|
|

This chapter describes LocalDirector hardware platforms, including interface cards. This chapter contains the following sections:
LocalDirector introduced the 430 and 416 hardware platforms in Version 2.2.1. Support for the previous LocalDirector hardware platforms (the 410, 415, and 420, fully described in Version 2.1 of this guide) continues. Table 2-1 shows the features offered by the 416 and 430 platforms.
| LocalDirector 430 | LocalDirector 416 |
|---|---|
384 MB RAM | 32 MB RAM |
2 MB Flash memory | 2 MB Flash memory |
One 4-port 10/100 Ethernet interface card | Three 10/100 Ethernet ports |
LocalDirector 430 includes:
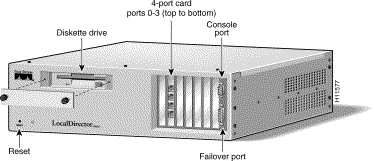
The front panel of LocalDirector 430 is shown in Figure 2-1. Note that the diskette drive, interfaces, console port, and failover port are accessed from the front panel.
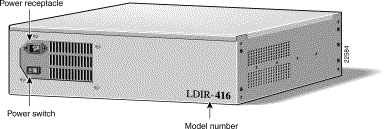
The back panel of both the LocalDirector 430 and 416 are shown in Figure 2-2. The power cord receptacle and power switch are located at the back of the units.
LocalDirector 416 includes:
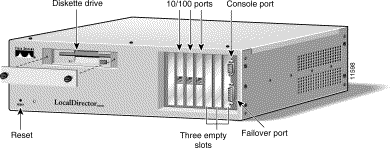
The front panel of LocalDirector 416 is shown in Figure 2-3.
Rack-mount brackets are optional on LocalDirector 430 and 416. Figure 2-4 shows you how to attach the brackets.
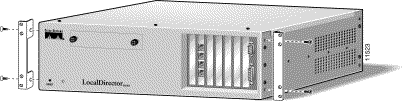
Table 2-2 shows the interfaces that are supported on LocalDirector platforms.
| Platform | 4-Port 10/100 Ethernet Card | 1-Port 10/100 Ethernet Card | FDDI |
|---|---|---|---|
| LocalDirector 430 |
| Not supported |
|
| LocalDirector 416 | Not supported |
| Not supported |
Interfaces on LocalDirector models are numbered left to right, top to bottom. Figure 2-5 shows the interface numbering for a LocalDirector 430 with four 4-port Ethernet interface cards installed.
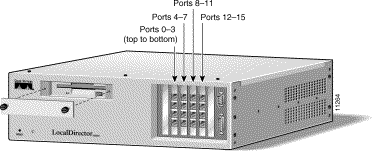
One 4-port Ethernet card is shipped standard with LocalDirector 430. Up to three more
4-port Ethernet cards can be added.
LocalDirector supports two types of 4-port Ethernet cards. To check the type of card you have, use the show interfaces command. The output of the command tells which type of card you have. Table 2-3 describes the types of 4-port Ethernet cards that ship with LocalDirector.
| Card Type | show interface Command Output | LED Color | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
RNS card | | Amber on left edge of card | Autodetection |
Intel card | | Green on right edge of card | Autonegotiation |
Each interface port has two LEDs, one amber and one green. Table 2-4 explains the states of the LEDs on the 4-port interface cards.
| LED | LED State | Indication |
|---|---|---|
Green | Off | No data transmission. |
On | Steady data transmission. | |
Flashing | Intermittent data transmission. | |
Amber | Off | Disabled or unused. If the interface is configured with the 10baset, 100basetx, or 100full options, the link is not up yet. |
On | The connection is active. | |
Flashing | Autosensing. If the interface is configured with the auto option, the link is not up yet. |
The 4-port rns23x0 Ethernet card does not accept the auto option with the interface ethernet command, and returns the following error message:
ERROR: this port does not have autonegotiation capability.
The ports on the 4-port rns23x0 Ethernet card default to 100BaseTX. The 10baset, 100basetx, and 100full options are available, but the auto option is not.
If the peer port autonegotiates, the 4-port rns23x0 Ethernet interface speed must be set with the 10baset or 100basetx options; setting it to 100full confuses the auto-negotiation process on the peer port, resulting in unpredictable behavior.
The LocalDirector 416 single-port Ethernet card and the LocalDirector 430 i82557 Ethernet card perform autonegotiation, but your network interface must support autodetection.
FDDI interface cards are optional on LocalDirector 430, and they cannot be mixed with Ethernet interfaces. FDDI interface cards support SMT 7.3.
An easy way to understand FDDI topology is to disregard the dual-attached interfaces. Treat dual-attached interfaces like single-attached interfaces; then treat FDDI like Ethernet; then the network topology looks like an Ethernet topology. Once the topology is determined, put the dual-attached interfaces back into the mix by keeping in mind that the dual-attached interfaces only provide topology redundancy---if a wire is cut, you have another wire to use as a backup. It does not mean you can attach additional servers because you have extra ports.
When installed in LocalDirector, port A is on the bottom of the interface, and port B is on the top as shown in Figure 2-6.

FDDI interface boards for LocalDirector have dual-attached SC connectors as shown in Figure 2-7.

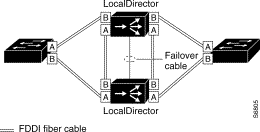
Figure 2-8 shows a LocalDirector failover implementation with FDDI interfaces.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Tue Feb 22 15:28:48 PST 2000
Copyright 1989 - 2000©Cisco Systems Inc.