollment commands:
ca identity example.com 209.165.202.130
ca configure example.com ca 2 100 crloptional
These commands are stored in the configuration. "2" is the retry period, "100" is the retry count, and the crloptional option disables CRL checking.
Step 6 Generate an RSA key pair:
ca generate rsa key 512
This command is not stored in the configuration.
Step 7 Get the public key and the certificate of the CA server:
ca authenticate example.com
This command is not stored in the configuration.
Step 8 Contact your CA administrator and send your certificate request:
ca enroll example.com abcdef
"abcdef" is a challenge password. This can be anything. This command is not stored in the configuration.
Step 9 Configure supported IPSec transforms:
crypto ipsec transform-set strong esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
Step 10 Save keys, certificates, and CRLs in Flash memory:
ca save all
 |
Note Use the ca save all command any time you add, change, or delete ca commands in the configuration. This command is not stored in the configuration. |
Step 11 Create a partial access list:
access-list 90 permit ip 192.168.12.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
Step 12 Define a crypto map:
crypto map toSanJose 20 ipsec-isakmp
crypto map toSanJose 20 match address 90
crypto map toSanJose 20 set transform-set strong
crypto map toSanJose 20 set peer 209.165.200.229
Step 13 Apply the crypto map to the outside interface:
crypto map toSanJose interface outside
Step 14 Specify that IPSec traffic be implicitly trusted (permitted):
sysopt connection permit-ipsec
Table 5-13 lists the configuration for PIX Firewall 1.
| Configuration | Description |
nameif ethernet0 outside security0
nameif ethernet1 inside security100
| PIX Firewall provides nameif command statements for the interfaces in the configuration. |
enable password 8Ry2YjIyt7RRXU24 encrypted
passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted
| Default values for the privileged mode password and the Telnet password. |
hostname NewYork
| Define a host name for the PIX Firewall. |
domain-name example.com
| Set the domain name. |
fixup protocol ftp 21
fixup protocol http 80
fixup protocol smtp 25
fixup protocol h323 1720
fixup protocol rsh 514
fixup protocol sqlnet 1521
| Default fixup protocol values that define port usage. |
names
pager lines 24
no logging on
| Default values that let you use names instead of an IP addresses, display 24 lines of text before you are prompted to continue, and disable syslog output. |
interface ethernet0 auto
interface ethernet1 auto
| Default interface definitions indicating that each Ethernet interface has automatic sensing capabilities to determine line speed and duplex. |
mtu outside 1500
mtu inside 1500
| Set the maximum transmission unit values for the Ethernet interfaces. |
ip address outside 209.165.201.8 255.255.255.224
ip address inside 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
| The IP addresses for each PIX Firewall interface. |
no failover
failover ip address outside 0.0.0.0
failover ip address inside 0.0.0.0
| Default values to disable failover. |
arp timeout 14400
| Default value specifying that the ARP cache be reinitialized every four hours. |
nat (inside) 0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0 0
| Disable NAT for the inside interface. |
nat 0 access-list 90
access-list 90 permit ip 192.168.12.0
255.255.255.0 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
| The nat 0 access-list command statement lets you to exempt traffic that is matched by the access-list command statement from the NAT services. Adaptive Security remains in effect with the nat 0 access-list command. The access-list command statement permits IP traffic on all hosts on the inside network to be accessed by the hosts on PIX Firewall 2. |
no rip outside passive
no rip outside default
rip inside passive
no rip inside default
| Default values to disable RIP listening or broadcasting. However, the inside interface does listen for RIP broadcasts. |
route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 209.165.200.227 1
| Specify the router on the outside interface for default routes. |
timeout xlate 3:00:00 conn 1:00:00 half-closed
0:10:00 udp 0:02:00
timeout rpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00
timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute
| Default timer values. |
aaa-server TACACS+ protocol tacacs+
aaa-server RADIUS protocol radius
| Default values that permit access to the TACACS+ or RADIUS protocols; however, AAA is not used in this configuration. |
no snmp-server location
no snmp-server contact
snmp-server community public
no snmp-server enable traps
| Default values to disable SNMP access. |
crypto ipsec transform-set strong esp-3des
esp-sha-hmac
crypto map toSanJose 20 ipsec-isakmp
crypto map toSanJose 20 match address 90
crypto map toSanJose 20 set peer 209.165.200.229
crypto map toSanJose 20 set transform-set strong
crypto map toSanJose interface outside
| Define the crypto map transforms, specify ISAKMP access, match the map to the access list (both use ID 90 to be associated), set the tunnel peer to be the outside interface IP address of PIX Firewall 2 (209.165.200.229), and apply the crypto map to the outside interface. |
isakmp enable outside
isakmp policy 9 encryption 3des
| Configure the ISAKMP policy. |
ca identity example.com
209.165.202.130:cgi-bin/pkiclient.exe
ca configure example.com ca 1 100 crloptional
| Define VeriSign-related enrollment commands. |
sysopt connection permit-ipsec
| Specify that IPSec traffic be implicitly trusted (permitted). |
telnet timeout 5
terminal width 80
| Default values for how long a Telnet console session can be idle and that a console session should display up to 80 characters wide on the console computer. |
Follow these steps to configure PIX Firewall 2:
Step 1 Define a host name:
hostname SanJose
Step 2 Define the domain name:
domain-name example.com
Step 3 Create a net static:
static (inside,outside) 192.168.12.0 192.168.12.0
Step 4 Configure an ISAKMP policy:
isakmp enable outside
isakmp policy 8 auth rsa-signature
Step 5 Define VeriSign-related enrollment commands:
ca identity example.com 209.165.202.130
ca configure example.com ca 1 20 crloptional
These commands are stored in the configuration. 1 is the retry period, 20 is the retry count, and the crloptional option disables CRL checking.
Step 6 Generate an RSA key pair:
ca generate rsa key 1024
This command is entered at the command line and does not get stored in the configuration.
Step 7 Get the public key and the certificate of the CA server:
ca authenticate example.com
This command is entered at the command line and does not get stored in the configuration.
Step 8 Contact your CA administrator and send your certificate request:
ca enroll example.com abcdef
"abcdef" is a challenge password. This can be anything. This command is entered at the command line and does not get stored in the configuration.
Step 9 Configure supported IPSec transforms:
crypto ipsec transform-set strong esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
Step 10 Save keys, certificates, and CRLs in Flash memory:
ca save all
 |
Note Use the ca save all command any time you add, change, or delete ca commands in the configuration. This command is not stored in the configuration. |
Step 11 Create a partial access list:
access-list 80 permit ip 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 192.168.12.0 255.255.255.0
Step 12 Define a crypto map:
crypto map newyork 10 ipsec-isakmp
crypto map newyork 10 match address 80
crypto map newyork 10 set transform-set strong
crypto map newyork 10 set peer 209.165.201.8
Step 13 Apply the crypto map to the outside interface:
crypto map toSanJose interface outside
Step 14 Specify that IPSec traffic be implicitly trusted (permitted):
sysopt connection permit-ipsec
Table 5-14 lists the configuration for PIX Firewall 2.
| Configuration | Description |
nameif ethernet0 outside security0
nameif ethernet1 inside security100
nameif ethernet2 dmz security50
nameif ethernet3 perimeter security40
| PIX Firewall provides nameif command statements interfaces in the default configuration, but in this case, the configuration required different names and security levels for the perimeter interfaces. |
enable password 8Ry2YjIyt7RRXU24 encrypted
passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted
| Default values for the privileged mode password and the Telnet password. |
hostname SanJose
| Define a host name for the PIX Firewall. |
domain-name example.com
| Set the domain name. |
fixup protocol ftp 21
fixup protocol http 80
fixup protocol smtp 25
fixup protocol h323 1720
fixup protocol rsh 514
fixup protocol sqlnet 1521
| Default fixup protocol values that define port usage. |
names
pager lines 24
no logging on
| Default values that let you use names instead of an IP addresses, display 24 lines of text before you are prompted to continue, and disable syslog output. |
interface ethernet0 auto
interface ethernet1 auto
interface ethernet2 auto
interface ethernet3 auto
| Default interface definitions indicating that each Ethernet interface has automatic sensing capabilities to determine line speed and duplex. |
mtu outside 1500
mtu inside 1500
mtu dmz 1500
mtu perimeter 1500
| Set the maximum transmission unit values for the Ethernet interfaces. |
ip address outside 209.165.200.229 255.255.255.224
ip address inside 10.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
ip address dmz 192.168.101.1 255.255.255.0
ip address perimeter 192.168.102.1 255.255.255.0
| The IP addresses for each PIX Firewall interface. |
no failover
failover ip address outside 0.0.0.0
failover ip address inside 0.0.0.0
failover ip address dmz 0.0.0.0
failover ip address perimeter 0.0.0.0
| Default values to disable failover. |
arp timeout 14400
| Default value specifying that the ARP cache be reinitialized every four hours. |
nat (inside) 0 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 0 0
| Disable NAT for the inside interface. |
nat 0 access-list 80
access-list 80 permit ip 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
192.168.12.0 255.255.255.0
| The nat 0 access-list command statement lets you to exempt traffic that is matched by the access-list command statement from the NAT services. Adaptive Security remains in effect with the nat 0 access-list command. The access-list command statement permits IP traffic on all hosts on the inside network to be accessed by the hosts on PIX Firewall 1. |
no rip outside passive
no rip outside default
no rip inside passive
no rip inside default
no rip dmz passive
no rip dmz default
no rip perimeter passive
no rip perimeter default
| Default values to disable RIP listening or broadcasting. |
route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 209.165.200.227 1
| Specify the router on the outside interface for default routes. |
timeout xlate 3:00:00 conn 1:00:00 half-closed
0:10:00 udp 0:02:00
timeout rpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00
timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute
| Default timer values. |
aaa-server TACACS+ protocol tacacs+
aaa-server RADIUS protocol radius
| Default values that permit access to the TACACS+ or RADIUS protocols; however, AAA is not used in this configuration. |
no snmp-server location
no snmp-server contact
snmp-server community public
no snmp-server enable traps
| Default values to disable SNMP access. |
crypto ipsec transform-set strong esp-3des
esp-sha-hmac
crypto map newyork 10 ipsec-isakmp
crypto map newyork 10 match address 80
crypto map newyork 10 set peer 209.165.201.8
crypto map newyork 10 set transform-set strong
crypto map newyork interface outside
| Define the crypto map transforms, specify ISAKMP access, match the map to the access list (both use ID 80 to be associated), set the tunnel peer to be the outside interface IP address of PIX Firewall 1 (209.165.201.8), and apply the crypto map to the outside interface. |
isakmp enable outside
isakmp key cisco1234 address 209.165.201.8 netmask
255.255.255.255
isakmp policy 8 encryption 3des
| Configure the ISAKMP policy. |
ca identity example.com
209.165.202.130:cgi-bin/pkiclient.exe
ca configure example.com ca 1 20 crloptional
| Define VeriSign-related enrollment commands. |
sysopt connection permit-ipsec
| Specify that IPSec traffic be implicitly trusted (permitted). |
telnet timeout 5
terminal width 80
| Default values for how long a Telnet console session can be idle and that a console session should display up to 80 characters wide on the console computer. |
This section includes the following topics:
This example uses the network diagram shown in Figure 5-12:
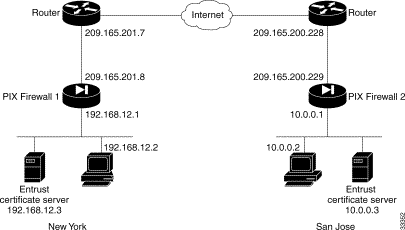
Follow these steps to configure PIX Firewall 1:
Step 1 Define a host name:
hostname NewYork
Step 2 Define the domain name:
domain-name example.com
Step 3 Create a net static:
static (inside,outside) 192.168.12.0 192.168.12.0 netmask 255.255.255.0
Step 4 Configure an ISAKMP policy:
isakmp enable outside
isakmp policy 8 auth rsa-sig
Step 5 Define Entrust-related enrollment commands:
ca identity abcd 209.165.200.228 209.165.200.228
ca configure abcd ra 1 20 crloptional
These commands are stored in the configuration. 1 is the retry period, 20 is the retry count, and the crloptional option disables CRL checking.
Step 6 Generate an RSA key pair:
ca generate rsa specialkey 512
This command is entered at the command line and does not get stored in the configuration.
Step 7 Get the public key and the certificate of the CA server:
ca authenticate abcd
This command is entered at the command line and does not get stored in the configuration.
Step 8 Contact your CA administrator and send your certificate request:
ca enroll abcd cisco
"cisco" is a challenge password. This can be anything. This command is entered at the command line and does not get stored in the configuration.
Step 9 Configure supported IPSec transforms:
crypto ipsec transform-set strong esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
Step 10 Save keys, certificates, and CRLs in Flash memory:
ca save all
 |
Note Use the ca save all command any time you add, change, or delete ca commands in the configuration. This command is not stored in the configuration. |
Step 11 Create a partial access list:
access-list 90 permit ip 192.168.12.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
Step 12 Define a crypto map.
crypto map toSanJose 20 ipsec-isakmp
crypto map toSanJose 20 match address 90
crypto map toSanJose 20 set transform-set strong
crypto map toSanJose 20 set peer 209.165.200.229
Step 13 Apply the crypto map to the outside interface:
crypto map toSanJose interface outside
Step 14 Specify that IPSec traffic be implicitly trusted (permitted):
sysopt connection permit-ipsec
Table 5-15 lists the configuration for PIX Firewall 1.
| Configuration | Description |
nameif ethernet0 outside security0
nameif ethernet1 inside security100
| PIX Firewall provides nameif command statements for the inside and outside interfaces in the default configuration. |
enable password 8Ry2YjIyt7RRXU24 encrypted
passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted
| Default values for the privileged mode password and the Telnet password. |
hostname NewYork
| Define a host name for the PIX Firewall. |
domain-name example.com
| Set the domain name. |
fixup protocol ftp 21
fixup protocol http 80
fixup protocol smtp 25
fixup protocol h323 1720
fixup protocol rsh 514
fixup protocol sqlnet 1521
| Default fixup protocol values that define port usage. |
names
pager lines 24
no logging on
| Default values that let you use names instead of an IP addresses, display 24 lines of text before you are prompted to continue, and disable syslog output. |
interface ethernet0 auto
interface ethernet1 auto
| Default interface definitions indicating that each Ethernet interface has automatic sensing capabilities to determine line speed and duplex. |
mtu outside 1500
mtu inside 1500
| Set the maximum transmission unit values for the Ethernet interfaces. |
ip address outside 209.165.201.8 255.255.255.224
ip address inside 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
| The IP addresses for each PIX Firewall interface. |
no failover
failover ip address outside 0.0.0.0
failover ip address inside 0.0.0.0
| Default values to disable failover. |
arp timeout 14400
| Default value specifying that the ARP cache be reinitialized every four hours. |
nat 0 access-list 90
access-list 90 permit ip 192.168.12.0
255.255.255.0 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
| The nat 0 access-list command statement lets you to exempt traffic that is matched by the access-list command statement from the NAT services. Adaptive Security remains in effect with the nat 0 access-list command. The access-list command statement permits IP traffic on all hosts on the inside network to be accessed by the hosts on PIX Firewall 2. |
no rip outside passive
no rip outside default
rip inside passive
no rip inside default
| Default values to disable RIP listening or broadcasting. However, the inside interface does listen for RIP broadcasts. |
route outside 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 209.165.200.229 1
route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 209.165.200.227 1
| Specify a static route to access the inside network of PIX Firewall 2. Specify the router on the outside interface for default routes. |
timeout xlate 3:00:00 conn 1:00:00 half-closed
0:10:00 udp 0:02:00
timeout rpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00
timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute
| Default timer values. |
aaa-server TACACS+ protocol tacacs+
aaa-server RADIUS protocol radius
| Default values that permit access to the TACACS+ or RADIUS protocols; however, AAA is not used in this configuration. |
no snmp-server location
no snmp-server contact
snmp-server community public
no snmp-server enable traps
| Default values to disable SNMP access. |
crypto ipsec transform-set strong esp-3des
esp-sha-hmac
crypto map toSanJose 20 ipsec-isakmp
crypto map toSanJose 20 match address 90
crypto map toSanJose 20 set peer 209.165.200.229
crypto map toSanJose 20 set transform-set strong
crypto map toSanJose interface outside
| Define the crypto map transforms, specify ISAKMP access, match the map to the access list (both use ID 90 to be associated), set the tunnel peer to be the outside interface IP address of PIX Firewall 2 (209.165.200.229), and apply the crypto map to the outside interface. |
isakmp enable outside
isakmp policy 9 encryption 3des
| Configure the ISAKMP policy. |
ca identity abcd
209.165.200.228:cgi-bin/pkiclient.exe
209.165.200.228
ca configure abcd ra 1 100 crloptional
| Define Entrust-related enrollment commands. |
sysopt connection permit-ipsec
| Specify that IPSec traffic be implicitly trusted (permitted). |
telnet timeout 5
terminal width 80
| Default values for how long a Telnet console session can be idle and that a console session should display up to 80 characters wide on the console computer. |
Follow these steps to configure PIX Firewall 2:
Step 1 Define a host name:
hostname SanJose
Step 2 Define the domain name:
domain-name example.com
Step 3 Create a net static:
static (inside,outside) 10.0.0.0 10.0.0.0 netmask 255.0.0.0
Step 4 Configure an ISAKMP policy:
isakmp enable outside
isakmp policy 8 auth rsa-sig
Step 5 Define Entrust-related enrollment commands:
ca identity my_nickname 209.165.200.228 209.165.200.228
ca configure my_nickname ra 1 20 crloptional
These commands are stored in the configuration. 1 is the retry period, 20 is the retry count, and the crloptional option disables CRL checking.
Step 6 Generate an RSA key pair:
ca generate rsa specialkey 512
This command is entered at the command line and does not get stored in the configuration.
Step 7 Get the public key and the certificate of the CA server:
ca authenticate abcd
This command is entered at the command line and does not get stored in the configuration.
Step 8 Contact your CA administrator and send your certificate request:
ca enroll abcd cisco
"cisco" is a challenge password. This can be anything. This command is entered at the command line and does not get stored in the configuration.
Step 9 Configure supported IPSec transforms:
crypto ipsec transform-set strong esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
Step 10 Save keys, certificates, and CRLs in Flash memory:
ca save all
 |
Note Use the ca save all command any time you add, change, or delete ca commands in the configuration. This command is not stored in the configuration. |
Step 11 Create a partial access list:
access-list 80 permit ip 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 192.168.12.0 255.255.255.0
Step 12 Define a crypto map:
crypto map newyork 20 ipsec-isakmp
crypto map newyork 20 match address 80
crypto map newyork 20 set transform-set strong
crypto map newyork 20 set peer 209.165.201.8
Step 13 Apply the crypto map to the outside interface:
crypto map newyork interface outside
Step 14 Specify that IPSec traffic be implicitly trusted (permitted):
sysopt connection permit-ipsec
Table 5-16 lists the configuration for PIX Firewall 2.
| Configuration | Description |
nameif ethernet0 outside security0
nameif ethernet1 inside security100
nameif ethernet2 dmz security50
nameif ethernet3 perimeter security40
| PIX Firewall provides nameif command statements for the inside and outside interfaces in the default configuration. In addition, the default configuration provides default names for the perimeter interfaces, but in this case, the configuration required different names and security levels for the perimeter interfaces. |
enable password 8Ry2YjIyt7RRXU24 encrypted
passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted
| Default values for the privileged mode password and the Telnet password. |
hostname SanJose
| Define a host name for the PIX Firewall. |
domain-name example.com
| Set the domain name. |
fixup protocol ftp 21
fixup protocol http 80
fixup protocol smtp 25
fixup protocol h323 1720
fixup protocol rsh 514
fixup protocol sqlnet 1521
| Default fixup protocol values that define port usage. |
names
pager lines 24
no logging on
| Default values that let you use names instead of an IP addresses, display 24 lines of text before you are prompted to continue, and disable syslog output. |
interface ethernet0 auto
interface ethernet1 auto
interface ethernet2 auto
interface ethernet3 auto
| Default interface definitions indicating that each Ethernet interface has automatic sensing capabilities to determine line speed and duplex. |
mtu outside 1500
mtu inside 1500
mtu dmz 1500
mtu perimeter 1500
| Set the maximum transmission unit values for the Ethernet interfaces. |
ip address outside 209.165.200.229
255.255.255.224
ip address inside 10.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
ip address dmz 192.168.101.1 255.255.255.0
ip address perimeter 192.168.102.1 255.255.255.0
| The IP addresses for each PIX Firewall interface. |
no failover
failover ip address outside 0.0.0.0
failover ip address inside 0.0.0.0
failover ip address dmz 0.0.0.0
failover ip address perimeter 0.0.0.0
| Default values to disable failover. |
arp timeout 14400
| Default value specifying that the ARP cache be reinitialized every four hours. |
nat 0 access-list 80
access-list 80 permit ip 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
192.168.12.0 255.255.255.0
| The nat 0 access-list command statement lets you to exempt traffic that is matched by the access-list command statement from the NAT services. Adaptive Security remains in effect with the nat 0 access-list command. The access-list command statement permits IP traffic on all hosts on the inside network to be accessed by the hosts on PIX Firewall 1. |
no rip outside passive
no rip outside default
no rip inside passive
no rip inside default
no rip dmz passive
no rip dmz default
no rip perimeter passive
no rip perimeter default
| Default values to disable RIP listening or broadcasting. |
route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 209.165.200.227 1
| Specify the router on the outside interface for default routes. |
timeout xlate 3:00:00 conn 1:00:00 half-closed
0:10:00 udp 0:02:00
timeout rpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00
timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute
| Default timer values. |
aaa-server TACACS+ protocol tacacs+
aaa-server RADIUS protocol radius
| Default values that permit access to the TACACS+ or RADIUS protocols; however, AAA is not used in this configuration. |
no snmp-server location
no snmp-server contact
snmp-server community public
no snmp-server enable traps
| Default values to disable SNMP access. |
crypto ipsec transform-set strong esp-3des
esp-sha-hmac
crypto map newyork 10 ipsec-isakmp
crypto map newyork 10 match address 80
crypto map newyork 10 set peer 209.165.201.8
crypto map newyork 10 set transform-set strong
crypto map newyork interface outside
| Define the crypto map transforms, specify ISAKMP access, match the map to the access list (both use ID 80 to be associated), set the tunnel peer to be the outside interface IP address of PIX Firewall 1 (209.165.201.8), and apply the crypto map to the outside interface. |
isakmp enable outside
isakmp policy 8 authentication pre-share
isakmp policy 8 encryption 3des
| Configure the ISAKMP policy. |
ca identity abcd
209.165.200.228:cgi-bin/pkiclient.exe
209.165.200.228
ca configure abcd ra 1 100 crloptional
| Define Entrust-related enrollment commands. |
sysopt connection permit-ipsec
| Specify that IPSec traffic be implicitly trusted (permitted). |
telnet timeout 5
terminal width 80
| Default values for how long a Telnet console session can be idle and that a console session should display up to 80 characters wide on the console computer. |
This section includes the following topics:
This example has several advantages:
Figure 5-13 illustrates the example network.
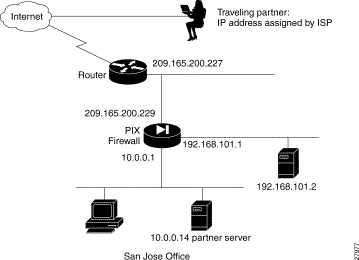
Follow these steps to configure the PIX Firewall to work with the VPN Client:
Step 1 Define AAA related parameters:
aaa-server TACACS+ protocol tacacs+
aaa-server partnerauth protocol tacacs+
aaa-server partnerauth (dmz) host 192.168.101.2 abcdef timeout 5
Step 2 Configure the IPSec-supported transforms:
crypto ipsec transform-set strong-des esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
Step 3 Create an access list that defines the virtual IP addresses for VPN Clients:
access-list 80 permit ip host 10.0.0.14 host 192.168.15.1
access-list 80 permit ip host 10.0.0.14 host 192.168.15.2
access-list 80 permit ip host 10.0.0.14 host 192.168.15.3
access-list 80 permit ip host 10.0.0.14 host 192.168.15.4
access-list 80 permit ip host 10.0.0.14 host 192.168.15.5
Step 4 Configure NAT 0.
nat 0 access-list 80
Step 5 Create a dynamic crypto map:
crypto dynamic-map cisco 4 set transform-set strong-des
Step 6 Define a crypto map:
crypto map partner-map 20 ipsec-isakmp dynamic cisco
Step 7 Apply the crypto map to the outside interface:
crypto map partner-map interface outside
Step 8 Configure a wildcard, pre-shared key:
isakmp key cisco1234 address 0.0.0.0 netmask 0.0.0.0
Step 9 Configure the ISAKMP policy:
isakmp enable outside
isakmp policy 8 authentication pre-share
isakmp policy 8 encr 3des
isakmp policy 8 hash md5
Step 10 Configure Xauth:
crypto map partner-map client authentication partnerauth
Step 11 Configure IKE mode config related parameters:
ip local pool dealer 192.168.15.1-192.168.15.5
crypto map partner-map client configuration address initiate
isakmp client configuration address-pool local dealer outside
Step 12 Tell PIX Firewall to implicitly permit IPSec traffic:
sysopt connection permit-ipsec
Table 5-17 provides the complete PIX Firewall configuration.
| Configuration | Description |
|---|---|
nameif ethernet0 outside security0
nameif ethernet1 inside security100
nameif ethernet2 dmz security10
| PIX Firewall provides nameif command statements for the inside and outside interfaces in the default configuration. This example shows the default name for the perimeter interface "dmz." |
enable password 8Ry2YjIyt7RRXU24 encrypted
passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted
| Default values for the privileged mode password and the Telnet password. |
hostname SanJose
| Define a host name for the PIX Firewall. |
domain-name example.com
| Set the domain name. |
fixup protocol ftp 21
fixup protocol http 80
fixup protocol smtp 25
fixup protocol h323 1720
fixup protocol rsh 514
fixup protocol sqlnet 1521
| Default fixup protocol values that define port usage. |
names
pager lines 24
no logging on
| Default values that let you use names instead of an IP addresses, display 24 lines of text before you are prompted to continue, and disable syslog output. |
interface ethernet0 auto
interface ethernet1 auto
interface ethernet2 auto
| Default interface definitions indicating that each Ethernet interface has automatic sensing capabilities to determine line speed and duplex. |
mtu outside 1500
mtu inside 1500
mtu dmz 1500
| Set the maximum transmission unit values for the Ethernet interfaces. |
ip address outside 209.165.200.229 255.255.255.224
ip address inside 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0
ip address dmz 192.168.101.1 255.255.255.0
| The IP addresses for each PIX Firewall interface. |
no failover
failover ip address outside 0.0.0.0
failover ip address inside 0.0.0.0
failover ip address dmz 0.0.0.0
| Default values to disable failover. |
arp timeout 14400
| Default value specifying that the ARP cache be reinitialized every four hours. |
nat (inside) 1 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0 0
| Let users on the inside interface start connections on an interface with a lower security level. |
global (outside) 1 209.165.200.45-209.165.200.50
netmask 255.255.255.224
| Establish a pool of global addresses on the outside interface for translated addresses to use when users on the inside start connections to the outside. |
|
|
route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 209.165.200.227 1
| Set the default route to be the router on the outside. |
timeout xlate 3:00:00 conn 1:00:00 half-closed
0:10:00 udp 0:02:00
timeout rpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00
timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute
| Default timeout values. |
ip local pool dealer 192.168.15.1-192.168.15.5
| Create a pool of IP addresses that remote users access after they are authenticated by the AAA server. |
aaa-server TACACS+ protocol tacacs+
aaa-server RADIUS protocol radius
aaa-server partnerauth protocol tacacs+
aaa-server partnerauth (dmz) host 192.168.101.2
abcdef timeout 5
| Establish the AAA parameters. The first two command statements enable access to the TACACS+ and RADIUS protocols. The next command statement associates the partnerauth protocol to TACACS+. |
no snmp-server location
no snmp-server contact
snmp-server community public
no snmp-server enable traps
| Default values to disable SNMP. |
crypto map partner-map client configuration
address initiate
| Specify the IKE mode configuration parameters. |
isakmp client configuration address-pool local
dealer outside
| Establish association to local pool of IP addresses. |
crypto ipsec transform-set strong esp-3des
esp-sha-hmac
| Create a transform set for Triple DES, ESP, SHA, and HMAC. |
crypto dynamic-map cisco 4 set transform-set
strong
| Create a dynamic crypto map that associates the access list and the transform set. |
crypto map partner-map 20 ipsec-isakmp dynamic
cisco
| Define a crypto map that enables the ISAKMP policy. |
crypto map partner-map client authentication
TACACS+
| Enable the Extended Authentication feature. Be sure to specify the same AAA server name within the crypto map client authentication command statement as was specified in the aaa-server command statement. |
crypto map partner-map interface outside
| Apply the crypto map to the outside interface. |
isakmp key cisco1234 address 0.0.0.0 netmask
0.0.0.0
| Create a wildcard, pre-shared key. |
isakmp enable outside
isakmp policy 8 authentication pre-share
isakmp policy 8 encryption 3des
isakmp policy 8 hash md5
| Create the ISAMP policy on the outside interface, to handle pre-shared keys, to have Triple DES encryption, and to provide an MD5 hash for additional security. |
sysopt connection permit-ipsec
| Implicitly permit IPSec connections through the PIX Firewall. |
telnet timeout 5
terminal width 80
| Default values for how long a Telnet console session can be idle and that a console session should display up to 80 characters wide on the console computer. |
This section describes how to configure the Cisco Secure VPN Client for use with the PIX Firewall. Refer to the Release Notes for the Cisco Secure VPN Client Version 1.1 or later for the most current information. Before performing the information in this section, install the VPN Client as described in the release notes. You can find the Cisco Secure VPN Client release notes online at the following site:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/iaabu/csvpnc/index.htm
Follow these steps to configure the Cisco Secure VPN Client:
Step 1 Click Start>Programs>Cisco Secure VPN Client>Security Policy Editor.
Step 2 Click Options>Secure>Specified Connections.
Step 3 In the Network Security Policy window, click Other Connection and click Non-Secure from the panel on the right.
Step 4 Click File>New Connection. Rename New Connection. For example, ToSanJose.
Step 5 In the Network Security Policy window, click the plus sign beside the ToSanJose entry to expand the selection, and click My Identity. Enter the following values in the panel on the right:
a. Select Certificate—Click None.
b. ID Type—Click IP address.
c. Port—Click All.
d. Local Network Interface—Click Any.
e. Click Pre-Shared Key. When the Pre-Shared Key dialog box appears, click Enter Key to make the key field editable. Enter cisco1234 and click OK.
Step 6 In the Network Security Policy window, expand Security Policy and enter the following values in the panel on the right:
a. Click Phase 1 Negotiation Mode—Click Main Mode.
b. Enable Replay Detection—Select the check box.
Leave any other values as they were in the panel.
Step 7 Click Security Policy>Authentication (Phase 1)>Proposal 1 and enter the following values in the panel on the right:
a. Authentication Method—Click Pre-shared Key.
b. Encrypt Alg—Click Triple DES.
c. Hash Alg—Click MD5.
d. SA Life—Click Unspecified to accept the default values.
e. Key Group—Click Diffie-Hellman Group 1.
Step 8 Click Security Policy>Key Exchange (Phase 2)>Proposal 1 and enter the following values in the panel on the right:
a. Select the Encapsulation Protocol (ESP) check box.
b. Encryption Alg—Click Triple DES.
c. Hash Alg—Click SHA-1.
d. Encapsulation—Click Tunnel.
Step 9 Click File>Save Changes.
The VPN Client is now activated.
You can view connection process by right-clicking the SafeNet/Soft-PK icon in the Windows taskbar. Unless the taskbar is changed, this icon appears in lower right of the screen. Click Log Viewer to display the View Log feature.
An example of a typical View Log session follows:
time_stamp ToSanJose - Deleting IKE SA
time_stamp ToSanJose - SENDING>>>>ISAKMP OAK QM *(HASH, SA, NON, ID, ID)
time_stamp ToSanJose - RECEIVED<<<ISAKMP OAK TRANS *(HASH. ATTR)
time_stamp ToSanJose - Received Private IP Address = 192.168.15.3
time_stamp ToSanJose - SENDING>>>>ISAKMP OAK TRANS *(HASH, ATTR)
time_stamp ToSanJose - RECEIVED<<<ISAKMP OAK QM *(HASH, SA, NON, ID, ID,
NOTIFY:STATUS_RESP_LIFETIME)
time_stamp ToSanJose - SENDING>>>> ISAKMP OAK QM *(HASH)
time_stamp ToSanJose - Loading IPSec SA keys...
time_stamp
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Tue Oct 22 15:15:26 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.