- Preface
- 1. General Overview
- 2. Introduction to the SCE Platform
- 3. Topology
- 4. Installation and Maintenance
- 5. Connecting the Management Interfaces and Performing Initial System Configuration
- Connecting the Local Console
- Initial System Configuration
- Setup Command Parameters
- Step 1: Configuring Initial Settings
- Step 2: Configuring the Hostname
- Step 3: Setting the Passwords
- Step 4: Configuring Time Settings
- Step 5: Configuring the DNS Settings
- Step 6: Configuring the RDR Formatter Destination
- Step 7: Configuring Access Control Lists (ACLs)
- Step 8: Configuring SNMP
- Step 9: Configuring the Topology-Dependent Parameters
- Step 10: Completing and Saving the Configuration
- Connecting the Management Interface
- 6. Cabling the Line Ports and Completing the Installation
- 7. Basic SCE 1000 Platform Operations
- 8. Troubleshooting
- A. The External Optical Bypass Module
This preface describes who should read the SCE 1000 2xGBE Installation and Configuration Guide, how it is organized, and its document conventions.
|
Cisco Service Control Release |
Part Number |
Publication Date |
|---|---|---|
|
Release 3.0.5 |
OL-7821-05 |
November, 2006 |
Description of Changes
Added maximum hostname length.
|
Cisco Service Control Release |
Part Number |
Publication Date |
|---|---|---|
|
Release 3.0 |
OL-7821-04 |
February, 2006 |
Description of Changes
Updated circuit breaker information.
|
Cisco Service Control Release |
Part Number |
Publication Date |
|---|---|---|
|
Release 3.0 |
OL-7821-03 |
December, 2005 |
Description of Changes
Added the following new features:
Redundant management (Mng) port
|
Cisco Service Control Release |
Part Number |
Publication Date |
|---|---|---|
|
Release 2.5.7 |
OL-7821-02 |
August, 2005 |
Description of Changes
Complete reorganization and revision of product documentation.
This guide is for the networking or computer technician responsible for installing and configuring the SCE 1000 platform on-site. To use this publication, you should be familiar with telecommunications equipment and installation procedures, as well as electronic circuitry and wiring practices. You should also have experience as an electronic or electromechanical technician.
This installation guide explains the initial hardware installation and basic configuration procedures for the SCE 1000. It contains procedures for unpacking and installing the device and performing basic configuration via the setup wizard. After completing the installation and basic configuration procedures covered in this guide, you will then use the appropriate companion publications to more completely configure your system.
This guide contains instructions on how to install and run the SCE 1000 platform. This guide assumes a basic familiarity with telecommunications equipment and installation procedures.
The major sections of this guide are as follows:
|
Chapter |
Title |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Chapter 1 |
This chapter provides a brief introduction to Cisco Service Control. | |
|
Chapter 2 |
This chapter provides a hardware overview of the SCE 1000 platform. | |
|
Chapter 3 |
This chapter describes the possible deployment topologies of the SCE 1000 and explains how various aspects of the topology determine the configuration of the system. | |
|
Chapter 4 |
This chapter explains how to install a SCE 1000 platform in a rack or in a general tabletop installation and how to install or replace the power supply units and fan modules. | |
|
Chapter 5 |
Connecting the Management Interfaces and Performing Initial System Configuration |
This chapter explains how to connect the SCE 1000 platform to a local console and perform the initial system configuration via the setup wizard that runs automatically. |
|
Chapter 6 |
This chapter provides instructions for cabling the Gigabit Ethernet ports for one SCE 1000 topologies and for configuring Gigabit Ethernet (GBE) interface parameters. | |
|
Chapter 7 |
This chapter describes how to start up the SCE 1000 platform, reboot, and shutdown. It also describes how to manage configurations. | |
|
Chapter 8 |
This chapter provides basic system startup troubleshooting information. | |
|
Appendix A |
This appendix explains how to install the optional external optical bypass module. |
Your SCE 1000 platform and the software running on it contain extensive features and functionality, which are documented in the following resources:
Cisco CLI software:
Cisco Service Control Engine (SCE) Software Configuration Guide
Cisco Service Control Engine (SCE) CLI Command Reference
Note
You can access Cisco software configuration and hardware installation and maintenance documentation on the World Wide Web at Cisco Website URL. Translated documentation is available at the following URL: International Cisco Website
For initial installation and startup information, refer to the SCE 1000 2xGBE Quick Start Guide.
For international agency compliance, safety, and statutory information for wide-area network (WAN) interfaces for the SCE 1000 platform, refer to the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for Cisco Service Control Engine (SCE).
For installation and configuration of the other components of the Service Control Management Suite refer to:
Cisco SCMS Subscriber Management User Guide
Cisco SCMS Collection Manager User Guide
Cisco Service Control Application for Broadband User Guide
Cisco Service Control Application Reporter User Guide
To view Cisco documentation or obtain general information about the documentation, refer to the following sources:
Obtaining Documentation
The Cisco Information Packet that shipped with your SCE 1000 platform.
This document uses the following conventions:
|
Convention |
Description |
|---|---|
|
boldface font |
Commands and keywords are in boldface. |
|
italic font |
Arguments for which you supply values are in italics. |
|
[ ] |
Elements in square brackets are optional. |
|
{x | y | z} |
Alternative keywords are grouped in braces and separated by vertical bars. |
|
[x | y | z] |
Optional alternative keywords are grouped in brackets and separated by vertical bars. |
|
string |
A nonquoted set of characters. Do not use quotation marks around the string, or the string will include the quotation marks. |
|
|
Terminal sessions and information that the system displays are in |
|
|
Information you must enter is in |
|
|
Arguments for which you supply values are in |
|
< > |
Nonprinting characters, such as passwords, are in angle brackets. |
|
[ ] |
Default responses to system prompts are in square brackets. |
|
!, # |
An exclamation point (!) or a pound sign (#) at the beginning of a line of code indicates a comment line. |
Note
Means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions or references to materials not covered in this manual.
Caution
Means reader be careful. In this situation, you might do something that could result in equipment damage or loss of data.
Warning
Means reader be warned. In this situation, you might do something that could result in bodily injury.
The following sections provide sources for obtaining documentation from Cisco Systems.
You can access the most current Cisco documentation on the World Wide Web at the following sites:
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available in a CD-ROM package that ships with your product. The Documentation CD-ROM is updated monthly and may be more current than printed documentation. The CD-ROM package is available as a single unit or as an annual subscription.
Cisco documentation is available in the following ways:
Registered Cisco Direct Customers can order Cisco Product documentation from the networking Products MarketPlace:
Registered Cisco.com users can order the Documentation CD-ROM through the online Subscription Store:
Nonregistered Cisco.com users can order documentation through a local account representative by calling Cisco corporate headquarters (California, USA) at 408 526-7208 or, in North America, by calling 800 553-NETS(6387).
If you are reading Cisco product documentation on the World Wide Web, you can submit technical comments electronically. Click Feedback in the toolbar and select Documentation. After you complete the form, click Submit to send it to Cisco.
You can e-mail your comments to bug-doc@cisco.com.
To submit your comments by mail, use the response card behind the front cover of your document, or write to the following address:
Attn Document Resource Connection Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-9883
We appreciate your comments.
Cisco provides Cisco.com as a starting point for all technical assistance. Customers and partners can obtain documentation, troubleshooting tips, and sample configurations from online tools. For Cisco.com registered users, additional troubleshooting tools are available from the TAC website.
Cisco.com is the foundation of a suite of interactive, networked services that provides immediate, open access to Cisco information and resources at any time, from anywhere in the world. This highly integrated Internet application is a powerful, easy-to-use tool for doing business with Cisco.
Cisco.com provides a broad range of features and services to help customers and partners streamline business processes and improve productivity. Through Cisco.com, you can find information about Cisco and our networking solutions, services, and programs. In addition, you can resolve technical issues with online technical support, download and test software packages, and order Cisco learning materials and merchandise. Valuable online skill assessment, training, and certification programs are also available.
Customers and partners can self-register on Cisco.com to obtain additional personalized information and services. Registered users can order products, check on the status of an order, access technical support, and view benefits specific to their relationships with Cisco.
To access Cisco.com, go to http://www.cisco.com.
The Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) website is available to all customers who need technical assistance with a Cisco product or technology that is under warranty or covered by a maintenance contract.
If you have a priority level 3 (P3) or priority level 4 (P4) problem, contact TAC by going to the TAC website http://www.cisco.com/tac.
P3 and P4 level problems are defined as follows:
P3—Your network is degraded. Network functionality is noticeably impaired, but most business operations continue.
P4—You need information or assistance on Cisco product capabilities, product installation, or basic product configuration.
In each of the above cases, use the Cisco TAC website to quickly find answers to your questions.
To register for Cisco.com, go to http://tools.cisco.com/RPF/register/register.do.
If you cannot resolve your technical issue by using the TAC online resources, Cisco.com registered users can open a case online by using the TAC Case Open tool at http://www.cisco.com/tac/caseopen.
If you have a priority level 1 (P1) or priority level 2 (P2) problem, contact TAC by telephone and immediately open a case. To obtain a directory of toll-free numbers for your country, go to http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/687/Directory/DirTAC.shtml.
P1 and P2 level problems are defined as follows:
P1—Your production network is down, causing a critical impact to business operations if service is not restored quickly. No workaround is available.
P2—Your production network is severely degraded, affecting significant aspects of your business operations. No workaround is available.
This <part> provides a general overview of the Cisco Service Control solution. It introduces the Cisco Service Control concept and the Service Control capabilities. It also briefly describes the hardware capabilities of the Service Control Engine (SCE) platform and the Cisco specific applications that together compose the total Cisco Service Control solution.
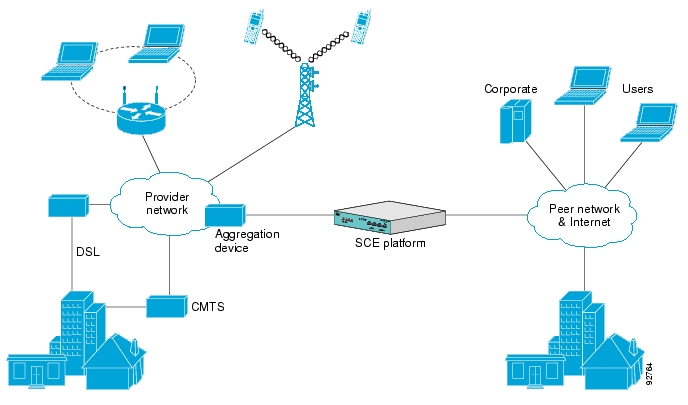
The Cisco Service Control solution is delivered through a combination of purpose-built hardware and specific software solutions that address various service control challenges faced by service providers. The SCE platform is designed to support classification, analysis, and control of Internet/IP traffic.
Service Control enables service providers to create profitable new revenue streams while capitalizing on their existing infrastructure. With the power of Service Control, service providers have the ability to analyze, charge for, and control IP network traffic at multigigabit wire line speeds. The Cisco Service Control solution also gives service providers the tools they need to identify and target high-margin content-based services and to enable their delivery.
As the downturn in the telecommunications industry has shown, IP service providers’ business models need to be reworked to make them profitable. Having spent billions of dollars to build ever larger data links, providers have incurred massive debts and faced rising costs. At the same time, access and bandwidth have become commodities where prices continually fall and profits disappear. Service providers have realized that they must offer value-added services to derive more revenue from the traffic and services running on their networks. However, capturing real profits from IP services requires more than simply running those services over data links; it requires detailed monitoring and precise, real-time control and awareness of services as they are delivered. Cisco provides Service Control solutions that allow the service provider to bridge this gap.
Service providers of any access technology (DSL, cable, mobile, and so on) targeting residential and business consumers must find new ways to get maximum leverage from their existing infrastructure, while differentiating their offerings with enhanced IP services.
The Cisco Service Control Application for Broadband adds a new layer of service intelligence and control to existing networks that can:
Report and analyze network traffic at subscriber and aggregate level for capacity planning
Provide customer-intuitive tiered application services and guarantee application SLAs
Implement different service levels for different types of customers, content, or applications
Identify network abusers who are violating the Acceptable Use Policy
Identify and manage peer-to-peer, NNTP (news) traffic, and spam abusers
Enforce the Acceptable Use Policy (AUP)
Integrate Service Control solutions easily with existing network elements and BSS/OSS systems
The core of the Cisco Service Control solution is the purpose-built network hardware device: the Service Control Engine (SCE). The core capabilities of the SCE platform, which support a wide range of applications for delivering Service Control solutions, include:
Subscriber and application awareness—Application-level drilling into IP traffic for real-time understanding and controlling of usage and content at the granularity of a specific subscriber.
Subscriber awareness—The ability to map between IP flows and a specific subscriber in order to maintain the state of each subscriber transmitting traffic through the SCE platform and to enforce the appropriate policy on this subscriber’s traffic.
Subscriber awareness is achieved either through dedicated integrations with subscriber management repositories, such as a DHCP or a Radius server, or via sniffing of Radius or DHCP traffic.
Application awareness—The ability to understand and analyze traffic up to the application protocol layer (Layer 7).
For application protocols implemented using bundled flows (such as FTP, which is implemented using Control and Data flows), the SCE platform understands the bundling connection between the flows and treats them accordingly.
Application-layer, stateful, real-time traffic control—The ability to perform advanced control functions, including granular BW metering and shaping, quota management, and redirection, using application-layer stateful real-time traffic transaction processing. This requires highly adaptive protocol and application-level intelligence.
Programmability—The ability to quickly add new protocols and easily adapt to new services and applications in the ever-changing service provider environment. Programmability is achieved using the Cisco Service Modeling Language (SML).
Programmability allows new services to be deployed quickly and provides an easy upgrade path for network, application, or service growth.
Robust and flexible back-office integration—The ability to integrate with existing third-party systems at the Service Provider, including provisioning systems, subscriber repositories, billing systems, and OSS systems. The SCE provides a set of open and well-documented APIs that allows a quick and robust integration process.
Scalable high-performance service engines—The ability to perform all these operations at wire speed.
The SCE family of programmable network devices is capable of performing application-layer stateful-flow inspection of IP traffic, and controlling that traffic based on configurable rules. The SCE platform is a purpose-built network device that uses ASIC components and RISC processors to go beyond packet counting and delve deeper into the contents of network traffic. Providing programmable, stateful inspection of bidirectional traffic flows and mapping these flows with user ownership, the SCE platforms provide real-time classification of network usage. This information provides the basis of the SCE platform advanced traffic-control and bandwidth-shaping functionality. Where most bandwidth shaper functionality ends, the SCE platform provides more control and shaping options, including:
Layer 7 stateful wire-speed packet inspection and classification
Robust support for over 600 protocols and applications, including:
General—HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, TELNET, NNTP, SMTP, POP3, IMAP, WAP, and others
P2P file sharing—FastTrack-KazaA, Gnutella, BitTorrent, Winny, Hotline, eDonkey, DirectConnect, Piolet, and others
P2P VoIP—Skype, Skinny, DingoTel, and others
Streaming and Multimedia—RTSP, SIP, HTTP streaming, RTP/RTCP, and others
Programmable system core for flexible reporting and bandwidth control
Transparent network and BSS/OSS integration into existing networks
Subscriber awareness that relates traffic and usage to specific customers
The following diagram illustrates a common deployment of an SCE platform in a network.
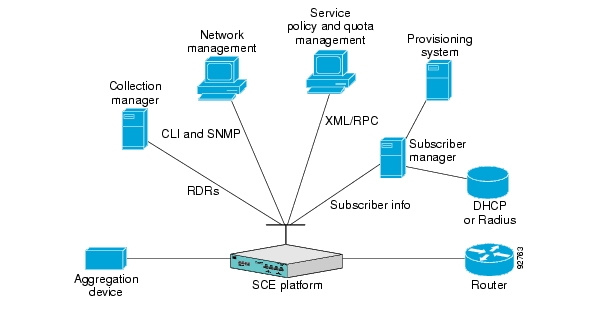
The Cisco Service Control solution includes a complete management infrastructure that provides the following management components to manage all aspects of the solution:
Network management
Subscriber management
Service Control management
These management interfaces are designed to comply with common management standards and to integrate easily with existing OSS infrastructure.
Cisco provides complete network FCAPS (Fault, Configuration, Accounting, Performance, Security) Management.
Two interfaces are provided for network management:
Command-line interface (CLI)—Accessible through the Console port or through a Telnet connection, the CLI is used for configuration and security functions.
SNMP—Provides fault management (via SNMP traps) and performance monitoring functionality.
Where the Cisco Service Control Application for Broadband (SCA BB) enforces different policies on different subscribers and tracks usage on an individual subscriber basis, the Cisco Service Control Management Suite (SCMS) Subscriber Manager (SM) may be used as middleware software for bridging between the OSS and the SCE platforms. Subscriber information is stored in the SM database and can be distributed between multiple platforms according to actual subscriber placement.
The SM provides subscriber awareness by mapping network IDs to subscriber IDs. It can obtain subscriber information using dedicated integration modules that integrate with AAA devices, such as Radius or DHCP servers.
Subscriber information may be obtained in one of two ways:
Push Mode—The SM pushes subscriber information to the SCE platform automatically upon logon of a subscriber.
Pull Mode—The SM sends subscriber information to the SCE platform in response to a query from the SCE platform.
Service configuration management is the ability to configure the general service definitions of a service control application. A service configuration file containing settings for traffic classification, accounting and reporting, and control is created and applied to an SCE platform. SCA BB provides tools to automate the distribution of these configuration files to SCE platforms. This simple, standards-based approach makes it easy to manage multiple devices in a large network.
Service Control provides an easy-to-use GUI to edit and create these files and a complete set of APIs to automate their creation.
The Cisco Service Control solution generates usage data and statistics from the SCE platform and forwards them as Raw Data Records (RDRs), using a simple TCP-based protocol (RDR-Protocol). The Cisco Service Control Management Suite (SCMS) Collection Manager (CM) software implements the collection system, listening in on RDRs from one or more SCE platforms and processing them on the local machine. The data is then stored for analysis and reporting functions, and for the collection and presentation of data to additional OSS systems such as billing.
This chapter provides an introduction to the SCE 1000 2xGBE Platform, the Service Control hardware component.
The Service Control Engine (SCE) platform, which is the hardware component of the Cisco Service Control solution, is designed to support observation, analysis, and control of Internet/IP traffic. The following table summarizes model information for the SCE 1000 platform
Table 2.1. SCE Platform Model Information
|
Model number |
SCE 1010 2xGBE |
|
Link Type |
Gigabit Ethernet |
|
Number of Ports |
2 |
|
Number of Links |
1 |
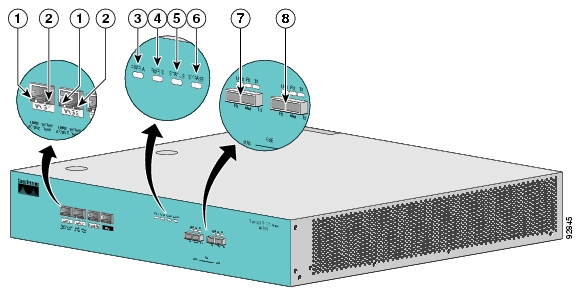
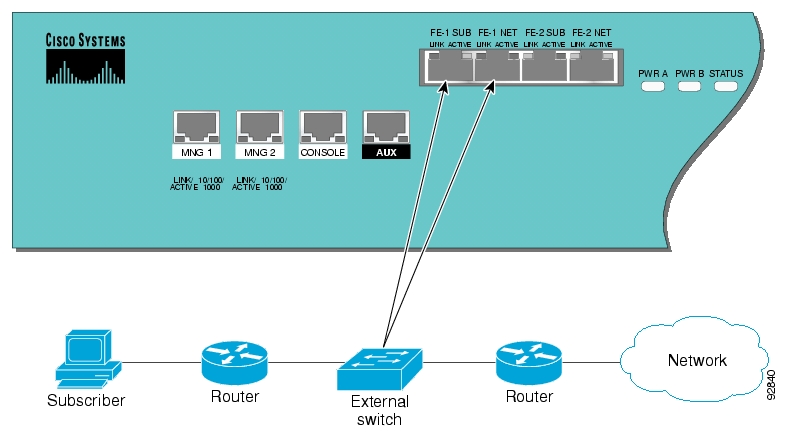
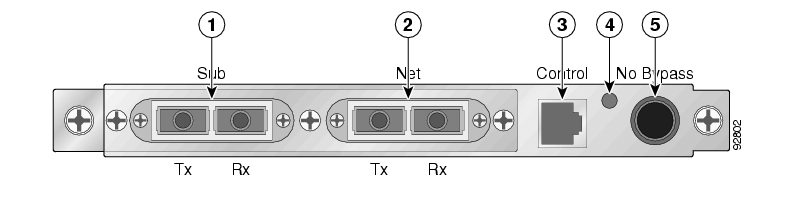
The SCE 1000 Front Panel consists of ports and LEDs as shown in the following figures and tables.
Table 2.2. SCE 1000 Ports
|
Port |
Quantity |
Description |
Connect This Port To… |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Mng1/ Mng2 |
2 |
10/100/1000 Ethernet RJ-45 ports for management of the SCE 1000. CLI designation: interface Management 0/1, 0/2. |
A LAN using an FE cable with an RJ-45 connector. If both interfaces are used to provide a redundant management interface, connect both ports to the LAN via a switch. |
|
Console |
1 |
RS-232 RJ-45 port for use by technicians |
A local terminal (console) using an RS-232 cable with an RJ-45 connector, as provided in the SCE 1000 kit. |
|
AUX |
1 |
RS-232 RJ-45 port used by technicians |
|
|
GBE ports 1 and 2 |
2 |
GigabitEthernet ports for connecting to the link. CLI designation: interface GigabitEthernet 0/1 and 0/2 |
Refer to Connecting the Line Ports for cabling diagrams for various topologies |
Table 2.3. SCE 1000 LED Groups
|
LED Groups |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Power A |
|
|
Power B |
|
|
Status |
The Status LED indicates the operational status of the SCE 1000 system, as follows:
Note that Alarms are hierarchical: Failure takes precedence over Warning, which takes precedence over operational. |
|
Bypass |
|
|
GBE ports |
The GBE LEDs indicate the operational status of the SCE 1000 line ports, as follows:
|
|
Mng |
The Mng port LEDs indicate the operational status of the SCE 1000 out-of-band LAN-based management port, as follows:
|
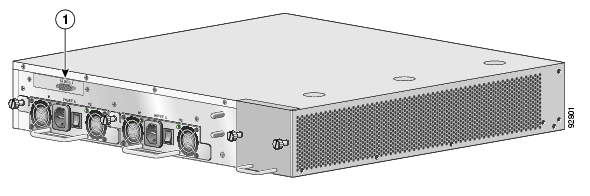
The SCE 1000 platform back-panel contains the following components:
Two field-replaceable power supply units with ON/OFF switches
One field-replaceable fan drawer
Ground connections
One connector to the external bypass module
The rear panels of both the AC- and DC-powered SCE 1000 platforms are shown in the following pair of figures.
Use the SCE 1000 Component List to check the contents of the SCE 1000 platform shipping container.
Do not discard the shipping container. You need the container if you move or ship the SCE 1000 platform in the future.
Table 2.4. SCE 1000 Component List
|
Component |
Description |
Received |
|---|---|---|
|
SCE 1000 platform |
SCE 1010 2xGBE platform configured with either AC or DC power supplies. |
|
|
Accessories |
The following accessories might arrive in separate shipping containers: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Two AC power supply cords,if ordered with AC-input power supply units |
|
|
|
|
|
If ordered, SCE 1000 hardware and software documentation set and the Cisco Documentation CD-ROM package* |
|
|
Optional Equipment |
Four rubber feet for tabletop installation |
|
|
External Optical Bypass module kit |
|
|
*Titles and quantities of documents will vary. You must order the type and quantity of documentation sets when you order the hardware.
Note
We no longer ship the entire SCE 1000 documentation set automatically with each system. You must specifically order the documentation as part of the sales order. If you ordered documentation and did not receive it, we will ship the documents to you within 24 hours. To order documents, contact a customer service representative.
To assist you with your installation and to provide a historical record of what was done by whom, photocopy the following SCE 1000 Installation Checklist. Indicate when each procedure or verification is completed. When the checklist is completed, place it in your site log along with the other records for your new SCE 1000 platform.
Table 2.5. SCE 1000 Installation Checklist
|
Task |
Verified By |
Date |
|---|---|---|
|
Date SCE 1000 received |
|
|
|
SCE 1000 and all accessories unpacked |
|
|
|
Safety recommendations and guidelines reviewed |
|
|
|
Topology verified: number of SCE 1000 platforms, number of links, and whether inline or receive-only |
|
|
|
Installation Checklist copied |
|
|
|
Site log established and background information entered |
|
|
|
Site power voltages verified |
|
|
|
Site environmental specifications verified |
|
|
|
Required passwords, IP addresses, device names, and so on, needed for initial configuration available (refer to Setup Command Parameters) |
|
|
|
Required tools available |
|
|
|
Network connection equipment available |
|
|
|
SCE 1000 mounted in rack (optional) |
|
|
|
AC/DC power cables connected to AC/DC sources and SCE 1000 platform |
|
|
|
Console port set for 9600 baud, 8 data bits, no parity, and 1 stop bit (9600 8N1) |
|
|
|
ASCII terminal attached to console port |
|
|
|
FE management port is operational |
|
|
|
GBE line ports operational |
|
|
|
Network interface cables and devices connected |
|
|
|
System power turned on |
|
|
|
System boot complete (SYSTEM–UP LED is on) |
|
|
|
Correct hardware configuration displayed after system banner appears |
|
|
This chapter describes the possible deployment topologies of the SCE 1000. The Cisco SCE solution offers a number of basic topology options that permit the user to tailor the SCE Platform to fit the needs of a particular installation. An understanding of the various issues and options is crucial to designing, deploying, and configuring the topology that best meets the requirements of the individual system.
There are several issues that must be considered in order to arrive at the optimum configuration of the topology-related parameters:
Functionality — Will the system be used solely to monitor traffic flow, with report functionality only, or will it be used for traffic flow control, with enforcement as well as report functionality?
Physical installation configuration — Will the SCE Platform be installed as inline? Or will the SCE Platform use an optical splitter?
Redundancy — Must the system be designed to guarantee uninterrupted service? If so, there must be a backup SCE Platform to assume operation in case of failure of the primary data link.
Link failure and recovery — How should the SCE Platform respond to platform failure and subsequent recovery? Should traffic flow continue even though the unit is not operating, or be halted until the platform is repaired/replaced? Should the unit actually resume operation when it is again operational?
There are four topology-related parameters:
Connection mode — Can be Inline or Receive-only, depending on the physical installation of the SCE 1000:
May be configured via either the
setupcommand or theconnection-modecommand.Bypass mode when the SCE 1000 is not operational (on-failure) — This parameter determines whether the system cuts the traffic or bypasses it when the SCE 1000 has failed.
May be configured via either the
setupcommand or theconnection-modecommand.Status after reboot caused by fatal error or abnormal shutdown — This parameter determines whether the SCE 1000 returns to normal operational state after a failure.
May be configured via either the
setupcommand or thefailure-recovery operation-modecommand.Link failure reflection — This parameter determines the behavior of the system when there is a link problem. In some topologies it is required that link failure on one port be reflected to the other port, to allow the higher layer redundancy protocol in the network to function correctly.
May be configured via the
link failure-reflectioncommand only.
The SCE 1000 contains various mechanisms to monitor the status and to detect failures. The main mechanisms are:
Boot time diagnostics failure. When there is a failure in diagnostics testing at boot time the system will remain in failure status.
Watchdog mechanism. There are two types of watchdogs:
HW watchdog. A hardware mechanism that detects control entity failure.
SW watchdog. A software mechanism that periodically checks for software failures in the SCE 1000. If a failure is detected, an error massage is sent and the SCE 1000 reboots.
Run time hardware tests. The system periodically tests the hardware components for error. If a hardware component is malfunctioning, it will be discovered by the system within seconds.
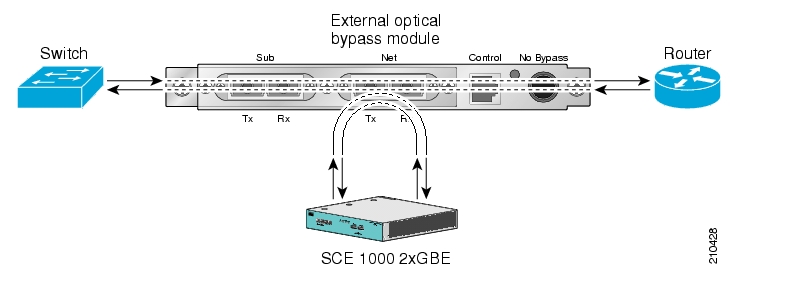
The SCE 1000 includes a Network Interface Card with a bypass mechanism that is enabled upon SCE 1000 failure. In addition, when connected in-line it can also be enabled in normal operation to simultaneously bypass traffic flow to the other side and direct it internally for analysis. In this case it maintains "receive-only"-like monitoring functions, when control functionality is not required.
The bypass card supports the following four modes:
Bypass — The bypass mechanism preserves the network link, but traffic is not processed for monitoring or for control.
Forwarding — This is the normal operational mode, in which the SCE 1000 processes the traffic for monitoring and control purposes.
Sniffing — The bypass mechanism preserves the network link, while in parallel allowing the SCE 1000 to process the traffic for monitoring only.
Cutoff — There is no forwarding of traffic, and the physical link is forced down (cutoff functionality at layer 1).
The SCE 1000 can serve one of two general functions:
Monitoring and Control — The SCE 1000 monitors and controls traffic flow. Decisions are enforced by the SCE 1000 depending on the results of the monitoring functions of the SCE 1000 and the configuration of the Service Control Application for Broadband or Mobile solution.
In order to perform control functions, the SCE 1000 must be physically installed as an inline installation and the connection mode must be “inline”.
Monitoring only — The SCE 1000 monitors traffic flow, but cannot control it.
Either an inline installation or an optical splitter installation may be used for monitoring only. In the latter case connection mode must be “receive-only”.
There are two options for the physical installation configuration of the SCE 1000 Platform:
Inline installation (provides control functionality).
Out-of-line installation utilizing an external optical splitte
The physical installation determines the connection mode that should be configured.
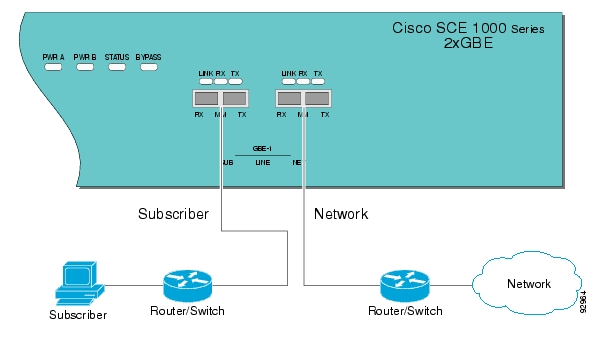
Typically, the SCE 1000 is connected on a full duplex line between two devices (Router, BRAS, etc.). When the SCE 1000 is installed as a bump-in-the-wire, it physically resides on the data link between the subscriber side and the network side, and can both receive and transmit traffic.
A bump-in-the-wire installation is referred to as inline connection mode.
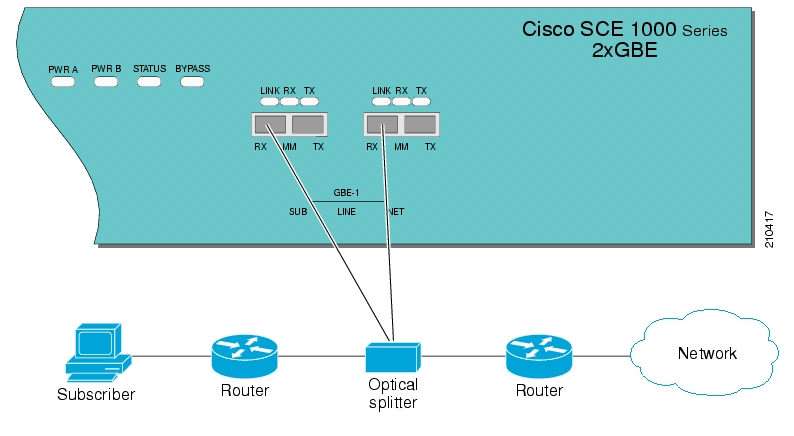
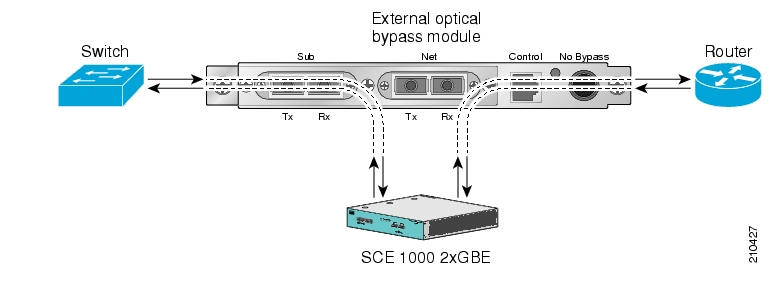
In external splitting, an external optical splitter resides physically on the GBE link between the subscriber side and the network side. In this topology, the traffic passes through the external splitter, which splits traffic to the SCE 1000. The external splitter is connected to the SCE 1000 via Rx links only. The SCE 1000, therefore, receives traffic only. It does not transmit.
An external splitting installation is referred to as receive-only connection mode.
Note that in an external splitting installation, the SCE 1000 has only traffic monitoring capabilities.
Note
Receive-only topologies can also be implemented using a switch. Such a switch must support SPAN functionality that includes separation between ingress and egress traffic and multiple SPAN-ports destinations.
When a high degree of reliability is desired, a second SCE 1000 Platform should be installed to provide backup operation capabilities. This redundant SCE 1000 guarantees uninterrupted functioning of all SCE 1000 operations.
Note
Redundancy is possible in inline installations only.
A single SCE 1000 platform does not provide redundancy for SCE 1000 control functions. In case of failure of the SCE 1000 unit, the SCE 1000 simply bypasses the traffic; the traffic link is not cut, but no control or monitoring functionality is available.
Using two SCE 1000 platforms on parallel links provides redundancy for all SCE 1000 features. In case of failure in the active platform, the backup SCE 1000 unit takes over.
Using redundant SCE 1000 platforms is applicable as an overlay to a customer’s redundant topology, on condition that the entire traffic of a specific subscriber (end station, subnet or VLAN) is flowing through one link only. Both links may be active, providing that the subscriber traffic is mutually exclusive.
This redundancy solution addresses any failure in the SCE 1000 platform itself. It is based on the idea that any fatal hardware or software failure will cause the platform to “cut” the link. A “cut” link will cause the routers/switches on both ends to switch the traffic to the standby link. On the standby link, the traffic is analyzed and policies enforced by the standby SCE 1000, which, after the failure, acts as the active SCE 1000.
Note that when both links are simultaneously independently active and redundant for the other link (as is the case when HSRP with two virtual routers is used), if one link fails, its traffic is directed to the other link. However, the overall supported load in the link that is now carrying all the traffic is only equal to one link, not two.
During setup of this topology, the configuration of the two SCE 1000 platforms is done through multi-box configuration. This ensures that both hold the same configurations and policies. The functional operation of switching from the active to standby, SCE 1000 is contingent upon the fact that the two SCE 1000 platforms are in the same Domain. All configurations performed on this Domain are automatically updated on both SCE Platforms. Both boxes should also be assigned to the same Subscriber Domain. For more information on Domains, see the Cisco SCMS Subscriber Manager User Guide.
The common protocols used for redundancy traffic switching between network elements such as routers and switches in networks are Spanning-Tree in layer2, HSRP in layer3 (usually used in data-centers), and other common routing protocols like OSPF or RIP.
Note
When using routing/switching protocols that perform load balancing as well, the load balancing capabilities should be disabled.
The transition to the backup SCE 1000 platform is transparent. Once the routers/switches detected that traffic has been cut, they start sending traffic through the redundant link. After this occurs, the failed SCE 1000 can be fixed/replaced with no downtime, since the box is effectively disconnected from the network. After fixing/replacing the failed SCE 1000, you must copy the configuration of the current active SCE 1000 to the fixed/replaced SCE 1000.
The backup and restore procedures used for copying policies and Service Configurations from one SCE 1000 to the next are detailed in the Service Control Application Suite for Broadband User Guide.
It is important to decide how the system should behave in case of the failure of the SCE 1000, both during the time that the unit is down and after recovery. This decision is influenced by several factors:
Physical installation (connection mode)
Redundancy
Relative importance of maintaining connectivity vs. the continuity of the value-added services that the SCE 1000 enables.
In a link connection via an external optical splitter, SCE 1000 failure does not affect traffic flow, which continues through the external optical splitter. When the SCE 1000 detects a failure that requires a recover by reboot, it immediately switches to Cutoff mode, stopping all traffic flow over the link until the SCE 1000 unit is restored to operation.
When operation resumes, the defined operational bypass mode is automatically resumed.
The configuration of a bump-in-the-wire installation depends on the remaining two factors.
Redundancy requires two platforms on parallel links, one active and one standby, in inline topology. When the active SCE 1000 platform detects a failure situation, it will immediately switch to Cutoff mode, causing the routers/switches on both ends to switch the traffic to the standby link and thus activate the standby SCE 1000 platform.
There are two options when the failed SCE 1000 platform is finished reloading:
It may either actually resume operation in the defined operational bypass mode, returning to its status as the active SCE 1000 platform.
It may remain inactive in the failure bypass mode.
When a single SCE 1000 is deployed, the user may decide that in case of a failure, maintaining the network link is more important than providing the SCE 1000 functionality. In this scenario, when the SCE 1000 detects a failure that requires a reboot process for recovering, it immediately switches to Bypass mode, allowing all traffic to bypass the SCE 1000. The SCE 1000 stays in Bypass mode maintaining the network link, albeit without SCE 1000 processing, until the SCE 1000 fully recovers from the failure and is ready to resume normal functioning.
Alternatively, the user may decide that the SCE 1000 functionality is sufficiently crucial to require severing the link if the SCE 1000 platform fails. In this case, when the SCE 1000 detects a failure that requires a reboot process for recovering, it immediately switches to Cutoff mode, stopping all traffic flow. The SCE 1000 stays in Cutoff mode, halting all traffic, until it fully recovers from the failure and is ready to resume normal functioning. In Cutoff the physical interface is blocked, enabling the network device connected to the SCE 1000 to sense that the link is down.
Refer to the following sections to determine the correct values for all topology-related parameters before beginning run the initial setup of the SCE 1000.
The connection mode parameter refers directly to the physical topology in which the SCE 1000 is installed. Installation is possible in either of the two following modes:
Inline — The SCE 1000 resides on the data link between the subscriber side and the network side, thus both receiving and transmitting packets.
Receive-only — The SCE 1000 does not reside physically on the data link. Data is forwarded to the SCE 1000 via an external optical splitter. The SCE 1000 itself receives only and does not transmit.
Note
Default value = Inline
The connection mode parameter is determined by the physical deployment of the SCE 1000 as follows:
Bump-in-the-wire installation = Inline connection mode.
External optical splitter installation = Receive-only connection mode.
As described in the section The Bypass Mechanism, the bypass card supports four different modes. The following two modes are possible when the SCE 1000 is not operational due to platform failure or boot:
Bypass — The optical splitter forwards traffic with no intervention of the control application running in the SCE 1000 platform, but monitoring functions continue uninterrupted.
Cutoff — There is no forwarding of traffic. The link is forced down, resulting in traffic cutoff at Layer1.
The Forwarding mode enables control of traffic flow and is not compatible with the non-operational status.
In a single SCE 1000 topology, the value of this parameter is determined by whether or not the link can be completely cut when the SCE 1000 fails, or whether traffic flow should continue across the link in spite of platform failure.
Cutoff mode is required for the following:
Redundant inline topology.
Non-redundant inline topology if value-added services are crucial and are more important than maintaining connectivity.
Bypass mode is required for the following:
Non-redundant inline topology if connectivity is crucial.
The link failure reflection refers to the behavior of the SCE 1000 when one of the data links fails. Some network redundant topologies require a layer 1 cutoff in order for the network element to recognize the link failure and translate it into action (switch to redundant link). In this case, if one of the ports fails, it must be reflected to the other port as well.
Link failure-reflection — When one data port link fails, the SCE 1000 forces the other port link down as well. The port will be forced down as long as the first port link is down. When the problematic port link goes up, the other port link will also be turned on again.
No link failure-reflection — Link failure is not reflected to the other port.
Note
Default value = no link failure-reflection
This parameter determines whether the SCE 1000 returns to normal operational state after a reboot caused by fatal error or abnormal shutdown. In general, it is desirable that the SCE 1000 resume operation, and as promptly as possible. However, in a redundant topology, a recovered SCE 1000 may remain non-operational. In this case the platform that had been the backup and is currently active will remain active.
The two options for this parameter are:
Operational — The status of the SCE 1000 after abnormal boot is operational. The platform automatically resumes functioning in the defined operational link bypass mode.
Not Operational — The status of the SCE 1000 after abnormal boot is not operational. The platform remains in the defined failure link bypass mode.
This option is to be used only in a redundant topology where a second, operational platform exists.
Note
Default value = Operational for all non-redundant systems.
Must be explicitly configured for redundant topologies.
Table 3.1. Topology Configuration Summary Table
|
Description |
Connection mode |
On-failure link bypass mode |
Admin status after abnormal boot |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Link connection via external switch with port-mirroring |
Receive-only |
Bypass |
Operational |
|
Bump-in-the-wire |
|
|
|
|
Bump-in-the-wire, monitor and control, not redundant |
Inline |
Bypass |
Operational |
|
Bump-in-the-wire, monitor only, not redundant |
Inline |
Bypass |
Operational |
|
Bump-in-the-wire, monitor and control, redundant |
Inline |
Cutoff |
Operational[1] |
|
Bump-in-the-wire, monitor only, redundant |
Inline |
Cutoff |
Operational[1] |
* Italicized values represent automatically applied defaults that are applied based on previously defined parameters. These values can be changed only via specific CLI commands.
[1]: In a redundant topology, it is also possible to configure admin status after abnormal boot to be Not operational. In this case, though, the SCE 1000 would have to be manually reloaded in order to resume full functionality.
This chapter explains how to install a SCE 1000 platform in a rack or in a general tabletop or workbench installation. Additionally, this chapter contains instructions for installing or replacing the power supply units and fan modules.
Warning
Before you install, operate, or service the system, read the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco Service Control Engine. This guide contains important safety information you should know before working with the system.
Before installing your SCE 1000 platform, you should consider the power and cabling requirements that must be in place at your installation site, the equipment you need to install the platform, and the environmental conditions your installation site must meet to maintain normal operation. This section guides you through the process of preparing for your SCE 1000 platform installation and the installation in a rack. The section contains the following topics:
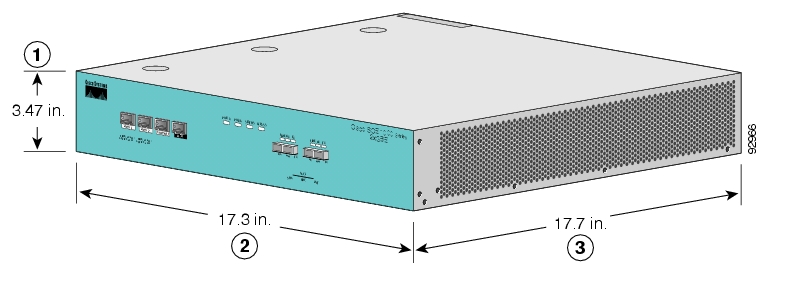
Table 4.1. SCE 1000 Dimensions
|
Dimension |
Measurement |
|---|---|
|
Height |
3.47 inches (9.5 cm) |
|
Width |
17.4 inches (4.43 cm) |
|
Depth |
18 inches (4.6 cm) |
|
Weight |
33 lb (15 kg) |
The SCE 1000 chassis is fully assembled at the factory, including the application and software packages. No assembly is required. However, you need the following tools and equipment to install the SCE 1000 chassis and the rack-mount kit (if installing the SCE 1000 platform in a rack), fan modules, and power supplies:
Number 1 and 2 Phillips screwdriver
1/4 inch flat-blade screwdriver
#¼” Hex Wrench
Screws compatible with your rack (for mounting the SCE 1000 to the rack)
12 AWG or 2.5-mm copper installation wire with hex or loop connectors for DC power leads
Ring terminals must be UL approved and suitable for 12 AWG wire.
Level (optional)
Tape measure (optional)
Appropriate cables to connect the SCE 1000 to the network and console terminal
Rack-mounting kit (optional)
A new AC-input or DC-input power supply
A new fan module
The environmental monitoring functionality in the SCE 1000 protects the system and components from potential damage from over-voltage and over-temperature conditions. To ensure normal operation and to avoid unnecessary maintenance, plan your site configuration and prepare your site before installation. After installation, make sure the site maintains an ambient temperature of 41°F to 104°F (5°C to 40°C) with short term temperatures ranging from 23°F to 131°F (–5°C to 55°C), and keep the area around the SCE 1000 chassis free from dust.
Planning a proper location for the SCE 1000 and the layout of your equipment rack or wiring closet is essential for successful system operation. Equipment placed too close together or inadequately ventilated can cause system over-heating. In addition, chassis panels made inaccessible by poor equipment placement can make system maintenance difficult.
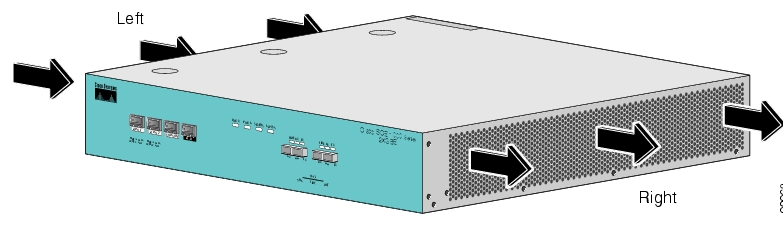
When you plan the location and layout of your equipment rack or wiring closet you need to consider how air flows though your system. The SCE 1000 draws cooling air in through the intake vents on the left side of the chassis, moves the air across the internal components, and out through the right side and rear panel of the chassis. The above figure illustrates the airflow through the SCE 1000.
Note
Remember to leave a two inch (5 cm) clearance on both sides of the SCE 1000 and five inches (12.7 cm) at the rear for adequate airflow for the inlet and exhaust vents.
The following tables contain the site requirement specifications for the SCE 1000.
Table 4.2. SCE 1000 Environmental Requirements
|
Specification |
Acceptable Range |
|---|---|
|
Temperature - |
nominal 41°F to 104°F (5°C to 40°C) |
|
Short term temperatures* |
23°F to 131°F (-5°C to +55°C) |
|
Relative humidity |
5% to 95% (non-condensing) |
|
Heat dissipation |
683 BTU/hour |
*Short term is defined as not more than 96 consecutive hours, not more than 15 days in one year. 360 hours total in any given year, but no more than 15 occurrences in a one-year period.
Table 4.3. SCE 1000 Approvals Specifications
|
Approval |
Specification |
|---|---|
|
EMC |
|
|
Safety |
UL/CSA 60950, IEC60950, EN60950, AS/NZS, 60950, NOM-019,IEC/EN60825-1, -2, 21CFR1040, 73/23/ECC |
For more complete information regarding safety and regulatory compliance, refer to the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco Service Control Engine document.
Warning
The DC-powered SCE 1000 should be installed in a Restricted Access Location only.
The SCE 1000 operates as either a tabletop or a rack-mounted unit. A rack-mounting kit is included with the SCE 1000 when it is shipped from the factory. The kit provides the hardware needed (see SCE 1000 Component List) to mount the SCE 1000 in either of two types of standard 19-inch equipment rack:
19-inch rack with only two posts in the front — Use the supporting brackets included in the kit
19-inch rack with four posts, two in the front and two in the back — Use the crossrail supports included in the kit
If you are not rack-mounting your SCE 1000, place it on a sturdy tabletop or workbench. A rubber feet kit is included for tabletop installations.
This section provides instructions for the physical installation of the SCE 1000 platform, including how to install the SCE 1000 in a rack, how to install the SCE 1000 on a tabletop or workbench, and how to properly ground the SCE 1000 platform. The section contains the following topics:
The router should already be in the area where you will install it, and your installation location should already be determined. If not, see Site Requirement Guidelines and the Site Preparation and Safety Guide.
When installing the SCE 1000, please observe the following conditions:
Allow at least 2 inches (5 cm) of clearance at its left and right sides for airflow clearance from the inlet and exhaust vents, and that no exhaust air from other equipment is drawn into the SCE 1000. For descriptions and illustrations regarding airflow, see Airflow.
Do not place the SCE 1000 on the floor during installation. Dust that accumulates on the floor is drawn into the interior of the SCE 1000 by the cooling fans. Excessive dust inside the SCE 1000 can cause over-temperature conditions and component failures.
Allow at least 5 inches (12.7 cm) of clearance at the front and rear of the SCE 1000 for installing and rudimentary maintenance for accessing network cables or equipment.
Ensure that the SCE 1000 will receive adequate ventilation. Do not install the SCE 1000 in an enclosed cabinet where ventilation is inadequate!
Provide an adequate chassis Ground (earth) connection for the SCE 1000 (see Attaching a Chassis Ground Connection for instructions).
You can install the SCE 1000 platform on any flat surface as long as the surface is large enough for the SCE 1000 (see the table in SCE 1000 Dimensions), and allows for adequate airflow/ventilation around the sides of the SCE 1000, as described in the Installation Precautions. When installing the SCE 1000 on a workbench or tabletop or in a rack, ensure that the surface is clean and in a safe location.
To install a SCE 1000 platform on a workbench or tabletop, complete the following steps:
Remove any debris and dust from the tabletop or workbench, as well as the surrounding area. Also make sure your path between the SCE 1000 platform and its new location is unobstructed.
Place the SCE 1000 platform on the tabletop or workbench.
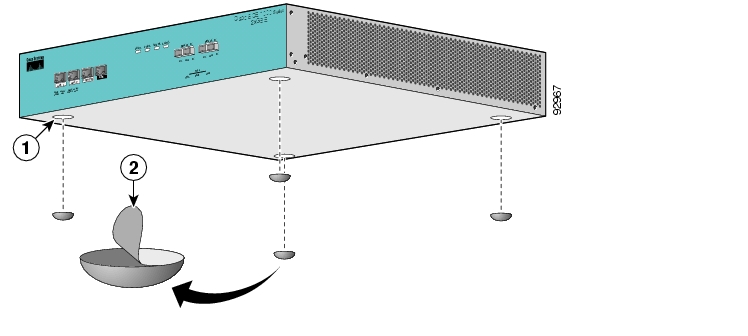
View the bottom panel by lifting the SCE 1000, placing your hands around the SCE 1000 sides and lifting the SCE 1000 from underneath. To prevent injury, avoid sudden twists or moves.
There are four marked locations, indicating where to affix the rubber feet (see figure above).
Attach the rubber feet by removing the adhesive strips and affix the rubber feet onto the marked locations (on the bottom panel).
Replace the SCE 1000 platform firmly on the tabletop or workbench.
Remember to check for proper ventilation. Allow at least 2 inches (5 cm) on each side for proper ventilation and 5 inches (12.7 cm) at the back for ventilation.and power cord clearance.
This completes the general workbench or tabletop installation.
Proceed to section, Attaching a Chassis Ground Connection to continue the installation.
You can mount the SCE 1000 platform to a 19” rack. There are two standard types of equipment racks, and the appropriate brackets for each are provided in the enclosed kit.
19” rack with front rack posts — the mounting kit includes two mounting brackets as illustrated below.
19” rack with front and back rack posts — in addition to the mounting brackets illustrated below, the mounting kit includes two crossrail supports that the unit slides onto.
|
Mounting Brackets for 2-post Rack |
Mounting Brackets for 4-post Rack |
|---|---|
|
|
|
The SCE 1000 mounts to the two front rack posts with brackets that attach to the front of the SCE 1000 The inside width between the two posts or mounting strips (left and right) must be at least 17.3 inches (44 cm).
Note
Remember to leave a two-inch (5 cm) clearance on both sides of the SCE 1000 and at the rear for adequate airflow for the inlet and exhaust vents.
Because the inlet and exhaust ports (vents) for cooling air are located at both sides of the chassis, respectively, multiple SCE 1000s can be stacked in a rack with no vertical clearance.
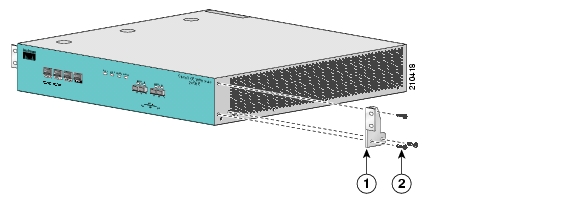
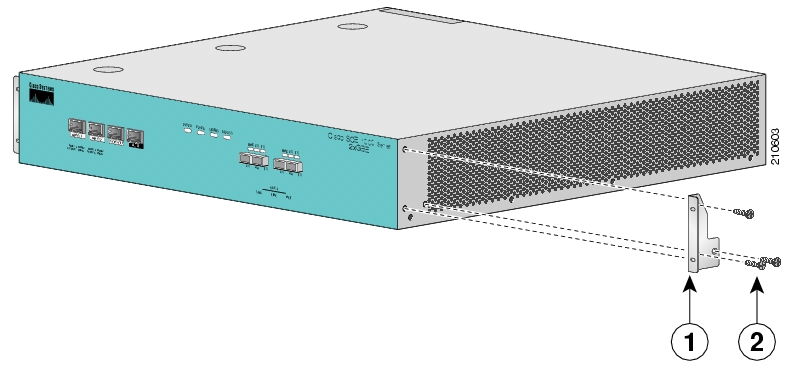
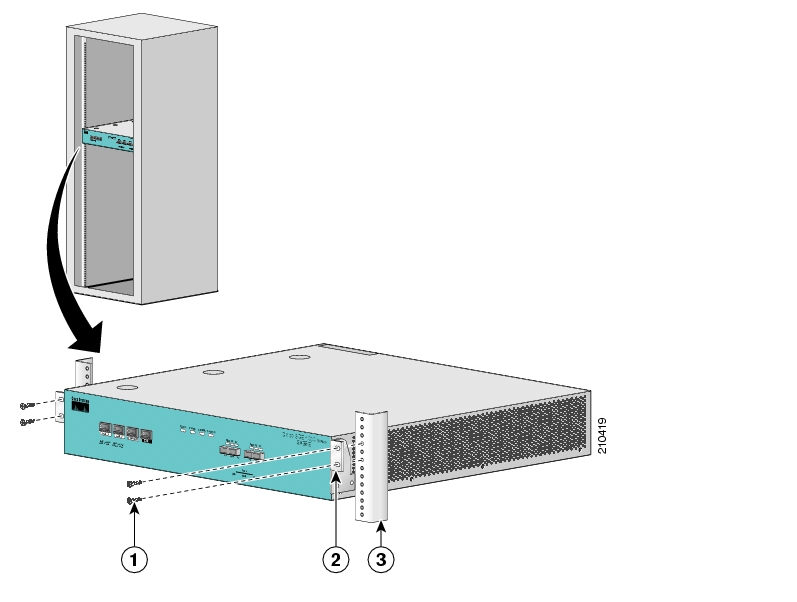
Before installing the SCE 1000 in the rack, you must first install an appropriate rack-mount bracket on each side of the front of the SCE 1000, as illustrated in the following figure. See Tools and Parts Required for a listing of the parts and tools required for installing the rack–mount.
To install the rack-mount brackets on the SCE 1000 chassis, complete the following steps:
Align the rack-mount bracket to the side of the SCE 1000. Choose the proper bracket for your installation (2-post rack or 4-post rack) as illustrated in Rack-Mounting a SCE 1000 Platform.
Insert and tighten three screws.
Repeat steps 1 and 2 on the other side of the SCE 1000.
This completes the steps for attaching the rack-mount brackets to the SCE 1000.
If mounting the SCE 1000 in a rack with only two posts, skip to Mounting the System to a Rack.
If mounting the SCE 1000 in a rack with four posts, proceed to the next step to attach the crossrail supports to the rack.
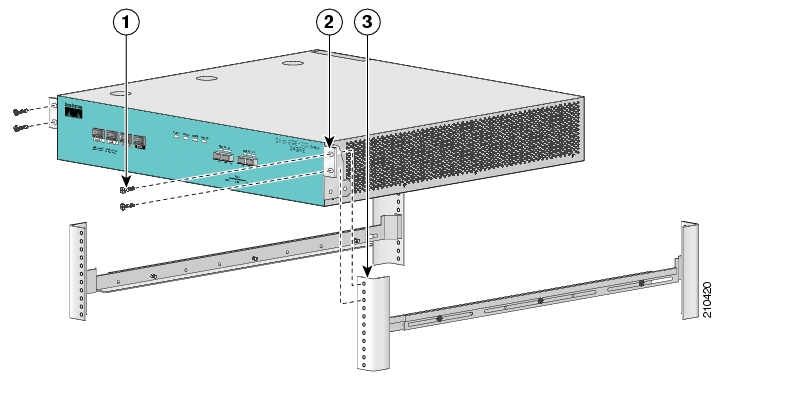
When mounting in a rack with four posts (front and back) the two crossrail supports are mounted one on each side of the rack. The SCE 1000 then slides into these crossrails, which support the weight of the unit.
Note
Cisco recommends that you allow at least 1 or 2 inches (2.54 or 5.08 cm) of vertical clearance between the SCE 1000 and any equipment directly above and below it.
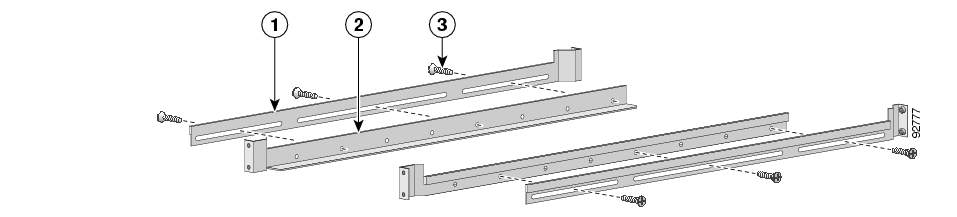
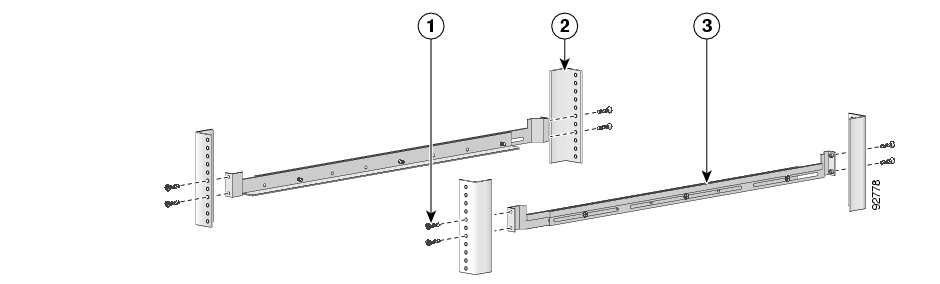
To install the crossrail supports on a four-post rack (both front and back posts), complete the following steps:
Assemble the two crossrail supports as illustrated below. Use three screws for each crossrail assembly.
Make sure that they are oriented so that both crossrails will support the SCE 1000 when they are attached to the rack.
Align the crossrail supports with the side of the rack, parallel to the floor.
Insert and tighten two screws to the front posts or mounting strips of the rack
Insert and tighten two screws to the Back posts of the rack.
Repeat steps 2 through 4 on the other side of the rack, keeping the brackets flush against the posts and parallel to the supporting bracket on first side of the rack.
This completes the steps for attaching the rack-mount supporting brackets to the rack.
You are now ready to mount the SCE 1000 to the rack.
When the appropriate mounting brackets are securely installed, the SCE 1000 can be installed into the rack.
To mount the SCE 1000 to the rack after the brackets are installed, complete the following steps:
Make sure that your path to the rack is unobstructed. If the rack is on wheels, ensure that the brakes are engaged or that the rack is otherwise stabilized.
Position the SCE 1000 so that the front end is closest to you, and lift it carefully to place it into the rack. To prevent injury, avoid sudden twists or moves.
Slide the SCE 1000 into the rack, pushing it back until the brackets (installed at the front of the SCE 1000) meet the mounting strips or posts on both sides of the rack.
A rack with both front and back posts will have the crossrail supports installed. Slide the SCE 1000 onto these crossrails and push it all the way back.
While keeping the brackets flush against the posts or mounting strips, align the holes in the brackets with the holes on the rack or mounting strip.
For each bracket, insert and tighten two appropriate screws to the rack.
Note
Since the brackets support the weight of the entire SCE 1000 chassis, be sure to use all four screws to fasten the two rack-mount brackets to the rack posts.
Before you connect the power or turn on the power to the SCE 1000 platform, it is required that you provide an adequate chassis ground (protective earth) connection for the SCE 1000 chassis. A grounding kit is provided with each SCE 1000.
Use the grounding kit to properly ground the SCE 1000 chassis (see SCE 1000 Component List for details).
Warning
When installing the unit, the chassis ground connection must always be made first and disconnected last.
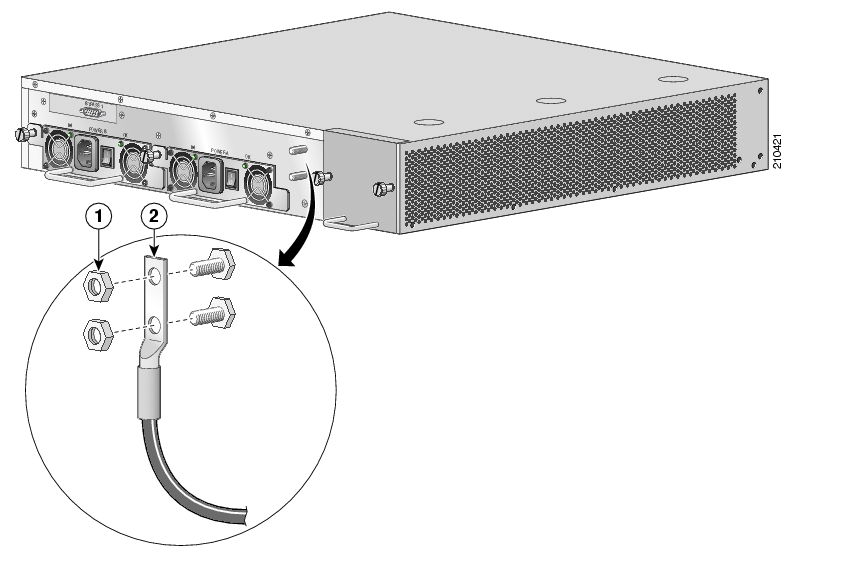
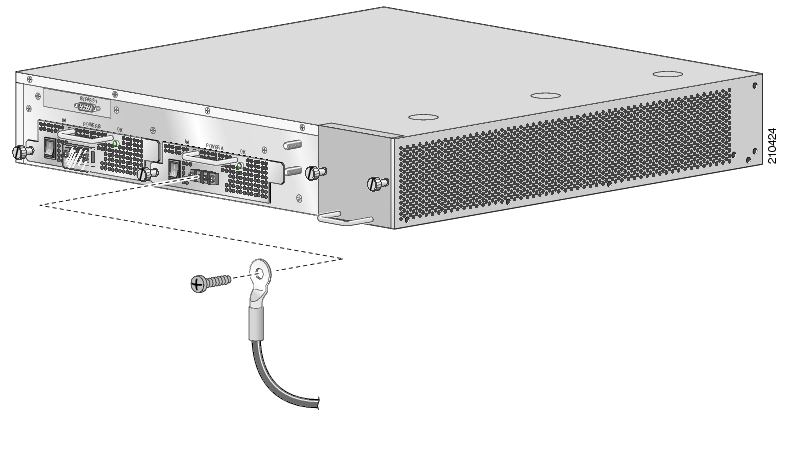
To connect the grounding cable to the chassis grounding connector on the SCE 1000, complete the following steps:
From the enclosed grounding kit, remove the necessary materials — the grounding cable (green and yellow colored cable) and pairs of hex nuts and spring washers.
On the rear panel of the SCE 1000, locate the chassis grounding connector (refer to the appropriate figure for an AC- or DC-powered SCE 1000 below).
Attach the grounding cable (green and yellow colored cable), firmly fastening the (enclosed) hex nuts and spring washers with a #¼” hex wrench (refer to the appropriate figure for an AC- or DC-powered SCE 1000 below).
The other side of the grounding cable must be connected to the site equivalent of the AC earth.
This completes the procedure for installing the SCE 1000 chassis. Proceed to the next section, Connecting to the Power Supply, to continue the installation.
The SCE 1000 is available in two power options:
Dual line feed AC power — SCE 1000 is shipped with two appropriate AC power supply cords.
Dual line feed DC power — requires appropriate cables (hex or loop connectors) (see Reconnecting DC-Input Power Supply Unit).
The dual power supply units supply hot-swappable, redundant power. Redundant power is useful as a failover; if a situation occurs where one power supply is down (for instance, a power supply fails or a new power supply needs to be installed), the SCE 1000 can continue to run properly using the other power supply.
Each power supply has fans that cool the power supply unit. These fans also help to cool the internal components of the SCE 1000, as they direct the air flow to the outside through vents in the rear of the power supply unit.
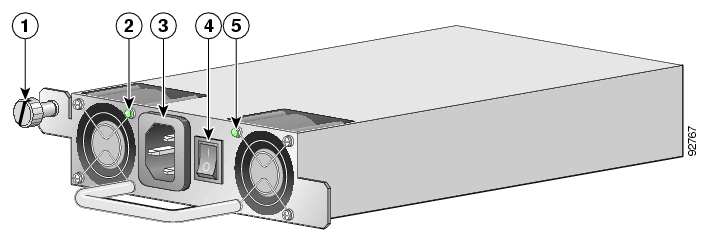
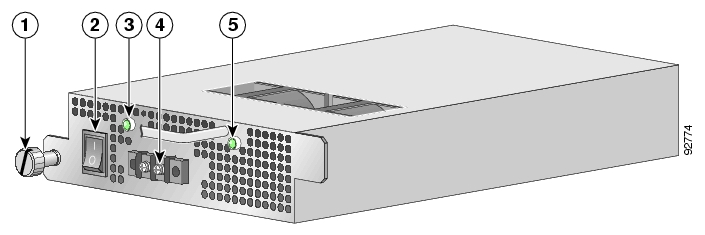
The faceplates of both power supplies have a handle, an on/off switch, and one captive installation screw. An AC-input power receptacle is available on the AC-input power supply and a DC-input terminal block is available on the DC-input power supply.
Note that the power supply units are asymmetrical, with a screw in only one corner of the unit. Therefore, both power supply units can be fastened only if both units are inserted in the proper orientation. This also prevents the accidental installation of one DC unit and one AC unit. (Refer to the following figures).
The handle of the AC unit is at the bottom of the unit.
The handle of the DC unit is at the top of the unit.
The following LEDs are used to monitor the functioning of the power supply units:
On the power supply unit (both AC-input and DC-input):
IN LED (green)
OK LED (green)
On the Front Panel:
Power LED — There are two Power LEDs on the front panel (Power A and Power B), one LED corresponding to each power supply unit
On both the AC-input and DC-input power supplies, the IN LED iis used to monitor the voltages received by the platform from the power source. If the input voltages are within normal operating ranges, the green IN LED is illuminated. If the input voltages are above or below normal ranges, the IN LED is not illuminated.
On both the AC-input and DC-input power supplies, the OK LED is used to monitor the power supply DC output voltages used to power the platform. The normal operating ranges for the 12 VDC output voltage is between 11.9V and 12.1V. If the output voltages are within normal operating ranges, the green OK LED is illuminated. If the 12 VDC output voltages are above (more than 12.1V) or below (less than 11.9V) normal ranges, the OK LED is not illuminated.
The Power A and Power B LEDs on the front panel indicate whether the corresponding power supply unit is functioning normally.
Refer to the following tables for LED status information
Table 4.4. IN LED Status for AC-input and DC-input Power Supply Units
|
LED State |
Power Supply Unit Condiiton |
|---|---|
|
On (green) |
The input voltage is in the required range. |
|
Off |
The input voltage is not in the required range. |
Table 4.5. OK LED Status for AC-input and DC-input Power Supply Units
|
LED State |
Power Supply Unit Condiiton |
|---|---|
|
On (green) |
The output voltage is in the required range (between 11.9 and 12.1 VDC). |
|
Off |
The output voltage is not within the required range. (is greater than 12.1 VDC or less than 11.9 VDC) |
Table 4.6. Power LED (on front panel) Status for AC-input and DC-input Power Supply Units
|
LED State |
Power Supply Unit Condiiton |
|---|---|
|
Continuous green |
Corresponding power supply unit is present and functioning normally |
|
Red |
Corresponding power supply unit present, but malfunctioning |
|
Unlit |
Corresponding power supply unit is either not present or has failed. |
Note
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) monitors the activity of the power supplies. In most cases when a power supply problem occurs, an SNMP trap is sent in SNMP and the appropriate message is posted on the SCE 1000 CLI.
The following table lists the AC-input and DC-input power supply specifications for the SCE 1000 platform:
Table 4.7. SCE 1000 Power Supply Specifications
|
AC-input power |
200W maximum |
|
AC-input voltage rating |
100 to 240 VAC |
|
AC-input current rating |
Rated for 4.5A when Vin = 100 VAC or 2A when Vin = 200 VAC |
|
AC-input frequency rating |
50 to 60 Hz |
|
AC-input cable |
18 AWG three-wire cable, with a three-lead IEC-320 receptacle on the power supply end, and a country-dependent plug on the power source end. |
|
DC-input power |
200W maximum |
|
DC-input voltage rating |
–48/-60 VDC nominal (–36 to–72 VDC supply tolerance) |
|
DC-input current rating |
7A at –48 VDC |
|
DC-input cable |
12 AWG or 2.5-mm copper installation wire with hex or loop connectors |
|
DC-input circuit breaker |
One Fast 10A for each power supply unit |
Note
For AC-input power, we recommend powering the SCE 1000 platform from a 120 VAC, 15A receptacle U.S. (240 VAC, 10A international) at the power source.
The procedures for removing and replacing the AC-input or DC-input power supply are explained in the following sections:
ESD Warning
Do not remove or install modules without using appropriate anti-static guard measures. The SCE 1000 includes an anti-static wrist strap in the accessory kit. Attach the copper tape strap to an unpainted metal surface on the chassis. You may leave the strap connected to the chassis when your have finished.
Warning
Never install an AC power module and a DC power module in the same chassis.
The following sections describe how to remove power from an AC-input power supply and a DC-input power supply:
To power down an AC-input power supply to the SCE 1000 platform, complete the following steps:
Warning
Make sure that the power supply unit is switched off before replacing it (NO hot-swap).
Note that one AC-input power supply can be running when the other power supply is being removed or replaced.
Place the on/off switch on the AC-input power supply in the OFF (¡) position.
Observe that the corresponding Power LED on the front panel turns off.
Remove the cable from the AC-input power receptacle
This completes the procedure for powering down an AC-input power supply unit on a SCE 1000 platform. Proceed to Removing the Power Supply Unit.
To power down a DC-input power supply to the SCE 1000 platform, complete the following steps:
Warning
Before completing any of the following steps, and to prevent short-circuit or shock hazards, ensure that power is removed from the DC circuit. To ensure that all power to the power supply unit is OFF, locate the circuit breaker on the panel board that services the DC circuit, switch the circuit breaker to the OFF position, and tape the switch handle of the circuit breaker in the OFF position.
Note that the power to the relevant power supply unit should be off, not necessarily all power to the SCE 1000 platform. One DC-input power supply can be running when the other power supply is being removed or replaced.
Place the on/off switch on the DC-input power supply in the OFF (¡) position.
Make sure that that power is removed from the DC circuit by turning off the circuit breaker or switch providing power to the DC-input power supply.
Observe that the corresponding Power LED on the front panel turns off.
Remove the screw from one DC power line input lead receptacle and pull the lead from the connector. Repeat this step for the remaining lead.
This completes the procedure for powering down a DC-input power supply unit on a SCE 1000 platform. Proceed to Removing the Power Supply Unit.
To remove the AC-input or DC-input power supply unit from the SCE 1000 platform, complete the following steps:
Using a 1/4-inch flat-blade screwdriver, loosen the captive installation screw on the corner of the faceplate of the power supply.
Grasp the power supply handle and pull the power supply from the router.
This completes the procedure for removing the power supply from a SCE 1000 platform.
Warning
Do not mix AC-input and DC-input power supply units in the same SCE 1000 platform.
To install a new power supply into a SCE 1000 platform, complete the following steps:
Grasp the power supply unit handle with one hand and place your other hand underneath the power supply for support.
Fit the groove in the side of the new power supply module into the guide in the chassis.
Gently, but firmly, slide the module into the chassis until its faceplate is flush with the chassis rear panel.
Warning
When inserting a power supply into the SCE 1000 platform, do not use unnecessary force; slamming the power supply into the chassis can damage the connectors on the rear of the power supply.
Seat the power supply in the SCE 1000 platform by tightening the captive installation screw with a 1/4-inch flat-blade screwdriver.
Note
The power supply is not fully seated until you tighten the installation screw on the faceplate.
This completes the procedures for replacing a power supply in a SCE 1000 platform.
The following sections describe how to reconnect the AC or DC power:
The following procedures explain how to reconnect an AC-input power to the SCE 1000 platform.
If you are reconnecting DC-input power, proceed to Reconnecting DC-Input Power Supply Unit.
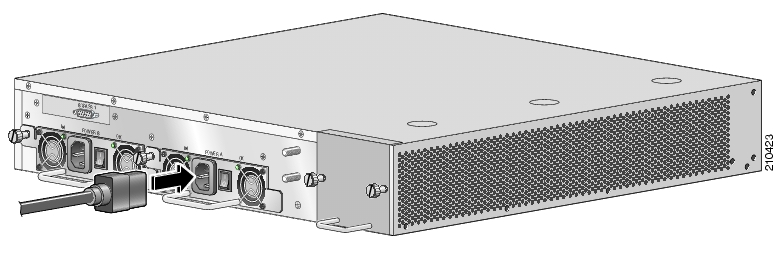
To reconnect the AC-input power to the SCE 1000 platform, complete the following steps:
Plug the AC-input power cable into the AC-input power receptacle on the AC-input power supply
Note
For AC-input power, we recommend powering the SCE 1000 platform from a 120 VAC, 15A receptacle U.S. (240 VAC, 10A international) at the power source.
15 A branch circuit protection is recommended.
Plug the AC power supply cable into the AC power source.
Turn the on/off switch to the on (½) position.
Look at the IN and OK LEDs on the power supply unit and the corresponding Power LED on the front panel. If the new AC-input power supply unit is operating properly, these LEDs will be glowing green.
Ensure that the power supply is properly aligned and the installation screw is tightened.
This completes the steps for reconnecting the AC-input power supply to the SCE 1000 platform.
The following procedures explain how to reconnect a DC-input power to the SCE 1000 platform.
Warning
Before completing any of the following steps, and to prevent short-circuit or shock hazards, ensure that power is removed from the DC circuit. To ensure that all power to the power supply unit is OFF, locate the circuit breaker on the panel board that services the DC circuit, switch the circuit breaker to the OFF position, and tape the switch handle of the circuit breaker in the OFF position.
Note that the power to the relevant power supply unit should be off, not necessarily all power to the SCE 1000 platform. One DC-input power supply can be running when the other power supply is being removed or replaced.
Warning
Wiring should be done by a professional in accordance with state and local electrical codes.
To reconnect the DC-input power to the SCE 1000 platform, complete the following steps:
Ensure that the DC power line input leads are disconnected from the power source.
Using the number 2 Phillips screwdriver, remove the protective plate from the terminal block.
Insert one receptacle screw into the hex or loop connector on one power line input, insert the screw with the connector into the corresponding lead receptacle and tighten the receptacle screw using the number 2 Phillips . Repeat for the remaining power line input lead.
Note
The color coding of the DC-input power supply leads depends on the color coding of the DC power source at your site. Make certain the lead color coding you choose for the DC-input power supply matches lead color coding used at the DC power source.
Note
Use 12 AWG (2.5 mm) copper wire only with hex or loop connectors. Ring terminals must be UL approved and suitable for 12 AWG wire.
Using the number 2 Phillips screwdriver, securely fasten the protective plate to the terminal block.
Connect the DC power line input leads to the DC power source through a fast 10A circuit breaker.
Turn the on/off switch to the on (½) position.
Look at the IN and OK LEDs on the power supply unit and the corresponding Power LED on the front panel. If the new DC-input power supply unit is operating properly, these LEDs will be glowing green.
Ensure that the power supply is properly aligned and the installation screw is tightened.
This completes the steps for reconnecting the DC-input power supply to the SCE 1000 platform.
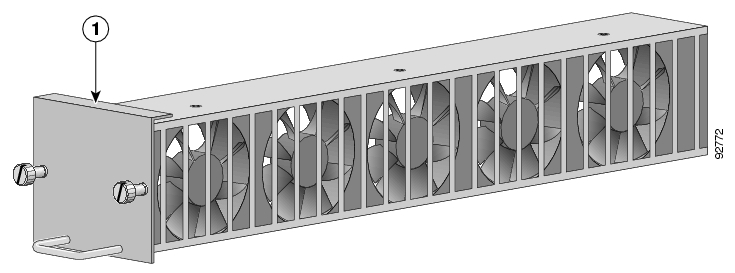
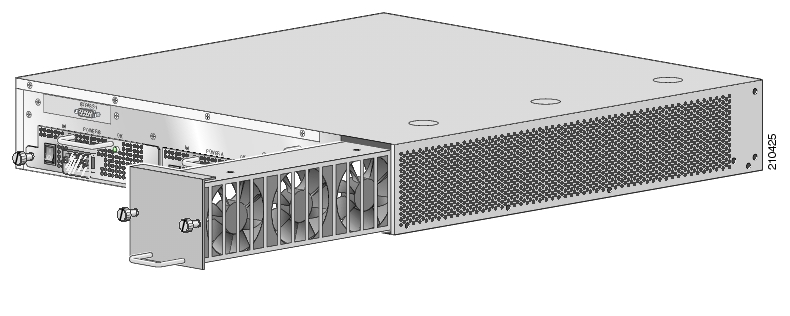
The fan module provides cooling for the internal components. The fan drawer is a field-replaceable unit containing five fans, and is installed at the right rear of the SCE 1000 platform.
When a fan malfunctions, the fan module should be replaced as promptly as possible. Although it is possible for the unit to function for some time with one non-functioning fan, this is not optimal or recommended.
When a fan failure occurs, the environment monitor will send an error message to the console. An SNMP trap indicating that the fan is not functioning properly is also sent. Note that a fan failure is often audible.
The following sections explain how to remove and replace a fan module in a SCE 1000 platform:
ESD Warning
Do not remove or install modules without using appropriate anti-static guard measures. The SCE 1000 includes an anti-static wrist strap in the accessory kit. Attach the copper tape strap to an unpainted metal surface on the chassis. You may leave the strap connected to the chassis when your have finished.
Warning
When removing the fan drawer, keep hands and fingers away from the spinning fan blades. Let the fan blades stop completely before removing the fan drawer.
To remove the fan module, complete the following steps:
Using a 1/4-inch flat-blade screwdriver, loosen the two captive screws on the faceplate of the fan module.
Grasp the fan module handle and remove it from the router.
This completes the procedure for removing the fan module from a SCE 1000 platform.
To install a new fan module into a SCE 1000 platform, complete the following steps:
Grasp the fan module handle with one hand and place your other hand underneath the fan module for support. The handle of the unit should be at the bottom.
Fit the groove in the side of the new fan module into the guide in the chassis.
Gently, but firmly, slide the module into the chassis until its faceplate is flush with the chassis rear panel.
Warning
When inserting a fan module into the SCE 1000 platform, do not use unnecessary force; slamming the fan module into the chassis can damage the connectors on the rear of the module.
Seat the fan module in the SCE 1000 platform by tightening the two captive installation screws with a 1/4-inch flat-blade screwdriver.
Note
The fan module is not fully seated until you tighten the installation screws on the faceplate.
This completes the procedures for replacing a fan module in a SCE 1000 platform.
The SCE 1000 has a lithium battery on its main circuit board. When the battery loses its charge, call Cisco Technical Support to replace the battery.
Warning
Do not attempt to replace this battery yourself
Warning
There is danger of explosion if the lithium battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only with the same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
This chapter explains how to connect the SCE 1000 platform to a local console and perform the initial system configuration via the setup wizard that runs automatically.
Additionally, this chapter contains instructions for cabling the Fast Ethernet Management interfaces.
Even if you will be managing the SCE 1000 from a remote location, you must first connect the unit to a local console and configure the initial settings for the SCE 1000 to support remote management. When the initial connection is established, the setup utility will run automatically, prompting you to perform the initial system configuration.
This section provides instructions for setting up your local terminal at your workstation, to enable you to perform the initial system configuration of the SCE 1000 system using the setup utility.
Make sure that the terminal configuration is as follows:
9600 baud
8 data bits
No Parity
1 stop bits
No flow control
The above SCE 1000 port parameters are fixed and are not configurable.
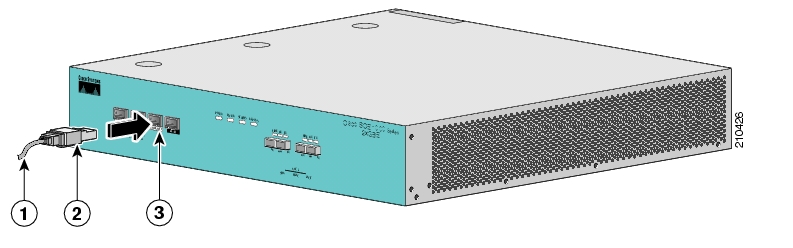
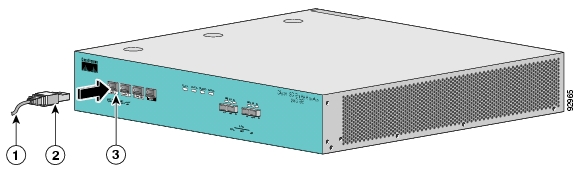
To set up the local console, complete the following steps:
Plug the RS-232 serial cable provided with the SCE 1000 into the CON port on the front panel of the SCE 1000.
Make sure that you push on the RJ-45 connector (attached to the RS-232 serial cable) until you hear a “click”, which indicates that the connector is fully inserted and secured in the receptacle. Gently pull on the plug to confirm whether the plug is locked into the socket.
Connect the other end of the serial cable (with an attached DB-9 connector) to the VT100 compatible local (serial) terminal.
Make sure the local terminal is configured as a VT-100 terminal, according to the fixed SCE 1000 CON port parameters.
Press Enter several times until the Cisco logo appears on the local terminal and the setup configuration dialog is entered.
--- System Configuration Dialog --- At any point you may enter a question mark ‘?’ followed by ‘Enter’ for help. Use ctrl-C to abort configuration dialog at any prompt. Use ctrl-Z to jump to the end of the configuration dialog at any prompt. Default settings are in square brackets ‘[]’. Would you like to continue with the System Configuration Dialog? [yes/no]: yType y and press Enter.
The system configuration dialog begins.
Upon initial connection to the local terminal, as described above, the system configuration wizard automatically runs to guide the user through the entire setup process. The wizard prompts for all necessary parameters, displaying default values, where applicable. You may accept the default values or define other values.
With the exception of the time settings, which take effect immediately when entered, the new configuration is applied and saved only at the end of the dialog when approved by the user. Therefore, if the setup dialog is aborted, no change takes place in the configuration, other than time settings (if entered).
When the dialog is complete, you may review the new configuration before applying it. The system displays the configuration, including parameters that were not changed. The system also displays any errors that are detected in the configuration. When the configuration is satisfactory, you may apply and save the new configuration.
The following table lists all the parameters included in the initial configuration. It is recommended that you obtain values for any parameters that you will configure at this time before beginning the setup.
Note
For further information regarding any configuration step or specific parameter, refer to the relevant section in the Cisco Service Control Engine (SCE) Software Configuration Guide.
Table 5.1. Setup Command Parameters
|
Parameter |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
IP address |
IP address of the SCE 1000. |
|
subnet mask |
Subnet mask of the SCE 1000. |
|
default gateway |
Default gateway. |
|
hostname |
Character string used to identify the SCE 1000. Maximum 20 characters. |
|
admin password |
Admin level password. Character string from 4-100 characters beginning with an alpha character. |
|
root password |
Root level password. Character string from 4-100 characters beginning with an alpha character. |
|
password encryption status |
Enable or disable password encryption? |
|
Time Settings |
|
|
time zone name and offset |
Standard time zone abbreviation and minutes offset from UTC. |
|
local time and date |
Current local time and date. Use the format: 00:00:00 1 January 2002 |
|
SNTP Configuration |
|
|
broadcast client status |
Set the status of the SNTP broadcast client. If enabled, the SCE will synchronize its local time with updates received from SNTP broadcast servers. |
|
unicast query interval |
Interval in seconds between unicast requests for update (64 – 1024) |
|
unicast server IP address |
IP address of the SNTP unicast server. |
|
DNS Configuration |
|
|
DNS lookup status |
Enable or disable IP DNS-based hostname translation. |
|
default domain name |
Default domain name to be used for completing unqualified host names |
|
IP address |
IP address of domain name server. ( maximum of 3 servers) |
|
RDR Formatter Destination Configuration | |
|
IP address |
IP address of the RDR-formatter destination |
|
TCP port number |
TCP port number of the RDR-formatter destination |
|
Access Control Lists |
|
|
Access Control List number |
How many ACLs will be necessary? What IP addresses will be permitted/denied access for each management interface? You may want ACLs for the following :
|
|
list entries (maximum 20 per list) |
IP address, and whether permitted or denied access. |
|
IP access ACL |
ID number of the ACL controlling IP access. |
|
telnet ACL |
ID number of the ACL controlling telnet access. |
|
SNMP Configuration |
|
|
SNMP agent status |
Enable or disable SNMP management. |
|
GET community names |
Community strings to allow GET access and associated ACLs (maximum 20). |
|
SET community names |
Community strings to allow SET access and associated ACLs (maximum 20). |
|
trap managers |
Trap manager IP address, community string, and SNMP version. (maximum 20) |
|
Authentication Failure trap status |
Set the status of the Authentication Failure trap. (See Traps.) |
|
enterprise traps status |
Set the status of the enterprise traps. (See Traps.) |
|
system administrator |
Name of the system administrator. |
|
Topology Configuration | |
|
connection mode |
Is the SCE 1000 installed in inline topology or receive-only using an optical splitter? |
|
link bypass mode on operational status |
When the SCE 1000 is operational, should it bypass traffic or not? |
|
redundant SCE 1000 platform? |
Is there a redundant SCE 1000 installed as a backup? |
|
link bypass mode on non-operational status |
When the SCE 1000 is not operational, should it bypass traffic or cut it off? |
|
operational status of the SCE after abnormal boot |
After a reboot due to a failure, should the SCE 1000 remain in a Failure status or move to operational status provided no other problem was detected? |
Following are some general instructions regarding the setup dialog:
All default values appear in square brackets [default].
If no value appears in the brackets [], or more than one option appears [yes/no], then this parameter does not have a default value.
To accept the default value, press Enter.
If you need more information about any parameter, type ? and press Enter.
A help message will appear describing the expected format of the parameter and any other requirements.
To jump to the end of the setup dialog at any point, accepting all remaining default values, press ^z.
In certain cases, there will be two or more logically related parameters within a menu. In these situations, it is not permitted to jump to the end of the setup dialog until all related parameters are configured. If you try to jump to the end of the setup dialog, the following message will appear: “
Sorry, Skipping is not allowed at this stage.”Certain groups of related parameters, such as time, date, and SNTP settings, form sub-dialogs or menus within the setup dialog. You may skip an entire menu, thereby accepting all default values for the parameters within the menu.
Each group of related parameters is prefaced by a question, asking whether you want to enter the menu. To skip the menu, answer no (“n”) to the question.
Example:
Would you like to enter the SNMP configuration menu? nTo abort the setup dialog at any point without making any configuration changes, press ^c. All changes already entered will be lost, with the exception of time settings.
Verify the following initial settings for the SCE 1000:
IP address
Subnet mask
Default gateway
All values are Internet addresses of the form ‘X.X.X.X’, where each letter corresponds to a decimal number between 0 and 255.
To configure the initial settings, complete the following steps:
The current IP address is displayed.
To accept the displayed value, press Enter.
To change the value, type the desired value in the format “x.x.x.x” and press Enter.
The current subnet mask is displayed.
To accept the displayed value, press Enter.
To change the value, type the desired value in the format “x.x.x.x” and press Enter.
The current IP address of the default gateway is displayed.
To accept the displayed value, press Enter.
To change the value, type the desired value in the format “x.x.x.x” and press Enter.
Example:
The following example displays a typical configuration of the IP address (10.1.5.109), subnet mask (255.255.0.0), and default gateway (10.1.1.3).
Since the IP address and the subnet mask are related, when the IP address is changed, there is no longer a default value of the subnet mask, and it must be entered explicitly.
Enter IP address [10.1.1.201]:10.1.5.109 Enter IP subnet mask:255.255.0.0 Enter IP address of default gateway [10.1.1.3]:
The hostname is used to identify the SCE 1000. It appears as part of the CLI prompt and is also returned as the value of the MIB-II object sysName.
The maximum length is 20 characters.
The default hostname is SCE 1000.
Configure the passwords as follows:
Set the password for each authorization level (User, Admin, Root).
Enable/disable password encryption. When password encryption is enabled, it encrypts the previously entered passwords.
Note
Passwords are needed for all authorization levels in order to prevent unauthorized users from accessing the SCE 1000. Admin level should be used by the network administrator. Root level is for use by Cisco technician.
Passwords must meet the following criteria:
Minimum length — 4 characters
Maximum length — 100 characters
Begin with an alpha character
May contain only printable characters
Note
Passwords are case sensitive.
Note
The default password for all levels is “cisco”.
To change the passwords, complete the following steps:
The default User password is displayed.
To accept the displayed value, press Enter.
To change the value, type the desired string and press Enter.
The default Admin password is displayed.
To accept the displayed value, press Enter.
To change the value, type the desired string and press Enter.
The default Root password is displayed.
To accept the displayed value, press Enter.
To change the value, type the desired string and press Enter.
Configure password encryption. By default, password encryption is not enabled.
To disable password encryption, press Enter.
To enable password encryption, type
yand press Enter.
Example:
Following is an example of changing all passwords. Password encryption is not enabled (default).
Enter a User password [cisco]:userinEnter an Admin password [cisco]:mng123Enter a Root password [cisco]:cistechEnable passwords encryption? [no]:
The time settings menu configures all time and date related parameters in the system. The time settings menu includes the following:
Time zone
Local time
Date
SNTP menu
You must enter the time setting menu in order to configure SNTP settings. You may choose to skip the time settings menu if you wish to accept all default values.
Note
Unlike all other settings defined in the system configuration, setting the time is done immediately and not at the end of the setup process.
To configure the time settings, complete the following steps:
Enter the time settings menu.
Would you like to enter the Time settings menu? [no]:yType
yand press Enter.The time settings dialog begins.
Type the time zone abbreviation and press Enter.
Enter time zone name [UTC]:
CETType the minutes offset from UTC and press Enter.
Enter time zone minutes offset from UTC:
60The local time and date are displayed, and you are asked whether you want to change them.
The local time and date is 15:00:01 CET FRI 01 July 2002 Would you like to set a new time and date? [no]:
If the time and date are correct, go to step5.
If the time and date are not correct, answer yes to the above question, and press Enter.
Would you like to set a new time and date? [no]:yConfirm your response and type the new time and date. This change will take effect immediately both on the system clock and calendar; it will also set the time zone you entered. Are you sure? [yes/no]: y Enter new local time and date:14:00:01 1 July 2002Time zone was successfully set. The system clock and the calendar were successfully set.You are asked whether you wish to enter the SNTP configuration menu.
If you do not wish to configure the SNTP, skip the rest of this section and go to Step 5: Configuring the DNS Settings.
To enter the SNTP configuration dialog, type
y, and press EnterWould you like to enter the SNTP configuration menu? [no]:yConfigure the SNTP broadcast client. By default the SNTP broadcast client is not enabled.
To disable the SNTP broadcast client, press Enter.
To enable the SNTP broadcast client, type
yand press Enter.Enable SNTP broadcast client? [no]:
Define the time interval between unicast updates.
To accept the displayed default value, press Enter.
To change the value, type the desired number of seconds (64 through 1024) and press Enter.
Enter time interval in seconds between unicast updates [1024]:
You may enter an IP address for the SNTP unicast server. Type in the hostname or the IP address in the form x.x.x.x, and press Enter
Would you like to configure SNTP unicast servers? [no]:
yEnter IP address or hostname of SNTP unicast server:10.1.1.1
Example:
Following is a sample time setting dialog. In addition to setting the time zone, time and date are changed, and SNTP unicast updates are configured.
Would you like to enter the Time settings menu? [no]: y
Enter time zone name [UTC]: ISR
Enter time zone minutes offset from UTC: 120
The local time and date is 15:35:23 ISR FRI July 19 2002
Would you like to set a new time and date? [no]: y
This change will take effect immediately both on the system clock
and the calendar; it will also set the time zone you entered.
Are you sure? [yes/no]: y
Enter new local time and date: 14:35:23 19 July 2002
Time zone was successfully set.
The system clock and the calendar were successfully set.
Would you like to enter the SNTP configuration menu? [no]: y
Enable SNTP broadcast client? [no]: y
Enter time interval in seconds between unicast updates [900]:
Would you like to configure SNTP unicast servers? [no]: y
Enter IP address or hostname of SNTP unicast server: 10.1.1.1The DNS configuration menu defines the IP address of the domain name server, which is used for DNS lookup, as well as the default domain name, which is used to complete unqualified host names.
You may choose to skip the DNS configuration menu if you wish to accept all default values.
To configure DNS settings, complete the following steps:
Enter the DNS settings menu.
Would you like to enter the DNS configuration menu? [no]:yType
yand press Enter.The DNS settings dialog begins.
Enable or disable DNS lookup.
To enable DNS lookup, press Enter.
To disable DNS lookup, type
nand press Enter.Enable IP DNS-based hostname translation? [yes]:
If you choose to disable DNS lookup, skip the rest of this section and go to Step 6: Configuring the RDR Formatter Destination. The rest of the dialog is not presented, as it is irrelevant when DNS lookup is disabled.
Type the default domain name to be used, and press Enter.
Note that there is no default domain name.
You may accept the default domain name or enter a new one.
Enter default domain name []:
Type the IP address of the primary domain name server and press Enter.
Enter Primary DNS IP address:
Note that there is no default for this parameter.
You may configure up to three domain servers.
Would you like to add another Name Server? [no]:
To exit the DNS settings dialog, press Enter.
To add another domain server, type
yand press Enter.You are asked to enter the IP address of the next domain name server.
Enter Secondary DNS IP address:
When IP addresses for all servers have been entered, exit the dialog by pressing Enter.
Would you like to add another Name Server? [no]:
Example:
Following is a sample DNS configuration dialog. The default domain name is pcube.com, and the IP address of the Domain Name Server is 10.1.1.230.
Would you like to enter the DNS configuration menu? [no]:yEnable IP DNS-based hostname translation? [yes]: Enter default domain name []:pcube.comEnter Primary DNS IP address:10.1.1.230Would you like to add another Name Server? [no]:
The SCE 1000 passes Raw Data Records (RDRs) to an external collection system via the RDR-Formatter. In order for the data to reach the correct location, the IP address of the external collection system and its port number must be configured.
To configure the RDR-formatter destination, complete the following steps:
Enter the RDR formatter configuration menu.
Would you like to enter the RDR-formatter configuration menu? [no]:yType
yand press Enter.The RDR-formatter destination dialog begins.
Type the IP address of the RDR-formatter destination and press Enter.
Enter RDR-formatter destination’s IP address:
Note that there is no default for this parameter.
Type the TCP port number of the RDR-formatter destination and press Enter.
Note that there is no default for this parameter.
Enter RDR-formatter destination’s TCP port number:
Example:
Following is a sample RDR-formatter configuration dialog, assigning the IP address and TCP port number.
Would you like to enter the RDR-formatter configuration menu? [no]:yEnter RDR-formatter destination’s IP address:10.1.1.230Enter RDR-formatter destination’s TCP port number:33000
The SCE 1000 can be configured with Access Control Lists (ACLs), which are used to permit or deny incoming connections on any of the management interfaces.
Note
ACL #0 is a pre-defined list that permits access to all IP addresses.
Configuration of access control lists is done in two stages:
Create the access control lists.
You may create 99 ACLs with a maximum of 20 entries per list. Each entry consists of an IP address, and an indication of whether access is permitted or denied to this IP address.
Assign the ACLs to the appropriate management interface. (See Step 9: Configuring the Topology-Dependent Parameters.)
The dialog permits you to skip the creation/editing of the ACLs and go directly to assigning ACLs to the management interfaces.
Each ACL may permit/deny access to any IP address, one or more ranges of IP addresses, or one or more individual IP address. Three entry formats are available to support these options:
Any IP address — Type the word “any”. Any IP address will be permitted or denied access.
Range of IP addresses — Type the beginning IP address in the desired range, then enter the wildcard bits that define the range.
This wildcard functions like a reverse mask, in that all “1” bits in the wildcard indicate the corresponding bit in the IP address should be ignored. All other bits must match the corresponding bit in the specified IP address. Refer to the table below for examples.
Each range of IP addresses can be configured to be permitted or denied access.
Individual IP address — Type the desired IP address, then enter the wildcard bits 0.0.0.0.
Each individual IP address can be configured to be permitted or denied access.
Table 5.2. IP address/Wildcard bit examples
|
Initial IP address |
Wildcard bits |
Range |
|---|---|---|
|
10.1.1.0 |
0.0.0.255 |
10.1.1.0–10.1.1.255 |
|
10.1.1.0 |
0.0.0.63 |
10.1.1.0–10.1.1.63 |
|
10.1.1.0 |
0.0.0.0 |
10.1.1.0 (individual entry) |
The order of the entries in the list is important. The entries in the list are tested sequentially, and the action is determined by the first entry that matches the connecting IP address. Therefore, when the entry “any” appears in an Access Control List, all succeeding entries are irrelevant.
Consider two hypothetical ACLs containing the same entries in a different order.
The following list would permit access to all IP addresses, including 10.1.1.0:
permit any
deny 10.1.1.0
Note that the above list could not actually be created using the setup utility, since after the “any” entry, no other entries could be added to the list.
The following list will deny access to IP address 10.1.1.0, but permit access to all others:
deny 10.1.1.0
permit any
If no entry in the assigned Access Control List matches the connection, or if the Access Control List is empty, the default action is deny.
To create the access control lists, complete the following steps:
Enter the Access Control Lists configuration menu.
Would you like to enter the Access lists configuration menu? [no]:yType
yand press Enter.The Access Control Lists configuration dialog begins.
You have the option of creating or modifying Access Control Lists, or skipping this section and proceeding directly to assign the existing ACLs to the desired management interfaces.
Would you like to create new Access lists or modify existing lists? [no]:
yIf you choose not to create or edit Access Control Lists, skip to Step 9: Configuring the Topology-Dependent Parameters.
Type the number of the Access Control List to be configured (1 through 99) and press Enter.
Note that there is no default for this parameter.
Begin adding entries to the selected list.
Indicate whether this entry is permitted access or denied access.
To permit access press Enter.
To deny access type
nand press Enter.Does this entry permit access? [yes]:
Type the IP address to be added to this list, and press Enter.
Type “
any” and press Enter to include any IP address in the ACL.Note that there is no default for this parameter.
Enter IP address or the word ‘any’ to denote any IP address:
If you entered a specific IP address, enter the wildcard bits to define a range of IP addresses and press Enter. (See Entry Formats.)
To define an individual IP address, type 0.0.0.0 and press Enter.
There is no default for this parameter.
Enter wildcard bits:
The maximum number of entries in an ACL is 20.
If the “any” option was used, no other IP addresses may be added to the list.
To add more entries, type
yand press EnterWould you like to add another entry to this list? [no]:
y
Enter up to 20 entries as described in step 5 and step 6.
When all entries have been added, press Enter Would you like to add another entry to this list? [no]:When all entries are added to one list, you are asked whether you would like to create another ACL. You may define up to 99 ACLs.
To create another ACL, type
yand press EnterWould you like to configure another list? [no]:y
Enter up to 20 IP addresses in this new ACL, as described in step 5 and step 6.
When all ACLs have been created, press Enter.
Would you like to configure another list? [no]:
You are now prompted to assign the desired ACLs to restrict IP and Telnet access.
Restrict IP access to the SCE 1000 by assigning the appropriate ACL.
Type the number of the ACL to be assigned to IP access and press Enter.
To accept the default ACL, press Enter.
Enter IP access-class [0]:
Restrict Telnet access to the SCE 1000 by assigning the appropriate ACL.
Type the number of the ACL to be assigned to the Telnet interface and press Enter.
To accept the default ACL, press Enter.
Enter Telnet access-class [0]: 2
Example 1:
This example illustrates a common access control scenario. Let us assume the following:
We want to permit every station to access the SCE platform on the management port (e.g. ping, SNMP polling etc.).
We want to restrict Telnet access to only a few permitted stations.
We therefore need to create two access control lists:
For general IP access — permit access to all IP addresses.
For Telnet — permit access to the specified IP address, and deny to all others.
ACL #1 = permit any IP address. Assign to IP access.
ACL #2 = permit access to 10.1.1.0, 10.10.10.1, deny to all others. Assign to Telnet access.
Would you like to enter the Access lists configuration menu? [no]:yWould you like to create new Access lists or modify existing lists? [no]:yEnter ACL number:1Does this entry permit access? [yes]: Enter IP address or the word ‘any’ to denote any IP address:anyThis entry matches every IP address, no use in adding more entries to this list. Would you like to configure another list? [no]:yEnter ACL number:2Does this entry permit access? [yes]: Enter IP address or the word ‘any’ to denote any IP address:10.1.1.0Enter wildcard bits: 0.0.0.0Would you like to add another entry to this list? [no]:yDoes this entry permit access? [yes]: Enter IP address or the word ‘any’ to denote any IP address:10.10.10.1Enter wildcard bits: 0.0.0.0Would you like to add another entry to this list? [no]:yDoes this entry permit access? [yes]:n Enter IP address or the word ‘any’ to denote any IP address:anyThis entry matches every IP address, no use in adding more entries to this list. Would you like to configure another list? [no]: Enter IP access-class [0]:1Enter Telnet access-class [0]:2Example 2:
This example skips the first section of the dialog (creating/modifying), and proceeds directly to assign existing ACLs.
Would you like to enter the Access lists configuration menu? [no]:yWould you like to create new Access lists or modify existing lists? [no]: Enter IP access-class [0]:10Enter Telnet access-class [0]:22
Managing the SCE 1000 is possible also via a Network Management System (NMS) that supports SNMP. By default, SNMP is disabled on the SCE 1000.
To enable SNMP management you must configure the following basic SNMP parameters:
SNMP traps status and managers.
Community strings (where an SNMP community string is a text string that acts like a password to permit access to the SNMP agent on the SCE 1000).
To configure SNMP parameters, complete the following steps:
Enter the SNMP configuration menu.
Would you like to enter the SNMP configuration menu? [no]:yType
yand press Enter.The SNMP configuration dialog begins.
Enable SNMP management.
Type
yand press Enter.Enable SNMP management? [no]: y
If you choose to disable SNMP management, skip the rest of this section and go to Step 9: Configuring the Topology-Dependent Parameters. The rest of the dialog is not presented, as it is irrelevant when SNMP management is disabled.
Type the SNMP GET community name and press Enter.
The SNMP agent that resides inside the SCE 1000 will respond only to GET requests that use this community string.
Enter SNMP GET community name:
Note that there is no default for this parameter.
Assign an access list to restrict the SNMP management stations that may use this GET community.
Type a number (1 through 99) or type “0” to permit access to all IP addresses, and press Enter.
Enter Access list number allowing access with this community string, use ‘0’ to allow all:
The maximum number of GET communities is 20.
To add more entries, type
yand press EnterWould you like to add another SNMP GET community? [no]:
y
Enter up to 20 SNMP GET communities as described in step 3 and step 4.
When all entries have been added, press Enter
Would you like to add another SNMP GET community? [no]:
Type the SNMP SET community name and press Enter.
The SNMP agent that resides inside the SCE 1000 will respond only to SET requests that use this community string.
Enter SNMP SET community name:
Note that there is no default for this parameter.
Assign an access list to restrict the SNMP management stations that may use this SET community.
Type a number (1 through 99) or type “0” to permit access to all IP addresses, and press Enter.
Enter Access list number allowing access with this community string, use ‘0’ to allow all:
The maximum number of SET communities is 20.
To add more entries, type
yand press EnterWould you like to add another SNMP SET community? [no]:
y
Enter up to 20 SNMP SET communities as described in step 6 and step 7.
When all entries have been added, press Enter
Would you like to add another SNMP SET community? [no]:
Enter the SNMP trap managers menu.
Would you like to configure SNMP trap managers? [no]: yType
yand press Enter.The SNMP trap managers dialog begins.
If you choose not to configure SNMP trap managers, the dialog skips to the authentication failure trap status. (See step 14.)
Type the trap manager IP address and press Enter.
Enter SNMP trap manager IP address:
Note that there is no default for this parameter.
Type the trap manager community string and press Enter.
Note that there is no default for this parameter.
Enter SNMP trap manager community string:
Type the number of the trap manager SNMP version (1 or 2c) and press Enter
Note that there is no default for this parameter.
Enter trap manager SNMP version:
The maximum number of trap managers is 20.
To add more entries, type
yand press EnterWould you like to add another SNMP trap manager? [no]:
y
Enter up to 20 trap managers as described in step 10 through step 12.
When all entries have been added, press Enter
Would you like to add another SNMP trap manager? [no]:
Configure the Authentication Failure trap status.
To disable the Authentication Failure trap, press Enter.
To enable the Authentication Failure trap, type
yand press Enter.Enable the ‘Authentication Failure’ trap [no]:
Configure the SCE enterprise trap status.
To disable the SCE enterprise traps, type
npress Enter.To enable the SCE enterprise traps, type
yand press Enter.Enable the SCE enterprise traps []:
Type the name of the system administrator and press Enter.
Note that there is no default for this parameter.
Enter system administrator contact name []:
Example:
Following is a sample SNMP configuration, configuring one trap manager, one GET community, and one SET community, and enabling the authentication failure trap, as well as all enterprise traps.
Would you like to enter the SNMP configuration menu? [no]:yEnable SNMP management? [no]:yEnter SNMP GET community name[]:publicEnter Access list number allowing access with this community string, use ‘0’ to allow all:0Would you like to add another SNMP GET community? [no]: Enter SNMP SET community name[]:privateEnter Access list number allowing access with this community string, use ‘0’ to allow all:2Would you like to add another SNMP SET community? [no]: Would you like to configure SNMP trap managers? [no]:yEnter SNMP trap manager IP address:10.1.1.253Enter SNMP trap manager community string:publicEnter trap manager SNMP version:2cWould you like to add another SNMP trap manager? [no]: Enable the ‘Authentication Failure’ trap [no]:yEnable SCE enterprise traps []: y Enter system administrator contact name []:John Smith
The topology configuration menu is a series of guided questions relating to the deployment of the SCE 1000 in the network and its mode of operation. Values for the parameters are configured based on the user answers.
The correct value for each parameter must be ascertained before configuring the system to make sure that the system will function in the desired manner. (See Topology for a comprehensive discussion of topology and the related parameters.)
There are three topology-related parameters:
Connection mode — Can be either Inline or Receive-only, depending on the physical installation of the SCE 1000.
Bypass state when the SCE 1000 is not operational (on-failure) — This parameter determines whether the system cuts the traffic or bypasses it when the SCE 1000 has failed.
Status after reboot caused by fatal error or abnormal shutdown — This parameter determines whether the SCE 1000 returns to normal operational state after a failure.
The procedure described below is a hypothetical presentation of all the questions in the topology configuration. In actual practice, it is impossible for all questions to be presented in any one configuration, as this part of the dialog is not linear like the other sections, but branches depending on the parameter values entered.
Study the examples that follow to understand the procedure for various topologies.
To configure topology dependent parameters, complete the following steps:
Enter the topology configuration menu.
Would you like to enter the Topology configuration menu? [no]: yType y and press Enter.
The topology configuration dialog begins.
Specify the connection mode.
To define inline connection mode, press Enter.
To define receive-only connection mode, type 2 and press Enter.
Enter Connection mode: 1- inline 2- receive-only Enter your choice [1]:
Specify the On-failure link behavior.
To specify Bypass, press Enter.
To specify Cutoff, type 2 and press Enter.
Enter On-failure behavior: 1- bypass 2- cutoff Enter your choice [1]:
Specify the admin status of the SCE 1000 after abnormal boot.
To specify Not-Operational status after abnormal boot, press Enter.
To specify Operational status after abnormal boot, type 1 and press Enter.
Enter admin status of the SCe after abnormal boot: 1- Operational 2- Not-Operational Enter your choice [1]:
The following examples present the procedure for configuring the topology-related parameters for various topologies. Refer the Topology Configuration Summary Table for a summary of appropriate values for the parameters for each topology.
Example 1:
Following is a sample topology configuration for a topology using an external switch.
All other parameter values are automatically assigned by the system as follows:
Link bypass mode on-failure — Bypass
Admin status of the SCE after abnormal boot — Operational
Would you like to enter the Topology configuration menu? [no]: y Enter Connection mode: 1- inline 2- receive-only Enter your choice [1]: 2
Example 2:
Following is a sample topology configuration for a non-redundant bump-in-the-wire (inline) topology. All values are the system default values, so it is not necessary to type in the response. Simply press enter at each line.
Connection mode — Inline
For a non-redundant topology, link bypass on-failure should be Bypass, so that traffic continues to flow through the link.
After operation of the system resumes, and the SCE 1000 reboots, the SCE 1000 will resume operation. (Admin status after abnormal reboot is Operational.)
Would you like to enter the Topology configuration menu? [no]: y Enter Connection mode: 1- inline 2- receive-only Enter your choice [1]: Enter On-failure behavior: 1- Bypass 2- Cutoff Enter your choice [1]: Enter admin status of the SCe after abnormal boot: 1- Operational 2- Not-Operational Enter your choice [1]: Data collection for the system configuration is completed.
Example 3:
Following is a sample topology configuration for a redundant inline topology.
Connection mode — Inline
For a redundant topology, link bypass on-failure should be Cutoff, so that operation switches to the backup link.
After operation of the system resumes, and the SCE 1000 reboots, the SCE 1000 will resume operation. (Admin status after abnormal reboot is Operational.)
Would you like to enter the Topology configuration menu? [no]: y Enter Connection mode: 1- inline 2- receive-only Enter your choice [1]: 2 Enter On-failure behavior: 1- Bypass 2- Cutoff Enter your choice [1]:2 Enter admin status of the SCE after abnormal boot: 1- Operational 2- Not-Operational Enter your choice [1]: Data collection for the system configuration is completed.
When you have completed the entire configuration, the system checks for errors. If errors are found, a warning message appears. When the configuration is error-free, you may apply and save it.
To complete and save the configuration, complete the following steps:
The system informs you that data collection is complete.
We recommend that you view the entire new configuration before it is applied.
Type y and press Enter.
Note that there is no default.
If there are no errors, go to step 3.
Data collection for the system configuration is completed. Would you like to view the new configuration before it is applied? [yes/no]: yIf any errors are detected, you may choose to view them.
Press Enter.
Found errors in the new configuration, would you like to view them? [yes]: The following errors were found: Warning - RDR formatter destination 10.1.1.1 is not allowed in the IP access-class.You are asked whether to apply and save the configuration.
Apply and Save this configuration? [yes/no]:To apply and save the configuration, type y and press Enter.
To abort the setup procedure without applying or saving the configuration (recommended if there are errors), type n and press Enter.
Setup procedure aborted, no configuration changes made.
If the setup is aborted, the dialog is ended.
If there are no errors, the system requests confirmation of either a yes or no answer, in order to prevent mistakes.
Type the appropriate answer (y or n) and press Enter.
The running configuration would be overwritten by the changes you have just entered, are you sure? [yes/no]:
The selected action is carried out by the system.
If the apply and save action is not confirmed (no), the setup is aborted.
Setup procedure aborted, no configuration changes made.
If the apply and save action is confirmed (yes), the configuration is applied and saved.
The new running configuration will be saved to the startup configuration.
If the configuration was applied and saved, you may also save it to a file at a remote station.
Do you want to save a copy of the startup configuration file in a remote station? [no]:
To save the configuration to a remote station, type y and press Enter.
The system will ask for FTP path:
Enter a full FTP path of the remote destination:
The system informs you that the configuration is complete.
Committing configuration... Configuration completed successfully. Saving configuration... Writing general configuration file to temporary location... Backing-up general configuration file... Copy temporary file to final location... Done!
This completes the procedures for initial configuration of the SCE 1000 platform.
Example 1:
Following is an example of a configuration that the user aborted due to errors detected in the configuration.
Note that no confirmation is requested for the decision to abort the setup. Had there been no errors, confirmation would have been requested before aborting.
Data collection for the system configuration is completed.
Would you like to view the new configuration before it is applied? [yes/no]: n
Found errors in the new configuration, would you like to view them? [yes]: y
The following errors were found:
Warning - RDR formatter destination 10.1.1.1 is not allowed in the IP access-class.
Warning - default Gateway 10.1.1.1 is not allowed in the IP access-class.
Warning - IP Access list (1) conflicts with Telnet Access list (2) as follows:
Access list 2 permits all addresses while Access list 1 denies it.
Apply and Save this configuration? [yes/no]: n
Setup procedure aborted, no configuration changes made.Example 2:
Following is an example of a configuration that was applied and saved to the startup configuration as well as to an FTP site.
Although not demonstrated in this example, it is recommended that you always view the configuration before applying it.
Data collection for the system configuration is completed.
Would you like to view the new configuration before it is applied? [yes/no]:
Apply and Save this configuration? [yes/no]: y
(New configuration would be displayed here)
The running configuration would be overwritten by the changes you have just entered, are you sure? [yes/no]:y
The new running configuration will be saved to the startup configuration.
Do you want to save a copy of the startup configuration file in a remote station? [no]:y
Enter a full FTP path of the remote destination: ftp://vk:vk@10.1.1.253/h:/copyofstartup.txt
Committing configuration...
Configuration completed successfully.
Saving configuration...
Writing general configuration file to temporary location...
Backing-up general configuration file...
Copy temporary file to final location...
Done!Example 3:
Following is an example of a configuration that was aborted, although no errors were detected.
Data collection for the system configuration is completed.
Would you like to view the new configuration before it is applied? [yes/no]:
Apply and Save this configuration? [yes/no]: n
The changes you have just entered would be discarded, are you sure? [yes/no]:y
Setup procedure aborted, no configuration changes made.The SCE platform is equipped with two RJ-45 management (MNG) ports. These ports provide access from a remote management console to the SCE platform via a LAN. The two management ports provide the possibility for a redundant management interface, thus ensuring management access to the SCE platform even if there is a failure in one of the management links.
If only one management port is used, the desired port is simply connected directly to the LAN. If both management ports are used, they must both be connected to the management console via a switch. In this way, the IP address of the MNG port is always the same, regardless of which physical port is currently active.
The procedures for cabling the management port and testing connectivity between the SCE 1000 and the remote management host are explained in the following sections:
The SCE 1000 has two management ports, labeled Mng1 and Mng 2.
To cable the management port, complete the following steps:
Take the Ethernet cable provided (with attached RJ-45 connector) and plug it into the desired MNG port on the front panel of the SCE 1000, as shown in the following figure.
Connect the other end of the Ethernet cable into your management network.
If only one management port is used — connect the port directly to the LAN.
If both management ports are used — connect both ports to the LAN via a switch.
Make sure that you push on the RJ-45 connector attached to the cable until you hear a click, which indicates that the connector is fully inserted and secured in the receptacle. Gently pull on the plug to confirm whether the plug is locked into the socket.
If the Link LED on the SCE 1000 management port does not light, try removing the cable and reinserting it firmly into the module socket. To disconnect the plug from the socket, press down on the raised portion on top of the plug, releasing the latch. You should hear an audible click indicating the latch has released. Carefully pull the plug out of the socket.
If the management port Link LED on the SCE 1000 still does not light, verify that the cable is connected correctly to the appropriate network element on its second end.
If the SCE 1000 platform has been powered up, test now to verify that connectivity has been established between the SCE 1000 and the remote management host. If the SCE 1000 platform is not powered up, perform this step after starting the SCE 1000 platform.
To verify that connectivity has been established between the SCE 1000 and the remote management host, complete the following steps:
After you connect the cable to the appropriate Mng port and to your network, check the relevant Mng port LEDS.
There are two Mng LEDs — Link/Active, and 10/100/1000 (refer to Front Panel).
At this point, check that the Link/Active LED is green.
The state of the 10/100/1000 LED will depend on the Ethernet network settings.
Green indicates 100 Mbps and ‘Off’ indicates 10 Mbps.
Test connectivity. From the host that you intend to use for remote management, ping to the SCE 1000 by typing ping and the SCE 1000 IP address, and pressing Enter (see the example, below).
Note
Please note that only step 2 above, is performed from the remote management host (Mng port connection).
This verifies that an active connection exists between the specified station and the management port.
The ping program sends an echo request packet to an IP address and then awaits a reply. Ping output can help you evaluate path-to-host reliability, delays over the path, and whether the host can be reached or is functioning.
This completes the procedures for connecting the management interfaces and for initial configuration of the SCE 1000 platform. Proceed to the next chapter for a description of the procedures for cabling the Gigabit Ethernet ports and for configuring Gigabit Ethernet (GBE) interface parameters.
Example:
The following example displays a typical ping response where the target IP address is 10.1.1.201.
C:\>ping 10.1.1.201
pinging 10.1.1.201 ...
PING 10.1.1.201: 56 data bytes
64 bytes from host (10.1.1.201): icmp_seq=0. time=0. ms
64 bytes from host (10.1.1.201): icmp_seq=1. time=0. ms
64 bytes from host (10.1.1.201): icmp_seq=2. time=0. ms
64 bytes from host (10.1.1.201): icmp_seq=3. time=0. ms
----10.1.1.201 PING Statistics----
4 packets transmitted, 4 packets received, 0% packet loss
round-trip (ms) min/avg/max = 0/0/0This chapter provides instructions for cabling the Gigabit Ethernet ports and for configuring Gigabit Ethernet (GBE) interface parameters.
Note
When installing an External Optical Bypass module, the SCE 1000 line ports are connected to the module. See Cabling the External Optical Bypass Module for complete instructions.
The procedures for cabling the line ports, configuring the interface parameters, and testing connectivity of the links are explained in the following sections:
Before beginning, find the appropriate cabling diagram for the topology in your installation:
Single SCE 1000 topologies
In the inline or bump-in-the-wire topology, illustrated in the diagram above, the SCE 1000 resides physically on the data link between the subscriber side, usually either a BRAS (in DSL access), a PDSN (in wireless access), a CMTS (in the Cable access), or a switch or router aggregator (in other topologies), and the network side, usually a router or layer 3 switch network element. This is the inline topology, providing both traffic monitoring and control capabilities.
In this topology, all the traffic of the SCE 1000 is deployed as a transparent layer2 overlay on the customer’s existing network.
In this topology, an external optical splitter resides physically on the GBE link between the subscriber side and the network side. The external splitter is connected to the SCE 1000 via Rx links only.
In this topology, the traffic passes through the external splitter, which splits traffic to the SCE 1000. The SCE 1000, therefore, is in receive-only topology, having only traffic monitoring capabilities.
Note
Receive-only topologies can also be implemented using a switch. Such a switch must support SPAN functionality that includes separation between ingress and egress traffic and multiple SPAN-ports destinations.
By default, the SCE 1000 GBE line interface ports are configured with auto-negotiation disabled. The procedure for enabling auto-negotiation for the GBE line interface ports is explained in the following section.
Note
Autonegotiation must be disabled when the SCE 1000 is deployed via an external optical splitter (receive-only topology)
Note
If you change any parameters, you must save the new configuration settings.
Type copy running-config startup-config, and press Enter
By default, the SCE 1000 line interface ports are configured with auto-negotiation enabled. However, when using an external splitter, the auto-negotiation must be disabled.
Note
In order to prevent errors when in bypass mode, the system must be configured so that the speed and duplex of both line interfaces is the same.
Note
If you change any parameters, you must save the new configuration settings. Type copy running-config startup-config, and press Enter.
To configure GBE auto-negotiation for speed and duplex for the first GBE port (subscriber side) interface:
To enter the Global Configuration Mode, at the SCE 1000# prompt, type configure, and press Enter.
The SCE 1000(config)# prompt appears.
To enter the first GBE port interface, type interface GigabitEthernet 0/1, and press Enter.
The SCE 1000(config if)# prompt appears.
Type auto-negotiate and press Enter.
The SCE 1000(config if)# prompt appears.
To return to Global Configuration Mode, type exit and press Enter.
The SCE 1000(config)# prompt appears.
Follow the next procedure to configure auto-negotiation for the second GBE port interface
To configure speed and duplex for the second GBE port (network side) interface:
At the SCE 1000(config)# prompt, to enter the second GBE port interface, type interface GigabitEthernet 0/2, and press Enter.
The SCE 1000(config if)# prompt appears.
Type auto-negotiate and press Enter.
The SCE 1000(config if)# prompt appears.
To return to Global Configuration Mode, type exit and press Enter.
The SCE 1000(config)# prompt appears.
To exit Global Configuration Mode, type exit and press Enter.
The SCE 1000# prompt appears.
Note
Autonegotiation must be disabled when the SCE 1000 is deployed via an external optical splitter (i.e. receive-only topology).
By default, the SCE 1000 GBE line interface ports are configured with auto-negotiation disabled.
Note
Autonegotiation must be disabled when the SCE 1000 is deployed via an external optical splitter (receive-only topology)
Note
If you change any parameters, you must save the new configuration settings.
Type copy running-config startup-config, and press Enter
To enter the Global Configuration Mode, at the SCE 1000# prompt, type configure and press Enter.
The SCE 1000(config)# prompt appears.
To enter the desired GBE port interface, type interface GigabitEthernet 0/
portnumber, and press Enter, whereportnumberis the number of the selected port (1 or 2).The SCE 1000(config if)# prompt appears.
Type auto-negotiate and press Enter.
The SCE 1000(config if)# prompt appears.
To return to Global Configuration Mode, type exit and press Enter.
The SCE 1000(config)# prompt appears.
Repeat this procedure to configure auto-negotiation for the other GBE port interfaces as needed.
The following sections present the general procedure for cabling the GBE interface ports. Refer to Cabling Diagrams to find the appropriate cabling diagram for the topology of your system for the specific connections required.
Note
When installing an External Optical Bypass module, the SCE 1000 line ports are connected to the module. See Cabling the External Optical Bypass Module for complete instructions.
The following table presents the fiber specifications. The SCE 1000 may be ordered with either Multimode or Single Mode transceivers The transceiver type is indicated on the front panel under the ports. Note that both transceivers on any individual SCE 1000 are the same, either 850nm Multimode OR 1310nm Single Mode.
Table 6.1. Fiber Specifications
|
SCE Model |
Transceiver |
Transmit Power |
Receive Power |
Typical (Max.) Distance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
SCE 1000 2xGBE MM |
850nm Multimode |
–9.5 to –4 dBm |
–17 to 0 dBm |
|
|
SCE 1000 2xGBE SM |
1310nm FRP laser Single Mode |
–9.5 to –3 dBm |
–20 to 3 dBm |
10 km for 9.0µm Core Diameter SMF |
Warning
Class 1 laser. Avoid exposure to radiation and do not stare into open aperture.
To cable the SCE 1000 GBE line port, complete the following steps:
Take the appropriate fiber optic cable (see Fiber Specifications) and plug it into the appropriate GBE port on the front panel of the SCE 1000.
Make sure to push on the connector until you hear a click, which indicates that the connector is fully inserted and secured in the receptacle. Always make sure that you insert the connector completely into the socket.
Verify that the link LED is green.
If the link LED does not light, try removing the network cable plug and reinserting it firmly into the module socket.
If the SCE 1000 platform has been powered up, test now to verify that connectivity has been established on all links. If the SCE 1000 platform is not powered up, perform this step after starting the SCE 1000 platform.
The GBE Link LED must be green in order to verify that an active connection exists.
The GBE Rx and Tx LEDs (if flashing green) indicate that traffic is being received or transmitted by the SCE 1000 platform, respectively.
Note that in an inline topology, the Rx and Tx LEDs indicate that packets are being received/transmitted by the SCE 1000 platform.
In optical splitter topologies, the Rx LEDs are the sole indicators. The Tx LEDs do not “blink”, since the Tx is not connected to the port in this topology.
In inline topology, you can monitor traffic via the platform counters for both the Rx and Tx connections. The counters increase, together with the increased number of packets that flow through the SCE 1000 for both Rx and Tx.
However, in receive-only topologies, the counters for the Tx do not increment, that is, Tx does not have a function in monitoring traffic, as it is disconnected.
To view the Gigabit Ethernet port status:
Type show interface Gigabit Ethernet 0/interface number.
This displays the port link and auto-negotiation status.
Example:
The following example displays a system response.
SCE 1000#show interface Gigabit Ethernet 0/1
Auto negotiation configured: Enabled
Actual Status:
Link is on, Auto negotiation: Enabled,
Bandwidth: 100000Kbps,
Burst-size: 50000bytesAgain, auto-negotiation for bump-in-the-wire topology may be enabled or disabled. For receive-only topologies, using an external splitter, auto-negotiation must be disabled.
To view the Gigabit Ethernet counters:
Type show interface Gigabit Ethernet 0/interface counters.
This displays the Gigabit Ethernet counters. This command enables you to verify that traffic is taking place. You can see that the counters increase, together with the increased number of packets that flow through the SCE 1000.
Again, in bump-in-the-wire topology, both the Rx and Tx counters are relevant as traffic monitors. For receive-only topologies, using an external switch, only the Rx counters are relevant.
Example:
The following example shows the counters of the first Gigabit Ethernet interface:
SCE 1000#show interface Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 counters
In total octets: 100
In good unicast packets: 90
In good multicast packets: 0
In good broadcast packets: 10
In packets discarded: 0
In packets with CRC/Alignment error: 0
In undersized packets: 0
In oversized packets: 0
Out total octets: 93*2^32+1022342538
Out unicast packets: 858086051
Out non unicast packets: 0
Out packets discarded: 0You are now ready to continue to the next stage, loading and activating an Service Control Application.
The SCE 1000 platform provides the basic functionalities of Service Control analysis and enforcement. A Service Control solution requires that a Service Control application be loaded into the platform, to take advantage of the unique SCE platform capabilities.
Loading and activating an application includes the following stages:
Downloading the application provided as an SLI file to the SCE 1000 disk.
Activating the application.
Configuring the application.
The detailed procedure of how to perform these operations is not specified and described in this manual. For further details, refer to the following documentation:
Service Control Application for Broadband User Guide
Service Control Application for Broadband Reference Guide
This chapter describes how to start up the SCE 1000 platform, reboot, and shutdown. It also describes how to manage configurations.
The procedures for starting the SCE 1000 platform are explained in the following sections:
Check the following conditions before you start your SCE 1000 platform:
Both power supply units are installed and connected
First-time startup at installation:
SCE 1000 platform connected to local console (CON port)
The console terminal is turned on and properly configured
Subsequent startups
Line and Cascade interfaces are properly cabled (optional)
SCE 1000 platform is connected to at least one of the following types of management stations:
Direct connection to local console (CON port)
Remote management station via the LAN (Mng port)
You are now ready to start your SCE 1000 platform. Proceed to the section Starting the System and Observing Initial Conditions.
After installing your SCE 1000 platform and connecting cables, complete the following steps to start the SCE 1000 platform:
Make sure the power cables are connected to the SCE 1000 platform.
Plug the AC power supply cables into the AC power source, or make sure the circuit breakers at the DC panels are turned to the on position. Turn both power switches on.
Listen for the fans; you should immediately hear them operating.
During the boot process, observe the following LEDs:
Both Power LEDs should be green.
Bypass LED should be green while the SCE 1000 is on bypass and unlit when the bypass is turned off.
The Status LED should be a constant orange while booting. After a successful boot, the Status LED is flashing green.
Note
It takes a several minutes for the SCE 1000 to boot and for the status LED to change from orange to flashing orange or flashing green.
Observe the initialization process. When the system boot is complete, the console screen displays a script and system banner similar to the following:
Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software IOS (tm) 7300 Software (C7300-JS-M), Version 12.1(9), CISCO RELEASED VERSION Copyright (c) 1986-2006 by Cisco Systems, Inc. Compiled Tue 17-MAY-06 01:51 by biff Image text-base:0x40008970, data-base:0x40BF8000When you start up the SCE 1000 platform for the first time, the system automatically enters the setup wizard, which prompts you for configuration information for initial system configuration. On the console terminal, after the system displays the system banner and hardware configuration, you will see the System Configuration Dialog prompt. (Refer to Initial System Configuration for a complete description of the setup wizard.)
You have the option of proceeding with the setup wizard to configure the system, or exiting from setup and using configuration commands to configure global (system-wide) and interface-specific parameters. You do not have to configure the interfaces immediately.
If the system does not complete each of the steps in the startup procedure, proceed to Troubleshooting for troubleshooting recommendations and procedures.
The procedures for performing the final tests to verify that the SCE 1000 is functioning properly are explained in the following sections:
After all the ports are connected, verify that the SCE 1000 is not in a Warning state.
To verify that the SCE 1000 is not in a warning state, complete the following steps:
On the SCE 1000 Front panel, examine that the Status LED is flashing green.
To display the operation status of the system, at the
SCE 1000#prompt, typeshow system operation-statusand press Enter.A message displaying the operation status of the system appears. If the system is operating in order, the following message appears:
System Operation status is Operational.
Example:
The following example displays a sample output where the LEDs appear red/orange:
SCE 1000#show system operation-statusSystem Operation status is Operational
View the user log for errors that occurred during the installation process.
To display the user log device counters, complete the following steps:
At the
SCE 1000#prompt, typeshow logger device User-File-Log countersand press Enter.
Example:
The following example shows the current User-File-Log device counters.
SCE 1000#show logger device user-file-log counters
Logger device User-File-Log counters:
Total info messages: 1
Total warning messages: 0
Total error messages: 0
Total fatal messages: 0If there are “Total error messages” or “Total fatal messages”, use the show logger device User-File-Log command to display details about the errors.
The procedures for managing SCE 1000 configurations are explained in the following sections:
When you enter configuration commands, it immediately effects the SCE platform operation and configuration. This configuration, referred to as the running-config, is saved in the SCE platform volatile memory and is effective while the SCE platform is up. After reboot, the SCE platform loads the startup-config, which includes the non-default configuration as saved by the user, into the running-config.
The SCE platform provides commands for:
Viewing the running configuration
Viewing the startup configuration
After configuring the SCE platform, you may query for the running configuration using the command show running-config. This command displays the non-default running configuration. To view all SCE platform running configuration, whether it is the default or not, you may use the option all-data in the show running-config command.
To view the running configuration, complete the following steps:
At the
SCE 1000#prompt, typeshow running-config.The system shows the running configuration.
SCE 1000#show running-config #This is a general configuration file (running-config). #Created on 15:50:56 CET MON December 11 2005 #cli-type 1 #version 1 clock timezone CET 1 snmp-server community “public” ro snmp-server host 10.1.1.253 traps version 1 “public” interface LineCard 0 connection-mode active no silent no shutdown flow-aging default-timeout UDP 60 interface FastEthernet 0/0 ip address 10.1.5.109 255.255.0.0 interface FastEthernet 0/1 interface FastEthernet 0/2 exit line vty 0 4 no timeout exit SCE 1000#
One of the useful show commands is the show version command. This command displays global static information on the SCE 1000 as software and hardware version, image build time, system uptime, last open packages names and information on the SLI application assigned.
To show the version information for the SCE 1000 software and hardware, complete the following steps:
At the
SCE 1000#prompt, typeshow version.The system shows the version information.
SCE 1000#show version System version: Version 3.0.0 Build 240 Build time: Jan 11 2006, 07:34:47 Software version is: Version 2.5.2 Build 240 Hardware information is: rx : 0x0075 dp : 0x1808 tx : 0x1708 ff : 0x0077 cls : 0x1721 cpld : 0x0025 Lic : 0x0176 rev : G001 Bootrom : 2.1.0 L2 cache : Samsung 0.5 lic type : MFE optic mode : Part number: 53AA-BXC1-AAAA Revision: A02A Software revision: G001 Serial number: 043P6982 Power Supply type: AC SML Application information is: Application file: /tffs0/temp.sli Application name: Application help: Original source file: H:\work\Emb\jrt\V2.5\sml\actions\drop\drop_basic_anyflow.san Compilation date: Wed, December 21 2005 at 21:25:21 Compiler version: SANc v2.50 Build 32 gcc_codelets=true built on: Tue December 23 2005 09:51:57 AM.;SME plugin v1.1 Default capacity option used. Logger status: Enabled Platform: SCE 2000 - 4xFE Management agent interface version: SCE Agent 3.0.0 Build 18 Software package file: ftp://vk:vk@10.1.8.22/P:/EMB/LatestVersion/3.0.0/se1000.pkg SCE 2000 uptime is 21 minutes, 37 seconds SCE 1000#
Another useful show command is the show system-uptime command. This command displays information similar to the last line above, which indicates how long the system has been running since the last reboot.
To show the system uptime for the SCE platform software and hardware, complete the following steps:
At the
SCE 1000#prompt, typeshow system-uptime.The system shows how long the system has been running since the last reboot.
SCE 1000#show system-uptime SCE 1000 uptime is 21 minutes, 37 seconds SCE 1000#
When you make changes to the current running configuration and you want those changes to continue to be valid when the system restarts, you must save the changes before leaving the management session, that is, you must save the running configuration to the startup configuration file.
The SCE platform provides multiple interfaces for the purpose of configuration and management. All interfaces supply an API to the same database of the SCE platform and any configuration made through one interface is reflected through all interfaces. Furthermore, when saving the running configuration to the startup configuration from any management interface, all configuration settings are saved regardless of the management interface used to set the configuration.
To save configuration changes, complete the following steps:
At the
SCE 1000#prompt, typeshow running-configto view the running configuration.The running configuration is displayed.
Check the displayed configuration to make sure that it is set the way you want. If not, make the changes you want before saving.
Type
copy running-config startup-config.The system saves all running configuration information to the configuration file, which is used when the system reboots.
The configuration file holds all information that is different from the system default in a file called config.txt located in the directory: tffs0:system.
Example:
The following example shows the running configuration file.
SCE 1000#show running-config
#This is a general configuration file (running-config).
#Created on 15:50:56 CET MON February 11 2006
#cli-type 1
#version 1
clock timezone CET 1
snmp-server community “public” ro
snmp-server host 10.1.1.253 traps version 1 “public”
interface LineCard 0
connection-mode active
no silent
no shutdown
flow-aging default-timeout UDP 60
interface FastEthernet 0/0
ip address 10.1.5.109 255.255.0.0
interface FastEthernet 0/1
interface FastEthernet 0/2
exit
line vty 0 4
no timeout
exit
SCE 1000#
SCE 1000#copy running-config startup-config
Writing general configuration file to temporary location...
Backing-up general configuration file...
Copy temporary file to final location...
SCE 1000#For backup purposes, the old startup-config file is saved under the directory: tffs0:system/prevconf. Refer to Recovering a Previous Configuration for an explanation on how to recover previous configuration.
To remove a configuration command from the running-config, use the no form of the command.
Example:
The following example illustrates how to remove all DNS settings from the running configuration.
SCE 1000(config)#no ip name-server
SCE 1000(config)#When you save a new configuration, the system automatically backs up the old configuration in the directory tffs0:system/prevconf/. Up to nine versions of the startup configuration file are saved, namely config.tx1-config.tx9, where config.tx1 is the most recently saved file.
You can view the old startup configuration files using the CLI command more.
Restoring a previous startup configuration means renaming the file so it overwrites the startup configuration (config.txt) file.
To restore a previous startup configuration, complete the following steps:
At the
SCE 1000#prompt, typemore tffs0:system/prevconf/config.txtto view the configuration file.The system displays the configuration information stored in the file.
Read the configuration information to make sure it is the configuration you want to restore.
Note that you cannot undo the configuration restore command.
Type
copy tffs0:system/prevconf/config.tx1 tffs0:system/config.txt.The system sets the startup configuration to the configuration from config.tx1.
Example:
The following example displays a saved configuration file and then restores the file to overwrite the current configuration.
SCE 1000#more tffs0:system/prevconf/config.tx1
#This is a general configuration file (running-config).
#Created on 19:36:07 UTC THU February 14 2006
#cli-type 1
#version 1
interface LineCard 0
no silent
no shutdown
interface FastEthernet 0/0
ip address 10.1.5.109 255.255.0.0
interface FastEthernet 0/1
interface FastEthernet 0/2
exit
line vty 0 4
exit
SCE 1000#copy tffs0:system/prevconf/config.tx1 tffs0:system/config.txt
SCE 1000#After you have installed your SCE 1000 platform hardware, checked all external connections, turned on the system power, allowed the system to boot up, and performed the initial system configuration, you might need to perform more complex configurations, which are beyond the scope of this publication.
For further information on system and interface configuration, refer to the following documents:
Cisco Service Control Engine (SCE) Software Configuration Guide
Cisco Service Control Engine (SCE) CLI Command Reference
Rebooting the SCE platform is required after installing a new firmware, in order for that firmware to take effect. There might be other occasions where rebooting the SCE platform is necessary.
Note
When the SCE restarts, it loads the startup configuration, so all changes made in the running configuration will be lost. You are advised to save the running configuration before performing reload, as described in Saving the Configuration Settings.
To reboot your SCE platform, complete the following steps:
At the
SCE 1000#prompt, typereloadand press Enter.A confirmation message appears.
Type
Yto confirm the reboot request and press Enter.
Example:
The following example shows the commands for system reboot.
SCE 1000# reload
Are you sure? y
the system is about to reboot, this will end your CLI sessionShutting down the SCE platform is required before turning the power off. This helps to ensure that non-volatile memory devices in the SCE platform are properly flushed in an orderly manner.
Note
When the SCE platform restarts, it loads the startup configuration, so all changes made in the running configuration will be lost. You are advised to save the running configuration before performing reload, as described in Saving the Configuration Settings.
To shut down your SCE platform, complete the following steps:
Connect to the serial console port (The CON connector on the SCE platform front panel, 9600 baud).
The SCE 1000# prompt appears.
Type
reload shutdown.A confirmation message appears.
Type
Yto confirm the shutdown request and press Enter.
Example:
The following example shows the commands for system shutdown.
SCE 1000#reload shutdown
You are about to shut down the system.
The only way to resume system operation after this
is to cycle the power off, and then back on.
Continue?
y
IT IS NOW SAFE TO TURN THE POWER OFF.Note
Since the SCE platform can recover from the power-down state only by being physically turned off (or cycling the power), this command can only be executed from the serial CLI console. This limitation helps prevent situations in which a user issues this command from a Telnet session, and then realizes he/she has no physical access to the SCE platform.
Your SCE 1000 platform went through extensive testing before leaving the factory. However, if you encounter problems starting it, use the information in this chapter to help isolate the cause of the problems. The procedures in this chapter assume that you are troubleshooting the initial system startup, and that your SCE 1000 platform is in the original factory configuration. If you have removed or replaced components or changed any default settings, the recommendations in this chapter might not apply. Make sure to review the safety warnings listed in the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco Service Control Engine document that accompanied your SCE 1000 platform before using the troubleshooting procedures in this chapter.
This section describes the troubleshooting methods used in this chapter and describes how the SCE 1000 platform is divided into subsystems for more efficient problem solving. If you are unable to easily solve the problem, contact a customer service representative for assistance and further instructions. Provide the representative with the following information:
Date you received the router
Chassis serial number
Type of software and release number
Brief description of the problem you are having
Brief explanation of the steps you have taken to isolate and resolve the problem
Maintenance agreement or warranty information
The following table shows the general troubleshooting strategy described in this chapter. Refer to this table, as necessary, to follow the steps to isolate problems to a specific subsystem and resolve the problem if possible.
Table 8.1. Troubleshooting Strategy for Startup Problems
|
Action |
Yes |
No | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 |
Turn power on. Go to Step 2 |
|
|
|
Step 2 |
Power A/Power B LEDs on? |
Go to Step 3 |
Refer to Troubleshooting the power subsystem and go to Step 3. |
|
Step 3 |
Status LED red (failure) |
Refer to Troubleshooting the firmware package installation and go to Step 4. |
Go to Step 4 |
|
Step 4 |
Management interface operational? |
Go to Step 5 |
Refer to Troubleshooting the management subsystem and go to Step 4. |
|
Step 5 |
Link interfaces operational? |
Go to Step 6 |
Refer to Troubleshooting the link interface subsystem and go to Step 5. |
|
Step 6 |
System startup successful (all interfaces operating normally). |
¾ |
¾ |
There are three tools that will help you to successfully troubleshoot your SCE 1000 installation:
Check the LEDs
Use the following commands to provide information to help you troubleshoot installation of your SCE 1000 platform. Refer to Cisco Service Control Engine (SCE) Software Configuration Guide or the Cisco Service Control Engine (SCE) CLI Command Reference for more information.
Note
Remember that if the management interface is not operational, you should connect the SCE 1000 platform to a local console so that you can enter CLI commands for troubleshooting.
Troubleshooting firmware package installation:
Boot system<filename> —Specifies and verifies the package file to be installed. Error messages or other output identify problems with the package file.Following is a sample output from the
Boot systemcommand.SCE 1000(config)#boot system ftp://vk:vk@10.1.1.230/downloads/SENum.pkg.pkg Verifying package file SENum.pkg.pkg… Package file verified OK.
Troubleshooting the management subsystem:
show interface
Mng—Displays IP address and auto-negotiation information for the management interfaces.Following is a sample output from the show interface
Mngcommand.ip address: 10.1.6.145 subnet mask: 255.255.0.0 Configured speed: auto, configured duplex: auto AutoNegotiation is On, link is Up, actual speed: 100, actual duplex: halfshow ip default-gateway — Displays the IP address of the configured default gateway.
Following is a sample output from the show ip default-gateway
Default gateway: 10.1.1.1show ip route — Displays the entire routing table and the destination of last resort (default-gateway).
Following is a sample output from the show ip route
gateway of last resort is 10.1.1.1
show access-lists — Shows all access-lists or a specific access list.
Following is a sample output from the show access-lists
Standard IP access list 1 Permit 10.1.1.0, wildcard bits 0.0.0.255 deny anyshow telnet — Displays the status of the telnet server daemon (
status) or any active Telnet sessions (sessions).Following is a sample output from the show telnet
show telnet sessions There is 1 active telnet session: Index | Source ================ 0 | 10.1.1.201 show telnet status Telnet deamon is enabled.show line vty timeout — Shows the timeout configured for Telnet sessions.
Following is a sample output from the show line vty timeout command.
Timeout is 30 minutes
Troubleshooting the link interface subsystem:
show interface
GigabitEthernet 0/# —Displays information for a specific GBE Interface.Following is a sample output from the show interface
ip address: 10.1.6.145 subnet mask: 255.255.0.0 Configured duplex: auto AutoNegotiation is On, link is Up, actual duplex: half
show interface
GigabitEthernet 0/#counters — Displays the values of counters of a GBE interface.Following is a sample output from the show interface
counterscommand.In total octets: 191520 In good unicast packets: 560 In good multicast packets: 0 In good broadcast packets: 0 In packets discarded: 0 In packets with CRC/Alignment error: 0 In undersized packets: 0 In oversized packets: 0 Out total octets: 0 Out unicast packets: 0 Out non unicast packets: 0 Out packets discarded: 0
Refer to The User Log for an explanation of commands related to the user log.
The user log is an ASCII file that can be viewed in any editor. It contains a record of system events, including startup, shutdown and errors. You can use the Logger to view the user log to determine whether or not the system is functioning properly, as well as for technical support purposes.
Events are logged to one of two log files. After a file reaches maximum capacity, the events logged in that file are then temporarily archived. New events are then automatically logged to the alternate log file. When the second log file reaches maximum capacity, the system then reverts to logging events to the first log file, thus overwriting the temporarily archived information stored in that file.
Basic operations include:
Copying the User Log to an external source
Viewing the User Log
Clearing the User Log
Viewing/clearing the User Log counters
You can view the log file by copying it to an external source or to disk. This command copies both log files to the local SCE platform disk or any external host running a FTP server.
Note
This command is not recommended when the user log is large. Copy a large log to a file to view it (see Copying the User Log)
You can clear the contents of the user log at any time. The user log contains important information regarding the functioning of the system. It is recommended that a copy be made before the log is cleared.
There are two types of log counters:
User log counters — count the number of system events logged from the SCE platform last reboot.
Non-volatile counters — are not cleared during boot time
To view the user log counters for the current session, use the following command:
From the
SCE 1000#prompt, typeshow logger device user-file-log countersand press Enter.The logger lines information appears, followed by the
SCE 1000#prompt.
In order for technical support to be most effective, the user should provide them with the information contained in the system logs. Use the logger get support-file command to generate a support file for the use of Cisco technical support staff.
The front panel LEDS are the most immediate problem-detection mechanism of the platform. Refer to the following sections for information on SCE 1000 platform LEDS:
The following table lists the operational states of the SCE 1000. The Status LED on the SCE 1000 Front Panel reflects the current SCE 1000 operational status. The operational status can be displayed using CLI command show system operation-status.
Table 8.2. SCE 1000 Operational States
|
SCE 1000 Operational Status |
Description |
Status LED State |
|---|---|---|
|
Booting |
Initial state after reset |
Orange |
|
Operational |
SCE 1000 becomes operational after completing the following process:
|
Flashing green |
|
Warning |
SCE 1000 is fully operational (as above) but one of the following occurred:
Note: If the condition that caused the SCE 1000 to be in Warning state is resolved (for example, link is up) the SCE 1000 reverts to Operational state. |
Flashing orange |
|
Failure |
System is in Failure state after Boot due to one of the following conditions:
Note: Depending on the cause of failure, the management interface and the platform configuration may or may not be active/available. |
Red |
Startup problems are commonly due to the source power or to a poor cable connection.
When you start up the SCE 1000 platform for the first time, you should observe the startup sequence described in the Starting the SCE 1000 Platform. This section contains a more detailed description of the normal startup sequence and describes the steps to take if the system does not perform that sequence as expected. LEDs indicate all system states in the startup sequence. By checking the state of the LEDs, you can determine when and where the system failed in the startup sequence. Use the following descriptions to isolate the problem to a subsystem, and then proceed to the appropriate sections to try to resolve the problem.
When you start up the system by turning on the power supply switch, the following should occur:
You should immediately hear the fans operating.
When all LEDs come on to indicate that the system has booted successfully, the initial system banner should be displayed on the console screen. If it is not displayed, see Connecting the Local Console to verify that the terminal is set correctly and that it is properly connected to the console port.
If the banner is displayed, but the Status LED is flashing orange, indicating a warning state, check the user log:
At the prompt, type:
more user logIf any of the following warning messages appear, turn the SCE 1000 platform off and call technical support.
"voltage problem:"
"fans problem"
"abnormal raise in interior temperature:"
If the following warning message appears, delete unneeded files from the disk.
“insufficient disk space:”
Check the following to help isolate a problem in the power subsystem. In the normally configured SCE 1000 platform with redundant power supply units, it is unlikely that the device will not start at all. However, at startup it should be verified that both power supply units are operational, and therefore the following steps should be followed if one of the Power LEDs on the front panel remains unlit when the SCE 1000 platform is powered up.
Note
If the system powers off due to an environmental shutdown, wait at least one minute before manually rebooting the system, or it will pause indefinitely.
Table 8.3. Troubleshooting the Power Subsystem
|
Symptom |
Possible Cause |
Possible Solution |
|---|---|---|
|
Power LED on the front panel and LEDs on the power supply unit are not lit, or do not remain lit continuously. |
Power cable not fully seated at system. |
Turn the power switch to the off position and reseat the power cable in the system. |
|
|
Power cable not fully seated at source. |
Turn the switch to the off position and reseat the power cable at the power source. |
|
|
Power source is faulty. |
Turn the switch to the off position, connect the power cable to another power source, if available, and turn the switch back on. |
|
|
Faulty power cable. |
Turn the switch to the off position, remove the cable and replace it. |
|
|
Faulty power supply. |
If the system still fails to come up when the power supply is connected to a different power source with a new power cable, the power supply unit is probably faulty. Contact a service representative. |
Table 8.4. Power Supply LEDs
|
LED Label |
Color |
State |
Function |
|---|---|---|---|
|
IN |
Green |
On |
The input voltage is in the required range. |
|
|
|
Off |
The input voltage is not in the required range. |
|
OK |
Green |
On |
The output voltage is in the required range (between 11.9 and 12.1 VDC). |
|
|
|
Off |
The output voltage is not within the required range (is greater than 12.1 VDC or less than 11.9 VDC). |
|
Power A/B (front panel) |
Green |
Steady |
Corresponding power supply unit is present and functioning normally. |
|
|
Red |
Steady |
Corresponding power supply unit present, but malfunctioning. |
|
|
|
Off |
Corresponding power supply unit is either not present or has failed. |
Check the following to help isolate a problem in the installation of the firmware package.
Problems related to the installation of the firmware package could be any of the following:
File not found in the expected location
Wrong file type.
Device to which the file is to be extracted is full.
Table 8.5. Troubleshooting the Firmware Package Installation
|
Diagnostic Action | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Enter the CLI command:
| ||
|
Symptom |
Possible Cause |
Possible Solution |
|
Returned error is:
|
The package file does not exist in the specified location. |
Verify package file location and try again. |
|
In the output of the command, the package file type is |
Package file type mismatch. |
Verify that you are trying to open the correct package file. |
|
In the output of the command, the package file platform is not the correct installation file for the SCE 1000. |
Package file platform mismatch. |
Verify that you have the package file appropriate to your platform type. |
|
Returned error is:
|
The file is not a software installation package file. |
Verify that you are trying to open the correct package file. |
|
Returned error is:
|
/tffs0/ device is full. |
Delete old and unnecessary files and try the package extraction again. |
Check the following to help isolate a problem in the management subsystem.
Problems in the management subsystem could be any of the following:
Management link is down. (Mng LINK LED not lit--also Status is WARNING)
Management link is up (Mng LINK LED lit) but does not answer ping
Telnet connection cannot be established due to link problems (Mng LINK LED not lit)
Management link is up (Mng LINK LED lit) but Telnet connection cannot be established
Telnet connection established, but terminates automatically
Note
When the management link is down and/or a Telnet connection cannot be established, you must open a CLI session on a local terminal connected to the CON port. This enables you to solve the problem and then reconnect through the management port.
Table 8.6. Troubleshooting the Management Subsystem
|
Symptom |
Diagnostic Action |
Possible Cause |
Possible Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Management link down:
|
show interface
|
RJ 45 connector is not connected to the platform or to the network. |
Reconnect the cable to the Mng port and to network. |
|
|
|
Cable not connected to configured Mng port. |
Reconnect the cable to the appropriate port or reconfigure active port.
|
|
|
|
Cable is broken. |
Check / Replace the cable. |
|
Management link up:
|
CLI commands
|
One of the following configurations may be wrong:
|
See Initial System Configuration Refer to "IP Configuration" in the Cisco Service Control Engine (SCE) Software Configuration Guide. |
|
|
CLI command show access-lists |
An ACL may be assigned that denies entry. |
See Initial System Configuration Refer to "Access Control Lists" in the Cisco Service Control Engine (SCE) Software Configuration Guide. |
|
show interface |
Management interface IP address or subnet mask is incorrect. |
Check / reconfigure management port IP address and subnet mask |
|
CLI command: show telnet status |
Telnet server is disabled. |
Enable Telnet server: service telnetd |
|
|
CLI command: show telnet sessions |
Too many Telnet connections (up to 5 concurrent sessions are supported). |
Close one or more of the open Telnet sessions. |
|
|
CLI command: show ip default-gateway |
Default gateway is incorrect (when the host used as client is not in the same network as the SCE Platform). |
Check / reconfigure default gateway. See Initial System Configuration Refer to "IP Configuration" in the Cisco Service Control Engine (SCE) Software Configuration Guide. |
|
|
CLI command:
|
Routing tables are incorrectly configured (when the host used as client is not in the same network as the SCE Platform, and there is more than one gateway on the SCE Platform network). |
Check / reconfigure routing tables. See Initial System Configuration Refer to "IP Configuration" in the Cisco Service Control Engine (SCE) Software Configuration Guide. |
|
|
CLI commands:
|
Host is not a member of a valid access-list. |
Check / reconfigure access-list. See Initial System Configuration Refer to "Access Control Lists" in the Cisco Service Control Engine (SCE) Software Configuration Guide. |
|
Telnet connection terminates automatically
|
CLI commands:
|
Telnet connection may be timing out. |
Reconfigure line timeout. timeout <time in seconds> |
Check the following to help isolate a problem in the link interface subsystem.
In general, the case where no traffic is coming out of the SCE 1000 is often caused by link problems or GBE interface configuration. Note that in some cases, the problem which seems as a transmit problem could be in the Rx (no traffic is being received by the SCE 1000 or there is actually no traffic on the line, which could be a normal situation).
Note
In CLI commands of GigabitEthernet interfaces, # stands for the number of the interface. This can be 1 or 2.
Problems in the link interface subsystem could be any of the following:
Link is down. (LINK LED not lit and system status is WARNING)
Peer does not receive traffic from SCE 1000 (GBE link is lit and Tx LED is flashing)
GBE link is up but not receiving from peer (GBE link is lit, but Rx LED is not flashing)
Table 8.7. Troubleshooting the Link Interface Subsystem
|
Symptom |
Diagnostic Action |
Possible Cause |
Possible Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
|
CLI command:
|
Connector is not connected to the platform or to the network |
Reconnect the cable to the GBE port and to network. |
|
|
|
GBE cable is broken
|
Reconnect / replace the cable to the GBE port. |
|
|
|
|
If GBE counters are incrementing, this indicates LED problem. Contact customer support. |
|
|
Check output of show interface |
Auto-negotiation may be incorrectly configured. |
Check auto-negotiation configuration in the SCE 1000 and in its peers. |
|
CLI commands:
Check printout of this command for: “Out unicast packet”. This counter should be constantly incrementing.
|
Auto-negotiation is disabled at the SCE 1000 but enabled at peer. |
Check auto-negotiation configuration in the SCE 1000 and in peer. |
|
|
No traffic is being transmitted to the SCE 1000 from its peers |
Check traffic connection at pee |
|
|
|
Auto-negotiation is disabled at the SCE 1000 but enabled at peer |
Check auto-negotiation configuration in the SCE 1000 and in peer. |
The SCE 1000 platform External Optical Bypass module preserves the service provider GBE links in case of complete power failure of the SCE 1000 platform, or for implementing a maintenance window.
The SCE 1000 platform state-of-the-art Service Control platform is being deployed at ISPs, Cable and Wireless Tier1 provider networks, and is therefore required to comply with the carrier grade availability requirements of these mission critical networks.
The SCE 1000 platform already includes an internal Electrical Bypass module that puts the SCE 1000 platform into bypass state in case of a software or hardware failure at the platform main board, thereby preserving the GBE network link.
The External Optical Bypass module provides additional service protection by enabling automatic preservation of the network GBE link in two additional important scenarios:
Complete loss of power in the SCE 1000 platform — The SCE 1000 platform includes redundant Power Supply Units and redundant power feeds, in both the DC and AC versions. However, in case either both PSUs fail, or both power feeds stop providing power to the SCE 1000 platform simultaneously, the network link will be preserved by the External Optical Bypass module.
Maintenance window implementation — In certain situations the SCE 1000 platform should be pulled from the network for replacement, such as:
Hardware failure in the SCE 1000 platform.
Hardware upgrade on the SCE 1000 platform
In these cases, a maintenance window is implemented, during which the SCE 1000 platform is pulled from the network. It may be replaced by another SCE 1000 platform, either almost immediately, or after several hours or days. An External Optical Bypass module enables the implementation of such replacement while preserving normal operation of the network link.
The External Optical Bypass module is another important component in the Cisco overall carrier-grade solution for high-availability service provider networks.
The External Optical Bypass module is connected bump-in-the-wire in the GBE link. It is then connected to the SCE 1000 platform with two types of connections:
GBE optical connections for data link traffic — GBE connections from the External Optical Bypass module to both GBE line ports.
Power and Control connection — Connection to a dedicated connector on the SCE 1000 platform back panel, so the SCE 1000 platform can provide power to the External Optical Bypass module. (Note that the power connection also provides the logical control functionality.)
The External Optical Bypass module is normally inactive, (not in bypass), and simply transfers the two GBE signals to and from the SCE 1000 platform.
In case the SCE 1000 platform stops providing power to the External Optical Bypass module, or in case the power cable is disconnected from the optical bypass module, the External Optical Bypass module becomes active, bypassing the two GBE links to the SCE 1000 platform, and thus preserving network connectivity.
The figure below illustrates the operation of the bypass module when it is inactive (not in bypass). The data traffic is simply transferred through the bypass module to the SCE 1000 platform.
The figure below illustrates the operation of the bypass module when it is active (in bypass). The data traffic flows through the bypass module, and the GBE link no longer includes the SCE 1000 platform. Note that when the bypass module is active, it puts the SCE 1000 platform into a loop connection, creating a shortcut between the SCE 1000 platform GBE interfaces.
The front panel of the External Optical bypass module contains the following components:
SUB Rx/Tx — GBE port that connects to the network element on the Subscriber side of the link.
NET Rx/Tx — GBE port that connects to the network element on the Network side of the link.
CONTROL — RJ-45 port that connects to the Bypass connector on the rear panel of the SCE 1000 platform. The SCE 1000 platform controls the External Optical Bypass module via this connection, by the presence or absence of electrical power.
Pigtail fiber connectors — Four fiber cables that connect to the GBE link ports on the front panel of the SCE 1000 platform
NET Tx
NET Rx
SUB Tx
SUB Rx
No Bypass LED:
ON = Bypass module is not active (GBE traffic flows through the SCE 1000 platform)
OFF = Bypass module is active (GBE traffic flows through the bypass module)
Installation of the External Optical Bypass module requires two main steps, which are described in detail in the following sections.
The following procedure describes how to install the module in the rack.
Note that, although each module is shipped with its own mounting panel, it is not necessary to install each module in a separate mounting panel. Up to three modules may be installed in one mounting panel.
To install the External Optical Bypass module in a 19" rack, complete the following steps:
Using the screws attached to the module, screw it into an empty position in the mounting panel.
Secure the module panel to the two front posts of the rack above the SCE 1000 platform. Leave at least 1.5 cm vertical clearance between the SCE 1000 platform and the module panel to provide space for the cables from the front panel of the module to the rear of the SCE 1000 platform.
The module can now be cabled as explained in the next section.
Note
If only one or two External Optical Bypass modules are deployed in one panel, the empty third position can be used for transferring the cables, thus saving rack space.
The following procedure describes how to cable the External Optical Bypass module. Note the following:
All connections to the External Optical Bypass module are on the front panel of the module.
Connect the fiber (steps 3 and 4) to the GBE ports 1 and 2 on the front panel of the SCE 1000 platform.
Connect the control cable to the Bypass 9-pin D-Type connector on the rear of the SCE 1000 platform.
The following figure illustrates the connectivity of the External Optical Bypass module.

To cable the External Optical Bypass module:
Connect an optical cable (user supplied) between the GBE port on the Subscriber side network element and the SUB port on the External Optical Bypass module.
Connect an optical cable (user supplied) between the GBE port on the Network side network element and the NET port on the External Optical Bypass module.
Verify that the links between the two network elements are active.
Connect the SUB cable of the fiber of the External Optical Bypass module to the SUB GBE port of the SCE 1000 platform.
Rx <-> Tx
Connect the NET cable of the fiber of the External Optical Bypass module to the NET GBE port of the SCE 1000 platform.
Rx <-> Tx
Power up the SCE 1000 platform, as explained in Starting the System and Observing Initial Conditions.
Warning
Auto-Negotiation should be configured identically for the two SCE 1000 platform GBE interfaces and the GBE interfaces of the switch/router on either side of the External Optical Bypass module.
It is recommended that the two GBE interfaces of the SCE 1000 platform, as well as the GBE interfaces of the switch/router on either side of the External Optical Bypass module, should be configured to Auto-Negotiation = OFF
Verify that the relevant GBE interfaces of the SCE 1000 platform are now in sync, as the External Optical Bypass module is now active (in bypass), and is performing a loop back on these interfaces.
Connect the control cable (supplied in the kit) from the Bypass 9-pin D-Type connector on the rear panel of the SCE 1000 platform to the Control connector on the External Optical Bypass module.
The SCE 1000 platform immediately starts providing power to the External Optical Bypass module, so the bypass module becomes inactive, and starts transferring the traffic to the SCE 1000 platform. The “No Bypass” LED should therefore be lit.
|
Item |
Value |
|---|---|
|
Optical Connectors |
SC |
|
Switching Speed |
15 ms max |
|
Operating Wavelength |
|
|
Operating Temperature |
-10° C to +65° C (14° F to 149° F) |
|
Storage Temperature |
-30° C to +70° C (-22° F to 158° F) |
|
Weight |
12 oz (340 g) |
Table A.1. Control cable pinouts
|
Function |
Pin (D-type side) |
Pin (RJ-45 side) |
|---|---|---|
|
Bypass Present (common to 2) |
1 |
1 |
|
Bypass Present (common to 1) |
2 |
2 |
|
GND |
3 |
3 |
|
GND |
4 |
4 |
|
+5V |
5 |
5 |
|
+5V |
6 |
6 |
|
-- |
7-NC |
7 |
|
-- |
8-NC |
8 |
|
-- |
9-NC |
-- |
|
Shield |
Shield |
Shield |