|
|

Product Numbers:
CSC-C2CTR=
APP-LTR2=
MC-C2CTR-V10.2=
This document contains instructions for installing the multiport ciscoBus Token Ring interface card (CSC-C2CTR) and Token Ring applique (APP-LTR2) in your AGS+ chassis. This document also provides instructions for upgrading the C2CTR microcode by replacing a single erasable programmable read-only memory (EPROM) component on the CSC-C2CTR card. The CSC-C2CTR provides two or four high-speed Token Ring interfaces for connection to IEEE 802.5 and IBM-compatible Token Ring media at speeds of 4 or 16 Mbps. The APP-LTR2 provides the interface between the CSC-C2CTR and your Token Ring network. Both the card and applique must be installed in an AGS+ with a CSC/3 or CSC/4 processor card and a ciscoBus II controller card (CSC-CCTL2).
The sections in this document include the following:
The following sections contain physical descriptions and brief functional overviews of the CSC-C2CTR card and the APP-LTR2 applique.
The CSC-C2CTR resides in the AGS+ system card cage. Each port on the CSC-C2CTR provides one Token Ring interface and connects to an APP-LTR2 applique with an internally routed ribbon cable. The APP-LTR2, which resides in an applique card cage, are installed in the two far right large plate areas in the rear of the AGS+. The appliques provide the external interface to the Token Ring network.
A typical installation, showing the interface card, the (internal) interface cable, and the interface applique, is shown in Figure 1. The system card cage and applique card cages are not included in the drawing in order to more clearly show the cable routing.

The CSC-C2CTR, shown in Figure 2, contains four ports. The card supports two interfaces when used with one APP-LTR2 and four interfaces when used with two APP-LTR2s. Each port (interface) is individually configured to operate at 4 or 16 Mbps. The C2CTR-specific microcode (firmware) resides on an EPROM in socket position U98, which may need to be replaced when the system software is upgraded or when operating enhancements are implemented. Instructions for the microcode upgrade can be found in the section "Upgrading Microcode" on page 34.
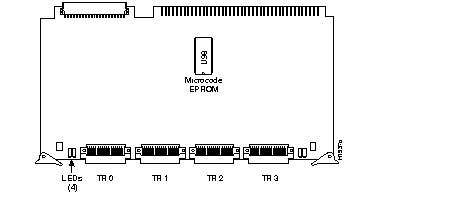
The four interface ports are numbered from left to right TR 0 through TR 3 when viewing the card as installed in the system card cage. (See Figure 3.) Each port is connected to an APP-LTR2 with an internal ribbon cable. Four green LEDs indicate the status of each port (interface). When an interface is up, or active in the ring, the corresponding LED is on. The LED is off when the interface is inactive, administratively down, not internally connected to the applique, or the applique is not externally connected to the ring.
The C2 designator in the product number indicates that the CSC-C2CTR card must be installed in an AGS+ with a ciscoBus II controller card (CSC-CCTL2). The CSC-C2CTR can be installed in any available ciscoBus slot except the center slot, which contains the CSC-CCTL2. However, for optimum performance, the CSC-C2CTR should be installed in the highest-priority slot available in accordance with the slot priority scheme described on page 9. Instructions for determining your current system software version and the type of ciscoBus controller installed are provided in the section "System Compatibility Requirements" on page 6.
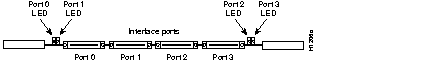
The APP-LTR2, shown in Figure 4, provides the required high-speed interfaces between the CSC-C2CTR and your Token Ring network. Each applique contains two female DB-9 Token Ring connectors and the Media Access Control (MAC) circuitry for each interface. The green power LED goes on to indicate the applique is receiving power from the CSC-C2CTR. Two ribbon cables provide the internal connection between the applique and two ports on the CSC-C2CTR.

The APP-LTR2 is installed in an applique card cage mounted on the rear panel of an AGS+. One or two appliques can be installed in each card cage. Because of internal space limitations, no more than two applique card cages can be installed in the AGS+ chassis; therefore, a maximum of four APP-LTR2s can be installed. A grounding strap, which is included with the applique, must also be installed to prevent noise on the interface. Detailed instructions for installing the applique and card cage are provided in the section "Installing the APP-LTR2 Applique" on page 20.
This section describes the minimum compatibility requirements that your system hardware and software must meet before you install a new CSC-C2CTR. It describes the various commands you can use to verify the compatibility requirements.
Before installing a new CSC-C2CTR, ensure that your existing system components meet the following minimum configuration requirements for compatibility with the card:
You can display the current software version and the type of processor card installed with the show version command. The current system software version is displayed in the first line of the output, and the processor card information is displayed on the eighth line, followed by a list of the installed interface cards. A sample of the display follows:
router# show version
GS Software (GS3-BFX), Version 9.1
Copyright (c) 1986-1992 by cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Wed 03-Jun-92 01:24
System Bootstrap, Version 4.5(0.8)
router uptime is 11 days, 8 hours, 41 minutes
System restarted by power-on
System image file is "router-system", booted via tftp from 131.108.1.111
CSC3 (68020) processor with 4096K bytes of memory.
X.25 software.
Bridging software.
1 MCI controller (2 Ethernet, 2 Serial).
1 cBus controller.
1 MEC controller (6 Ethernet).
1 CTR controller (4 Token Ring).
Environmental Controller.
8 Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 interface.
4 Token Ring/IEEE 802.5 interface.
2 Serial network interface.
1 HSSI network interface.
1 FDDI network interface.
You can display a description of the current ciscoBus controller card with the show controller cbus EXEC command. The ciscoBus controller type is displayed, followed by a description of each ciscoBus interface card, the ciscoBus slot in which it is installed, and the microcode version of each. A sample of the display follows. For complete descriptions of all of the displayed fields, refer to the Router Products Configuration Guide and Router Products Command Reference publications. In the following display, note that the microcode version on all ciscoBus interface cards is Version 10.0 or later, indicating that the ciscoBus controller is a CSC-CCTL2.
router# show cont cbus
ciscoBus 1, controller type 6.0, microcode version 10.0
512 Kbytes of main memory, 128 Kbytes cache memory
(display text omitted)
FDDI-T 0, controller type 7.1, microcode version 10.1
Interface 0 - Fddi0, station address 0000.0c02.6aa3
(display text omitted)
CTR 1, controller type 9.0, microcode version 10.1
Interface 8 - TokenRing0, station address 0000.3040.e004
13 buffer RX queue threshold, 31 buffer TX queue limit,
(display text omitted)
Interface 9 - TokenRing1, station address 0000.3040.e084
(display text omitted)
Interface 10 - TokenRing2, station address 0000.3040.e044
(display text omitted)
Interface 11 - TokenRing3, station address 0000.3040.e0c4
(display text omitted)
HSCI 2, controller type 10.0, microcode version 10.0
Interface 16 - Hssi0, electrical interface is Hssi DTE
(display text omitted)
You can display a description of the current Multibus Token Ring interfaces with the show controller token command. There is no card name or controller type displayed with this command. Although it is not apparent, the card type is distinguishable in the first line of the show controller token display (CSC-1R/2Rs are displayed as TR Unit n on the first line of the display; CSC-R16Ms are labeled TRn in the first line.) The microcode version (labeled f/w ver) is displayed on about the twelfth line of the display.
The following example shows a CSC-1R with Microcode Version 1.2 installed:
router# show cont token
TR Unit 0 is board 0 - ring 0
(11 lines of text omitted)
f/w ver: 1.2 expr 0, chip f/w:00000.ME31100,[bridge capable]
SMT versions: 1.01 kernel, 4.02 fastmac
(text omitted)
The following example shows a CSC-R16M with Microcode Version 3.2:
router# show cont token
TR0: state 3, dev blk: 0x1C98A4, mailbox: 0x21000B0, sca: 0x2010000
(11 lines of text omitted)
f/w ver: 3.2, chip f/w: '000000.ME31100', [bridge capable]
For field descriptions and additional commands, refer to the Router Products Configuration Guide and Router Products Command Reference publications.
Before installing a new CSC-C2CTR, ensure that all ciscoBus interface cards are the C2 type (all have Microcode Version 10.0 or later installed), that any new ciscoBus cards you are installing will not exceed the maximum port limits for ciscoBus interfaces, and that the ciscoBus cards will be placed in the correct order of priority in the ciscoBus slots. The following sections describe how to determine all of these requirements.
All ciscoBus interface cards, which are listed in Table 1, contain card-specific microcode that determines whether the card is compatible with the first- or second-generation ciscoBus controller card. Following are compatibility guidelines:
| CCTL Controller Card | CCTL2 Controller Card | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CSC-CCTL | CSC-CCTL2 | ciscoBus controller |
| CSC-FCI | CSC-C2FCI | Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) |
| CSC-C2FCIT | FDDI with translational bridging | |
| CSC-HSCI | CSC-C2HSCI | High-Speed Serial Interface (HSSI) |
| CSC-C2CTR | ciscoBus Token Ring interface, 4/16Mbps | |
| CSC-MEC | CSC-C2MEC1 | Multiport Ethernet Controller interface |
The C2 designator added to the name of a ciscoBus interface card indicates that the card is running Microcode Version 10.0 or later and is, therefore, compatible with the second-generation ciscoBus controller card, the CSC-CCTL2. With the exception of a Revision 5.0 CSC-MEC (see Note following), the first- and second-generation ciscoBus interface cards are otherwise the same. For example, you can upgrade a revision 5.1 CSC-MEC to a CSC-C2MEC by replacing the microcode with Version 10.0 or later. When you upgrade the microcode on the revision 5.1 CSC-MEC to Version 10.0, the name of the card also changes from CSC-MEC to CSC-C2MEC to indicate that it is CCTL2-compatible. When you replace a CSC-CCTL ciscoBus controller card with a CSC-CCTL2 ciscoBus controller card, you must upgrade the microcode on all ciscoBus interface cards to Microcode Version 10.0 or later.
You can display a description of the current ciscoBus controller and ciscoBus interface cards with the EXEC show controller cbus command, an example of which is shown on page 7. The name and controller type of each ciscoBus card, the ciscoBus slot in which it is installed, and the microcode version of each is displayed. (Additional statistical information is also displayed for each interface card, but is omitted from the example.)
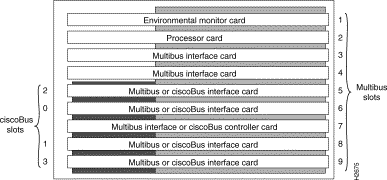
The system card cage, shown in Figure 5, has nine slots, five of which are designated ciscoBus slots. The center ciscoBus slot is reserved for the ciscoBus controller card, leaving four ciscoBus slots available for ciscoBus interface cards.
The system uses a slot priority scheme that assigns a priority to each ciscoBus card according to the ciscoBus slot in which the card resides. The card in ciscoBus slot 0 receives the highest ciscoBus priority, while the card in ciscoBus slot 3 receives the lowest ciscoBus priority.
Slot priorities are set to accommodate the amount of traffic generated by each interface card and the amount of card buffering required. Each ciscoBus interface card is placed in a specific slot with regard to other ciscoBus interface cards, if any. The order of priority is the same for both first- and second-generation ciscoBus controllers, except that the cards with the C2 designation can only be used with the CSC-CCTL2.
Following is a list of ciscoBus interface cards in order of priority, from highest to lowest:
Install CSC-MEC or C2MEC cards in the lowest-numbered slots, beginning with slot 0 (which has the highest priority), followed by CSC-C2CTR cards. After all CSC-MEC and CSC-C2CTR cards are installed, install CSC-HSCI and C2HSCI cards with the APP-LHS applique in the lowest-numbered available slots. Follow with the CSC-FCI and C2FCI cards. Next, install CSC-C2FCIT cards. Last, install the CSC-HSCI and C2HSCI cards with the APP-ULA (UltraNet) applique. Always install cards in the lowest-numbered available slot. For example, if using only CSC-C2HSCI cards (with APP-ULA), place the first in slot 0, the second in slot 1, and so forth.
The CSC-C2CTR will interoperate with any of the C2-designated ciscoBus interface cards. The maximum number of CSC-C2CTR ports that can be used when other ciscoBus interfaces are installed are shown in Table 2.
| C2CTR Ports (Cards) | C2FCIT/(C2)FCI 1 Ports (Cards) | (C2)MEC Ports (Cards) | (C2)HSSI Ports (Cards) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | (0) | 0 | (0) | 24 | (4) | 0 | (0) |
| 0 | (0) | 1 | (1) | 18 | (3) | 0 | (0) |
| 0 | (0) | 0 | (0) | 18 | (3) | 1 | (1) |
| 4 | (1) | 0 | (0) | 18 | (3) | 0 | (0) |
| 0 | (0) | 2 | (2) | 12 | (2) | 0 | (0) |
| 0 | (0) | 1 | (1) | 12 | (2) | 1 | (1) |
| 4 | (1) | 1 | (1) | 12 | (2) | 0 | (0) |
| 0 | (0) | 0 | (0) | 12 | (2) | 2 | (2) |
| 4 | (1) | 0 | (0) | 12 | (2) | 1 | (1) |
| 8 | (2) | 0 | (0) | 12 | (2) | 0 | (0) |
| 6 | (2) | 1 | (1) | 6 | (1) | 0 | (0) |
| 6 | (2) | 0 | (0) | 6 | (1) | 1 | (1) |
| 0 | (0) | 3 | (3) | 6 | (1) | 0 | (0) |
| 0 | (0) | 0 | (0) | 6 | (1) | 3 | (3) |
| 0 | (0) | 2 | (2) | 6 | (1) | 1 | (1) |
| 4 | (1) | 2 | (2) | 6 | (1) | 0 | (0) |
| 4 | (1) | 0 | (0) | 6 | (1) | 2 | (2) |
| 4 | (1) | 1 | (1) | 6 | (1) | 1 | (1) |
| 0 | (0) | 1 | (1) | 6 | (1) | 2 | (2) |
| 2 | (1) | 3 | (3) | 0 | (0) | 0 | (0) |
| 2 | (1) | 2 | (2) | 0 | (0) | 1 | (1) |
| 2 | (1) | 1 | (1) | 0 | (0) | 2 | (2) |
| 2 | (1) | 0 | (0) | 0 | (0) | 3 | (3) |
| 0 | (0) | 4 | (4) | 0 | (0) | 0 | (0) |
| 0 | (0) | 3 | (3) | 0 | (0) | 1 | (1) |
| 0 | (0) | 2 | (2) | 0 | (0) | 2 | (2) |
| 0 | (0) | 1 | (1) | 0 | (0) | 3 | (3) |
| 0 | (0) | 0 | (0) | 0 | (0) | 4 | (4) |
The AGS+ uses a card numbering scheme to identify cards in the chassis, and an interface addressing scheme to identify the ports (interfaces) on each card. Each Multibus interface card and the ciscoBus controller card (CSC-CCTL2) has a unique card number that you set with switch S1 on each card. Figure 6 shows the location of switch S1 on the CSC-CCTL2. The system processor uses the card numbers to assign interface addresses to the ports on each card and to control traffic across the Multibus. Because the CSC-CCTL2 controls the traffic between the Multibus and all ciscoBus cards, it is the only ciscoBus card that needs a card number. The card number of the CSC-CCTL2 is always 0, which is the factory default; no Multibus cards can be set for card
number 0. Figure 6 illustrates the correct switch settings for card number 0; all four pins are in the down (off) position when the CSC-CCTL2 is viewed from the front edge of the card (viewed as installed in the card cage).

At startup, the system polls each Multibus interface card, beginning with the lowest card number, and assigns a sequential interface address to each port (interface) on each card. When all Multibus interfaces are assigned, the system proceeds to the ciscoBus cards and continues the interface address sequence as it polls the ciscoBus cards according to the ciscoBus slot priority. (Refer to the section "Slot Priority" on page 9.)
These numbering schemes allow the system to distinguish each interface card while sequentially numbering like interfaces (such as Token Ring interfaces on CSC-2Rs and CSC-C2CTRs). Table 3 is an example of how the system assigns Token Ring interface addresses in a chassis with two CSC-2Rs (two ports each) and two CSC-C2CTRs (four ports each). The CSC-2R is a Multibus card, and the CSC-C2CTR is a ciscoBus card; therefore, the CSC-2R interface addresses are assigned first. The example in Table 3 shows the maximum number of 16 Token Ring interfaces allowable in an AGS+ without exceeding the power budget (also see the section "Compatibility with Other Cards" on page 15).
A maximum number of two CSC-C2CTRs can be installed in an AGS+ chassis. This limit is due to the internal space available for the APP-LTR2s, which are installed in an applique card cage. Each APP-LTR2 provides two interface ports; therefore, each CSC-C2CTR requires two APP-LTR2s when all four ports are used. Since each applique card cage holds two appliques, and a maximum of two applique card cages can be installed in an AGS+, a maximum of two CSC-C2CTRs and four APP-LTR2s can be installed in an AGS+. A top-down view of the AGS+ with two card cages installed is shown in Figure 7.
| Card | Port on Card | Interface Address Assigned |
|---|---|---|
| First CSC-2R | Port 0 | Token Ring 0 |
| Port 1 | Token Ring 1 | |
| Second CSC-2R | Port 0 | Token Ring 2 |
| Port 1 | Token Ring 3 | |
| First CSC-C2CTR | Port 0 | Token Ring 4 |
| Port 1 | Token Ring 5 | |
| Port 2 | Token Ring 6 | |
| Port 3 | Token Ring 7 | |
| Second CSC-C2CTR | Port 0 | Token Ring 8 |
| Port 1 | Token Ring 9 | |
| Port 2 | Token Ring 10 | |
| Port 3 | Token Ring 11 |
 | Caution The maximum number of Token Ring interfaces in a chassis is 16, which is the result of installing 4 CSC-2Rs and 2 CSC-C2CTRs. (Two ciscoBus slots are used as Multibus slots.) The number of ciscoBus interfaces is limited by space available for applique card cages and power budget limits. Because the slower Multibus interfaces always have higher priority than ciscoBus interfaces, traffic on the Multibus may degrade performance of ciscoBus interfaces that are not autonomously switched; therefore, we do not recommend this configuration for performance-sensitive applications. |
In an AGS+ shipped on or after October 1, 1991, the total power drawn by all installed cards must not exceed 300W per chassis. In AGS+ chassis shipped before October 1, 1991, the total power must not exceed 260W. (The earlier chassis contained a 5A circuit breaker, rather than the 7.5A circuit used in the current chassis configuration.) Table 4 lists the power requirements for each card available for the AGS+, including the CSC-C2CTR. The values for the CSC-C2CTR were measured with four Token Ring interfaces active and include power drawn by the appliques.
| Card | Power (Watts) |
|---|---|
| CSC/3 | 31 |
| CSC/4 | 35 |
| CSC-ENVM | 10 |
| CSC-MC+ | 3 |
| CSC-MCI | 281 |
| CSC-SCI | 20 |
| CSC-R16M | 34 |
| CSC-1R or CSC-2R | 30 |
| CSC-CCTL (cannot be used with CSC-C2CTR) | 29 |
| CSC-CCTL2 | 34 |
| CSC-FCI | 50 |
| CSC-FCIT | 36 |
| CSC-MEC | 221 |
| CSC-HSCI | 48 |
| CSC-C2CTR with 1 applique (2 ports) | 30 |
| CSC-C2CTR with 2 appliques (4 ports) | 42 |
Before installing new cards, check the power requirements of the existing system and the new card(s) to avoid exceeding the power budget. To calculate the power requirements of an existing system, add the values for each card in the chassis; the sum is the power requirement. To determine the available power budget, subtract that sum from 300 watts (W) (260W for chassis shipped before 10/1/91); the result is the power budget available for new interface cards. For example, to determine if you can install two CSC-C2CTRs in an AGS+ that already contains two CSC-MCIs and a CSC-C2MEC, determine the power requirements of the existing system, then subtract that sum from 300. Compare the result to the total power requirement of the two new cards. If the result is greater than the power requirement for the new cards, you can install the new cards without exceeding the power budget. The following shows a sample calculation to determine whether two new CSC-CTRs can be added to an AGS+ that already contains several other interface cards. (All calculations are in watts [W].)
| One CSC-ENVM card | 1 x 10 = 10 |
| One CSC/4 processor card | 1 x 35 = 35 |
| One CSC-CCTL2 card | 1 x 34 = 34 |
| One CSC-C2MEC card | 1 x 22 = 22 |
| Two CSC-MCI cards | 2 x 28 = 56 |
| Ten Ethernet transceivers | 10 x 4 = 40 |
| Power requirement of present system | 197 |
| Available power budget | 300 - 197 = 103 |
| Two CSC-C2CTRs, each with 2 appliques | 2 x 42 = 84 |
| New cards within power budget | 84 < 103 |
The CSC-C2CTR will interoperate with any other CSC-CCTL2-compatible ciscoBus cards (within the limits specified in the section "ciscoBus Port Limitations" on page 10), and with any Multibus interface card that is compatible with the current system software. However, as new features are added with system software releases, the microcode on interface cards may need to be upgraded in order to take advantage of the new features.
For example, the CSC-C2CTR requires a CSC-CCTL2 ciscoBus controller card and System Software Release 9.1 or later. (See the section "System Compatibility Requirements" on page 6.) If you are upgrading your system software and ciscoBus controller card to a CSC-CCTL2 along with this card installation, you must upgrade the microcode on all existing ciscoBus interfaces to Version 10.0 or later and, to ensure that all the features of a software release are available, and you must upgrade the microcode on existing Multibus interface cards to the minimum versions required for Software Release 9.1 compatibility.
The Microcode Release Note publication (Part Number 78-1069-xx, where xx is the latest version) provides the latest information on both the recommended and minimum required microcode versions for using all cards with Software Releases 8.2 through 9.1. If the latest version implements features that you are not using in your system, and you already have the minimum required version installed, there is no requirement to update the microcode. However, new microcode versions occasionally fix bugs and provide performance enhancements in addition to implementing new features. You will obtain maximum performance and reliability by upgrading to the recommended version. Refer to the latest Microcode Release Note publication for current microcode requirements and recommendations and for a microcode revision history for each card.
To display the current microcode on any interface card, use the show controller command with appropriate variables (cbus, token, serial, or ethernet). To display the current CSC-ENVM microcode, use the show environment command (available with Software Release 9.0 and later). An example of the show controller cbus command is shown on page 7. The following partial sample display of the show controller mci command shows a CSC-MCI with Microcode Version 1.10 installed.
router# show cont mci
MCI 1, controller type 1.1, microcode version 1.10
(additional display text omitted from example)
The following partial sample display shows a CSC-ENVM with Microcode Version 2.2 installed.
router# show env
Environmental controller firmware version 2.2
(additional display text omitted from example)
With the required microcode versions installed, the CSC-C2CTR is compatible with the followingthree currently available Token Ring Multibus interface cards:
 | Caution The maximum number of Token Ring interfaces in a chassis is 16, which is the result of installing 4 CSC-2Rs and 2 CSC-C2CTRs. (Two ciscoBus slots are used as Multibus slots.) The number of ciscoBus interfaces is limited by space available for applique card cages and power budget limits. Because the slower Multibus interfaces always have higher priority than ciscoBus interface, traffic on the Multibus may degrade performance of ciscoBus interfaces that are not autonomously switched; therefore, we do not recommend this configuration for performance-sensitive applications. |
Before installing the CSC-C2CTR, determine the ring speed (4 or 16 Mbps) of each ring to be connected. There is no factory default for the interface speed; you must use the ring-speed command to set the speed of each interface when you bring the interface up and insert it into a ring. The CSC-C2CTR interfaces are independent, and each can be configured for either 4 Mbps or 16 Mbps.
 | Caution If an interface has an undefined or incorrect ring speed and is not shut down, the ring will beacon, which effectively takes the ring down and makes it inoperable. |
Verify that you received all of the following parts. If any parts are missing, contact a customer service representative.
You need some or all of the following tools to perform installation and upgrade procedures. Before you begin, read through the procedure to determine which tools you need for your chassis.
Follow these guidelines when working with any electrical equipment:
In addition, use the guidelines that follow when working with any equipment that is connected to telephone wiring or other network cabling.
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a discharge of stored static electricity that can damage equipment and impair electrical circuitry. It occurs when electronic components are improperly handled and can result in complete or intermittent failures.
Following are guidelines for preventing ESD damage:
 | Caution For safety, periodically check the resistance value of the antistatic strap. The measurement should be between 1 and 10 megohms. |
The following sections describe the procedures for installing CSC-C2CTRs and APP-LTR2s. The CSC-C2CTR is installed in the system card cage, which you access by removing the access panel on the front of the chassis. It is not necessary to disconnect cables from the rear of the chassis or to remove the top cover of the chassis to access the system card cage.
The APP-LTR2 is installed in the rear of the chassis; access to the rear of the chassis requires removing the front panel and top cover from the chassis. The appliques are installed in an applique card cage, which is then installed in one of the two far right connector areas in the rear of the chassis.
A typical installation, showing the interface card, the applique, and the internal connections, is shown in Figure 1. Before proceeding, ensure that your system and equipment meet the requirements listed in the section "Installation Prerequisites" on page 6.
Install the CSC-C2CTR in the predetermined ciscoBus slot in the system card cage. (Refer to the section "Slot Priority" on page 9 for slot priority requirements.) The card cage in the AGS+ is accessible from the front of the chassis. To install system cards, you need to remove only the front access panel; it is not necessary to remove the top cover. All interface cards have ejector levers that lock into place when the card is seated in the card cage, which allow the card to be extracted easily from its slot. Handle cards as little as possible; try to limit contact to only the ejector levers and card edges. Install the CSC-C2CTR as follows:
Step 1 Ensure that the chassis is firmly seated on a stable surface. The cards that connect to the ciscoBus require substantial force to slide them into the card cage and seat them properly.
Step 2 On the front access panel (shown in Figure 8), turn the two thumbscrews counterclockwise to loosen them; do not attempt to remove them from the panel. Pull the panel off the chassis and set it aside.
Step 3 Slip on an ESD wrist or ankle strap and connect it to the chassis as described in the previous section, "Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage." Make certain that power to the chassis is OFF, but that the power cord is fully connected.

Step 4 If necessary, disconnect the cables from other interface cards that are obstructing access to the center ciscoBus slot. Before disconnecting cables, ensure that they are properly labeled to avoid mixing up interfaces when you reconnect them.
Step 5 If you are installing a new CSC-C2CTR, proceed to step 7, but if you are replacing an existing CSC-C2CTR, disconnect the cables from the front of the card to be removed.
Step 6 Use your thumbs to pull the eject levers out and away from the card edge to loosen it and pull the card out of its slot. Place the removed card on an antistatic mat or antistatic foam pad.
Step 7 Hold the new CSC-C2CTR by the eject levers and the card edges, component side up, with the bus edge away from you, and insert it into any empty ciscoBus slot. An AGS+ card cage is shown in Figure 5.
Step 8 Place your thumbs on the eject levers and push the card in firmly until it snaps into place and is firmly seated in the slot.
Step 9 If APP-LTR2s are already installed, connect the internal ribbon cables to the ports corresponding to the labels on the cables (0-3). When viewing the card in the card cage, the far left port is port 0.
Step 10 To install the APP-LTR2(s), proceed to the next section.
or
If the appliques are already installed, proceed to the section "Installing Short Ground Straps" on page 23 or "Installing Long Ground Straps" on page 24.
The APP-LTR2 is installed in an applique card cage in the rear of the chassis; access to the rear of the chassis requires removing the front panel and top cover from the chassis. The following describes how to first install the applique in the applique card cage and then install the card cage in the chassis.
 | Warning Before removing any cables or fasteners from the chassis, turn off the power and unplug the power cable from the power source. When the cover is off the chassis, the power supply is exposed and dangerous voltages are present. |
The following steps describe how to install the applique in the applique card cage:
Step 1 Remove the top cover of the chassis by loosening and removing the seven screws that secure it. (See Figure 8.)
Step 2 Slip on an ESD-preventive wrist or ankle strap and connect it to the chassis as described in the section "Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage." Make certain that power to the chassis is OFF, but that the power cord is fully connected.
Step 3 If you have an empty card cage that is not installed in the chassis, proceed to step 5, but if the applique card cage is installed in the chassis, disconnect any external connections to the applique it contains.
Step 4 Remove the card cage from the chassis by removing the six screws that secure it to the rear panel of the chassis. Carefully lift the card cage up and out of the chassis, using care not to strain any internal ribbon cables.
Step 5 Remove the top cover of the applique card cage by loosening the four cover fasteners that secure it. (See Figure 9.)
Step 6 If the card cage is empty, remove both filler plates from the rear. (See Figure 9.) If an applique is currently installed, leave the faceplate of the installed applique intact and remove only the filler plate.
Step 7 Using the orientation shown in Figure 9, install the first APP-LTR2, with its attached faceplate, into the right side of the card cage. Position the applique so that the tab on the bottom of the applique faceplate is inserted into the slot in the bottom of the applique card cage, and the applique is seated in the card guide. (See Figure 9.)
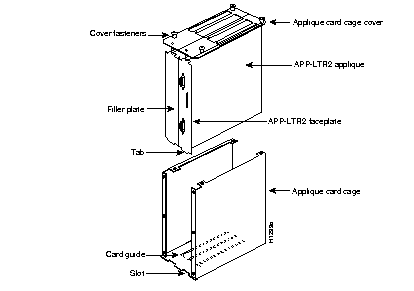
Step 8 If you are installing only one applique, replace the filler plate on the left side of the card cage, sliding it down so that the edge interlocks with the faceplate of the applique on the right.
or
If you are installing a second APP-LTR2 in the card cage, install it in the left side of the card cage by sliding it down so that the faceplate interlocks with the faceplate of the applique on the right of the card cage. Insert the applique into the card cage so that the tab on the bottom of the applique card faceplate is inserted into the slot in the bottom of the applique card cage, and the applique is seated in the card guide.
Step 9 Replace the top cover of the applique card cage. Ensure correct alignment of the cover with the two guide pins on the bottom of the cover. The guide pins should pass through the alignment holes in the tabs on the top of each applique and faceplate assembly. (See Figure 9.)
Step 10 Secure the top cover to the card cage with the four cover fasteners you loosened in step 5.
The following steps describe how to install the applique card cage in the chassis. The applique card cage can only be installed in one of the two far right large plate areas. (See Figure 10.) If you removed the card cage to install the applique, proceed to step 2. (The large plate area will already be open.)
Step 1 Remove a blank large plate from one of the two far right large plate areas (shown in Figure 10) by removing the six screws that secure it.

Step 2 Label each internal ribbon cable with a Token Ring interface number so that you can connect the applique interfaces to the correct ports on the CSC-C2CTR.
Step 3 Place a corresponding external interface label on the face of each applique connector below each Token Ring connector (Token0 on the top and Token1 on the bottom). Be sure to match the interface numbers with the labels on the internal cables.
Step 4 Connect the appropriate internal Token Ring ribbon cable to the connectors on each applique (Token0 to the top connector and Token1 to the bottom connector).
Step 5 Slide the applique card cage down into the rear of the chassis, and align the six holes in the rear panel of the chassis with those in the applique card cage. (See Figure 10.)
Step 6 Secure the card cage with the connector plate screws you removed in step 1, leaving appropriate holes empty for the ground straps. See Figure 11 and Figure 12 for ground strap configurations.
Step 7 Route each internal ribbon cable under the system card cage then up to the corresponding connector on the CSC-C2CTR. Be sure to connect each cable to the correct port on the CSC-C2CTR; card ports are numbered 0 to 3 (from left to right when viewed from the front of the chassis).
Step 8 Decide if your installation requires short or long ground straps. Use a short ground strap when you install the applique next to a blank connector plate (see Figure 11) or next to an applique that does not contain a hole for the long ground strap screw. Use a long ground strap when you install the applique next to an applique that contains a hole for the long ground strap, for example, another APP-LTR2 (see Figure 12).
Ground straps, which are included with all appliques, ground the applique to the chassis to prevent EMI noise on your network interface. The applique card cage containing the APP-LTR2(s) should already be installed in the chassis and secured with at least three screws. Refer to Figure 11 while you install the short ground straps.

Step 1 Remove the Phillips screw from the top center of the applique.
Step 2 Position the ground strap so that it straddles the applique and the rear panel of the chassis. Align the holes in the ground strap with those on the rear panel and the applique.
Step 3 Secure the ground strap with the two Phillips screws.
Step 4 Repeat the same process for the bottom ground strap.
Step 5 Connect ground straps to other appliques as necessary, and proceed to the section "Finishing the Installation" on page 25.
Ground straps, which are included with all appliques, ground the applique to the chassis to prevent EMI noise on your network interface. The applique card cage containing the APP-LTR2(s) should already be installed in the chassis and secured with at least two screws. Refer to Figure 12 while you install the long ground straps.

Step 1 Remove the Phillips screw from the top center of each applique.
Step 2 Position the ground strap so that it straddles both appliques and the rear panel of the chassis. Align the holes in the ground strap with those on the rear panel and the appliques.
Step 3 Secure the ground strap with the four Phillips screws.
Step 4 Repeat the same process for the bottom ground strap.
Step 5 Connect ground straps to other appliques as necessary, and proceed to the next section, "Finishing the Installation."
The following steps describe the final installation procedure:
Step 1 Connect the external cables from your Token Ring network to the Token Ring connectors on the appliques.
Step 2 If necessary, reconnect other cables on the rear of the chassis.
Step 3 Replace the chassis cover, but do not secure it with the cover screws until you have verified successful installation.
 | Caution You must replace the chassis cover before powering up the system for an installation check. However, you do not need to tighten the screws. |
Step 4 Proceed to the next section to check the installation before configuring the interface.
After you have installed a CSC-C2CTR and/or APP-LTR2, verify the installation before you replace the front panel by observing the LEDs on the system processor card, the CSC-CCTL2 ciscoBus controller card, the CSC-C2CTR card, and the APP-LTR2 in the rear of the chassis. The LEDs on the CSC-C2CTR will not light until the new interfaces are configured and brought up. After you configure the interfaces (as described in the section "Configuring the Interfaces" on page 29), you will check the CSC-C2CTR LEDs and use the show EXEC commands to verify the interfaces.
 | Warning Never power up the system when the top cover is removed because the power supply and dangerous voltages are exposed. Also, the internal airflow is misdirected when the cover is off, which can cause the system to overheat and subsequently shut down. |
The LEDs on the CSC/3 and CSC/4 processor cards indicate the status of the system software. If the system detects a problem at startup, the system error LED on the processor card will be on or will flash. The CSC-CCTL2 LEDs verify the presence (correct installation) of all cards installed in the ciscoBus. Also, on the APP-LTR2 (see Figure 4), a single, green, power LED goes on to indicate that the applique is receiving power from the CSC-C2CTR. After the interfaces are configured and brought up, the LEDs on the CSC-C2CTR go on for each active port. (See the section "CSC-C2CTR Interface Card" on page 4.)
Either a CSC/3 or a CSC/4 can be installed in your system. Both have three LEDs with similar functions. When viewing either card when it is installed in the system card cage, the right LED is the system OK light, which goes on to indicate that the system is operating correctly. The far left LED on both is a system error LED, which goes on or flashes if the system detects an error during startup or is unable to start up the operating system.
The three CSC/4 LEDs are shown in Figure 13. The left yellow status LED goes on momentarily during initialization, flashes if there is an error, and is off under normal conditions. The middle, yellow LED is not used. The right, green, OK LED goes on at startup and remains on to indicate that the system software has booted and is operational.
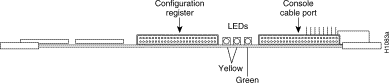
The three CSC/3 LEDs are shown in Figure 14. The far left, red, status LED goes on momentarily during initialization, flashes if there is an error, and is off under normal conditions. The middle, red, halt LED goes on only when the processor is in a halt state (which indicates an error). The far right green OK LED lights at startup and remains on to indicate that the system software has booted and is operational.

The CSC-CCTL2 contains a bank of five LEDs, one red LED for each ciscoBus slot and one green OK LED. Figure 15 shows the LEDs as viewed with the card installed in the card cage. The numbers above each LED indicate the corresponding ciscoBus slot number. (Slot numbers and locations are shown in Figure 5.)

On power up, all the LEDs go on indicating that the CSC-CCTL2 is active. When the system boot is completed, only those LEDs that indicate the presence of a card in the corresponding ciscoBus slot should remain on; the LEDs for empty ciscoBus slots should go off. Before you power up the system, make a note of the ciscoBus slot(s) that contain a new CSC-C2CTR so that you can verify that the corresponding CSC-CCTL LED lights. All ciscoBus slot numbers are shown in Figure 5.
Take the following steps to verify correct installation:
Step 1 Plug in the power cord and turn ON the system power.
Step 2 Verify that all five LEDs on the ciscoBus controller card (CSC-CCTL2) goes on while the system boots. If they do not go on, do the following:
Step 3 When the system has booted, check the LEDs on the CSC/3 or CSC/4 system processor card. The right, green OK LED should be lit; the other two LEDs should be off. (See Figure 13 and Figure 14.) If the right, green LED is not on, or if either of the other two LEDs is on or flashing, do the following:
Step 4 When the system has completed its boot cycle (indicated by a beep), verify that the right, green OK LED on the CSC-CCTL2 goes on and remains on. (See Figure 15.) If it does not, proceed with the installation to determine whether the LED is faulty.
Step 5 Verify that the power LED on the APP-LTR2 is lit. (See Figure 4.) If it is not on, do the following:
Step 6 Check the four red LEDs on the CSC-CCTL2. (See Figure 15.) Ensure that each LED goes on for each ciscoBus slot occupied by a ciscoBus card; the ciscoBus controller LEDs do not light for ciscoBus slots that contain Multibus cards. (See the section "Checking LEDs" on page 27 for LED descriptions.) If any do not go on, do the following:
Step 7 Check the system console terminal and ensure that the system banner is displayed, followed by a list of the installed hardware. (See page 6 for an example of this display, which is the same as the output for the show version command.) CSC-C2CTRs are displayed as CTR interfaces, and the number of interfaces displayed should include the new interfaces you just installed.
When the installation check is successful, proceed as follows:
Step 1 Turn OFF the system power.
Step 2 Replace and tighten any remaining cover screws.
Step 3 Replace and secure the front access panel.
Step 4 Turn ON the system power to configure your network interface.
You must configure new interfaces and bring them up before you can verify them with screen displays. Proceed to the following section to configure each new interface.
If you installed a new CSC-C2CTR or if you want to change the configuration of an existing interface, you must enter configuration mode. After you verify that the new equipment is installed correctly, use the privileged-level configure command to configure each new Token Ring interface. Be prepared with the information you will need, which includes the following:
Refer to the Router Products Configuration Guide and Router Products Command Reference publications for a complete summary of the configuration options available and instructions for configuring a Token Ring interface.
Before you use the configure command, you must enter the privileged level of the EXEC command interpreter with the enable command. The system will prompt you for a password if one has been set. The system prompt for the privileged level ends with a pound sign (#) instead of an angle bracket (>). At the console terminal, enable the privileged level as follows:
Step 1 At the user-level EXEC prompt, enter the enable command. The EXEC prompts you for a privileged-level password, as follows:
enable
Step 2 Enter the password. (The password is case sensitive.) For security purposes, the password is not displayed.
Step 3 When you enter the correct password, the system displays the privileged-level prompt (#):
Proceed to the next section to configure the interface.
Following are instructions for a basic configuration: enabling an interface and specifying IP routing. You might also need to enter other configuration subcommands, depending on the requirements for your system configuration and the protocols you plan to route on the interface. For complete descriptions of configuration subcommands and the configuration options available for Token Ring, refer to the Router Products Configuration Guide and Router Products Command Reference publications.
The system banner and a list of all installed interfaces, including those you just installed, should be displayed. (See page 6 for an example of this display, which is the same as the output from the show version command.) If this information is not displayed, return to the section "Installing Long Ground Straps" on page 24 and perform the steps to isolate the problem.
You must enter the privileged level of the EXEC in order to use the configure command. After specifying an interface, you will enter the configuration information with interface subcommands. Before beginning this procedure, use the show interfaces command to determine which interfaces you need to configure.
The show configuration EXEC command displays the configuration information stored in nonvolatile memory. Before entering any new interface information, you may want to use this command to review the current configuration. The following example shows a partial display of the show configuration command output:
router# show config
Using 2648 out of 65536 bytes
version 9.1
!
hostname router
!
enable-password secretword
!
(display text omitted)
!
interface TokenRing 0
ip address 131.108.8.35 255.255.255.0
ip helper-address 131.108.7.255
ip helper-address 131.108.9.255
ring-speed 4
appletalk cable-range 4035-4035 4035.8
appletalk zone Engineering
!
interface TokenRing 1
no ip address
shutdown
!
(remainder of display text omitted)
In configuration mode, you identify the specific interface to be configured with the interface configuration command, which begins the configuration subcommand collection mode for the specified interface. The syntax is interface type unit, where type identifies the type of interface (such as Token Ring), and unit identifies the interface unit address. Then you enter the configuration subcommands that define the specific configuration for the interface. For example, new interfaces are shut down by default; you must enable each one with the no shutdown interface subcommand. You need other interface subcommands to assign the ring speed (4 or 16 Mbps) to each interface, specify encapsulation methods, and define routing protocols. The speed of each Token Ring interface must be configured before you bring the interface up and insert it into the ring. The interfaces are independent and can be configured for different speeds. There is no factory default speed; you must configure each interface for either 4 or 16 Mbps. For complete descriptions of the configuration subcommands, refer to the Router Products Configuration Guide and Router Products Command Reference publications.
In the following sample configuration, two new Token Ring interfaces are enabled and assigned ring speeds and IP addresses using the configure command from the terminal (the config term command); then the configuration is written to memory (using the write memory command).
router# enable
Password:
router# config term
Enter configuration commands, one per line.
Edit with DELETE, CTRL/W, and CTRL/U; end with CTRL/Z
interface token ring 0
ring-speed 16
ip address 145.22.4.67 255.255.255.0
no shut
interface token ring 1
ring-speed 4
ip address 145.22.4.68 255.255.255.0
no shut
^z
router# write memory
[ok]
router#
The following steps provide instructions for a basic configuration: enabling an interface, setting the ring speed, and specifying IP routing. You may also need to enter other configuration subcommands, depending on the requirements for your system configuration. (Configuration subcommands are described in the Router Products Configuration Guide and Router Products Command Reference publications.) Refer to the previous example as necessary.
 | Caution By default, all interfaces are configured as shut down until you enter no shut. After you enter no shut (or if the interface is already configured as up), the interface is inserted into the ring as soon as your press Return. Failure to match the interface speed to the ring speed will bring down the ring. The speed of each interface on the CSC-C2CTR must be configured to match the speed of the ring to which the interface is connected; only values of 4 or 16 will be accepted by the system. Each interface on the CSC-C2CTR can be configured for either 4 or 16 Mbps (for instance, Token Ring interface 0 can be set for 4 Mbps and Token Ring interface 1 set for 16 Mbps). |
The following steps provide line-by-line instructions for configuring the interfaces. Refer to the previous examples as necessary.
Step 1 To enter the EXEC command level, enter enable and the appropriate password and the system prompt.
Step 2 Enter configuration mode by entering the following:
configure terminal <Return>
Step 3 At the prompt, specify the first Token Ring interface to configure by entering the following:
interface token ring 0 <Return>
Step 4 Specify the ring speed for Token Ring 0, either 4 or 16 (Mbps), by entering the following (where n is either 4 or 16):
ring-speed n <Return>
Step 5 If IP routing is enabled on the system, you can assign an IP address and subnet mask to the interface with the ip address configuration subcommand as follows:
ip address 111.111.111.111 255.255.255.0 <Return>
(where 111.111.111.111 represents whatever address you assign to this interface)
Step 6 Change the default shutdown state and bring the interface up by entering the following:
no shut <Return>
Step 7 Specify the next Token Ring interface to configure by entering the following:
interface token ring 1 <Return>
Step 8 Repeat steps 3 through 6 for each new Token Ring interface.
Step 9 When all new interfaces are configured, enter Ctrl - Z (hold the Control key down and
press z).
Step 10 Write the new configuration to memory by entering the following:
write memory <Return>
The system will display an OK message to indicate that the configuration has been stored.
Step 11 To exit configuration mode, enter quit.
Step 12 Check the configuration as described in the following section.
After you have configured the ring speed of each interface, check the LEDs on the CSC-C2CTR and use EXEC command displays to verify the new Token Ring interfaces. When the system is started, the interface cards query the appliques for interface information. If an applique is not connected to its interface card when the system initializes, it will be not be recognized until it is properly connected to the card, and the system is restarted.
To check the configuration, proceed as follows:
Step 1 Turn the system power OFF, wait approximately five seconds, then turn the power ON again to reboot the system. (The system will beep when it has booted.)
Step 2 Open the front access panel and check the LEDs on the CSC-C2CTR. Two LEDs are located on each side of the card, numbered 0 through 3 from left to right as shown in Figure 3. Each LED goes on to indicate that the corresponding interface is active. The LED for each active interface should be on.
Step 3 If any of the LEDs indicate that an interface is not active (but should be), return to the configuration mode as described in steps 1 through 3 on page 31. Enter the interface unit address, then enter no shut as shown in the following example:
config term
Enter configuration commands, one per line.interface token ring 1
no shut
^z
router# write memory
[ok]Step 4 When the LEDs indicate that all interfaces are configured correctly, replace and secure the front access panel.
Step 5 You can now enter the commands described in the following paragraphs to verify the configuration.
The show controller cbus EXEC command (described in "System Compatibility Requirements" on page 6) displays the current internal status of the CSC-C2CTR(s), including the interfaces and how the CSC-C2CTR has identified them. The display lists the interfaces connected to each CSC-C2CTR and indicates that the system has identified new interfaces, but it does not indicate the state of the line or protocol.
The show controller token EXEC command displays the current internal status of Multibus Token Ring interface cards (CSC-1R, CSC-2R, and CSC-R16M). Following is a sample display:
TR0: state 3
current address: 0000.3080.2d6f, burned in address: 0000.3080.2d6f
Last Ring Status: none
(displayed text omitted)
TR1: state 3
current address: 0000.3080.2def, burned in address: 0000.3080.2def
Last Ring Status: none
To obtain more extensive information about the interfaces, such as the state of the lines and protocol types, use the show interface tokenring EXEC command [unit number] to display statistics about a specific Token Ring interface. The first line of the show interfaces display names the interface and its interface address (TR 0) and indicates whether the hardware and line protocol are up or down. If the line protocol is down (and you did not administratively shut it down), the hardware is not functioning properly; ensure that the network interface is properly connected and terminated. Following is a partial sample display:
router# show interface tokenring 0
TokenRing 0 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is ciscoBus Token Ring, address is 0000.3040.e004
Internet address is 131.108.35.6, subnet mask is 255.255.255.0
MTU 4464 bytes, BW 4000 Kbit, DLY 2500 usec, rely 255/255
Encapsulation SNAP, loopback not set, keepalive set (10 sec)
ARP type: SNAP, ARP Timeout 4:00:00
Ring speed: 4 Mbps
Single ring node, Source Route Transparent Bridge capable
Use the show interfaces command (without variables) to display all network interfaces: serial, Ethernet, FDDI, and Token Ring. Each new Token Ring interface should be appended to the list of existing interfaces, with the next sequential number assigned to it.
For descriptions of additional commands and examples, refer to the Router Products Configuration Guide and Router Products Command Reference publications.
Network interface cards contain microcode, which is interface-specific software that interoperates with the system software. The CSC-C2CTR microcode is contained on a single erasable programmable read-only memory (EPROM) component, which is located in socket U98. You may need to replace the CSC-C2CTR EPROM when upgrading your system software or to add new functionality to the card when it becomes available. Use the show controller cbus command (described in the section "System Compatibility Requirements" on page 6) to display the current microcode version installed on the CSC-C2CTR and all ciscoBus interface cards. Refer to Figure 16 for component locations while performing the following steps.
Step 1 Turn OFF the chassis power, open the front access panel, and remove the CSC-C2CTR as described in steps 1 through 7 of "Installing the CSC-C2CTR Interface Card" on page 19.
Step 2 Slip on an ESD-preventive wrist strap and connect it to the chassis as described in the section "Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage." Make certain that power to the chassis is OFF, but that the power cord is fully connected.
Step 3 Referring to Figure 16, locate the EPROM in socket U98. Note the orientation of the notch; the new EPROM must be inserted with the same orientation.

Step 4 Use a chip extractor to remove the EPROM from its socket. If you do not have a chip extractor available, use the tip of the screwdriver blade to gently pry the EPROM out of its socket.
Step 5 Install the new EPROM in socket U98. Make sure that the notched end has the same orientation as the EPROM you removed. Do not use the orientation of the label to align the new EPROM.
 | Caution If the microcode EPROM is installed backwards when the power is turned on, it will be damaged and will have to be replaced. |
Step 6 Replace the card in the card cage. Place your thumbs on the ejector levers, and push the card in firmly until it snaps into place and is firmly seated in the slot.
Step 7 Reconnect the internal ribbon cables to the connectors on the front of the card. Be sure to match the interface numbers labeled on the cables with the interface ports on the CSC-C2CTR. Interface ports on the card are numbered 0 to 3, from left to right as shown in Figure 16.
Step 8 Turn on the system for an installation check, which is described in the section "Installing Long Ground Straps" on page 24.
For descriptions of additional commands and examples, refer to the Router Products Configuration Guide and Router Products Command Reference publications.
This completes the CSC-C2CTR and APP-LTR2 installation, replacement, and microcode upgrade procedures.
Cisco Information Online (CIO) is Cisco Systems' primary, real-time support channel. You can use your product serial number to activate CIO for a single user during your warranty period. Maintenance customers and partners can self-register on CIO to obtain additional content and services.
Available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, CIO provides a wealth of standard and value-added services to Cisco's customers and business partners. CIO services include product information, software updates, release notes, technical tips, the Bug Navigator, configuration notes, brochures, descriptions of service offerings, and download access to public and authorized files.
CIO serves a wide variety of users through two interfaces that are updated and enhanced simultaneously--a character-based version and a multimedia version that resides on the World Wide Web (WWW). The character-based CIO (called "CIO Classic") supports Zmodem, Kermit, Xmodem, FTP, Internet e-mail, and fax download options, and is excellent for quick access to information over lower bandwidths. The WWW version of CIO provides richly formatted documents with photographs, figures, graphics, and video, as well as hyperlinks to related information.
You can access CIO in the following ways:
http://www.cisco.com.
cio.cisco.com (198.92.32.130).
For a copy of CIO's Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ), contact ciohelp@cisco.com. For additional information, contact cioteam@cisco.com.
If you are a network administrator and need personal technical assistance with a Cisco product that is under warranty or covered by a maintenance contract, contact Cisco's Technical Assistance Center (TAC) at 800 553-2447, 408 526-7209, or tac@cisco.com. To obtain general information about Cisco Systems, Cisco products, or upgrades, contact 800 553-6387, 408 526-7208, or csrep@cisco.com.

|
|