|
|

This feature module describes the Cisco IOS Inverse Multiplexing over ATM (IMA) features that are available for the Cisco 6015 and Cisco 6160 digital subscriber line access multiplexers (DSLAMs) with installed DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 cards. The IMA feature is available for the Cisco 6015 DSLAM in Cisco IOS Releases 12.1(4)DA and above. The IMA feature is available for the Cisco 6160 DSLAM in Cisco IOS Releases 12.1(5)DA and above.
This document includes the following sections:
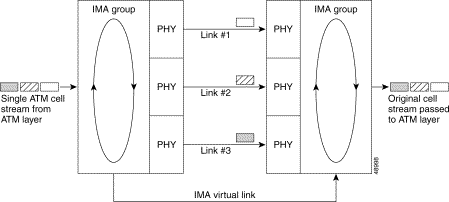
The T1/E1 inverse multiplexing over ATM (IMA) feature uses IMA technology to aggregate multiple low-speed links (T1/E1) into one or more IMA groups at speeds between 1.5 Mbps 16 Mbps. IMA breaks up the ATM cell stream and distributes the cells over the multiple physical links of an IMA group and then recombines the cells into a single stream at the other end of the connection. The multiple links of an IMA group increase the logical link bandwidth to approximately the sum of the individual link rates.
How IMA Works
IMA links transmit IMA control protocol (ICP) cells, which enable the reconstruction of the original ATM cell stream. ICP cells define and separate IMA frames passing through each physical link in an IMA group. ICP cells also control the operation of IMA by accounting for cell delay variation (CDV), which is introduced by ICP cells, and the link differential delays on physical links to ensure the proper reassembly of IMA frames. Using an IMA frame length of 128 cells, one out of every 128 cells on a physical link is an ICP cell. In this scenario, a frame containing fewer than 128 cells is injected with filler cells. The receiving end of an IMA group extracts the ICP and filler cells as the IMA stream is reconstructed into an ATM cell stream and passed to the ATM layer. IMA operation is transparent to ATM layer protocols. Therefore, the ATM layer operates as if a single physical interface were being used.
Figure 1 illustrates IMA with three bundled links.
Depending upon the installed I/O module (1DS3+8T1 I/O or 8xE1 I/O), IMA can be configured by grouping the following physical links (refer to the "Supported Platforms" section):
 |
Note Refer to the "Supported Platforms" section for detailed information on platform-specific support of the network I/O modules. |
The DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 supports three modes of operation:
 |
Note The type of network I/O module (1DS3+8T1 I/O or 8xE1 I/O) detected at system startup determines the mode of operation. |
The eight links on the DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 can be independent ATM links or can be configured into one or more IMA groups. There are four static IMA groups. Each IMA group can contain from zero to eight T1/E1 links. Any combination of independent T1/E1 links and IMA groups is allowed, up to eight T1/E1 links total.
Some examples of allowed combinations are
The T1/E1 IMA features for the Cisco 6015 and the Cisco 6160 offer the following benefits:
The DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 card supports the trunk selection feature for IOS Release 12.1(4)DA. This feature allows you to configure any WAN interface (the DS3, any T1 link, any E1 link, or any IMA group) as the trunk.
 |
Note When you configure a T1 link or an IMA group as the trunk (1DS3+8xT1 I/O module only), the DS3 port is disabled. When you select the DS3 port as the trunk, the T1 links and IMA groups are all treated as subtended ports. |
E1 IMA group bandwidth is limited to six links. Cell loss will occur if an IMA group has more than six links and more than 12 Mbps are sent through it. The loss only occurs on groups with greater than six E1 links. All eight links can be used in different groups, however (for example, six in group 0, two in group 1). This does not affect T1 operation (that is, all eight T1 links may be used in a group). Refer to the Release Notes for Cisco IOS Release 12.1(4)DA for Cisco DSLAMs with NI-2 DDTS report CSCdr45623 for more information.
Hardware Documents
A complete list of all DSL hardware product related documentation is available on the World Wide Web at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/dsl_prod/index.htm.
Software Documents
A complete list of all DSL IOS software product related documentation is available on the World Wide Web at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/dsl_prod/ios_dsl/rel121/index.htm.
In the following ATM software guides, look for information pertaining to the Cisco LightStream 1010, which uses the same software base as the NI-2 DSLAMs:
This Cisco 6015 and Cisco 6160 DSLAMs and the following components support the IMA feature:
| NI-2 | Chassis | I/O Module | Minimum IOS Release |
|---|---|---|---|
DS3+T1/E1 IMA | 6015 | 1DS3+8xT1 | 12.1(4)DA |
DS3+T1/E1 IMA | 6015 | 8xE1 | 12.1(4)DA |
DS3+T1/E1 IMA | 6160 | 1DS3+8xT1 | 12.1(5)DA |
DS3+T1/E1 IMA | 6260 | 8xE1 | Future |
Standards
The IMA feature supports the ATM Forum Technical Committee: Inverse Multiplexing for ATM (IMA) Specification Version 1.1 (AF-PHY-0086.001).
The IMA feature supports the ATM Forum Technical Committee: Inverse Multiplexing for ATM (IMA) Specification Version 1.0 (AF-PHY-0086.000).
MIBs
For descriptions of supported MIBs and how to use MIBs, see the Cisco MIB web site on CCO at http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml
RFCs
The IMA feature supports RFC 1406 and RFC 1407 (for DS3 trunks).
Before you can configure a Cisco 6015 or Cisco 6160 DSLAM to provide T1/E1 IMA service, you must perform the following tasks:
Perform the following tasks to configure ATM interfaces for IMA. Each task in the list is required.
Each link can be used as an independent T1/E1 ATM link with all the properties and functionality of ATM interfaces. When the link becomes part of an IMA group, its independent ATM functionality ceases; however, the IMA group can use ATM commands.
The DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 card supports the trunk selection feature for Release 12.1(4)DA. This feature allows you to configure any WAN interface (the DS3, any T1 link, any E1 link, or any IMA group) as the trunk. When you configure a T1 link or an IMA group as the trunk, the DS3 port is disabled. When you select the DS3 port as the trunk, the T1 links and IMA groups are all treated as subtended ports.
| Command | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 | DSLAM> enable
Password: <password>
DSLAM#
| Enter enable mode. Enter the password. You have entered enable mode when the prompt changes to |
Step 2 | DSLAM# configure terminal
| Enter global configuration mode. You have entered global configuration mode when the prompt changes to |
Step 3 | DSLAM(config)#atm ni2-switch trunk atm 0/1
| Select the interface to use as the trunk. |
Step 4 | DSLAM(config)#interface atm 0/1
| Enter interface configuration mode. You have entered interface configuration mode when the prompt changes to |
Step 5 | DSLAM(config-if)# | Disable the individual link by enabling the shutdown command. |
Step 6 | DSLAM(config-if)#clock source network-derived
| Select the transmit clock source for the link. |
Step 7 | DSLAM(config-if)# | Select the framing type for the link. |
Step 8 | DSLAM(config-if)# | Enable DS3 cell payload scrambling on the link. |
Step 9 | DSLAM(config-if)#lbo short
| Specify the line build out (short or long), followed by the length. You can view the acceptable lengths by including the? option after the long or short commands. |
Step 10 | DSLAM(config-if)# | Enable the individual link by canceling the shutdown state. |
Step 11 | DSLAM(config-if)#end
| Return to enable mode when you finish configuring interfaces. |
Use the show running-config command to verify that the DSLAM running configuration contains the atm ni2-switch trunk ATM0/1 statement.
If the trunk interface is not the interface you meant to select, using the atm ni2-switch trunk command, repeat the "Configuring a Trunk Interface" procedure.
To configure a T1 or E1 interface, use the following procedure:
| Command | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 | DSLAM> enable
Password: <password>
DSLAM#
| Enter enable mode. Enter the password. You have entered enable mode when the prompt changes to |
Step 2 | DSLAM# configure terminal
| Enter global configuration mode. You have entered global configuration mode when the prompt changes to |
Step 3 | DSLAM(config)#interface atm 0/2
| Enter interface configuration mode. You have entered interface configuration mode when the prompt changes to |
Step 4 | DSLAM(config-if)# | Enable the individual link by canceling the shutdown state. Repeat steps 3 through 8 if your DSLAM has more than one interface that you need to configure. |
Step 5 | DSLAM(config-if)# linecode ami
NoteIf ami linecoding is selected, enable scrambling on thelink. DSLAM(config-if)# linecode hdb3
| Select the linecode type of the T1 link. |
Step 6 | DSLAM(config-if)# framing esf
DSLAM(config-if)# framing pcm30
| Select the frame type for the T1 data link. |
Step 7 | DSLAM(config-if)#lbo short 133
| Specify the line length (short or long), followed by the length. You can view the acceptable lengths by including the ? option after the long or shortcommands. |
Step 8 | DSLAM(config-if)#clock source loop-timed
| Select the transmit clock source for a link. |
Step 9 | DSLAM(config-if)# | When you finish configuring interfaces, return to enable mode. |
After configuring your T1/E1 interfaces, use the following commands to verify their operational status.
| Command | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 | DSLAM# show interface atm0/2
| Displays the interface configuration, status, and statistics of the ATM interface. |
Step 2 | DSLAM# show controller atm0/2
| Displays diagnostic information for the specified interface. |
If an interface is down and you configured it as up, or if the displays indicate that the hardware is not functioning properly, make sure that the T1/E1 interface is properly connected and configured.
To configure an IMA interface, you must use configuration mode (manual configuration). In this mode, you enter Cisco IOS commands at the DSLAM prompt.
| Command | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 | DSLAM> enable
| Enter enable mode. |
Step 2 | DSLAM# configure terminal
| Enter global configuration mode. You have entered global configuration mode when the prompt changes to |
Step 3 | DSLAM(config)#interface atm 0/2
| Enter interface configuration mode. You have entered interface configuration mode when the prompt changes to |
Step 4 | DSLAM(config-if)#ima-group 2
| Assign the ATM interface to an IMA group (numbered from 0 to 3). After the interface is assigned to an IMA group, individual ATM functionality is no longer available on the link. |
Step 5 | DSLAM(config-if)# | Enable the individual link by canceling the shutdownstate. Repeat Step 3 through Step 5 if your DSLAM has more than one interface that you need to configure. |
Step 6 | DSLAM (config-if) # interface atm0/ima2
| Begin configuring the IMA interface. |
Step 7 | DSLAM(config-if)# | Select the transmit clock mode for the selected IMAgroup. |
Step 8 | DSLAM(config-if)# | Enter the maximum differential delay in milliseconds for the selected IMA group. |
Step 9 | DSLAM(config-if)# | Enter the minimum number of links that need to be operational for the selected IMA group. |
Step 10 | DSLAM(config-if)# | Enable the IMA group by canceling the shutdownstate. |
Step 11 | DSLAM(config-if)#end
| When you finish configuring interfaces, return to enable mode. |
After configuring your IMA interfaces, use the following commands to verify their operational status.
| Command | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 | DSLAM# show interface atm0/ima2
| Displays interface configuration, status, and statistics for the IMA interface. |
Step 2 | DSLAM# show controller atm0/ima2
| Displays diagnostic information for the specified IMA group. |
Step 3 | DSLAM# show ima interface atm0/ima2
| Displays configuration information and operational status for the specified IMA group. |
Step 4 | DSLAM# show ima interface atm0/2
| Displays information for a single link in an IMAgroup. |
If an interface is down and you configured it as up, or if the displays indicate that the hardware is not functioning properly, make sure that the new interface is properly connected and configured.
Use the following general guidelines to troubleshoot IMA groups and the individual links of an IMA group.
Make Sure T1/E1 Links are Error Free
| Command | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 | DSLAM# show interface atm0/2
| Use the show interface atm command to verify the status of a T1 link. Verify that the administrative and protocol statuses are both up. Also, check for CRC errors and loopback status. |
Step 2 | DSLAM# show running-config
interface atm0/2
| Verify that the interface is not shutdown. Also, compare the interface configuration with the far end interface to ensure that there are no configuration mismatches. |
Step 3 | DSLAM# show controllers
| Use the show controllers command to verify the port status and view any active alarms states. |
Troubleshoot the IMA Groups and Links
| Command | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 | DSLAM# show ima interface
atm0/ima0
| Verify that the IMA group status is up. Also, use the command output to verify the IMA configuration at the near and far end. |
Step 2 | DSLAM# show ima interface
atm0/2
| Verify that the member links of the IMA group are up. |
Step 3 | DSLAM# show ima counters
| The show ima counters command reports IMA statistics in 15 minute intervals with 24 hour totals. |
See http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/dsl_prod/6015/user/hig/index.htm for troubleshooting information.
This section describes commands that you can use for monitoring and maintaining IMA configurations. Table 1 lists the commands.
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
DSLAM#show ima interface
| Displays information about all IMA groups and the links in those groups. |
DSLAM#show ima interface
atm0/imaima-group-number
| Displays information about a single IMA group and the links in that group. |
DSLAM#show controllers
| Displays information about current settings and performance at the physical level. |
DSLAM# show ima interface
atm0/atm-interface-number
| Displays IMA information for an individual link in an IMA group. |
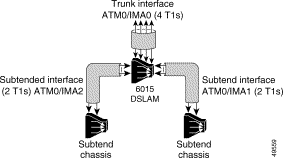
This section contains example configurations describing how to configure:
The following sample configuration describes how to configure:
Figure 2 illustrates the network topology being configured in the following configuration sample.
 |
Note Comments are written in boldface type and encapsulated with exclamation points. |
...
atm ni2-switch trunk ATM0/IMA0 !Configures interface ATM0/IMA0 as the trunk!
!
!
!
interface ATM0/0
no ip address
no ip route-cache
atm maxvp-number 0
atm maxvc-number 4096
atm maxvci-bits 12
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
no ip route-cache
!
interface ATM0/1
no ip address
no ip route-cache
shutdown
no atm ilmi-keepalive
!
interface ATM0/2
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
clock source loop-timed
scrambling cell-payload
linecode ami
lbo short 133
ima-group 0 !Adds this interface to IMA group 0!
!
interface ATM0/3
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
clock source loop-timed
scrambling cell-payload
linecode ami
lbo short 133
ima-group 0 !Adds this interface to IMA group 0!
!
interface ATM0/4
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
clock source loop-timed
scrambling cell-payload
linecode ami
lbo short 133
ima-group 0 !Adds this interface to IMA group 0!
!
interface ATM0/5
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
clock source loop-timed
scrambling cell-payload
linecode ami
lbo short 133
ima-group 0 !Adds this interface to IMA group 0!
!
interface ATM0/6
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
clock source loop-timed
scrambling cell-payload
linecode ami
lbo short 133
ima-group 1 !Adds this interface to IMA group 1!
!
interface ATM0/7
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
clock source loop-timed
scrambling cell-payload
linecode ami
lbo short 133
ima-group 1 !Adds this interface to IMA group 1!
!
interface ATM0/8
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
clock source loop-timed
scrambling cell-payload
linecode ami
lbo short 133
ima-group 2 !Adds this interface to IMA group 2!
!
interface ATM0/9
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
clock source loop-timed
scrambling cell-payload
linecode ami
lbo short 133
ima-group 2 !Adds this interface to IMA group 2!
!
interface ATM0/IMA0 !IMA group 0 configuration!
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
ima active-links-minimum 2
ima clock-mode independent
ima differential-delay-maximum 68
!
interface ATM0/IMA1 !IMA group 1 configuration!
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
ima active-links-minimum 2
ima clock-mode independent
ima differential-delay-maximum 68
!
interface ATM0/IMA2 !IMA group 2 configuration!
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
ima active-links-minimum 2
ima clock-mode independent
ima differential-delay-maximum 68
!
interface ATM0/IMA3
no ip address
no ip route-cache
shutdown
no atm ilmi-keepalive
...
The following sample configuration describes a network topology containing a mixture of IMA, T1, and DS3 interfaces. It is relevant only to IMA on platforms with the 1DS3+8xT1 I/O module installed.
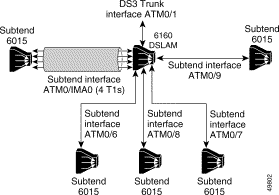
...
atm ni2-switch trunk ATM0/1 !DS3 is the default trunk!
!
!
!
interface ATM0/0
no ip address
no ip route-cache
atm maxvp-number 0
atm maxvc-number 4096
atm maxvci-bits 12
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
no ip route-cache
!
interface ATM0/1
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
!
interface ATM0/2
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
ima-group 0 !Adds this interface to IMA group 0!
!
interface ATM0/3
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
ima-group 0 !Adds this interface to IMA group 0!
!
interface ATM0/4
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
ima-group 0 !Adds this interface to IMA group 0!
!
interface ATM0/5
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
ima-group 0 !Adds this interface to IMA group 0!
!
interface ATM0/6 !T1 configuration!
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
clock source loop-timed
scrambling cell-payload
linecode ami
lbo short 133
!
interface ATM0/7 !T1 configuration!
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
clock source loop-timed
scrambling cell-payload
linecode ami
lbo short 133
!
interface ATM0/8 !T1 configuration!
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
clock source loop-timed
scrambling cell-payload
linecode ami
lbo short 133
!
interface ATM0/9 !T1 configuration!
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
clock source loop-timed
scrambling cell-payload
linecode ami
lbo short 133
!
interface ATM0/IMA0 !IMA group 0 configuration!
no ip address
no ip route-cache
no ip mroute-cache
no atm ilmi-keepalive
ima active-links-minimum 4
ima clock-mode independent
ima differential-delay-maximum 68
!
interface ATM0/IMA1
no ip address
no ip route-cache
shutdown
no atm ilmi-keepalive
!
interface ATM0/IMA2
no ip address
no ip route-cache
shutdown
no atm ilmi-keepalive
!
interface ATM0/IMA3
no ip address
no ip route-cache
shutdown
no atm ilmi-keepalive
...
This section documents the new and modified commands that are specific to the T1/E1 IMA feature. All other commands used with this feature are documented in the Command Reference for Cisco DSLAMS with NI-2. For information on other Cisco IOS commands that can be used on the NI-2 DSLAMs, see the Cisco ATM Switch Router Command Reference Guide.
To select the interface to use as the trunk, use the atm ni2-switch trunk command. To reset this command to the default value, use the no form of this command.
atm ni2-switch trunk {atm0/1 | atm0/2 | atm0/3 | atm0/4 | atm0/5 | atm0/6 | atm0/7 | atm0/8 | atm0/9 | atm0/ima0 | atm0/ima1 | atm0/ima2 | atm0/ima3}
Syntax Description
{atm0/1 | atm0/2 | atm0/3 | atm0/4 | atm0/5 | atm0/6 | atm0/7 | atm0/8 | atm0/9 | atm0/ima0 | atm0/ima1 | atm0/ima2 | atm0/ima3} Select the interface to use as the trunk.
Defaults
The DS3 link is the default trunk interface on the 1DS3+8xT1 I/O network I/O module (atm ni2-switch trunk atm0/1).
The first E1 link (atm0/2) is the default trunk interface on the 8xE1 network I/O module (atm ni2-switch trunk atm0/2).
 |
Note Before you reassign trunk status from an active link or IMA group to a different link or IMA group, you must administratively shut down both the current trunk and the interface to be assigned trunk status. |
Command Modes
Interface configuration.
Command History
12.1(4)DA This command was introduced.
Release
Modification
Usage Guidelines
| Interface | Name |
|---|---|
DS3 link | atm 0/1 |
T1/E1 link 0 | atm 0/2 |
T1/E1 link 1 | atm 0/3 |
T1/E1 link 2 | atm 0/4 |
T1/E1 link 3 | atm 0/5 |
T1/E1 link 4 | atm 0/6 |
T1/E1 link 5 | atm 0/7 |
T1/E1 link 6 | atm 0/8 |
T1/E1 link 7 | atm 0/9 |
IMA group 0 | atm 0/ima0 |
IMA group 1 | atm 0/ima1 |
IMA group 2 | atm 0/ima2 |
IMA group 3 | atm 0/ima3 |
Examples
In the following example, the trunk interface is set to T1/E1 link 2.
atm ni2-switch trunk atm0/4
Related Commands
show atm interface Shows ATM-specific information about all ATM interfaces.
Command
Description
To select the transmit clock source for a link, use the clock source interface command. When you assign a link to an IMA group interface, this command has no effect unless the link is the common clock source in the CTC IMA group. When you change the link back to g.804 mode, the system reflects the changes. To restore the default values, use the no form of this command.
clock source {loop-timed | network-derived}
Syntax Description
loop-timed Configures the link to use the received clock as the transmit clock. network-derived Configures the link to use the network clock source as the transmit clock.
Defaults
The clock source is network-derived by default (clock source network-derived).
Command Modes
Interface configuration.
Command History
12.1(4)DA This command was introduced.
Release
Modification
Examples
The following example shows how to set the clock source to loop-timed.
interface atm 0/1
clock source loop-timed
Related Commands
show controllers Displays information about a physical port device.
Command
Description
To select the frame type for the data link, use the framing interface configuration command. To restore the default values, use the no form of this command.
framing framingmode
Syntax Description
framingmode Specifies framingmode as follows:
Defaults
For E1: pcm30
For T1: esf
For DS3: cbitadm
Command Modes
Interface configuration.
Command History
12.1(4)DA This command was introduced.
Release
Modification
Usage Guidelines
In the E1 environment, the framing command allows selection of the E1 frame type to CRC4 enabled framing mode (crc4) or CRC4 disabled framing mode (pcm30).
In the T1 environment, the framing command allows selection of the T1 frame type to extended super frame (esf) or super frame (sf).
In the DS3 environment, the framing command allows the selection of the DS3 frame type to C-Bit ADM, C-Bit PLCP, M23 ADM, or M23 PLCP.
 |
Note The framing type must match on both sides of a link. |
Examples
The following example shows how to select m23plcp as the frame type.
interface atm 0/1
framing m23plcp
Related Commands
show controllers Displays information about a physical port device.
Command
Description
To configure the minimum number of active links required for an IMA group to function, use the ima active-links minimum interface configuration command. To restore the default value, use the no form of this command.
ima active-links minimum number
Syntax Description
number Configures the minimum number (1 to 8) of active links for an IMA group to function.
Defaults
No minimum links is the default (no ima active-links-minimum or ima active-links-minimum 1).
Command Modes
Interface configuration.
Command History
12.1(4)DA This command was introduced.
Release
Modification
Usage Guidelines
This command sets the minimum number of links that must be in the active state before the IMA group interface will become active. If at any time the number of active links is less than this value, then the IMA group interface will no longer be active.
Examples
The following example uses the ima active-links-minimum command to configure the minimum number of active links that must be active for the IMA group to function correctly.
interface atm 0/ima0
ima active-links-minimum 2
Related Commands
show ima interface Displays information about all IMA groups and the links in those groups. show ima interface atm0/ima group-number Displays information about a single IMA group and the links in that group.
Command
Description
To set the transmit clock mode for an ATM IMA group, use the ima clock-mode interface configuration command. To restore the default value, use the no form of this command.
ima clock-mode {common {2-9} | independent}
Syntax Description
common Configures the group with a link number that is used as a common clock source to all other links in the IMA group. If the specified link is not available, another link in the group will be used until the specified link is added. independent Configures the group so that each link in the group is clocked independently based on its own clock source setting.
Defaults
By default, the first link added to the group is used as the common clock source (ima clock-mode common).
Command Modes
Interface configuration.
Command History
12.1(4)DA This command was introduced.
Release
Modification
Usage Guidelines
This command controls the clock for the IMA group as a whole. When you set the independent keyword, the clock source interface configuration command is used under each interface to determine clocking individually. When you set the common keyword, the clock source interface configuration command for the common link determines clocking for all the links in the group.
 |
Note The IMA clock mode must match on both sides of an IMA link. |
Examples
The following example uses the ima clock-mode command to configure the IMA group clocking mode as independent.
interface atm 0/ima0
ima clock-mode independent
Related Commands
clock source Selects the transmit clock source for a link.
Command
Description
To set the maximum allowable differential delay in milliseconds allowed between links for the IMA group to be considerable, use the ima differential-delay-maximum interface configuration command. To restore the default value, use the no form of this command.
ima differential-delay-maximum {msecs}
Syntax Description n
msecs Configures the maximum differential delay in milliseconds as follows:
Defaults
The default is 25 milliseconds.
Command Modes
Interface configuration.
Command History
12.1(4)DA This command was introduced.
Release
Modification
Usage Guidelines
The transmitter on the T1/E1 IMA port adapter must align the transmission of IMA frames on all interfaces that are members of the IMA group. This allows the receiver to adjust for differential link delays among the interfaces that are members of the IMA group. Based on this required behavior, the receiver can detect the differential delays by measuring the arrival times of the IMA frames on each link.
At the transmitting end, the cells are transmitted continuously. If no ATM layer cells need to be sent between ICP cells with an IMA frame, then the transmit IMA sends filler cells to maintain a continuous stream of cells at the physical layer.
Examples
The following example configures the maximum allowable differential delay to 55 milliseconds for all interfaces assigned to the IMA group.
interface atm 0/ima0
ima differential-delay-maximum 55
Related Commands
show ima interface Displays information about all IMA groups and the links in those groups. show ima interface atm0/ima group-number Displays information about a single IMA group and the links in that group. DSLAM# show ima interface atm0/interface-number Displays information for a single link in an IMA group including delay on that link.
Command
Description
To set the IMA frame length in cells per frame, use the ima frame-length interface configuration command.
ima frame-length {32 | 64 | 128 | 256}
Syntax Description
32 Configures IMA frame length to 32 cells. 64 Configures IMA frame length to 64 cells. 128 Configures IMA frame length to 128 cells (default). 256 Configures IMA frame length to 256 cells.
Defaults
The default is 128 cells.
Command Modes
Interface configuration.
Command History
12.1(4)DA This command was introduced.
Release
Modification
Usage Guidelines
An IMA group uses the frame length parameter to set the insertion of the ICP cells at the beginning of frames in the transmit direction. Normally, one ICP cell is sent per IMA frame. The larger the IMA frame the less overhead there is at the expense of a decrease in allowable timing differences between the lengths.
Examples
The following example uses the ima frame-length command to configure the frame length transmitted as 64 cells for the IMA group.
interface atm 0/ima0
ima frame-length 64
Related Commands
show ima interface Displays information about all IMA groups and the links in those groups.
Command
Description
To assign a T1/E1 link to an IMA group, use the ima-group interface configuration command. To remove a link from an IMA group, use the no form of this command.
ima group number
Syntax Description
number Specifies the IMA group number (0 to 3).
Defaults
The links do not belong to any IMA group by default.
Command Modes
Interface configuration.
Command History
12.1(4)DA This command was introduced.
Release
Modification
Usage Guidelines
Use the ima-group interface command to configure a T1/E1 port adapter interface as part of an IMA group. IMA allows you to aggregate multiple low-speed links into one larger virtual trunk or IMA group and appears to your ATM switch router as one logical pipe. This IMA group provides modular bandwidth for user access to ATM networks for connections between ATM network elements that are at rates between traditional multiplexing levels, such as between T1/E1, and DS3/ E3.
IMA requires inverse multiplexing and demultiplexing of ATM cells in a cyclical fashion among links grouped to form a higher-bandwidth logical group with a rate of approximately the sum of the link rates. This grouping is called an IMA group.
Examples
The following example uses the ima group command to assigns link 0 to IMA group 0.
interface atm 0/2
ima-group 0
Related Commands
show controllers Displays information about a physical port device. show ima interface Displays information about all IMA groups and the links in those groups. show ima interface atm0/ima group-number Displays information about a single IMA group and the links in that group.
Command
Description
To configure an IMA group test pattern transmitted in the ICP cells, use the ima test interface configuration command. To restore the default value, use the no form of this command.
ima test [link link-value] [pattern pattern-value]
Syntax Description
link Configures the link that is transmitting the test pattern. link-value Specifies which IMA group member link (2 through 9) is transmitting the test pattern. pattern Configures the test pattern. pattern-value Specifies the test pattern (0 through 255) transmitted in the ICP cells.
Defaults
The link-value is 2.
The pattern-value is 0xa6.
The default is no ima test.
Command Modes
Interface configuration.
Command History
12.1(4)DA This command was introduced.
Release
Modification
Usage Guidelines
The test pattern procedure verifies the connectivity of a link within an IMA group. The procedure uses a test pattern sent over one link to verify the connectivity to the other links in the IMA group. The test pattern should be looped over all the other links in the group at the far end of the connection. All of the IMA test pattern procedures are performed over the ICP cells exchanged between both ends of the IMA virtual links. After the test is configured on the IMA group, the test continues explicitly until configured to the default.
Examples
The following example uses the ima test command to configure the test pattern of 100 to transmit over ATM interface 0 of IMA group 0.
interface atm 0/ima0
ima test link 2 pattern 100
Related Commands
show ima interface Displays information about all IMA groups and the links in those groups.
Command
Description
To set the operating mode of an IMA group, use the ima version interface configuration command. To restore the default value, use the no form of this command.
ima version {1.0 | 1.1}
Syntax Description
1.0 Specifies that the group run in version 1.0 mode. 1.1 Specifies that the group run in version 1.1 mode.
Defaults
The default is version 1.0 mode.
Command Modes
Interface configuration.
Command History
12.1(4)DA This command was introduced.
Release
Modification
Examples
The following example uses the ima version command to set the IMA version to 1.1.
interface atm 0/ima0
ima version 1.1
Related Commands
show ima interface Displays information about all IMA groups and the links in those groups. show ima interface atm0/ima group-number Displays information about a single IMA group and the links in that group.
Command
Description
To set the line build-out to various lengths, use the lbo interface configuration command. To restore the default values, use the no form of this command.
lbo {short {133 | 266 | 399 | 533 | 655} | long {gain10 | gain36} {0db | -7.5db | -15db | -22.5db}}
Syntax Description
short Specifies a short cable length. Must be followed by a length value. The range mapping for each value is shown below: Value Range (feet) 133 0 to 133 266 134 to 266 399 267 to 399 533 400 to 533 655 534 to 655 long Specifies a cable length line build out. Long must be followed by a gain and a margin value.
Defaults
The default setting is long haul with gain36 and 0db (lbo long gain36 0db).
Command Modes
Interface configuration.
Command History
12.1(4)DA This command was introduced.
Release
Modification
Usage Guidelines
This command is applicable to T1 links.
Examples
The following example shows how to select long as the cable length.
interface atm 0/2
lbo long gain36 -15db
The following example shows how to select short as the cable length.
interface atm 0/2
lbo short 266
Related Commands
show controllers Displays information about a physical port device.
Command
Description
To select the linecode type of the T1/E1 link, use the linecode interface configuration command. To restore the default values, use the no form of this command.
linecode {ami | b8zs | hdb3}
Syntax Description
ami Specifies alternate mark inversion (AMI) as the linecode type. Valid for T1 or E1 controllers. b8zs Specifies B8ZS as the linecode type. Valid for T1 controller. hdb3 Specifies HDB3 as the linecode type. Valid for E1 controller.
Defaults
T1 = b8zs
E1 = hdb3
Command Modes
Interface configuration.
Command History
12.1(4)DA This command was introduced.
Release
Modification
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to match the line code of the far end device.
Examples
The following example specifies AMI as the linecode type.
interface atm 0/ima0
linecode ami
Related Commands
show controllers Displays information about a physical port device.
Command
Description
To enable or disable T1/E1 cell payload scrambling on a link, use the scrambling interface configuration command. To restore the default values, use the no form of this command.
scrambling cell-payload
Syntax Description
cell payload This is the scrambling mode.
Defaults
Scrambling cell-payload is disabled.
Usage Guidelines
The scrambling type must match on both sides of a link.
Command Modes
Interface configuration.
Command History
12.1(4)DA This command was introduced.
Release
Modification
Examples
The following example uses the scrambling command to enable scrambling on the specified interface.
interface atm 0/ima0
scrambling cell-payload
| A |
|
| AAL-1 | ATM Adaption Layer. This layer maps higher layer user data into ATM cells, making the data suitable for transport through the ATM network. |
| AAL-5 | ATM Adaption Layer. This layer maps higher layer user data into ATM cells, making the data suitable for transport through the ATM network. |
| AIS | Alarm Indication Signal. In a T1 transmission, an all-ones signal transmitted in lieu of the normal signal to maintain transmission continuity and to indicate to the receiving terminal that there is a transmission fault that is located either at, or upstream from, the transmitting terminal. |
| Asynchronous Transfer Mode | See ATM. |
| ATM | Asynchronous Transfer Mode. A cell-based data transfer technique in which channel demand determines packet allocation. ATM offers fast pack technology, real time, demand led switching for efficient use of network resources. |
| |
| B |
|
| broadband | Characteristic of any network that multiplexes independent network carriers onto a single cable. This is usually done using frequency division multiplexing (FDM). Broadband technology allows several networks to coexist on one single cable; traffic from one network does not interfere with traffic from another since the "conversations" happen on different frequencies in the "ether" rather like the commercial radio system. |
| C |
|
| CCO | Cisco Connection Online. |
| chassis | The card cage (housing) where modules are placed. |
| Cisco Connection Online | See CCO. |
| D |
|
| digital signal level 3 | See DS3. |
| Distributed Defect Tracking System | See DDTS. |
| DS3 | digital signal level 3. Framing specification used for transmitting digital signals at 44.736 Mbps on a T3 facility. |
| DSLAM | Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer. Concentrates and multiplexes digital subscriber line signals at the telephone service provider location to the broadband wide area network. Replaces ADSLAM. |
| E |
|
| E1 | A digital carrier that is used to transmit a formatted signal at 2.048 Mbps. |
| E3 | A digital carrier that is used to transmit a formatted signal at 34.368 Mbps. |
| F |
|
| frame | A packet as it is transmitted over a serial line. The term derives from character oriented protocols where special start-of-frame and end-of-frame characters were added when transmitting packets. |
| I |
|
| IMA | inverse multiplexing over ATM. Standard protocol defined by the ATM Forum in 1997. |
| M |
|
| Management Information Base | See MIB. |
| MIB | Management Information Base. A collection of objects that can be accessed via a network management protocol, such as SNMP and CMIP (Common Management Information Protocol). |
| N |
|
| NI-2 | A second generation network interface card. |
| S |
|
| Simple Network Management Protocol | See SNMP. |
| slot | A numbered location within a chassis capable of housing a module. |
| SNMP | Simple Network Management Protocol. The network management protocol of choice for TCP/IP-based internets. |
| T |
|
| T3 | A digital carrier that is used to transmit a DS3 formatted digital signal at 45 Mbps. |
| U |
|
| UNI | User-Network Interface. ATM Forum specification that defines an interoperability standard for the interface between ATM-based products (a router or an ATM switch) located in a private network and the ATM switches located within the public carrier networks. Also used to describe similar connections in Frame Relay networks. |
| UNI signaling | User-Network Interface signaling for ATM communications. |
| V |
|
| VC | Virtual Circuit. A logical circuit created to ensure reliable communication between two network devices. A virtual circuit is defined by a VPI/VCI pair, and can be either permanent (PVC) or switched (SVC). In ATM, a virtual circuit is called a virtual channel. Sometimes abbreviated VC. See also PVC, SVC, VCI, and VPI. |
| virtual circuit | See VC. |
| VPI | Virtual Path Identifier. An 8-bit field in the header of an ATM cell. The VPI, together with the VCI, is used to identify the next destination of a cell as it passes through the network. See also VCI. |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Wed Jul 17 08:23:45 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.