|
|

The Web Management Interface chapter describes how to use your web browser to manage the a Cisco router.
The Web Management Interface is designed for individuals who prefer a GUI program, or who are familiar with web-based navigational principles. The Web Browser Interface enables you to set some configuration parameters in the browser, and to view other settings. The view-only functionalities are marked as "Display Only."
Internet Explorer 2.0 from Microsoft is incompatible with the Cisco 67x router. You must use Netscape 3.01 or higher or Internet Explorer 3.01 or higher for the Cisco Web Management Interface.
The user password comes in two modes: Exec, or read-only, and Enable. You must have Enable privileges to save changes made via the Web interface to NVRAM.
You must click on the Submit Changes button and issue a write command (at the command line interface) to apply any changes though the Web Management Interface.
Do the following to write to NVRAM.
Step 2 Logon to the CBOS using either the serial or Telnet interfaces.
Step 3 Write changes to NVRAM:cbos>write
Step 4 Reboot the system.cbos>reboot

The system disregards all changes when rebooted if you have not written the changes to NVRAM.
Do the procedure below to activate the Web Management Interface.
Step 2 Enter the user name exec or enable and press Enter to bypass the initial password if you have not yet created a password. If you have already created a password, proceed to Step 6.
Step 3 To set a new password for the exec login, enter:cbos>set password exec new-password
Set a new password for user logins by substituting enable for exec in the above example.
Step 4 To save the new password, enter:cbos>write
Step 5 Enable the Web Management Interfacecbos>set web enabled
Step 6 Launch your preferred web browser.
Step 7 Enter the IP address for the Cisco 67x Web Management page in the browser locator field. For example, instead of http//www.cisco.com/ insert the dotted decimal format (http://10.0.0.1/) of the Cisco 67x IP address. The following screen appears:
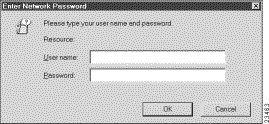
Step 8 Enter the user name and the password.
Step 9 Once the Web Management Interface home page appears, you should add a bookmark in your browser for the new Cisco 67x location. Once the bookmark has been added, simply activate the bookmark to access the Web Management Interface. Figure 6-2, on page 6-4 shows the interface home page.
The screen below is the Cisco Web Management Interface home page.
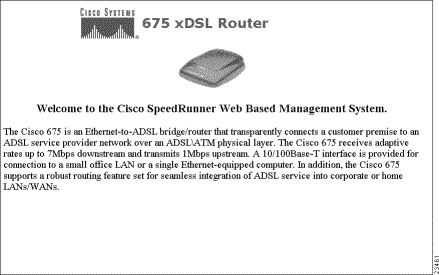
The Web Management Interface home page has four buttons that link to other Web pages. To navigate to the various pages, click on the icon or on the appropriate word in the navigation line at the bottom of each page. The purpose of each of the pages is as follows:
Click on the Configure button and five sub buttons appear.

The functions for each button are explained below.
The General button allows you to set general configuration parameters, such as the IP address of the Cisco 67x, the ADSL values given to you by your service provider, and the VC base and count metrics. The three sections of the General Configuration screen and instructions on how to use these options are described below.
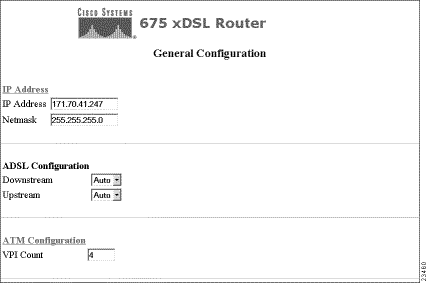
This option allows you to set the address and netmask for the Ethernet port of your Cisco equipment.
To use this option:
Step 2 To apply these addresses, click on the Submit Changes button.
Step 3 To reject these addresses, click on the Reset Values button.
Step 4 The new addresses are displayed.
This option allows you to set the up and downstream rates for your ADSL connection.
This option allows you to set up the total number of VPI addresses that you can configure. The VC Base drop down menu allows you to choose a base address, normally one greater than zero. The VC Count drop down menu allows you to specify the number of Virtual Paths to be supported by the Cisco equipment you are using.
To use this option:
Step 2 To apply these numbers, click on the Submit Changes button.
Step 3 To reject these numbers, click on the Reset Values button.
Click on the Apps button and the Application Configuration screen appears. The Apps button allows you to enable and disable applications associated with the Cisco 67x.
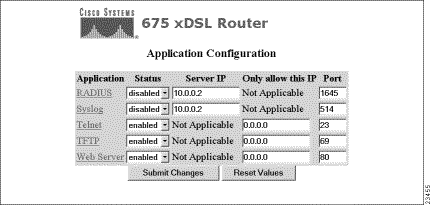
Each of the applications is described in the following sections.
Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS), authenticates users for access to a network. The RADIUS server uses an authentication scheme, such as PAP, to authenticate incoming messages from RADIUS clients. When a password is present, it is hidden using a method based on the RSA Message Digest Algorithm MD5.
Select whether you want to enable or disable RADIUS via the first drop down menu.
Step 2 Enter a port number.
Step 3 Click on the Submit Changes button to apply changes or the Reset Values button to discard changes.
Syslog logs system information to a specified Syslog server for processing without requiring large amounts of local storage or local processing.
Step 2 Specify the IP address of the Syslog server.
Step 3 Enter a port number.
Step 4 Click on the Submit Changes button to apply changes or the Reset Values button to discard changes.
Telnet provides access to the CBOS command line interface via a network.
Step 2 Specify the IP address of the machine allowed to use Telnet to connect to the Cisco 67x. To allow any machine to connect, specify 0.0.0.0.
Step 3 Enter a port number.
Step 4 Click on the Submit Changes button to apply changes or the Reset Values button to discard changes.
The Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server allows you to transfer a new configuration file or new software to and from Cisco equipment.
Step 2 Specify the IP address of the machine allowed to use TFTP to connect to the Cisco 67x. To allow any machine to connect, specify 0.0.0.0.
Step 3 Enter a port number.
Step 4 Click on the Submit Changes button to apply changes or the Reset Values button to discard changes.
The Web Server allows you to use the web interface to access Cisco equipment.
Step 2 Specify the IP address of the machine allowed to use the web interface to connect to the Cisco 67x. To allow any machine to connect, specify 0.0.0.0.
Step 3 Enter a port number.
Step 4 Click on the Submit Changes button to apply changes or the Reset Values button to discard changes.
Click on the Filtering button and the Filter Configuration screen appears. This option allows you to set up filters to prevent or allow the flow of IP packets into Cisco Equipment.
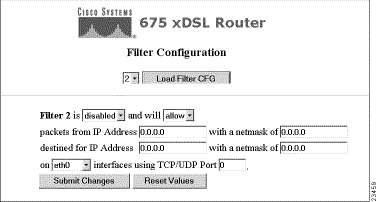
Step 2 Set filters by completing the sentence.
Step 3 Select either the enabled or disabled option from drop down menu to activate a filter.
Step 4 Select either the allow or deny option from the drop down menu. The allow option allows the specified filter to accept packets from a particular IP address. The deny option does not permit these packets to flow to a particular IP address.
Step 5 Enter the source address and netmask of where the packet is originating. The source address is the IP address of the source computer from which you will allow or deny traffic. The source netmask is the source network from which you will allow or deny traffic. By entering a source netmask, you can filter a group of incoming IP addresses.
Step 6 Enter the destination address and netmask. The destination address is the IP address of the computer that, if allowed, will receive packets originating from the source IP address. The destination netmask is the destination network that, if allowed, will receive packets originating from the source netmask. By entering a destination netmask, you can filter a group of outgoing IP addresses.
Step 7 Select the interface that this filter affects from the drop down menu. Select the all option for all interfaces.
Step 8 Select the TCP/UDP Port this affects from the drop down menu. Select 0 for all ports.
Click on the Routing button and the Routing Configuration screen appears. This option allows you to build a new routing table or change an existing routing table. Routes consist of the IP addresses of all machines you want to communicate with plus the netmask, gateway, and metric of those machines.
n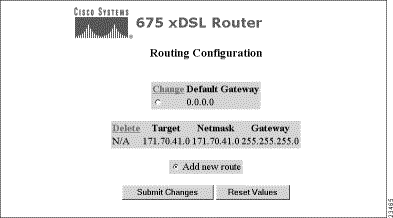
The Routing Configuration screen allows you to change your routing table. See the sections below for instructions on individual tasks.
Step 2 Click on the Enter key. A new screen appears that allows you to change the IP address of the default gateway.
Step 3 Enter the IP address.
Step 4 To apply changes, click on the Submit Changes button. To clear the changes, click on the Reset Values button.
Step 2 Click on the Enter button. A new screen appears that allows you to change the route.
Step 3 Enter the target address, the netmask, and the gateway.
Step 4 The target address is the IP address of the machine with which you are trying to communicate. You can modify or delete existing IP addresses by simply typing in the new address.
Step 5 The netmask is the address of the network with which you want to communicate. You can modify or delete existing netmask addresses by typing in the new address.
Step 6 The gateway is the address of the gateway machine through which the information you are sending is routed. Data is sent through the external gateway to the destination address. Therefore, this address must be the address of a gateway that is physically linked to your network. You can modify or delete existing gateway addresses by simply typing in the new address.
Step 7 To apply changes, click on the Submit Changes button. To clear the changes, click on the Reset Values button.
Step 8 The new routing information is displayed.
Step 2 Click on the Submit Changes button. A new screen appears.
Step 3 Enter the new route including the target IP address, the netmask, and the gateway. See the section above for further descriptions on these addresses.
Step 4 To apply changes, click on the Submit Changes button. To clear the changes, click on the Reset Values button.
Click on the User CFG button and the User Configuration screen appears. This option allows you to set up a user profile for each logical WAN connection. The user profile can be saved and reloaded each time you want to reuse it.
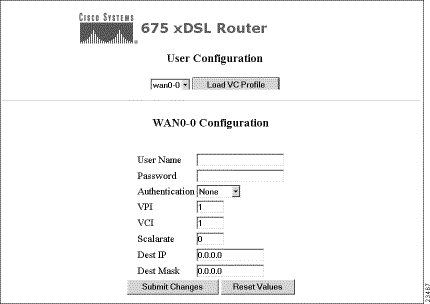
Step 2 Click on the Load VC Profile button.
Step 3 Enter or change existing user information. The field definitions are:
Step 4 To submit changes, click on the Submit Changes button. To undo all changes, click on the Reset Values button.
After you apply changes, the new user configuration information is displayed.
The Statistics button allows you to display statistics about applications, errors, and ports. The Statistics button has three sub-buttons shown below.

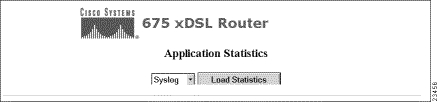
Click on the Apps button and the Application Statistics screen appears. This screen displays the applications that you can configure for the Cisco 67x.
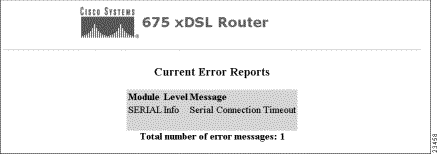
Click on the Errors button and the screen below appears. This screen displays the current errors reported by the CBOS.
Click on the Ports button and Port Statistics screen appears. This screen allows you to display statistics on the Ethernet and WAN ports.
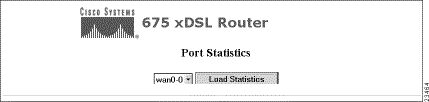
Step 2 Click on the Load Statistics button. The statistics for the port are displayed as shown below.
Step 3 Repeat for all ports for which you want to display statistics.
Click on the Information button to get information about the Cisco equipment you are working on and about Cisco, Inc. The Information button has four sub-buttons shown below.
For more information about Cisco and its products, go to the Cisco home page on the World Wide Web at http://www.cisco.com.
Cisco Connection Online (CCO) is Cisco Systems' primary, real-time support channel. Maintenance customers and partners can self-register on CCO to obtain additional information and services.
Available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, CCO provides a wealth of standard and value-added services to Cisco's customers and business partners. CCO services include product information, product documentation, software updates, release notes, technical tips, the Bug Navigator, configuration notes, brochures, descriptions of service offerings, and download access to public and authorized files.
CCO serves a wide variety of users through two interfaces that are updated and enhanced simultaneously: a character-based version and a multimedia version that resides on the World Wide Web (WWW). The character-based CCO supports Zmodem, Kermit, Xmodem, FTP, and Internet e-mail, and it is excellent for quick access to information over lower bandwidths. The WWW version of CCO provides richly formatted documents with photographs, figures, graphics, and video, as well as hyperlinks to related information.
You can access CCO in the following ways:
For a copy of CCO's Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ), contact cco-help@cisco.com. For additional information, contact cco-team@cisco.com.
For the latest information on caveats and known problems, follow these steps to consult CCO:
Step 2 On the CCO home page, click LOGIN, which appears in green in the menu bar at the top of the page, and log into CCO. (If you are not a registered CCO user, follow the instructions to register so that you can log in.)
Step 3 After you log in, click Software & Support on the CCO home page.
Step 4 On the Software & Support page, click Technical Tools.
Step 5 On the Technical Tools page, click Bug Toolkit II. (Bug Toolkit II is not visible on the Technical Tools page unless you log in to CCO as directed in Step 2.)
Step 6 Use one of the tools to get up-to-date bug information. For example, click Search for Bug by ID Number, then enter a bug ID, such as CSCdk09616, when prompted. For instructions on using the bug tools, go to the bottom of the Bug Toolkit II page and click Help—How to Use the Bug Toolkit.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Mon Dec 4 15:32:33 PST 2000
Copyright 1989-2000©Cisco Systems Inc.