|
|

October 2, 1998
These release notes discuss features and caveats for the Cisco 6200 advanced digital subscriber line access multiplexer (DSLAM) supported in Cisco IOS Release 11.3(1)DA3 and earlier releases in the 11.3(1)DA train.
For more detailed information about the features in these release notes, refer to the "Related Documentation" section. For more information about caveats, see the "Cisco Connection Online" section. Information about electronic documentation can be found in the "Cisco Connection Online" section and in the "Documentation CD-ROM" section.
These release notes discuss the following topics:
To determine the version of Cisco IOS software running on your system, log on and enter the show version user EXEC command:
c6200> show version
Output begins with the following. The Cisco IOS version appears in the second line.
Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software
IOS (tm) C6200 Software (C6200-DCM-M), Version 11.3(1)DA3
Copyright (c) 1986-1998 by cisco Systems, Inc.
The full output includes additional information, such as processor revision numbers, memory amounts, hardware IDs, and partition information.
Cisco IOS Release 11.3(1)DA3 includes the following new and changed CLI commands:
| Command | Description of Change | Example |
|---|---|---|
dsl check-bytes downstream value upstream value1 | Specifies the number of check bytes per symbol (DSL frame) used by the forward error correction (FEC) feature. Using more check bytes improves error correction, but also increases overhead, which lowers usable bandwidth. Valid values are even numbers from 0 to 16. The default value is 16 in both directions. You can set auto mode using the command no dsl check-bytes. In auto mode, the line card determines the best setting based on the line rate. This command is available for DMT interfaces only. | |
dsl interleaving {on | off}2 | Turns on (or off) the interleaving feature that mixes bytes of data from different frames on the line. When interleaving is on, error correction is more effective for protecting against impulse (bursty) noise on the line. The drawback to interleaving: it can add significant delay at the sending side. The amount of delay added is equivalent to the interleaving delay value that you set by means of the dsl int-delay command described below. By default, interleaving is turned on. This command is available for DMT interfaces only. | |
dsl int-delay downstream value upstream value2 | Sets delay values, in msec, for the interleaving feature (see also the dsl interleaving command, above). If bursty noise is a concern, set int-delay to a value greater than the longest expected duration of the noise. If delay is a concern, set int-delay as low as possible. Valid values are 0, 1, 2, 4, 8, and 16. The default value is 16 in both directions. This command is available for DMT interfaces only. | |
dsl loopback [local | dsl-line] | Runs a local or dsl-line loopback test. A local loopback tests transmission of data from the port, across the backplane, and back to the port. A dsl-line loopback tests the transmission of data from the CPE, through the modem on the subscriber line card (SLC), and back to the CPE. This command is available for DMT interfaces only. | |
dsl LOSconfig {off | on} | Controls the issuance of a minor alarm upon loss of signal (LOS), loss of frame (LOF), or loss of cell delineation (LOCD). By default, LOS, LOF and LOCD cause minor alarms; enter dsl losconfig on to disable the alarm. This command is available for DMT interfaces only. | |
dsl margin downstream value upstream value | Allows you to adjust the margin added to the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) to which the line trains. A higher margin results in fewer errors on the line; a lower margin results in longer reach and tends to increase the bit rate. The default is 6 (db). Valid values are whole numbers from 0 to 127.This command is available for DMT interfaces only. | |
dsl power_boost value2 | Allows you to increase the power of the signal that the Cisco 6200 sends downstream. Increasing the power improves the reach on the line, but can also cause cross-talk— resulting in higher error rates or failure to train. Valid values are whole numbers from 0 to 9 (db). The default value is 0. Cisco recommends against changing the power_boost value. If you do change it, we recommend that you set power_boost to a value no higher than 2 db. Performance for settings above 2 db varies with loop conditions. This command is available for DMT interfaces only. | |
dsl quick-training {off | on}2 | Allows you to turn on a faster training algorithm that may limit interoperabililty. When quick-training is on, the symbols-codeword and check-bytes options are ignored. By default, quick-training is off. This command is available for DMT interfaces only. | |
dsl symbols-codeword downstream value upstream value2 | Specifies the number of symbols (DSL frames) per FEC codeword. Valid values are 1, 2, 4, 8, and 16. You can set auto mode using the command no dsl symbols-codeword. In auto mode, the SLC determines the best setting based on the line rate. Auto mode is applied to the line in both directions; you cannot use auto mode in one direction and an explicit value in the other direction. Auto mode is the default setting. If you do not use auto mode, set the number of symbols per codeword so that the FEC codeword does not exceed the maximum size of 255 bytes. The total number of bytes in an FEC codeword includes user data bytes (which depend upon rate) plus check-bytes. (You can set check-bytes using the dsl check-bytes command, described above.) For a check-bytes setting of 16 bytes per codeword, use these guidelines to select a symbols-codeword value that is appropriate to the bit rate on the line:
For lower check-bytes settings, you can use higher symbols-codeword values at some bit rates. This command is available for DMT interfaces only. | |
dsl-ucode-load filename slot port | Loads microcode into modems (ports) on the SLC. | |
| 1Cisco recommends that you leave this parameter set either to its default value or to auto. 2Cisco recommends that you leave this parameter set to its default value. |
Release 11.3(1)DA2 included the following changes to CLI commands:
| Command | Description of Change | Example |
|---|---|---|
dsl bitrate | Two new downstream bit rates have been added: 3200 and 5120. | |
dsl lbo | The dsl lbo command has been changed to dsl local-tx-power. | |
dsl local-tx-power | A new command in interface configuration mode allows you to adjust the power of the signal transmitted from the Cisco 6200 to the CPE downstream. To avoid crosstalk, use the lowest power possible to achieve the desired bit rate. The default value is Full. The transmit power values you can use are
This command is available on CAP interfaces only. | |
dsl remote-tx-power | A new command in interface configuration mode allows you to adjust the power of the signal transmitted from the CPE to the Cisco 6200 upstream. To avoid crosstalk, use the lowest power possible to achieve the desired bit rate. The default value is Full. The transmit power values you can use are
This command is available on CAP interfaces only. | |
We strongly recommend that you use firmware Release 1.4.2 for the Cisco 675 (NetSpeed 204). Firmware Release 1.4.2 solves a problem with signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) that existed in earlier releases of the software.
Follow this procedure to verify the quality of a line attached to an SLC 8CAP:
Step 1 Enter these commands to enable the port you want to test; slot/port specifies the card's slot number and the port number:
config terminal
int dsl slot/port
no shut
exit
exit
Step 2 To determine the rate at which the modems trained, enter the following command:
show dsl interface dsl slot/port
Step 3 In the resulting display, locate the actual bit rates (downstream and upstream) and record them.
Step 4 Reconfigure the port for the rates you recorded. Use these commands:
config terminal
int dsl slot/port
dsl bitrate downstream bitrate_value upstream bitrate_value
exit
exit
The port retrains at the new bit rates.
Step 5 Enter this command to run the line test, where minutes is the number of minutes you want the test to run (1 to 60; at least 20 minutes is recommended):
linetest dsl slot/port linequality duration minutes
Step 6 Wait for the line test to complete, and then enter this command to display the results:
show dsl interface dsl slot/port
Step 7 If the line fails the test, repeat Step 4 through Step 6, choosing the next lowest available bit rate. (Enter dsl bitrate downstream ? and dsl bitrate downstream new_bitrate_value upstream ? to display lists of bit rates.)
The Cisco 6200 DSLAM is a Central Office (CO) grade multiplexer that supports up to 80 ADSL ports. The Cisco 6200 DSLAM sends and receives subscriber data (often Internet service) over existing copper telephone lines, concentrating all traffic onto a single high-speed trunk for transport to the Internet or the enterprise intranet. The Cisco 6200 DSLAM is supported by Cisco IOS software.
These interfaces are supported on the Cisco 6200 DSLAM under Cisco IOS Release 11.3(1)DA3:
This section describes features introduced in Cisco IOS Release 11.3(1)DA3.
The STS-1 network trunk cards (NTCs) are available in single-mode and multimode versions. The STM-1 NTCs concentrate the data traffic from all Cisco 6200 subscriber ports onto a single high-speed trunk to an ATM network. The interface operates at 155 Mbps.
Each subscriber line card (SLC) provides eight subscriber ports that support DSL access with discrete multitone (DMT) modems. The SLC DMT8 transports data at speeds up to 8 Mbps downstream and receives at speeds up to 800 kbps upstream. The Cisco 6200 DSLAM supports up to ten SLCs.
In the Cisco 6200, management activities like saving and loading of configuration files via TFTP, running CLI remotely over a Telnet session, and SNMP-based network management require IP connectivity.
The Cisco 6200 supports two ways to achieve this connectivity:
The typical network configuration for in-band management is shown in Figure 1.
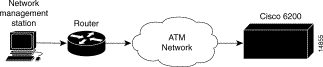
To use in-band management, configure the ATM port on the MPC to handle IP over ATM (RFC 1483) and either establish a static path between the management station and the ATM port, or set up a default gateway, as described below. Follow these steps at the Cisco 6200 console or via Telnet:
Step 1 Enter enable and the password to go to privileged EXEC mode.
c6200> enable
Password:
Step 2 Enter configure terminal to go to global configuration mode.
c6200# configure terminal
Step 3 Enter the interface command to go to interface configuration mode. Specify the ATM port (0/0) and subinterface (.1) on the MPC, and set up a point-to-point connection.
c6200(config)# interface atm 0/0.1 point-to-point
Step 4 Enter the ip address command to assign an IP address and subnet mask to the ATM subinterface.
c6200(config-if)# ip address <ip-address> <mask>
Step 5 Enter the atm pvc command to set up the ATM permanent virtual circuit (PVC).
c6200(config-if)# atm pvc <vc_num> vpi vci
Step 6 Do only one of the following:
c6200(config-if)# ip route <dest-ip-address> <mask> <forwarding interface>
c6200(config-if)# ip default-gateway <gateway-ip-addr>
Step 7 Set up the corresponding PVC, IP address, and static route (if you configured a static route in Step 6) on the router that connects the Cisco 6200 management station to the ATM network.
Step 8 Verify the connection by pinging from the management station to the Cisco 6200 ATM port's IP address.
See the "Changes to CLI Commands" section for descriptions of the new commands added to the command line interface in Cisco IOS Release 11.3(1)DA3.
There are no new features in Release 11.3(1)DA2. This is a maintenance release designed to improve the reliability and performance of the Cisco 6200 DSLAM.
The features discussed in the following paragraphs are supported by the Cisco 6200 DSLAM in Cisco IOS Release 11.3(1)DA1 and subsequent releases in the DA train.
The Cisco 6200 DSLAM runs Cisco's industry-leading IOS software. Cisco IOS software's command line interface (CLI) provides tools for managing the DSLAM. CLI commands support the following functions:
For configuration and management of the Cisco 6200 DSLAM, Cisco provides the Cisco 6200 Manager software application, an SNMP-based graphical user interface that runs under Windows NT. The Manager can be used in place of or in addition to the command line management tool provided by Cisco IOS software.
On the Cisco 6200 DSLAM, ATM permanent virtual channels (PVCs) are statically defined; you do not configure them. Enabling a port enables all associated PVCs.
The management processor card (MPC) performs management and storage tasks for the Cisco 6200 DSLAM. It supports
The STS-3c/OC-3c network trunk cards (NTCs) are available in single-mode and multimode versions. The NTCs concentrate the data traffic from all Cisco 6200 subscriber ports onto a single high-speed trunk to an ATM network. The interface operates at 155 Mbps.
Each subscriber line card (SLC) provides eight subscriber ports that support DSL access with rate-adaptive carrierless amplitude modulation/phase modulation (RADSL/CAP) modems. The CAP SLC transports data at speeds up to 7 Mbps downstream and receives up to 1 Mbps upstream. The Cisco 6200 DSLAM supports up to ten SLCs.
This section describes unexpected behavior in Release 11.3(1)DA3. A DDTs tracking number, if one exists, is provided in square brackets at the end of each description. Please refer to the DDTs number if you communicate with Cisco about any of these issues.
c6200# configure terminal
c6200(config)# interface dsl 8/2
c6200(config-if)# shutdown
c6200(config-if)# no shutdown
On DMT interfaces, the power-boost value (configured with the dsl power_boost command) is not displayed correctly when you enter show dsl int dsl slot/port. The system displays the correct value in the "Configured" section of the output, but not in the "Actual" section. [CSCdk47515]
On SLC 8CAP ports, modems train poorly while the phone on the line is ringing. [CSCdk02256]
The Cisco 6200 has limited cell buffers. If the upstream switch does not perform traffic shaping, extremely bursty traffic might cause buffers to overflow. As a result, in some cases, packets are dropped and throughput degrades. [CSCdk09616]
Workaround: If subscribers are experiencing poor performance, you might be able to alleviate the problem using the traffic shaping feature on the device upstream from the Cisco 6200 DSLAM. Set the VBR Peak Cell Rate and Sustainable Cell Rate to values in kbps that you are sure can be reliably reached in your environment. (On any line that connects at a rate lower than the rate you specify, packets will be lost and performance could be poor.) We recommend a value no greater than 7000 kbps for both VBR Peak Cell Rate and Sustainable Cell Rate.
This example, an excerpt from a configuration file, shows you how to set traffic shaping on a Cisco 7200 router with an ATM-CES card.
!
interface ATM4/0.1 multipoint
pvc 0/176
vbr-nrt 7000 7000
encapsulation aal5ciscoppp Virtual-Template1
!
interface Virtual-Template1
mtu 2048
no ip mroute-cache
no keepalive
no peer default ip address
ppp authentication pap callin
!
The key command in the example is vbr-nrt 7000 7000, which breaks down as follows:
vbr-nrt | Virtual bit rate |
7000 (first instance) | Peak Cell Rate |
7000 (second instance) | Sustainable Cell Rate |
The Cisco 6200 DSLAM functions as an IP host, not as an IP router. When IP routing is enabled on the MPC, the MPC cannot communicate with the trunk and line cards. Do not turn on IP routing.
The Cisco 6200 system reboots when using the IP name server to resolve a host name (for a Telnet connection, for example). Workaround: Use IP addresses instead of host names. [CSCdk13888]
Running the linetest command on one port changes the SNMP line test type object for other ports. [CSCdk18930]
The alarmcutoff CLI command does not stop audible alarms on the external alarm connector. Workaround: Use the ACO button on the front panel of the MPC to turn off alarms. [CSCdk22404]
This section describes unexpected behavior in Release 11.3(1)DA2. A DDTs tracking number, if one exists, is provided in square brackets at the end of each description. Please refer to the DDTs number if you communicate with Cisco about any of these issues.
Modems train poorly while the phone on the line is ringing. [CSCdk02256]
The Cisco 6200 has limited cell buffers. If the upstream switch does not perform traffic shaping, extremely bursty traffic might cause buffers to overflow. As a result, in some cases, packets are dropped and throughput degrades. [CSCdk09616]
Workaround: If subscribers are experiencing poor performance, you might be able to alleviate the problem using the traffic shaping feature on the device upstream from the Cisco 6200 DSLAM. Set the VBR Peak Cell Rate and Sustainable Cell Rate to values in kbps that you are sure can be reliably reached in your environment. (On any line that connects at a rate lower than the rate you specify, packets will be lost and performance could be poor.) We recommend a value no greater than 7000 kbps for both VBR Peak Cell Rate and Sustainable Cell Rate.
This example, an excerpt from a configuration file, shows you how to set traffic shaping on a Cisco 7200 router with an ATM-CES card.
!
interface ATM4/0.1 multipoint
pvc 0/176
vbr-nrt 7000 7000
encapsulation aal5ciscoppp Virtual-Template1
!
interface Virtual-Template1
mtu 2048
no ip mroute-cache
no keepalive
no peer default ip address
ppp authentication pap callin
!
The key command in the example is vbr-nrt 7000 7000, which breaks down as follows:
vbr-nrt | Virtual bit rate |
7000 (first instance) | Peak Cell Rate |
7000 (second instance) | Sustainable Cell Rate |
The Cisco 6200 DSLAM functions as an IP host, not as an IP router. When IP routing is enabled on the MPC, the MPC cannot communicate with the trunk and line cards. Do not turn on IP routing.
The Cisco 6200 system reboots when using the IP name server to resolve a host name (for a Telnet connection, for example). Workaround: Use IP addresses instead of host names. [CSCdk13888]
Running the linetest command on one port changes the SNMP line test type object for other ports. [CSCdk18930]
The alarmcutoff CLI command does not stop audible alarms on the external alarm connector. Workaround: Use the ACO button on the front panel of the MPC to turn off alarms. [CSCdk22404]
The bugs listed in Table 1, which were present in Cisco IOS Release 11.3(1)DA1, are fixed in Cisco IOS Release 11.3(1)DA2.
| Bug Number | Description |
|---|---|
CSCdk03274 | The line quality test (an option with the linetest command) failed when the line was overloaded with traffic in the upstream direction. This does not happen if the traffic rate is less than or equal to the xDSL line rate. |
CSCdk08345 | If you run the CAP hardware test (linetest dsl slot/port caphardware duration 3 berr 10) on a card that has gone down very recently (within 15 seconds or so), no error message is displayed. |
CSCdk15261 | When you put a DSL port (on the SLC card) into loopback mode, the traffic associated with that port gets looped back from the ATM port as well as from the DSL port. As a result, the ARP table on the upstream link might need to be cleared. |
CSCdk13842 | Cisco 675 (NetSpeed 204) modems using NetSpeed firmware prior to Version 1.4.2 default to a NO_CHANGE_MARGIN configuration. This maximizes the downstream line rate for a given loop length. It does not guarantee a 10-7 error rate over a line that is subjected to impairments such as crosstalk, POTS signaling, and impulse or background noise. For Cisco 675 modems that have not been upgraded to Firmware Version 1.4.2, refer to the release note for Cisco IOS Release 11.3(1)DA1. |
CSCdk14841 | In the output of the command show dsl interface dsl, incorrect values are displayed for margins. |
CSCdk03285 | When you enter the command show dsl interface dsl slot/port, "Statistics" counts appear at the end of the resulting display. Sometimes the "VPI,VCI (0, 33) cells" values exceed the "Total cells" values. These values are read from different registers, and the registers are not read simultaneously. |
CSCdk14272 | PRFI and LRFI should be critical alarms, not major alarms. |
Use these release notes in conjunction with the documents listed in this section.
The documents mentioned below can be found on Cisco Connection Online and on the Documentation CD-ROM. For more information, see the "Cisco Connection Online" section and the "Documentation CD-ROM" section. For location details, see the "Online Navigation for Cisco IOS Software Documentation" section.
The following Cisco 6200 documents are available:
The Cisco 6200 documentation contains all of the information on Cisco IOS software that you need to configure and manage the Cisco 6200. Cisco does not expect that users of the Cisco 6200 will need to refer to the Cisco IOS software documentation set. However, if you want more information about Cisco IOS commands, refer to the Cisco IOS software documentation set, which is described in this section.
The Cisco IOS software documentation is divided into nine modules and two master indexes. There are also four supporting documents.
Each module consists of two books: a configuration guide and a corresponding command reference. Chapters in a configuration guide describe protocols, configuration tasks, and Cisco IOS software functions and contain comprehensive configuration examples. Chapters in a command reference provide complete command syntax information. Each configuration guide can be used with its corresponding command reference.
Two master indexes provide indexing information for the Cisco IOS software documentation set: an index for the configuration guides and an index for the command references. In addition, each book has its own index.
The Cisco IOS documentation set consists of the following books and chapter topics:
| Book | Chapter Topic |
|---|---|
| Configuration Fundamentals Overview Cisco IOS User Interfaces File Management Interface Configuration System Management |
| IP Addressing IP Services IP Routing Protocols |
| AppleTalk Novell IPX |
| Apollo Domain Banyan VINES DECnet ISO CLNS XNS |
| ATM Frame Relay SMDS X.25 and LAPB |
| AAA Security Services Security Server Protocols Traffic Filtering Network Data Encryption Passwords and Privileges Neighbor Router Authentication IP Security Options |
| Dial Business Solutions and Examples Dial-In Port Setup DDR and Dial Backup Remote Node and Terminal Service Cost-Control and Large-Scale Dial Solutions VPDN |
| Switching Paths for IP Networks Fast Switching Autonomous Switching NetFlow Switching Optimum Switching Virtual LAN (VLAN) Switching and Routing Inter-Switch Link Protocol Encapsulation IEEE 802.10 Encapsulation LAN Emulation |
| Transparent Bridging Source-Route Bridging Remote Source-Route Bridging DLSw+ STUN and BSTUN LLC2 and SDLC IBM Network Media Translation DSPU and SNA Service Point SNA Frame Relay Access Support APPN NCIA Client/Server Topologies IBM Channel Attach |
|
|
You can access the Cisco IOS software electronic documents either on the Cisco Documentation CD-ROM or at Cisco Connection Online (CCO) on the World Wide Web:
The following are some of the Cisco IOS Release 11.3 documents:
For product bulletins on CCO, the path is as follows from Cisco Connection Online:
Products and Ordering: More Information: Product Bulletins. In the Software area, under Cisco IOS 11.3, click Cisco IOS Software Release 11.3 Upgrade Paths.
Cisco IOS Release 11.3 master indexes for the configuration guides and command references can be accessed on the Documentation CD-ROM or through the CCO (Cisco Connection Online) page of the Cisco web site. The CD-ROM is updated monthly, and can be ordered through CCO. To access the Cisco IOS Release 11.3 master indexes, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Access the Cisco home page at http://www.cisco.com.
Step 2 Select Software and Support.
Step 3 Under the Software Center bullet, select Cisco IOS Software.
Step 4 Under the Additional Information bullet, select Software Configuration. The Cisco IOS Software Configuration page should now be displayed. It lists the Cisco IOS releases currently available.
Step 5 Select Cisco IOS Release 11.3, which accesses the Cisco IOS Release 11.3 page. This page lists the various documents available for Release 11.3.
Step 6 Select Cisco IOS 11.3 Configuration Guides, Command References, and then select the particular document index you would like to view.
For additional information about the Documentation on CCO and the CD-ROM, refer to the sections "Cisco Connection Online" and "Documentation CD-ROM" at the end of these release notes.
Cisco Connection Online (CCO) is Cisco Systems' primary, real-time support channel. Maintenance customers and partners can self-register on CCO to obtain additional information and services.
Available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, CCO provides a wealth of standard and value-added services to Cisco's customers and business partners. CCO services include product information, product documentation, software updates, release notes, technical tips, the Bug Navigator, configuration notes, brochures, descriptions of service offerings, and download access to public and authorized files.
CCO serves a wide variety of users through two interfaces that are updated and enhanced simultaneously: a character-based version and a multimedia version that resides on the World Wide Web (WWW). The character-based CCO supports Zmodem, Kermit, Xmodem, FTP, and Internet e-mail, and it is excellent for quick access to information over lower bandwidths. The WWW version of CCO provides richly formatted documents with photographs, figures, graphics, and video, as well as hyperlinks to related information.
You can access CCO in the following ways:
For a copy of CCO's Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ), contact cco-help@cisco.com. For additional information, contact cco-team@cisco.com.
For the latest information on caveats and known problems, follow these steps to consult CCO:
Step 1 Connect to CCO as directed in the section above.
Step 2 On the CCO home page, click LOGIN, which appears in green in the menu bar at the top of the page, and log into CCO. (If you are not a registered CCO user, follow the instructions to register so that you can log in.)
Step 3 After you log in, click Software & Support on the CCO home page.
Step 4 On the Software & Support page, click Technical Tools.
Step 5 On the Technical Tools page, click Bug Toolkit II. (Bug Toolkit II is not visible on the Technical Tools page unless you log in to CCO as directed in Step 2.)
Step 6 Use one of the tools to get up-to-date bug information. For example, click Search for Bug by ID Number, then enter a bug ID, such as CSCdk09616, when prompted. For instructions on using the bug tools, go to the bottom of the Bug Toolkit II page and click Help—How to Use the Bug Toolkit.
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available in a CD-ROM package, which ships with your product. The Documentation CD-ROM, a member of the Cisco Connection Family, is updated monthly. Therefore, it might be more current than printed documentation. To order additional copies of the Documentation CD-ROM, contact your local sales representative or call customer service. The CD-ROM package is available as a single package or through an annual subscription. You can also access Cisco documentation on the World Wide Web at http://www.cisco.com, http://www-china.cisco.com, or http://www-europe.cisco.com.
If you are reading Cisco product documentation on the World Wide Web, you can submit comments electronically. Click Feedback in the toolbar and select Documentation. After you complete the form, click Submit to send it to Cisco. We appreciate your comments.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Sat Sep 28 04:57:00 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.