|
|

The Cisco Virtual Point-of-Presence Dial Access Platform (VPOP-DAP) Solution is a distributed system used for interconnecting Cisco network access servers (NASs) to a circuit-switched TDM network using Signaling System #7 (SS7) protocols for signaling. The interconnections are achieved using a protocol conversion platform called the Cisco Signaling Controller combined with the Cisco Signaling Link Terminal. The Cisco SC2200 comprises the hardware and software package that provides the signaling controller function in the Cisco VPOP-DAP Solution. It provides high availability, high performance, and key scaling.
When large points of presence (POPs) receive calls from the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), the traffic is running over legacy architectures that use in-band signaling (such as Integrated Services Digital Network Primary Rate Interfaces (ISDN PRIs), in-band channel-associated signaling (CAS), or single analog lines) rather than out-of-band signaling like SS7. With both signaling and bearer traffic running over the lines, these legacy switches become congested with modem traffic and limited circuits. Cisco offers the Cisco VPOP-DAP Solution that offloads the signaling to an out-of-band network so that available bandwidth increases.
The Cisco VPOP-DAP Solution is a distributed system that adds SS7 signaling interfaces to large ISP POPs. SS7 interfaces are connected to the PSTN by using the same signaling technology as a PSTN switch. The Cisco VPOP-DAP Solution consists of the Cisco signaling controller (also referred to as the Cisco SC2200 product), which includes the Cisco Signaling Link Terminal (Cisco SLT) and the network access server (NAS). The Cisco VPOP-DAP Solution turns a POP into an end-office switching system in the PSTN, allowing direct peer-to-peer signaling connectivity. The POP, as a switch, connects directly to the rest of the network as a peer. After connections to the Internet are aggregated at a POP, streams of user packets are statistically multiplexed for efficient transport over the backbone network.
Figure 1-1 illustrates the PSTN-to-POP network without a Cisco VPOP-DAP Solution. Because of Internet and additional data calls with hold times that average 30 minutes, the PSTN network experiences more busy signals and overloads network resources.
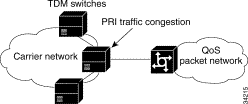
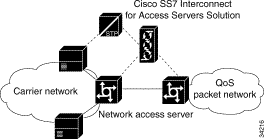
Figure 1-2 illustrates where the Cisco VPOP-DAP Solution is located when it is dropped into a PSTN, so as to offload calls. Note that the NAS are connected with a Cisco SS2200. By placing the Cisco VPOP-DAP Solution as close to the ingress switch as possible, data traffic ties up fewer PSTN resources. The direct connection of the Cisco VPOP-DAP Solution to the SS7 network provides advantages such as faster call setups and teardowns, as well as SS7's look-ahead capabilities for rerouting to avoid downed network nodes and links.
The Cisco SC2200 product is a signaling controller (SC) that converts telephony signals from one format to another. For example, the Cisco SC2200 converts Signaling System 7 (SS7) signaling information from the PSTN to the signaling format required to establish calls between the PSTN and a packet data network.
The Cisco SC2200 product is part of the Cisco Media Gateway Controller (MGC) product line. The Cisco MGC product line consists of hardware and software packages that you can use to connect your packet data network to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). Cisco MGC products manage call signaling conversion between the PSTN and the packet data network, and depending on the product, Cisco MGC products can control the routing of calls across the PSTN or packet data network.
 |
Note Your Cisco VPOP-DAP Solution documentation suite includes Cisco media gateway controller (MGC) reference books. |
 |
Note Some product labels and packaging might use the term telephony controller. Any references to the telephony controller apply to the media gateway controller (MGC). |
The Cisco VPOP-DAP Solution architecture, shown in Figure 1-3, provides SS7 signaling connectivity for network access servers (NASs) to operate in an environment where SS7 is used to establish calls on bearer channels on T1/E1 trunks connected to the NAS.
The solution consists of the following required components that are described in more detail in the Cisco VPOP-DAP Solution Components section of this document:
| | ||
| | ||
| | ||
| |
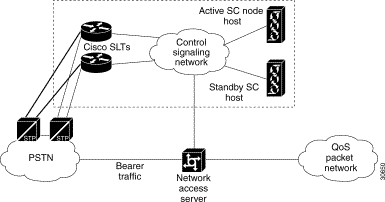
The following key terms are used in this document to describe the Cisco VPOP-DAP Solution architecture:
Using the Cisco VPOP-DAP Solution provides the following benefits:
Table 1-1 briefly lists features that are provided with your Cisco VPOP-DAP Solution. For an overview of scalability and performance, system redundancy, management, and software requirements, see subsequent sections of this document.
| Feature | Purpose |
|---|---|
Directly connects access servers to PSTN in a peer-to-peer interconnect |
|
Intelligent Network (IN) triggers |
|
Provides a reliable IP link between signaling controllers and NASs with Redundant Link Manager (RLM) | No single point of failure in connection between NAS and signaling controller. |
Dial outsourcing | Signaling controller and NAS can be provisioned by telephone service providers and local exchange carriers. Calls can be directed to NASs belonging to various ISPs. |
Facility-associated signaling provided by the Cisco Signaling Link Terminals (Cisco SLTs) |
|
Resource management |
|
Introduces services such as wholesale dial, Virtual Private Dial-up Networks (VPDNs), and virtual modem pooling |
|
Supports co-located and distributed access servers |
|
Supports Cisco AS5800 | Investment in Cisco equipment protected. |
Terminates and originates switching-system functions |
|
Provides software upgrade of:
|
|
|
|
| Meet PSTN requirements to create new service opportunities. |
Call Tracker support | Captures data for active and historical call sessions, allowing external applications to access the data via SNMP, CLI, or SYSLOG |
Exec-VPDN support | Enables IP traffic to travel securely over a public TCP/IP network by encrypting all traffic from one network to another. |
Attribute 8 support | Allows a network access server (NAS) to provide the RADIUS server with a hint of the user IP address in advance of user authentication |
RPMS support | Enables telephone companies and Internet service providers (ISPs) to share dial resources for wholesale and retail dial network services |
The Table 1-2 lists the scalability and performance of the Cisco VPOP-DAP Solution
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
For maximum reliability and resilience, we recommend the following options:
Table 1-3 provides an overview of the management components of the signaling controller.
| Management Component | Description |
|---|---|
Configuration Management | The Cisco MGC Manager (CMM) is a graphical user interface (GUI) that uses SNMP to configure and provision your Cisco SC2200. You can access the CMM remotely, using Xterminals, and manage all the signaling controllers in your network with a single CMM system. Dial Provisioning Plan (DPP) is used to format the dial plan and routing data for deployment on the signaling controller. |
Fault Management | The signaling controller supports a comprehensive set of alarms:
You can customize the severity of alarm and thresholds to match your carrier's severity level definitions. You can also configure the system to generate real-time alarms to local or remote terminals. All alarms are written to a log file in an uncompressed format for easy retrieval. The signaling controller is SNMP capable, and MIBs are available. |
Performance Management | You can get a variety of usage statistics from the signaling controller. The data is recorded real-time and is written to a file. You can specify the statistics to be collected and the time intervals for collection and writing to the file. The signalling controller is SNMP capable, and MIBs are available. Each performance measurement record includes:
|
Accounting Management | Every call that passes through the signaling controller produces call detail records (CDRs), which include:
Call detail records are written to a spool file that is automatically closed at defined intervals or when the file exceeds a specified size. You can also specify when to retrieve or send closed files to processing systems. |
The Cisco IOS software installed on the NASs provides an array of network management components (described in Table 1-4). These management features do the following:
Cisco's integrated management simplifies administrative procedures and shortens the time required to diagnose and fix geographically dispersed networks with a small, centrally located staff of experts. Configuration services reduce the cost of installing, upgrading, and reconfiguring network equipment.
| Management component | Description |
|---|---|
SNMP and RMON Support | NASs are fully manageable by using the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) and imbedded Remote Monitoring (RMON) capabilities:
By using the Alarm RMON group, you can set a threshold on any integer-valued Management Information Base (MIB) variable. When the threshold is crossed, an event, defined in the Event RMON group, is triggered. With these capabilities, the system can detect and analyze overloaded conditions and congestion in real time. |
Network Management Systems | The NASs both support CLI and the CiscoView graphical user interface (GUI) for comprehensive, flexible network management. CiscoView provides dynamic status, statistics, and comprehensive configuration information for Cisco switches, routers, NASs, Cisco SLTs, concentrators, and adapters. It displays a graphical view of Cisco devices, provides configuring and monitoring functions, and offers basic troubleshooting. |
RPMS Support | Cisco Resource Pool Manager Server (Cisco RPMS) enables telephone companies and Internet service providers (ISPs) to count, control, manage, and provides accounting data for shared resources for wholesale Virtual Private Dial-up Network (VPDN) and retail dial network services across one or more network access server (NAS) stacks. Cisco RPMS offers a web browser-based configuration utility that enables you to:
|
Modem Management | Cisco offers two types of modems: basic and managed. Managed modems offer superior reporting and statistics in the CiscoView application, including troubleshooting and monitoring modem connections on individual or groups of modems, while calls are in progress. You can manage modems using the same tools used to manage the rest of the network. In addition, managed modems provide an out-of-band management feature that allows you to reduce problem detection and resolution time from a remote site. Through out-of-band management, you can view real-time information (for current or previous calls) such as modem modulation scheme, modem protocol, modem EIA/TIA-232 signal states, modem transmit and receive states, and analog signal-to-noise ratio. |
The Session Manager software, running on the Cisco SLT, manages the communication sessions between the SLT and the SC host.
The session manager:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Sun Oct 1 19:10:14 PDT 2000
Copyright 1989-2000©Cisco Systems Inc.