|
|

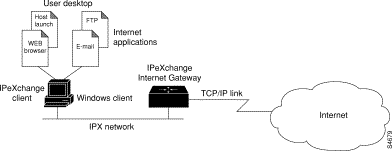
The IPeXchange Internet Gateway is an IPX-to-IP gateway: it connects Novell NetWare users to the Internet, an intranet, or other TCP/IP-based network services. IPeXchange allows NetWare client workstations to use TCP/IP-based applications such as Telnet, FTP, and Netscape Navigator without requiring a TCP/IP protocol stack on each workstation. Instead, the IPeXchange Internet Gateway provides a TCP/IP gateway with a single IP address for the IPX network.
The IPeXchange Internet Gateway is a client/server product.
The server is a Cisco router that runs the Cisco Internetwork Operating System (Cisco IOS) software as the IPeXchange server software. The server, which is also sometimes referred to as a gateway, is connected to both an IPX network and a TCP/IP-based network, such as the Internet.
An IPeXchange client is a Windows-based PC that runs the IPeXchange client software. The PC is connected to an IPX network.
Figure 1-1 illustrates the relationship between the IPeXchange components.
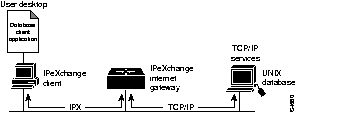
For sites with TCP/IP-based resources, such as UNIX databases, the IPeXchange Internet Gateway server acts as a protocol bridge that enables you to run client-based applications such as Oracle's SQL*Net or the Service Advertising Protocol (SAP) R3 client. Figure 1-2 illustrates how the IPeXchange Internet Gateway server can be used as an internal protocol bridge.
Cisco IOS software features--such as the ability to use access lists to control the traffic allowed to enter the IPX network--provide a security firewall between the IPX network and the Internet. These features eliminate the risk of intrusion from the Internet.
Some sites might benefit from having multiple Cisco routers acting as Internet gateways. Using multiple gateways can improve network performance and can provide backup access to the Internet. Figure 1-3 shows a network with multiple IPeXchange gateways.
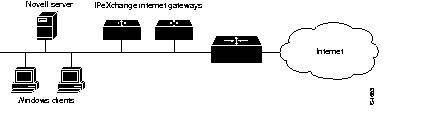
A bottleneck at the gateway's connection to the Internet, or excessive load on the gateway, can affect performance at the desktop. To determine whether the gateway is overloaded, monitor its CPU usage. Heavy CPU usage can indicate a need for additional IPeXchange gateways.
IPeXchange gateways perform automatic load sharing. Each IPeXchange gateway broadcasts Service Advertising Protocol (SAP) messages to advertise itself to clients.
If you want to manually divide your user community among gateways, you can specify each client's preferred gateway, as described in the chapter "Configure the IPeXchange Client Software" in the section "Perform Advanced Configuration Tasks."
Service can be interrupted by failure at the IPeXchange gateway or at the Internet connection. To provide uninterrupted service, consider adding redundancy. A fault-tolerant environment includes multiple IPeXchange gateways or multiple Internet connections, or both.
If an IPeXchange gateway fails, applications on IPeXchange clients connected to that gateway also fail. If you have additional gateways, IPeXchange client software automatically connects to the gateways that are running when desktop users restart their applications.
To ensure against failure of the network link to the service provider, consider adding a backup link.
For Windows 3.1, the IPeXchange client has these files:
For Windows 95, the IPeXchange client has these files:
The IPeXchange client components are shown in Figure 1-4.
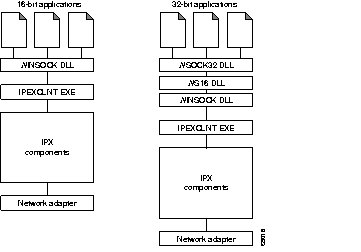
Windows Sockets (WinSock) is the application programming interface (API) generally used for writing Microsoft Windows applications over TCP/IP. WinSock is implemented as a dynamic link library (DLL), which is a set of executable functions that links with an application at runtime. The WINSOCK.DLL and WSOCK32.DLL provided with the IPeXchange client is an implementation of the WinSock 1.1 specifications that has been customized to run over IPX.
The ipexclnt.exe executable file encapsulates WinSock application requests into outgoing IPX packets and decapsulates incoming IPX packets to pass WinSock responses to applications. The client is resource-efficient: when Internet applications are not in use, the client releases memory by disconnecting from the gateway.
ipexclnt.exe uses approximately 180 kilobytes and WINSOCK.DLL approximately 90 kilobytes of high memory only. WSOCK32.DLL and WS16.DLL together use about 10 kilobytes of high memory.
IPeXchange client software supports the following Windows versions:
The IPeXchange server software runs with the Cisco IOS software.
Figure 1-5 shows the relationship between the IPeXchange server software, the network software, and the network hardware.
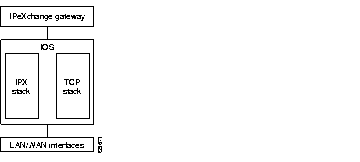
|
|