|
|

This appendix discusses all aspects of the command set. A list of top-level commands is provided in Table A-1.
The user interface for the admin. port on the concentrator is a basic command-line interpreter. Commands and parameters are not case sensitive and can be abbreviated if they contain enough characters to eliminate any ambiguity with other commands at the same level. Command-line editing is provided along with history substitution. If you incorrectly enter a command, a usage message gives you the correct command format. Pressing Ctrl-W deletes the last word typed and pressing Ctrl-U deletes the entire line.
Commands entered during a terminal session are stored in a history substitution buffer. Commands in this buffer can be repeated or edited in a style similar to the UNIX C shell. The buffer stores the last 20 commands entered during a terminal session. (See the section "history Command" later in this appendix.)
To repeat a recent command, do the following:
!! -- repeat the most recent command
!nn -- repeat command nn
!aaa -- repeat the command beginning with string aaa
!?aaa -- repeat the command containing the string aaa
To modify and repeat the most recent command, do the following:
^aaa^bbb -- replace the string aaa with the string bbb in
the most recent command
To add a string to the end of a previous command and repeat it, do the following:
!!aaa -- add string aaa to the end of the most recent command
!nn aaa -- add string aaa to the end of command nn
!aaa bbb -- add string bbb to the end of the command beginning
with string aaa
!?aaa bbb -- add string bbb to the end of the command containing the string aaa
You can connect to the admin. interface through the admin. port (EIA/TIA-232) or via Telnet. The admin. port allows fixed baud rates. Telnet and admin. port sessions are automatically logged out if they are idle for 20 minutes.
Use the admin. interface to perform the following functions:
You can connect through the admin. port via EIA/TIA-232. Following is a sample display:
Cisco Systems Console
Enter password:
console>
console>
console> quit
To use Telnet, you must have the IP address configured on the concentrator. To access the concentrator with Telnet, use the following procedure:
Step 1 On the remote host, enter the following command, where hostname is the host name or IP address of the concentrator:
%telnet hostname
Step 2 Enter the admin. interface password.
Step 3 When you finish, enter quit to exit the Telnet session. Following is a sample Telnet session:
% telnet concentrator1
Trying 192.XXX.XXX.XXX ...
Connected to concentrator1.
Escape character is '^]'.
Cisco Systems Console
Enter password:
console>
console>
console> quit
Connection closed by foreign host.
There are two categories of commands: normal and privileged.
(See Table A-1.)
You can enter help or ? to see the list of commands. Additional help is available for some commands when you enter the command followed by help or ?.
| Command | Description | Mode1 |
|---|---|---|
| clear | Use clear help for information on clear commands | P |
| configure | Configure from the terminal or the network | P |
| connect fddi | Connect to the FDDI ring | P |
| copy flash tftp | Upload the Flash memory image to a network host | P |
| copy tftp flash | Copy files to and from Flash memory | P |
| disable | Disable privileged mode | P |
| disconnect fddi | Disconnect from the FDDI ring | P |
| download | Download new code to Flash memory | P |
| enable | Enable privileged mode | N |
| help | Display top-level commands and a description of how the command is used | N |
| history | Show the contents of the history substitution buffer | N |
| macreinit | Reinitializes all MACs2 | P |
| ping | Send echo request packets to a node on the network | N |
| quit | Exit from the console | N |
| reset | Reset the system | P |
| set | Use set help for information on the set commands | N |
| show | Use show help for information on the show commands | N |
| test | Use test help for information on the test commands | P |
| traffic | Send continuous traffic on the ring | P |
| upload | Upload Flash memory code to the network | P |
| write | Write configuration information to the terminal or to a file | P |
Some commands had different nomenclature in the Workgroup WS-C1100 Concentrator software (Version 2.3). Predefined aliases for these commands are available. Table A-2 lists the current commands and the predefined aliases.
| Alias | Current Command |
|---|---|
| action port | set port |
| clearlem | clear lem |
| di | show |
| coalias | clear/set/show coalias |
| ipalias | clear/set/show ipalias |
| di conc | show system |
| di hw | show test |
| download now | download serial |
| exit, logout | quit |
| netdownload | download |
| resetclr | clear config |
| set debug off | disable |
| set debug on | enable |
| set insert-mode | set insertmode |
| set trap invalid | clear trap |
| sysclr | clear log |
| set name | set sysname |
| sysdis | show log |
| trap | test trap |
Table A-3 lists the clear commands.
| Command | Description | Mode1 |
|---|---|---|
| clear arp | Clear ARP2 table entries | P |
| clear coalias | Clear MAC address alias | P |
| clear config | Clear configuration and reset the system | P |
| clear counters | Clear MAC and port counters | P |
| clear help | Displays clear commands and descriptions | P |
| clear ipalias | Clear alias of IP addresses | P |
| clear lem | Clear link error monitor counters | P |
| clear log | Clear the system error log | P |
| clear mac | Clear MAC counters | P |
| clear port | Clear port counters | P |
| clear route | Clear IP routing table entries | P |
| clear trap | Clear SNMP trap receiver address | P |
The clear arp command clears individual ARP table entries and clear arp all clears the entire ARP table. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) clear arp ?
Usage: clear arp all
clear arp <ip_addr>
(ip_addr is ipalias or IP dot notation: a.b.c.d)
Console> (enable) clear arp 192.XXX.XXX.XX
Arp entry deleted.
Console> (enable) clear arp all
ARP table cleared. (1)
Console> (enable)
See also set arp and show arp.
The clear coalias command clears individual aliases of the MAC prefix and clear coalias all clears all coalias entries. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) clear coalias ?
Usage: clear coalias all
clear coalias <name> [company_prefix]
(company_prefix is 3 hex words separated by ":", ex 00:02:d0)
Console> (enable) clear coalias 3com
Company MAC alias deleted.
Console> (enable)
See also set coalias and show coalias.
The clear config command clears the configuration information stored in nonvolatile random-access memory (NVRAM) and changes all configuration variables to the default. It also causes the system to be reset. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) clear config
This command will reset the system after clearing configuration in NVRAM.
This command will disconnect your telnet session.
Do you want to continue (y/n) [n]? y
Connection closed by foreign host.
%
See also show config and write Command.
The clear counters command clears all the MAC and port counters, as follows:
Console> (enable) clear counters
MAC and port counters cleared.
Console> (enable)
See also clear mac and clear port.
The clear help command displays the following message in normal mode.
Console> (enable) clear help
Clear commands:
---------------------------------------------------------------------
clear arp Clear ARP table entries
clear coalias Clear aliases of company MAC addresses
clear config Clear configuration and reset system
clear counters Clear MAC and port counters
clear help Show this message
clear ipalias Clear aliases of IP addresses
clear lem Clear link error counters
clear log Clear system error log
clear mac Clear MAC counters
clear port Clear port counters
clear route Clear IP routing table entries
clear trap Clear SNMP trap receiver address
Console> (enable)
The clear ipalias command clears the IP aliases that were assigned using the set ipalias command. The clear ipalias all command clears all IP alias entries. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) clear ipalias ?
Usage: clear ipalias all
clear ipalias <name>
Console> (enable) clear ipalias montreux
IP alias deleted.
Console> (enable)
See also set ipalias and show ipalias.
The clear lem command clears the link error monitor (LEM) counters. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) clear lem
Link error counters cleared.
Console> (enable)
See also show port.
The clear log command clears the system error log. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) clear log
System error log cleared.
Console> (enable)
See also show log.
The clear mac command clears the following MAC counters:
Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) clear mac
MAC counters cleared.
Console> (enable)
See also show mac.
The clear port command clears the following port counters:
Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) clear port
Port counters cleared.
See also show port.
The clear route command clears IP routing table entries that were set using the set route command. The clear route all command clears all route entries except the local entry. The default metric value is 1.
Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) clear route ?
Usage: clear route all
clear route <destination> <gateway> [metric]
(destination and gateway are ipalias or IP address in
dot notation: a.b.c.d)
Console> (enable) clear route host1 gateway1 0
Route deleted.
Console> (enable)
See also set route and show route.
The clear trap command clears an individual entry in the SNMP trap receiver table. The command clear trap all clears all trap receiver entries.
Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) clear trap
Usage: clear trap all
clear trap <receiver>
(receiver is ipalias or IP address in dot notation: a.b.c.d)
Console> clear trap 198.XXX.XXX.XXX
Trap receiver cleared.
Console> (enable)
See also set trap and show snmp.
The configure command downloads a configuration file or a batch file from the network and executes each command in that file. It is only available in privileged mode. The file should contain only American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII) text and should not exceed 9,216 bytes (9 kilobytes [KB]) in length. Administrator commands are entered one per line.
The list of commands should end with the word "end" followed by a carriage return. The file may also contain comment lines, which are indicated by a pound (#) character at the beginning of each line. Some commands prompt for user input or confirmation. Responses to such commands should appear on the line after the command prompt.
Following are examples of configuration files:
show time
set ipalias conc5 192.1.1.205
set ipalias montreux 192.1.1.10
set ipalias bigbird 198.1.1.8
set prompt conc5>
set password
#the next line is empty because the old password is an empty string
pingpong
pingpong
end
Console> (enable) configure help
Usage: configure network
configure terminal
configure <host> <file>
Console> (enable) configure 198.1.1.8 conc5.cfg
Configure using file conc5.cfg from host 198.1.1.8.(y/n) [n]? y
Configuring using conc5.cfg from 198.1.1.8
Done. Finished Network Download. (224 bytes)
>> show time
Wed Mar 30 1994, 17:42:50
>> set ipalias conc5 192.1.1.205
IP alias added.
>> set ipalias oscar 192.1.1.10
IP alias added.
>> set ipalias bigbird 198.1.1.8
IP alias added.
>> set prompt conc5>
>> set password
Enter old password:
Enter new password: pingpong
Retype new password: pingpong
Password changed.
conc5> (enable)
See also show config and write Command.
The connect fddi command connects the concentrator to the FDDI ring. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) connect
Usage: connect fddi
Console> (enable) connect fddi
Connected to FDDI ring.
Console> (enable)
See also the disconnect fddi Command.
The copy flash tftp command uploads the Flash memory image file from the concentrator to a network host to create a backup file. The file must be created in advance and saved in the tftpboot directory. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) copy flash tftp
IP address or name of remote host? oscar
Name of file to copy to? c1100_conc3.net
Upload image from flash to file c1100_conc3.net on host oscar (y/n) [n]? y
Uploading image to c1100_conc3.net on oscar
/
Done. Finished Network Upload. (446468 bytes)
Console> (enable)
The copy tftp flash command downloads a Flash memory image file from the tftpboot directory to Flash memory. The binary file is searched for in the tftpboot directory of the host designated by IP address or name. The file transfer process can be stopped by pressing Ctrl-C. The copy tftp flash command and the download command are identical.
 | Caution Do not reset the concentrator after the Flash memory initialization process begins. The Flash memory image file may be incomplete and would cause system failure. |
Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) copy tftp flash
IP address or name of remote host? oscar
Name of file to copy from? c1100_10.net
This command will disconnect your telnet session.
Download image c1100_10.net from host oscar to flash (y/n) [n]? y
Downloading image c1100_10.net from oscar
/
Done. Finished Network Download. (440324 bytes)
Initializing flash...Erasing Flash..Done
Programming Flash
Base...Code...Length...Time...Done
Disconnected from FDDI ring.
Connection closed by foreign host.
%
The disable command returns you to normal mode. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) disable
Console>
See also enable and set enablepass.
The disconnect fddi command disconnects all CDDI/FDDI ports from the FDDI ring. The disconnect fddi command will also terminate any network connections, including services such as Telnet. After the concentrator is reset, it attempts to connect all ports even if you had previously issued a disconnect fddi command.
Following are samples of the disconnect fddi command with two connection types:
Console> (enable) disconnect
Usage: disconnect fddi
Console> (enable) disconnect fddi
This command will disconnect all CDDI/FDDI ports.
Do you want to continue (y/n) [n]? y
Disconnected from FDDI ring.
Console> (enable)
Console> (enable) disconnect fddi
This command will disconnect all CDDI/FDDI ports and your
telnet session.
Do you want to continue (y/n) [n]? y
Disconnected from FDDI ring.
Connection closed by foreign host.
%
See also the connect fddi Command.
There are two ways to download a new image to Flash memory: through the serial port using the download serial command or over the network using the download host file command.
The download command enables you to download data to the concentrator over the network. When you download over the network, the concentrator expects a binary image. Network download is achieved via TFTP. The binary file image is searched for in the tftpboot directory. You can cancel the download command during the TFTP process by pressing Ctrl-C. The download command and the copy tftp flash are identical.
 | Caution Do not reset the concentrator after the download process begins. The Flash memory image file may be incomplete and would cause system failure. |
Following is an example of a network download in a Telnet session:
Console> (enable) download
Usage: download serial
download <host> <file>
(serial downloads via the administration RS-232 port,
host is ipalias or IP address: a.b.c.d for a network download
(NOTE: FDDI ring will go down)
Console> (enable) download cres c1100_10.net
This command will disconnect your telnet session.
Download image c1100_10.net from host cres to flash (y/n) [n]? y
Downloading image c1100_10.net from cres
/
Done. Finished Network Download (409604 bytes)
Initializing flash...Erasing Flash....Done
Programing Flash
Base....Code....Length....Time....Done
Disconnecting from the FDDI ring.
Connection closed by foreign host.
%
When you download through the serial port, the concentrator expects an ASCII image. You must ensure that the baud rates from the sending and receiving end are the same.
The following display shows a serial download session through the EIA/TIA-232 port using Kermit for a UNIX workstation:
workstation% cd /tmp
workstation% tar -xvfp /dev/rfd0
x c1100_26.rom, 1156046 bytes, 2258 tape blocks
workstation% ls -la
total 1150
drwxrwsrwt 5 bin 512 Sep 28 04:15 .
drwxr-xr-x 18 root 1536 Sep 27 15:41 ..
-r--r--r-- 1 60000 1156046 Jul 18 10:32 c1100_26.rom
workstation% kermit
C-Kermit, 4E(072) 24 Jan 89, SUNOS 4.x
Type ? for help
C-Kermit>set line /dev/ttya
C-Kermit>set speed 9600
/dev/ttya: 9600 baud
C-Kermit>connect
Connecting thru /dev/ttya, speed 9600.
The escape character is CTRL-\ (28).
Type the escape character followed by C to get back,
or followed by ? to see other options.
Console> enable
Console> (enable) download serial
Concentrator Boot ROM (Ver 2.01)
Waiting for DOWNLOAD!!
Return to your local Machine by typing its escape sequence
Issue Kermit send command from there[ Send `Filename`]
[Back at Local System]
C-Kermit>send c1100_26.rom
SF
c1100_26.rom => C1100_26.ROM, Size: 1156046
CTRL-F to cancel file, CTRL-R to resend current packet
CTRL-B to cancel batch, CTRL-A for status report: ..............................................................................................................................
*** Display Truncated ***
...............................................................
.................................... [OK]
ZB?
C-Kermit>connect
Connecting thru /dev/ttya, speed 9600.
The escape character is CTRL-\ (28).
Type the escape character followed by C to get back,
or followed by ? to see other options.
Download OK
Initializing flash
Programming Flash
Base....Code....Length....Time....Done
Cisco Systems Console
Enter password:
Wed Feb 12, 1992, 17:35:08
Console>
The enable command is used to enter privileged mode. Following is a sample display:
Console>
Console> enable
Enter password:
Console> (enable)
See also disable and set enablepass.
The help command displays the following information in normal mode. (The ? command is the same as the help command.) Following is a sample display:
Console> help
Commands:
------------------------------------------------------------------------
enable Enable privileged mode
help Show this message
history Show contents of history substitution buffer
ping Send echo packets to hosts
quit Exit out of the console
set Set, use 'set help' for more info
show Show, use 'show help' for more info
Console>
The help command displays the following information in privileged mode. (The ? command is the same as the help command.) Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) help
Commands:
------------------------------------------------------------------------
clear Clear, use 'clear help' for more info
configure Configure system from terminal/network
connect Connect to FDDI ring
copy Copy code to/from flash
disable Disable privileged mode
disconnect Disconnect from FDDI ring
download Download new code to the flash
enable Enable privileged mode
help Show this message
history Show contents of history substitution buffer
macreinit Reinitialize all MACs
ping Send echo packets to hosts
quit Exit out of the console
reset Reset the system
set Set, use 'set help' for more info
show Show, use 'show help' for more info
test Test, use 'test help' for more info
traffic Send continuous traffic on the ring
upload Upload flash code to network
write Write system configuration to terminal/network
Console> (enable)
The history command shows the last 20 commands you entered, as follows:
Console> history
2 history
3 history
4 configure help
5 show help
6 show system
7 show snmp
8 show time
9 show port
10 show mac
11 help
12 set ipalias 198.122.174.205 marketing
13 set netmask 255.255.255.0
14 show snmp
15 set ipalias bedrock 192.122.173.125
16 set ipalias marketing 192.122.173.40
17 set ipalias bigbird 192.122.173.42
18 show ipalias
19 show time
20 disable
21 history
Console>
The macreinit command reinitializes the primary and secondary MACs. You could use the macreinit command to clear a halted concentrator. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) macreinit
MACs reinitialized.
Console> (enable)
The ping command sends Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo request packets to a node on the network. When the -s option is specified, the ping command sends one datagram per second and prints one line of output for every response it receives. No output is produced if there is no response. Also, when the -s option is specified, round-trip times and packet-loss statistics are computed, and a summary of this information is shown on termination or timeout. The default packet size is 64 bytes, or you can specify a size from 1 to 2,000 bytes.
If you give an optional packet count, the ping command sends only that number of requests. Following is a sample display of the ping command:
Console> ping
Usage: ping <host>
ping -s <host> [data_size] [packet_count]
(host is ipalias or IP address in dot notation: a.b.c.d)
Console> ping bedrock
no answer from bedrock
Console> ping elvis
elvis is alive
Console> ping -s elvis 58 5
PING elvis: 58 data bytes
66 bytes from elvis: icmp_seq=0. time=13 ms
66 bytes from elvis: icmp_seq=1. time=5 ms
66 bytes from elvis: icmp_seq=2. time=5 ms
66 bytes from elvis: icmp_seq=3. time=5 ms
66 bytes from elvis: icmp_seq=4. time=7 ms
----elvis PING Statistics----
5 packets transmitted, 5 packets received, 0% packet loss
round-trip (ms) min/avg/max = 5/7/13
Console> ping -s ariel
PING ariel: 56 data bytes
64 bytes from ariel: icmp_seq=46. time=14 ms
64 bytes from ariel: icmp_seq=47. time=8 ms
64 bytes from ariel: icmp_seq=48. time=7 ms
64 bytes from ariel: icmp_seq=49. time=8 ms
64 bytes from ariel: icmp_seq=50. time=9 ms
64 bytes from ariel: icmp_seq=51. time=7 ms
64 bytes from ariel: icmp_seq=52. time=6 ms
64 bytes from ariel: icmp_seq=53. time=8 ms
64 bytes from ariel: icmp_seq=54. time=9 ms
^C
----ariel PING Statistics----
55 packets transmitted, 9 packets received, 83% packet loss
round-trip (ms) min/avg/max = 6/8/14
Console>
Following are several examples of responses to the ping command.
Console> ping 130.125.132.108
Console> 130.125.132.108 is alive
Console> ping hub20
Console> hub20 is alive
Console> ping 130.125.132.108
Console> no answer from 130.125.132.108
Console> ping 192.54.56.122
ping: network unreachable
Console>
Console> ping 130.28.99.76
ping: host unreachable
Console> no answer from 130.28.99.76
Console> ping 192.9.201.4
Console> ping: dest unreachable response from 130.128.136.53
ping: dest unreachable response from 130.128.136.53
^C
no answer from 192.9.201.4
Console> ping -s 192.XXX.XXX.XXX
Console> 64 bytes from 192.XXX.XXX.XXX: icmp_seq=0. time=10 ms
64 bytes from 192.XXX.XXX.XXX: icmp_seq=1. time=6 ms
64 bytes from 192.XXX.XXX.XXX: icmp_seq=2. time=4 ms
64 bytes from 192.XXX.XXX.XXX: icmp_seq=3. time=3 ms
64 bytes from 192.XXX.XXX.XXX: icmp_seq=4. time=4 ms
64 bytes from 192.XXX.XXX.XXX: icmp_seq=5. time=4 ms
64 bytes from 192.XXX.XXX.XXX: icmp_seq=6. time=6 ms
^C
----192.XXX.XXX.XXX PING Statistics----
7 packets transmitted, 7 packets received, 0% packet loss
round-trip (ms) min/avg/max = 3/5/10
Console>
Console> ping -s 130.XXX.XXX.XXX
Console> ping 130.XXX.XXX.XXX
Pinger busy, use ctrl-c for ping statistics
^C
no answer from 130.XXX.XXX.XXX
Console>
Console> ping -s 192.XXX.XXX.XXX 2000 5
Console> 2008 bytes from 192.XXX.XXX.XXX: icmp_seq=0. time=38 ms
2008 bytes from 192.XXX.XXX.XXX: icmp_seq=1. time=10 ms
2008 bytes from 192.XXX.XXX.XXX: icmp_seq=2. time=10 ms
2008 bytes from 192.XXX.XXX.XXX: icmp_seq=3. time=10 ms
2008 bytes from 192.XXX.XXX.XXX: icmp_seq=4. time=10 ms
----192.XXX.XXX.XXX PING Statistics----
5 packets transmitted, 5 packets received, 0% packet loss
round-trip (ms) min/avg/max = 10/15/38
Console>
The quit command quits the administration session. Following is a sample display:
Console> quit
Connection closed by foreign host.
%
The reset command resets the system. Following are sample displays of two different connections:
Console> (enable) reset
This command will reset the system.
Do you want to continue (y/n) [n]? y
Concentrator Boot ROM (Ver 2.00)
ATE0
ATS0=1
Cisco Systems Console Fri Apr 01 1994, 10:22:34
Enter Password:
Console> (enable) reset
This command will reset the system and disconnect your telnet session.
Do you want to continue (y/n) [n]? y
%
Table A-4 lists the set commands.
| Command | Description | Mode1 |
|---|---|---|
| set agingtime | Set the ARP aging time | P |
| set agingtime | Set the port line error rate alarm | P |
| set arp | Set ARP table entry | P |
| set attach | Set system attach type | P |
| set baud | Set serial port baud rate | P |
| set broadcast | Set SNMP broadcast address | P |
| set coalias | Set alias for company MAC address | P |
| set community | Set SNMP community string | P |
| set cutoff | Set port line error rate cutoff | P |
| set defaultTTL | Set default TTL2 for packets | P |
| set echo | Set echo mode (enable or disable) | P |
| set enablepass | Set enable password | P |
| set help | Display set commands and descriptions | P |
| set insertmode | Set system insert mode | P |
| set ipaddress | Set SNMP IP, netmask, and broadcast addresses | P |
| set ipalias | Set alias for IP address | P |
| set length | Set number of lines in terminal display | N |
| set meter | Set system traffic meter path | P |
| set netmask | Set module name | P |
| set netmask | Set SNMP netmask | P |
| set password | Set the console password | P |
| set path | Set port requested path | P |
| set port | Set port state (enable or disable) | P |
| set portname | Set port name | P |
| set prompt | Set the command-line prompt | P |
| set redirect | Set ICMP redirects on or off | P |
| set route | Set IP routing table entry | P |
| set syscontact | Set system contact name | P |
| set syslocation | Set system location | P |
| set sysname | Set system name | P |
| set time | Set the system clock | P |
| set tnotify | Set SMT Time Notify | P |
| set trap | Set SNMP trap receiver address | P |
| set treq | Set the token request value of the MAC | P |
| set userdata | Set SMT parameter user data | P |
The switch uses an aging mechanism for the ARP address table that removes an address that has been inactive for a number of seconds set by the user. Removing addresses of inactive stations keeps the address table from filling up. Aging ensures that the old address/port association is removed if a station is moved from one switch port to another. The set agingtime command sets the aging time. The default value is 300 seconds. To disable aging, enter 0. A sample display follows:
Console> (enable) set agingtime
Usage: set agingtime <seconds>
Console> (enable) set agingtime ?
Usage: set agingtime <0..1000000>
Console> (enable) set agingtime 1200
ARP aging time set.
Console> (enable)
The set alarm command sets the port line error rate alarm value. The alarms generated are sent to the Network Management System. The default LER-alarm value is 8. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) set alarm
Usage: set alarm <port_number> <value>
Console> (enable) set alarm 3 5
Port 3 Ler-Alarm set to 5.
Console> (enable)
See also show port.
The set arp command adds ARP table entries. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) set arp
Usage: set arp <ip_addr> <hw_addr>
(ip_addr is ipalias or IP dot notation: a.b.c.d)
(hw_addr is in canonical form)
Console> (enable) set arp bedrock 08:00:20:08:f1:ac
ARP entry added.
Console> (enable)
See also clear arp and show arp.
The set attach command sets the system attach type, including single, dual, or null, as follows:
Console> (enable) set attach
Usage: set attach <attachment_type>
Console> (enable) set attach ?
Usage: set attach <dual|single|null>
Console> (enable) set attach single
Attachment type changed to single attach.
Must reset concentrator for this to take effect!
Console> (enable)
Following are the three attachment types for the set attach command:
See also show port and show system.
The set baud command sets the serial port baud rate. The following line speeds are available: 600, 1,200, 2,400, 4,800, 9,600, 19,200, and 38,400. The default line speed is 9,600 baud. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) set baud
Usage: set baud <baud_rate>
Console> (enable) set baud ?
Usage: set baud <600|1200|2400|4800|9600|19200|38400>
Console> (enable) set baud 9600
Baud rate set to 9600.
Console> (enable)
See also show system.
The set broadcast command sets the IP broadcast address. A broadcast address specifies the address of the network. All stations on the network receive any packets with the broadcast address in the destination field. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) set broadcast ?
Usage: set broadcast <a.b.c.d>
Console> (enable) set broadcast 192.54.16.255
Broadcast address changed.
Console> (enable)
See also show snmp.
The set coalias command assigns company aliases, up to eight characters long, for MAC addresses. Only the first three bytes of the MAC address are mapped to an alias. For example, the globally assigned MAC address for Cisco Systems Workgroup is 00:02:d0 in FDDI format.
Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) set coalias ?
Usage: set coalias <name> <company-prefix>
Company-prefix is 3 hex words separated by ":", ex 00:02:d0
Console> (enable) set coalias sgi 10:00:96
Company MAC alias added.
Console> (enable)
See also clear coalias and show coalias.
The set community command sets one of the four SNMP community strings, as follows:
Console> (enable) set community
Usage: set community <access_type> [community_string]
Console> (enable) set community ?
Usage: set community <none|read-only|read-write|read-write-all> [community_stri]
Console> (enable) set community read-only public
SNMP community string set.
Console> (enable)
You can set a community string for each the following access types:
See also show snmp.
The set cutoff command sets the port line error rate (LER) cutoff value. The default LER-cutoff is 7. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) set cutoff
Usage: set cutoff <port_number> <value>
Console> (enable) set cutoff 3 10
Port 3 Ler-Cutoff set to 10.
Console> (enable)
The set defaultTTL command sets the Time-To-Live field of the IP header datagrams whenever a TTL value is not supplied by the transport layer protocol. The default defaultTTL value is 60 seconds. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) set defaultTTL ?
Usage: set defaultTTL <seconds>
(TTL must be 0..255)
Console> (enable) set defaultTTL 15
DefaultTTL set to 15.
Console> (enable)
See also show snmp.
The set echo command sets echo mode on or off. Echo mode determines whether or not what you enter at the console will display on the screen. The default value is enabled. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) set echo
Usage: set echo <enable|disable>
Console> (enable) set echo disable
Echo mode disabled.
Console> (enable)
Echo mode enabled.
Console> (enable) quit
See also show system.
The set enablepass command changes the privileged-level password for the admin. interface. After initializing the set enablepass command, you are prompted for the old password, the new password, and to confirm the new password. A zero-length password is allowed. The default password is no password. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) set enablepass
Enter old password:
Enter new password:
Retype new password:
Password changed.
Console> (enable)
The set help command displays the following information in normal mode:
Console> set help
Commands:
---------------------------------------------------------------------
set help Show this message
set length Set number of lines in terminal display
The set help command displays the following information in privileged mode:
Console> (enable) set help
Commands:
---------------------------------------------------------------------
set alarm Set port ler-alarm
set arp Set ARP table entry
set attach Set system attach type
set baud Set system admin port baud rate
set broadcast Set SNMP broadcast address
set coalias Set alias of company MAC address
set community Set SNMP community string
set cutoff Set port ler-cutoff
set defaultttl Set default TTL for packets
set echo Set echo mode (enable/disable)
set enablepass Set privileged password
set help Show this message
set insertmode Set system insert mode
set ipaddress Set SNMP IP address, netmask, and broadcast address
set ipalias Set alias for IP address
set length Set number of lines in terminal display
set meter Set system traffic meter path
set modname Set module name
set module Set module (enable/disable)
set netmask Set SNMP netmask
set password Set the console password
set path Set port requested path
set port Set port state (enable/disable)
set portname Set port name
set prompt Set system prompt
set redirect Set ICMP redirects (enable/disable)
set route Set IP routing table entry
set syscontact Set system contact
set syslocation Set system location
set sysname Set system name
set time Set time and date
set tnotify Set system SMT T-Notify
set trap Set SNMP trap receiver address
set treq Set MAC T-Request
set userdata Set system SMT User Data
Console> (enable)
Workgroup WS-C1100 Concentrators support insertion of stations attached to the concentrator M port into the FDDI ring so that no data frames are lost in the process. This form of insertion is called scheduled insertion. Without scheduled insertion, frames can be lost while connecting to a new station.
You can change port insertion mode using the set insertmode command, which sets the system insert mode to standard or scheduled. The default is scheduled.
Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) set insertmode
Usage: set insertmode <standard|scheduled>
Console> (enable) set insertmode standard
System insert mode set to standard.
Console> (enable) set insertmode scheduled
System insert mode set to scheduled.
Console> (enable)
You can display the insertion mode of the concentrator by using the show system command. The Ins-Mode field displays the insert mode of the M ports.
The set ipaddress command sets the IP address. The netmask and broadcast addresses needed for SNMP, ping, Telnet, or TFTP can be set at the same time. Following are two sample displays.
EIA/TIA 232 example:
Console> (enable) set ipaddress
Usage: set ipaddress <ip_address> [net_mask [broadcast_address]]
(all values given in IP dot notation: a.b.c.d)
Console> (enable) set ipaddress 192.54.16.205
IP address changed.
Console> (enable) !! 255.255.255.0 192.54.16.205
set ipaddress 192.54.16.205 255.255.255.0 192.54.16.255
IP address, netmask, broadcast address changed.
Console> (enable)
Telnet example:
Console. (enable) set ipaddress 192.54.16.205
This command will disconnect your telnet session.
Do you want to continue (y/n) [n] ? y
Connection closed by foreign host.
%
See also set ipalias.
The set ipalias command adds aliases for IP addresses. The maximum length allowed for a character string is 19. There is one predefined default alias, 0.0.0.0. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) set ipalias oscar 192.XXX.XXX.XXX
IP alias set.
Console> (enable)
See also clear ipalias and show ipalias.
The set length command sets the maximum number of lines you want displayed on the terminal screen so information does not scroll off the screen. A partial display ends with the following prompt:
--More--
At the prompt, press Ctrl-C to terminate the display or press any key to scroll to the next screen of information. Setting the value to 0 disables this feature. The default value is 0. Following is a sample display:
Console> set length 19
Screen length set to 19.
Console>
A sample display with more information follows:
Console> show port
Port Name Status Req-Path Cur-Path Conn-State Type Neigh
---- -------------------- ------ -------- -------- ---------- ---- -----
1 ok secondary concat active A M
2 other primary isolated connecting B U
3 other primary isolated connecting M U
4 other primary isolated connecting M U
5 other primary isolated connecting M U
6 other primary isolated connecting M U
7 other primary isolated connecting M U
8 other primary isolated connecting M U
9 other primary isolated connecting M U
10 other primary isolated connecting M U
11 other primary isolated connecting M U
12 other primary isolated connecting M U
13 other primary isolated connecting M U
14 other primary isolated connecting M U
15 other primary isolated connecting M U
--More--
The set meter command sets the ring path to be shown on the traffic meter. The variables available are as follows:
The default setting is primary. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) set meter
Usage: set meter <path>
Console> (enable) set meter help
Usage: set meter <primary|secondary|local|none>
console> (enable) set meter secondary
Traffic meter now monitoring secondary path.
console> (enable)
See also show system.
The set netmask command sets the IP subnet mask. The subnet mask specifies the subnet field of IP addresses and consists of a 32-bit mask written in dotted-decimal format. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) set netmask
Usage: set netmask <a.b.c.d>
Console> (enable) set netmask 255.255.255.0
Netmask changed.
Console> (enable)
The set password command sets the concentrator login password. You are prompted for the old password followed by the new password twice if the old password checks. A zero-length password is allowed, but passwords must not exceed 20 characters.
If you forget your password, you have 30 seconds after power up or pressing the reset button to log in without a password and change the password. This requires physical access to the concentrator.
Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) set password
Enter old password:
Enter new password:
Retype new password:
Password changed.
Console> (enable)
The set path command sets individual ports to primary or secondary ring paths. The default is primary. Following is a sample display:
Console> set path
Usage: set path <port_number> <primary|secondary>
Console> set path 4 secondary
Port 4 requested path set to secondary.
Console>
See also show port.
The set port command enables and disables a port. The default is enabled. Following is a sample display:
Console> set port
Usage: set port <port_number> <enable|disable>
Console> set port 1 enable
Port 1 enabled.
Console> set port 15 disable
Port 15 disabled.
The format of the set port command follows:
See also show port.
The set portname command configures a name for a port. The default port name is no name. The variables available are as follows:
Console> set portname
Usage: set portname <port_number> [name_string]
Console> set portname 1 A
Console> set portname 2 B
Console> set portname 14
Console>
The port name you enter will appear in the port information display of the show port command. You can enter any port name up to 20 characters in length. A zero-length port name is allowed. Port names are only meaningful to network administrators and are not used by the concentrator.
The set prompt command changes the prompt for the command line of the admin. interface. The default prompt is Console>. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) set prompt
Usage: set prompt <prompt_string>
Console> (enable) set prompt conc5>
conc5>
The set redirect command enables or disables the ICMP redirects, allowing or disallowing dynamic updates to the routing table. The default is enabled. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) set redirect ?
Usage: set redirect <enable|disable>
Console> (enable) set redirect enable
ICMP Redirects enabled.
Console> (enable)
See also show snmp.
The set route command adds IP routing table entries. Its variables are as follows:
Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) set route ?
Usage: set route <destination> <gateway> [metric]
(destination and gateway are ipalias or IP address in
dot notation: a.b.c.d)
Console> (enable) set route fddi 198.133.219.40
Route added.
Console> (enable)
You can enter either an IP address in dotted-decimal format or an alias, if one is set. Add an entry for the destination network and the gateway IP address if you want to manage the concentrator from a network management workstation that is not on the local network.
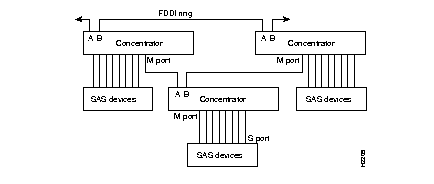
Figure A-1 shows two sample networks. In example A, the concentrator needs a path to a network management workstation located on another network through a router. In this case, you must add an entry in the routing table using the set route command. For example:set route 192.4.34.0 192.45.67.4
In example B, the network management workstation is located on the same network as the concentrator, so you do not need to add an entry in the table.
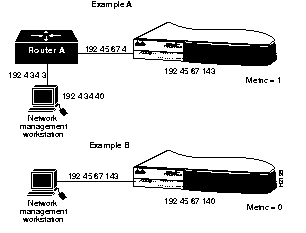
See also clear route and show route.
The set syscontact command sets the name of the person to contact that is displayed in the show system display. The entry can be up to 19 characters long. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) set syscontact ?
Usage: set syscontact [name_string]
Console> (enable) set syscontact Alysa P.Hacker X 6742
System contact set.
Console> (enable)
See also show system.
The set syslocation command sets the location of this concentrator, which is displayed in the show system display. The entry can be up to 19 characters long. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) set syslocation ?
Usage: set syslocation [name_string]
Console> (enable) set syslocation Bldg 12 Rm 403 B-3
System location set.
Console> (enable)
See also show system.
The set sysname command sets the name of this concentrator, which is displayed in the show system display. The entry can be up to 19 characters long. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) set sysname ?
Usage: set sysname [name_string]
Console> (enable) set sysname dragon
System name set.
Console> (enable)
See also show system.
The set time command changes the day of the week, date, and/or time of day in the system clock, as follows:
Console> (enable) set time
Usage: set time [day_of_week] [mm/dd/yy] [hh:mm:ss]
Console> (enable) set time tuesday 05/10/94 18:00:00
Tue May 10 1994, 18:00:00
Console> (enable)
See also show time.
The set tnotify command changes the Time Notify (TNotify) timer value for the concentrator. The TNotify timer specifies the interval between neighbor information broadcasts (NIF frames) to other stations in the network. Enter an integer value from 2 to 30 seconds. The default is 30 seconds. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) set tnotify
Usage: set tnotify <seconds>
Console> (enable) set tnotify 20
System SMT T-Notify set to 20.
Console> (enable)
The set trap command enables, disables, or adds an entry in the SNMP authentication trap receiver table. The default is disabled. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) set trap
Usage: set trap enable
set trap disable
set trap <rcvr_address> <rcvr_community>
(rcvr_address is ipalias or IP address, rcvr_community is string)
Console> (enable) set trap disable
SNMP authentication traps disabled.
Console> (enable) set trap 192.16.54.12 public
SNMP trap receiver added.
Console> (enable) set trap enable
SNMP authentication traps enabled.
Console> (enable)
When you enter addresses in the table, you must specify the community string that will appear in the trap message.
See also clear trap and test trap.
The set treq command changes the token request (TReq) value of the specified MAC. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) set treq
Usage: set treq <mac_number> <usecs>
Console> (enable) set treq 1 165111
MAC T-Request must be in the range 2502..165000 usec
Console> (enable) set treq 1 165000
MAC 1 T-Request set to 165000 usec.
Console> (enable)
The MAC number is either 1 (the primary MAC) or 2 (the secondary MAC). You can enter any new value from TMin to TMax. The default is 165,000 microseconds.
See also show mac.
The set userdata command configures the user data string in the SMT MIB. The user data field can be used to identify a station. The default is set as "CDDI/FDDI Concentrator." Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) set userdata
Usage: set userdata <userdata_string>
Console> (enable) set userdata Workgroup C1100
System SMT user data set.
Console> (enable)
Table A-5 lists the show commands.
| Command | Description | Mode1 |
|---|---|---|
| show arp | Show ARP table entries | N |
| show coalias | Show company aliases | N |
| show config | Show concentrator configuration | P |
| show cspsig | Show CSP2 signal history | P |
| show driver | Show frame driver status or counts | P |
| show help | Use this for information on the show commands | N |
| show ipalias | Show IP aliases assigned | N |
| show log | Show the system error log | P |
| show mac | Show MAC information | N |
| show macdbg | Show MAC debug information | P |
| show macstatus | Show the history of the MAC status register | P |
| show mbuf | Show mbuf3 and malloc4 statistics | P |
| show phy | Show PHY5 | P |
| show pmac | Show primary MAC registers | P |
| show port | Show port information | N |
| show portdbg | Show port debug information | P |
| show porthistory | Show port events | |
| show remotemib | Show a remote MIB | N |
| show ringmap | Show the ringmap for the primary MAC | N |
| show route | Show IP routing table | N |
| show smac | Show secondary MAC registers | P |
| show snmp | Show SNMP information | N |
| show system | Show the system information | N |
| show test | Show the results of diagnostic tests | P |
| show time | Show time of day | N |
The show arp command displays the ARP table entries. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) show arp
Aging time = 1200 sec
montreux at 08:00:20:08:f1:ac
Console> (enable) show arp raw
Aging time = 1200 sec
198.133.219.40 at 08:00:20:08:f1:ac
Console> (enable)
See also clear arp and set arp.
The show coalias command displays the aliases of company MAC addresses. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) show coalias
cisco 00:02:d0
ods 00:00:4a
codenoll 00:00:52
amd 00:00:58
s&k 00:00:5a
netframe 00:00:7e
proteon 00:00:80
synoptx 00:00:81
netwgnrl 00:00:a6
northern 00:00:ae
fibrncs 00:00:b0
cabltrn 00:00:b8
cmc 00:00:bc
eagle 00:00:d8
tekelec 00:00:e8
intrphse 00:00:ee
npi 00:01:1b
summit 00:01:51
synern 00:01:7c
3com 00:06:31
ub 00:bb:10
ibm 08:00:5a
ibm 10:00:5a
sun 10:00:04
sgi 10:00:96
dec 10:00:d4
Console> (enable)
See also clear coalias and set coalias.
The show config command lists all commands used to create the current configuration.
Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) show config
set password
set enablepass
set prompt CONC6>
set attach dual
set baud 9600
set echo enable
set tnotify 30
set meter primary
set sysname alpha
set syslocation BETA
set syscontact gamma
set userdata WS-C1100 (CONC6)
set insertmode scheduled
set ipaddress 198.133.219.206
set netmask 255.255.255.0
set broadcast 198.133.219.255
set agingtime 1200
set redirect disable
set defaultTTL 255
set community none
set community read-only public
set community read-write private
set community read-write-all secret
set trap 198.133.219.40 private
set trap 192.122.173.125 public
set trap enable
set route 192.122.173.0 198.133.219.40 1
set route 192.122.174.0 198.133.219.40 1
set ipalias default 0.0.0.0
set ipalias montreux 198.133.219.40
set ipalias conc3 198.133.219.203
set ipalias conc4 198.133.219.204
set ipalias conc5 198.133.219.205
set ipalias conc6 198.133.219.206
set ipalias conc7 198.133.219.207
set ipalias conc8 198.133.219.208
set ipalias conc9 198.133.219.209
set ipalias conc10 198.133.219.210
set ipalias conc11 198.133.219.211
set ipalias conc12 198.133.219.212
set ipalias conc21 198.133.219.221
set ipalias fddi 192.122.173.0
set ipalias cres-fddi 192.122.173.42
set ipalias sade 192.122.173.82
set ipalias kiss 192.122.173.125
set ipalias hub6 192.122.173.206
set ipalias ether 192.122.174.0
set ipalias montreux- 192.122.174.40
set ipalias cres 192.122.174.42
set ipalias strauss 192.122.174.51
set coalias cisco 00:02:d0
set coalias cisco 00:00:30
set coalias ods 00:00:4a
set coalias codenoll 00:00:52
set coalias amd 00:00:58
set coalias s&k 00:00:5a
set coalias netframe 00:00:7e
set coalias proteon 00:00:80
set coalias synoptx 00:00:81
set coalias netwgnrl 00:00:a6
set coalias northern 00:00:ae
set coalias fibrncs 00:00:b0
set coalias cabltrn 00:00:b8
set coalias cmc 00:00:bc
set coalias eagle 00:00:d8
set coalias tekelec 00:00:e8
set coalias intrphse 00:00:ee
set coalias npi 00:01:1b
set coalias summit 00:01:51
set coalias synern 00:01:7c
set coalias 3com 00:06:31
set coalias ub 00:bb:10
set coalias ibm 08:00:5a
set coalias ibm 10:00:5a
set coalias sun 10:00:04
set coalias sgi 10:00:96
set coalias dec 10:00:d4
set treq 1 15000
set treq 2 15000
set portname 1
set path 1 secondary
set alarm 1 8
set cutoff 1 7
set port 1 enable
set portname 2
set path 2 primary
set alarm 2 8
set cutoff 2 7
set port 2 enable
set portname 3
set path 3 primary
set alarm 3 8
set cutoff 3 7
set port 3 enable
set portname 4
set path 4 primary
set alarm 4 8
set cutoff 4 7
set port 4 enable
set portname 5
set path 5 primary
set alarm 5 8
set cutoff 5 7
set port 5 enable
set portname 6
set path 6 primary
set alarm 6 8
set cutoff 6 7
set port 6 enable
set portname 7
set path 7 primary
set alarm 7 8
set cutoff 7 7
set port 7 enable
set portname 8
set path 8 primary
set alarm 8 8
set cutoff 8 7
set port 8 enable
set portname 9
set path 9 primary
set alarm 9 8
set cutoff 9 7
set port 9 enable
set portname 10
set path 10 primary
set alarm 10 8
set cutoff 10 7
set port 10 enable
set portname 11
set path 11 primary
set alarm 11 8
set cutoff 11 7
set port 11 enable
set portname 12
set path 12 primary
set alarm 12 8
set cutoff 12 7
set port 12 enable
set portname 13
set path 13 primary
set alarm 13 8
set cutoff 13 7
set port 13 enable
set portname 14
set path 14 primary
set alarm 14 8
set cutoff 14 7
set port 14 enable
set portname 15
set path 15 primary
set alarm 15 8
set cutoff 15 7
set port 15 enable
set portname 16
set path 16 primary
set alarm 16 8
set cutoff 16 7
set port 16 enable
set portname 17
set path 17 primary
set alarm 17 8
set cutoff 17 7
set port 17 enable
set portname 18
set path 18 primary
set alarm 18 8
set cutoff 18 7
set port 18 enable
CONC6> (enable)
See also clear config and write Command.
The show cspsig command displays the connection services process (CSP) signal history, as follows:
Console> (enable) show cspsig
Signal History Index == 12
Signal Type Signal Entity Signal Data
----------- ------------- -----------
0 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3383
1 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3384
2 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3385
3 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3386
4 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3387
5 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3388
6 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3389
7 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3390
8 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3391
9 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3392
10 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3393
11 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3394
12 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3345
13 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3346
14 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3347
15 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3348
16 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3349
17 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3350
18 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3351
19 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3352
20 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3353
21 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3354
22 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3355
23 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3356
24 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3357
25 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3358
26 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3359
27 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3360
28 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3361
29 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3362
30 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3363
31 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3364
32 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3365
33 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3366
34 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3367
35 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3368
36 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3369
37 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3370
38 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3371
39 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3372
40 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3373
41 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3374
42 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3375
43 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3376
44 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3377
45 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3378
46 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3379
47 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3380
48 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3381
49 LEM:SIG_LEM_Start 1 3382
Console> (enable)
The show driver command displays frame driver status and counts, as follows:
Console> (enable) show driver
MACs on board 2
Frames/poll value 3
Intrs seen (P & S) 10929
Primary Secondary
Ring Operational status up up
Frame Recieved flag 0 0
Rcv buffer full flag 0 0
Entered get_rcv_pkt 9164 8552
MSVALID bit not set 0 0
MAC Aborted frames 0 0
Packet length errors 0 0
No Rcv buffers 0 0
Frame type errors 0 0
Xfered packets 9665 9652
Adjust RPR wrapped 8 8
Xfer packet wrapped 8 8
Rcv Q resets 0 0
Rcv lock clears 0 0
Rcv SMT frames 8698 8698
Rcv LLC frames 967 954
Enter SendSMTFrame 479 680
Sent SMT Frames 479 680
Wrapped SMT Xmit Buffer 10 15
SMT RP Out Of Bounds 0 0
SMT Ptr Out Of Bounds 0 0
SMT Restart Xmit, No Space 0 0
No Space In SMT Buffer 0 0
Wrapped LLC Xmit Buffer 0 0
LLC RP Out Of Bounds 0 0
No Space in LLC Buffer 0 0
MACReInitCt 0 0
Xtra Xmit Issued 0 0
Xmit Stuck 0
Console> (enable)
The show help command displays the following information in normal mode:
Console> show help
Show commands:
-------------------------------------------------------------------
show help Show this message
show mac Show MAC information
show port Show port information
show remotemib Show a remote mib
show ringmap Show the ring map for the primary mac
show snmp Show SNMP information
show system Show system information
show time Show time
Console>
The show help command displays the following information in privileged mode:
Console> (enable) show help
Show commands:
-----------------------------------------------------------------
show arp Show ARP table
show coalias Show alias of company MAC addresses
show config Show commands to set current configuration
show cspsig Show CSP signal history
show driver Show frame driver status/counts
show help Show this message
show ipalias Show aliases for IP addresses
show log Show system error log
show mac Show MAC information
show macdbg Show MAC debug information
show macstatus Show history of MAC status register
show mbuf Show mbuf and malloc stats
show phy Show PHY registers
show pmac Show primary MAC registers
show port Show port information
show portdbg Show port debug information
show porthistory Show port management history
show remotemib Show a remote mib
show ringmap Show FDDI ring map
show route Show IP routing table
show smac Show secondary MAC registers
show snmp Show SNMP information
show system Show system information
show test Show results of diagnostics tests
show time Show time and date
Console> (enable)
The show ipalias command displays IP aliases assigned using the set ipalias command. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) show ipalias
default 0.0.0.0
Console> (enable)
See also clear ipalias and set ipalias.
The show log command displays the system error log. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) show log
Magic Pattern: 55aa Interrupt level not zero count : 0
Last Restart reason : S/W Watchdog failure
DRAM Failures : 0 S/W Watchdog : 58648
H/W Watchdogs : 0 Warm Start : 0
MAC Failures : 0
Path Test Failures : 0
Last CPU exception was : 11
PC = 0 Status Regs = 0
D0-D7: 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000
A0-A7: 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000
Access Bits: Read/Write: W Instr/Data: D FC code: 0
Access Addr: 50000 Instruction Reg: 0
Console> (enable)
See also clear log.
The show mac command displays information on both MACs, as follows:
Console> (enable) show mac ?
Usage: show mac [raw]
(raw - no alias conversions,
otherwise use FDDI format with aliasing)
Console> (enable) show mac raw
MAC SMT-Address Curr-Path TReq TNeg TMax TVX
--- ----------------- --------- -------- -------- -------- --------
1 00:02:d0:03:0b:58 primary 165000 10000 165004 2509
(00:40:0b:c0:d0:1a)
2 00:02:d0:03:0b:59 secondary 165000 10000 165004 2509
(00:40:0b:c0:d0:9a)
MAC Rcv-Frms Rcv-Smt Rcv-llc Tvx-Exp-Ct RingOp-Ct RMT-St
--- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------
1 100286 91269 9017 0 94 ring-op
2 96067 91257 4810 0 59 ring-op
MAC Xmit-Frms Xmit-Smt Xmit-llc Error-Frms Lost-Frms Total-Frms
--- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------
1 24743 9363 15380 1 2 440372753
2 9298 9298 0 0 0 440383810
MAC Upstream-Nbr Downstream-Nbr Old-Upstream-Nbr Old-Downstream-Nbr
--- ----------------- ----------------- --------------- -----------------
1 00:02:d0:50:c0:f3 00:02:d0:03:0b:59 10:00:04:10:8f:35 00:02:d0:50:c0:f3
(00:40:0b:0a:03:cf)(00:40:0b:c0:d0:9a)(08:00:20:08:f1:ac)(00:40:0b:0a:03:cf)
2 00:02:d0:03:0b:58 57:53:2d:03:00:48 00:00:1f:00:00:00 00:02:d0:03:06:00
(00:40:0b:c0:d0:1a)(ea:ca:b4:c0:00:12)(00:00:f8:00:00:00)(00:40:0b:c0:60:00)
Last-Time-Cleared
--------------------------
Mon Jul 11 1994, 20:45:19
Console> (enable)
Following are descriptions of the display fields of the show mac command:
MAC SMT-Address
--- -----------------
1 cisco:01:07:1e (FDDI version)
(00:40:0b:80:e0:78) (canonical version)
See also clear mac.
The show macdbg command shows MAC debug information, as follows:
Console> (enable) show macdbg
MAC TMax-Cap TVX-Cap FS-Cap Avl-Path Rq-Path DA-Test DA-Flg Frm-Mac-Flg
--- -------- -------- ------ -------- ------- ------- ------ -----------
1 167769 5202 0 3 4 pass false false
2 167769 5202 0 3 2 pass false false
MAC Xmit-Abort Dir-Beacon Rcv-Invald Rcv-Reset Rcv-Short
--- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------
1 0 0 0 0 0
2 0 0 0 0 0
MAC Trace-Init Trace-Prop Trace-Term DownstrmType
--- ---------- ---------- ---------- ------------
1 0 0 0 B
2 0 0 0 B
Following are descriptions of the display fields of the show macdbg command:
The show macstatus command displays the history of the FDDI MAC status registers, as follows:
Console> (enable) show macstatus
index ST1U ST1L ST2U ST2L
----- ------ ------ ------ ------
65 000000 000000 0x8000 0x8100
64 000000 000000 0x8000 0x8100
63 000000 000000 0x8000 0x8100
62 000000 000000 000000 0x8010
61 000000 000000 0x8000 0x8100
60 000000 000000 0x8000 0x8100
59 000000 000000 0x8000 0x8100
58 000000 000000 0x8000 0x8100
57 000000 000000 0x8000 0x8100
56 000000 000000 0x8000 0x8100
55 000000 000000 0x8000 0x8100
54 000000 000000 0x8000 0x8100
53 000000 000000 0x8000 0x8100
52 000000 000000 0x8000 0x8100
51 000000 000000 0x8000 0x8100
50 000000 000000 0x8000 0x8100
49 000000 000000 0x8000 0x8100
48 000000 000000 0x8000 0x8100
47 000000 000000 0x8000 0x8100
46 000000 000000 0x8000 0x8100
45 000000 000000 0x8000 0x8100
The show mbuf command displays memory buffer (mbuf) and memory allocation (malloc) statistics, as follows:
Console> (enable) show mbuf
total free in use drops drains panics
------- ------- ------- ------- ------- -------
mbufs 240 228 12 0 0 0
clusters 20 20 0
scc bufs 4096 3938 158
malloc blocks 128 93 35
mbuf usage: (current number)/(maximum number since last show)
data= 0/7 header= 0/1 socket= 4/5
pcb= 5/6 rtable= 2/2 htable= 0/0
atable= 0/0 soname= 0/1 zombie= 0/0
soopts= 0/1 ftable= 0/0 rights= 0/0
ifaddr= 1/1
Console> (enable)
The show phy command displays the values stored in PHY registers and the Tl-min of the PHY.
The variables available are as follows:
Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) show phy ?
Usage: show phy <port_num> [hex_register]
show phy <port_num> tlmin
(mod_num=1..2, port_num=1..16, hex_register=0..1f,80..8d)
Console> (enable) show phy 2 10
PHY 2 register 0x10 = 0x3e6
Console> (enable) show phy 2 tlmin
PHY 2 register tlmin (0x07) = 0xfff1
Console> (enable)
The show pmac command displays the values stored in primary MAC registers, as follows:
Console> (enable) show pmac 44
Usage: show pmac [hex_register]
(hex_register=0 to 43)
Console> (enable) show pmac 3
Primary MAC register 0x3 = 0x8110
The show port command displays status and configuration information about each of the concentrator ports, as follows:
Console> show port
Port Name Status Req-Path Cur-Path Conn-State Type Neigh
---- -------------------- ------ -------- -------- ---------- ---- -----
1 ok secondary concat active A M
2 other primary isolated connecting B U
3 other primary isolated connecting M U
4 other primary isolated connecting M U
5 other primary isolated connecting M U
6 other primary isolated connecting M U
7 other primary isolated connecting M U
8 other primary isolated connecting M U
9 other primary isolated connecting M U
10 other primary isolated connecting M U
11 other primary isolated connecting M U
12 other primary isolated connecting M U
13 other primary isolated connecting M U
14 other primary isolated connecting M U
15 other primary isolated connecting M U
16 other primary isolated connecting M U
17 other primary isolated connecting M U
18 other primary isolated connecting M U
Port Ler-Cond Ler-Est Ler-Alrm Ler-Cutoff Lem-Ct Lem-Rej-Ct Media
---- -------- ------- -------- ---------- ---------- ---------- --------
1 false 15 8 7 0 0 mlt-3
2 false 16 8 7 0 0 mlt-3
3 false 16 8 7 0 0 cddi
4 false 16 8 7 0 0 cddi
5 false 16 8 7 0 0 cddi
6 false 16 8 7 0 0 cddi
7 false 16 8 7 0 0 cddi
8 false 16 8 7 0 0 cddi
9 false 16 8 7 0 0 cddi
10 false 16 8 7 0 0 cddi
11 false 16 8 7 0 0 mlt-3
12 false 16 8 7 0 0 mlt-3
13 false 16 8 7 0 0 mlt-3
14 false 16 8 7 0 0 mlt-3
15 false 16 8 7 0 0 mlt-3
16 false 16 8 7 0 0 mlt-3
17 false 16 8 7 0 0 mlt-3
18 false 16 8 7 0 0 mlt-3
Last-Time-Cleared
----------------------------
00 2000, 00:00:00
Console>
Following are descriptions of the display fields of the show port command:
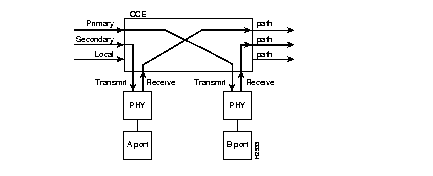
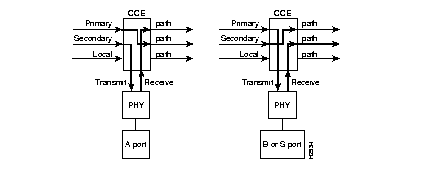
See also clear port, set port, set portname, set path, set agingtime, and set cutoff.
The show portbg command displays port debug information, as follows:
Console> (enable) show portdbg
Port Con-Pol Rq-Path Av-Path Mac-Plmt LCT-Fail Rem-Mac PC-Wthld BS-Flg EB-Ct
---- ------- ------- ------- -------- -------- ------- -------- ------ -----
1 0 015999 3 0 0 false none false 0
2 0 0169a9 3 1 0 false none false 0
3 0 012700 3 0 0 false none false 0
4 0 012700 3 2 0 true none false 0
5 0 012700 3 0 0 false none false 0
6 0 012700 3 0 0 false none false 0
7 0 012700 3 0 0 false none false 0
8 0 012700 3 0 0 false none false 0
9 0 012700 3 0 0 false none false 0
10 0 012700 3 0 0 false none false 0
Port MACLoop-Time PC-State Ins-Attmpt Ins-Ok Ins-Tout Ins-Cancel BreakCt
---- ------------ --------- ---------- -------- -------- ---------- -------
1 0 connect 0 0 0 0 0
2 0 active 0 0 0 0 0
3 0 connect 0 0 0 0 0
4 0 active 1 1 0 0 0
5 0 connect 0 0 0 0 0
6 0 connect 0 0 0 0 0
7 0 connect 0 0 0 0 0
8 0 connect 0 0 0 0 0
9 0 connect 0 0 0 0 0
10 0 connect 0 0 0 0 0
Console> (enable)
Following are descriptions of the display fields of the show portdbg command:
The show porthistory command displays the events for each port since the last system reset. A sample display follows:
Console> (enable) show porthistory
Port Management History Table
PHY Event
--- --------------------------------------------
0 PCM RCode=e T_Val=8, isW=0, isC=0, npc=0
7 PCM RCode=8 T_Val=e, isW=0, isC=1, npc=1
7 PCM RCode=8 T_Val=e, isW=0, isC=1, npc=1
7 PCM RCode=8 T_Val=e, isW=0, isC=1, npc=1
0 PCM RCode=e T_Val=8, isW=0, isC=0, npc=0
*********** Information Deleted **********
Console> (enable)
The show remotemib command displays remote MIB information, as follows:
Console> show remotemib
Usage: show remotemib <macaddr> [raw]
(macaddr is hex separated by :, ex: 00:02:d0:02:06:e1
macaddr can also use coalias, ex: cisco:02:06:e1
If raw, then company aliases are not displayed.)
Console>
For example, the following command displays SMT parameters from the station with the MAC address of cisco:02:23:3e.
Console> (enable) show remotemib cisco:02:23:3e
Station-ID MACs Ports Attach Op-Ver Hi-Ver Lo-Ver CF-State
------------------------ ---- ----- ------ ------ ------ ------ --------
00:00:00:02:d0:02:23:3e 1 1 1 1 1 1 NA
(00:00:00:40:0b:40:c4:7c)
MAC TReq TNeg TMax TVX RingOp-Ct
--- --------- -------- -------- -------- ---------
1 15000 10000 167772 2621 NA
MAC Upstream-Nbr Downstream-Nbr Frame-Ct Error-Ct Lost-Ct
--- ----------------- ----------------- --------- -------- --------
1 cisco:03:06:7f cisco:01:0d:f0 1008945 1 2
(00:40:0b:c0:60:fe)(00:40:0b:80:b0:0f)
Port Ler-Est Ler-Alrm Ler-Cutoff Lem-Ct Lem-Rej-Ct
---- ------- -------- ---------- ---------- ----------
1 15 8 7 0 0
Manu-Data User-Data
----------------------------- --------------------------------
Cisco Systems FDDI EISA Adapter
Console> (enable)
You can also use a company alias as part of the MAC address. Use the raw option to show MAC addresses without company aliases.
The show remotemib display contains parts of the show mac and show port displays, with the following new fields:
See also show ringmap.
The show ringmap command displays the FDDI ringmap for the primary or secondary MAC.
The variables available are as follows:
The equal sign (=) after a MAC address denotes the default MAC. An asterisk (*) after a MAC address denotes mismatched neighbor information.
Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) show ringmap ?
Usage: show ringmap [raw|canonical]
(raw - show with no alias conversions,
canonical - show with canonical format,
otherwise use FDDI format with aliasing)
Console> (enable)
In the following sample displays of the show ringmap command, token flow is from the top to the bottom of the list.
Console> (enable) show ringmap raw
Ring Map for Primary Ring
1=00:00:ae:03:0c:57
2=00:02:d0:02:23:4b
3=00:02:d0:03:06:7f
4=00:02:d0:03:06:00
5=00:02:d0:50:c0:f3
6=00:02:d0:03:00:48
7=00:02:d0:03:0b:58=
8=00:02:d0:03:0b:59
9=00:02:d0:03:00:49
10=00:02:d0:02:15:8e
11=00:02:d0:03:0b:5b
12=00:02:d0:03:0b:5c
13=00:02:d0:01:16:51
14=00:02:d0:02:02:f1
15=00:02:d0:05:20:f8
16=00:02:d0:01:00:24
17=00:02:d0:01:0a:24*
18=10:00:04:10:8f:35
19=00:00:ae:03:0c:58
Update ring map again (y/n) [y]? n
Console> (enable)
Console> (enable) show ringmap canonical
Ring Map for Primary Ring
1=00:40:0b:c0:d0:f2
2=00:40:0b:40:c4:d2
3=00:40:0b:c0:60:fe
4=00:40:0b:c0:60:00
5=00:40:0b:0a:03:cf
6=00:40:0b:c0:00:12
7=00:40:0b:c0:d0:1a=
8=00:40:0b:c0:d0:9a
9=00:40:0b:c0:00:92
10=00:40:0b:40:a8:71
11=00:40:0b:c0:d0:da
12=00:40:0b:c0:d0:3a
13=00:40:0b:80:68:8a
14=00:40:0b:40:40:8f
15=00:40:0b:a0:04:1f
16=00:40:0b:80:00:24
17=00:40:0b:80:50:24*
18=08:00:20:08:f1:ac
19=00:40:0b:c0:d0:0a*
20=00:00:75:c0:30:1a*
Update ring map again (y/n) [y]? n
Console> (enable)
Console> (enable) show ringmap
Ring Map for Primary Ring
1= cisco:02:23:4b
2= cisco:03:06:7f
3= cisco:03:06:00
4= cisco:50:c0:f3
5= cisco:03:00:48
6= cisco:03:0b:58=
7= cisco:03:0b:59
8= cisco:03:00:49
9= cisco:02:15:8e
10= cisco:03:0b:5b
11= cisco:03:0b:5c
12= cisco:01:16:51
13= cisco:02:02:f1
14= cisco:05:20:f8
15= cisco:01:00:24
16= cisco:01:0a:24*
17= sun:10:8f:35
18= cisco:03:0b:50
19= cisco:03:0b:4f
Update ring map again (y/n) [y]? n
Console> (enable)
The show route command displays the IP routing table entries set using the set route command. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) show route
destination gateway metric
default 192.1.1.3 1
192.1.1.0 192.1.1.203 0
192.1.2.0 192.1.1.10 1
Console> (enable)
See also clear route and set route.
The show smac command displays the values stored in secondary MAC registers, as follows:
Console> (enable) show smac 5
Secondary MAC register 0x5 = 0xfff9
The show snmp command displays two levels of the SNMP and IP information. Privileged mode allows read-write and read-write-all community access. Following are sample displays:
Console> show snmp
IP-Address IP-Netmask IP-Broadcast
--------------- --------------- ---------------
192.54.16.205 255.255.255.0 192.54.16.255
ICMP Redirects DefaultTTL
-------------- ----------
enabled 60
Community-Access Community-String
---------------- --------------------
none
read-only public
Trap-Rec-Address Trap-Rec-Community Auth Traps Disabled
---------------- --------------------
Console>
Console> (enable) show snmp
IP-Address IP-Netmask IP-Broadcast
--------------- --------------- ---------------
192.54.16.205 255.255.255.0 192.54.16.255
ICMP Redirects DefaultTTL
-------------- ----------
enabled 60
Community-Access Community-String
---------------- --------------------
none
read-only public
read-write private
read-write-all secret
Trap-Rec-Address Trap-Rec-Community Auth Traps Disabled
---------------- --------------------
Console> (enable)
Following are descriptions of the display fields of the show snmp command:
The show system command displays system information. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) show system
Maximum Installed Attach Attach
Station-ID MACs Port-Ct Port-Ct Type Count Uptime d,h:m:s
------------------------ ---- ------- --------- ------ ------ --------------
00:00:00:02:d0:03:00:48 2 18 18 dual 2 7,23:42:17
(00:00:00:40:0b:c0:00:12)
Baud Echo T-Notify Conn-Pol CF-St ECM-St Hold-St Bypass Traffic
----- -------- -------- -------- -------- --------- -------- ------- --------
9600 enabled 30 8000 c-Wrap-A in not-hold absent 31%(P)
Ps-Type Ps-Status Fan-Status Temp-Alarm Sys-Status
------- ----------- ---------- ----------- ----------
80w ok ok off ok
Model Serial-Num Hw Fw Sw
-------- ---------- ------ ------ ------
WS-C1100 000000220 1.0 2.1 2.704
System-Name System-Location System-Contact
------------------------ ------------------------ ------------------------
alpha BETA gamma
SMT User-Data Op-Ver Hi-Ver Lo-Ver Ins-Mode
-------------------------------- ------ ------ ------ ---------
WS-C1100 (CONC6) 2 2 2 scheduled
Ins-Pending Phy-to-Insert exitMACID #Connecting ExpansionBrd
----------- ------------- --------- ----------- ------------
0 0 0 0 present
Software compiled on Aug 16 1994, 11:22:28.
Software downloaded on 0 200, 00:00:00.
Console> (enable)
Following are descriptions of the display fields of the show system command:
| Bit Location | Connection Policy | Policy Definition |
|---|---|---|
| 0 (LSB)1 | Reject A-A | An undesirable peer connection that creates twisted primary and secondary rings. |
| 1 | Reject A-B | Normal trunk ring-to-peer connection. |
| 2 | Reject A-S | Undesirable peer connection that creates a wrapped ring. |
| 3 | Reject A-M | Tree connection with possible redundancy. |
| 4 | Reject B-A | Normal trunk ring-to-peer connection. |
| 5 | Reject B-B | Undesirable peer connection that creates twisted primary and secondary rings. |
| 6 | Reject B-S | Undesirable peer connection that creates a wrapped ring. |
| 7 | Reject B-M | Tree connection with possible redundancy. |
| 8 | Reject S-A | Undesirable peer connection that creates a wrapped ring. |
| 9 | Reject S-B | Undesirable peer connection that creates a wrapped ring. |
| 10 | Reject S-S | Connection that creates a single ring of two slave stations. |
| 11 | Reject S-M | Normal tree connection. |
| 12 | Reject M-A | Tree connection that provides possible redundancy. |
| 13 | Reject M-B | Tree connection that provides possible redundancy. |
| 14 | Reject M-S | Normal tree connection. |
| 15 (MSB)2 | Reject M-M | An illegal connection that creates a "tree of rings" topology. |
The value displayed in the connection policy field is a four-digit hexadecimal number in which each digit corresponds to four of the bit positions in the table. The interpretation of the number 8000 is shown in Figure A-8.
For example, assume the Connection-Policy value for the concentrator is 8000. Reading the hexadecimal numbers from right to left, note that bits 0 though 3 are not set, bits 4 through 7 are not set, bits 8 through 11 are not set, and bits 12 through 14 are not set; however, bit 15 is set. Check Table A-6 for the policy that corresponds to bit 15. In this case, an M-M port connection is rejected.
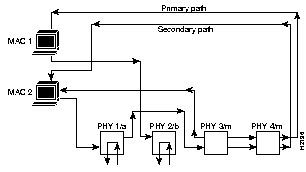
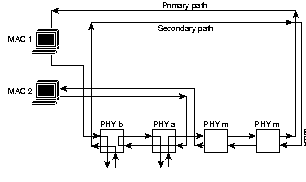
| Bit Location | Test |
|---|---|
| 0 | -12V |
| 1 | +12V |
The show test command displays the results of the diagnostic tests. This command generates a static test file each time the concentrator is reset. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) show test
M68302 Status: (.=Pass, F=Fail, .=Yes, N=No)
NMI: . DMA: .
Memory Status:
RAM: . ROM: . Flash-EEPROM: . NVRAM: . Ser-EEPROM: .
I/O Status:
FAN1: . FAN2: . POWER -12V: . POWER +12V: .
- MACS -
CCE Status: 1 2
-----------------------------
CCE Present . .
Revision read test . .
Password match test . .
Watch Dog Timer test . .
Parity clear test* . .
MUX Read/Write test . .
---------------------- Ports -----------------------
CCE Status: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
------------------------------------------------------------------------
CCE Present . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Revision read test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Password match test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Watch Dog Timer test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Parity clear test* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MUX Read/Write test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
* Bit 6=PHY, 5=DLI, 4=DSI, 3=DPI, 2=MLI, 1=MSI, 0=MPI
PHY Status: Port ---> 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Read/Write Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Interrupt Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Line Mod. Present . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
External Loopback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Full Int. Loopback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Half Int. Loopback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MAC Status: 1 2
-------------------------------
Read/Write Test . .
Buffer Mem. Test . .
MAC Ring Tests: 1 2
----------------------------------
Present . .
Interrupt Test . .
Token Capture Test . .
Int. Loopback Test . .
Ext. CCE Loopback . .
Ext. Ring Tests ... ...
Loopback: A B 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
------------------------------------------------------------------------
PMAC ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
SMAC ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
Console> (enable)
The show time command displays the system clock, as follows:
Console> show time
Tue May 10 1994, 16:47:03
Console>
See also set time.
Table A-8 list the test commands.
| Command | Description | Mode1 |
|---|---|---|
Display test commands | P | |
| test trap | Send a trap message to trap receivers | P |
The test help command displays the following message:
Console> (enable) test help
Commands:
---------------------------------------------------------------------
test help Show this message
test trap Send SNMP trap message to trap receivers
Console> (enable)
The test trap command sends an SNMP trap message to the trap receivers. Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) test trap
Usage: test trap <trap_num> [specific_num]
Console> (enable) test trap 1
SNMP trap message sent.
Console> (enable)
See also clear trap and set trap.
The traffic command sends continuous traffic on the ring, as follows:
Console> (enable) traffic
Usage: traffic <FC> <DA> <SA> random <LEN> <PKTS>
traffic <FC> <DA> <SA> percent <CENT>
(FC is any valid FDDI Frame Class in hex format.
DA and SA are hex MAC addresses in FDDI format
separated by :, ex: a:0:45:21:2:6
LEN = length of packet, PKTS = Number of packets)
Console> (enable) traffic 41 00:40:0b:80:e0:48 00:40:b0:80:e0:c8
random 64 100
Generating Random data at maximum rate....Done
Console> (enable) traffic 41 00:40:0b:80:e0:48 00:40:b0:80:e0:c8
percent 60
Generating Traffic at 60%
= Packet rate of 1666 packets/sec
= Inter-packet gap time of 239 usec
= Wait loop count of 225
HIT ANY KEY TO STOP TRAFFIC GENERATION
..Percentage traffic stopped
Console> (enable)
The traffic command sets the concentrator in traffic generation mode. You can specify the number, type, and content of packets to be generated. The traffic is generated by the primary MAC only.
The following options are available with the traffic command:
Refer to the sample network in Figure A-14 when you read the following examples of the traffic command.
To generate packets with random data, use the following command:
traffic 51 00:02:D0:02:00:35 00:02:D0:01:00:08 random 100 10000
This command generates 10,000 frames of 100 bytes, each containing random data. The traffic generation ceases either after all the frames have been generated or if the ring goes down for any reason.
The LEN parameter in the previous command (100) can be any valid FDDI frame length. Note that the length you specify includes the frame class and address fields. The data bytes in the frames are all set to zero and packets are generated by the MAC at the fastest possible rate.
To generate traffic at a fixed rate, use the following command:
traffic 51 00:02:D0:02:00:35 00:02:D0:01:00:08 percent 78
This command generates 78 percent traffic on the ring. Each frame contains the same random data and is 4,492 bytes in length. For every new percent traffic command, new random data is generated. The mode of traffic generation stops either if the ring goes down or if any key on the keyboard is pressed. Note that there may be a slight deviation from the exact percentage.
Always reset the concentrator following traffic generation. This will ensure proper behavior of the node.
The upload command uploads the Flash memory image file from the concentrator to a network host to create a backup file. The file must be created in advance and saved in the tftpboot directory.
The upload command performs the same function as the copy flash tftp command.
Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) upload
Usage: upload <host> <file>
(host is ipalias or IP address: a.b.c.d
file must already exist in tftp directory.)
Console> (enable) upload oscar c1100_conc3.net
Upload flash image to file c1100_conc3.net on host oscar (y/n) [n]? y
Uploading image to c1100_conc3.net on 198.133.219.40
/
Done. Finished Network Upload. (446468 bytes)
Console> (enable)
See also the copy tftp flash Command.
The write command writes the concentrator configuration either to an existing file in a network host tftpboot directory or to the terminal screen display.
The ASCII configuration file uploaded by the write terminal command can be used to configure the same concentrator or edited to configure another WS-C1100 concentrator. (See the section "configure Command" earlier in this appendix.) The uploaded file is the same output as the files generated by the show config and write terminal commands, with the following exceptions:
The write terminal command functions the same as the show config command.
Following is a sample display:
Console> (enable) write ?
Usage: write network
write terminal
write <host> <file>
Console> (enable) write cres 06.29.config
Write file 06.29.config on host cres (y/n) [n]? y
Uploading configuration to 06.29.config on cres
Done. Finished Network Upload (5135 bytes)
Console> (enable)
See also the configure Command.
|
|