|
|

Product Numbers: MC-HSCI-V1.2=, MC-HSCI-V10.1=
This document describes how to upgrade High-Speed Serial Communications Interface (CSC-HSCI) cards to Microcode Versions 1.2 and 10.1. Microcode Version 1.2 is compatible only with the first generation ciscoBus controller card (CSC-CCTL). Microcode Version 10.1 is compatible with, and required for use with, the second-generation ciscoBus controller (CSC-CCTL2). If you are replacing a first-generation ciscoBus controller (CSC-CCTL) with a CSC-CCTL2, you must upgrade the microcode on all ciscoBus interface cards to Version 10.0 or later. Compatibility requirements for the CSC-CCTL2 are described in the section "Verifying CCTL2 CompatibilityMicrocode Version 10.1 Only."
The upgrade procedure is the same for both microcode versions; only the component part numbers are different. References to part number tables are provided in the appropriate steps in the procedure. In the following sections of this document, the term HSCI is used to indicate both the CSC-HSCI (first-generation ciscoBus) and CSC-C2HSCI (second-generation ciscoBus) cards unless otherwise indicated.
To ensure that you have the proper tools and parts to complete this procedure without interruption, read the following requirements and procedures.
Your current system must meet the following compatibility requirements before you install the new microcode:
The latest version of the Microcode Release Note publication (Part Number 78-1069-nn) provides the latest information on both the recommended and minimum required microcode versions for using all cards with System Software Releases 8.2, 8.3, 9.1, and 9.21. If the latest version implements features that you are not using in your system and you already have the minimum required version installed, there is no requirement to update the microcode. However, new microcode versions occasionally fix bugs and provide performance enhancements in addition to implementing new features. You will obtain maximum performance and reliability by upgrading to the recommended version.
Electrostatic discharge damage (ESD) occurs when electronic printed circuit cards are improperly handled and can result in complete or intermittent failures. ESD can impair electronic circuitry and equipment. Always follow ESD prevention procedures when removing and replacing cards. Following are steps for handling printed circuit cards:
Step 1 Slip on an ESD-preventive wrist strap, ensuring that it makes good skin contact.
Step 2 Connect the strap to an unpainted chassis frame surface or another proper grounding point or surface to safely channel unwanted ESD voltages to ground.
Step 3 Use the ejectors to remove the card. Handle the card by its sides. Place the card on an antistatic surface or in a static shielding bag. To prevent further damage to the card by ESD voltages, defective cards must remain in the static shielding bag when returned for repair or replacement.
Step 4 Handling the new card by its edges only, insert it into the chassis. Avoid contact between the card and clothing. The wrist strap only protects the card from ESD voltages on the body; ESD voltages on clothing can still damage the card.
 | Caution Use an ohmmeter to check the ESD-preventive wrist strap to ensure that the resistor is providing proper ESD protection. For safety, the measurement should be between 1 to 10 mega ohms. |
The CSC-CCTL2 is required to run ciscoBus network interface cards with the C2 designator, as listed in Table 1. The C2 indicates that a ciscoBus card is running Microcode Version 10.0 or later and is, therefore, compatible with the second-generation ciscoBus controller, the CSC-CCTL2. When you upgrade the microcode on an HSCI card to Version 10.1, the name of the card also changes from CSC-HSCI to CSC-C2HSCI to indicate that it is CCTL2-compatible. If you are installing a new CSC-CCTL2, you must upgrade all ciscoBus interface cards to Microcode Version 10.0 or later.
| CCTL Controller | CCTL2 Controller | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CSC-CCTL | CSC-CCTL2 | ciscoBus controller |
| CSC-FCI | CSC-C2FCI | Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) |
| CSC-C2FCIT | FDDI with translational bridging | |
| CSC-HSCI | CSC-C2HSCI | High-Speed Serial Interface (HSSI) |
| CSC-C2CTR | ciscoBus Token Ring interface, 4/16Mbps | |
| CSC-MEC | CSC-C2MEC | Multiport Ethernet Controller interface |
Display a description of the current ciscoBus controller and ciscoBus interface cards with the EXEC command show controller cbus. The name and controller type of each ciscoBus card, the ciscoBus slot in which it is installed, and the microcode version of each is displayed (additional, statistical information is also displayed for each interface card, but is omitted from the example). When installing Microcode Version 10.0 (or later) on any ciscoBus interface card, the ciscoBus controller (listed first) must be a controller type 6.0 or later, and all other ciscoBus interface cards must be running Microcode Version 10.0 or later (or you must upgrade the microcode on those cards at the same time). The following sample display shows a CCTL2 controller with all ciscoBus interface cards upgraded to Microcode Version 10.0:
router# show cont cbus
cBus 1, controller type 6.0, microcode version 10.0
512 Kbytes of main memory, 128 Kbytes cache memory
(text omitted)
FDDI-T 0, controller type 7.1, microcode version 10.0
Interface 0 - Fddi0, station address 0000.0c02.6aa3 (bia
(text omitted)
CTR 1, controller type 9.0, microcode version 10.0
Interface 8 - TokenRing0, station address 0000.3040.e004 (bia
(text omitted)
HSCI 2, controller type 10.0, microcode version 10.0
Interface 16 - Hssi0, electrical interface is Hssi DTE
(text omitted)
MEC 3, controller type 5.1, microcode version 10.0
Interface 24 - Ethernet2, station address 0000.0c02.61b7
(text omitted)
Display the current software release and the type of processor card installed with the EXEC command show version. The current system software release is displayed in the first line of the output followed by a list of the installed interface cards. There is no minimum system software release requirement for Microcode Version 1.2 (CCTL-compatible); however, if you are installing Version 10.1 (CCTL2-compatible), you must be running System Software Release 9.1 or later. In the following example, the system is running System Software Release 9.1:
router# show version
GS Software (GS3-BFX), Version 9.1(6765) [trunkd 116]
Copyright (c) 1986-1992 by cisco Systems, Inc.
To perform this upgrade, you need the following:
 | Caution Observe proper ESD prevention procedures when handling cards and components to prevent damage from electrostatic discharge. |
Follow this procedure to upgrade the HSCI card. Before opening the chassis, refer to the section "System Compatibility" and ensure that your system meets the minimum requirements for the microcode version you are installing.
 | Caution Before performing these installation procedures, turn off power to the system. Removing or installing a card in the backplane when the system power is on will severely damage the card and can also damage other system components. |
Step 1 Turn OFF the system power and unplug the power cord.
Step 2 Loosen the two thumb fasteners and remove the front access panel to expose the card cage. The thumb fasteners are tightened with 12 in/lb of torque for shipping. If you are removing the front panel for the first time, use a large, flat-blade screwdriver to turn the thumb fasteners counterclockwise to loosen. When you replace the panel, turn the thumb fasteners clockwise until finger-tight.
Step 3 Attach the ESD-preventive wrist strap provided with the upgrade kit, or use your own ground strap. Attach the equipment end to an unpainted area on the chassis.
Step 4 Disconnect the internal ribbon cables that are attached to the front of the HSCI card. If other cables (to other cards) prevent you from removing the HSCI card, note the card and port locations of each before disconnecting them (to avoid misrouting cables when you reinstall the card).
Step 5 Use your thumbs to pull the ejector tabs out and away from the card edge to loosen it; then pull the card out of its slot. Place the card on an antistatic mat.
Step 6 Refer to Figure 1 for the socket locations of the 15 components to be replaced. Refer to the following for component part numbers:
Step 7 Insert the new components into the appropriate sockets, as shown in Figure 1 and listed in the tables. Align the notch on the component with the notch on its socket as shown.
Step 8 Be careful not to bend or crush any of the pins when inserting the new components. If any pins are bent, use needle-nosed pliers to straighten the pins, then carefully reinsert the component.
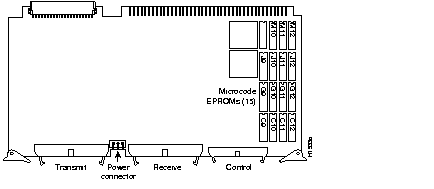
Step 9 Remove each of the old components with a chip extractor. If one is not available, use a flat-blade screwdriver to remove the components.
Step 10 When all 15 components have been replaced, reinsert the card, reconnect the internal cables, and restart the system for an installation check.
| Socket Location | 1.0 | 1.1 | 1.2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| C9 | 17-0786-01 C9 | 17-0786-02 C9 | 17-0786-03 C9 |
| C10 | 17-0787-01 C10 | 17-0787-02 C10 | 17-0787-03 C10 |
| C11 | 17-0788-01 C11 | 17-0788-02 C11 | 17-0788-03 C11 |
| J12 | 17-0789-01 J12 | 17-0789-02 J12 | 17-0789-03 J12 |
| J9 | 17-0790-01 J9 | 17-0790-02 J9 | 17-0790-03 J9 |
| J10 | 17-0791-01 J10 | 17-0791-02 J10 | 17-0791-03 J10 |
| J11 | 17-0792-01 J11 | 17-0792-02 J11 | 17-0792-03 J11 |
| C12 | 17-0793-01 C12 | 17-0793-02 C12 | 17-0793-03 C12 |
| M10 | 17-0794-01 M10 | 17-0794-02 M10 | 17-0794-03 M10 |
| M11 | 17-0795-01 M11 | 17-0795-02 M11 | 17-0795-03 M11 |
| M12 | 17-0796-01 M12 | 17-0796-02 M12 | 17-0796-03 M12 |
| G10 | 17-0797-01 G10 | 17-0797-02 G10 | 17-0797-03 G10 |
| G9 | 17-0798-01 G9 | 17-0798-02 G9 | 17-0798-03 G9 |
| G12 | 17-0799-01 G12 | 17-0799-02 G12 | 17-0799-03 G12 |
| G11 | 17-0800-01 G11 | 17-0800-02 G11 | 17-0800-03 G11 |
| Socket Location | 1.0 | 1.1 | 10.0 | 10.1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C9 | 17-0786-01 C9 | 17-0786-02 C9 | 17-1335-01 C9 | 17-1335-02 C9 |
| C10 | 17-0787-01 C10 | 17-0787-02 C10 | 17-1336-01 C10 | 17-1336-02 C10 |
| C12 | 17-0788-01 C11 | 17-0788-02 C11 | 17-1337-01 C11 | 17-1337-02 C11 |
| J12 | 17-0789-01 J12 | 17-0789-02 J12 | 17-1338-01 J12 | 17-1338-02 J12 |
| J9 | 17-0790-01 J9 | 17-0790-02 J9 | 17-1339-01 J9 | 17-1339-02 J9 |
| J10 | 17-0791-01 J10 | 17-0791-02 J10 | 17-1340-01 J10 | 17-1340-02 J10 |
| J11 | 17-0792-01 J11 | 17-0792-02 J11 | 17-1341-01 J11 | 17-1341-02 J11 |
| C12 | 17-0793-01 C12 | 17-0793-02 C12 | 17-1342-01 C12 | 17-1342-02 C12 |
| M10 | 17-0794-01 M10 | 17-0794-02 M10 | 17-1343-01 M10 | 17-1343-02 M10 |
| M11 | 17-0795-01 M11 | 17-0795-02 M11 | 17-1344-01 M11 | 17-1344-02 M11 |
| M12 | 17-0796-01 M12 | 17-0796-02 M12 | 17-1345-01 M12 | 17-1345-02 M12 |
| G10 | 17-0797-01 G10 | 17-0797-02 G10 | 17-1346-01 G10 | 17-1346-02 G10 |
| G9 | 17-0798-01 G9 | 17-0798-02 G9 | 17-1347-01 G9 | 17-1347-02 G9 |
| G10 | 17-0799-01 G12 | 17-0799-02 G12 | 17-1348-01 G12 | 17-1348-02 G12 |
| G11 | 17-0800-01 G11 | 17-0800-02 G11 | 17-1349-01 G11 | 17-1349-02 G11 |
After you reinstall the HSCI card and reconnect the internal ribbon cables, verify the installation before you replace the front panel by observing the following LEDs:
The HSCI card has no LEDs; status indicators for the HSSI interface are located on the applique connected to the card. You will have to be able to access the rear of the chassis to observe the LEDs on the applique.
The ciscoBus controller card (CSC-CCTL or CSC-CCTL2) is always installed in the center ciscoBus slot (Multibus slot number 7) as shown in Figure 2. After you verify that the LEDs come on correctly, use the EXEC show controller cbus command to display the new microcode version.
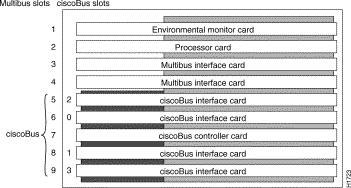
The bank of indicators used on the CSC-CCTL is different from that on the CSC-CCTL2. Descriptions of both types of ciscoBus controllers follow; review them to anticipate how the indicators should come on. Before turning on the chassis power to check the installation, note the ciscoBus slot number(s) that contain the CSC-MEC card(s) you just reinstalled.
The CSC-CCTL contains a bank of 16 LEDs as shown in Figure 3: four sets of four LEDs, one set for each interface slot in the ciscoBus. Figure 3 shows the LEDs as viewed with the card installed in the card cage--edge on, component side up. In the illustration, the numbers above each LED indicate the corresponding ciscoBus slot number (slot numbers and locations are shown in Figure 2). Only the first (far left) LED in each set of four is used as an indicator that comes on when an interface is present in a ciscoBus slot.
At power-up, all the LEDs come on indicating that the CSC-CCTL card is active. When the system boot is completed, only those LEDs that indicate the presence of a card in the corresponding ciscoBus slot should remain on; the LEDs for empty ciscoBus slots should be off.

The CSC-CCTL2 contains a bank of 5 LEDs, one red indicator for each ciscoBus slot and one green OK indicator. Figure 4 shows the indicators as viewed with the card installed in the card cage--edge on, component side up. In the illustration, the numbers above each LED indicate the corresponding ciscoBus slot number (slot numbers and locations are shown in Figure 2). At power-up, all the LEDs come on, indicating that the CSC-CCTL2 card is active. When the system boot is completed, only those LEDs that indicate the presence of a card in the corresponding ciscoBus slot should remain on; the LEDs for empty ciscoBus slots should go out.

The APP-HSA and APP-ULA appliques contain a bank of 12 LEDs which report the state of the HSSI interface. Figure 5 shows these LEDs and the normal operating state of each. The green OK indicator comes on after the software has performed its startup verification. The red ER indicator comes on if any of the internal cables (between the HSCI and the applique) are crossed.
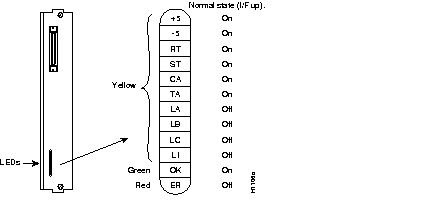
To check your upgrade installation, first verify the ciscoBus controller card LEDs, then the applique LEDs with the following steps. Before turning on the system power, ensure that you are able to access the rear of the chassis to observe the LEDs on the applique.
Step 1 Turn ON the system power. Verify that all the LEDs on the ciscoBus controller card (CSC-CCTL or CSC-CCTL2) come on according to the previous description of each.
Step 2 CSC-CCTL2 only: When the system has completed its boot cycle (it will beep when complete), verify that the far right, green OK indicator comes on and remains on. If it does not come on, check the following:
Step 3 Check the four red indicators on the ciscoBus controller card (refer to Checking LEDs, page 7 if necessary). Ensure that the indicator for each occupied ciscoBus slot is on. In particular, check the slots for all ciscoBus interface cards you just reinstalled. If the LEDs do not come on properly, check the following:
Step 4 Check the LEDs on the APP-HSA or APP-ULA applique and ensure that the red ER indicator (the bottom LED) is not on. If the ER LED is on, the internal ribbon cables between the applique and the HSCI card have been crossed, which must be corrected as follows:
Step 5 Ensure that the green OK indicator on the applique (the second LED from the bottom) is on. (See Figure 5.) If it is not on, check the following:
 | Caution Be sure to replace the chassis cover before restarting the system. Operating the system with the cover removed misdirects the flow of cooling air, and can cause the chassis to overheat and force the environmental monitor to shut down the system. |
To display the new microcode version, enter the EXEC command show controller cbus. The first line of the display for each installed HSCI card should indicate the new microcode version, as follows:
cBus 1, controller type 3.0, microcode version 2.0
(text omitted)
HSCI 2, controller type 10.0, microcode version 1.2
Interface 16 - Hssi0, electrical interface is Hssi DTE
(text omitted)
cBus 1, controller type 6.0, microcode version 10.0
(text omitted)
HSCI 2, controller type 10.0, microcode version 10.1
Interface 16 - Hssi0, electrical interface is Hssi DTE
(text omitted)
When the installation checks out successfully, replace the access cover and finger-tighten the two thumb fasteners.
This completes the CSC-HSCI and CSC-C2HSCI microcode upgrade.

|
|