|
|

This chapter gives a brief overview of the various areas where you might need troubleshooting and contains the following sections:
This ATM and Layer 3 Switch Router Troubleshooting Guide describes troubleshooting procedures for the following ATM switch routers:
The Catalyst 8500 series and LightStream 1010 hardware and software provide flexibility and performance in a single integrated ATM switch router. For example, your switch router could be configured to provide Layer 3 enabled ATM functionality, delivered through the ATM router module (ARM), which provides routing between ATM and Layer 3 interfaces on a single platform. Or, your switch could be configured to function as a simple ATM backbone switch with no Layer 3 connectivity at all.
To eliminate redundancy and allow you to quickly find your troubleshooting information, this guide is separated into the following parts:
Basic troubleshooting processes, such as troubleshooting Ethernet connections, not specific to the ATM switch router, are not described in this document. This information is found online in other troubleshooting guides such as the Internetwork Troubleshooting Guide.
Figure 1-1 illustrates the general problem-solving model. This process is not a rigid outline for troubleshooting an internetwork. It is a foundation on which you can build a problem-solving process for your environment.
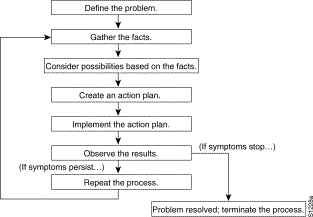
The following steps detail the problem-solving process outlined in Figure 1-1:
Step 1 Analyze the network problem and create a clear problem statement. Define symptoms and potential causes.
Step 2 Gather the facts you need to help isolate possible causes.
Step 3 Consider possible causes based on the facts you gathered.
Step 4 Create an action plan based on those causes. Begin with the most likely problem and devise a plan in which you manipulate only one variable.
Step 5 Implement the action plan, performing each step carefully while testing to see whether the symptom disappears.
Step 6 Analyze the results to determine whether the problem has been resolved. If it has, the process is complete.
Step 7 If the problem has not been resolved, create an action plan based on the next most probable cause on your list. Return to Step 4 and repeat the process until the problem has been solved.
Make sure that you undo anything you changed while implementing your action plan. Remember that you want to change only one variable at a time.
 |
Note If you exhaust all the common causes and actions (either those outlined in this publication or others that you have identified in your environment), contact customer service. See "Technical Support," for additional information. |
1. Do you have an accurate physical and logical map of your internetwork that outlines the physical location of all of the devices on the network and how they are connected, as well as a logical map of network addresses, network numbers, and subnetworks?
2. Do you have a list of all network protocols implemented in your network for each of the protocols implemented and a list of the network numbers, subnetworks, zones, and areas that are associated with them?
3. Do you know which protocols are being routed and the correct, up-to-date configuration information for each protocol?
4. Do you know which protocols are being bridged? Are there any filters configured in any of these bridges, and do you have a copy of these configurations?
5. Do you know all the points of contact to external networks, including any connections to the Internet? For each external network connection, do you know what routing protocol is being used?
6. Has your organization documented normal network behavior and performance so that you can compare current problems with a baseline?
If you can answer yes to these questions, then you should be able to recover from a failure quickly and easily.
This section describes where to find troubleshooting, installation, and configuration information for non-ATM related switch router problems, and includes:
Refer to the following publications for ATM-specific software configuration and command reference information:
Refer to the following publications for more detailed information about booting problems or specific hardware, including descriptions of specific LEDs and configurations and additional troubleshooting information:
The information referred to in this guide is by no means comprehensive. Instead, it offers solutions to the problems most commonly encountered when using Ethernet media.
 |
Note To troubleshoot ATM physical interface connections, refer to "Troubleshooting Switch Router ATM Interface Connections." |
Refer to the following publications for more detailed information about booting problems or specific hardware, including descriptions of specific LEDs, configuration, and additional troubleshooting information:
Refer to the Internetwork Troubleshooting Guide for general information describing Ethernet LAN media problems.
Refer to the Processor Installation Guide (Catalyst 8510 MSR and LightStream 1010) for more detailed information about specific Ethernet, auxiliary and console port connections, including descriptions of specific LEDs and configurations, and additional troubleshooting information.
Refer to the Internetwork Troubleshooting Guide for general information describing Ethernet, auxiliary, and console port connection problems.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Mon Sep 30 13:18:59 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.